Alkene and Alkyne Reactions Examination Review
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A comprehensive set of 50 flashcards covering the fundamental concepts, mechanisms, and key details of alkene and alkyne reactions, intended for exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What are the three key questions for every addition reaction?
Regiochemistry, Stereochemistry, Mechanism.
When do alkenes undergo addition reactions versus elimination?
Low heat leads to addition; high heat leads to elimination.
What is the regiochemistry of hydrohalogenation without peroxides?
Markovnikov.
What is the stereochemistry of hydrohalogenation?
Racemic mixture.
What is the mechanism of hydrohalogenation?
Carbocation mechanism involving protonation followed by nucleophile attack.
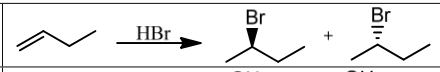
Are rearrangements possible during hydrohalogenation?
Yes.
What occurs when peroxide (ROOR) is present with HBr?
Anti-Markovnikov addition via radical mechanism, with no rearrangements.
Do HCl or HI work with peroxides?
No.
What is the regio-chemistry for acid-catalyzed hydration?
Markovnikov.
What is the stereochemistry for acid hydration?
Racemic mixture.
What is the mechanism of acid hydration?
Carbocation mechanism with possible rearrangements.
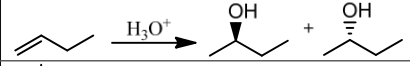
What does concentrated acid favor in reactions?
Elimination (E1).
What does dilute acid favor?
Hydration.
What is the regiochemistry of oxymercuration?
Markovnikov.
Are rearrangements possible in oxymercuration?
No.
What is the intermediate in oxymercuration?
Mercurinium ion.
What stereochemistry occurs during nucleophile attack in oxymercuration?
Anti attack.
What is the final stereochemistry after NaBH₄ in oxymercuration?
Mixed; stereochemistry becomes scrambled.
What is the regiochemistry of hydroboration?
Anti-Markovnikov.
What stereochemistry is observed in hydroboration?
Syn addition.
Are rearrangements possible in hydroboration?
No.
What type of mechanism does hydroboration follow?
Concerted, one-step addition.
What is the stereochemistry of halogenation?
Anti addition.
What is the mechanistic intermediate in halogenation?
Bromonium or chloronium ion.
Which group goes to the more substituted carbon in halohydrin formation?
OH.
What is the stereochemistry of halohydrin formation?
Anti.
What does ozonolysis form?
Carbonyl compounds, including aldehydes and ketones.
Why are terminal alkynes considered acidic?
sp hybridization leads to high s-character, stabilizing the negative charge.
Which type of alkyne can be deprotonated?
Only terminal alkynes.
What reagent is used to deprotonate terminal alkynes?
NaNH₂.
What is formed when terminal alkynes are deprotonated?
Alkynide ion, which is a strong nucleophile.
What converts vicinal or geminal dihalides to alkynes?
Excess NaNH₂.
What is required to protonate a terminal alkyne?
Water.
What type of reaction leads to new C–C bonds with alkynide ions?
SN2.
Which halides can be used in alkylation of alkynide ions?
Only methyl or primary halides.
What product results from the hydrogenation of an alkyne using Pt/Pd/Ni?
Alkane, representing full reduction.
What product is formed from an alkyne treated with H₂ and Lindlar’s catalyst?
Cis alkene, following syn addition.
What happens during Na/NH₃ reduction of alkynes?
It reduces to a trans alkene (anti).
What is the regiospecificity of hydrohalogenation with 1 equivalent?
Markovnikov addition leading to alkene.
What happens with 2 equivalents in hydrohalogenation?
Forms geminal dihalide.
What does HBr + ROOR yield?
Anti-Mark addition.
What does one equivalent of halogenation (X₂) produce?
Cis and trans alkene mixture.
What is produced by excess halogenation (X₂)?
Tetrahalide.
What is the final product from the hydration of a terminal alkyne using HgSO₄ and H₂SO₄?
Methyl ketone.
What intermediate is formed prior to tautomerization from terminal alkynes?
Enol.
What does an enol convert into during tautomerization?
Ketone (or aldehyde).
What does terminal alkyne + R₂BH oxidize to give?
Aldehyde (anti-Markovnikov).
What does an internal alkyne yield during oxidation?
Ketone.
What does ozonolysis of a terminal alkyne produce?
Carboxylic acid + CO₂.
What does ozonolysis of an internal alkyne yield?
Two carboxylic acids.