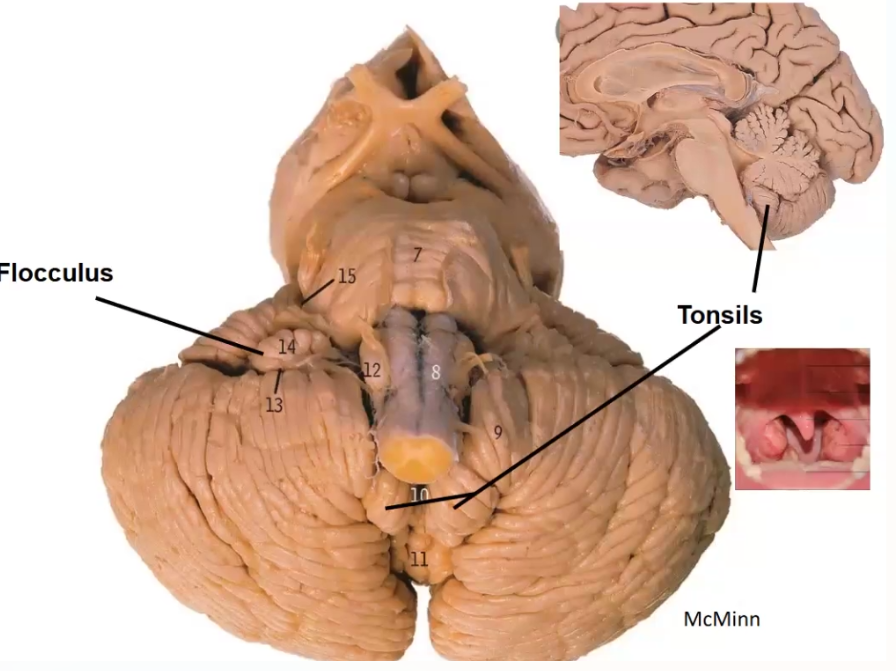
3. Cerebellum
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
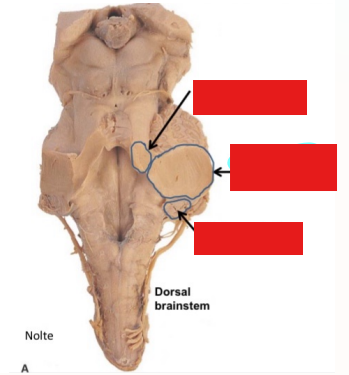
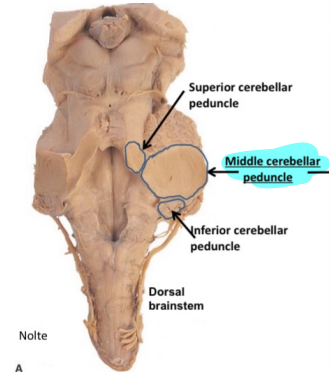
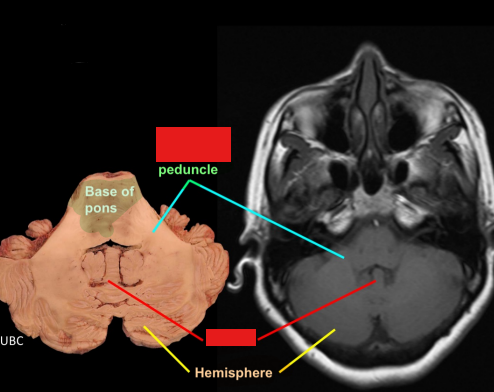
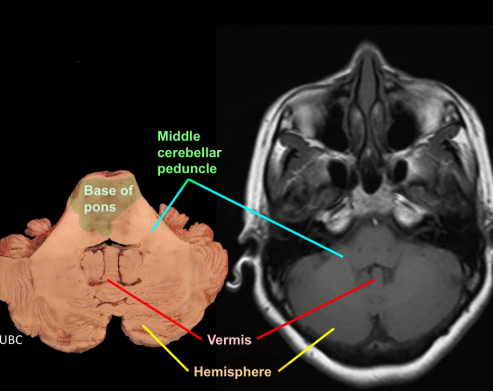
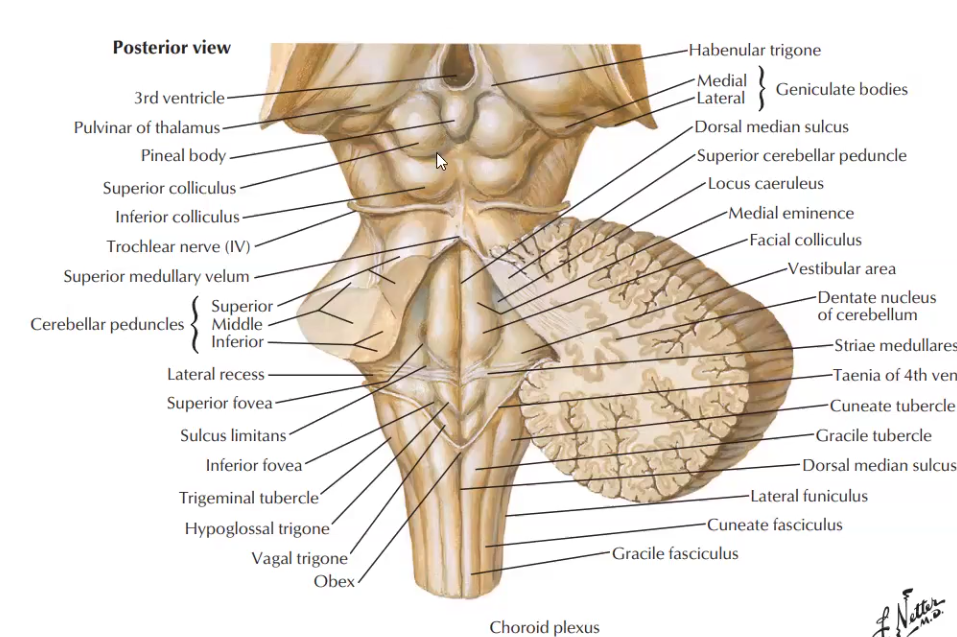
Label the cerebellar peduncles and name the structure they attach to in the brainstem
Superior: Midbrain
Middle: Pons
Inferior: medulla
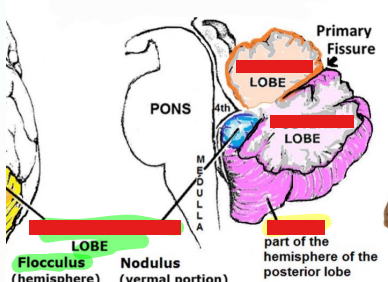
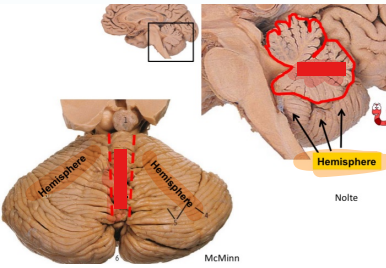
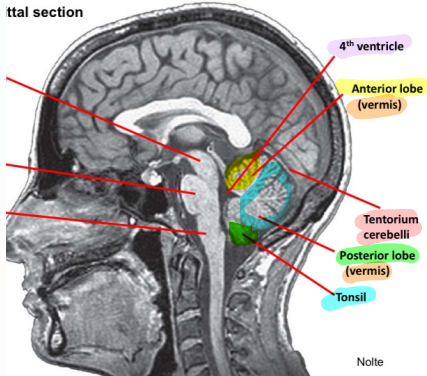
Label the cerebellar lobes
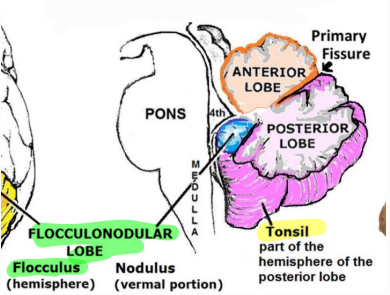
Label
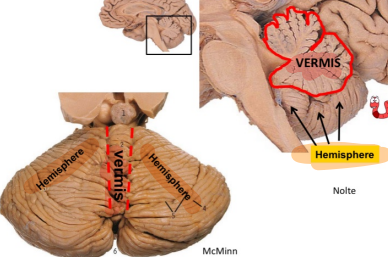
Label
Label
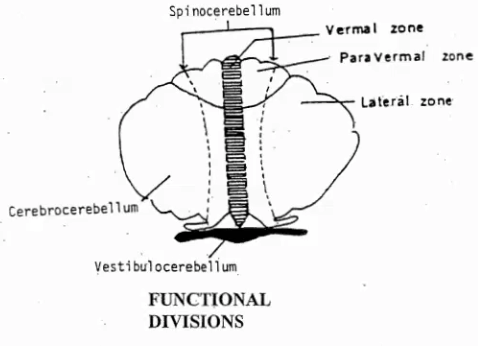
What are the 3 functional divisions of the cerebellum
Spinocerebellar
Cerebrocerebellar
Vestibulocerebellum
What nucleus is located in the cerebellum
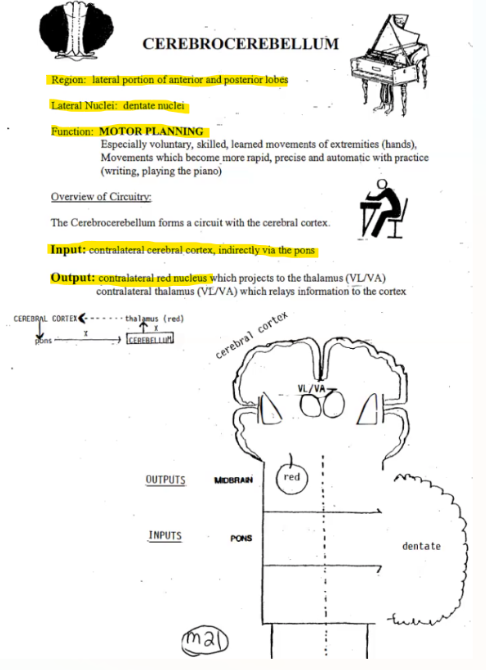
Cerebrocerebellum
Region of the cerebellum
Lateral Nuclei
Input
Output
Function
Region: Hemispheres
Lateral Nuclei: Dentate nuclei
Input: CONTRALATERAL Cerebral Cortex indirectly from pons via middle cerebellar peduncle
Output: CONTRALATERAL Red Nucleus of Midbrain via superior cerebellar peduncle
Function: MOTOR PLANNING; fine skilled movement
What nerve communicates with the cerebellum?
CN 8 Vestibulocochlear
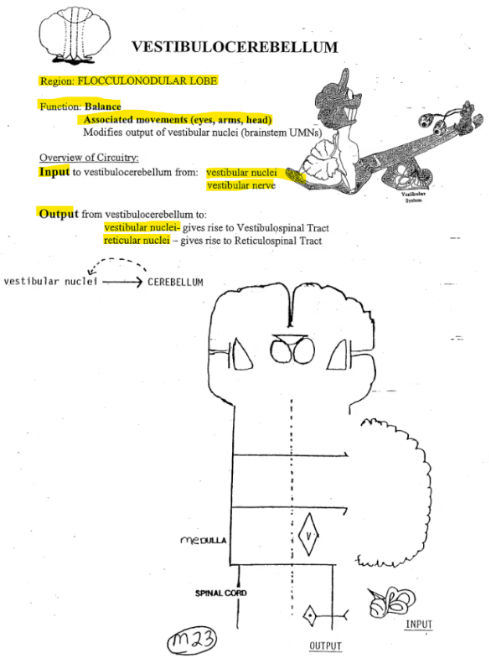
Vestibulocerebellum
Region of the cerebellum
Input
Output
Function
Flocconodular lobe
Input: vestibular nuclei and nerve
Output: vestibular and reticular nuclei, giving rise to Vestibulospinal and Reticulospinal tract
Function: Balance, Movements of arms, eyes and head
Spinocerebellar
Region of the cerebellum
Lateral Nuclei:
Input
Output
Function
Region: Vermal and paravermal
Nuclei: Fastigial, globose, emboliform
Input: cerebral cortex
Output: UMN’s
Function: Motor Execution

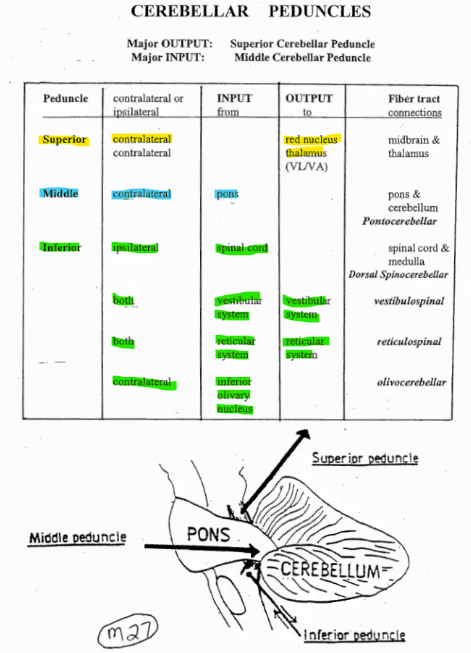
Name the output of the cerebellar peduncles:
Superior
Middle
Inferior
Superior
OUTPUT: contralateral to red nucleus and thalamus
Middle
INPUT: contralateral from pons
Inferior
INPUT:
ipsilateral from spinal cord
both from reticular and vestibular systems
contralateral from olivary nucleus
OUTPUT: to vestibular and reticular systems
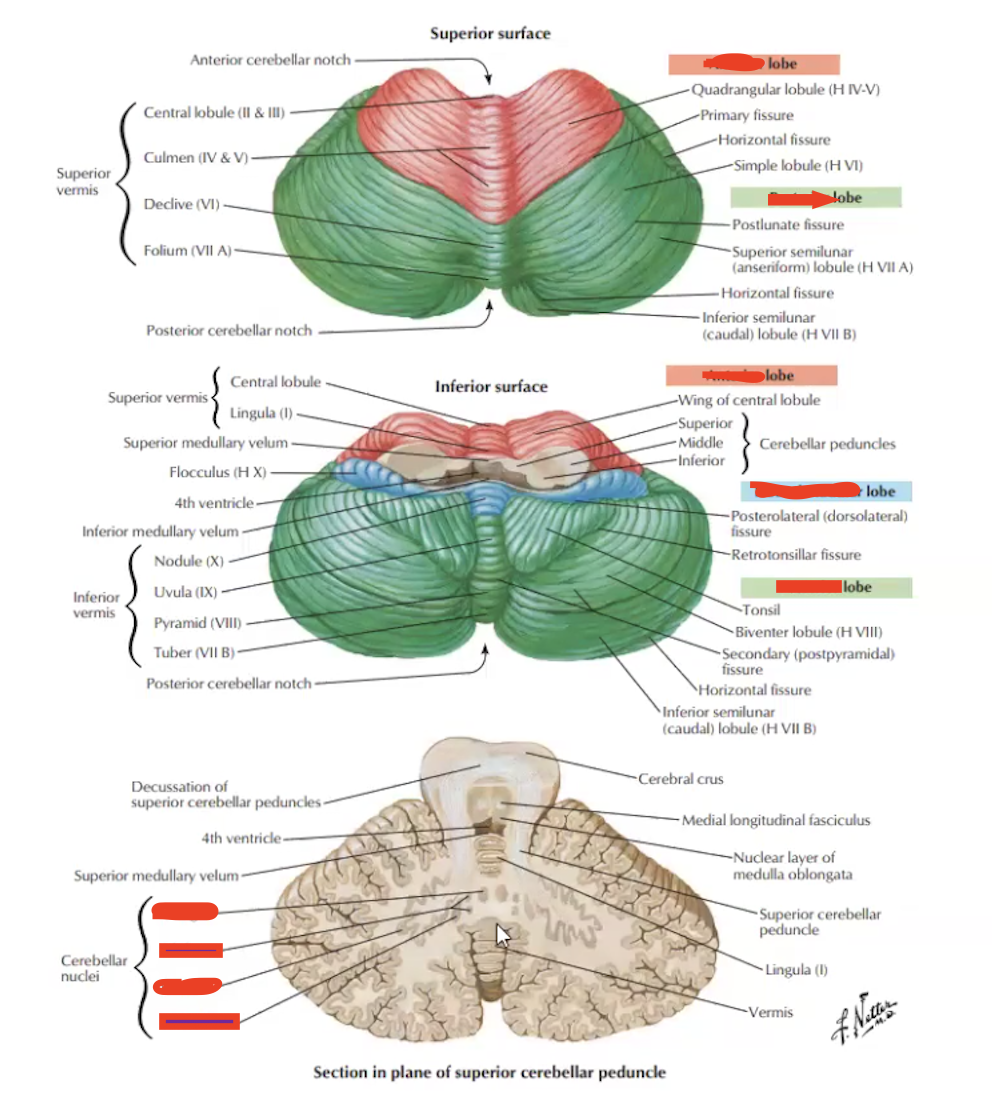
LABEL
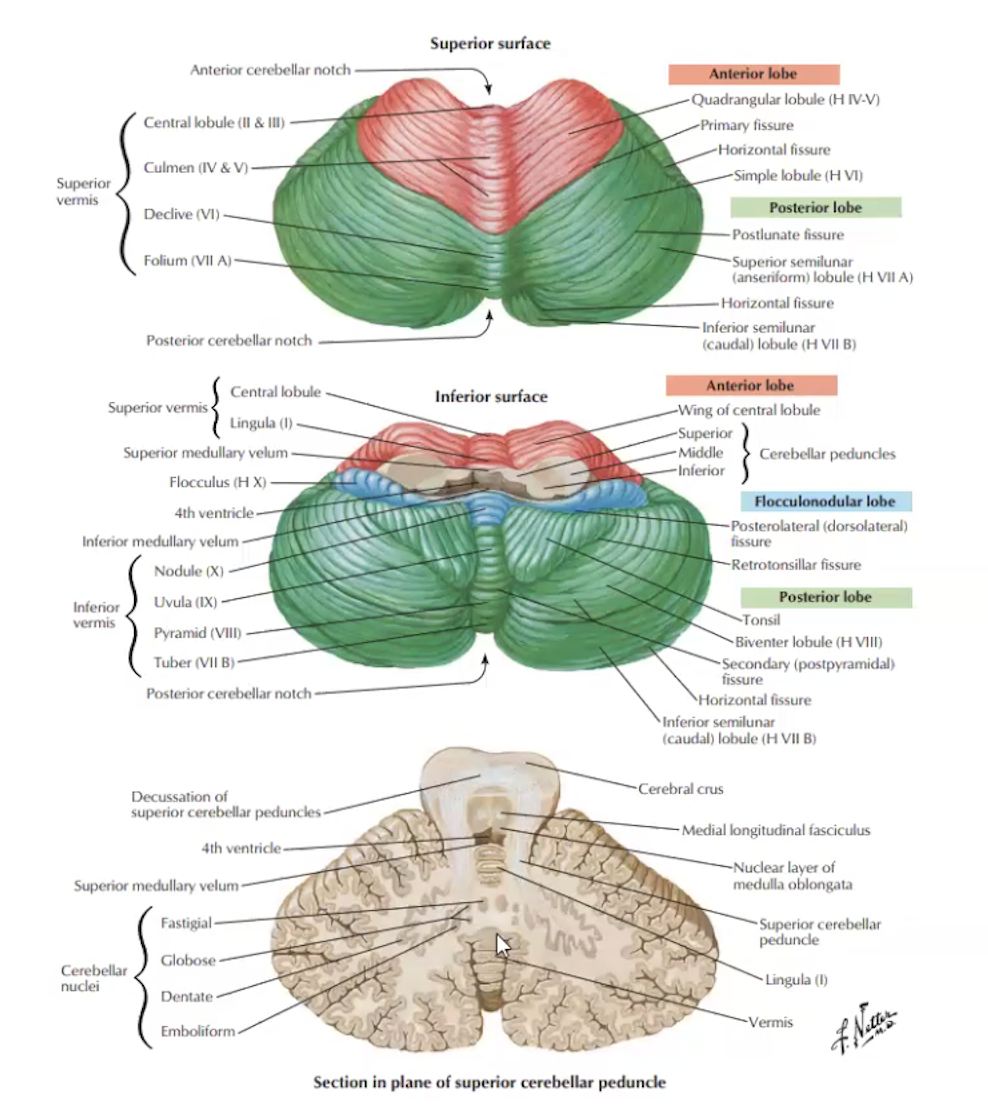
Blood Supply to the Cerebellum is done by 3 arteries
Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (PICA)
Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (AICA)
Superior Cerebellar Artery
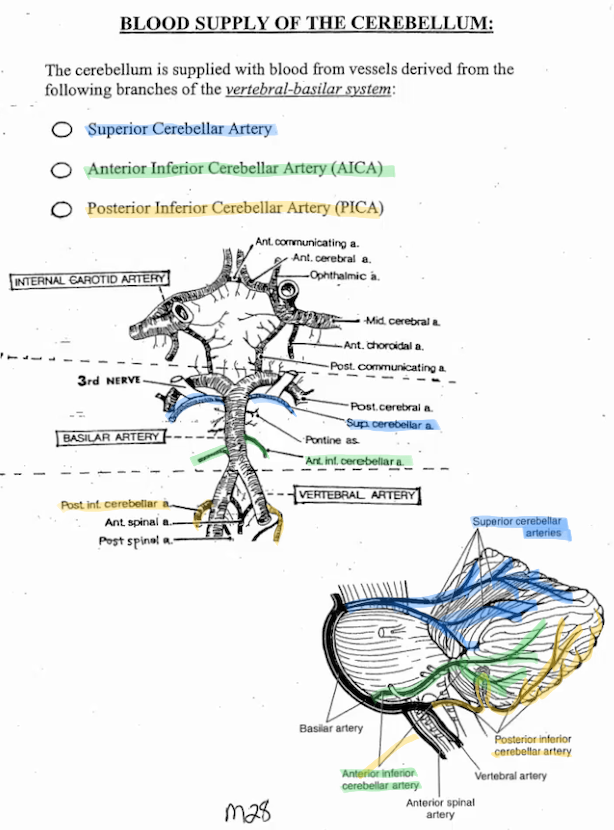
Functions of Cerebellum Areas
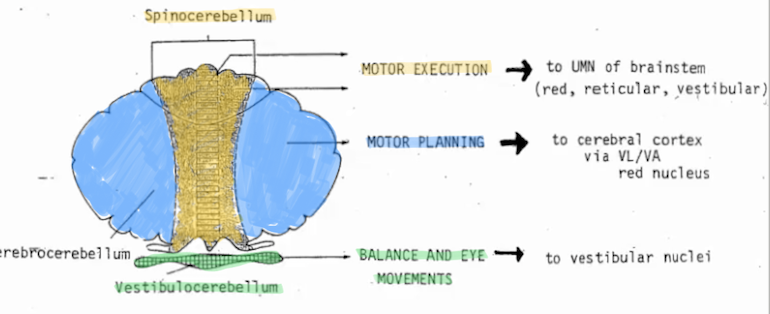
Cerebellum Tonsilar Herniation
How does it occur?
What can it result in?
Symptoms?
Tonsils of the cerebellum enlarge through foramen magnum
Results in blockage of flow of CSF through 4th ventricle, resulting in hydrocephalus
Pressure on cerebellum and medulla (which leads to cranial nerves 9, 10, 11 and 12 invlvement)
3 Functions of the Cerebellum and link them to the symptom resulting from damage
Maintenance of posture and balance (Vestibulocerebellum) → Disequilibrium
Maintenance of Muscle tone (cerebrocerebellum) → Hypotonia
Coordination of voluntary motor activity (spinocerebellum) → Dyssynergy
What is the difference between basal ganglia disorders and cerebellar disorders?
Basal ganglia disorders are characterized by meaningless involuntary movements such as resting tremors
Cerebellar Disorders are characterized by awkwardness of intentional movements such as intention tremors
General cerebellar dysfunction results in ipsilateral or contralateral damage?
Ipsilateral
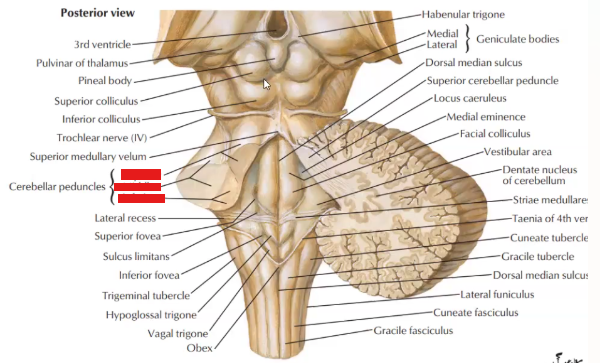
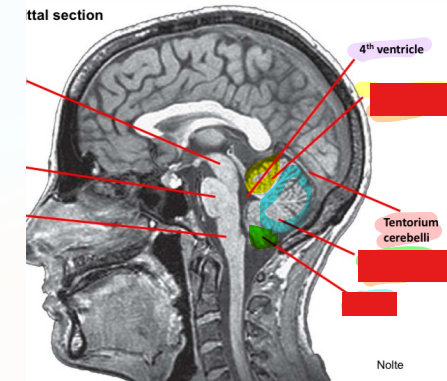
Label
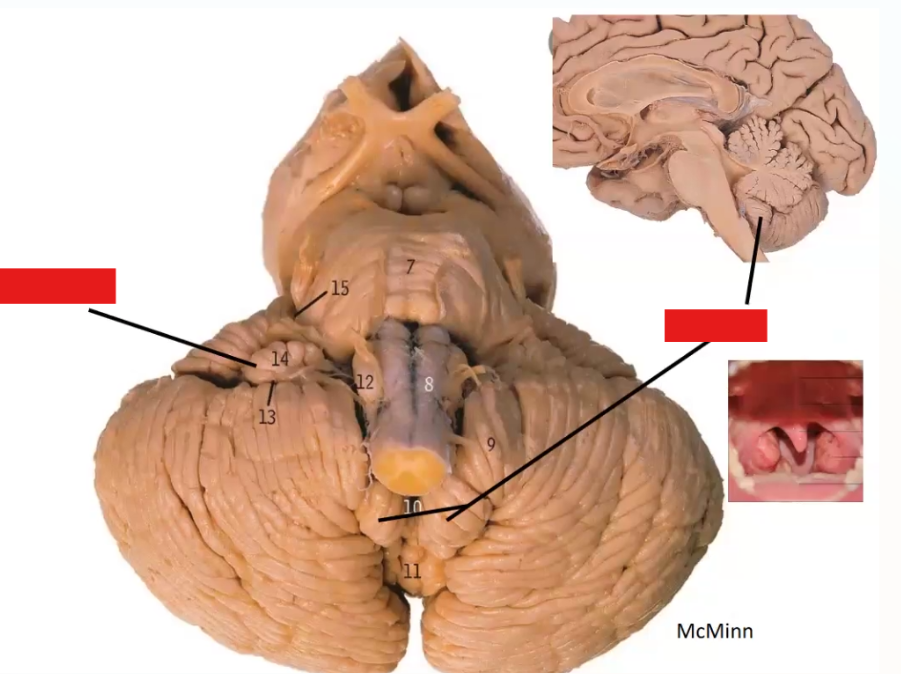
Label