14- Electromagnetic induction
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
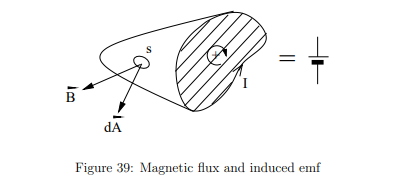
What is magnetic flux (ΦB)?
It represents the total magnetic field passing through a surface.
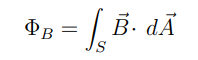
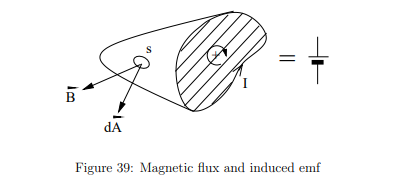
What does Gauss’s Law for Magnetism say about magnetic flux?
For a closed surface, the total magnetic flux is always zero
This means magnetic field lines never begin or end; they always form loop
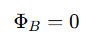
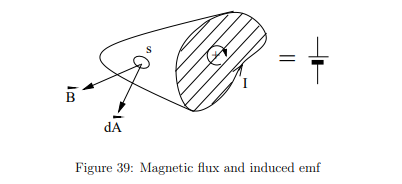
What is Faraday’s Law of Induction?
A changing magnetic flux through a circuit induces an emf
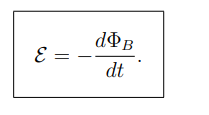
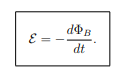
What does the negative sign in Faraday’s Law represent?
It follows Lenz’s Law, meaning the induced current opposes the change in flux.
What are the three ways to induce an emf in a circuit?
The circuit moves relative to a stationary magnetic field.
The magnetic field moves relative to a stationary circuit.
The current in a circuit (or a nearby one) changes with time.
How is the direction of the induced current determined?
The normal to the surface defines positive flux direction.
A positive change in flux induces a negative emf (Lenz’s Law).
The induced current flows in a direction that opposes the change in flux.
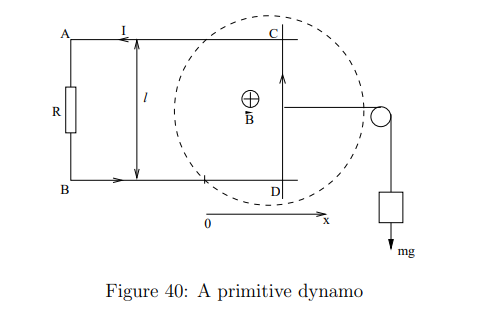
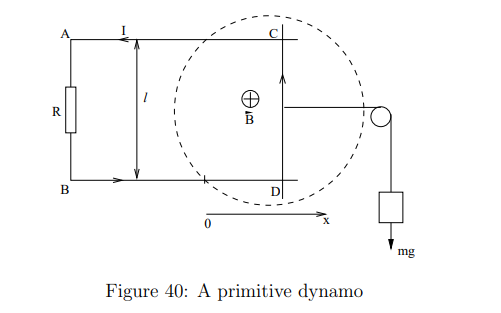
What is a dynamo?
A device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy by moving a conductor through a magnetic field, inducing an emf.
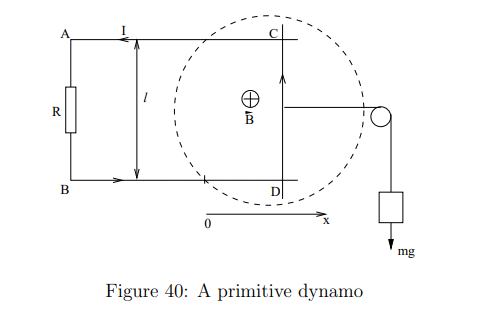
How is emf induced in a moving conductor?
When a conductor moves through a magnetic field, the Lorentz force acts on electrons
This creates a potential difference and inducing an emf.
What is the Lorentz force acting on electrons in a moving conductor?
This force causes electrons to move, leading to a conventional current opposite to electron flow.
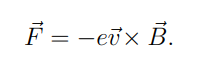
How does the induced current oppose motion?
The induced current interacts with the magnetic field
This creates a force that opposes the motion of the conductor (Lenz’s Law).
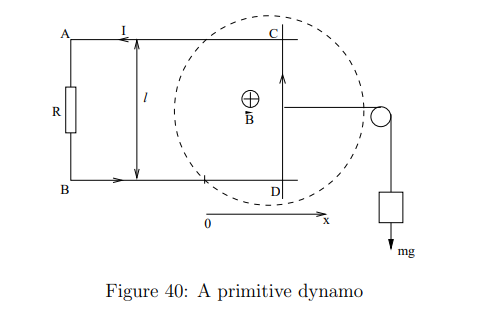
What is the equation for force balance in the dynamo system?
This means the gravitational force is balanced by the magnetic force when the system reaches a steady velocity.
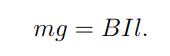
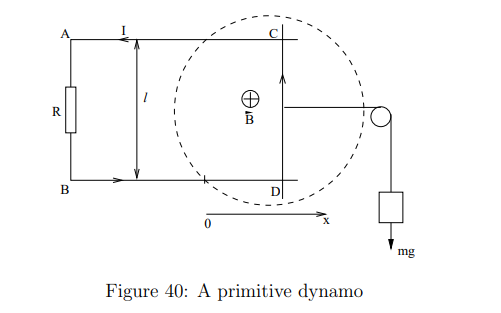
What is the equation for power conversion in a dynamo?
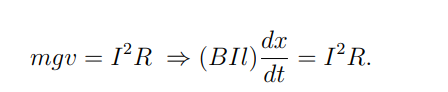
How does the magnetic flux change in the circuit?
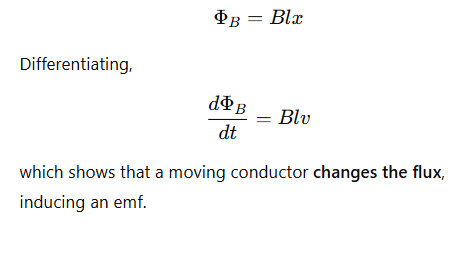
What fundamental law describes the induced emf in a dynamo?
Faraday’s Law of Induction
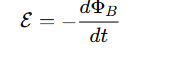
Why does the moving conductor behave like a battery?
The induced emf drives a current from low to high potential inside the conductor, just like a battery or generator.
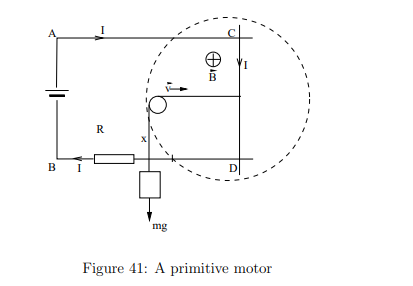
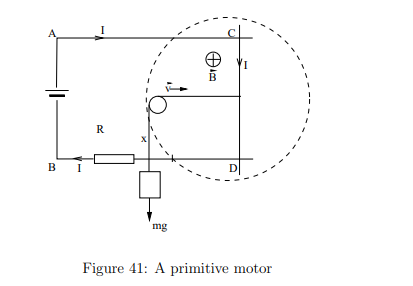
What happens when a battery with emf Eext is added to the circuit?
The current flows clockwise, and the rod CD experiences a force to the right, which can be used to lift a weight.
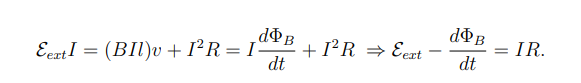
What does this equation represent?
The rate at which chemical energy is converted into electrical energy
This is then split between mechanical energy gained by the weight and power dissipated in the resistor.
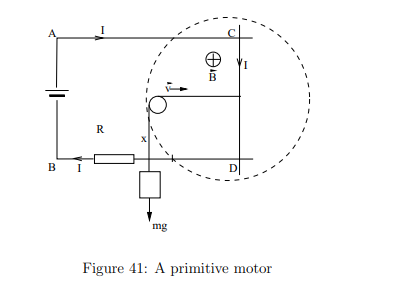


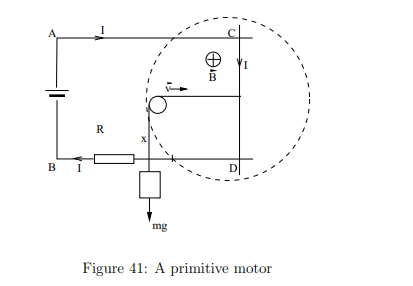
Why does a motor exert a 'back emf' on the power source?
The induced emf opposes the applied emf, which the power source must overcome to perform mechanical work.
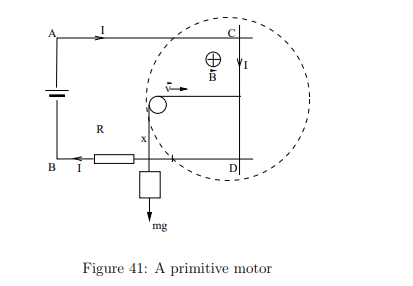
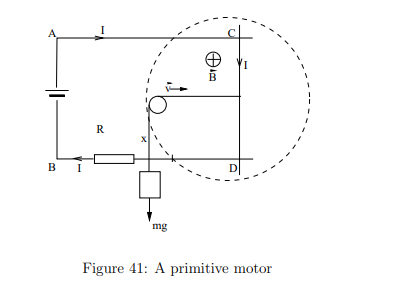
Why is stopping a motor while it is still connected to a power source dangerous?
If dΦB/dt=0, the current surges up, potentially blowing fuses or burning the motor windings.
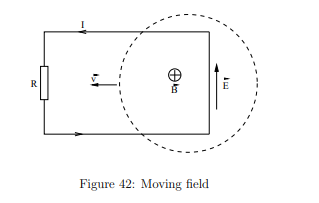
How is a moving circuit viewed differently in a moving magnetic field?
In a moving magnetic field, there are no Lorentz forces driving electrons; instead, an induced electric field drives the current.
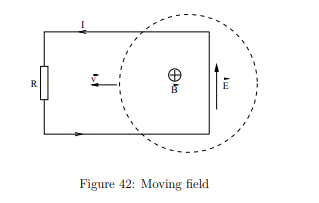
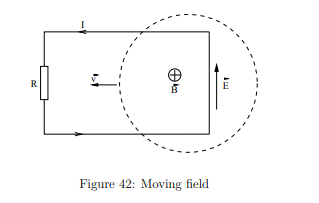
What is the relationship between induced emf and the electric field?
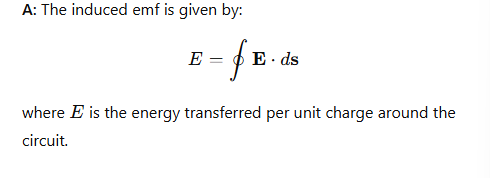
How does Faraday’s Law generalize the electrostatic circuital law?
In electrostatics, ∮E⋅ds=0, but with time-dependent magnetic fields, Faraday’s Law states:
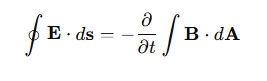
Why is Faraday’s Law important in electromagnetism?
It establishes a relationship between electric and magnetic fields, unifying electricity and magnetism within a single theory.
Does Faraday’s Law only apply to loops made of conducting wires?
No, it applies to any closed mathematical loop, even if there is no physical wire present.
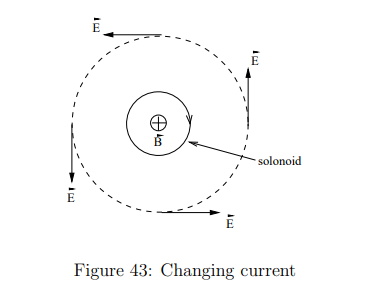
What happens when the magnetic flux through a stationary circuit changes?
An induced emf is found, even if there are no moving parts.
What equation still holds for a changing magnetic flux in a stationary circuit?
Faraday’s Law
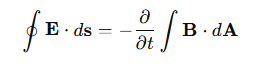
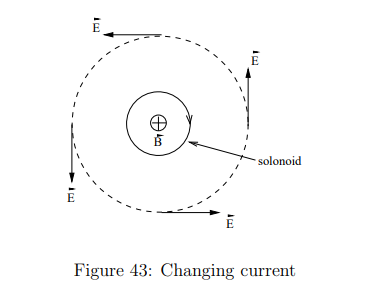
In a long solenoid with a changing current, what happens to a wire loop around it where B=0?
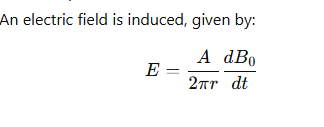
Does the induced electric field in the solenoid loop exist if the wire is not present?
Yes, the electric field exists regardless of the presence of the wire.