Behavioral Science I Module of the MCAT Self Prep eCourse: Lesson 6: Memory (Pro)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Lesson 6: Memory
Lesson 6: Memory
Compare the Information Processing Model of the nervous system to how a computer works.
In both the Information Processing Model and a computer, input is taken from the environment, processed, and outputs are produced.
In the information processing model, which of the following terms best describes the initial scent of fresh-cut grass that can easily be forgotten later?
(A) Echoic Memory
(B) Sensory Memory
(C) Working Memory
(D) Iconic Memory
(B) Sensory Memory
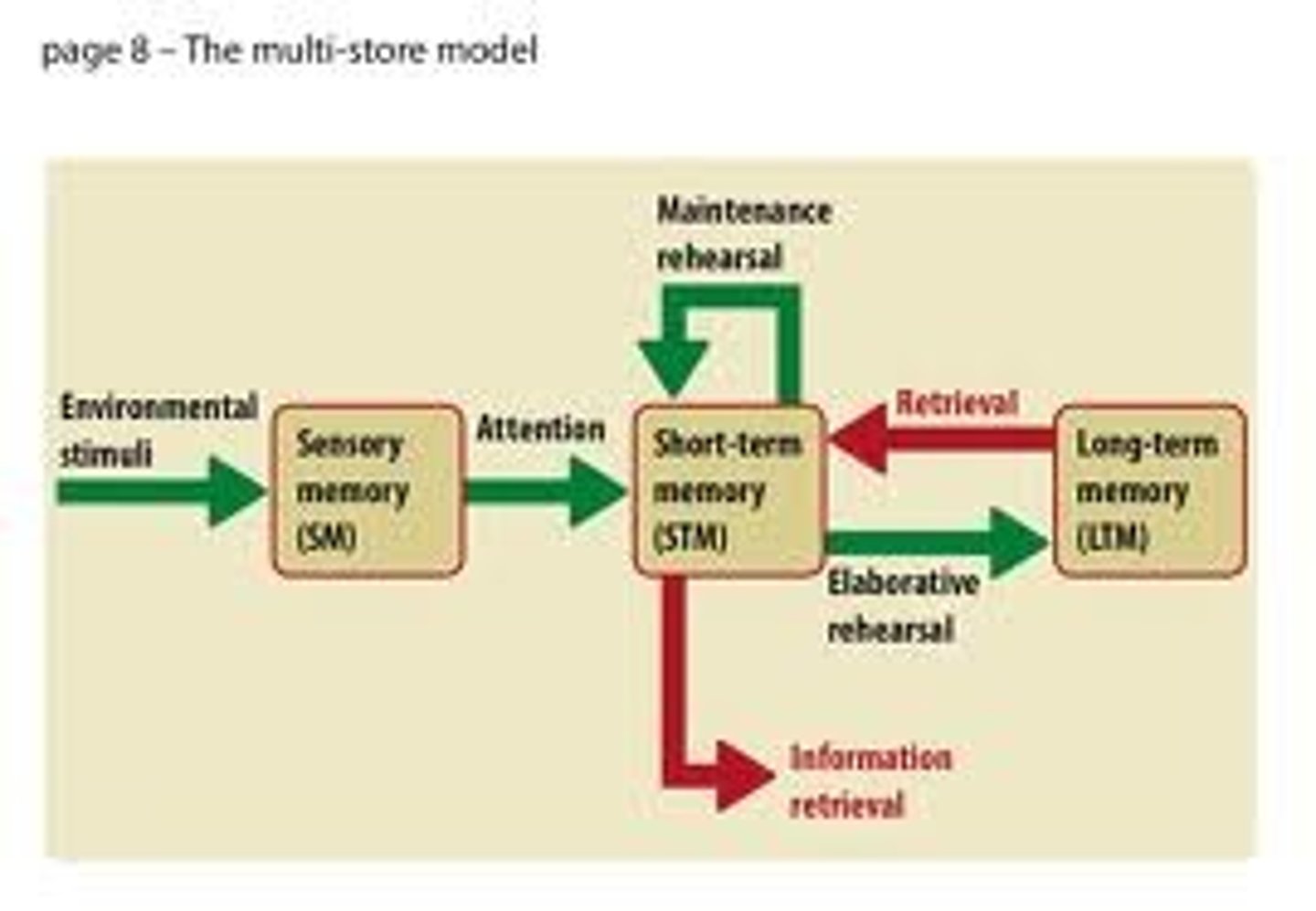
In the information processing model, which of the following terms best describes the initial sight of blood or seeing a white coat that is easily forgotten?
(A) Echoic Memory
(B) Sensory Memory
(C) Working Memory
(D) Iconic Memory
(D) Iconic Memory
Seeing either blood or a white coat would count as iconic memory, because they were seen but kept only in sensory memory.
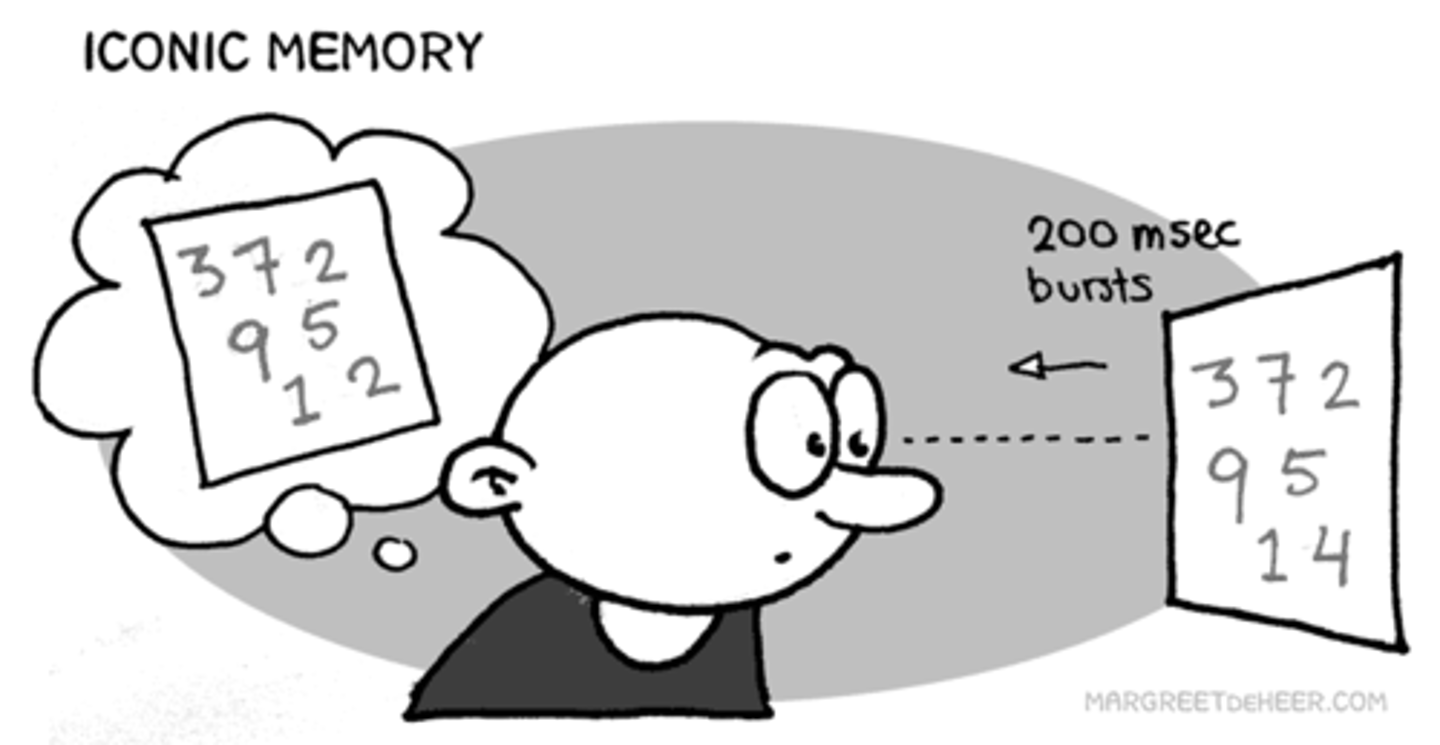
In the information processing model, which of the following terms best describes hearing a patient scream or noticing a cricket chirp, which is easily forgotten?
(A) Echoic Memory
(B) Sensory Memory
(C) Working Memory
(D) Iconic Memory
(A) Echoic Memory
Echoic memory is memory for what you hear and is kept only in sensory memory.

CRB In terms of strength of encoding information, rank each of the following ways we encode information from strongest to weakest.
I. Semantic Encoding
II. Visual Encoding
III. Acoustic Encoding
(A) I, II, III
(B) II, I, III
(C) I, III, II
(D) II, III, I
(C) I, III, II
In terms of strength of encoding information, the order of strongest to weakest encoding techniques are:
-Semantic Encoding
- Acoustic Encoding
- Visual Encoding
CRB Which of the following terms best describes the effect when we put information in context of our own lives, making it easier to recall later?
(A) Self-Reference Effect
(B) Context Effect
(C) Maintenance Rehearsal
(D) Triple-Repeat Effect
(A) Self-Reference Effect
The Self-Reference Effect explains how we recall information better once we put it into the context of our own lives.
CRB Which of the following terms is best described as repeating a piece of information to either store information in working memory or work to encode it into long-term memory?
(A) Self-Reference Effect
(B) Context Effect
(C) Maintenance Rehearsal
(D) Triple-Repeat Effect
(C) Maintenance Rehearsal
Maintenance Rehearsal is best described as repeating information to keep it stored in your memory longer, whether it be working memory or trying to encode it into long-term memory.

True or False? Because both echoic and iconic memory fall under sensory memory, they both last the same amount of time.
False. Even though both echoic and iconic memory fall under sensory memory, the MODALITY (form of acquiring the memory) will determine how long the memory lasts for. For instance, echoic memory lasts for about 4 seconds while iconic memory only lasts for 1/4 of a second!
Sometimes referred to as short-term memory, this type of memory can hold about 7 (plus or minus 2) pieces of information at a time and manipulate them.
(A) Echoic Memory
(B) Sensory Memory
(C) Working Memory
(D) Long-term Memory
(C) Working Memory
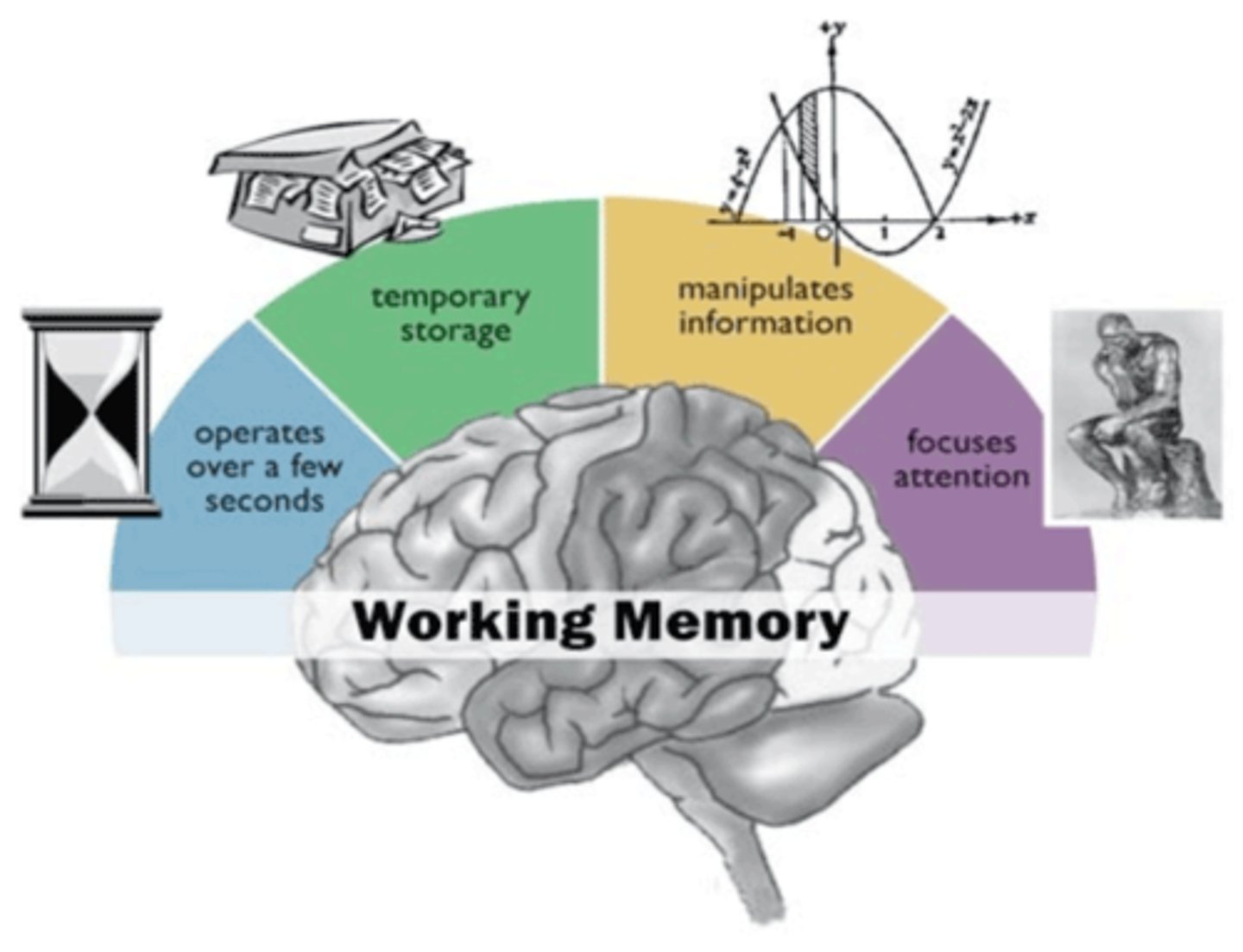
CRB Where is short-term memory primarily found?
(A) Cerebrum
(B) Medulla
(C) Amygdala
(D) Hippocampus
(D) Hippocampus
The Hippocampus is where short term-memory is mostly found, along with transforming short-term memories into long-term ones.
Compare the functions of the Visuo-Spatial Sketchpad with the Phonological Loop.
Both the Visuo-Spatial Sketchpad and Phonological Loop are part of Working Memory. The Visuo-Spatial Sketchpad is used for visual information (like schedules and maps) whereas the Phonological Loop is used for verbal information (words and numbers).
True or False? Words that are read will be stored in the Visuo-Spatial Sketchpad.
False. Words that are read will be stored in the Phonological Loop.
Remember, it is the type of information that determines where in the working memory it is stored, not the modality of acquiring the information!
In terms of the Visuo-Spatial Sketchpad, Phonological Loop, and Episodic Buffer, describe the function of the Central Executive.
The Central Executive functions to coordinate the efforts of the Visuo-Spatial Sketchpad and Phonological Loop, allowing them to work together and form an integrated representation, which is stored in the Episodic Buffer.
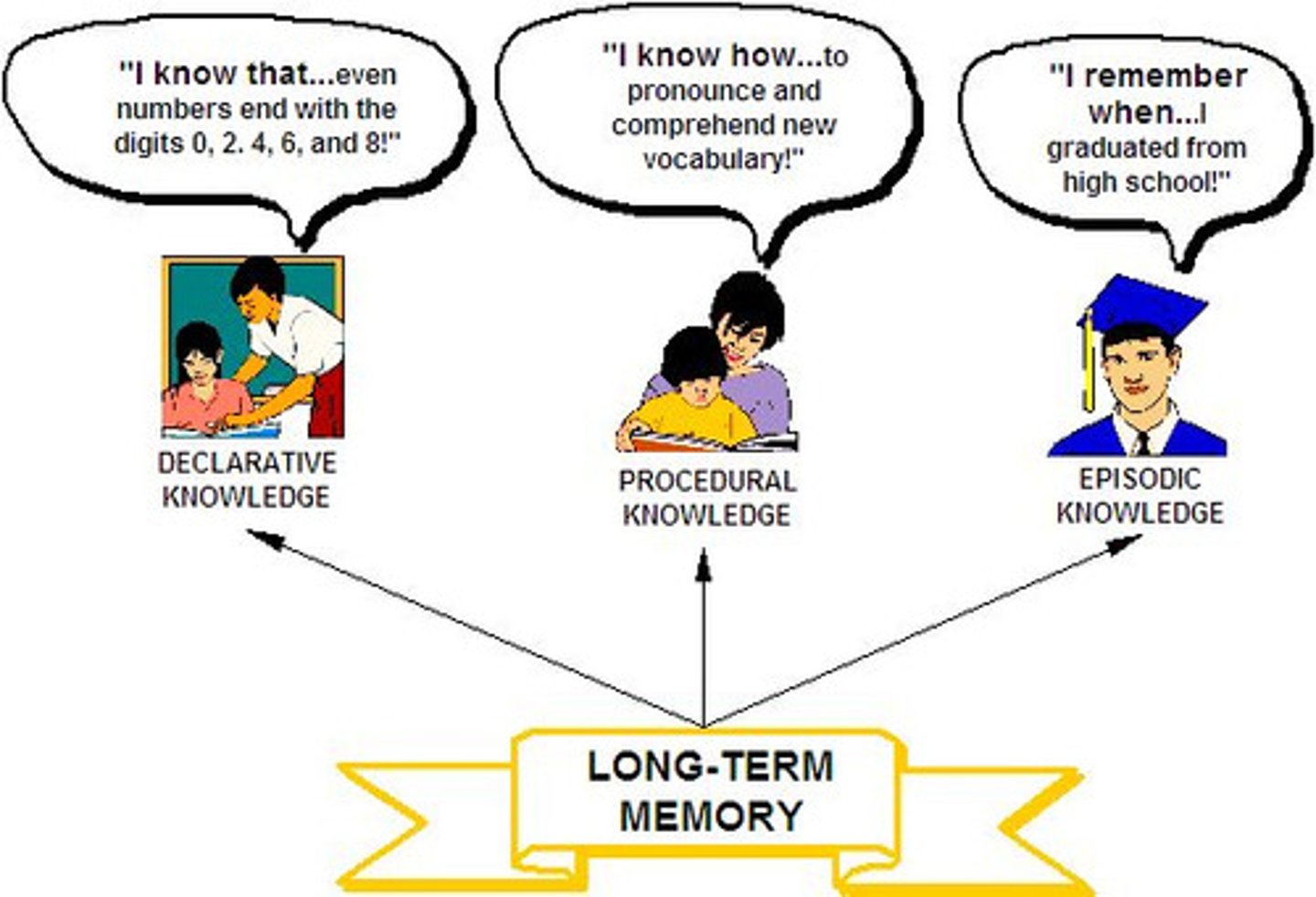
Which of the following terms refers to the form of memory that holds almost limitless amounts of information, including implicit and explicit memories?
(A) Long-term Memory
(B) Sensory Memory
(C) Working Memory
(D) Iconic Memory
(A) Long-term Memory
Long-term Memory can hold almost limitless amounts of information, and includes implicit and explicit memories.
People often compare familiar tasks to riding a bike. Which 2 of the following memory terms describe a skill like riding a bike?
I. Implicit
II. Non-Declarative
III. Explicit
(A) I Only
(B) I and II Only
(C) I and III Only
(D) II and III Only
(B) I and II Only
Implicit and Non-Declarative Memory are synonyms and describe riding a bike.
Declarative and Explicit are also synonyms.

Think about your high school graduation. What type of memory is that?
(A) Procedural Memory
(B) Semantic Memory
(C) Priming
(D) Episodic Memory
(D) Episodic Memory

Think about the vocabulary tests from elementary school. What type of memory was tested?
(A) Procedural Memory
(B) Semantic Memory
(C) Priming
(D) Episodic Memory
(B) Semantic Memory
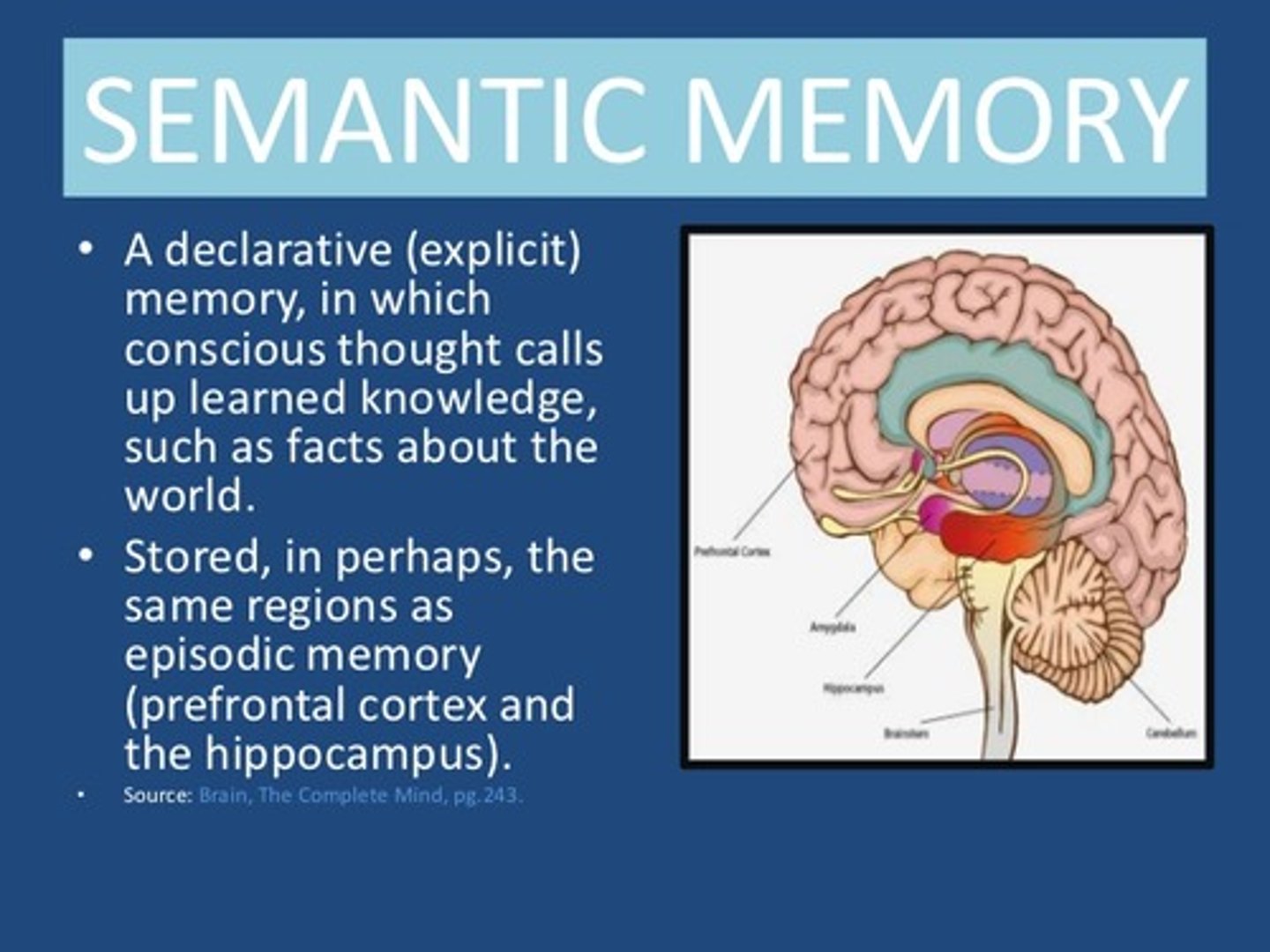
Which of the following terms refers to when a recent exposure to a stimulus will unconsciously influence a response to a later stimulus?
(A) procedural memory
(B) semantic memory
(C) priming
(D) episodic memory
(C) Priming
If you are trying to memorize which lights in a grid are lit, and the top row is lit, you may remember each of those lights by remembering "top row lit". Which of the following are used here?
I. Rote Rehearsal
II. Chunking
III. Method of Loci
(A) II only
(B) I and III only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(C) II and III only
Chunking was used by breaking the larger grid into more manageable parts.
The Method of Loci was used because a specific visualization/mental image was used to remember this.

If you are looking for supplies at a bookstore, and you are trying to learn your list by simply repeating the items over and over again, which encoding strategy are you using?
(A) Rote Rehearsal
(B) Chunking
(C) Pegword Mnemonic Device
(D) Method of Loci
(A) Rote Rehearsal
It is also the weakest method.

Compare the Pegword and Method of Loci mnemonic devices.
Pegword devices are number and verbally based (match numbers with rhyming words, "one is a gun"), whereas Method of Loci is based on location (putting items in different rooms of your house or something like that).

True or False? The encoding strategy of Spacing explains that learning occurs best when spread out over time, not cramming.
True. The encoding strategy of Spacing explains that learning occurs best spread out over time, not cramming.

A student shows up drunk to a psychology exam, claiming he is using a retrieval cue because he studied drunk. Which retrieval cue is he using?
(A) Priming
(B) Context Clues
(C) State-dependent
(D) Recency
(C) State-dependent
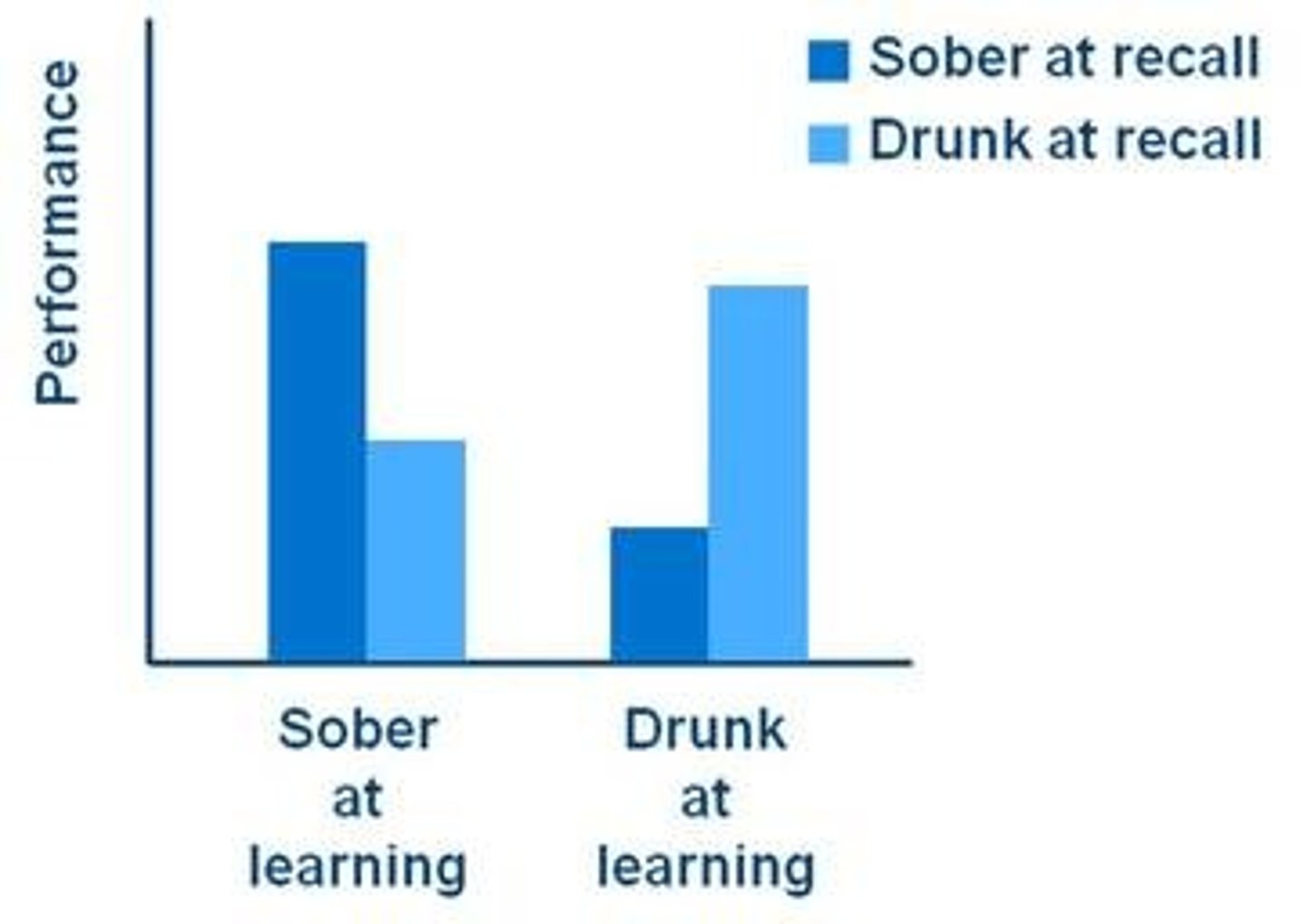
CRB True or false? Similar to State-Dependent memory, there is also a Mood-Dependent Memory; for example, if in a sad mood, someone is more likely to remember the tougher times in their life.
True. Similar to State-Dependent memory, there is also a Mood-Dependent Memory; for example, if in a sad mood, someone is more likely to remember the tougher times in their life.
This is part of what can make Depression so tough to break out of!
In free recall, the serial position effect says subjects are more likely to remember the beginning and end of a list than the middle. Which of these effects is not a cause of the serial position effect?
I. Context Clues
II. Primacy Effect
III. Recency Effect
(A) I Only
(B) II Only
(C) III Only
(D) II and III Only
(A) I Only
Context Clues is not a cause of the serial position effect.
The Primacy Effect says that the first few items in a series are more likely to be recalled than subsequent items.
The Recency Effect says the final items in a series are more likely to be recalled than other items.
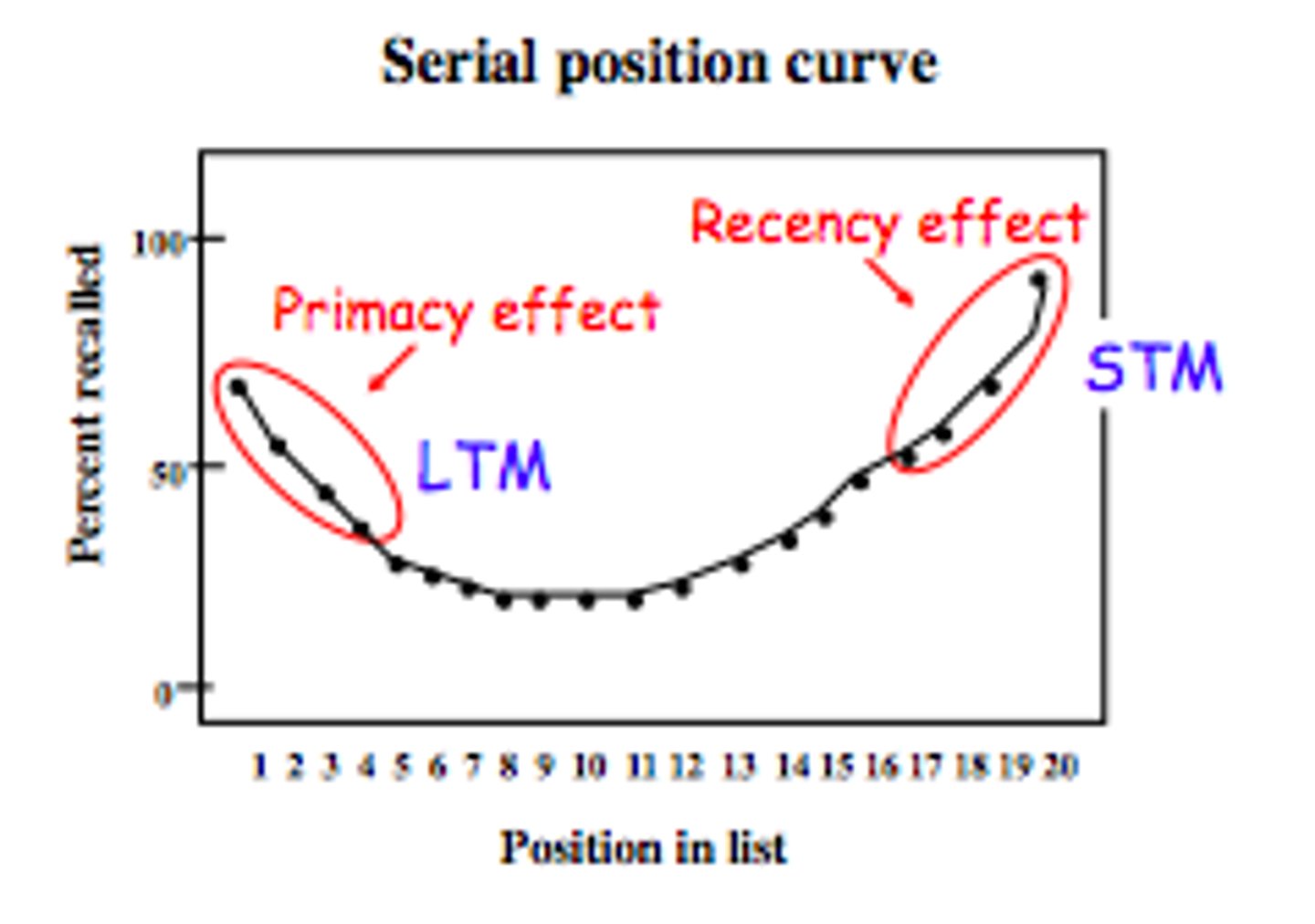
Rate the following retrieval tests in order of difficulty from hardest to easiest to complete.
I. Recognition
II. Free Recall
III. Cued Recall
(A) I > II > III
(B) II > I > III
(C) II > III > I
(D) I > III > II
(C) II > III > I
Because adding more cues makes retrieval easier, the order from hardest to easiest is:
II. Free Recall
III. Cued Recall
I. Recognition
CRB Another way retrieval can be improved is by changing what is being recalled. If given a 3x3 grid of letters, how would recall differ between needing to recall all of them (Whole-Report) or any specific row or column of them (Partial-Report)?
(A) There are no differences between Whole-Report and Partial-Report recall.
(B) There is better recall in Whole-Report, especially if told to memorize each letter.
(C) There is better recall in Partial-Report, but only for the first and last rows, not the middle ones.
(D) There is better recall in Partial-Report, no matter which row is chosen.
(D) There is better recall in Partial-Report, no matter which row is chosen.
This may be because, when asked to list all the items, the time it takes to list the first few can be long enough to forget the others.
CRB True or false? Based on the previous card's information, it is clear that all of the letters in the grid entered the iconic memory.
True. Based on the previous card's information, it is clear that all of the letters in the grid entered the iconic memory. This is clearly the case because the letter could have been in any row and still recalled accurately.
How does a human's Reconstructive Memory differ from a computer's memory?
Humans have reconstructive memory, which can slightly alter a memory as it is recalled due to one's mental state. A computer's memory, however, will recall information accurately time and time again.
If a subject watches a video and is later told incorrect information about the video, they are more likely to recall the video incorrectly. Which of the following is a cause of this?
(A) Context Clues
(B) Source monitoring error
(C) Recency Effect
(D) Primacy Effect
(B) Source monitoring error
Because the subject was told incorrect information about the video, they could recall that incorrect information and think it was from the video itself.
In other words, the subject is forgetting what they actually saw in the video (one source) because of what they were told (information from another source). This therefore a Source monitoring error.
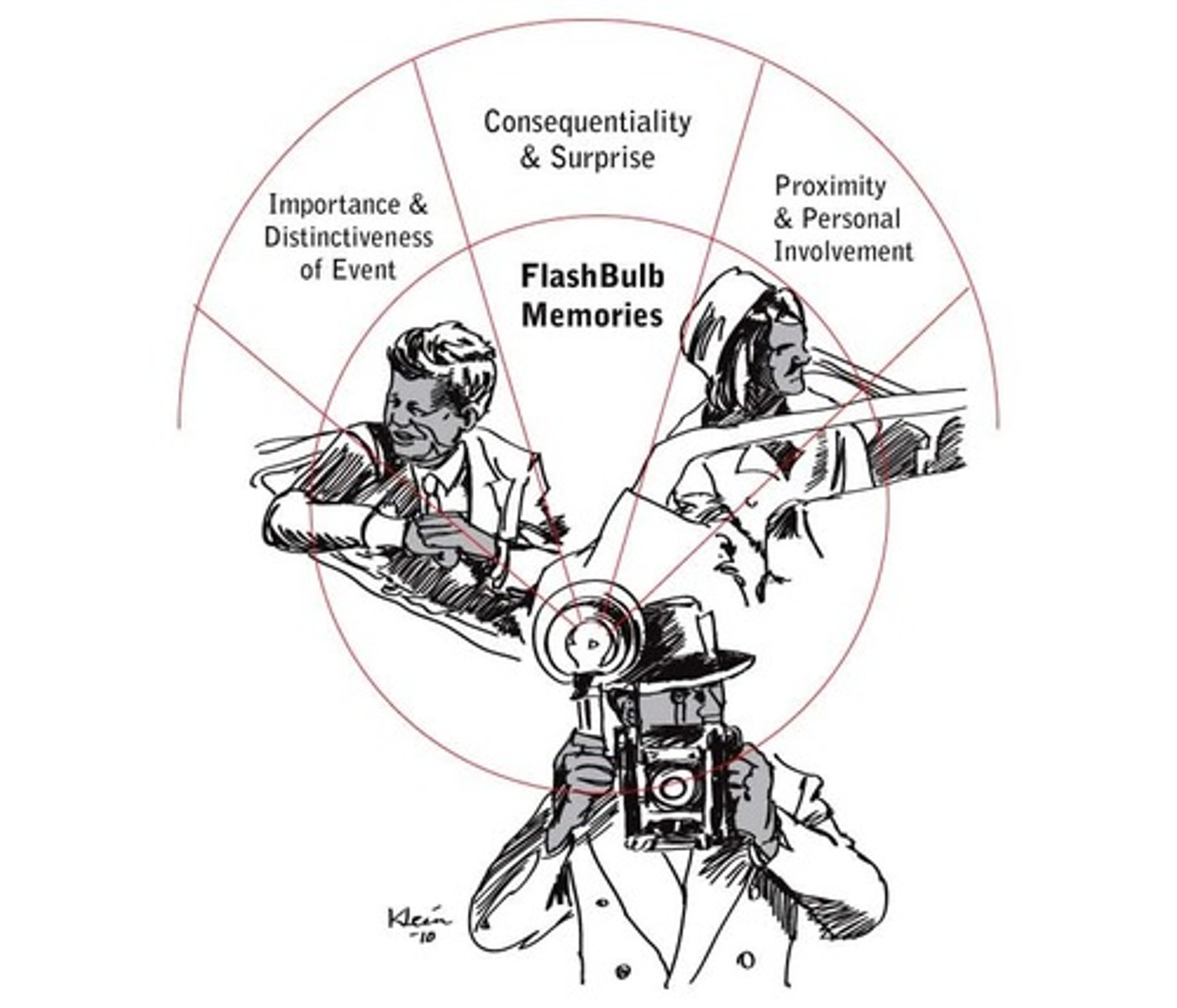
What is a flashbulb memory, and are they susceptible to reconstruction?
A flashbulb memory is an extremely emotional, vivid memory (positive or negative). They are still susceptible to reconstruction.
Synaptic plasticity allows neurons to improve their connectivity and strength. How does repeatedly firing a neuron increase its signaling strength?
(A) By triggering the growth of new neurons (cell division)
(B) By converting the pre-synaptic signals into more effective, stronger synapses (Long term potentiation)
(C) By changing which signaling molecules are released by the pre-synaptic neuron, the post-synaptic ion channels can be more activated
(D) By sensitizing the synapse to decrease the distance between the axon terminal and dendrite
(B) By converting the pre-synaptic signals into more effective, stronger synapses (Long term potentiation)
CRB Alternatively to this neuroplasticity, there must also be a removal of unused neural connections to counteract those strong ones being strengthened. Which of the following terms best describes this effect?
(A) Maintenance Effect
(B) Synaptic Pruning
(C) Synaptic Control
(D) Connection Potentiation
(B) Synaptic Pruning
Synaptic Pruning follows the "use it or lose it" principle, with unused neural connections being broken and oft-used ones being strengthened.
Even if Ebbinghaus could not recall his nonsense words he learned, they were not completely gone from his long-term memory. Which of the following ways can show information is still stored?
(A) By relearning the material faster than novel material is learned
(B) By recalling the sequences after context clues are given
(C) By learning a new set of letters and having proactive interference from previous sets.
(D) By teaching the material to someone else without realizing it.
(A) By relearning the material faster than novel material is learned.
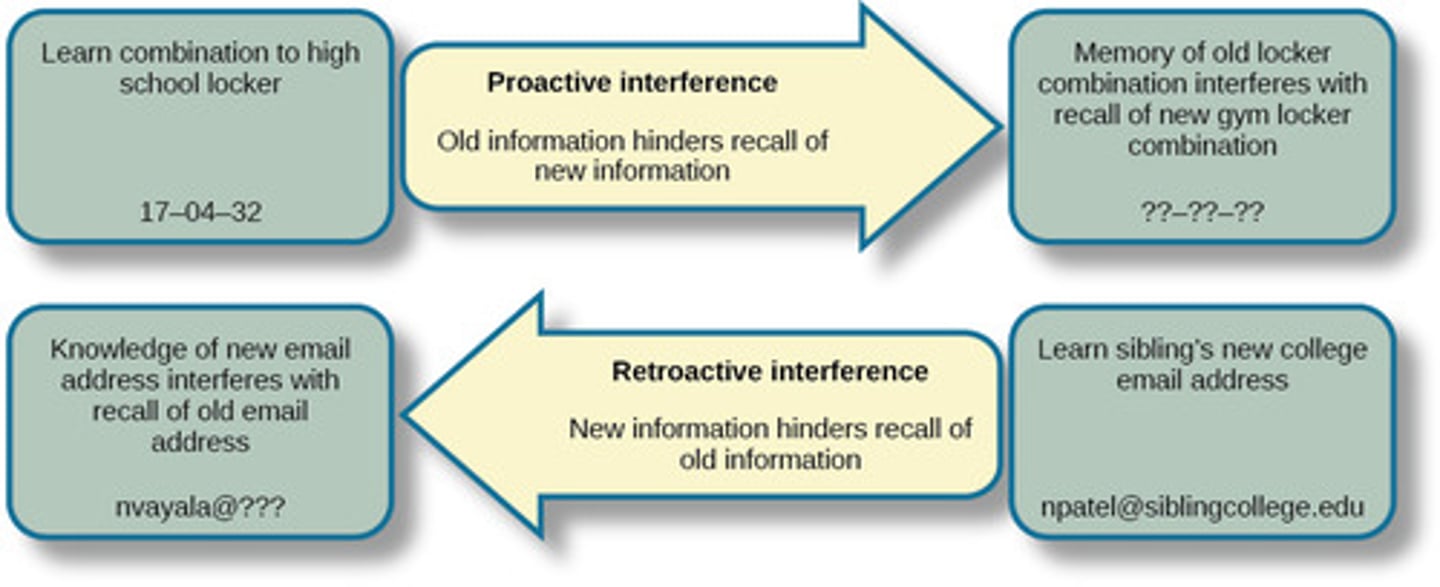
Compare retroactive and proactive interference in terms of memory.
Retroactive interference is when some new piece of information makes it harder to recall previously learned information/memoreis.
Proactive interference is when something learned in the past interferes with learning or retrieving something learned after.
CRB Alternatively to retroactive interference, Positive Transfer is when old information helps someone learn new information. Which of the following is NOT an example of this?
(A) Remembering "righty tighty lefty loosey", Jon successfully fixes his sink.
(B) A hockey referee quickly adapts to soccer's offsides rule, having some previous experience with offsides rulings.
(C) A lawyer has studied many cases before, so when he finds a novel case that would help his argument, he is able to learn it easily.
(D) A doctor recalls their triage training from previous ER and EMT work and learns the triage system for natural disaster settings in a similar fashion.
(A) Remembering "righty tighty lefty loosey", Jon successfully fixes his sink.
In this example, there is no new information being learned, only old information being applied.
Aging is almost always talked about with a decline in cognitive memory. Of the following, which is the only type of memory to decrease with age?
(A) Semantic Memory
(B) Recognition
(C) Emotional reasoning
(D) Episodic Memory
(D) Episodic Memory
Aging is almost always talked about with a decline in cognitive memory, however some cognitive abilites actually improve. Which of the following does NOT improve?
(A) Semantic Memory
(B) Crystallized Memory
(C) Emotional reasoning
(D) Dividing Attention
(D) Dividing Attention
Semantic Memory, Crystallized IQ (using knowledge and experience for problem solving) and Emotional Reasoning all improve with age.
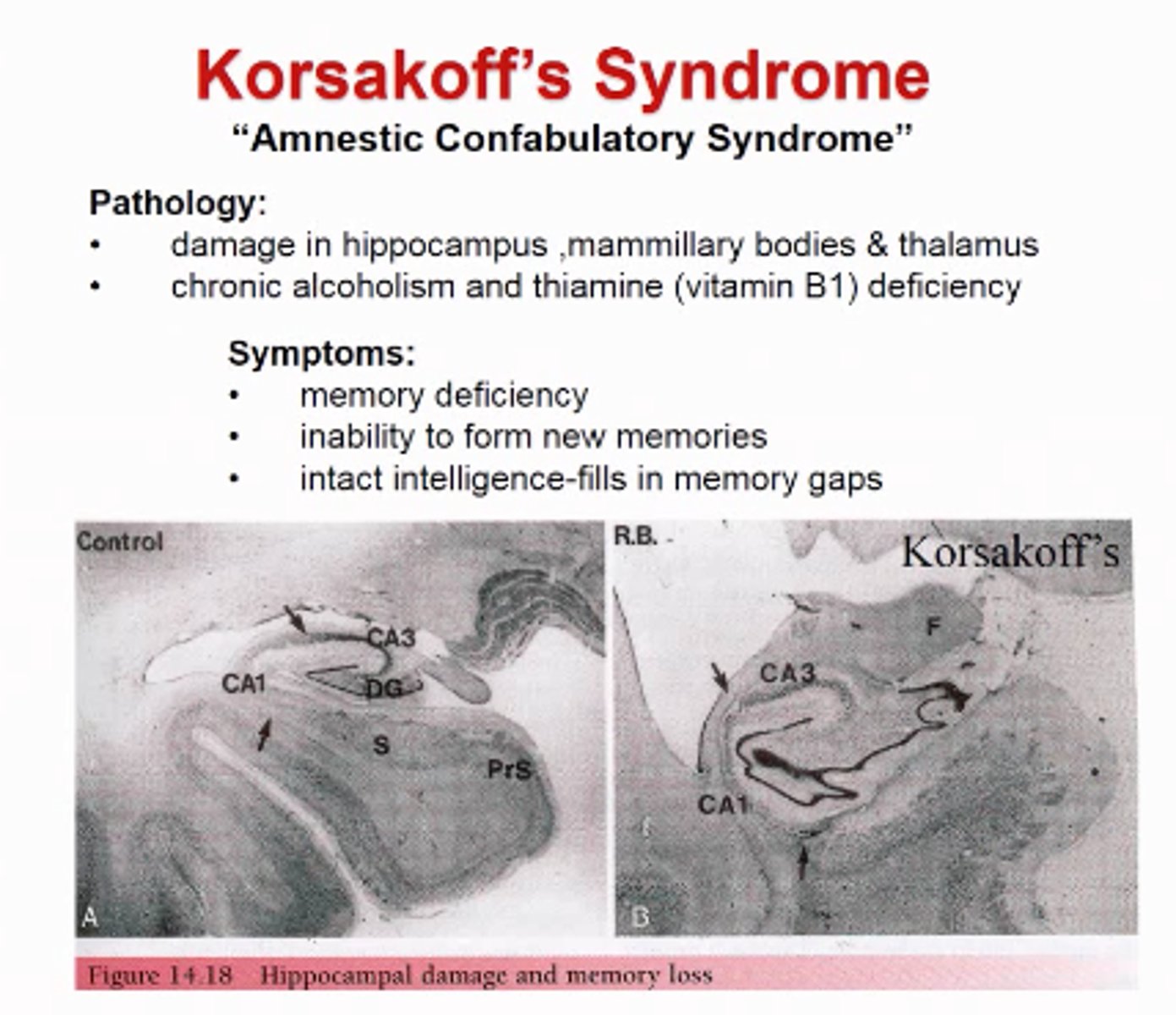
Compare Alzheimer's Disease with Korsakoff Syndrome:
- Cause of each?
- Symptoms?
- Treatment?
- Permanent or Treatable?
Alzheimers: Unknown cause, problems based more on attention, semantic and abstract thoughts. Progressive and terminal.
Korsakoff's Syndrome: Caused by lack of B1/thiamine, so lack of glucose metabolism, will have poor balance and abnormal eye movement along with memory/confusion issues. Can be treated and improve.
CRB One of the other common symptoms of Korsakoff's Syndrome is Confabulation. Which of the following is the best example of Confabulation?
(A) A patient has a newfound awe for a previously-disliked topic, like brussel sprouts.
(B) A patient couldn't remember the last three days actual events, but has vivid memories of leading troops at Waterloo yesterday.
(C) A patient combines two previous memories and cannot recall which details correspond with which event.
(D) A patient starts swindling former business clients unethically.
(B) A patient couldn't remember the last three days actual events, but has vivid memories of leading troops at Waterloo yesterday.
Confabulation is characterized by creating vivid and fabricated memories. This process is thought to be used to fill in gaps where there are a lack of memories.
In terms of storing memory, how is the Modified Semantic Networks (current theory) different than a simple hierarchical semantic network model?
The modified theory allows for a "hierarchy" based on experience and common knowledge, not necessarily just based on traits. This allows for individual differences in what connections exist in individuals, and differences in relative processing time.
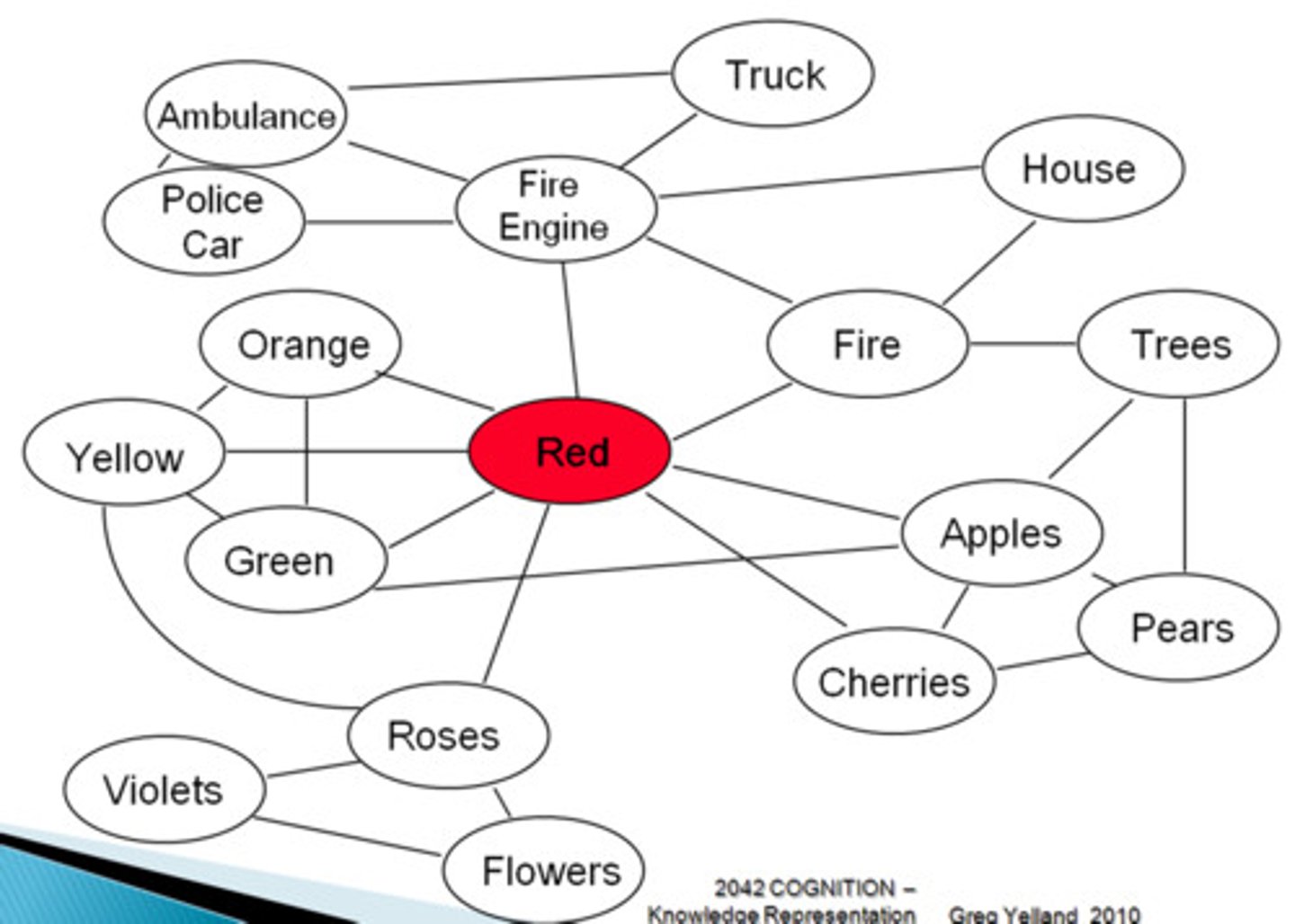
CRB Fill in the blanks: In a semantic network, the individual ideas are __________ and the connections between them are ___________.
Fill in the blanks using:
- Nodes
- Blocks
-Chunks
- Associations
- Links
Nodes, Links
In a semantic network, the individual ideas are Nodes and the connections between them are Links.
Not studied (43)
You haven't studied these terms yet!