Biology SL Unit 1 - Organic Molecules
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Chemical formula for glucose
C6H12O6
Alpha glucose’s OH is facing ___, beta glucose OH is facing ___
down, up
Glycosidic bond
Covalent bond between two glucose molecules
Starch is made up of ___
alpha glucose molecules
Starch’s function is:
energy storage in plants
Describe Amylose:
linear, 1-4 glycosidic bond, coiled structure.
Describe Amylopectin:
branched, both 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds, 3D branched structure (efficient storage of glucose)
Glycogen is made up of:
alpha glucose molecules
Name the three polysaccharides of glucose (carbs)
Starch
Glycogen
Cellulose
Describe Glycogen:
branched, both 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds, more branches than amylopectin
Glycogen’s function is:
Efficient storage of glucose in animals
Cellulose is made of:
beta glucose molecules
Describe Cellulose:
linear, 1-4 glycosidic bonds, repeating flat sheets held by hydrogen bonds. H-bonds between layers create tensile strength and stability. Straight linkage of b-glucose creates strong and rigid structure.
Cellulose’s function is:
in plant cell wall: maintain shape and integrity, withstand osmosis, protection.
Glycoproteins are:
proteins that have 1 or more carbs attached to it
Function of glycoproteins:
Cell-cell recognition: acts as markers on a surface of cells for identification
Receptors: receive signals from other cells
Ligands: binds to specific receptors to initiate things
Structural support: contribute to structural integrity
Properties of lipids:
hydrophobic
long term storage (higher atp yield)
Lipid’s functions:
SHIPS: Storage, hormonal, insulation, protection, structural
Triglycerides are made of:
1 glycerol + 3 fatty acids
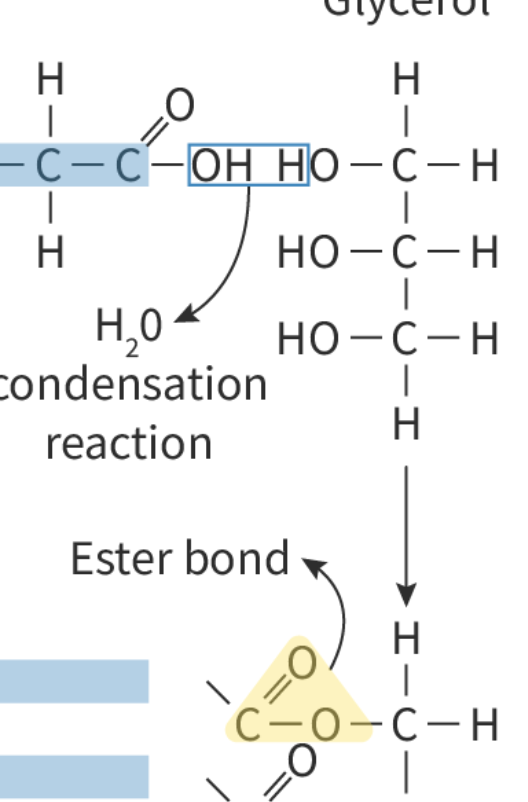
The covalent bond between fatty acids and glycerol is:
Ester bond
Phospholipids are made up of:
1 glycerol modified with phosphate + 2 fatty acids
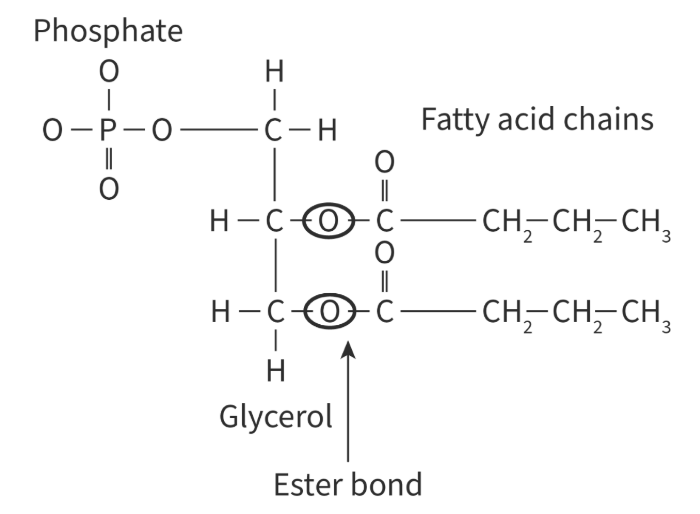
Phospholipid
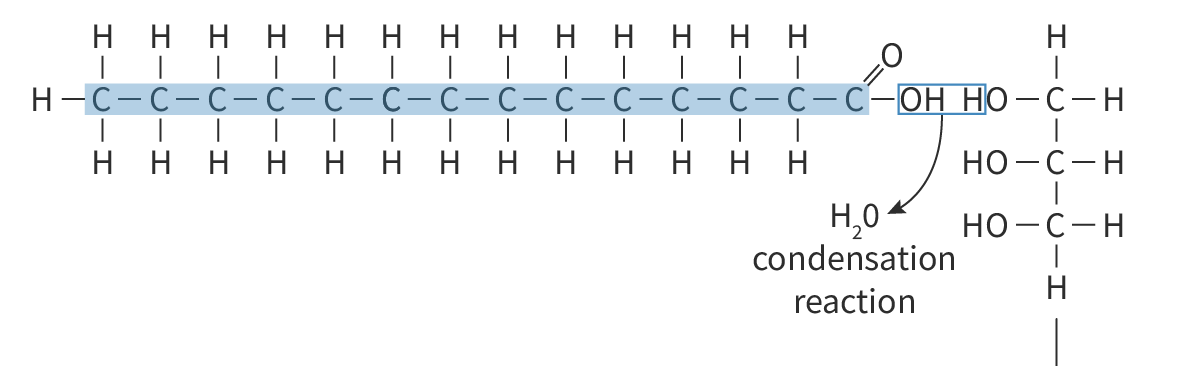
Triglycerides
Hydrocarbon chains are:
Backbone of fatty acids, long linear chains of hydrogen & carbon
Describe Saturated fatty acids:
linear and no double bonds, tightly packed, solid
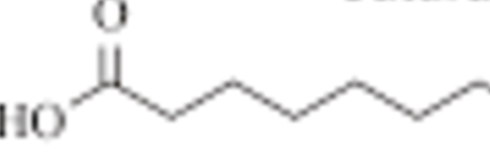
saturated fatty acid
Describe Unsaturated fatty acids:
bent structure, 1 or more double bond, hard to pack, liquid

unsaturated fatty acid
The more double bonds in fatty acids =
the weaker the fatty acid
Unsaturated fatty acid’s melting point is __ than saturated
lower
Describe cis unsaturated fatty acids:
bent, natural, loosely packed
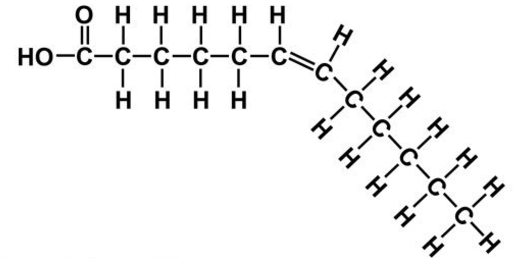
cis unsaturated fatty acid
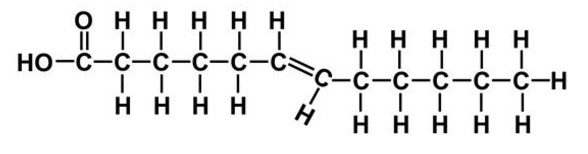
trans unsaturated fatty acid
Describe trans unsaturated fatty acids:
straight, man-made, rigid
Cis fats have H-atoms on ___ side, trans have on ___ side
same, different
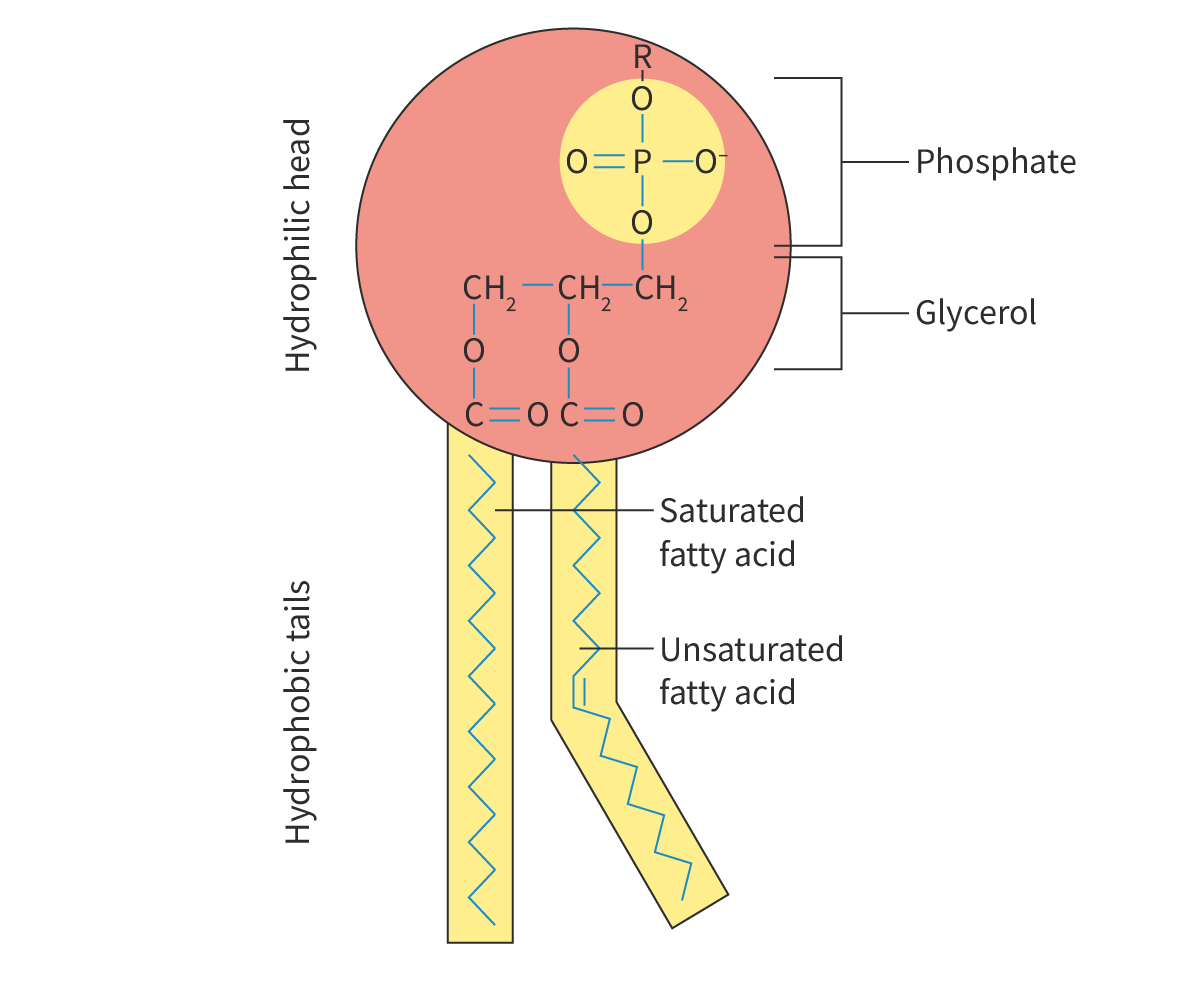
phospholipid bilayer
Describe the phospholipid bilayer:
hydrophilic phosphate head, hydrophobic fatty acid tail, amphipathic but overall hydrophobic
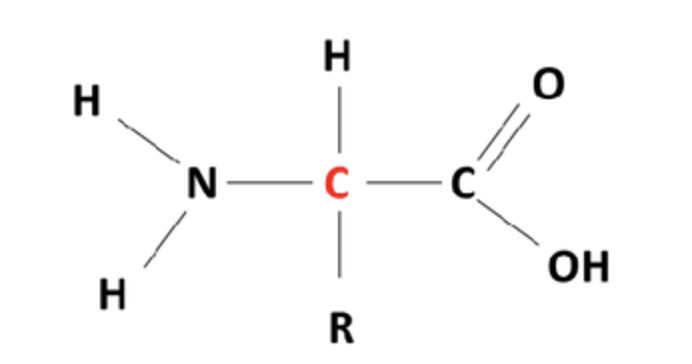
amino acid
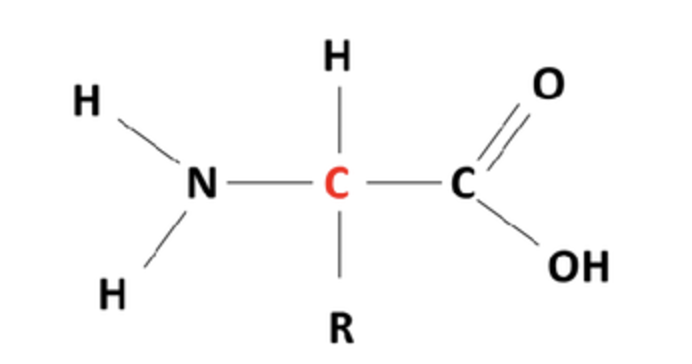
Label the different groups
Amino, side chain/R group, carboxyl
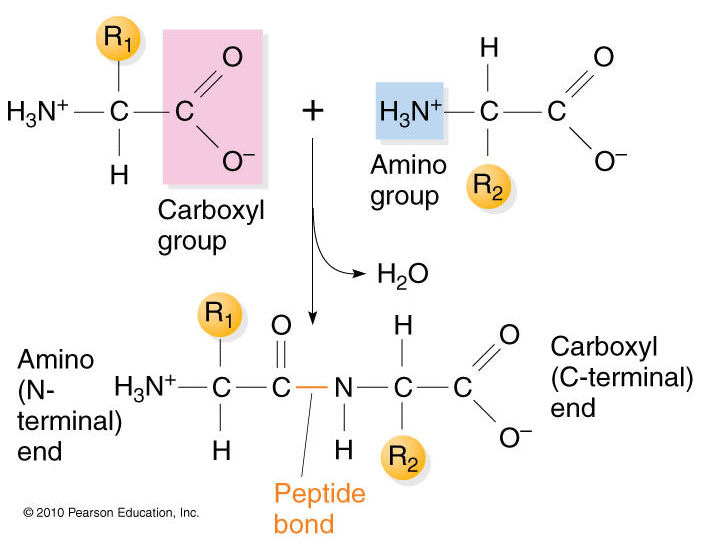
Peptide bond:
covalent bond between carboxyl + amino group
Draw the formation of peptide bond
Draw the formation of ester bond
What causes denaturation
temperature (breaks H-bonds)
pH (affects solubility and charge)
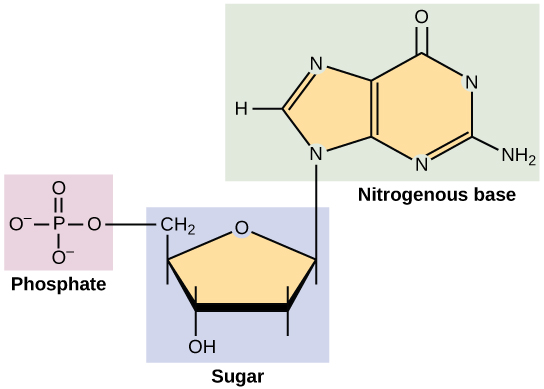
nucleotide
polymerization is
(condensation) forming nucleic acids from nucleotides
Purines are:
1 ringed base (Adenine and Guanine)
Pyrimidines are
2 ringed bases (cytosol & thymine & uracil)
Bond between nucleotides are:
phosphodiester bonds
G - C bonds have __ H-bonds, while A - T/U bonds have __ H-bonds
3, 2
Describe DNA
deoxyribose sugar, stable long term storage of information, no oxygen, double stranded, contains thymine
Describe RNA
ribose sugar, copy of DNA, short term information storage, contains uracil, single stranded, OH group
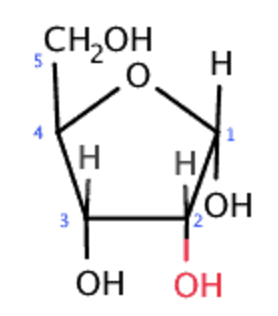
ribose sugar
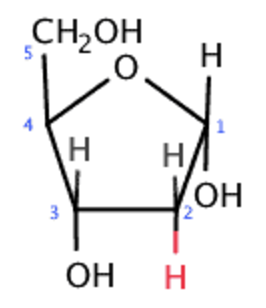
deoxyribose sugar
Define nucleosome
DNA wrapped around protein (histones)
Enzyme-substrate specificity models
lock and key (specific enzyme for specific chemical reaction)
induced fit model (enzyme active site changes to fit substrate)
What happens to an enzyme when substrate concentration is too high?
becomes saturated