Canine and Feline Infertility
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are important questions to ask during a clinical history of an infertility case?
define issue/problem
understand the previous breeding history
deterine the general health of animal
determine the general management of animal
any previous litters?
what should you observe for a clinical exam?
thorough exam of repro tract (and BCS!!!)
inspect vulva
palpate mammary glands
vestibule and vagina
palpate uterus
Diagnostic approach to infertility? (diagnostic tests used)
urinalysis
blood tests
hematology/biochem
plasma hormones
endocrine
infectious disease testing
imaging
US
endoscopy
vaginal cytology
semen collection and analysis
referral
what are some of the categories (causes) of infertility?
mating management
failure to show estrus
abnormal estrus cycle
abnormal mating
normal mating but infertile
pregnancy failure
male infertility
What are the primary causes for a failure to show/exhibit estrus? how would this manifest in testing?
primary:
delayed puberty- detection of elevated plasma progesterone concentrations
nothing before 24 months
poor management
poor observation by owner
abnormal physiology or pathology
What are the secondary causes for a failure to show/exhibit estrus? how would this manifest in testing?
Secondary:
physiological variation
variation in start of puberty
inadequate diet/poor bcs
chronic disease
inadequate observation- silent season
abnormal sexual differentiation
chromosomal abnormalities
hermaphroditism
ovarian agenesis/aplasia- increased FSH and LH, low estrogen
absence of ovaries
rare condition
already spayed
How would you treat a failure to show/exhibit estrus?
gonadotrophin (PMSG intervet/chorulon)
20 IU/kg SID 10 days
500 IU/dog hCG SID on day 10 for 10 days
administration of prolactin inhibitor (cabergoline)
5 mcg/kg once daily until 2 days after onset of pro-estrus
5 mcg/kg every other day for 10 days
can cause vomiting and coat color change
equine chronic gonadotrophin (eCG)
80IU eCG and 40 IU hCG/ml
single 5ml injection
Note: fertility of induced estrus is variable
why would the inter-estrus length be abnormally long? treatment?
abnormally long interval (>12 months)
breed (basenji, dingo, wolf-hybrid)
functional ovarian cyst
poor condition
hypothyroid/hyperadrenocorticism
rare cause
Treatment: induce estrus
cabergoline, usually takes 30 days to respond
why would the inter-estrus length be abnormally short?
Note: should be a min of 4m btwn estrus cycles
Breed: labs, american cocker spaniels, rottweilers
failure of ovulation (GSDs!!!)
other dogs in estrus
split estrus (2-12 weeks)
common at time of puberty in dogs (<4y)
signs of pro-estrus
no ovulation
returns to estrus with full ovulation 2-4 weeks later
Why would the mating be abnormal?
bitch doesnt allow mating:
dominant female
congenital vaginal septum/stricture
vaginal hyperplasia
male unable to achieve intromission/ejaculate:
submissive/frightened male
pain (spine, hindlimbs, prostate)
poor libido (GnRH)
Why would a bitch fail to conceive?
uterine tube aplasia
abnormal reproductive tract
no sperm in ejaculate (azoospermia)
too few sperm in ejaculate (oligozoospermia)
abnormal motility/morphology
confirm with sample!
Why would a bitch conceive and then not maintain the pregnancy?
canine herpes virus
infectious vaginal fluids or oronasal secretions
common cause of neonatal death
canine brucellosis (zoonotic!)
brucella canis
direct exposure to body fluids- semen, aborted fetus/placenta, milk
hypoluteoidism
subclinical uterine infection
premature parturition- loss of pregnancy when no cause can be identified
What is cystic endometrial hyperpalasia?
the uterine wall becomes hyperplastic and cystic due to alternating estrogen & progesterone influence
prone to pyometra
often infertile
ultrasound shows wall change
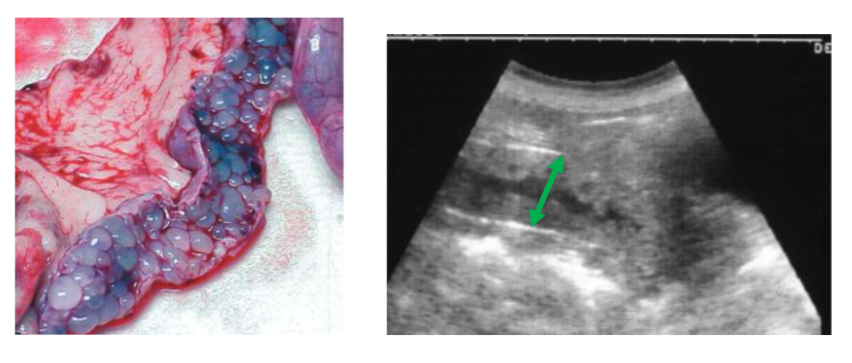
what is ovarian remnant syndrome?
persistence of ovarian activity
fragment or entire ovary left in situ
ectopic tissue- uncommon
estrogenic drugs
owner’s estrogenic medication
signs of pro-estrus and estrus
can appear 3 months- 7 years post sx
What are signs of an ovarian cyst? what type of cysts are common?
signs: prolonged anestrus, estrus, infertility, pain
ovarian cysts:
follicular (3-62%)
luteal (<10%)
What tumors are most commonly present in the ovaries?
note: ovarian neoplasia uncommon in dogs/cats
granulosa cell tumor, epithelial tumors, sometimes metastasize locally
OVH to treat (duh)
What are important things to consider in feline queen infertility?
infectious causes
feline panleukopenia
FIV, FeLV
toxoplasma (zoonotic)
chlamydphila felis
Endometritis- inflammation of uterus
discharge/licking
here is whatever tf this is
What are indications for terminating a pregnancy?
unwatned/accidental, size, too young/too old, comorbidities
Note: you wont always have a known pregnancy date, so use clinical signs to determine if pregnant prior to termination!!!
how is a pregnancy terminated surgically and medically?
surgery- only if not breeding and can be done at appropriate time
medical:
antibrogestogens- aglepristone (alizin)
two 10 mg/kg injections SC 24 hrs apart
larger dogs- multiple sites
dont abminister after 45th day!!!
what are side effects of aglepristone?
injection site pain, inflammation, edema, thickening
anorexia, depression, excitation, diarrhea, modified blood parameters
uterine infection
estrus interval shortened
late termination (after 20 days)- fetal expulsion
what are common causes of male infertility?
poor breeding behavior, poor libido, musculoskeletal problems, azoospermia, poor semen quality, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
why would a dog be azoospermic? how do you test for this?
absence of sperm
testicular trauma/injury
cryptorchidism
setoli cell tumor- unilateral
hypothyroidism
hyperadrenocorticism
doesnt ejaculate sperm-rich fraction
stress
lack of libido
immaturity
analyze sample for ALP
What are causes of poor semen quality?
sperm present but abnormal number, motility, or morphology
retrograde ejaculation (check cystocentesis)
systemic disease
prostatic disease
testicular disease
brucellosis
neoplasia
why would you observe poor infertility in male cats?
poor breeding behavior
poor libido
musculoskeletal problems
poor semen quality
in the tom cat also consider
dental disease
phimosis/persisten frenulum