(25.1) Gross Anatomy of the Kidneys
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
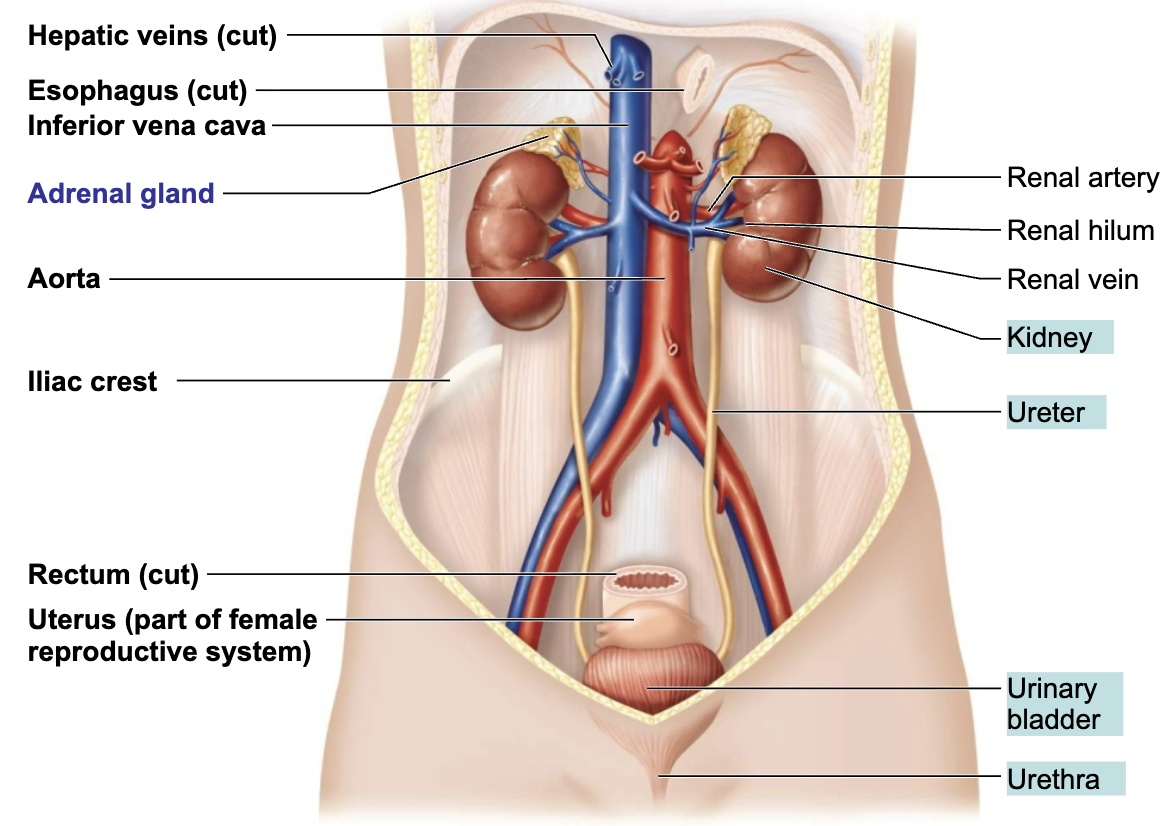
List the Organs of the Urinary System
Kidneys
Urters
Urinary bladder
Urethra
Describe the function of the Kidneys
Major excretory organ, maintain the body’s internal environment by:
Regulating total water volume and total solute concentration in water
Regulating ion concentration in extracellular fluid (ECF)
Ensuring long-term acid-base balance
Excreting metabolic wastes, toxins, drugs
Producing erythropoietin (regulates RBC) and renin (regulates blood pressure)
Activating vitamin D
Carrying out gluconeogenesis, if needed
Describe the function of the Ureters
Transport urine from kidneys to urinary bladder
Describe the function of the Urinary Bladder
Temporary storage reservoir for urine
Describe the function of the Urethra
Transport urine out of body
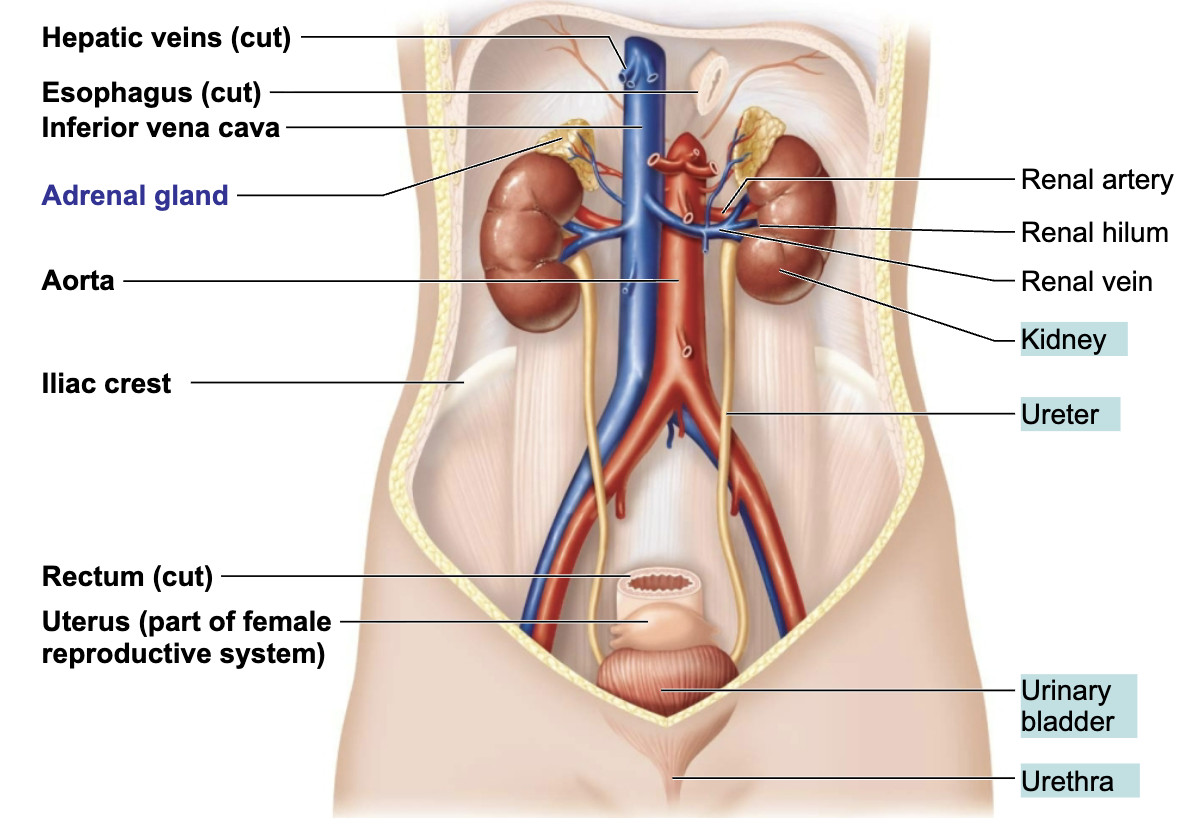
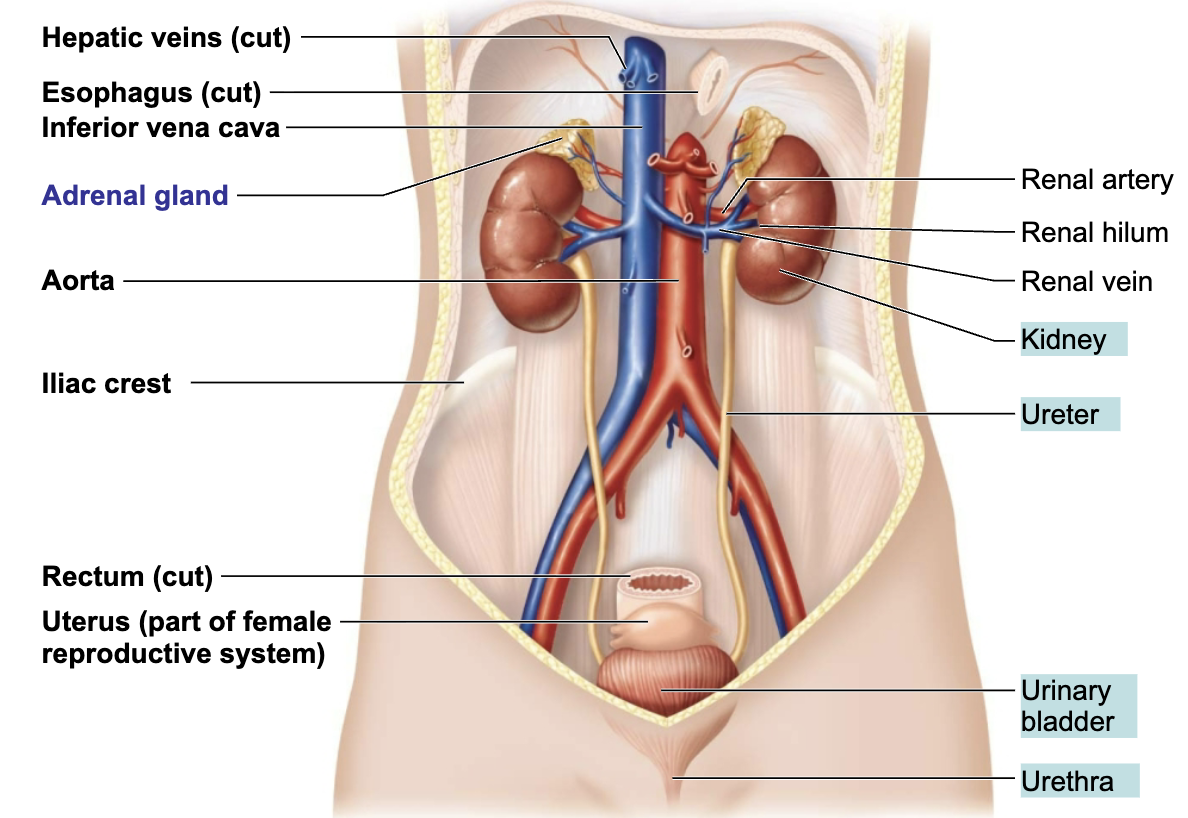
Describe the Location of the Kidneys
Retroperitoneal position → between the dorsal body wall and the parietal peritoneum
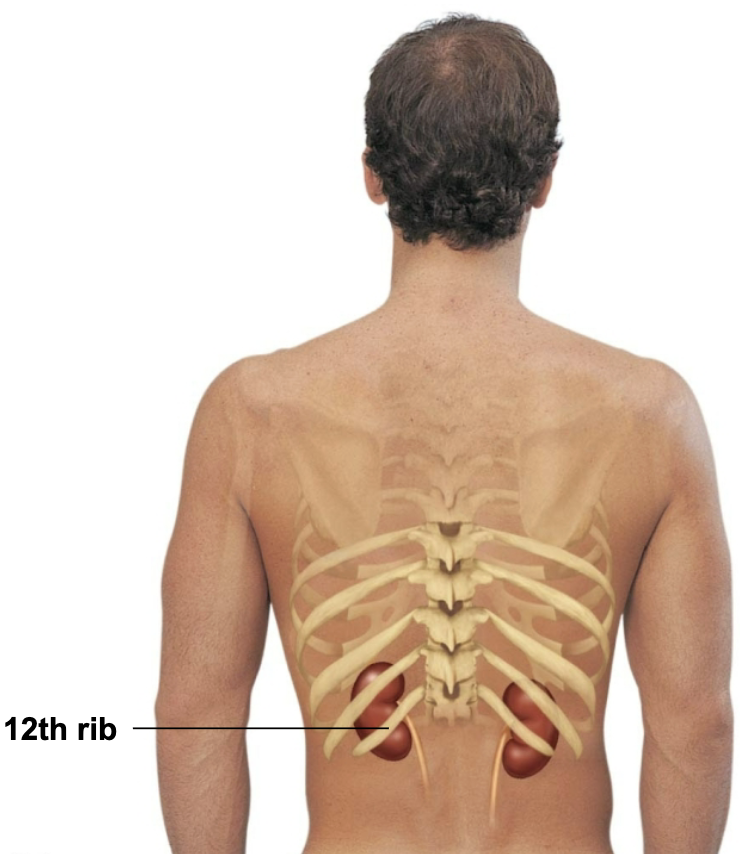
T/F: Kidneys are bean shape and same on both sides
→ FALSE
RIGHT kidney is crowded by the liver and lies slightly lower than the left
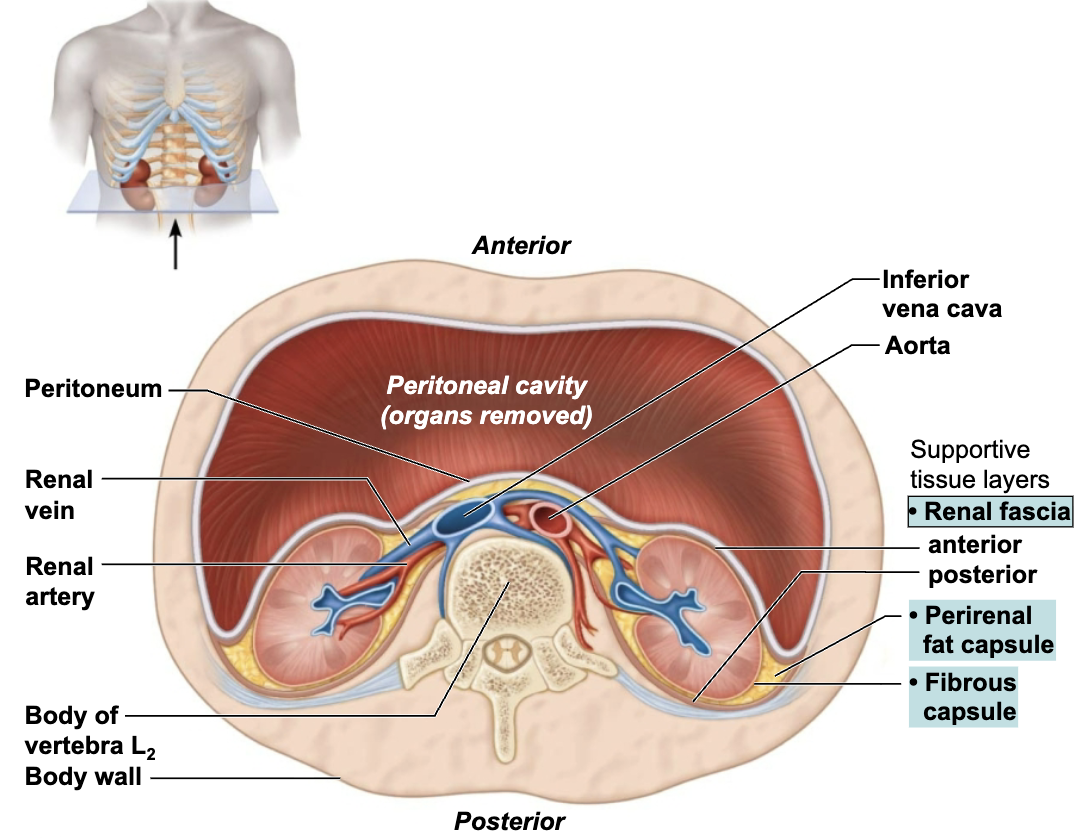
Describe the Location and the Function of the Connective Tissue Layers of the Kidneys
SUPPORTIVE TISSURE LAYERS
Renal fascia
Outermost layer
Anchors the kidney and the adrenal gland to surrounding structures
Perirenal fat capsule
Middle layer
Fatty mass that surrounds the kidney and cushions it against blows
Fibrous capsule
Innermost layer
Transparent capsule that prevents infections in surrounding regions from spreading to the kidney
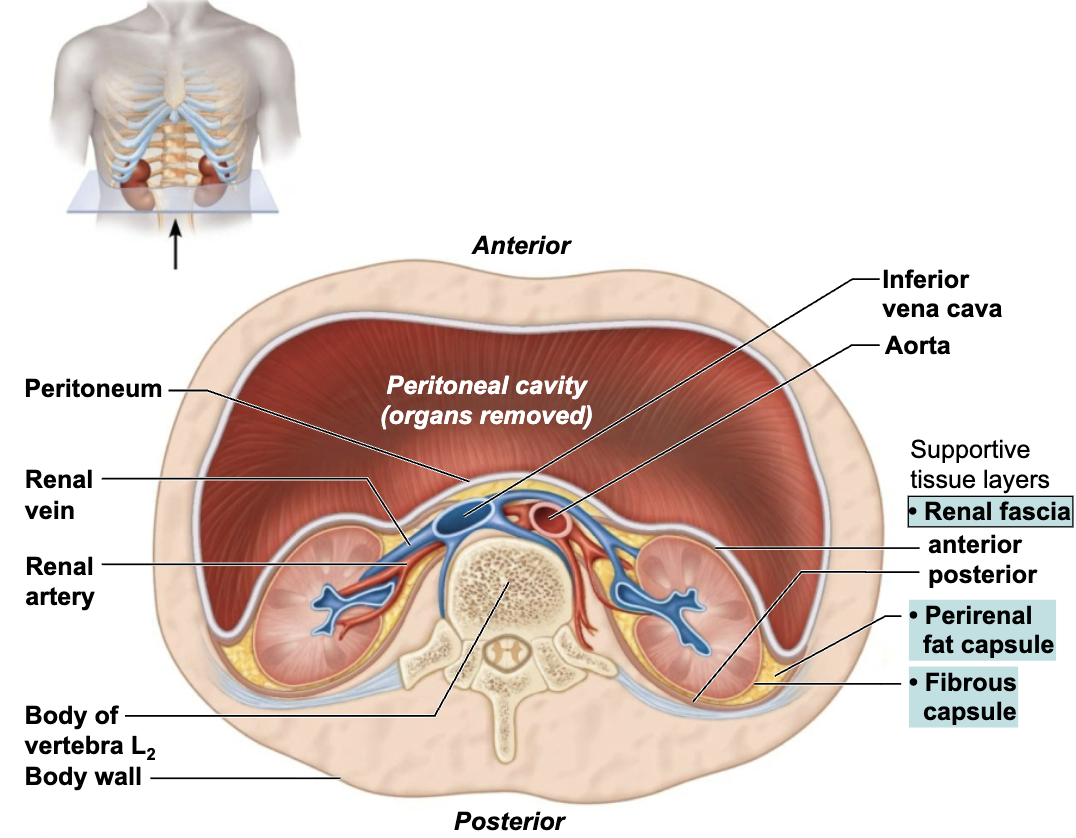
Explain Effect and Cause of Rena ptosis
EFFECT
Condition in which one or both kidneys drop to lower position
CAUSE
Can be caused by loss of surrounding fatty tissue capsule that holds kidneys in normal position
Seen with emaciation or rapid weight loss
Describe the Cross-Section Anatomy of the Internal Kidney
Renal cortex: granular-appearing superficial region
Renal medulla: deep to cortex, composed of cone-shaped medullary (renal) pyramids
Minor calyces: drain urine into the major calyces
Major calyces: collect urine and drain into the renal pelvis
Renal pelvis: kidney that receives urine from major calyces; continuous with the ureter leaving the renal hilum
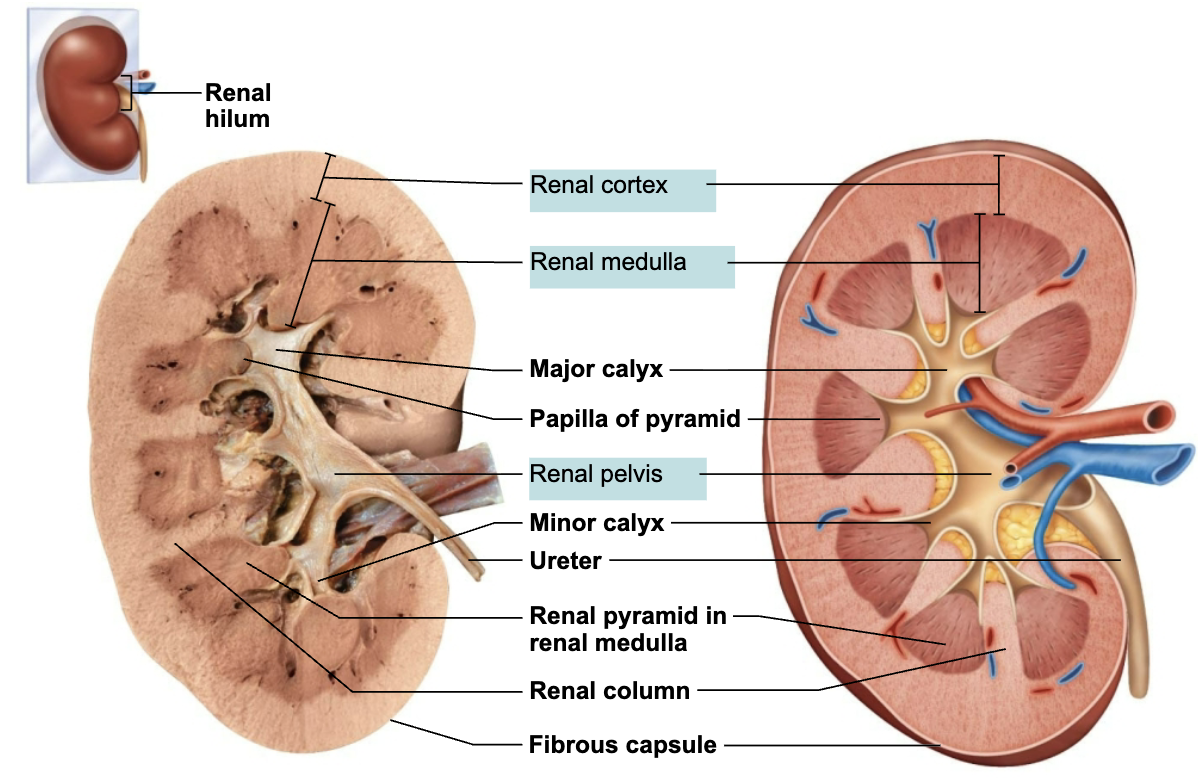
Know the Pathway of Urine Flow