Test 1
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
Overview of Biology
The study of living systems and their shared characteristics.
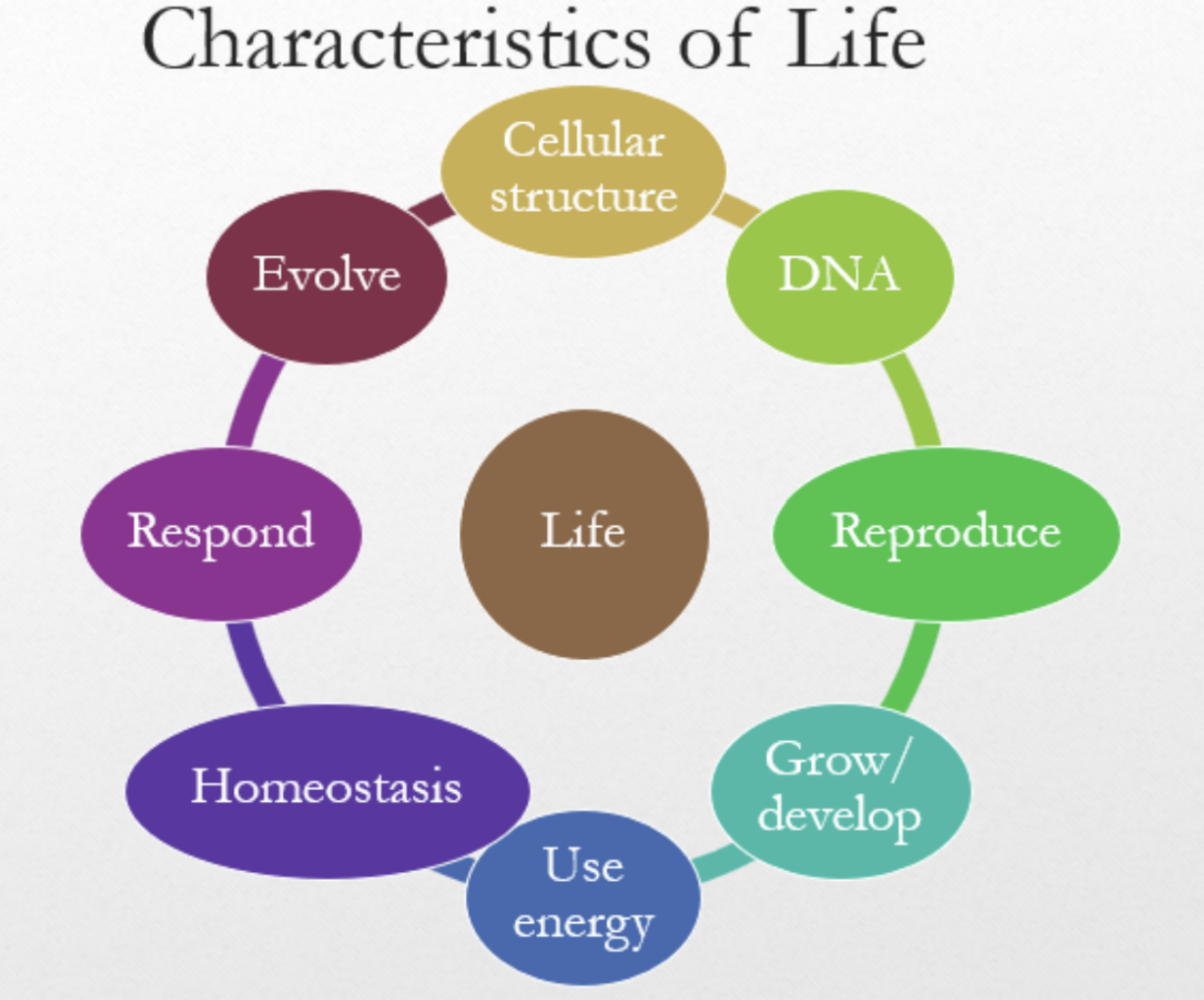
Shared Characteristics of Living Systems
Cellular structure, DNA, reproduction, growth/development, energy use, homeostasis, response to stimuli, and evolution.
order, sensitivity, adaptation
Basic Science
Pure science aimed at expanding knowledge without immediate practical application.
Applied Science
Technology-focused science that seeks to solve real-world problems.
Deductive Reasoning
A top-down approach where general premises lead to specific conclusions.

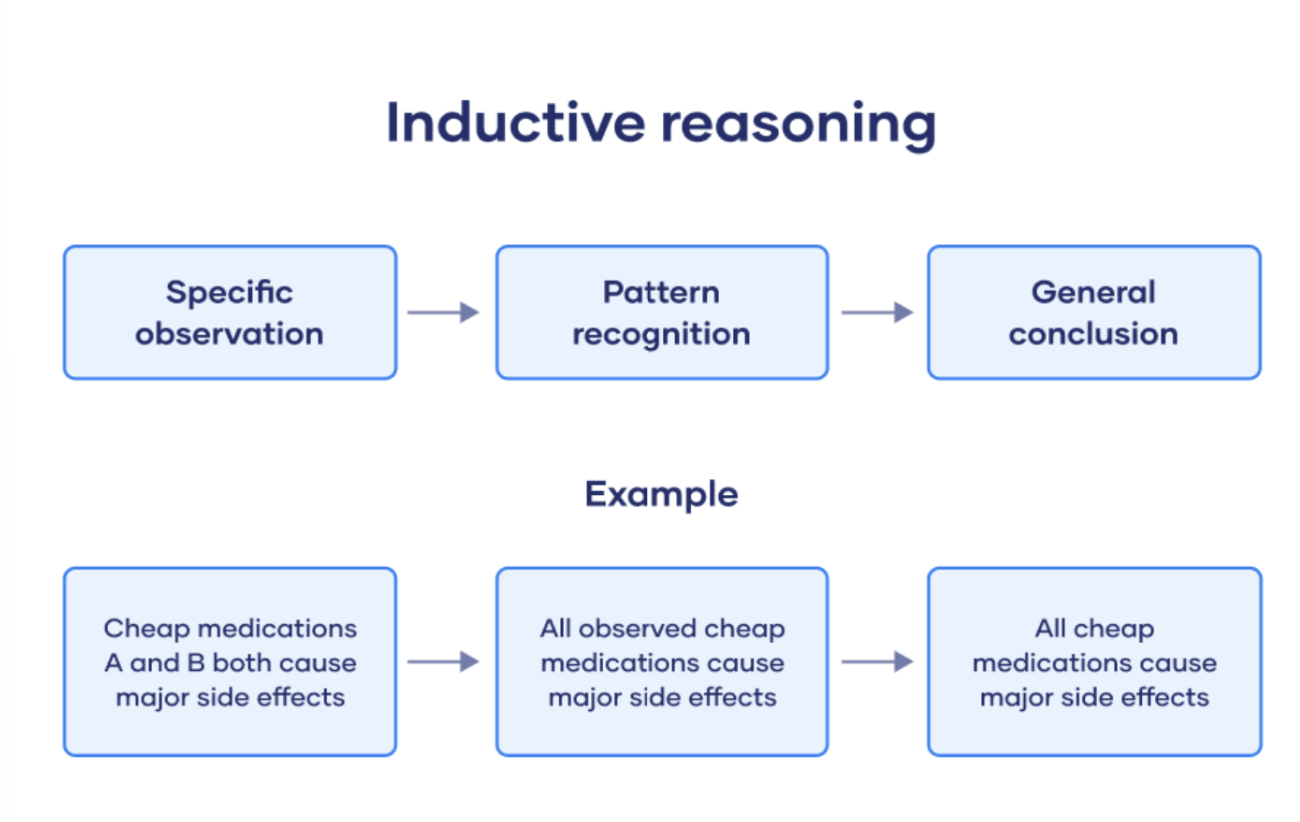
Inductive Reasoning
A bottom-up approach where specific premises lead to general conclusions.
Scientific Method
A systematic process involving observation, hypothesis formulation, testing, and analysis.
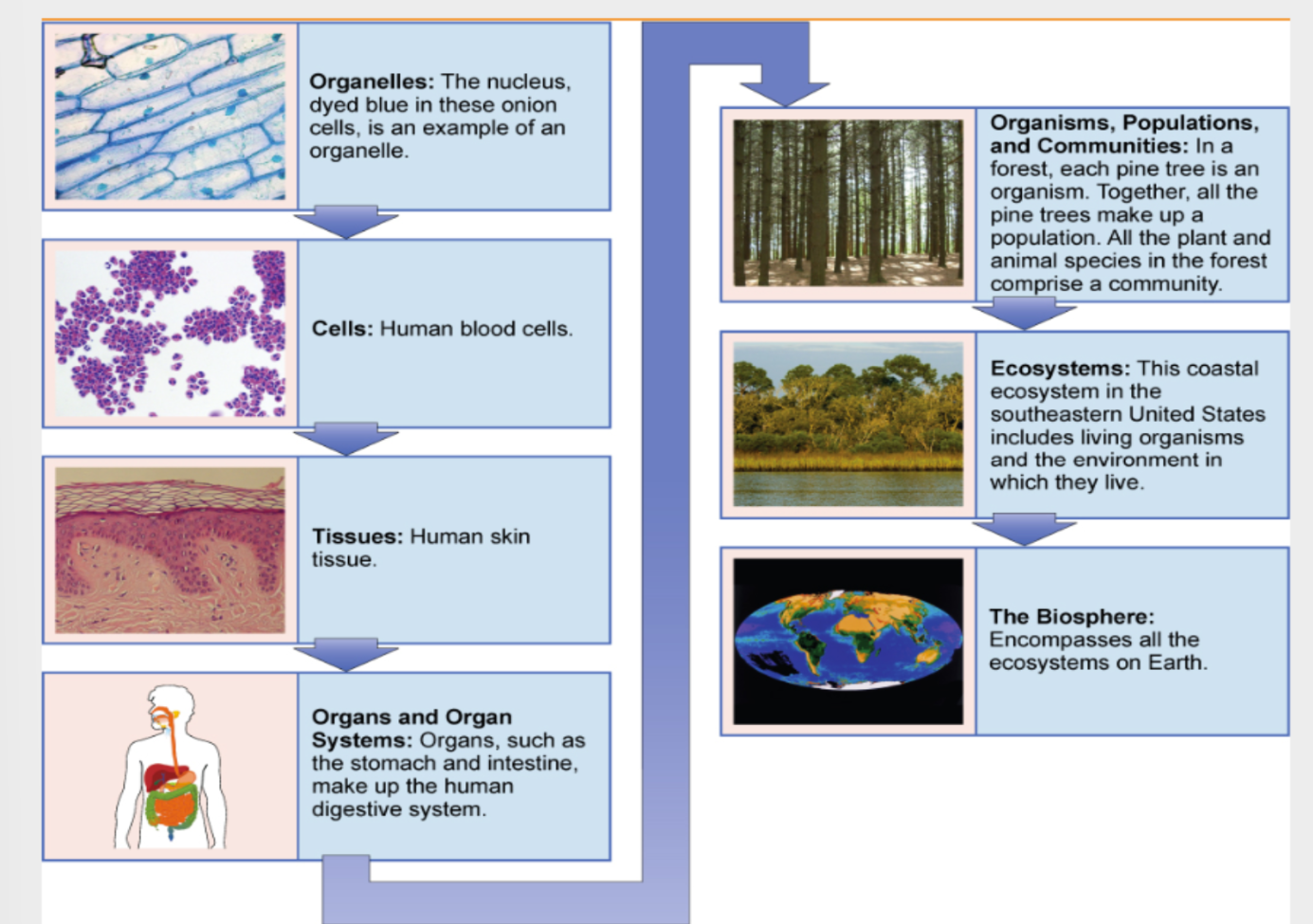
Levels of Biological Organization
Small → Large: Organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, ecosystems, biosphere.
3 Biological Domains
Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya
Isotopes
one or more forms of an element that have different numbers of neutrons
Ions
Atoms or chemical groups with unequal numbers of protons and electrons.
Molecules
Structures formed by two or more atoms bonded together.
Compounds
Substances made of molecules containing at least two different elements.
Organic Compounds
Contain C-H bonds and are derived from living organisms.
Inorganic Compounds
Typically lack C-H bonds and may contain other elements.
Covalent Bonds
Strong bonds formed by shared electrons between atoms.
glycosidic linkage
Ionic Bonds
Bonds formed between oppositely charged ions.
Hydrogen Bonds
weak bond between slightly positively charged hydrogen atoms and slightly negatively charged atoms in other molecules
Properties of Water (Some of it)
Includes states (solid, liquid, gas), high heat capacity, and unique density characteristics.
Water has the highest heat capacity of any liquid
Polar: Hydrogen positivity (+1 times 2) and oxygen’s negativity (-2 times 1)
neutral: Universal solvent
Dissociates into H+ (pure acid) and OH- (pure base) (disassociation of ions generating pH)
Cohesion and adhesion
Cohesion
Attraction between water molecules due to hydrogen bonding.
Adhesion
water is attracted to other substances and sticks to any polar substance
Hydrophobic
Non-polar substances that do not interact with water (water-fearing).
non polar compounds (afraid of water) + the receptors can be inside the cell.
Macromolecules
Large molecules essential for life, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Cell Theory
All living things are composed of cells
The cell is the basic unit of life
New cells arise from existing cells.
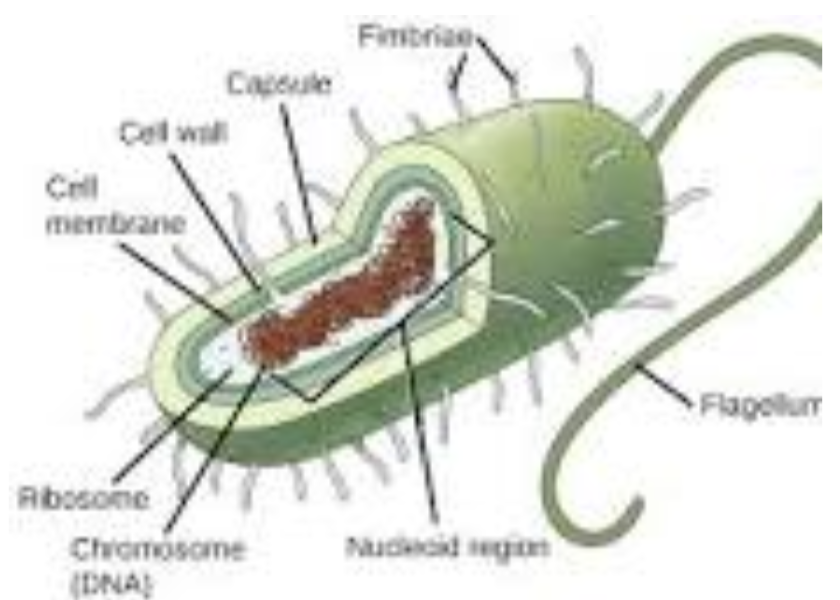
Prokaryotic Cells
Simple, unicellular organisms without a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles.
Most prokaryotes have a cell wall for an extra layer of protection, and some have a flagella or pili for locomotion. Prokaryotes are 10 to 100 times smaller than eukaryotes.
found only in the domains Bacteria and Archaea
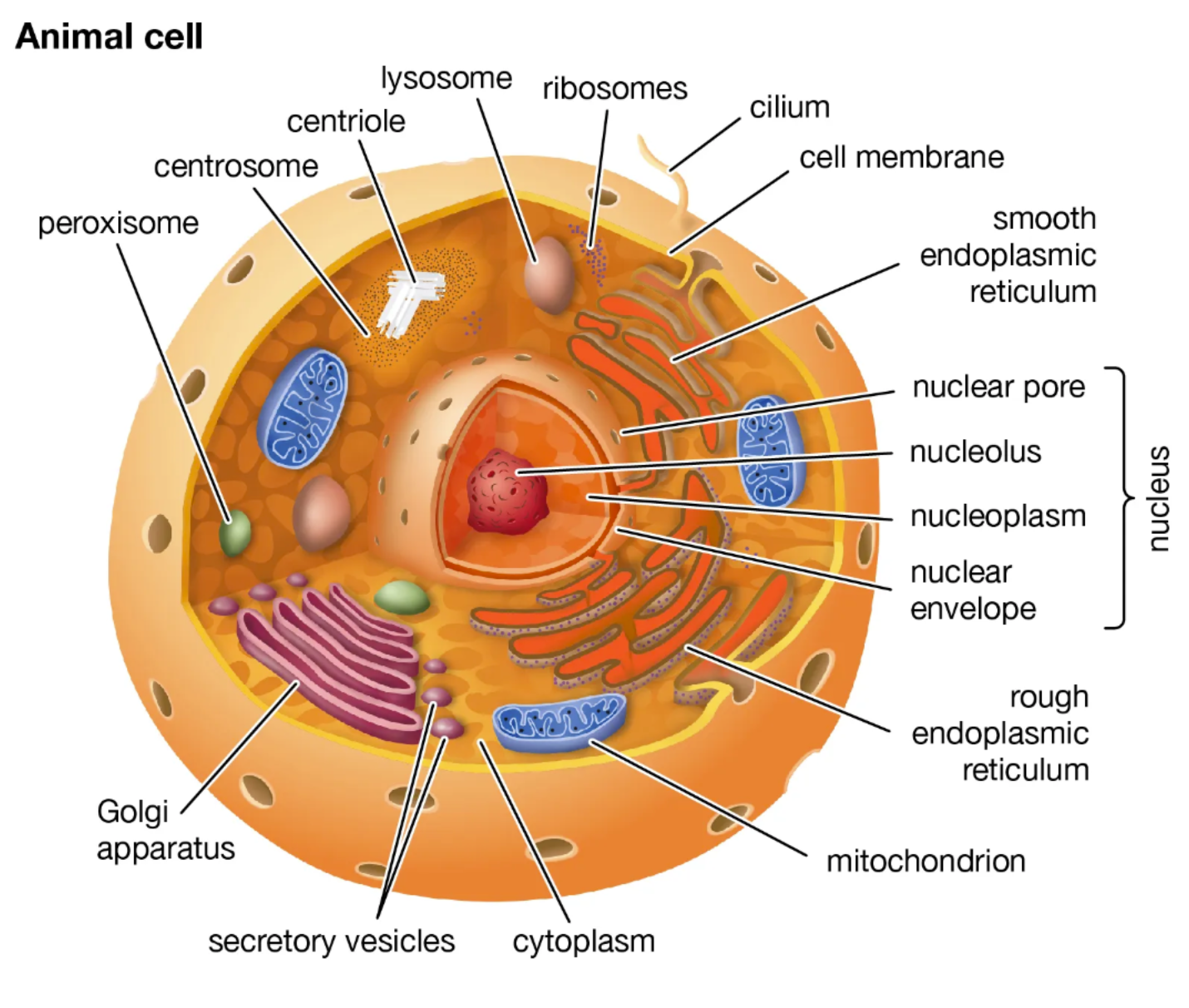
Eukaryotic Cells
Complex cells with a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles (endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, etc). Eukaryotes are 10 to 100 times larger than prokaryotes.
DNA tightly wrapped around histone proteins in chromosomes, cellulose in plant cell walls.
Plasma Membrane Transport
Includes simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport, and osmosis.
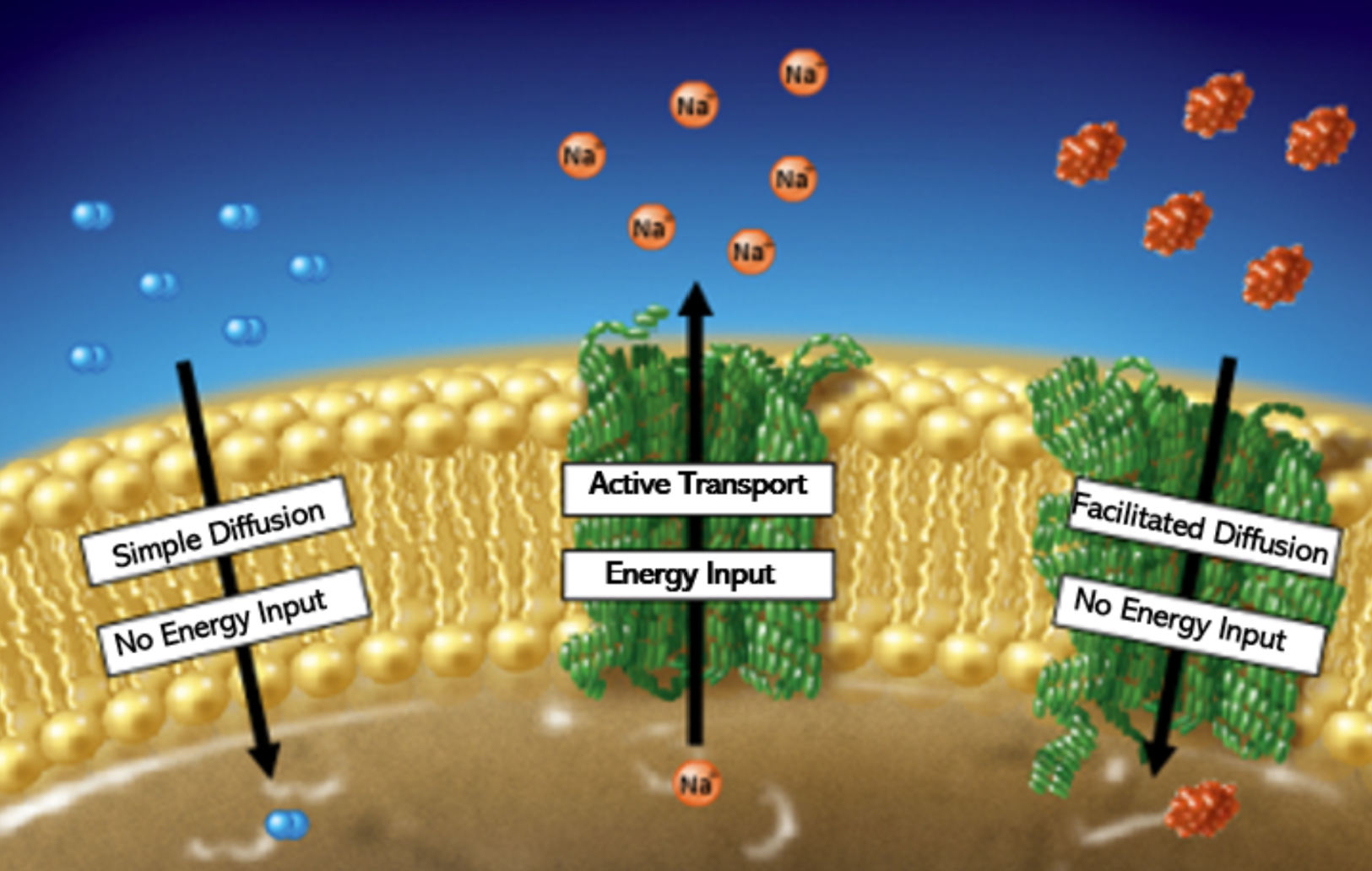
Simple Diffusion
Movement of small non-polar molecules from high to low concentration without energy.
Facilitated Diffusion
Does NOT use energy
Because Ions and polar molecules are impermeable to the membrane, a carrier/embedded protein lets them through
Embedded/transport/carrier protein: membrane protein that facilitates a substance's passage across a membrane by binding it
The inside of the carrier/embedded protein is polar, allowing polar molecules through
High → Low concentration
Active Transport
Requires energy (ATP)
Uses protein pump & ATP to cross
Protein pump: active transport mechanism that works against electrochemical gradients
Low -> High concentration
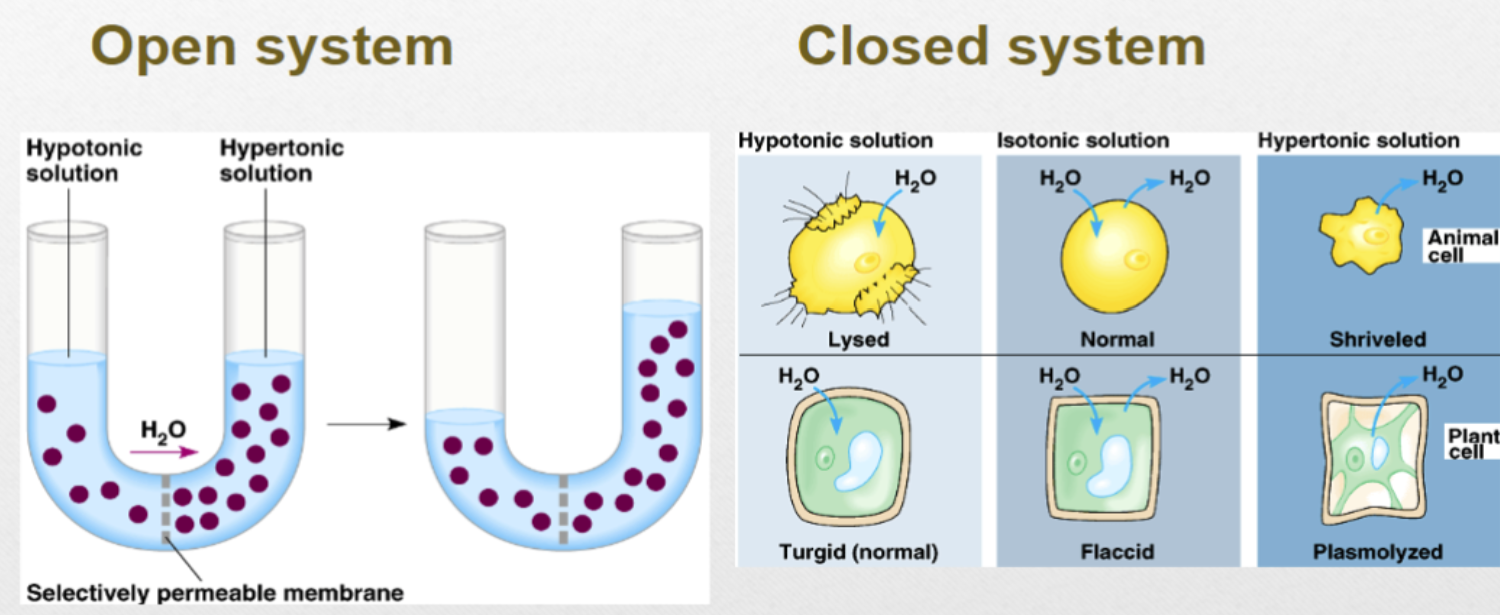
Osmosis
Water movement across the membrane
Water diffuses across cell membrane towards a lower water amount and higher solution concentration
Tonicity
Hypertonic solution, Hypotonic solution, and Isotonic solution
DNA
Stores the genetic information necessary for an organism to develop, function, and reproduce. “Blueprint for all living things.”
Reproduce
Organisms reproduce their own kind.
Grow/Develop
Organisms grow and develop as a result of genes providing specific instructions that will direct cellular growth and development.
occurs through genes/DNA providing for cellular growth
Homeostasis
The environment outside an organism can change, but the organism can adjust its internal environment/conditions.
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment as the outside environment is changing
Respond
All organisms respond to environmental stimuli.
Evolve
Mutations allow the possibility for organisms to adapt to a changing environment, a process of gradual change in a population or species over time, life on Earth has evolved from three lineages / “domains”: bacteria, archaea, and eukarya.
Archaea
Archaeabacteria: unicellular, are often extremophiles, living in harsh environments that have no nuclei or organelles. lacks intracellular organelles (like Bacteria)
Bacteria
Eubacteria: Prokaryotic cells with microbes that lack membrane-enclosed nuclei and organelles. unicellular that lack nuclei and organelles. have a cell wall and RNA.
Eukarya
Protist, Fungus, plant, and animal: multicellular containing a distinct nucleus and membrane bound organelles that have DNA. examples include animals, plants, fungi
Kinetic energy
causes the bonds to break because of high heat in the system (water vapor), allowing the water molecules to escape as gas
Facts about ice
Ice floats because of the density compared to liquid water
Water molecules are pushed farther apart
When ice forms at the surface of a lake, it protects water organisms from freezing and dying
One way cells can survive freezing is if another liquid (ex: glycerol) replaces the water in the cell.
Acid
substance increasing hydrogen ions concentration in solutions (usually because one of the hydrogen atoms dissociate)
A chemical that gives off hydrogen ions in water and forms salts by combining with certain metals
Base
H- concentration within a solution or OH- in a molecule
a substance that can neutralize the acid by reacting with hydrogen ions.
Hydrogen bonding
Intermolecular force
dipole-dipole
Hydrogens in water will attract highly electronegative atoms (F, O, Cl)
Cause for the high density of water
Cause for the “stickiness of water”
Hydrophilic
when polar substances interact readily or dissolve in water (water loving) + in membranes the ligands are on the cell membrane.
Surface tension
Occurs because of cohesion. How a substance will withstand rupturing when placed under tension or stress. Allows for water molecules to ‘float’ to the top.
Solvent Properties
Solvent: Substance capable of dissolving other polar molecules and ionic compounds.
Sphere of Hydration: charges of molecules allowing for forming of hydrogen bonds with water (hydration shells).
Dissociation: Separation of atoms from molecules resulting in formation of ions.
Carbohydrates and it’s Building Block
The body's primary source of energy and the brain's preferred energy source.
include sugars and the polymers of sugars
macromolecules are polysaccharides, polymers composed of many sugar building blocks
Glucose & Monosaccharides (simple sugars)
Lipids and it’s Building Block
Help control what goes in and out of your cells.
Fatty acids, glycerol
Proteins and it’s Building Block
Structural support, biochemical catalysts, hormones, enzymes, building blocks, and initiators of cellular death.
Amino acids
Nucleic acids and it’s Building Block
Storage and expression of genomic information.
Nucleotides
Simple Diffusion
Does NOT use energy
Small non polar molecules or gasses that are permeable and pass through without help
High → Low concentration
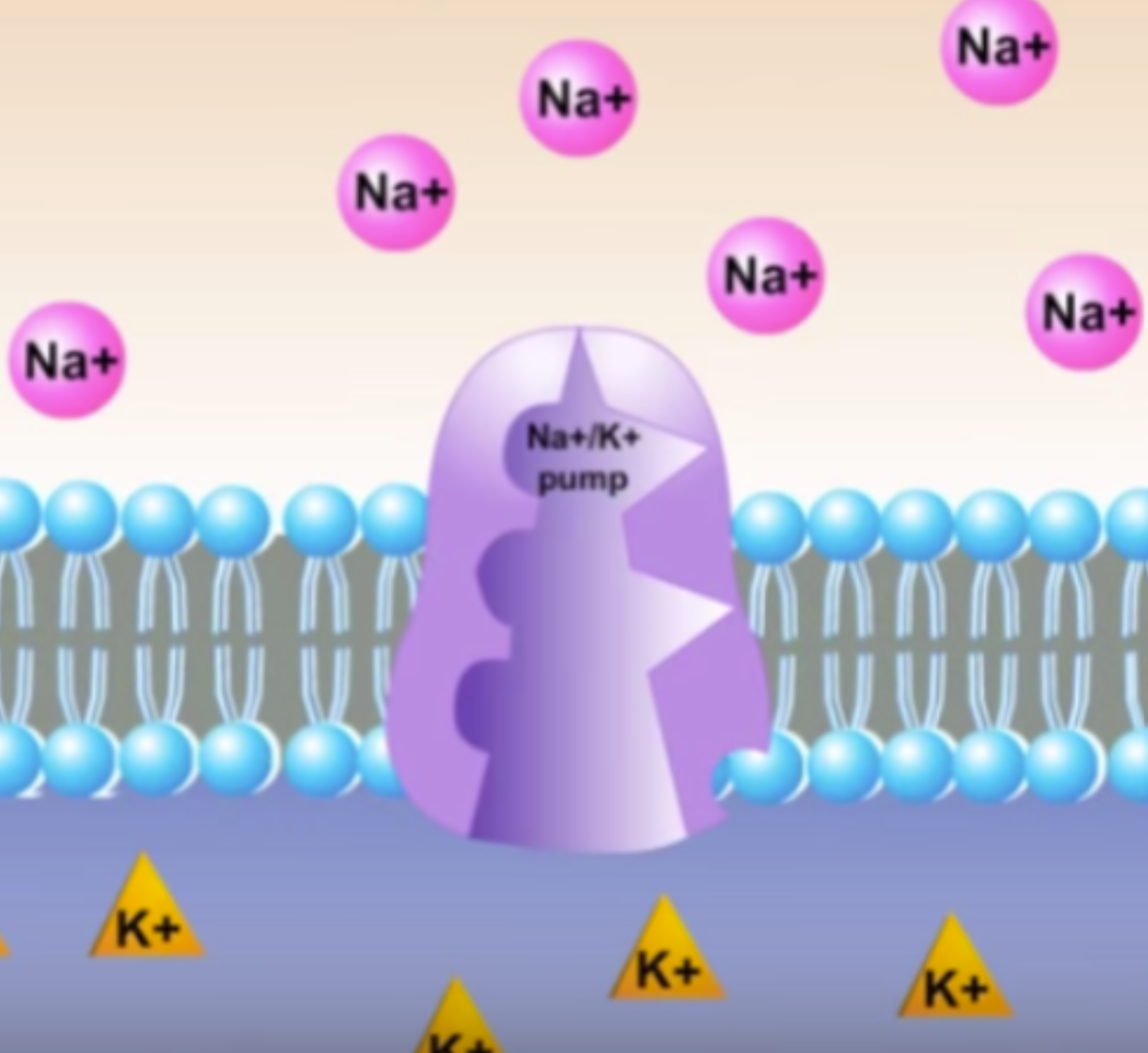
Sodium Potassium Pump and it’s steps
Active transport of Na+ to extracellular fluid and K+ ions to the intracellular fluid across the cell membrane re-establishes an electrochemical gradient which has potential energy.
1. 3 sodium ions (Na+) bind to the pump
2. A phosphate from ATP is donated to the pump (Energy used)
3. The pump changes shape and releases Na+ outside of the cell
4. 2 potassium ions (K+) bind to the pump and a transferred into the cell
5. The phosphate group is released and the pump returns to its original shape
Osmolarity
Describes the solute in a water solution
Solutes that dissociate, increase osmolarity
A solution with more water molecules than solute particles has low osmolarity
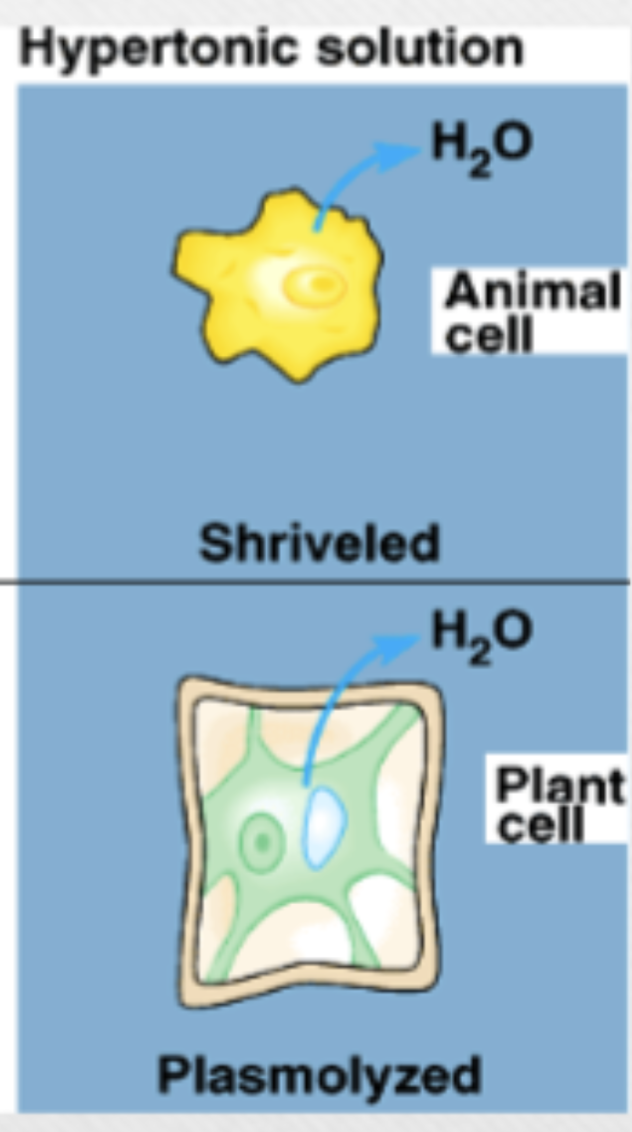
Hypertonic solution
higher osmolarity (higher solute particle, lower water) in extracellular fluid vs cytoplasm
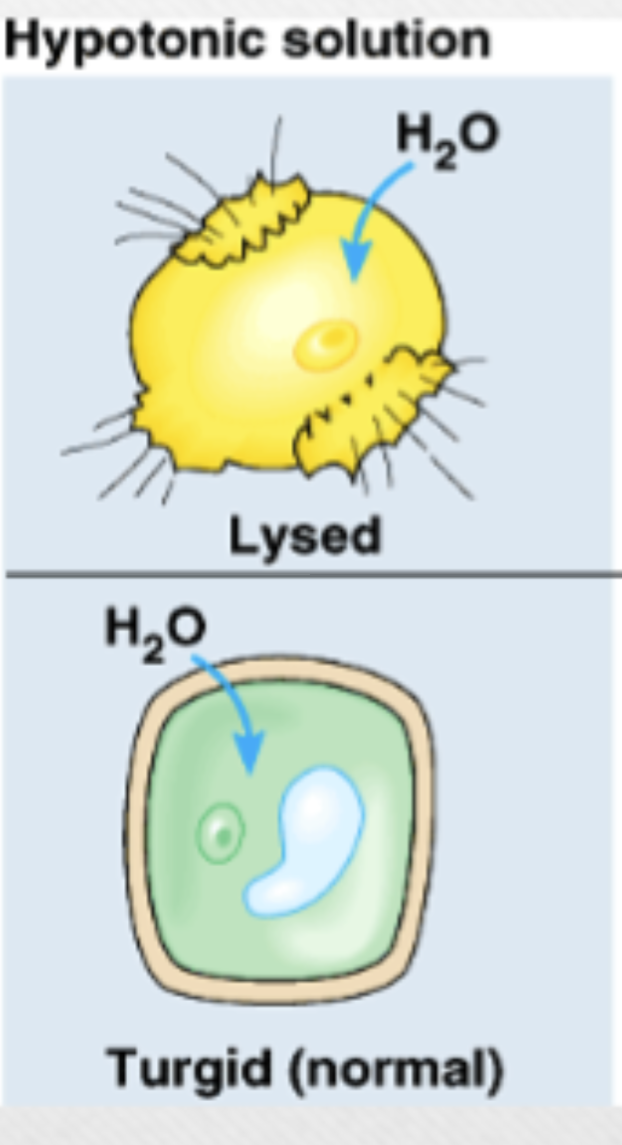
Hypotonic solution
lower osmolarity (lower solute partial, higher water) in extracellular fluid vs cytoplasm, plants cells prefer
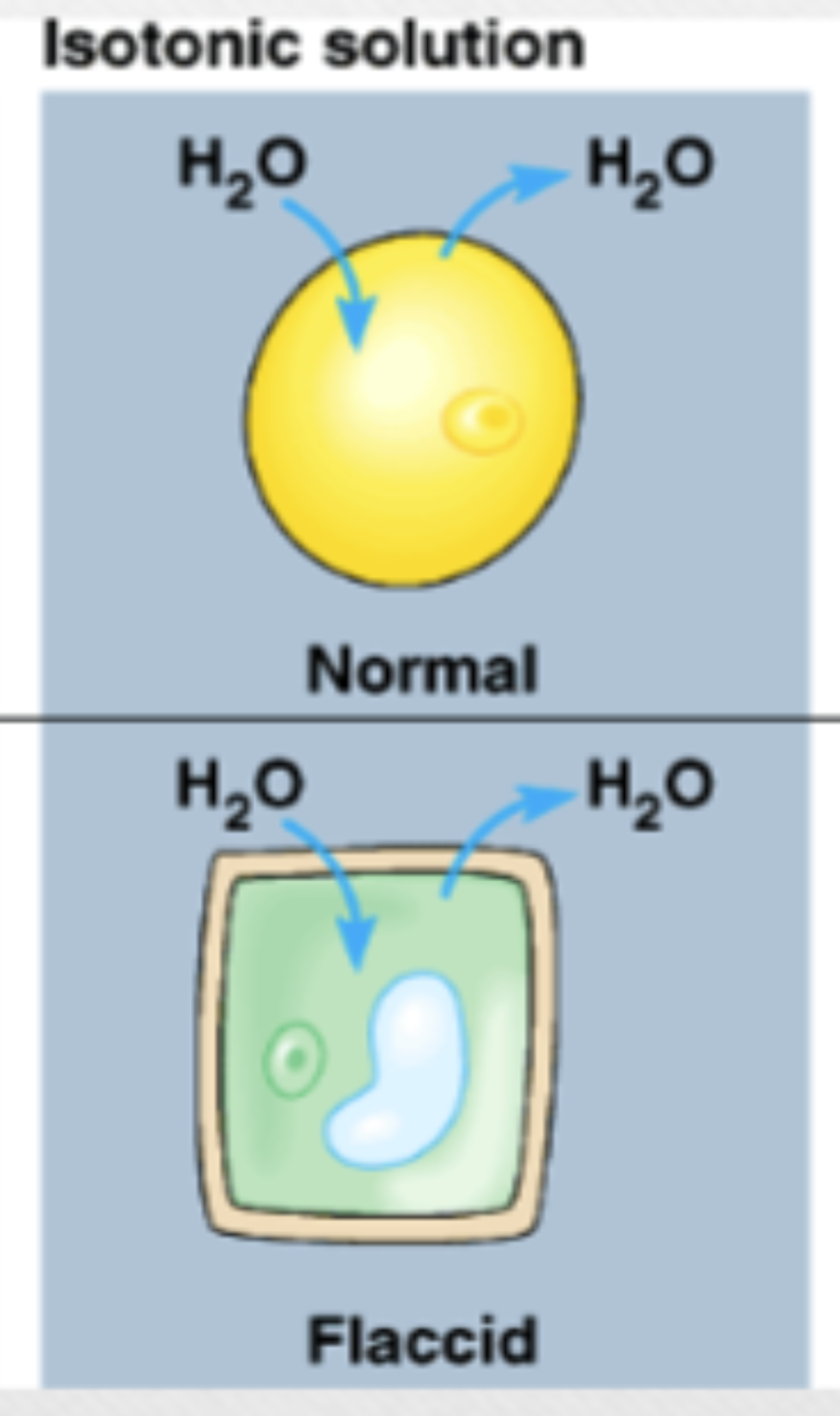
Isotonic solution
relatively equal osmolarity in extracellular fluid and cytoplasm, animal cells prefer
Water Heat Vaporization
Turns at 100 degrees Celsius, 212 degrees Fahrenheit
The evaporation of sweat, which is 90 percent water, allows the organism to cool so that it can maintain homeostasis of body temperature
An animal will sweat, burn the water off their body via their skin, and transfer the heat/energy used to evaporate the water into the gaseous state of water, therefore cooling them
Human Genome Project
a research effort to sequence and locate the entire collection of genes in human cells. relied on basic research to then later find cures for genetic diseases.
order
how organisms respond to environment
reproduction
the process of producing offspring
adaptation
characteristic that improves an individual's ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment.
energy processing
All organisms use a source of energy for their metabolic activities
evolution
Change in a kind of organism over time; process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms.
phylogenetic tree
A branching diagram that represents a hypothesis about the evolutionary history of a group of organisms.
levels of matter
atoms, molecules, macromolecules, organelles
Structure of atom. Know where protons, neutrons, and electrons are located.
Composed of subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, electrons) with specific properties.
neutrons: no charge, located in nucleus
protons: positive charge, located in nucleus
electrons: negative charge, located on outside shells (2 in first orbital, 6 in others)
what determines the element's mass number
the number of protons + neutrons together
what determines the element's atomic number
the protons
Cation
A positively charged ion formed by loosing electrons
anions
a negatively charged ions that gains electrons
non polar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which the bonding electrons are shared equally by the bonded atoms, resulting in a balanced distribution of electrical charge
hydrogen bonds
weak bond where a hydrogen covalently bonds to an electronegative atom
liquid state of water
hydrogen bonds constantly form and break as the hydrogen atoms slide past each other
gaseous state of water
the kinetic energy makes heat rise as the water boils therefore the water molecules escape into the air
hydrocarbons
Compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen
isomers
compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structures
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) attached to three phosphates that is main energy source that cells use for most of their work
RNA
Mostly involved in protein synthesis and is the communicator of the cell.
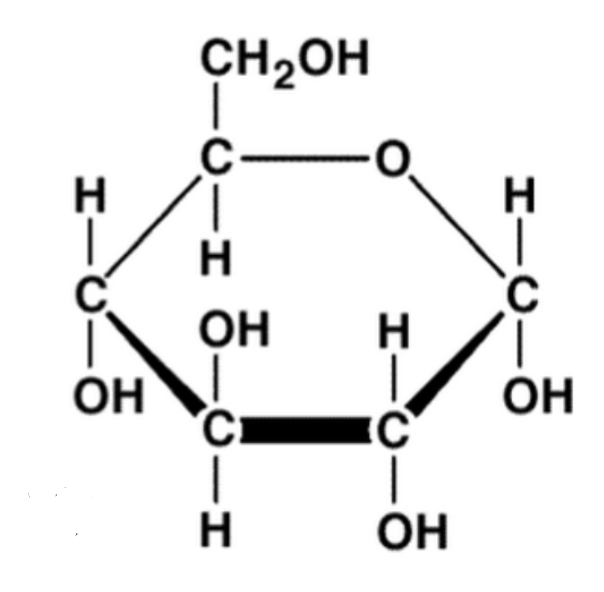
Monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose (simple sugars)
molecular formulas that are usually multiples of CH2O
– The location of the carbonyl group
– The number of carbons in the carbon skeleton
plant cell vs. animal cell organelles
plant cells: cell wall, chloroplasts, plasmodesmata, plastids
animal cells: centrioles, centrosomes, lysosomes
Rough ER vs Smooth ER function
- Rough ER: attached ribosomes, main site of protein synthesis
- Smooth ER: lacks attachment of ribosomes, main site for making lipids
Golgi apparatus function
modifies and packages proteins
Lysosomes function
Digestion and recycling (only in animal cells)
Plasmodesmata
An open channel in the cell wall of plants through which strands of cytosol connect from adjacent cells
allow connected plant cells to communicate and share resources
The three animal cell junctions
tight junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions
fluid mosaic model
Structural model of the plasma membrane that includes phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates giving the membrane a fluid character.
The fluid mosaic model describes the plasma membrane structure as a mosaic of components—including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates—that gives the membrane a fluid character. Plasma membranes range from 5 to 10 nm in thickness.
Phospholipids
a lipid consisting of a glycerol bound to two fatty acids and a phosphate group.
Mircomoleules
large molecules composed of thousands of covalently bonded atoms
polymers, built from monomers
polymer
a long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
– Carbohydrates
– Proteins
– Nucleic acids
monomers
small building-block molecules
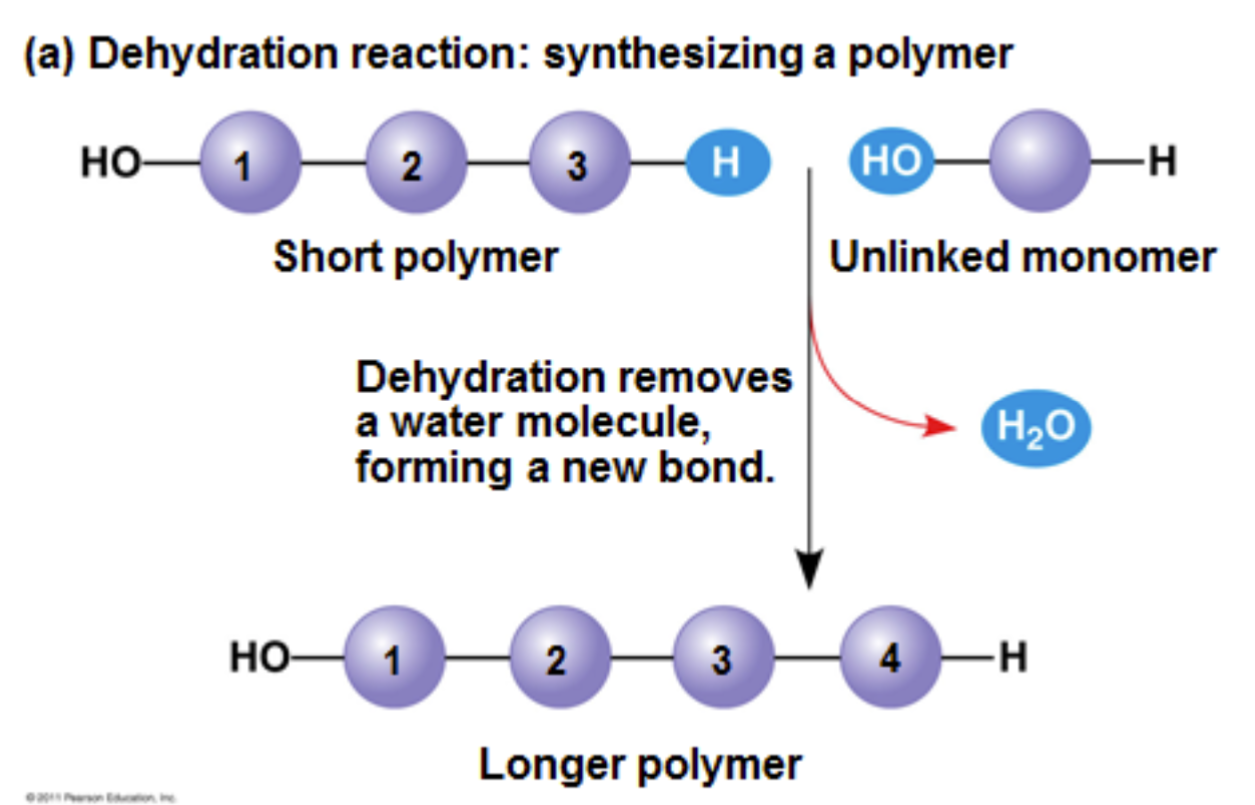
dehydration reaction
occurs when two monomers bond together through the loss of a water molecule
An enzyme reaction linking monomers through the loss of hydrogen from one monomer and hydroxide from the other monomer to form a bond whose name varies by macromolecule group
C – glycosidic linkage
L – ester linkage
P – peptide bond
N – phosphodiester linkage
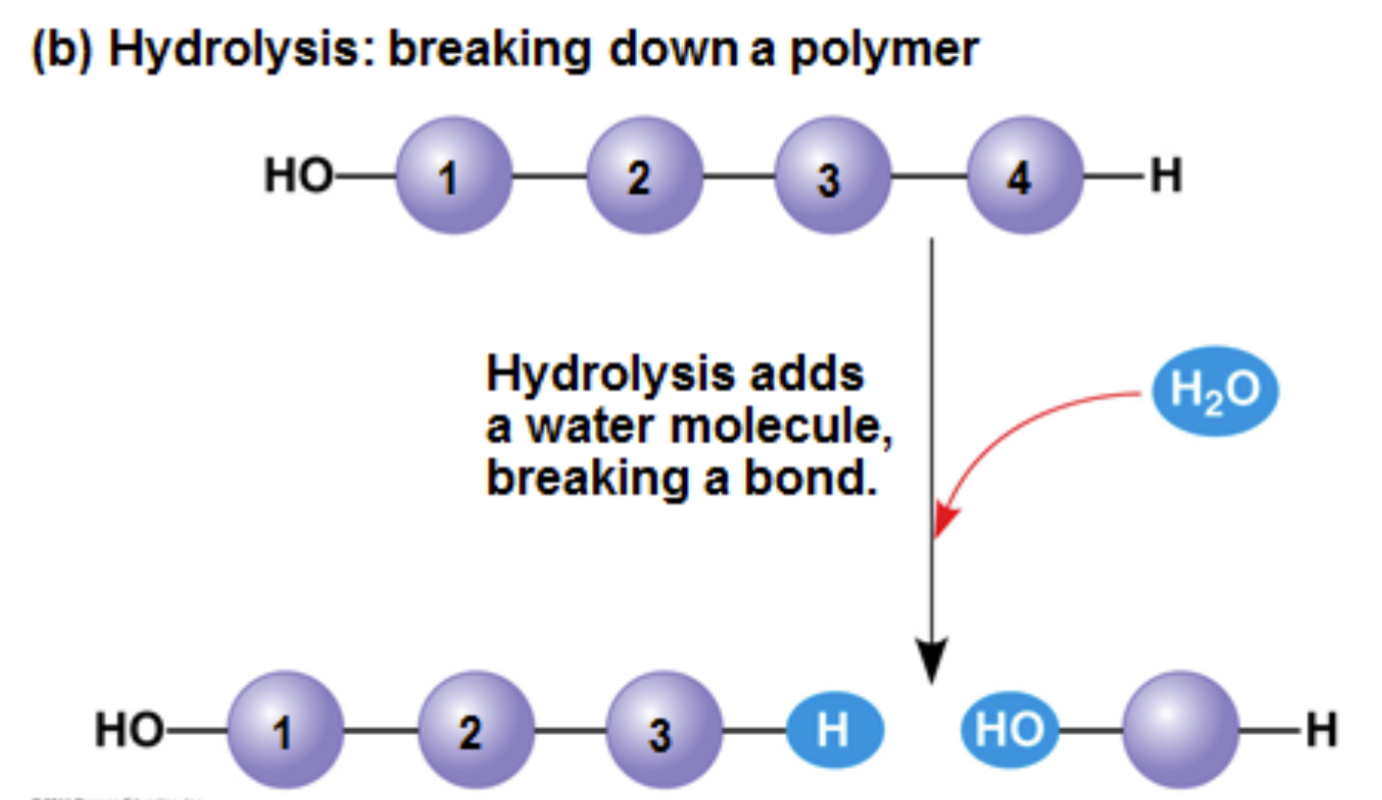
hydrolysis
Polymers are disassembled to monomers by by this process, a reaction that is essentially the reverse of the dehydration reaction
An enzyme reaction using water thereby adding hydrogen to one side and hydroxide to the other side of a bond within a polymer resulting in smaller molecules or monomers.
disaccharide
formed when a dehydration reaction joins two monosaccharides
Polysaccharides
polymers of sugars, have storage and structural roles
• The structure and function of a polysaccharide are
determined by its sugar monomers and the positions of
glycosidic linkages
Types of Polysaccharides
Starch, Glycogen, Cellulose, and Chitin
Starch
a storage polysaccharide of plants, consists entirely of glucose monomers
• Plants store surplus starch as granules within chloroplasts and other plastids
• The simplest form of starch is amylose
Glycogen
a storage polysaccharide in animals
Humans and other vertebrates store glycogen mainly in liver and muscle cells