A Level Music Technology
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
(A/D) Conversion
An electronic process in which a continuously variable (analog) signal is changed, without altering its essential content, into a multi-level (digital) signal.
ADSR
Attack, Decay, Sustain, Release

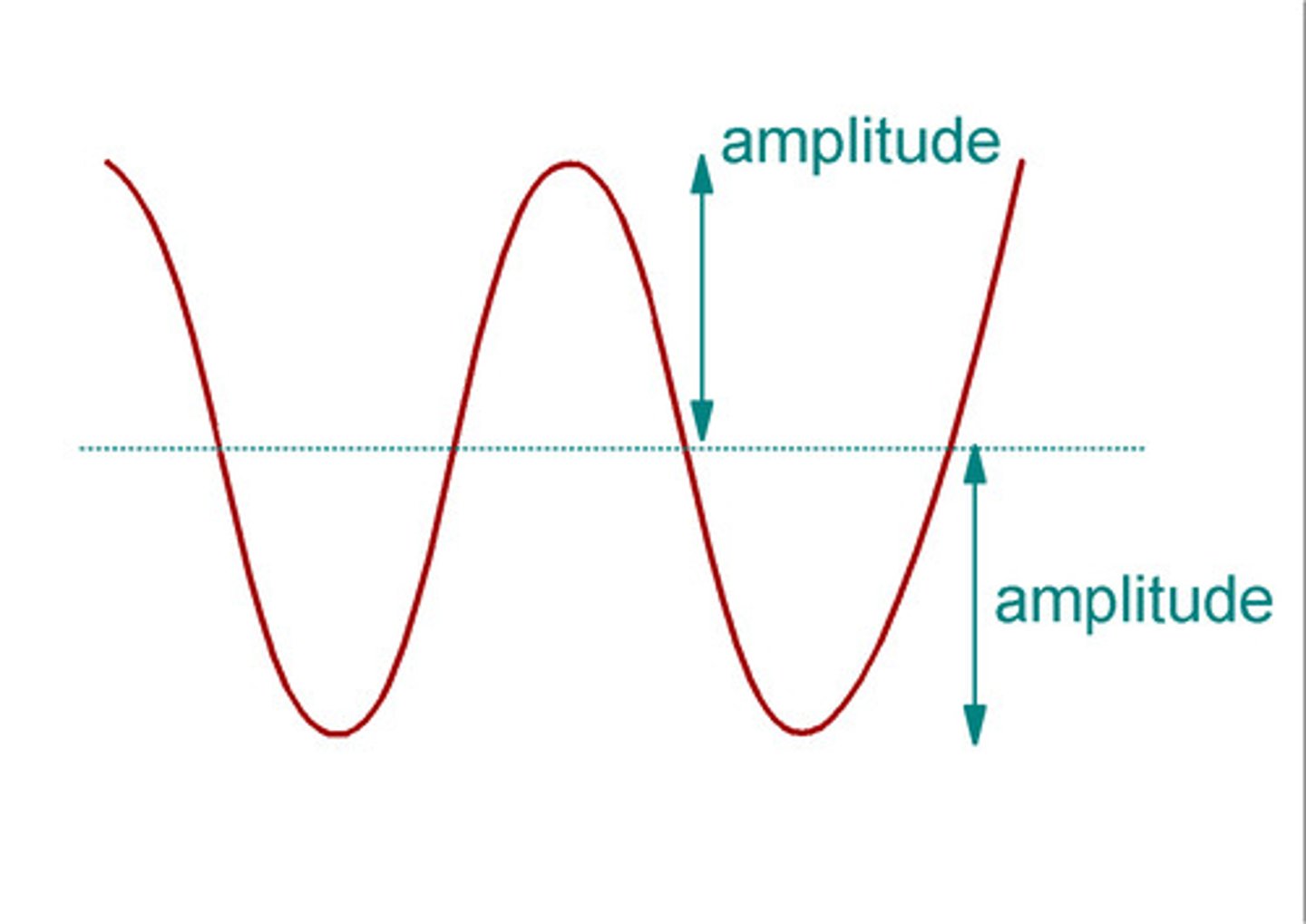
Amplitude
the fluctuation or displacement of a wave from its mean value.
Analogue
Recording audio in a format of continuous vibrations that are analogous to the original sound waves
Attack (Compression)
The time taken for the compressor to complete the gain reduction (or bring down the level) based on the compression ratio.
S/PDIF
allows the transfer of audio from one file to another without the conversion to and from an analog format, which could degrade the signal quality.
Balanced Cable
An audio cable, most commonly a three pin "XLR" type mic cable, which has two conduction channels surrounded by metallic shielding where each conductor is of equal impedance relative to the ground/ earth. Reduces unwanted noise.
Bounce
The process of exporting several tracks in an audio mix to one mono track or two stereo tracks.

BPM
Beats per minute, typically used as a measure of tempo in music and heart rate.
BUSS
A common electrical signal path along which signals may travel. In a mixer, there are several busses carrying the stereo mix, the groups, the PFL signal, the aux sends and so on.
Byte
consists of 8 bits
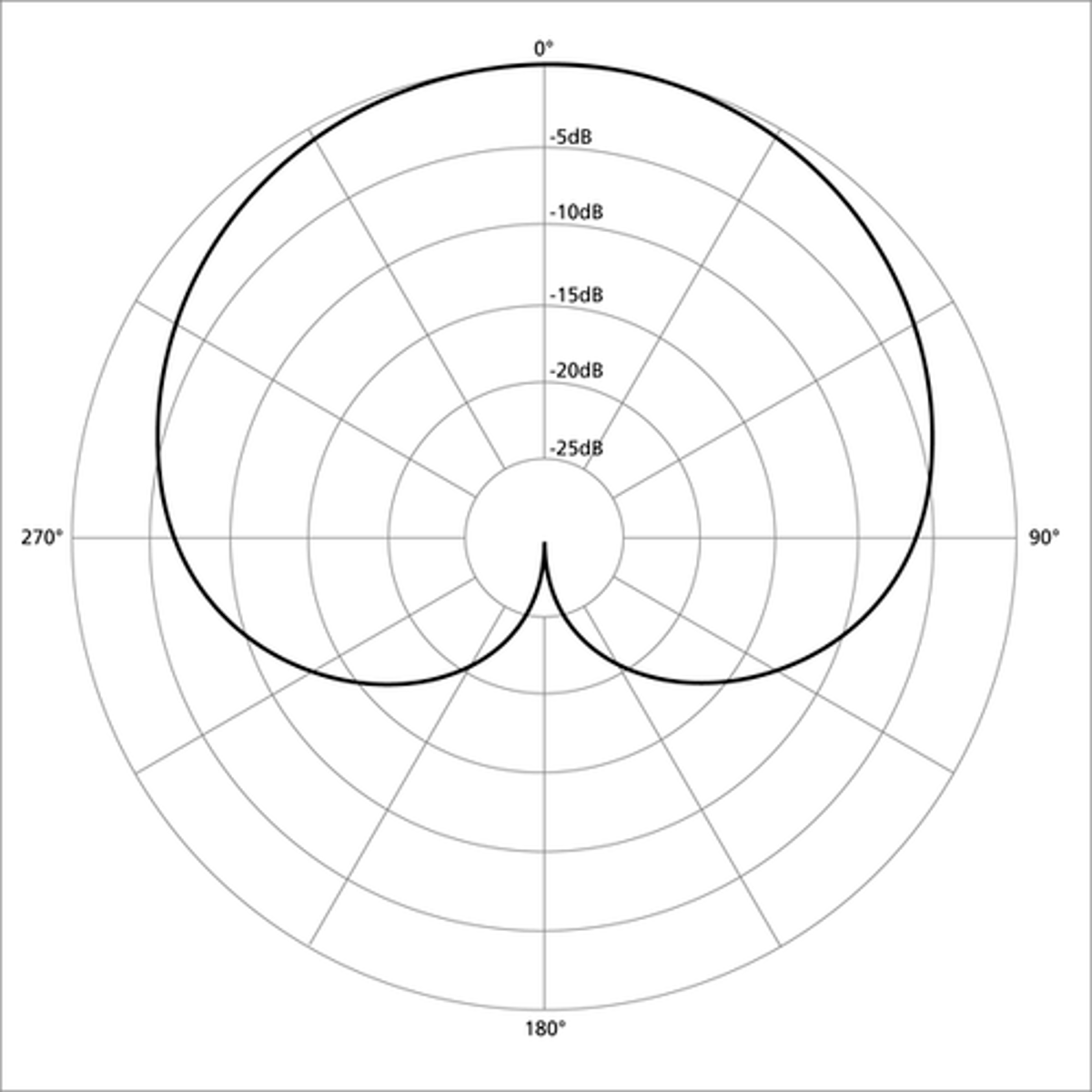
Cardioid Microphone/Pattern
a mic pattern that only picks up from front, rejects sound from side/back (only front diaphragm is turned on)
Channel
a path for passing data or digital audio.
Click track
Metronome pulse provided in software which assists musicians in keeping a consistent tempo.
Clipping
When the amplitude of a signal exceeds the maximum possible level of a device, the part of the waveform which is excessive is squared off resulting in a distortion of the sound.
Chorus
A voice doubling effect created by layering two identical sounds with a slight delay (20-50 mS) and slightly modulating the frequency of one or both of the sounds .
Compressor
reduces the dynamic range of audio signals by reducing the level of high signals or by increasing the level of low signals.
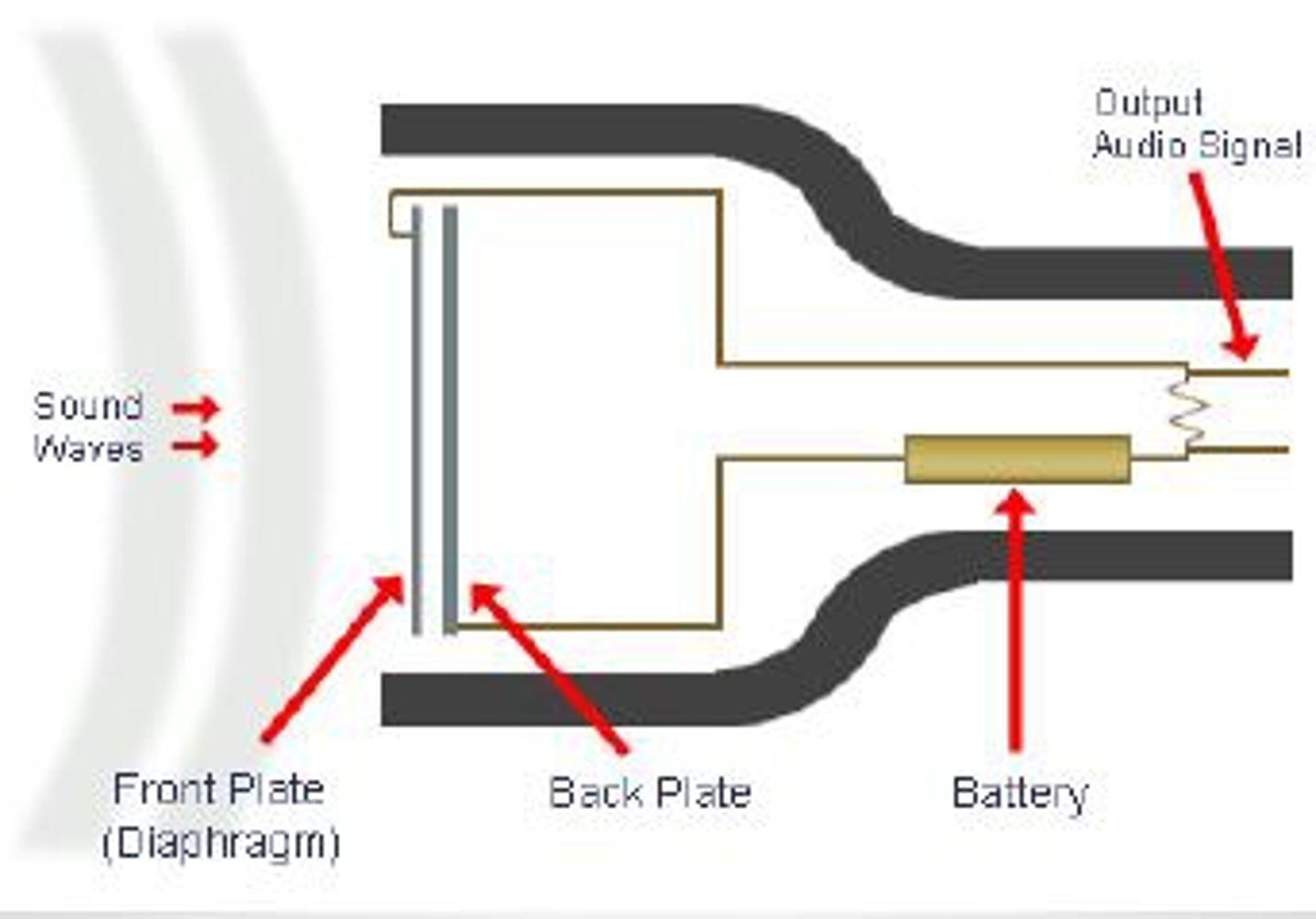
Condenser Microphone
Microphone that operates on the principle of measuring the change in electrical charge across a capacitor where one of the electrodes is a thin conductive membrane that flexes in response to sound pressure.
Controller
A device which let's you enter or change events into a computer or other digital device. Examples include keyboards, pitch and modulation wheels and wind controllers.
DAW
Digital Audio Workstation
dB
A measure of sound pressure level.
De-Esser
Signal processing device used to cut down on the sibilance or "hissy s's" which can sometime affect speech and singing through a microphone.
Delay
An effect that is used to add depth or space to an audio signal by repeating the input one or more times after a brief pause of a few milliseconds to a few seconds.
Digital
The use of Binary data to represent information, "Binary" meaning that the data (audio, video, whatever) has been reduced to many values which have one of two states, positive and non positive. Positive is represented by 1, and non positve by 0.
Distortion
a form of audio signal processing used to alter the sound of amplified electric musical instruments, usually by increasing their gain.
Dry (Signal)
A signal that has had no effects added.
Overdubbing
The ability to record one sound on top of another. Adding something to a previous recording, so that the two (or more) parts may be subsequently played together as a synchronous whole.
Ducking
used to automatically reduce signal levels when the level of a source signal exceeds a specified threshold.
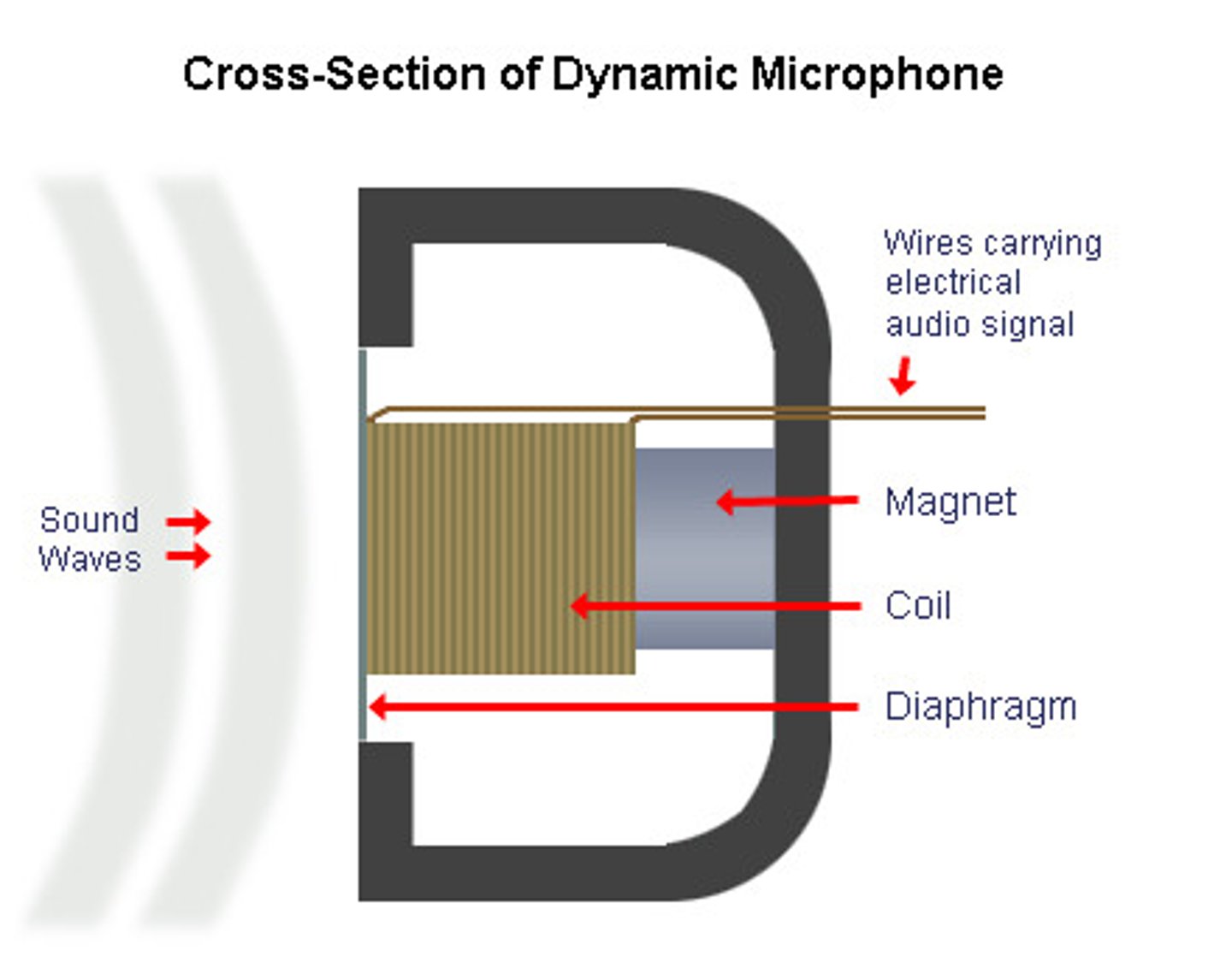
Dynamic Microphone
Microphone which works through a diaphragm being attached to a coil which operates within a strong magnetic field. The diaphragm vibrates in response to soundwaves, which, in turn stimulates motion of the coil.
Dynamic Range
Difference in signal level between the loudest and quietest parts of a performance / recording etc. Measured in dB
Echo
A very basic effect produced by repeating a sound with a delay long enough to be heard as a separate event.
Effect
A device for treating an audio signal in order to change it in some creative way.
Envelope
Creates changes in a sound over time, including alterations in a sound's amplitude, frequency and timbre.
Equalisation/EQ
boosting or attenuating the levels of different frequencies in a signal.
Exciter
A circuit designed to enhance the presence of an audio signal by synthesizing new high frequency harmonics to make it sound more clear, punchy, bright, or loud, without the use of ordinary EQ or gain.
Expander
designed to decrease the level of low level signals and increase the level of high level signals, thus increasing the dynamic range of the signal.
Fade in/out
A feature of most audio editing software that allows the user to apply a gradual amplitude increase or decrease over some segment of the sound.
Fader/slider/attenuator
allows the user to perform a gradual change to the amplitude of a signal.

Flanger
An effect created by layering two identical sounds with a slight delay (1- 20 mS) and slightly modulating the delay of one or both of the sounds.
Formant
Frequency component or resonance of an instrument or voice sound that doesn't change with the pitch of the note being played or sung
FM Synthesis
These produce sounds by generating a pure sine wave (carrier) and then mixing it with a second waveform (modulator). When the two waveforms are close in frequency, a complex waveform is produced.
Frequency
The rate per second at which an oscillating body vibrates. Usually measured in Hertz (Hz), humans can hear sounds whose frequencies are in the range 20 Hz to 20kHz.
Frequency Response
A graph which shows how a system or piece of equipment or even an environment such as a room responds to different frequencies.
Gain
The level of amplification of a given signal.
Glissando
A rapid slide through a series of consecutive tones in a scale like passage.
Global Editing
The editing of MIDI or audio events which affect an entire file or sequence.
Hard disk
A storage medium for digital data which can hold more information and can be accessed faster than a floppy disk.

Harmonics
All of the sounds that we hear gain their essential "character" through the presence of harmonics, which are sound waves whose frequency rises in incremental steps from a Fundamental frequency.
Harmony
Occurs when multiple pitches are being played simultaneously. (Chords)
Headroom
The safety margin in dBs between the highest peak signal being passed by a piece of equipment and the absolute maximum level the equipment can handle.
Hertz (Hz)
A unit of measurement denoting frequency.
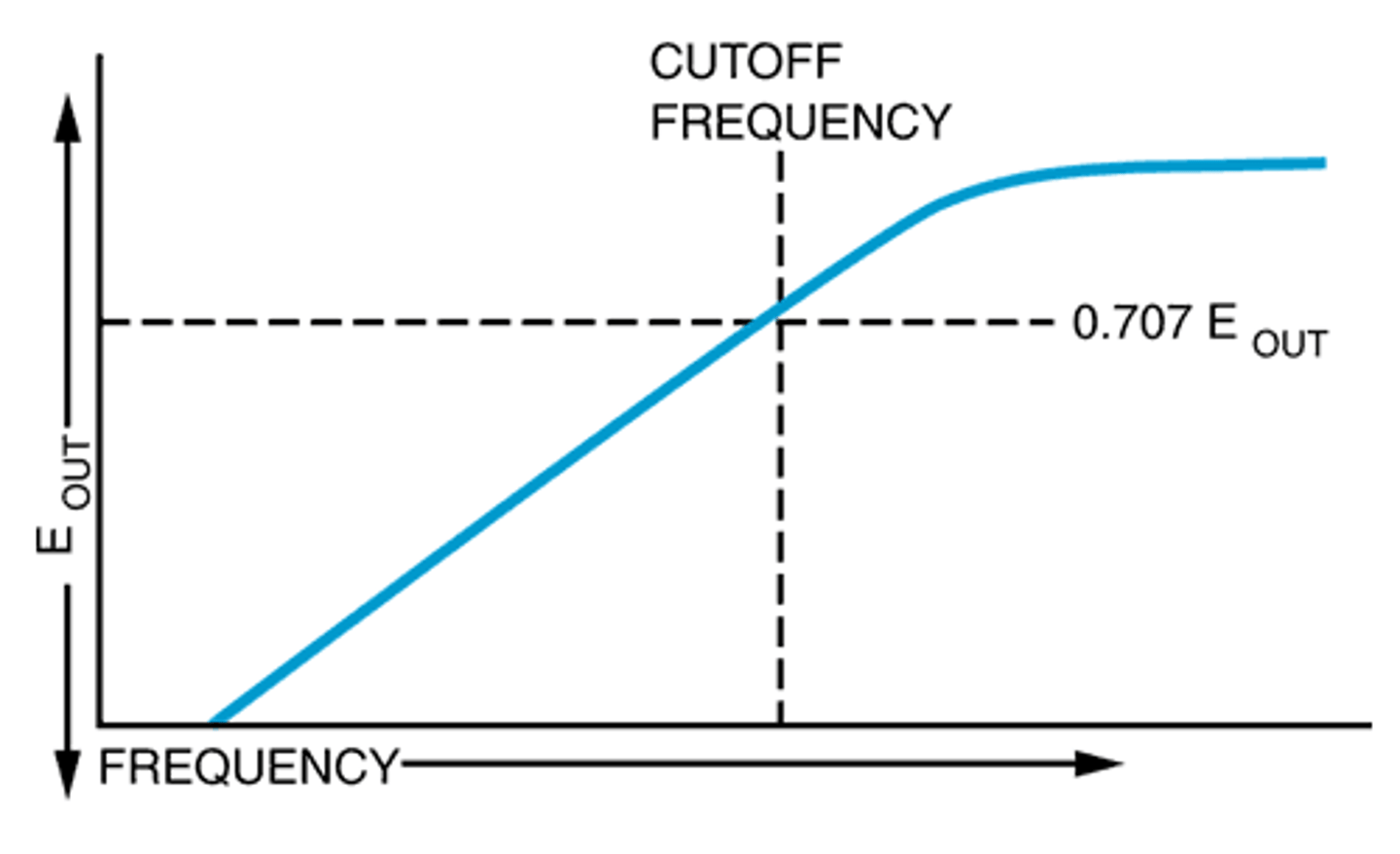
High Pass Filter (HPF)
passes signals with a frequency higher than a certain cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies lower than the cutoff frequency.
Impedance
The amount of resistance and / or reactance offered by an electronic circuit or device to the (AC) current which flows through it
Interface
An audio hardware that allows the computer to communicate with a microphone or line level device.
Jack (plug)
Very popular form of audio connector, available in stereo or mono formats (TS/TRS). usually ¼ “, but there are also smaller versions
LFO
A low frequency oscillator that is used to alter a sound's frequency or amplitude.
Limiter
Signal processing which sharply compresses (infinite:1) output once it reaches a certain preset level.
Linear
A device where the output is a direct multiple of the input.
Line Level Signal
A device that operates at this either has a very strong output signal, or only functions properly when you feed a very strong signal into it.
Loop
To repeat a sequencer pattern or portion of an audio sample repeatedly.
Low-Pass Filter (LPF)
A filter which attenuates frequencies above its cutoff frequency.
Mapping
In sequencing it is the process of identifying patches and keys so that sound files can be played properly.
Marker
In sequencing and audio software, used to record a position for easy editing navigation
MIDI
Musical Instrument Digital Interface provides a standardized method for devices such as synthesizers, samplers, sound cards, etc. to communicate musical events and data to each other.

Mixing
The process by which multiple sounds are combined into one or more channels. In the process, a source's volume level, frequency content, dynamics, and panoramic position are manipulated and or enhanced.
Modular Synthesis
A synthesiser where the individual sound generators or processors such as oscillators, filters, amplifiers, envelope generators etc. are physically separate units which can, or have to be, connected together by the user.
Modulation
The fast oscillation of one or more operators or sound waves of a synthesized sound.
Monophonic
Only one note of an instrument may be played at a time.
MP3
MPEG Layer III, digital audio compression format achieving smaller file sizes by eliminating sounds the human ear can't hear or doesn't easily pick up.
Multi-Track Recording
In traditional recording technology, the ability to layer multiple different audio signals at once.
Noise Gate
Cutting the signal for very short periods of time when it falls below a certain level - useful as a form of noise reduction.
Normalisation
An automatic process available in most audio software whereby the gain of all program material is adjusted so the peak level will just arrive at 0db.
Octave
A musical distance (interval) of 12 semitones.
Omni-Directional
polar pattern in the shape of a circle / sphere. Picks up sound equally from all angles.

Oscillator
A synthesis module used to create a cyclical waveform.
Pan
To move a signal left or right within the stereo field.
Parameter
A variable value that affects some aspect of a device's performance. Common ones include pitch bend, sustain, volume, and reverb.
Parametric Equalizer
A type of equalizer that provides control over each filter's frequency and the amount of cut or boost of each filter.
Patch Bay
A system of panel-mounted connectors used to bring inputs and outputs to a central point from where they can be routed using plug-in patch cords.
PCM (Pulse Code Modulation)
Digital audio recording format used since the late 1970s.
Peak
Maximum instantaneous level of a signal.
Phase
It is the amount by which one sine wave leads or lags a second wave of the same frequency
Pitch
The quality of a sound governed by the rate of vibrations producing it; the degree of highness or lowness of a tone.
Pitch Bend Wheel
A MIDI controller that can vary the pitch of a sound and allows notes to be bent up or down like when sequencing e.g sliding trombone
Plugins
Accessory programs that add functionality to digital audio software
Polar Pattern
A picture or graph of a transducer's sensitivity to soundwaves.
Polyphonic
More than one note of an instrument sound may be played at the same time.
Portamento
A gliding effect that allows a sound to change pitch at a gradual rate, rather than abruptly, when a new key is pressed or MIDI note sent.
Preamp
A device that takes a source signal, such as from a turntable, tape deck or CD player, and passes this signal at line level on to a power-amplifier.
Proximity Effect
When cardioid microphones are placed very close to the sound source, a boosting of the bass frequencies occurs which is known as the proximity effect.
Quantization
Used to adjust recorded material so it will be performed precisely on a selected division of the beat.
Resonant Frequency
A natural frequency of vibration determined by the physical parameters of the vibrating object.
Reverb
An effect that simulates natural reverberations (sound reflections) that occur in different rooms and environments to create an ambience or sense of spaciousness.
Ribbon Mic
A microphone where the sound capturing element is a thin metal ribbon suspended in a magnetic filed. When sound causes the ribbon to vibrate, a small electrical current is generated within the it.
Ripping
The process of taking audio data from a CD and making it into a sound file on your computer.
Sample rate
The resolution of digital audio that determines it's sound quality. (Measured in kHz)
Sampling
The act of taking a portion, or sample, of one sound recording and reusing it as an instrument or a sound recording in a different song or piece.
Sequencer
A hardware device, software application or module used to arrange timed events into some order.
Sibilance
High frequency whistling or lisping sound that affects vocal recordings, due either to poor mic technique or excessive equalisation.
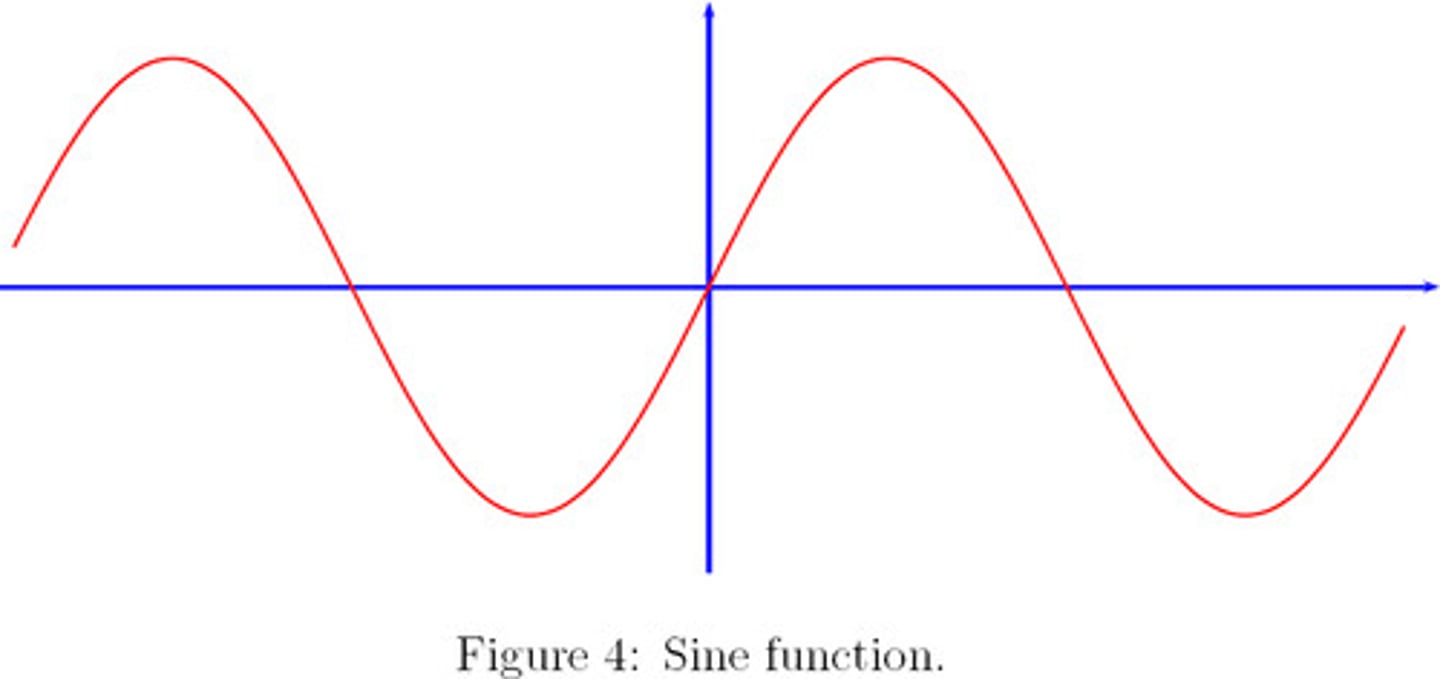
Sine wave
The most basic waveform, consisting of a single partial.