Ch. 4 - The Three-Dimensional Structure of Proteins
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
3D
Unlike most organic polymers, protein molecules adopt a specific _____ conformation
Native fold
The specific 3D conformation of a polypeptide is called the _____
Entropy
There is an _____ cost to folding the protein into one specific native fold
Native folding
The function of a protein is dependent on the _____
Hydrophobic effect
The release of water molecules from the structured solvation layer around the molecule as protein folds increases the net entropy
Hydrogen bonds
Interaction of N-H and C=O of the peptide bond leads to local regular structures such as alpha helices and beta sheets
London dispersion
Medium-range weak attraction between all atoms contributes significantly to the stability in the interior of the protein. Can be established between any two atoms
Electrostatic interactions
Long-range strong interactions between permanently charged groups
Salt bridges
_____, especially those buried in the hydrophobic environment, strongly stabilize the protein
Cysteine
In order to have a disulfide bond present, we need two _____ in the chain
Leu
What is the N-terminus of this chain?
Leu-Arg-Cys-Asp-His-Ile-Glu-Ala
Ala
What is the C-terminus of this chain?
Leu-Arg-Cys-Asp-His-Ile-Glu-Ala
2
How many salt bridges are present in this chain?
Leu-Arg-Cys-Asp-His-Ile-Glu-Ala
0
What is the net overall charge of this chain?
Leu-Arg-Cys-Asp-His-Ile-Glu-Ala
7
How many peptide bonds are present in this chain?
Leu-Arg-Cys-Asp-His-Ile-Glu-Ala
Primary structure
The first level of protein structure; the specific sequence of amino acids making up a polypeptide chain
Peptide bond
The primary structure of a protein is maintained by a _____
Resonance hybrid
The peptide bond is a _____ of two canonical structures
Rigid, planar
Resonance causes peptide bonds to be quite _____ and nearly _____
Large
Resonance causes peptide bonds to exhibit a _____ dipole moment in the favored trans configuration
True
T/F Rotation around the peptide bond is not permitted due to the resonance structure
Phi
Angle around the alpha carbon - amide nitrogen bond

Psi
Angle around the alpha carbon - carbonyl carbon bond

180
In a fully extended polypeptide, both psi and phi are _____ degrees
Secondary
The organization around the peptide bond, paired with the identity of R groups, determines the _____ structure of the protein
Steric crowding
Some psi and phi combinations are very unfavorable because of _____ of backbone atoms with other atoms in the backbone or side chains
H-bonding
Some psi and phi combinations are more favorable because of chance to form favorable _____ interactions along the backbone
Ramachandran
A _____ plot shows the distribution of psi and phi dihedral angles that are found in a protein
- Shows the common secondary structure elements
- Reveals regions with unusual backbone structure
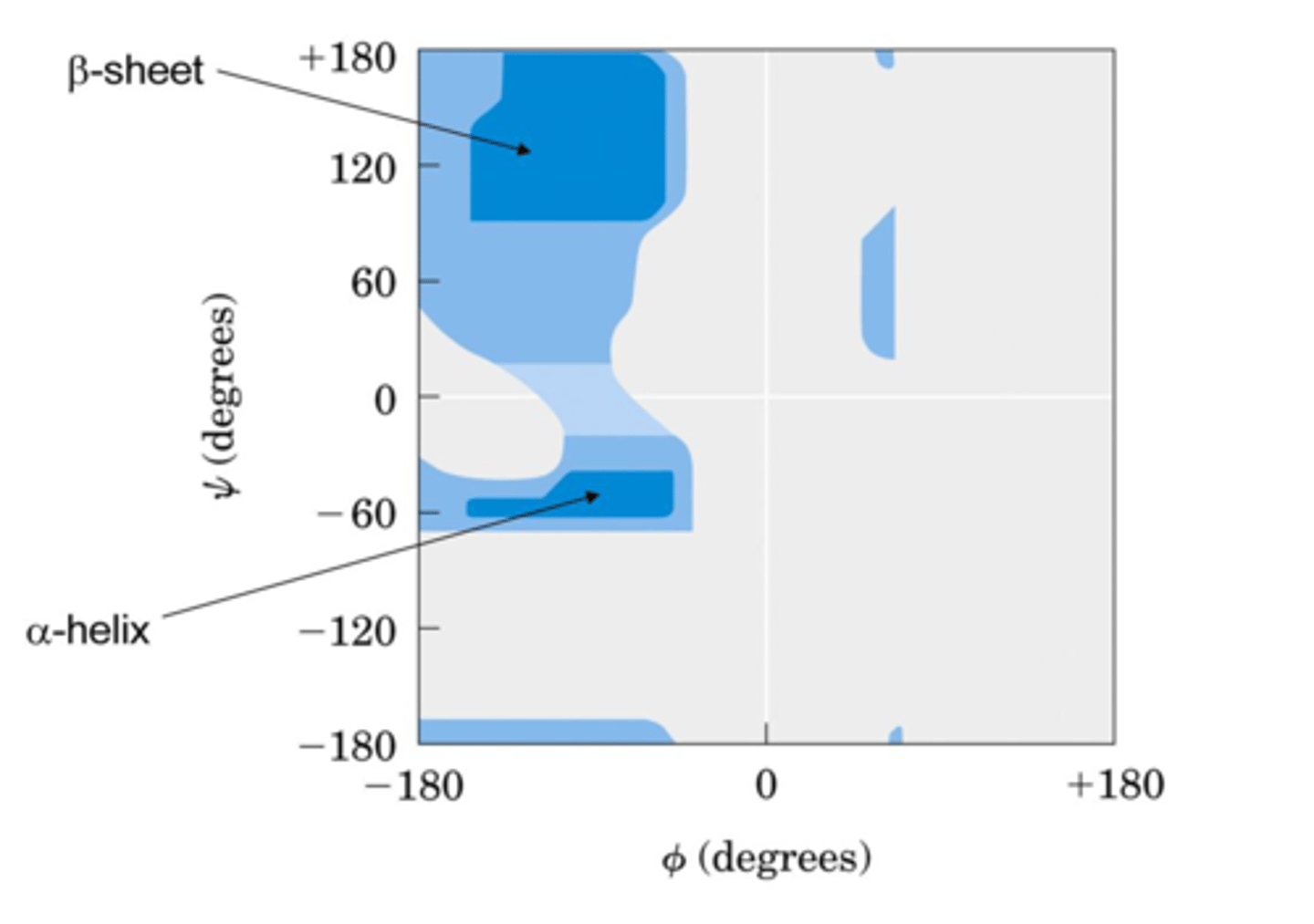
Secondary
_____ structure refers to a local spatial arrangement of the polypeptide backbone
Alpha helix
Secondary structure arrangement stabilized by hydrogen bonds between nearby residues; most abundant in right-handed alpha helix
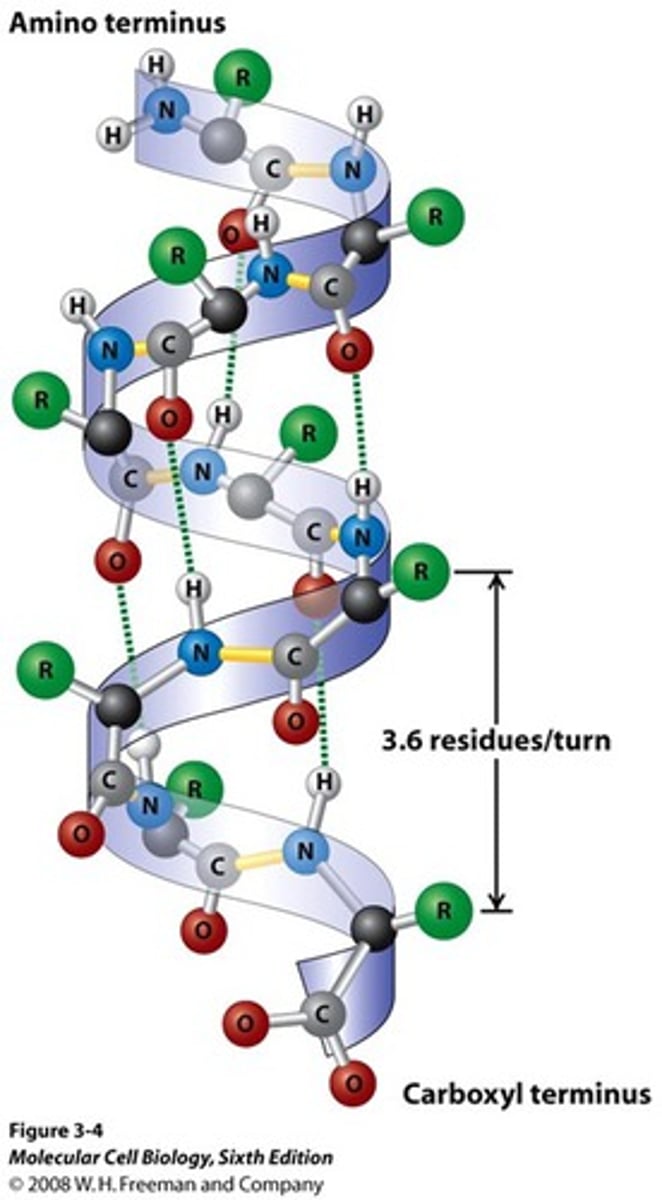
Right
The alpha helix is a _____-handed helix, with 3.6 residues per turn
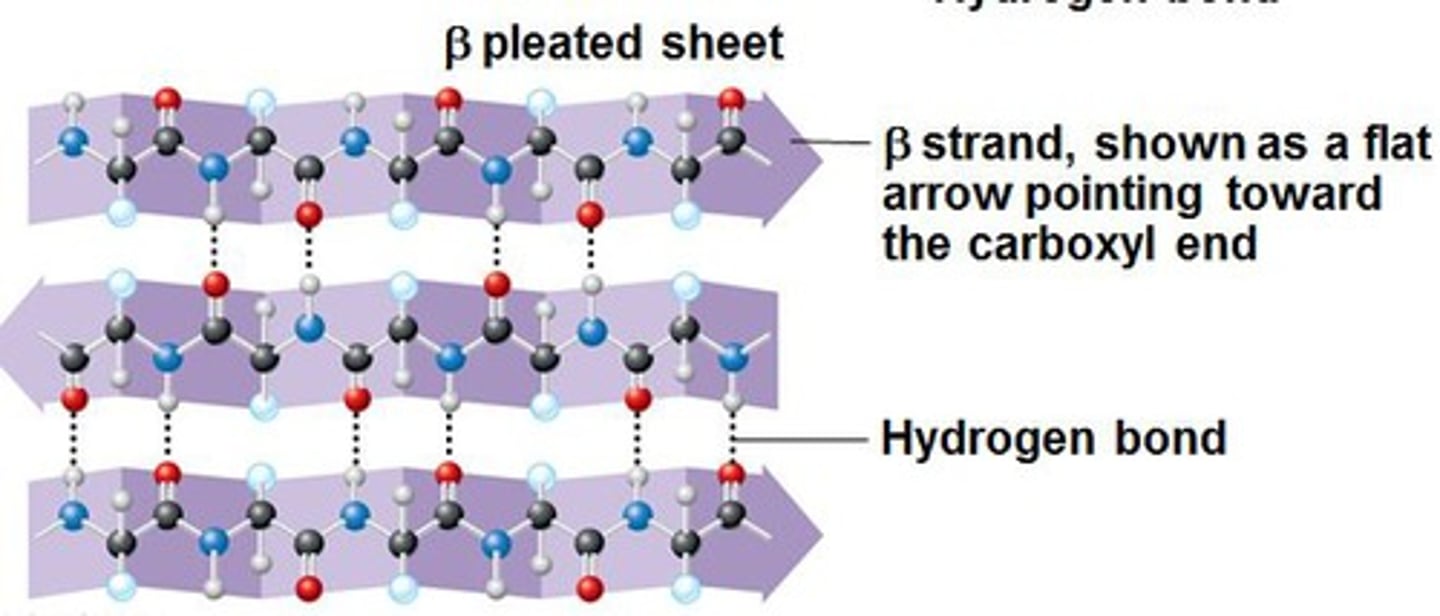
Beta sheet
Secondary structure arrangement stabilized by hydrogen bonds between adjacent segments that may not be nearby; second most abundant in right-handed alpha helix
Random coil
The irregular arrangement of the polypeptide chain is called the _____ (lack of distinguishable motif)
Parallel
Peptide bonds are aligned roughly _____ with the helical axis in the alpha helix
Perpendicular
Side chains point out and are roughly _____ with the helical axis in the alpha helix
Ala, Leu
Small hydrophobic residues such as _____ and _____ are strong helix formers
Pro
_____ acts as a helix breaker because the rotation around the N-Ca bond is impossible
Gly
_____ acts as a helix breaker because the tiny R group supports other conformations (too flexible to keep helix in line)
Macroscopic
The alpha helix has a large _____ dipole moment that is enhanced by unpaired amides and carbonyls near the ends of the helix
Negatively
_____ charged residues often occur near the positive end of the helix dipole
Sheets
Multi ß-strand interactions are called _____
Amide, carbonyl
Sheets are held together by the hydrogen bonding of _____ and _____ groups of the peptide bond from opposite strands
Same
Parallel sheets have strands that are oriented in the _____ direction
Opposite
Antiparallel sheets have strands that are oriented in _____ directions
Bent
In parallel ß sheets, hydrogen bonds between strands are _____ (weaker)
Linear
In antiparallel ß sheets, hydrogen bonds between strands are _____ (stronger)
Beta turns
_____ occur frequently whenever strands in ß sheets change the direction
4
The 180° ß turn is accomplished over _____ amino acids
3
The ß turn is stabilized by a hydrogen bond from a carbonyl oxygen to amide proton _____ residues down the sequence
Proline, glycine
_____ in position 2 or _____ in position 3 are common in ß turns
Flexible
Glycine is _____, which helps with the 180° ß turn
Stiff
Proline is _____, which helps with the 180° ß turn
Trans
Most peptide bonds not involving proline are in the _____ configuration (>99.95%)
Cis
For peptide bonds involving proline, about 6% are in the _____ configuration
Proline isomerases
Proline isomerization is catalyzed by _____
Circular dichroism
_____ (CD) measures the molar absorption difference of left- and right-circularly polarized light
Chromophores
_____ in the chiral environment produce characteristic signals
Conformation
Circular dichroism signals from peptide bonds depend on the chain _____
Tertiary
_____ structure refers to the overall spatial arrangement of atoms in a protein
Disulfide
Protein tertiary structure can be stabilized by _____ bonds
Fibrous, globular
What are the two major classes of tertiary structure?
Alpha helix, cross-linked by disulfide bonds
Tough, insoluble protective structures of varying hardness and flexibility (e.g. alpha keratin of hair, feathers, nails)
ß conformation
Soft, flexible filaments (e.g. silk fibroin)
Collage triple helix
High tensile strength, without stretch (e.g. collagen of tendons, bone matrix)
Connective tissue
Collagen is an important constituent of _____: tendons, cartilage, bones, cornea of the eye
Left
Each collagen chain is a long Gly- and Pro-rich _____-handed helix
Superhelical
Three collagen chains intertwine into a right-handed _____ triple helix
Collagen fibril
Many triple-helices assemble into a _____
Crosslinks
_____ are covalent bonds between Lys or HyLys, or His amino acid residues
Fibroin
Main protein in silk from moths and spiders with an antiparallel ß sheet structure
Ala, Gly
Small side chains of _____ and _____ allow for the close packing of sheets in fibroin
Motifs
Specific arrangement of several secondary elements
Globular
_____ proteins are composed of different motifs folded together
Disordered
_____ proteins contain protein segments that lack definable structure
Quaternary
A _____ structure is formed by the assembly of individual polypeptides into a larger functional cluster
X-ray crystallography
Steps needed:
- Purify the protein
- Crystallize the protein
- Collect diffraction data
- Calculate electron density
- Fit known amino acid residues into density
Pros
_____ of x-ray crystallography
- No size limits
- Well established
Cons
_____ of x-ray crystallography
- Difficult for membrane proteins
- Cannot resolve (see) hydrogens
Bimolecular NMR
Steps needed:
- Purify the protein
- Dissolve the protein
- Collect NMR data
- Assign NMR signals
- Calculate the structure
Pros
_____ of biomolecular NMR
- No need to crystallize the protein
- Can see many hydrogens
Cons
_____ of biomolecular NMR
- Difficult for insoluble proteins
- Works best with small proteins
Proteostasis
Maintenance of cellular protein activity is accomplished by the coordination of many different pathways
Chaperones
Proteins that assist in protein folding during post-translational processing
Ubiquitin
A protein that attaches itself to faulty or misfolded proteins and thus targets them for destruction by proteasomes
Denaturation
Loss of structural integrity with accompanying loss of activity is called _____
Denatured
Proteins can be _____ by:
- Heat or cold
- pH extremes
- Organic solvents
- Chaotropic agents (urea and guanidinium hydrochloride)
Chaotropic agents
Chemicals able to disrupt H bonds; everything above primary structure disrupted
Ribonuclease
Enzyme that breaks down RNA
Urea
_____ in the presence of 2-mercaptoethanol fully denatures ribonuclease
Renaturation
Regaining the correct tertiary structure after denaturation of a protein
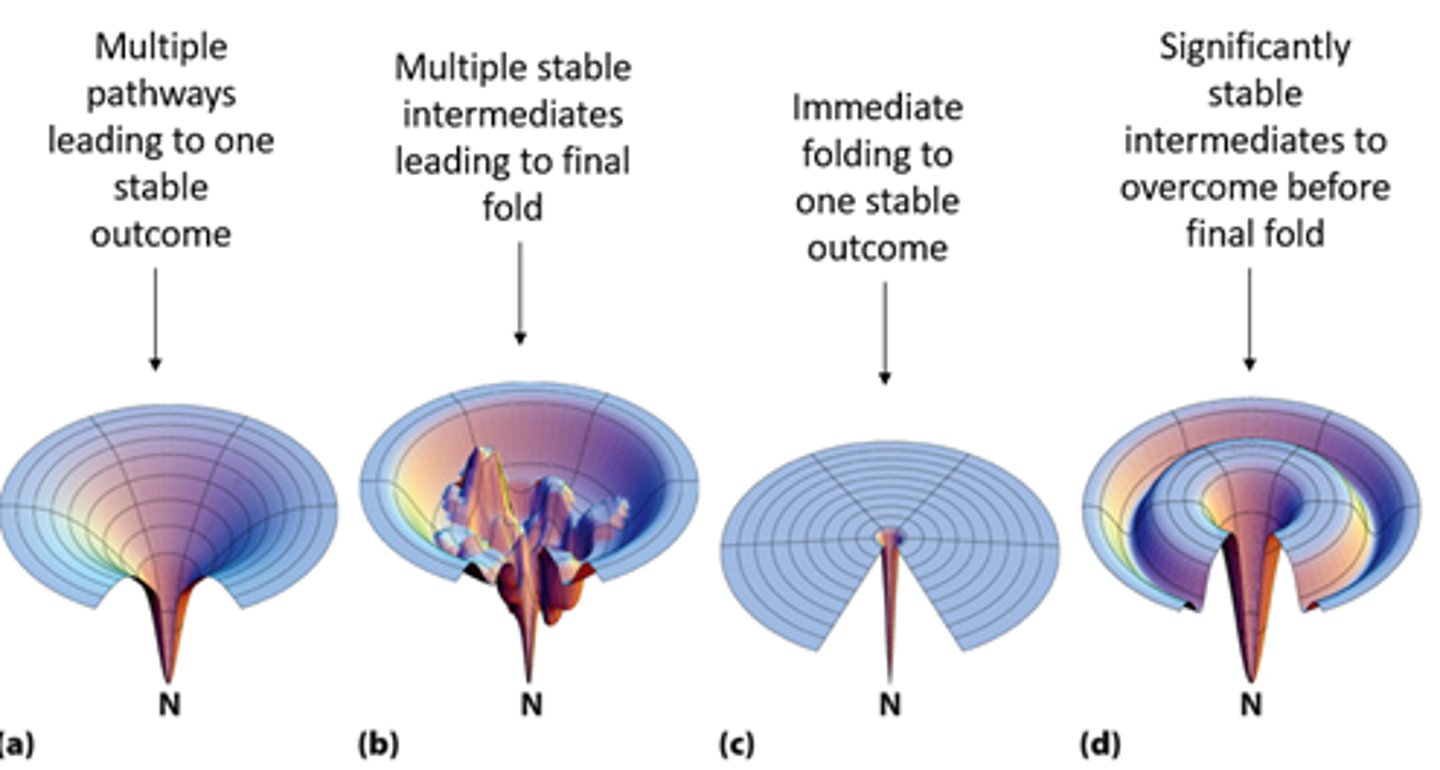
Lowest-energy
Proteins fold to the _____ fold in the microsecond to second time scales
Stability
Free-Energy Funnel of Protein Folding is dependent on the _____ of motifs within the protein
True
T/F Chaperones prevent misfolding and aggregation of unfolded peptides
Heat shock protein
Chaperones start with _____ (HSP)
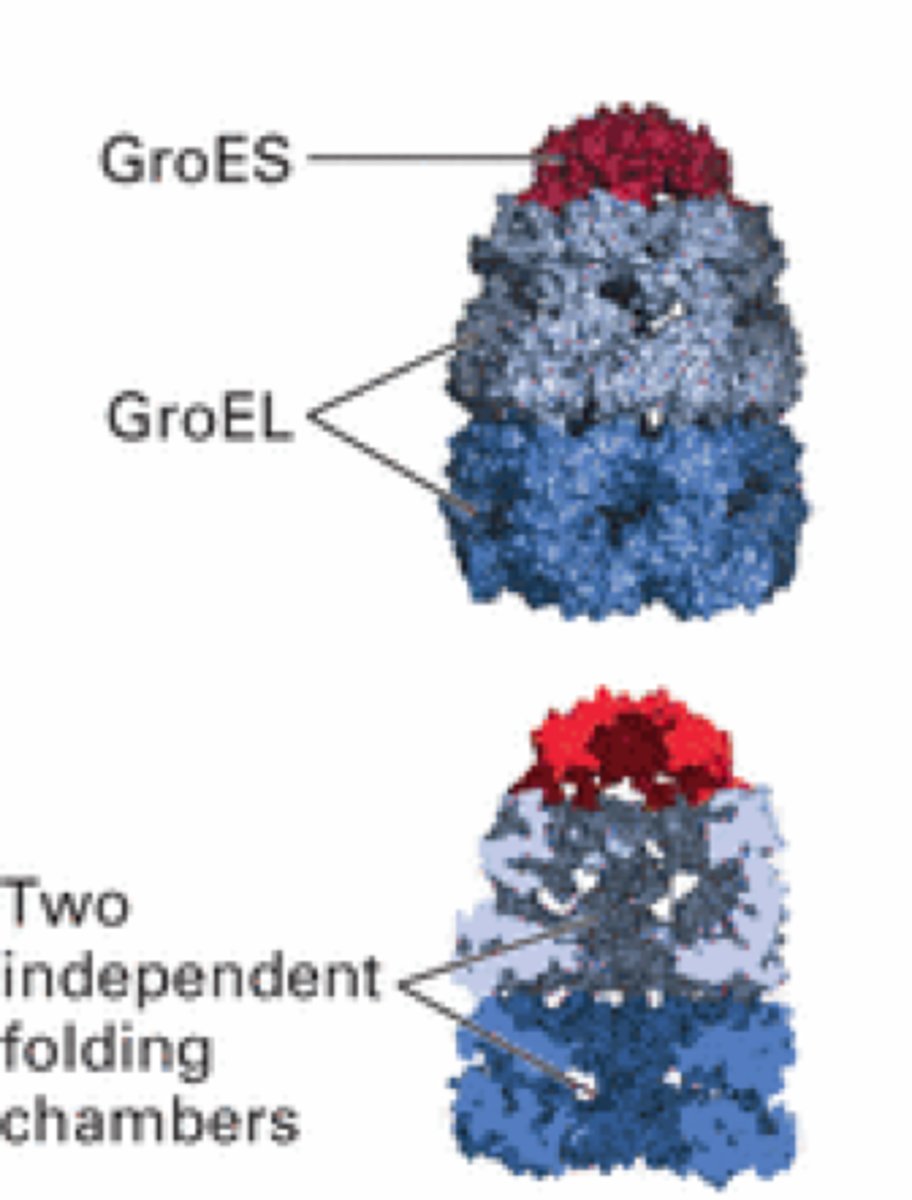
GroEs
Lid chaperonin
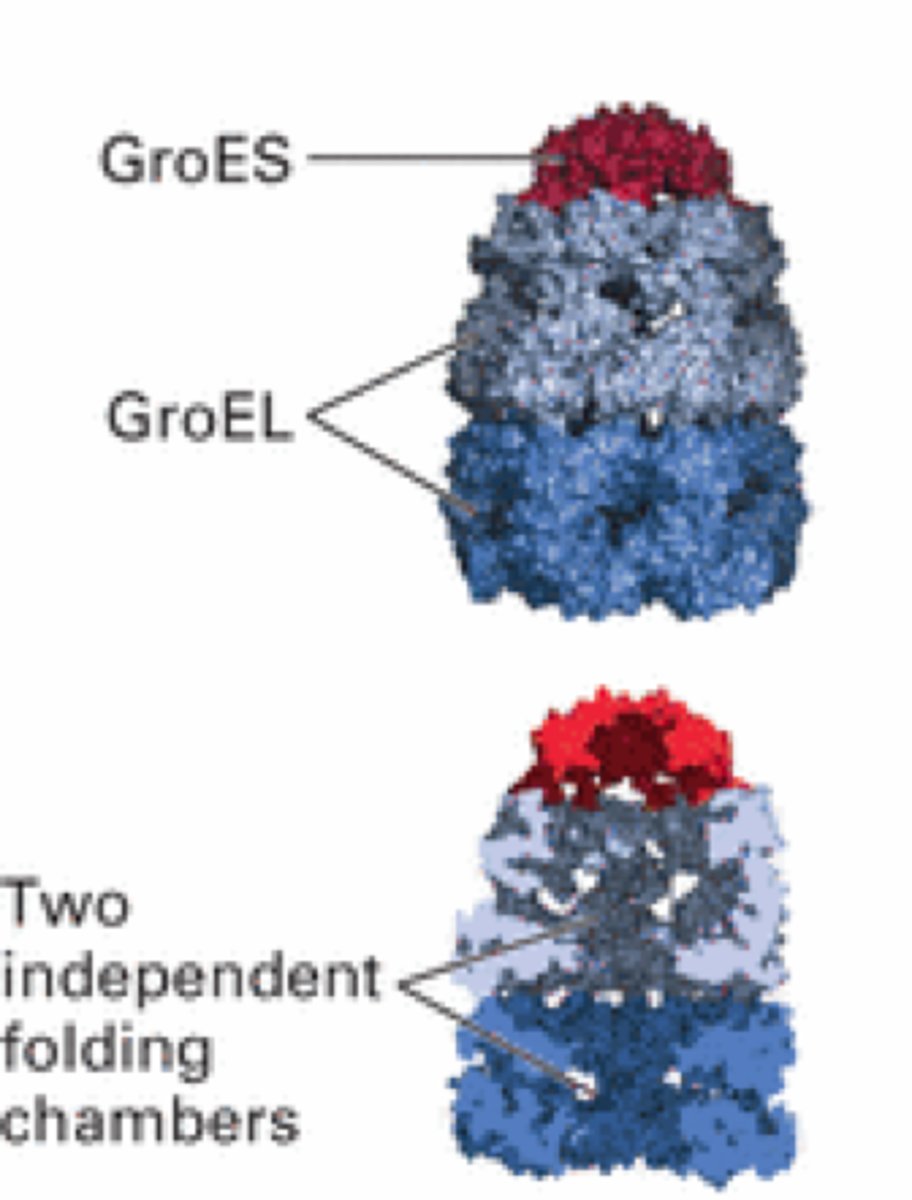
GroEl
Body of a protein folding machine
Soluble
Native (correctly folded) ß amyloid is a _____ globular protein
Misfolded
_____ ß amyloid promotes aggregation at newly exposed protein-protein interface