Minerals/Intrusive Igneous Rocks Quiz(2/4/26)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
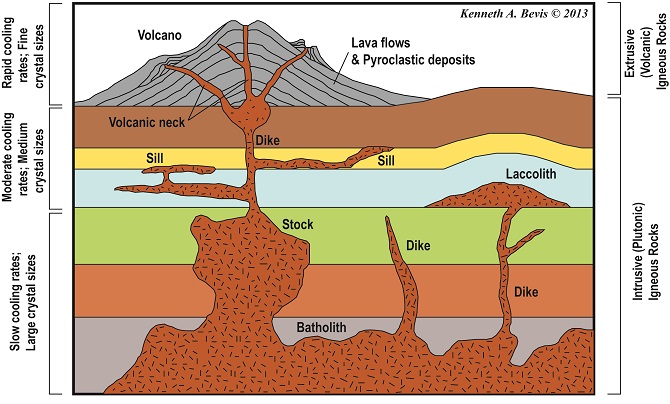
Pluton
solidified magma chamber
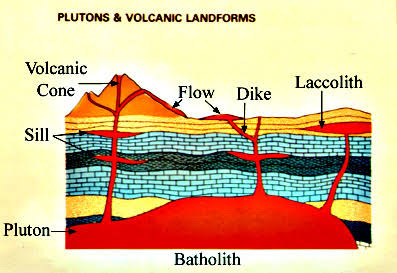
Batholiths
Large Pluton with significant surface exposure
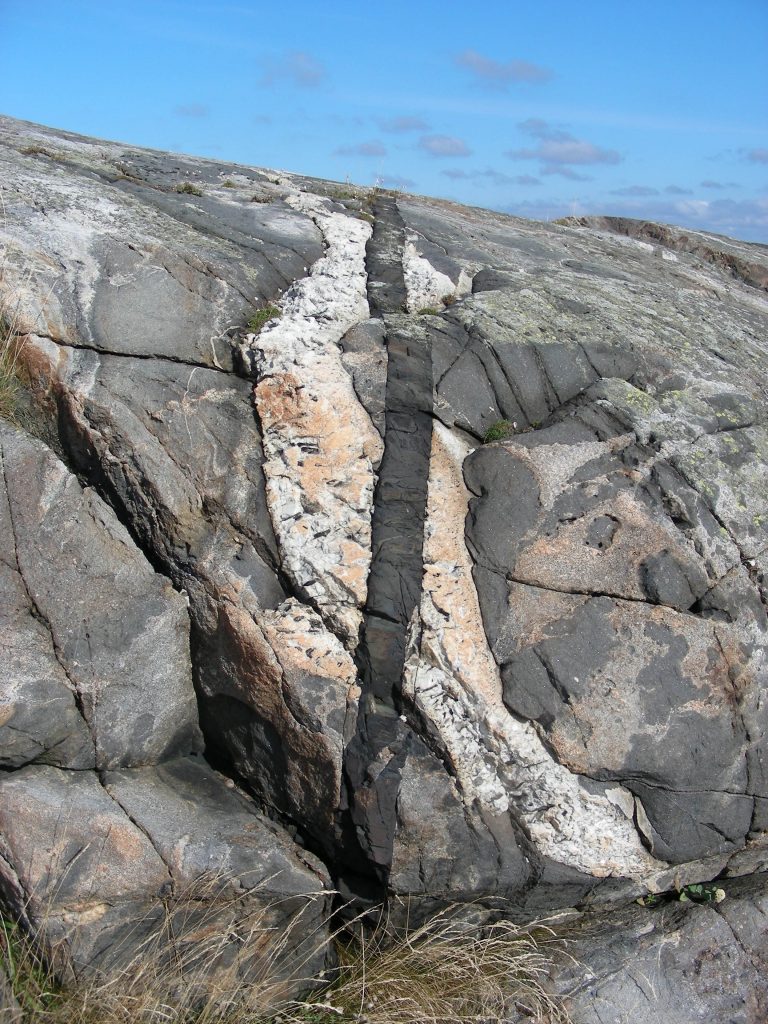

Dikes
Cut across bedding(following fractures) Planar Structure
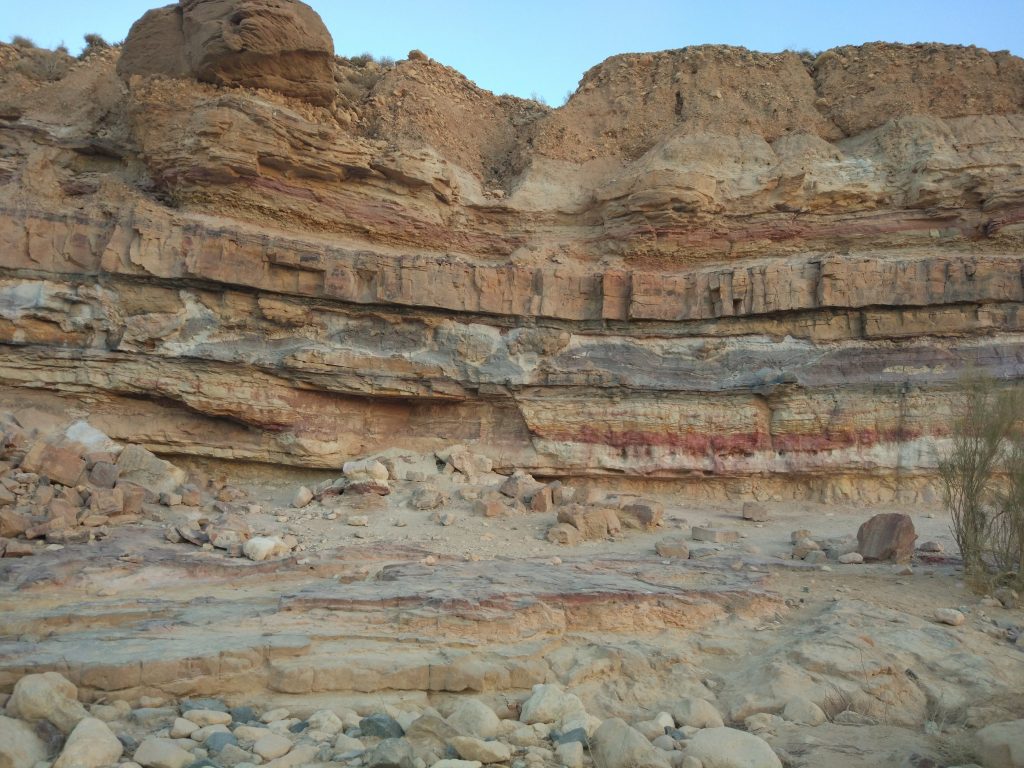

Sills
Along bedding planes planar structure parallel to layer
Phaneritic
-Course Grained
-Slow Cooling
-Intrusive rocks
Aphanitic
-Fine-Grained Texture
-Grained cannot be seen w/naked eye
-Quick Cooling
-Rocks erupted on the surface(or shallow intrusions)
Vesicular Texture
-Holes in the rock-vesicles
-Represent expanding gas bubbles
-Quick cooling preserved this shape
Felsic
SiO₂ rich
Light colored(White or Pink)
Intermediate
Light grey
Mafic
Fe, Mg rich
Dark(grey to black)
Ultramafic
Dark Minerals(Green)
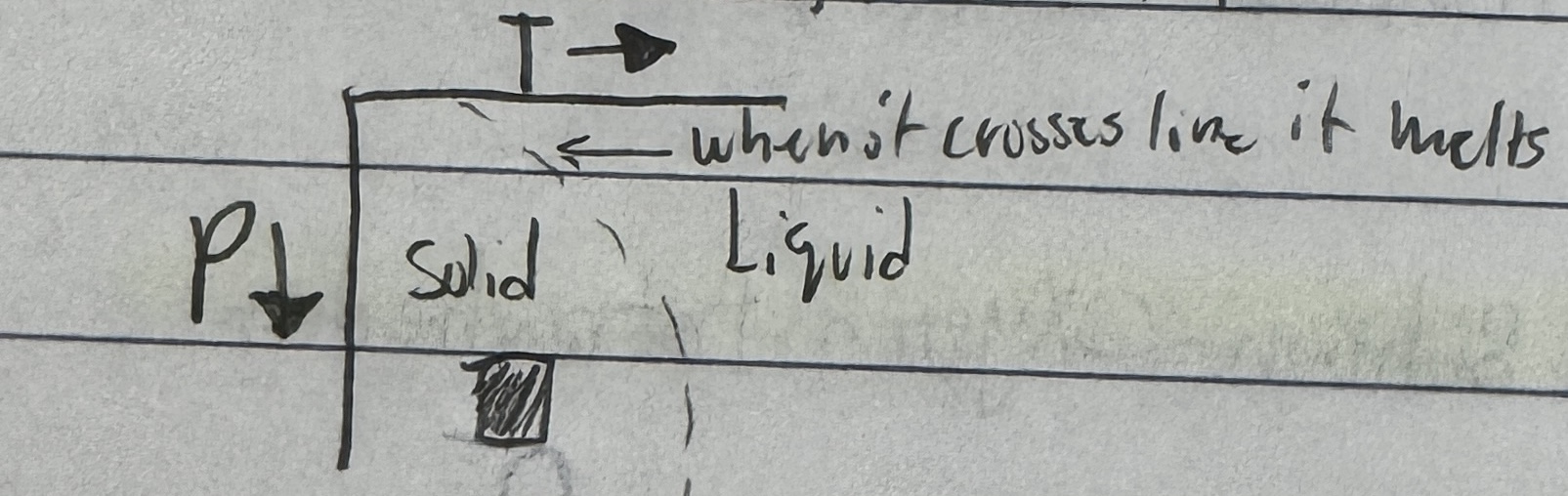
Decomposition Melting
Def: When pressure reduce, rocks melt
-At upwelling locations
-Midocean ridges
-Hotspots
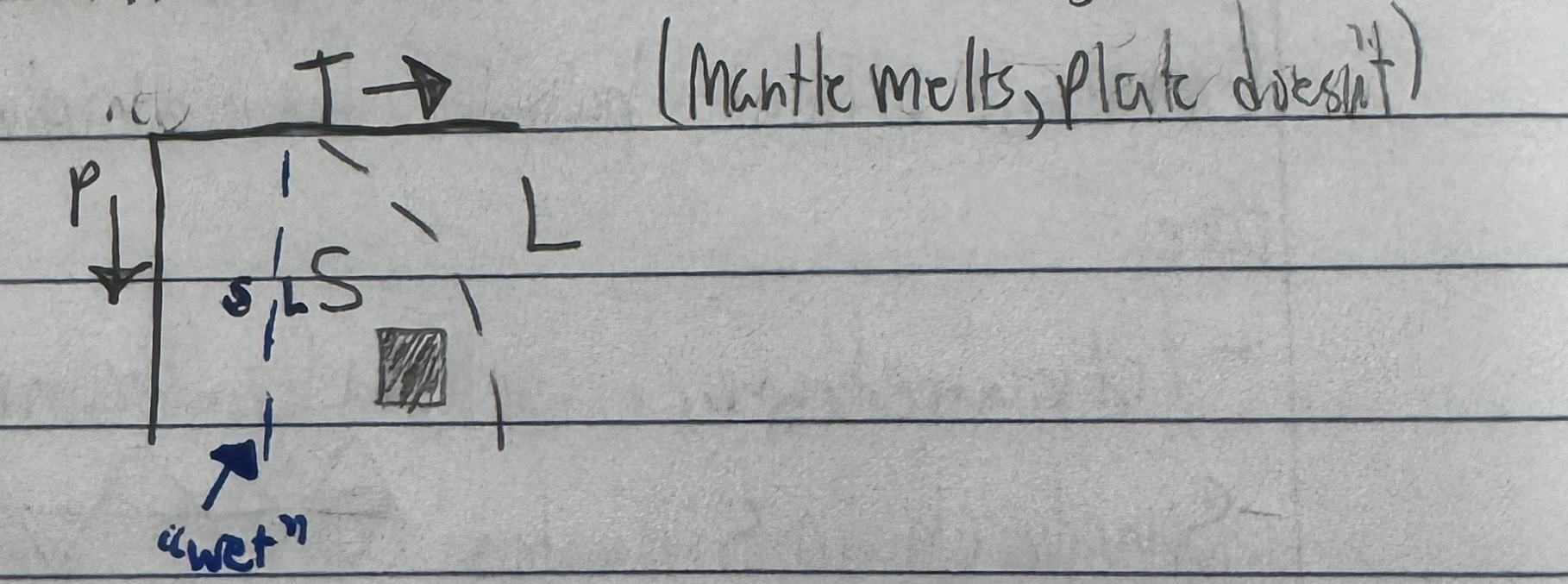
Flux Melting
Def: When water and other volute components
-Water and other volatile components are driven off of a sub ducting plate and get mixed into the mantle and cause melting in mantle wedge region
Precipitation
Ions come out of solution to form a solid
Crystallization
Minerals form during cooling
Metamorphism
New minerals due to heat or pressure
Weathering
New minerals form due to chemical reactions in the environment(hydrolosis)
Biological Process
Many organisms use ions from water to precipitate minerals