Basic Chemistry: Atomic Structure, Quantum Mechanics, and Electromagnetic Spectrum
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
What unexpected result did Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment reveal?
Most particles passed through the foil, but some were deflected and about 1 in 20,000 bounced back.
What conclusion did Rutherford draw from his Gold Foil Experiment?
Matter must contain large regions of empty space dotted with small regions of very dense matter.
What are the three basic parts of the nuclear theory of the atom?
1. Most of the atom's mass and all positive charge are in the nucleus. 2. Most of the atom's volume is empty space. 3. There are as many electrons outside the nucleus as protons inside, making the atom electrically neutral.
What is the mass and charge of a neutron?
A neutron has a mass similar to that of a proton and has no electrical charge.
What are the three subatomic particles that compose all atoms?
Protons, neutrons, and electrons.
How do the masses of protons, neutrons, and electrons compare?
Protons and neutrons have nearly identical masses, while the mass of the electron is significantly smaller.
What is the charge of protons and electrons?
Protons and electrons have equal magnitudes of charge but opposite signs; neutrons have no charge.
Who were some key scientists involved in the development of quantum mechanics?
Albert Einstein, Neils Bohr, Louis de Broglie, Max Planck, Werner Heisenberg, P. A. M. Dirac, and Erwin Schrödinger.
What is the wave-matter duality concept?
Subatomic particles, like electrons, can exhibit both particulate behavior and energy-like characteristics depending on experimental conditions.
Why is directly observing electrons in an atom impossible?
Observing an electron changes its behavior; even shining a light on it affects its state.
What does the quantum mechanical model explain about electrons in atoms?
It explains how electrons exist and behave in atoms.
What behavior do electrons exhibit that is different from larger matter?
Electrons behave strangely and can exist in two conditions, demonstrating wave-matter duality.
What was the significance of Rutherford's model in atomic theory?
It introduced the concept of a dense nucleus surrounded by electrons, fundamentally changing the understanding of atomic structure.
How does the number of electrons in a speck of dust compare to the number of people who have ever lived on Earth?
The number of electrons in a single speck of dust is higher than the total number of people who have ever lived.
What role do electrons play in determining the behavior of atoms?
Much of the behavior of atoms is determined by the electrons.
What did later work by Rutherford and Chadwick reveal about neutrons?
They demonstrated that neutrons account for the previously unaccounted mass in the nucleus.
What is the charge of a proton?
A proton has a positive charge.
What is the charge of an electron?
An electron has a negative charge.
What is the relationship between the number of protons and electrons in a neutral atom?
In a neutral atom, the number of protons equals the number of electrons.
What did early twentieth-century scientists discover about small matter?
They found that absolutely small matter, like electrons, behaves differently than larger macroscopic matter.
What is the significance of the quantum mechanical model in chemistry?
It provides a framework for understanding the behavior and properties of electrons in atoms.
What did Rutherford's model fail to account for?
It did not account for the mass of neutrons in the nucleus.
What does the quantum mechanical model explain about an atom's electrons?
It explains the periodic table trends, behavior of elements in chemical bonding, atomic colors and sizes, and predicts atomic properties related to electron behavior.
How does the quantum mechanical model differentiate between metals and nonmetals?
It explains why some elements are metals and others are nonmetals based on their electron behavior.
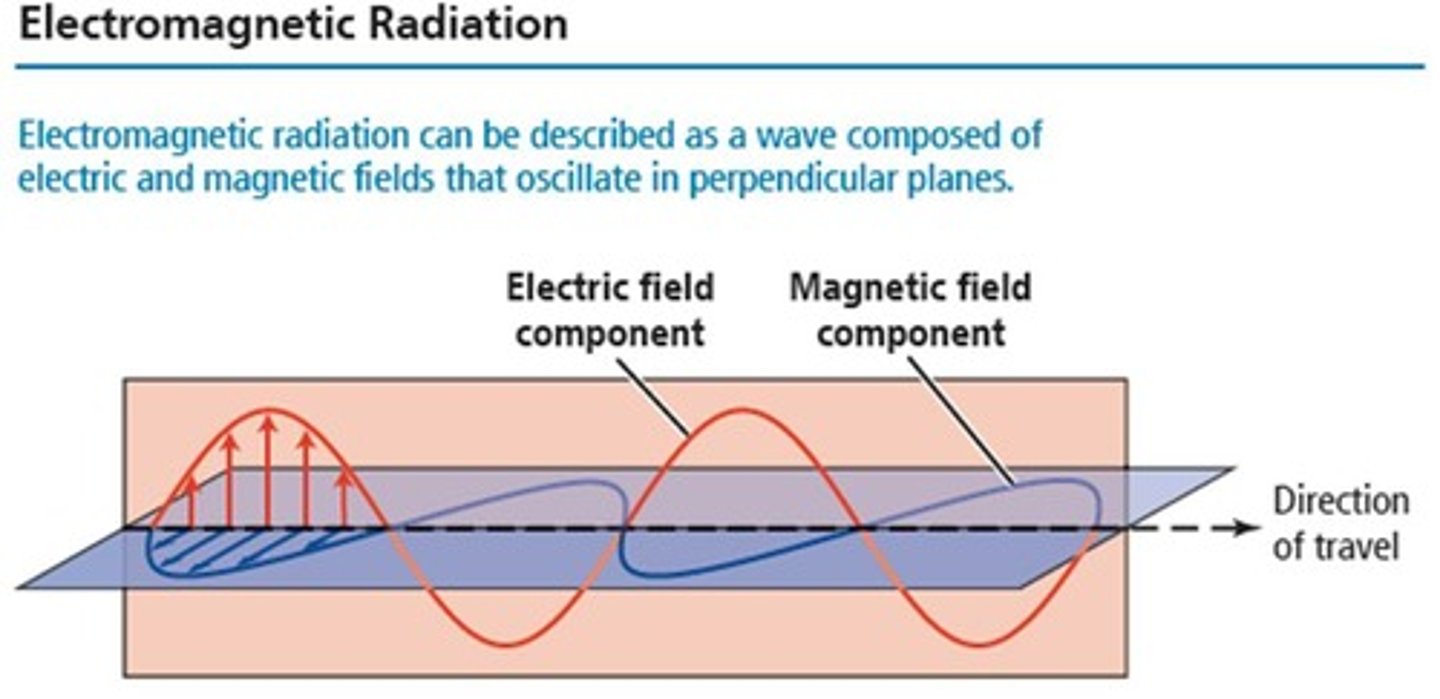
What does the wave nature of light consist of?
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation composed of perpendicular oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
What is the speed of light in a vacuum?
The speed of light is a constant value, approximately 3.00 x 10^8 meters per second.
What is amplitude in the context of energy waves?
Amplitude is the height of the wave and measures light intensity; larger amplitude means brighter light.
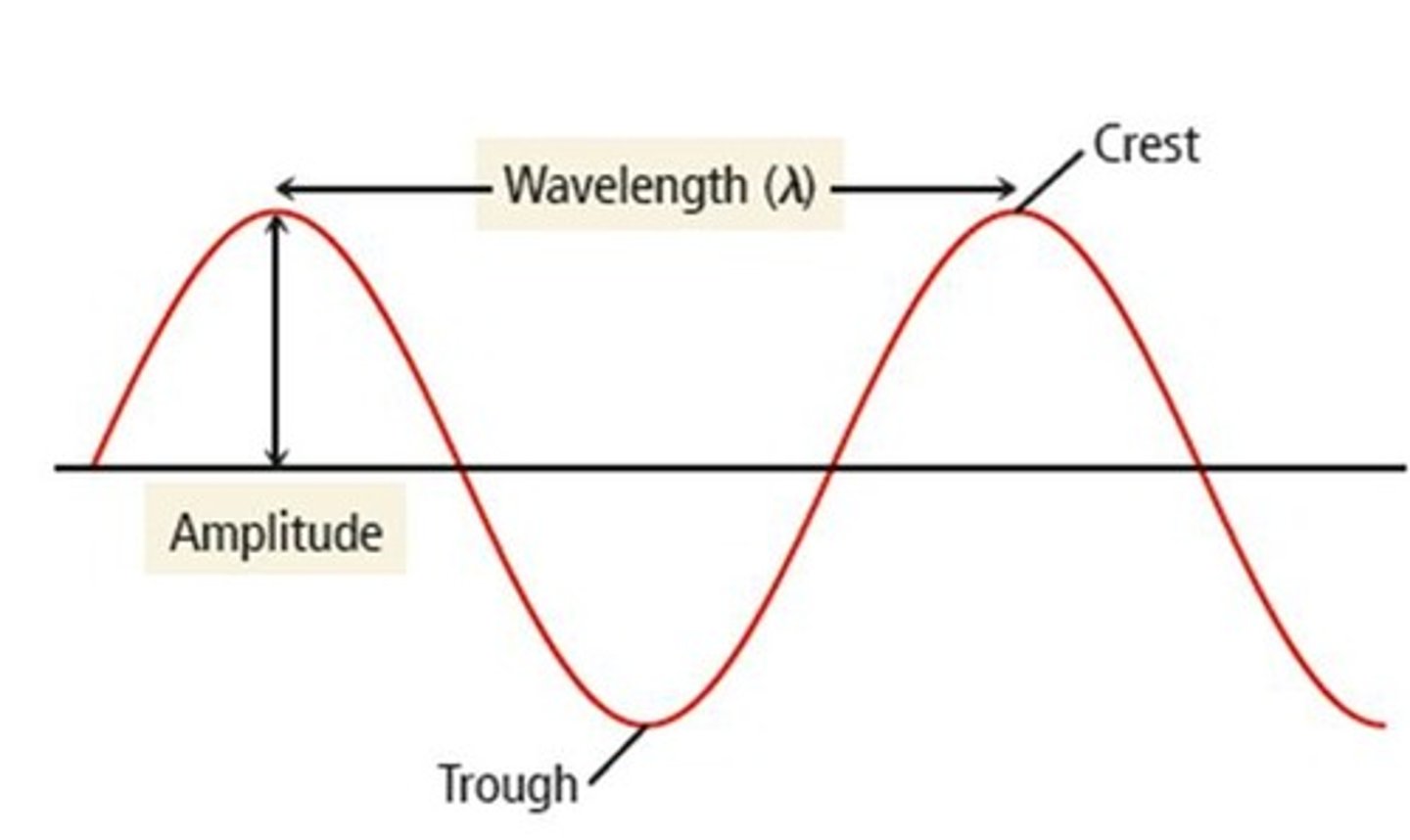
What does wavelength measure in a wave?
Wavelength measures the distance covered by the wave, such as the distance from one crest to the next.
How are wavelength and amplitude related?
Wavelength and amplitude are independent properties; wavelength determines color while amplitude determines brightness.
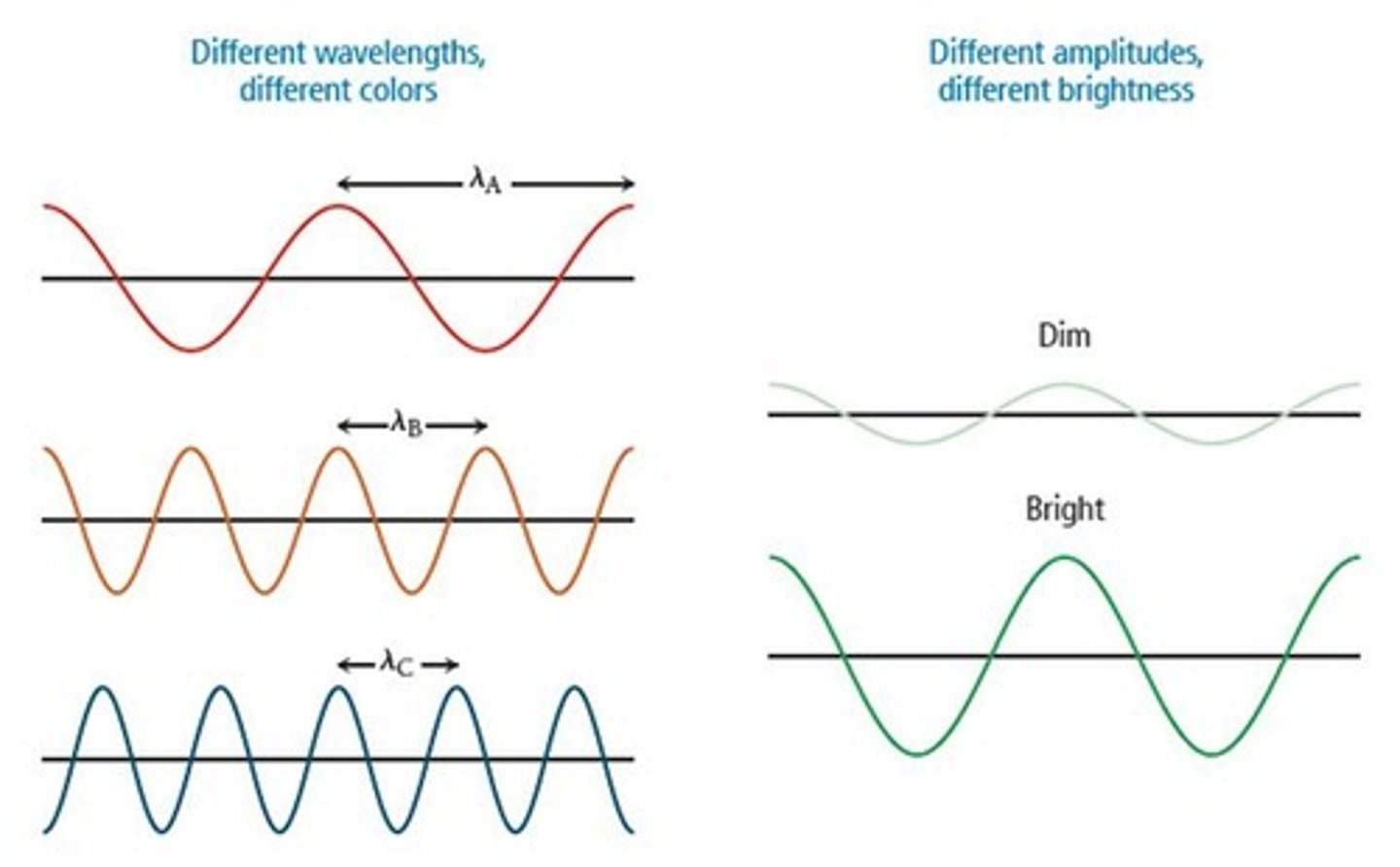
What determines the color of light?
The color of light is determined by its wavelength or frequency.
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency?
Wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional; as one increases, the other decreases.
What is frequency in the context of energy waves?
Frequency is the number of waves that pass a point in a given period of time, measured in hertz (Hz).
What is total energy in relation to energy waves?
Total energy is proportional to the amplitude of the waves and their frequency; larger amplitude and higher frequency result in more total energy.
What happens when an object absorbs some wavelengths of white light?
It appears colored by reflecting the remaining wavelengths; the observed color is predominantly the colors reflected.
What is the significance of the electromagnetic spectrum?
It encompasses all types of electromagnetic radiation, with visible light being a small part of the spectrum.
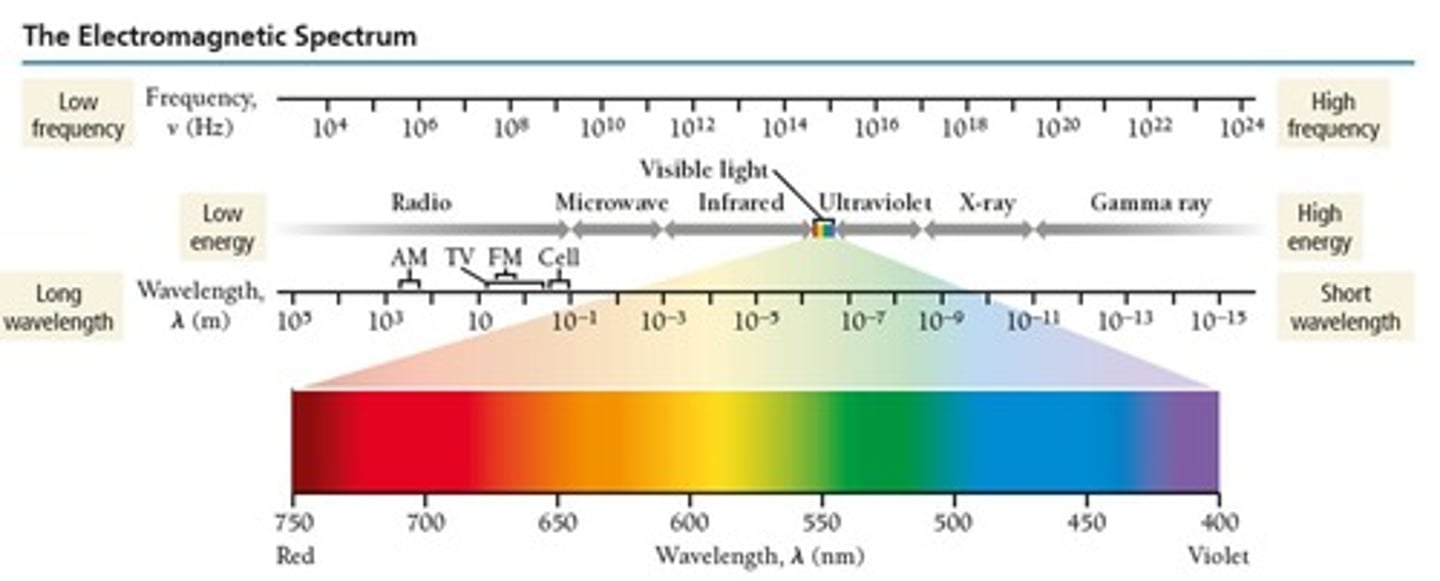
What are the colors of the visible light spectrum?
Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet (ROYGBIV).
How does a bright green laser differ from a dim red laser?
The bright green laser emits light of the same frequency as the dim red laser, but with a larger amplitude.
What is the effect of amplitude on light intensity?
A larger amplitude results in a brighter light.
What is the relationship between the speed of light, wavelength, and frequency?
The speed of light is constant; knowing the wavelength allows calculation of frequency, and vice versa.
What does the term 'oscillating waves' refer to in electromagnetic radiation?
It refers to the alternating electric and magnetic fields that make up the electromagnetic waves.
What is the significance of the periodic table in chemistry?
It organizes elements based on their properties and trends, which are explained by the quantum mechanical model.
What role does the quantum mechanical model play in chemical bonding?
It explains how electrons behave during bonding, influencing the properties of compounds.
Why are some elements very reactive while others are inert?
This is explained by the behavior of their electrons as described by the quantum mechanical model.
What is the relationship between the amplitude of a wave and its force?
The larger the amplitude, the more force the wave has.
What describes the difference in amplitude between a bright green laser and a dim red laser?
The green laser has a greater amplitude than the red laser.
What is the frequency relationship between a bright green laser and a dim red laser?
They emit light of different frequencies.
How is wavelength related to frequency in light?
Wavelength can be calculated from frequency using the equation that relates the two.
What is the wavelength of green light emitted by a laser at a concert if it is 515 nanometers?
The frequency of the light can be calculated from its wavelength.
What is the range of visible light in nanometers?
400 to 700 nanometers.
What type of electromagnetic radiation has the highest energy?
Gamma-ray light.
What type of electromagnetic radiation has the lowest energy?
Radio-wave light.
What is the order of electromagnetic radiation types from lowest to highest wavelength?
X-ray, visible, infrared.
What is constructive interference?
Waves that interact to add together and form a larger wave.
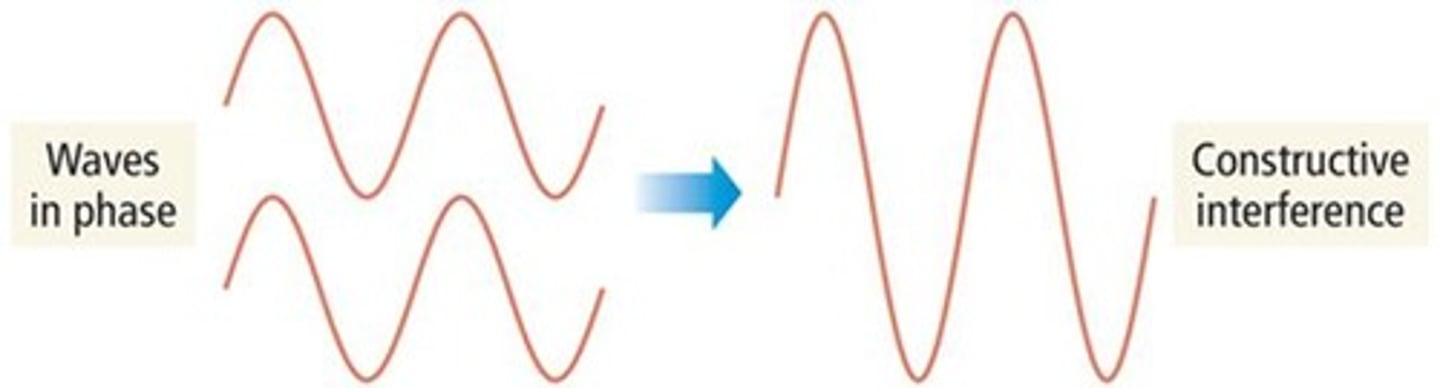
What is destructive interference?
Waves that interact to cancel each other out.
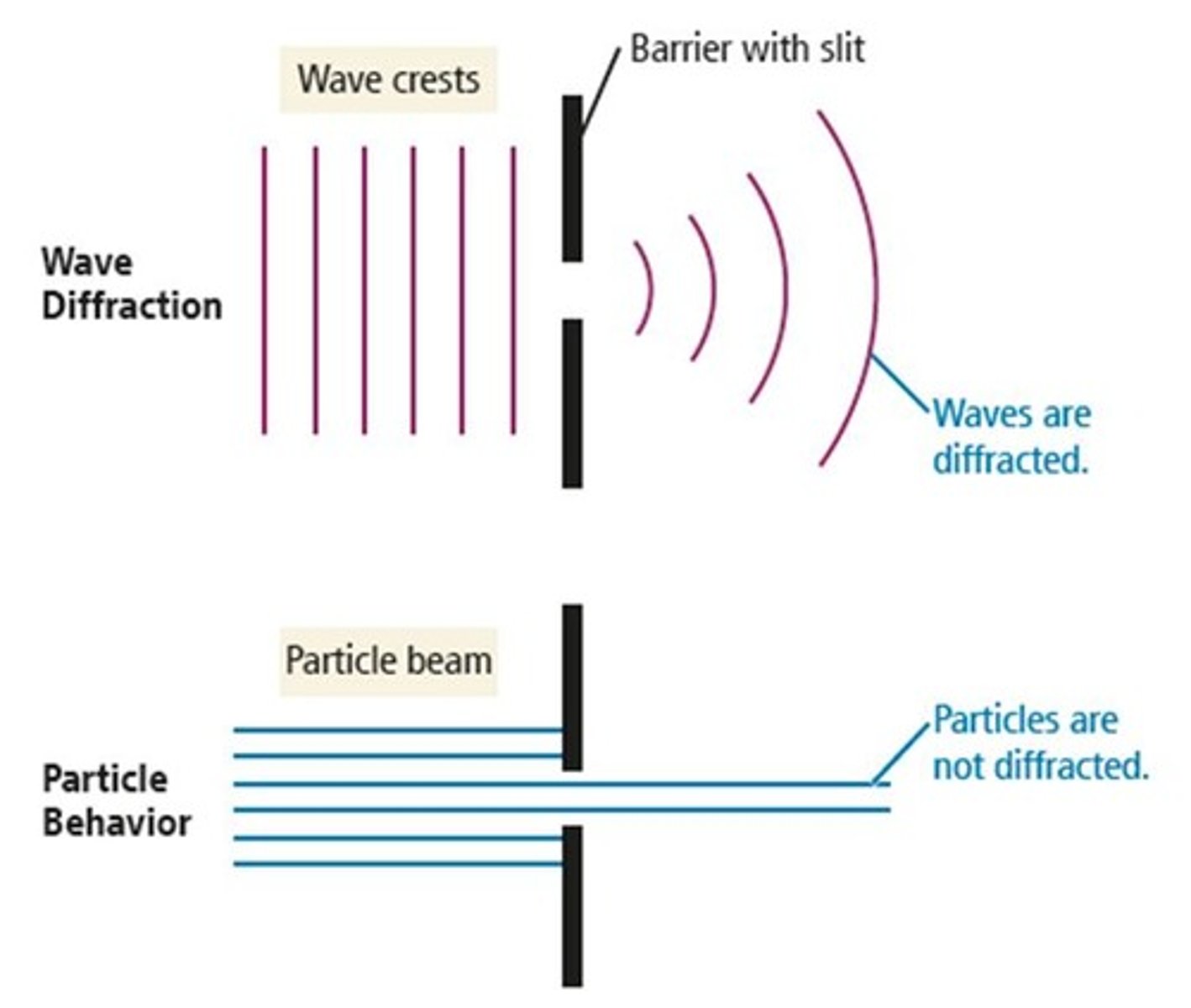
What phenomenon occurs when waves bend around obstacles?
Diffraction.
What results from light passing through two slits?
Two interfering waves that create an interference pattern.
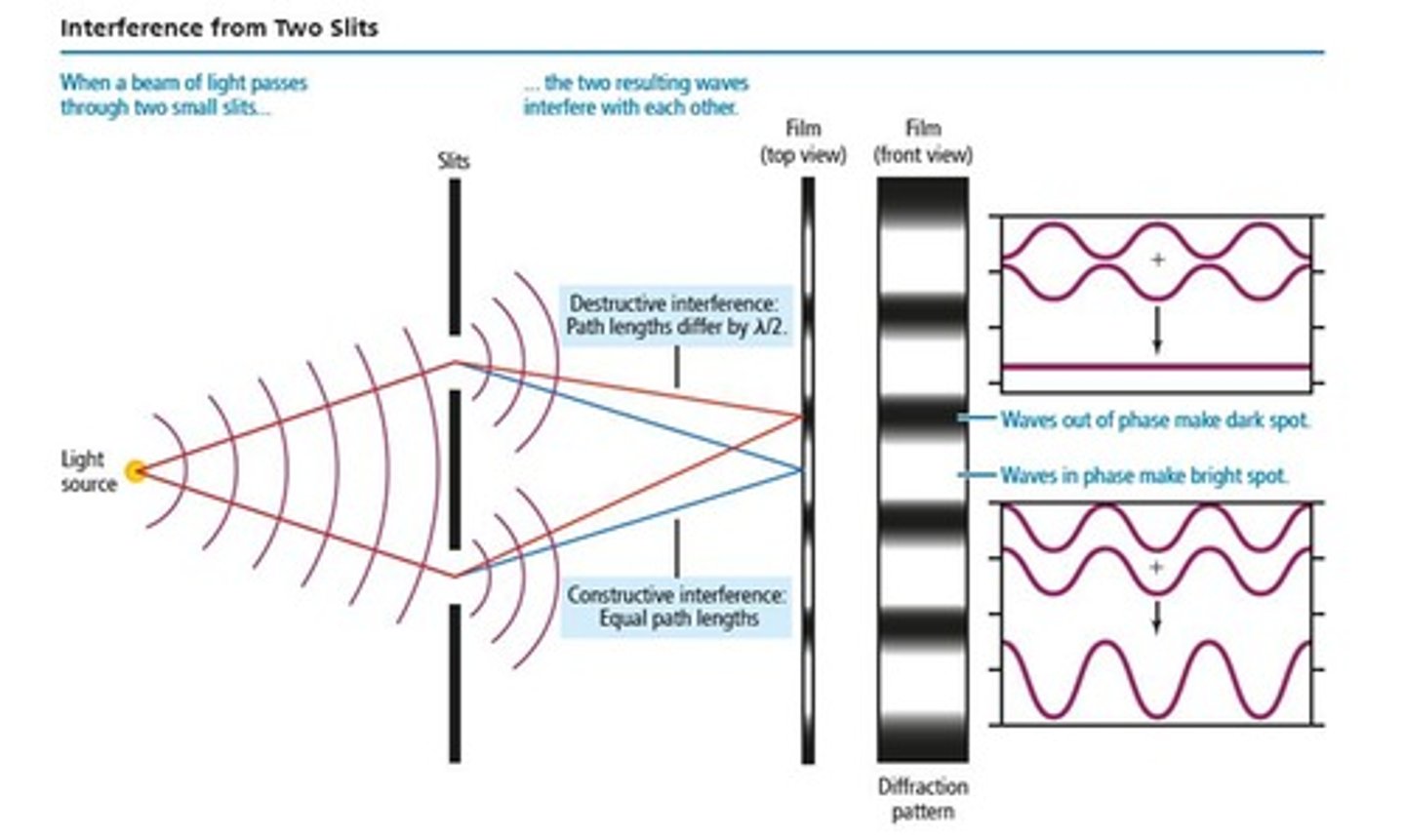
What determines whether interference is constructive or destructive in two-slit interference?
The difference in path length that the light travels.
What is an interference pattern?
A characteristic of all light waves resulting from diffraction.
What happens to high-energy electromagnetic radiation?
It can potentially damage biological molecules.
What is the relationship between wavelength and energy in electromagnetic radiation?
Shorter wavelengths correspond to higher energy.
How can wavelength be converted from meters to nanometers?
By using the appropriate conversion factor.
What is the role of the frequency in determining the properties of light?
Frequency determines the color and energy of the light.
What type of waves exhibit interference?
Both electromagnetic and ocean waves.
What occurs when traveling particles encounter obstacles?
Traveling particles do not diffract.
What is the effect of ionizing radiation on biological molecules?
It can potentially damage them.