GI E2- Biliary tract disease
1/99
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
The pancreaticobiliary system delivers _______ to the intestinal tract.
Bile
What composes the pancreaticobiliary system?
Gallbladder, cystic duct, intrahepatic duct, hepatic duct, common bile duct, & pancreas
What composes the common bile duct?
Cystic duct + common hepatic duct
What organ is a distensible sac that concentrates and stores bile, runs behind the duodenum and ends at ampulla of Vater?
Gallbladder
Bile is formed in the ______, and modified & stored in the ________
Liver ; gallbladder and bile ducts
What emulsifies lipids (micelles) and transports wastes such as bilirubin, toxins, cholesterol, and IGs?
Bile
What AST-ALT ratio suggests alcohol injury / alcohol hepatitis?
≥ 2:1
What is a useful marker to diagnose specific liver diseases?
AST-ALT ratio
What level of AST-ALT elevations would be due to ETOH alone?
< 300 IU/L
Besides ETOH, what are other causes for elevated AST/ALT?
Viral hepatitis & drug/toxin induced (both MC), ischemia, autoimmune liver dz, acute bile duct obstruction, hepatic vein obstruction, Wilson’s disease, acetaminophen
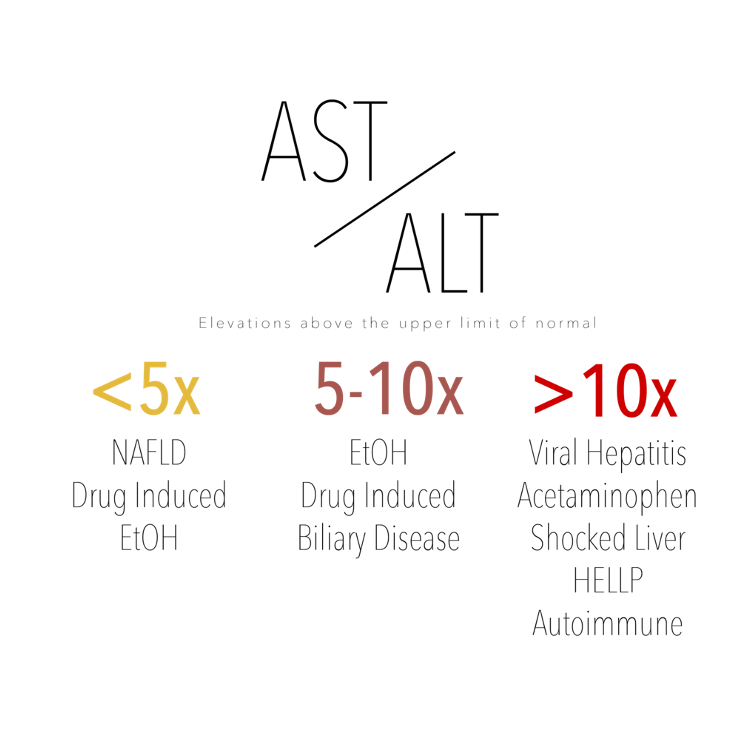
How elevated is ALP in biliary tract obstruction?
3-10x
How elevated ALP in hepatitis and cirrhosis?
less than 3x
How elevated is ALP in pregnancy (3rd trimester)?
1.5-2.5x
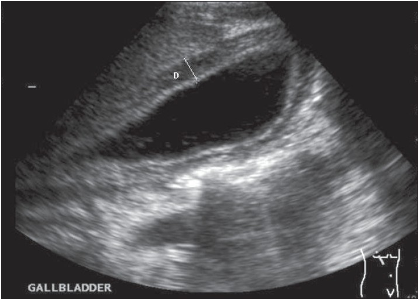
What common digestive disease consists of gallstones, most often asymptomatic and found incidentally during abd sonography?
Cholelithiasis
What are the majority of gallstones/cholelithiasis?
Cholesterol
What due black pigment stones in cholelithiasis indicate?
Cirrhosis, hemolysis, biliary stasis, CF
What do brown pigment gallstones in cholelithiasis indicate?
Parasites, infection
What is the pathogenesis of cholelithiasis?
Cholesterol supersaturation of bile → destabilization of bile → stasis of bile in gallbladder
Who is cholelithiasis 2-3x more common in?
Women
What are RF for cholelithiasis in adults (> 40)?
F, obese, mexican or Native American, DM, metabolic syndrome, pregnancy, OCs, prolonged fasting, rapid wt loss, spinal cord injuries
What are RF for cholelithiasis in children?
CF, sickle cell disease
What are the 4 Fs of cholelithiasis (predisposing factors)?
Fat, forty, female, fertile
What is often a precursor of gallstones that develops during gallbladder stasis?
Biliary sludge
How does biliary sludge develop in females?
Endogenous estrogens inc biliary cholesterol secretion & cholesterol saturation of bile
How does biliary sludge develop in obesity?
Overproduction of cholesterol → hypersecretion into bile → gallstone formation
How does biliary sludge develop during pregnancy?
Impaired gallbladder emptying from progesterone + effects of estrogen → inc cholesterol hypersecretion
The following ssx are associated with what condition?
biliary colic- steady epigastric or RUQ pain
radiate to R scapula or shoulder, lasts 15min-5 hrs
often develops after eating fatty foods
nocturnal awakening from pain
N, +/- V
most will have recurrent attacks
Cholelithiasis
What causes the steady epigastric or RUQ pain (biliary colic) associated with cholelithiasis?
Stone obstructs cystic duct or common bile duct → distension of viscus → visceral pain
*stone returns back to gallbladder after attack
How is uncomplicated symptomatic gallstone disease characterized?
Episodes of biliary pain < 5 hrs
How is complicated gallstone disease characterized?
Biliary pain lasts > 5 hours + labs might indicate acute cholecystitis, acute biliary pancreatitis, or biliary obstruction
What is the preferred modality to diagnosis cholelithiasis?
Abd US → gallbladder wall thickening, cystic duct dilation
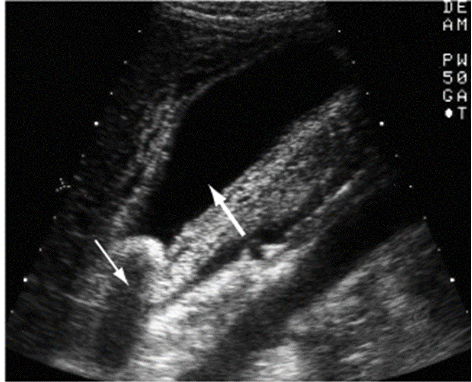
What are other dx modalities for cholelithiasis?
HIDA scan (GB contractility), CT scan, ERCP, PTC
What is a percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram (PTC)?
Transhepatic insertion of needle into bile duct w/ injection of contrast (for those who can’t have ERCP)
What comps can occur with cholelithiasis?
Acute cholecystitis
What condition is an acute GB wall inflammation due to mechanical, chemical, or bacterial causes and is a complication of cholelithiasis?
Acute cholecystitis
What is the pathophysiology of cholecystitis?
Cystic duct obstruction w/ stone PLUS another factor → circulation & lymph drainage become impaired → mucosal ischemia & necrosis
Secondary bacterial inflammation (e. coli, klebsiella, strep, clostridium)
The following PE findings are seen in what condition?
progressively worsening biliary pain/colic localized to RUQ
N, V
Murphys sign
palpable gallbladder, peritoneal inflammation
Triad: RUQ pain, fever, leukocytosis
Acute cholecystitis
What is the triad for acute cholecystitis?
RUQ pain, fever, leukocytosis
What sign?
Pt exhale → place hand below costal margin on right side at MCL → pt inhale
positive = pt stops breathing in & winces w/ a catch in breath
d/t inflamed gallbladder palpated as it descends → acute cholecystitis
Murphy’s sign
What will happen to acute cholecystitis if left untreated?
Inflammation → gangrene → GB wall rupture → peritonitis, septic shock, localized abscess, or cholecystoenteric fistula possible
What is the dx for acute cholecystitis?
Abd US, leukocytosis, mild elevation in AST/ALT, amylase, or bili
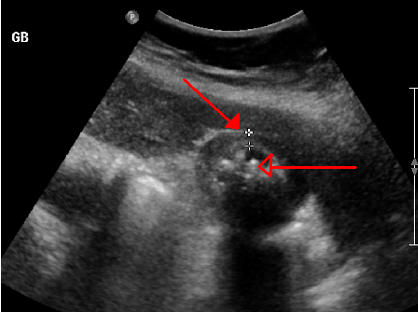
What is the treatment for acute cholecystitis?
NPO, NGT if V, IVF, broad spectrum abx, analgesics (toradol, opioids), chemodissolution (CDCA or UDCA), cholecystectomy
What condition is chronic inflammation of the GB wall that results from repeated attacks of acute/subacute cholecystitis OR mechanical irritation of GB mucosa by gallstones?
Chronic cholecystitis
What are possible complications of chronic cholecystitis?
Biliary sepsis, porcelain gallbladder
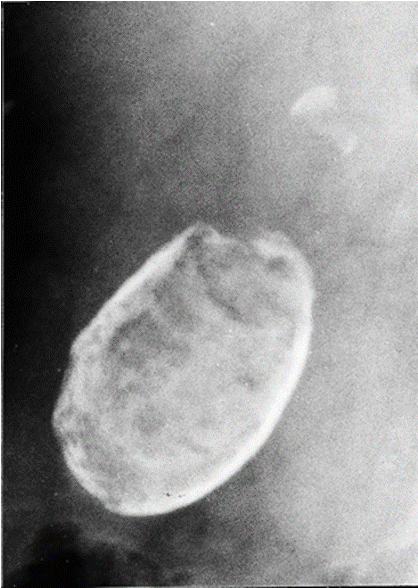
What condition?
calcium salts are deposited w/in GB wall of chronically inflamed GB (comp of chronic cholecystitis)
Dx: plain films
Rx: cholecystectomy
Porcelain gallbladder
What does porcelain gallbladder have a high association with?
Carcinoma of gallbladder
What is an acute necroinflammatory disease of the GB, presents with NO gallstone, can cause acute cholecystitis & has a high morbidity/mortality?
Acalculous cholecystitis
Who is acalculous cholecystitis MC in?
Males over 50
What is acalculous cholecystitis associated with?
Major surgery, critical illness, burns, trauma, TPN
What is the pathogenesis of acalculous cholecystitis?
Gallbladder stasis & ischemia → local inflammatory response in GB wall → endothelial injury leading to stasis → concentration of bile salts → GB distention & eventually necrosis
*Secondary infx can occur in severe cases
How is acalculous cholecystitis diagnosed?
Abd US & CT, HIDA scan, blood cultures
What is the treatment for acalculous cholecystitis?
Abx, cholecystectomy or cholecystectomy tube
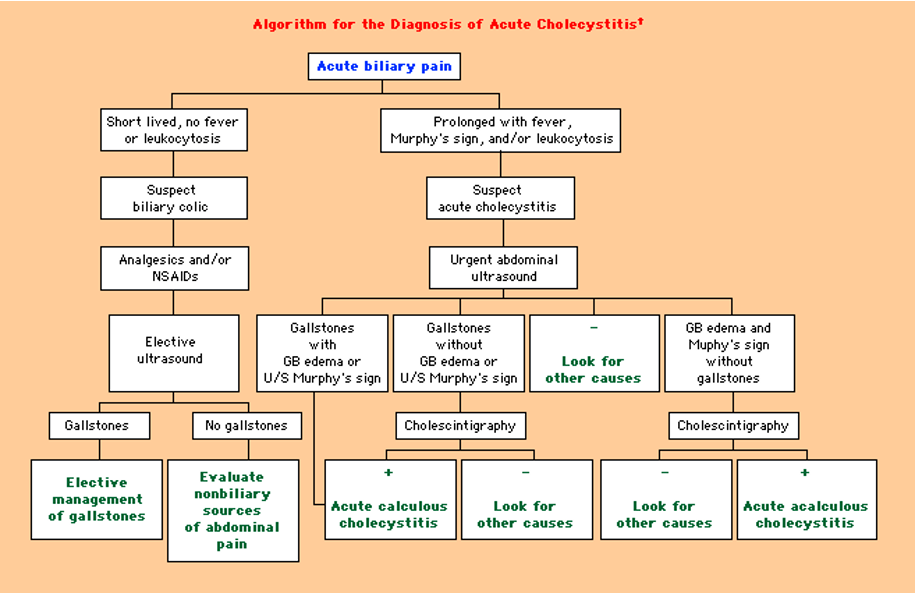
Algorithm for acute cholecystitis diagnosis
What condition is characterized by calculus in the common bile duct (CBD) & occurs in 15% of pts w/ gallstones?
Choledocholithiasis
How does choledocholithiasis form?
Stones usually originate in GB → smaller stones can progress further into duodenum
OR forms spontaneously in CBD s/p cholecystectomy
The following presentation is associated with what condition?
MC “silent”- no sx unless obstruction
Frequently occur in pts w/ hx of biliary colic episodes
+/- abd tenderness
Jaundice develops later on
Choledocholithiasis
What labs are seen in choledocholithiasis?
Initial- elevated LFTs & GGT
Later- elevated ALP & bilirubin (leads to jaundice)
How is choledocholithiasis diagnosed?
Abd US, ERCP
What diagnostic modality is highly sensitive and specific for choledocholithiasis, is completed if cholangitis or acute pancreatitis is also present, and allows for stone extraction?
ERCP
What condition is a bacterial infection superimposed over an obstructed biliary tree due to a gallstone, stricture, or neoplasm (uncommon, can develop after ERCP)?
Acute cholangitis
What is the pathophysiology of acute cholangitis?
Biliary tree obstruction → inc intraluminal pressure → bile infx → hepatic ducts → hepatic canaliculi → hepatic veins → lymph → bacteremia
What is the triad associated with acute cholangitis?
Charcot’s triad → RUQ pain, jaundice, fever w/ chills
The following labs can be seen in what condition?
WBCs: inc w/ left shift
Total bili: inc
ALP: inc
GGT: inc
AST, ALT: mild inc
Serum amylase & lipase: moderate inc
Acute cholangitis
What are the diagnostic modalities for acute cholangitis?
PTC, ERCP, MRCP
What is the pentad associated with acute suppurative cholangitis (presence of pus in biliary ducts)?
Reynold’s pentad → charcot’s triad + hypotension + mental confusion
If ERCP or cholecystectomy cannot be performed for acute cholangitis, what do radiologists need to do?
Percutaneous cholecystostomy → tubes placed through skin into GB for drainage
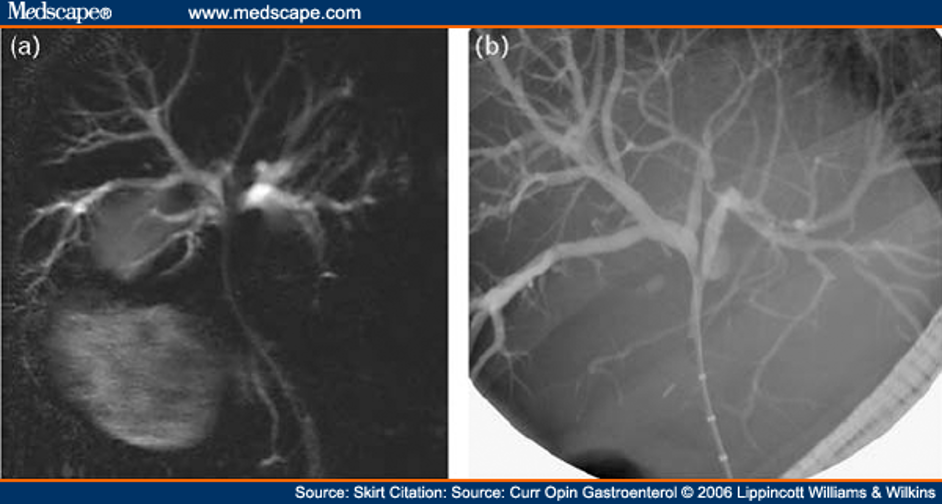
What can be used to provide road map for biliary endoscopist to define biliary anatomy prior to ERCP?
MRCP
How would acute cholangitis appear on MRCP/ERCP?
Generalized dilatation of intrahepatic bile ducts to level of hilum
What condition is pancreatic inflammation due to the passage of stones through the CBD during acute cholecystitis or in patients with choledocholithisis?
Biliary pancreatitis
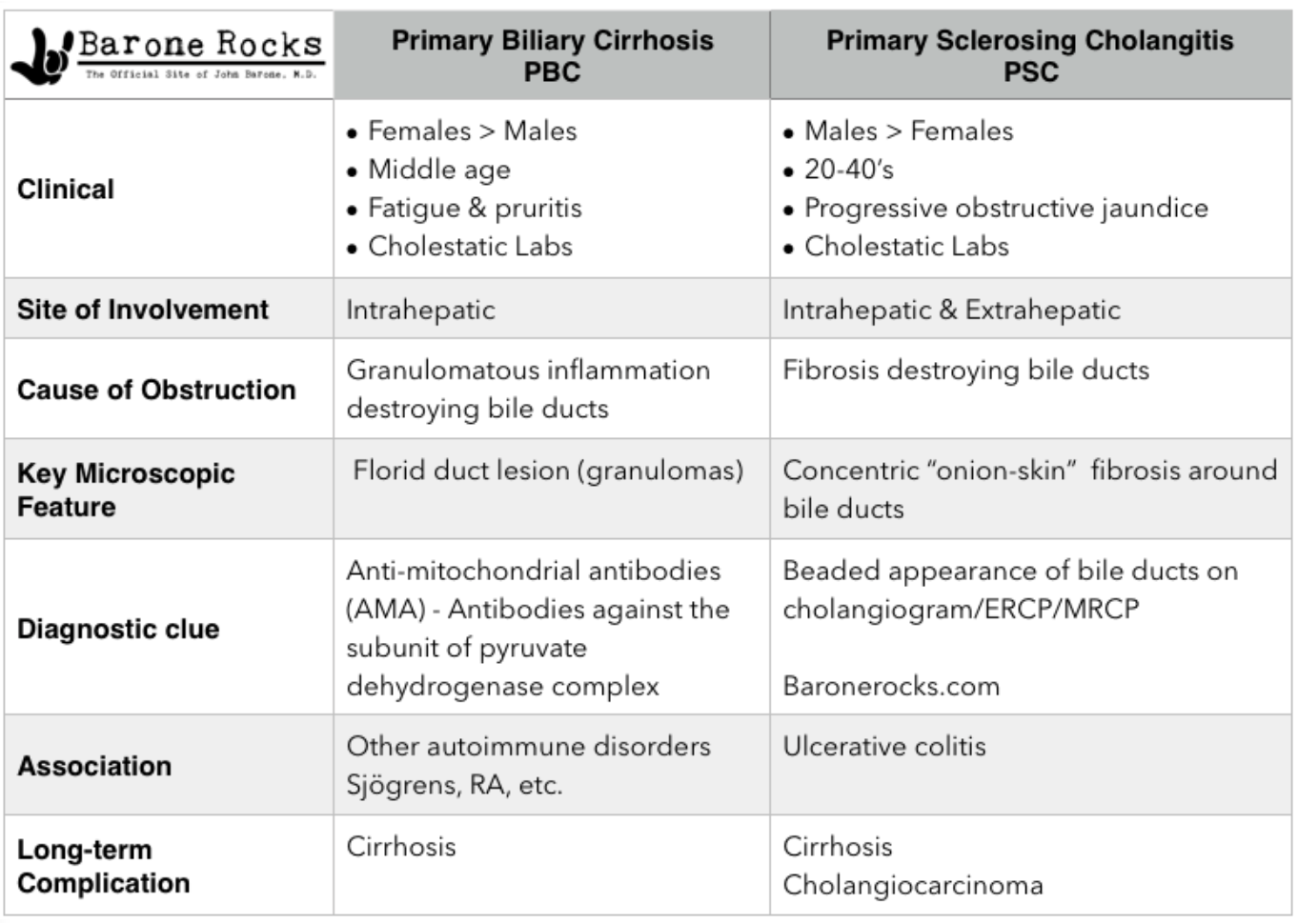
What condition is an autoimmune destruction of intrahepatic bile ducts & cholestasis?
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)
Who is PBC MC in?
Middle aged women
The inflammation & fibrosis associated with PBC can lead to what?
Portal HTN and eventual cirrhosis (in 10-12 yrs)
What is the pathogenesis of PBC?
Antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA) destroy intrahepatic bile ducts; possible role with genetics & environmental triggers, viruses or bacteria
What is the onset of PBC?
Insidious- often asx and found incidentally w/ inc LFTs on annual labs
The following symptoms are associated with what condition?
Fatigue
dry eyes & mouth
pruritus / excoriations- severe, local, or diffuse
unexplained RUQ discomfort- hepatomegaly
xanthelasma- yellow plaques around eyes
d/t dec LDL receptors in damaged hepatocytes
late finding → jaundice
PBC
What is the dx for PBC?
Cholestatic LFT pattern → 3-4x inc ALP
Positive AMA, positive ANA, liver bx (dz not uniform throughout)
What is the first line and only proven therapy for PBC?
Ursodiol (URSO) → decreases ALP
What are additional treatment options for PBC?
Cholestyramine for pruritus, Osteoporosis agents (Ca, Vit D), vaccines, hepatology referral, no alcohol
What is the only effective treatment for end stage PBC?
Liver transplant
What are possible complications of PBC?
Portal HTN, edema, ascites, esophageal or gastric varices, splenomegaly, hepatic encephalopathy, osteoporosis & fractures, cholelithiasis, steatorrhea
What condition is a progressive, inflammatory, sclerosis & obliterative disease of the extra hepatic bile ducts, intrahepatic bile ducts, or both?
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)
Can the progression of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) be halted?
No
Who is primary sclerosing cholangitis MC in?
Men 20-50 y/o
What is primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) often associated with?
UC (check in pts w/ IBD + persistent & unexplained elevated ALP)
What is the median survival rate of PSC?
12 yrs
What does PSC ultimately lead to?
Biliary obstruction, secondary biliary cirrhosis, hepatic failure, portal HTN w/ bleeding varices
What are PSC patients at an increased risk for developing?
Cholelithiasis, choledocholithiasis, cholangitis, & cholangiocarcinoma
The following ssx are associated with what condition?
often asx
if sx- fatigue & pruritus are common
RUQ pain
progressive jaundice
anorexia, indigestion
acute cholangitis
PSC
The following diagnostic workup is for what condition?
cholestatic LFT pattern → 4-10x inc ALP
liver bx → fibrous obliteration of connective tissue in onion skin pattern
fibroscan
MRCP (preferred) & ERCP→ narrowing & beading of bile ducts
PSC
Which is noninvasive and has no risk of pancreatitis or cholangitis?
MRCP
What is the tx for PSC?
Ursodiol (URSO), cholestyramine for pruritus, ERCP (to distinguish from PBC), liver transplant if advanced
What procedure?
endoscope placed into bile duct → IV contrast outlines duct/pancreas & XRs are taken
Therapeutic for:
sphincterotomy to remove stone
stent placed for drainage
ERCP
What is a noninvasive procedure that uses a powerful magnetic field, radio frequency pulses, and a computer to produce detailed pictures of hepatobiliary & pancreatic systems?
MRCP
PBC vs PSC
In what population is there an increased incidence of gallbladder carcinoma?
Elderly women
What are most gallbladder carcinomas?
Adenocarcinomas
What ist he 5th MC GI malignancy and has a poor prognosis?
GB carcinoma
What RF are associated with GB carcinoma?
Hx chronic cholecystitis, porcelain gallbladder** (calcification of GB itself)
The following ssx are associated with what condition?
early → usually asx, incidental finding
advanced → RUQ pain & mass, wt loss, malaise, jaundice
dx w/ radiologic imaging
GB carcinoma
What is the treatment for GB cancer?
Cholecystectomy, wedge resection, LAD w/ large tumors