biochem
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:44 AM on 2/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
1
New cards
how many key biological molecules are vital to the human body?
5 key biological molecules
2
New cards
what are the 5 key biological molecules that are vital to the human body?
1. lipids (fat)
2. carbohydrates
3. proteins
4. nucleic acid
5. water
3
New cards
what are the 5 key biological molecules called?
polymers
4
New cards
which of the 5 key biological molecules is organic?
proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids
5
New cards
which of the 5 key biological molecules is inorganic?
water
6
New cards
what is the difference between inorganic and organic molecules?
organic = with C-atoms \n inorganic = no C-atoms
7
New cards
what are monomers?
building blocks of polymers (basic units)
8
New cards
What are the monomers of proteins?
amino acids
9
New cards
what are the monomers of carbohydrates?
monosaccharides
10
New cards
what are the monomers of lipids?
fatty acids and glycerol
11
New cards
what are the monomers of nucleic acids?
nucleotides
12
New cards
what are the monomers of water?
no monomer
13
New cards
What is a synthesis (dehydration) reaction?
process where biological monomers join together to form polymers (macromolecules) releasing water
14
New cards
What is a hydrolysis (digestion) reaction?
process where water is used to split a polymer into its monomers
15
New cards
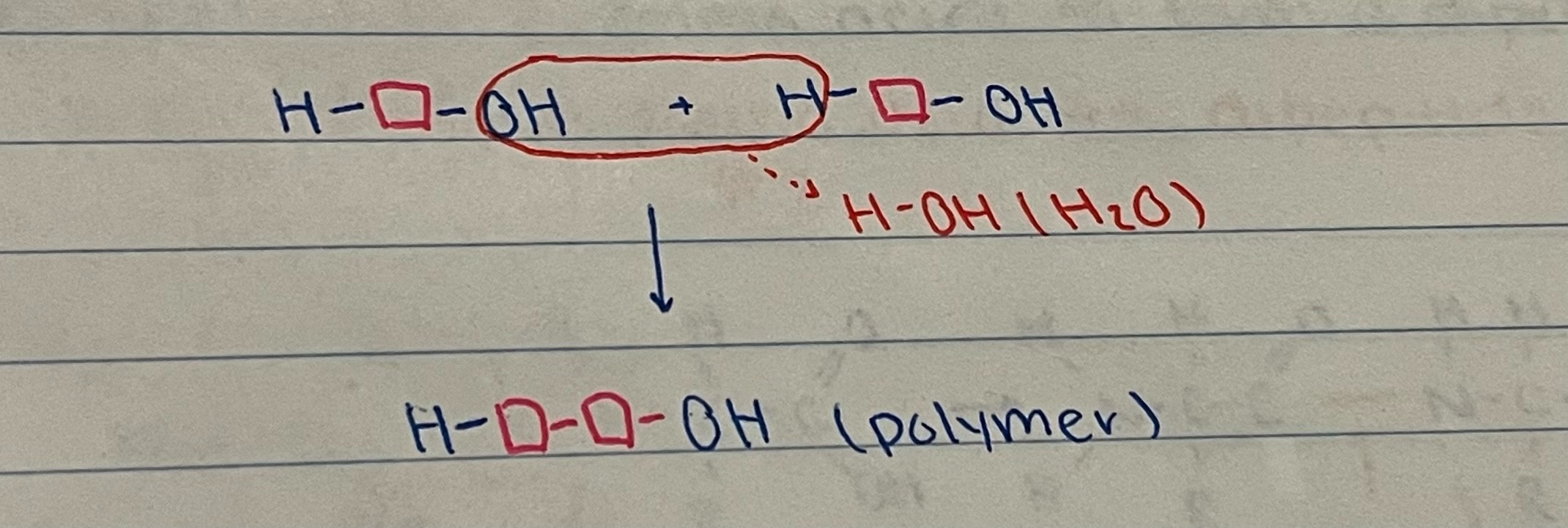
\
synthesis reaction
16
New cards
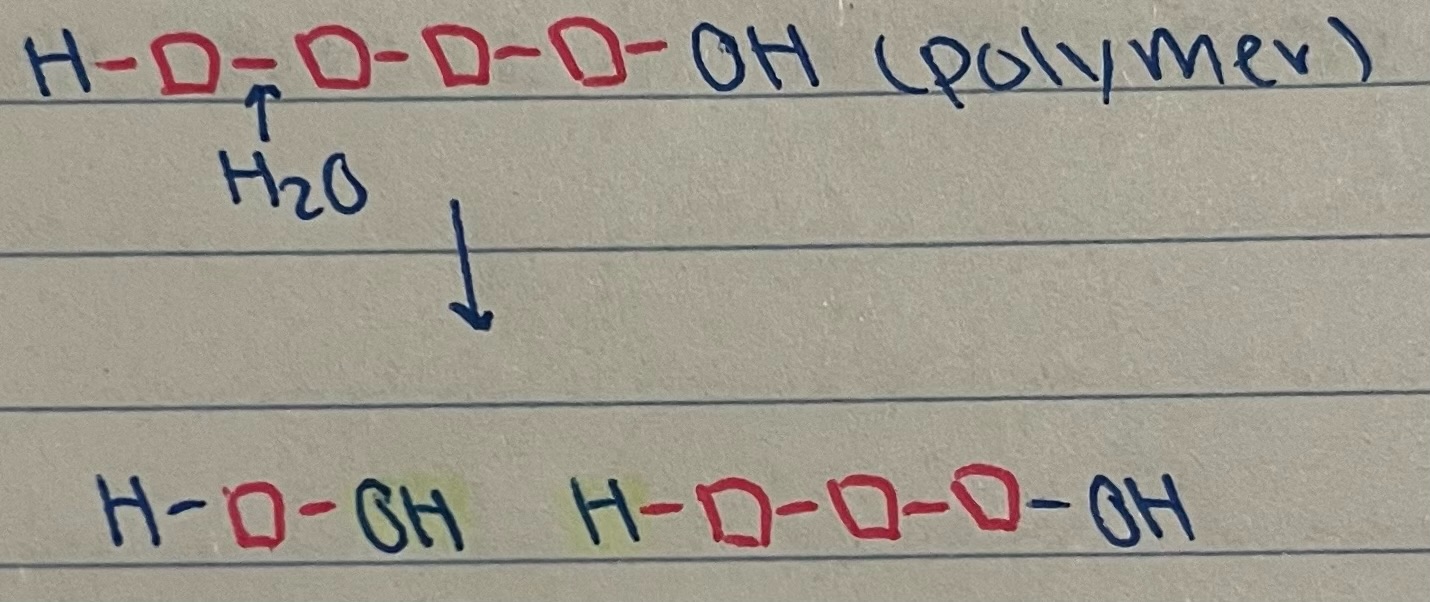
hydrolysis reaction
17
New cards
what is the biological purpose of proteins?
it is used in the body to build new tissues
18
New cards
what happens if proteins are in excess?
it is used to produce energy
19
New cards
what are the three main groups of each amino acid?
1. amine group/amine
2. carboxyl group/carboxylic acid
3. R (remainder) group
20
New cards
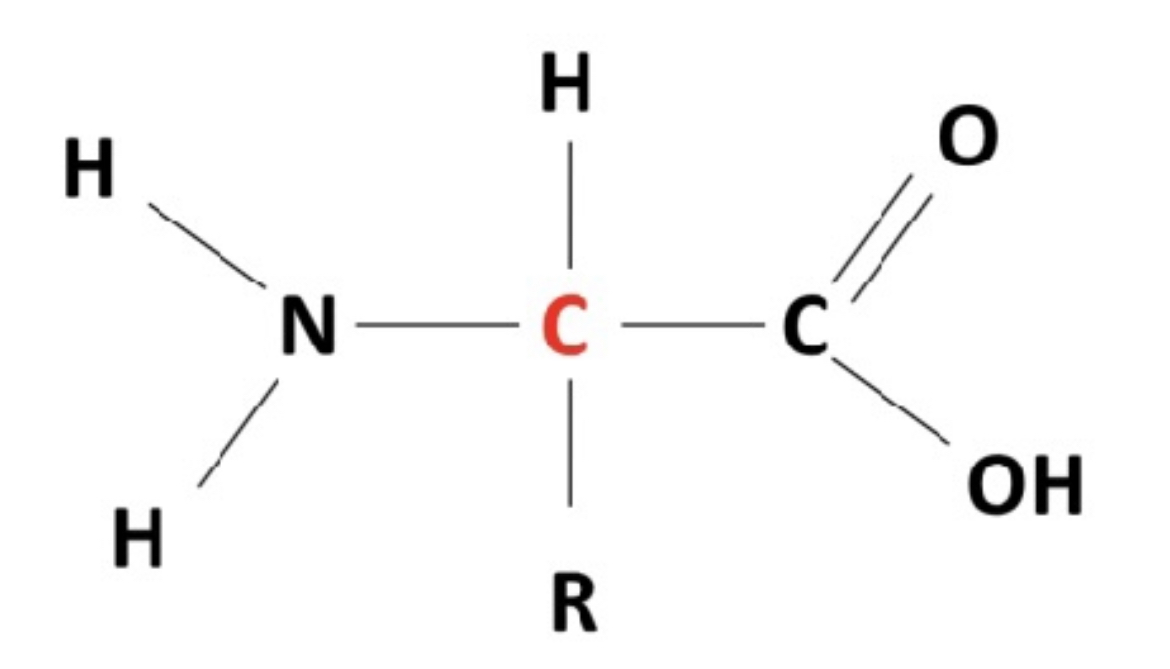
amino acid
21
New cards
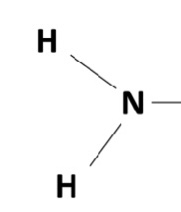
amino group/amine
22
New cards
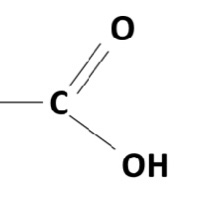
carboxyl group/carboxylic acid
23
New cards

R (remainder) group
24
New cards
how do each amino acid differ from each other?
in their R-group
25
New cards
how many different types of R-groups are there?
20 different R-groups
26
New cards
what is created when two amino acids synthesize?
dipeptide and water
27
New cards
name the type of bond that links amino acids together
peptide bond
28
New cards
what happens to the polymer of protein when water is added during hydrolysis?
it breaks down into many individual amino acids as water breaks down the peptide bond
29
New cards
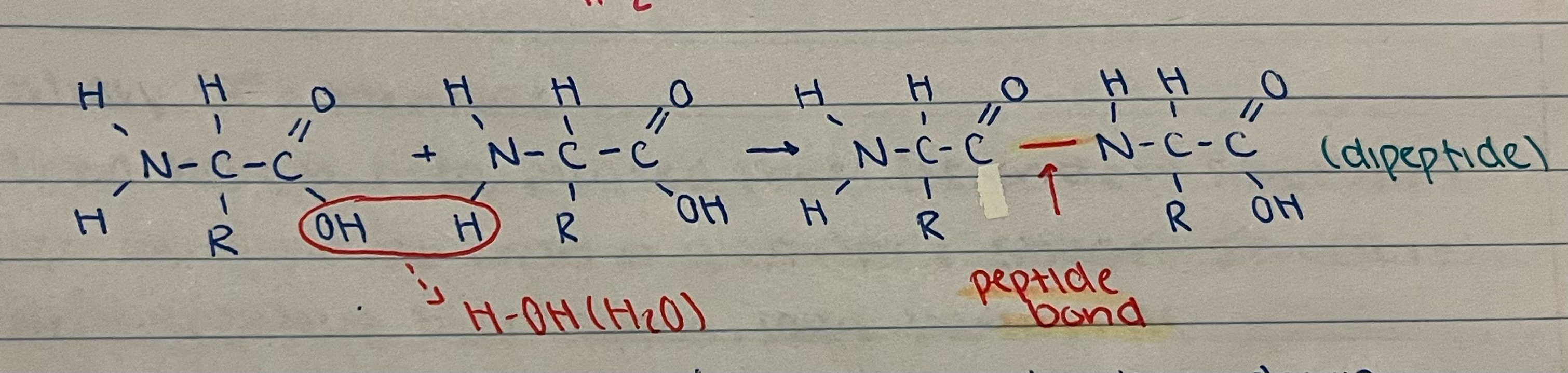
exaplain the process
amino acids synthesized to form dipeptide as the amino acids are linked together by a peptide bond releasing water
30
New cards
what are the four categories of proteins
1. primary (1°) structure
2. secondary (2°) structure
3. tertiary (3°) structure
4. quaternary (4°) structure
31
New cards
what is the primary structure of a protein?
amino acids linked together in a linear fashion
32
New cards
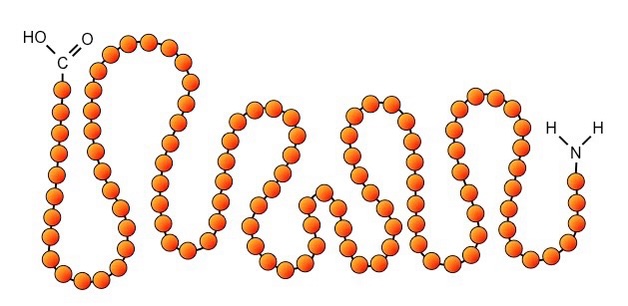
primary structure protein
33
New cards
what is the secondary structure of a protein?
* polypeptide chain (1° structure) forms a long coil called alpha helix
* can also have beta-pleated sheets
* can also have beta-pleated sheets
34
New cards
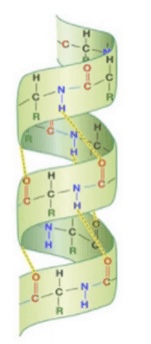
secondary structure protein (alpha helix)
35
New cards
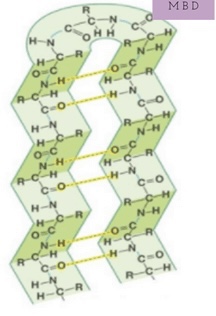
secondary structure protein (beta-pleated sheet)
36
New cards
what is the tertiary structure of a protein? what is it held together by?
* 2° structure folds on itself to form a globular structure
* held together by H-bonds, ionic bonds, etc
* held together by H-bonds, ionic bonds, etc
37
New cards
what also maintains this shape in 3° structure proteins?
attraction and repulsion of the R-groups also maintain this shape
38
New cards
what types of proteins are many tertiary structure proteins?
* functional proteins like hormones and enzymes
* structural proteins like hair, nails, skin
* structural proteins like hair, nails, skin
39
New cards

\
tertiary structure protein
40
New cards
what is the quaternary structure of a protein?
2 or more secondary structure polypeptides interlink to form one large complex molecule
41
New cards
when a group is added to a protein it is called a….
prosthetic group - is a heme
42
New cards

\
quaternary structure protein
43
New cards
what is denaturation?
process where the protein structure is disrupted
44
New cards
what factors can contribute to denaturation?
1. heat - curling iron to curl hair
2. acids - curdle milk
3. bases - perming or colouring hair
45
New cards
what does carbohydrates give your body?
energy
* it is the most readily available source of energy
* it is the most readily available source of energy
46
New cards
what is the biological purpose of carbohydrates?
used to maintain blood sugar levels at 0.1% (homeostatic level)
47
New cards
what is it called when someone has a blood sugar level of less than 0.1%?
hypoglycemia
48
New cards
what is it called when someone has a blood sugar level of greater than 0.1%?
hyperglycemia aka diabetes
49
New cards
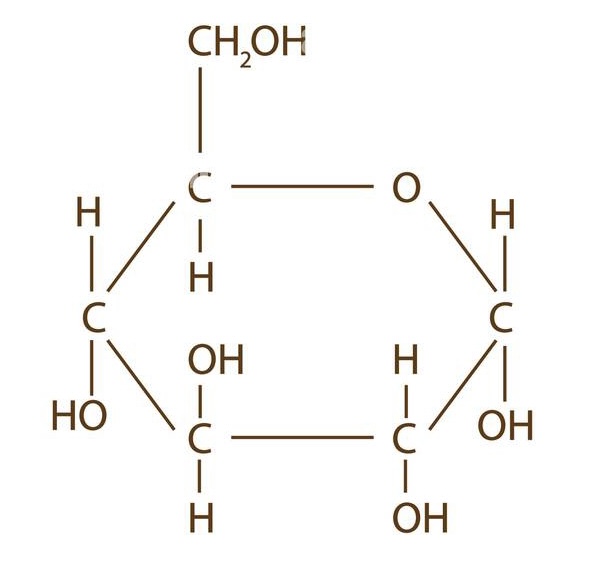
alpha-D-glucose
50
New cards
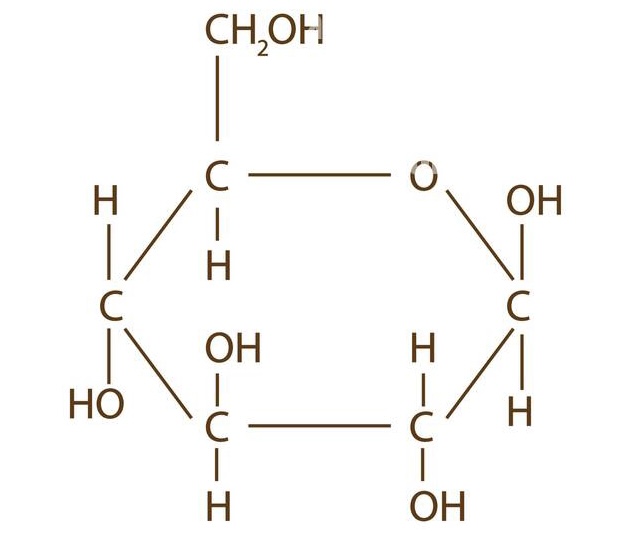
beta-D-glucose
51
New cards
what are the other monosaccharides and its source?
1. galactose (hexose) - milk
2. fructose (hexose) - fruits
3. ribose (pentose) - RNA/ATP
4. deoxyribose (pentose) - DNA
52
New cards
what is the empirical formula for carbohydrates?
CₙH₂ₙOₙ
53
New cards
name the type of bond that links monosaccharides together
glycosidic bond = ester bond
54
New cards
what is produced when tow monosaccharides are synthesized?
disaccharide and water
55
New cards
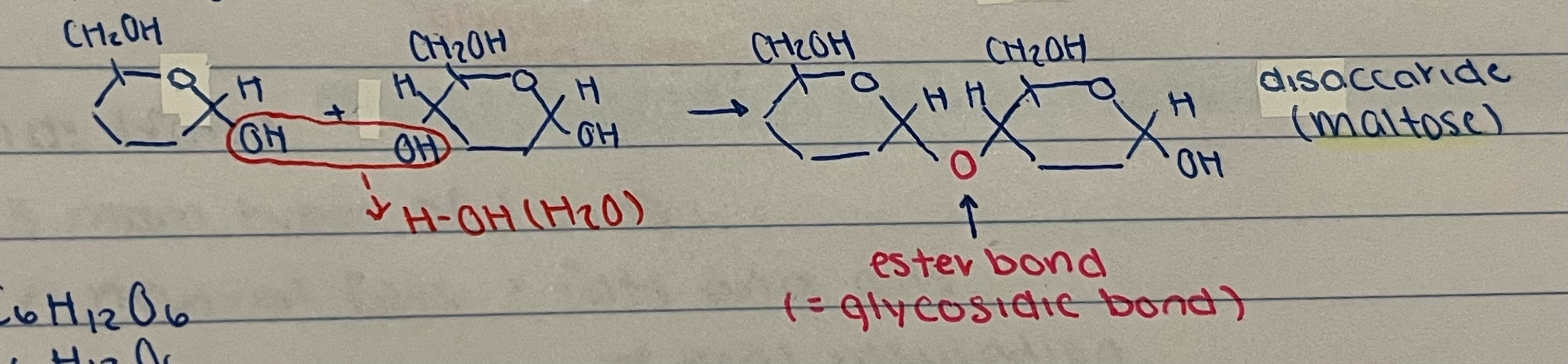
explain the process
two alpha glucose synthesize as they are held together by glycosidic bond forming a disaccharide (maltose) releasing water
56
New cards
what are other disaccharides?
1. sucrose = glucose + fructose
2. lactose = glucose + galactose
57
New cards
what are other carbohydrates (polysaccharides)?
1. starch
2. glycogen
3. cellulose
58
New cards
what is starch?
starch = a complex carbohydrate found in plant products
* storage form of glucose in plant
* branched polysaccharide
* storage form of glucose in plant
* branched polysaccharide
59
New cards
what is glycogen?
glycogen = storage form of glucose in animals
* more compact, easily stored
* stored in the liver and muscles of animals
* highly branched polysaccharide more so than starch
* more compact, easily stored
* stored in the liver and muscles of animals
* highly branched polysaccharide more so than starch
60
New cards
what is cellulose?
cellulose = found in plant cell walls
* very strong in nature
* very fibrous (fibre)
* undigestible by humans because we lack enzymes called cellulase to break it down
* unique structure as glycosidic bond
* very strong in nature
* very fibrous (fibre)
* undigestible by humans because we lack enzymes called cellulase to break it down
* unique structure as glycosidic bond
61
New cards
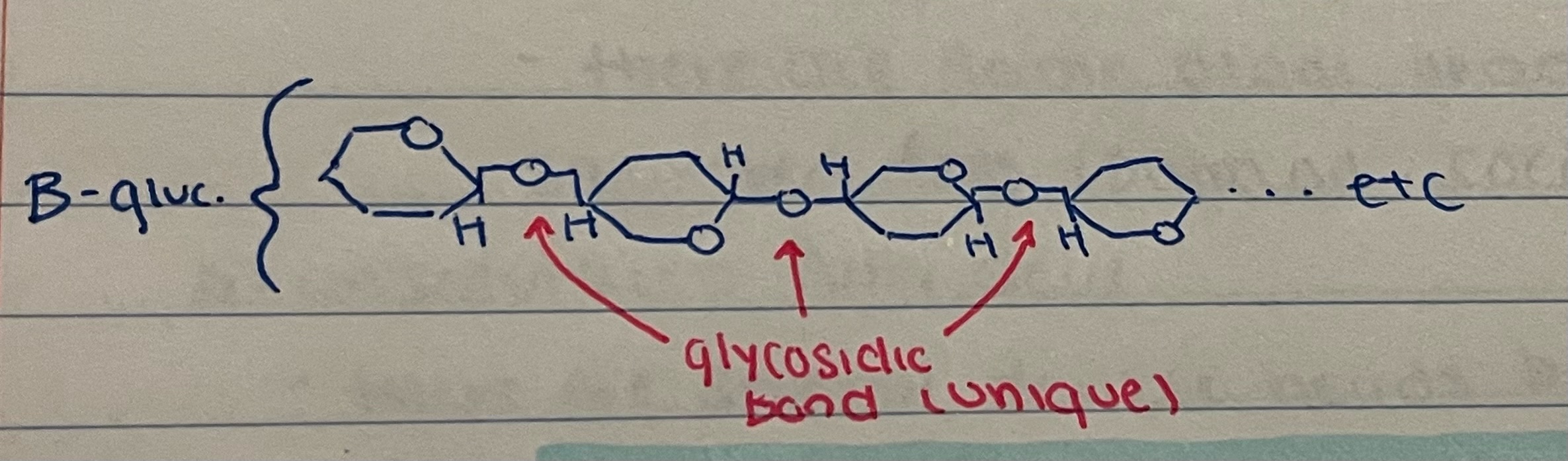
cellulose unique structure as glycosidic bond
62
New cards
what are the three main types of lipids?
1. neutral fats
2. steroids
3. phospholipids
63
New cards
what are neutral fats?
neutral fats = fats and oils
* heat insulation
* long term energy storage
* protective cushioning
* heat insulation
* long term energy storage
* protective cushioning
64
New cards
what are steroids?
steroids = lipids with a backbone of 4 fused carbon rings
* eg. cholesterol, testosterone, estrogen, progesterone
* eg. cholesterol, testosterone, estrogen, progesterone
65
New cards
where are phospholipids found?
phospholipids = found in cell membranes
66
New cards
what are the basic units of neutral fats?
3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol
* aka triglyceride
* aka triglyceride
67
New cards
what is the structure of fatty acids?
long chain of carbon and hydrogen
68
New cards
what do fatty acids and amino aids have in common?
carboxylic acid
69
New cards
how many carbons are there usually per fatty acid?
16 or 18 carbons
70
New cards
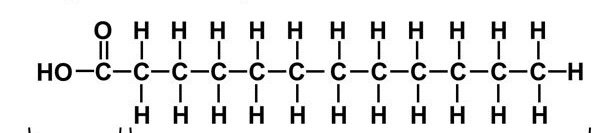
fatty acid
71
New cards
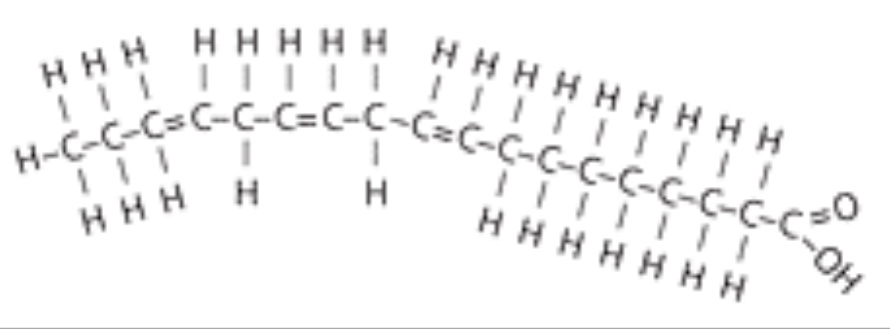
polyunsaturated fatty acid
72
New cards
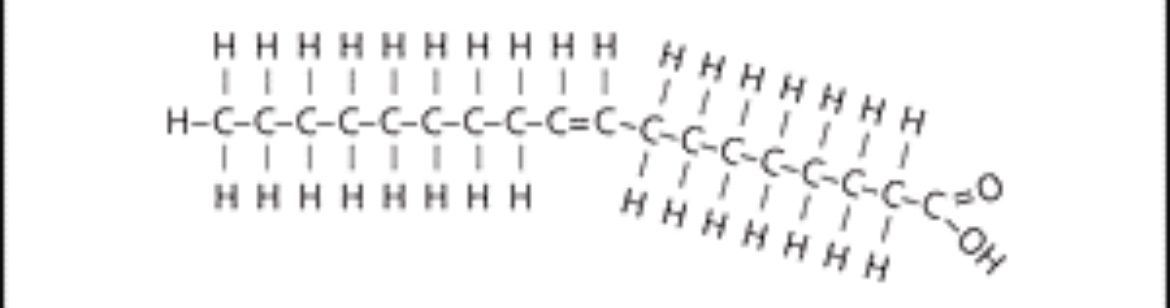
monounsaturated fatty acid
73
New cards
what are the two types of fatty acids?
1. saturated fatty acid
2. unsaturated fatty acid
74
New cards
what are saturated fatty acids? examples?
* animal products
* saturated with lots of hydrogen atoms
* no double bond betw. C and H
* usually solid at room/body temp.
eg. red meats, butter, cheese, palm oil, coconut oil
* saturated with lots of hydrogen atoms
* no double bond betw. C and H
* usually solid at room/body temp.
eg. red meats, butter, cheese, palm oil, coconut oil
75
New cards
what are unsaturated fatty acids? examples?
* there are several double bonds between carbon atoms (not as many carbon atoms)
* found in plant products
* usually liquid at room/body temp
eg. corn oil, canola oil, olive oil, fish (omega-3)
* found in plant products
* usually liquid at room/body temp
eg. corn oil, canola oil, olive oil, fish (omega-3)
76
New cards
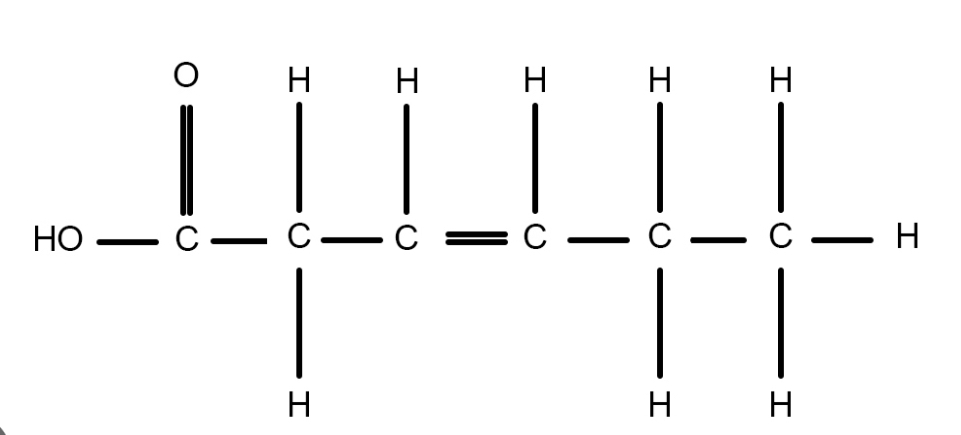
omega-3
77
New cards
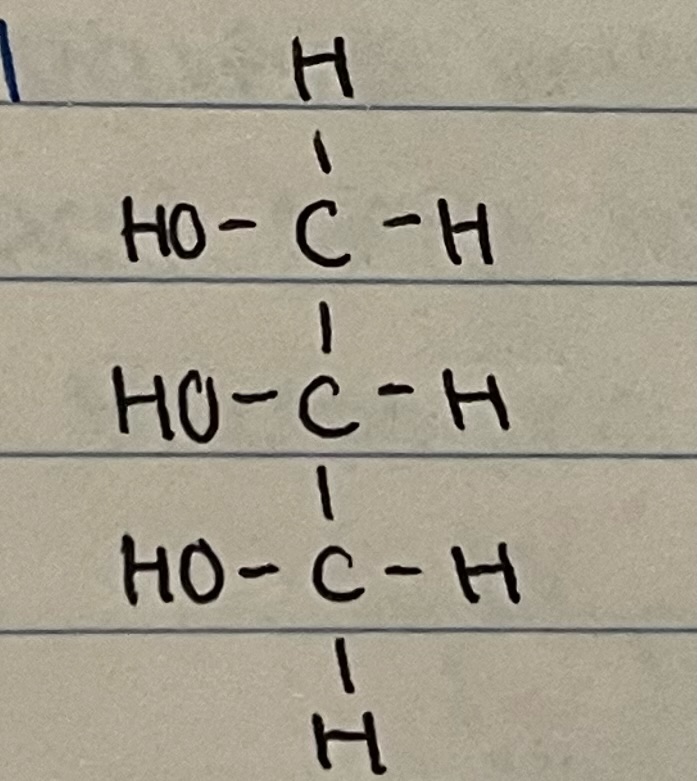
glycerol
78
New cards
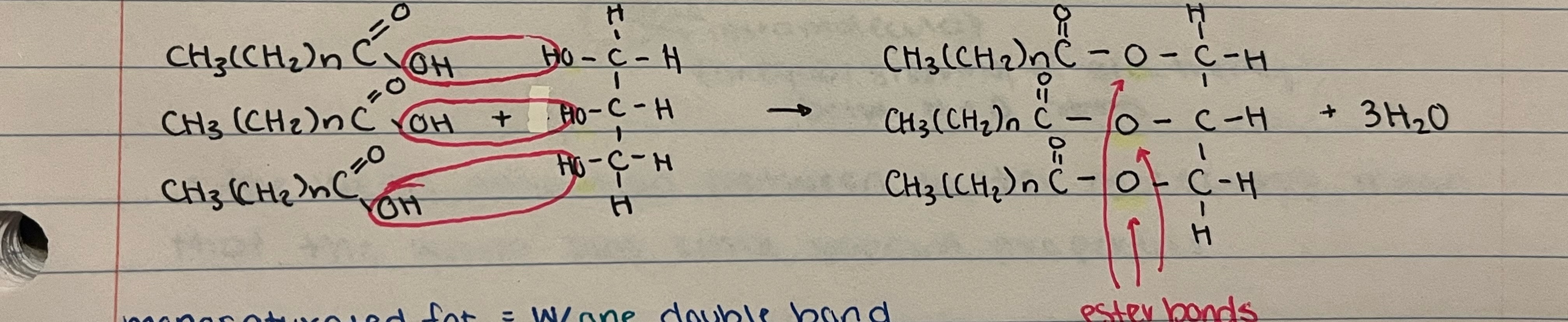
3 fatty acids (saturated) + 1 glycerol → triglyceride (neutral fat) + _H₂O
79
New cards
what bond is used in a triglyceride?
ester bond
80
New cards
what are monounsaturated fat?
with one double bond
81
New cards
what are polyunsaturated fat?
more than one double bond (better)
82
New cards
what makes a phospholipid?
one of the fatty acids is replaced by a phosphate group
83
New cards
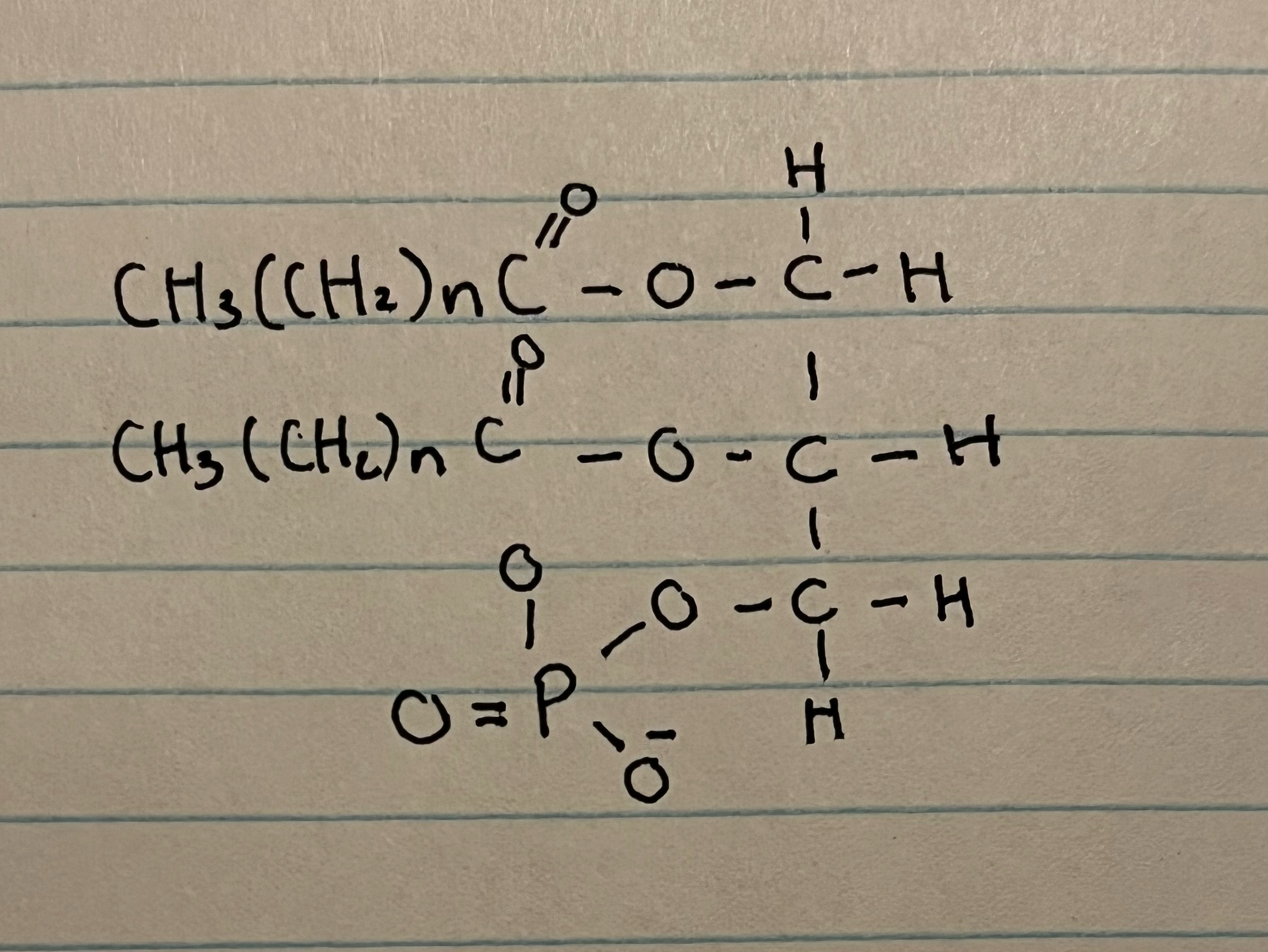
phospholipids
84
New cards
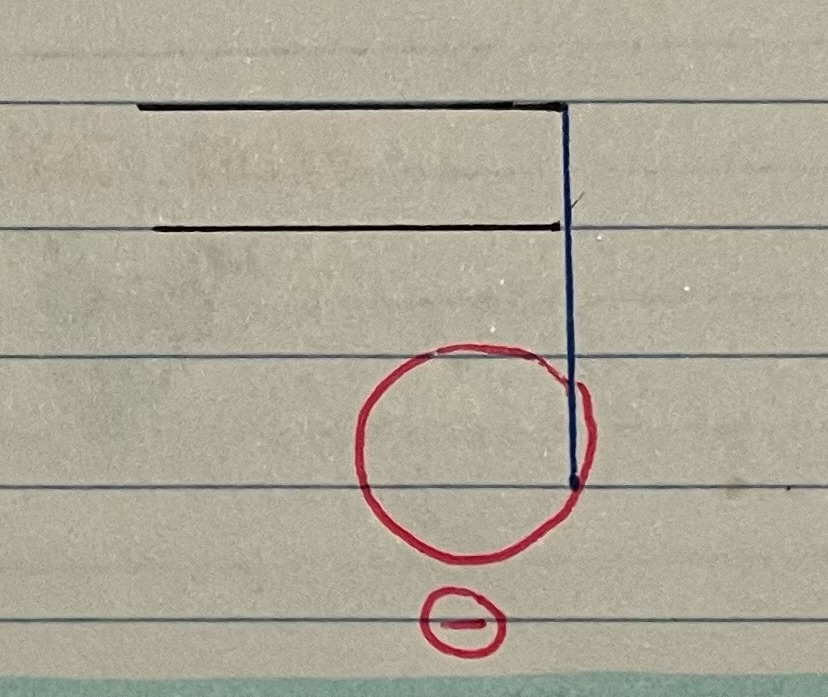
abbreviated phospholipids
85
New cards
where are nucleic acids found?
found in cells (esp. in nucleus) -- genetic material or energy molecules
86
New cards
what are the three types of nucleic acid?
1. DNA - deoxyribonucleic acid (genetic material)
2. RNA - ribonucleic acid (genetic material)
3. ATP - adenosine triphosphate (energy)
87
New cards
is water polar or nonpolar? explain
polar (partial positive and negative charges - unequal sharing of electrons)
* attracts other molecules (essential for transport)
* attracts other molecules (essential for transport)
88
New cards
what type of bonding does water have?
1. hydrogen bonding (intermolecular)
2. covalent bonding (intramolecular)
89
New cards
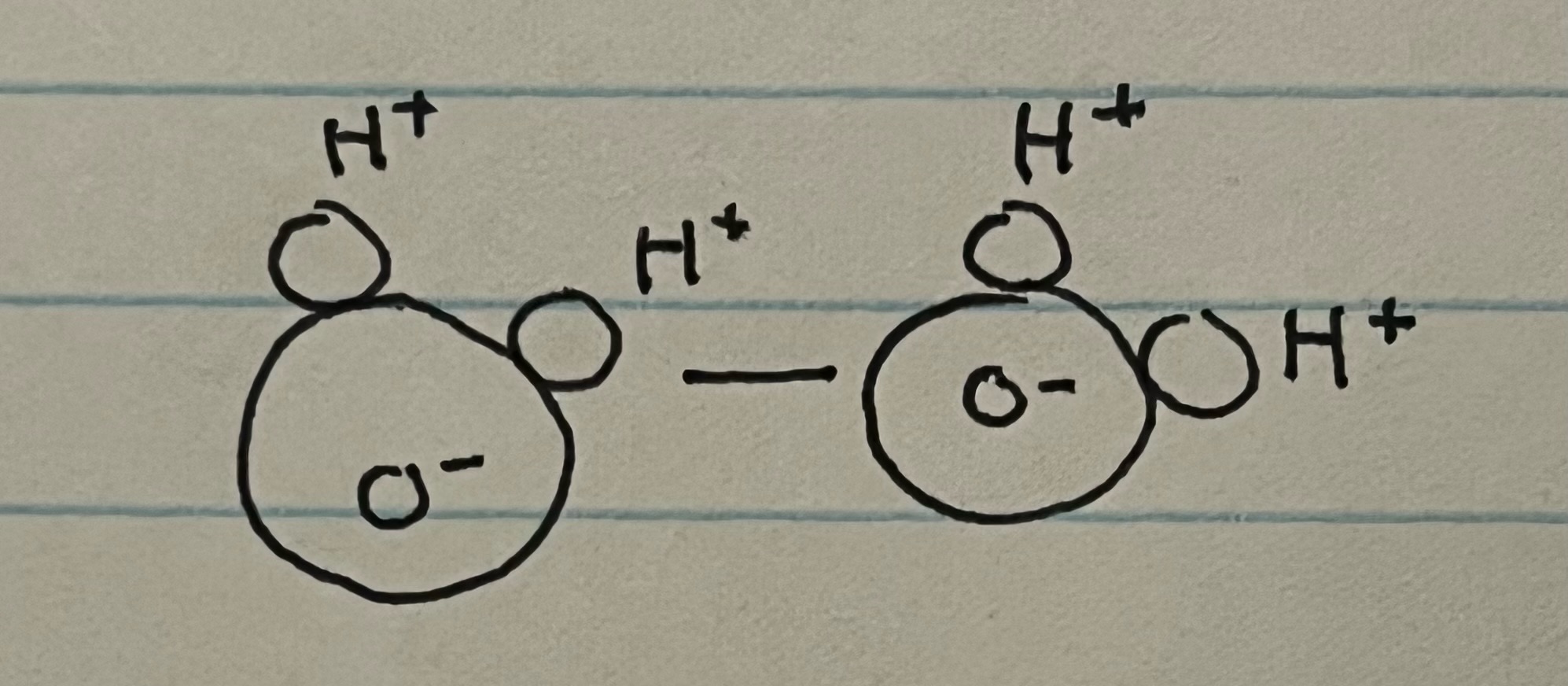
hydrogen bonding (intermolecular)
90
New cards
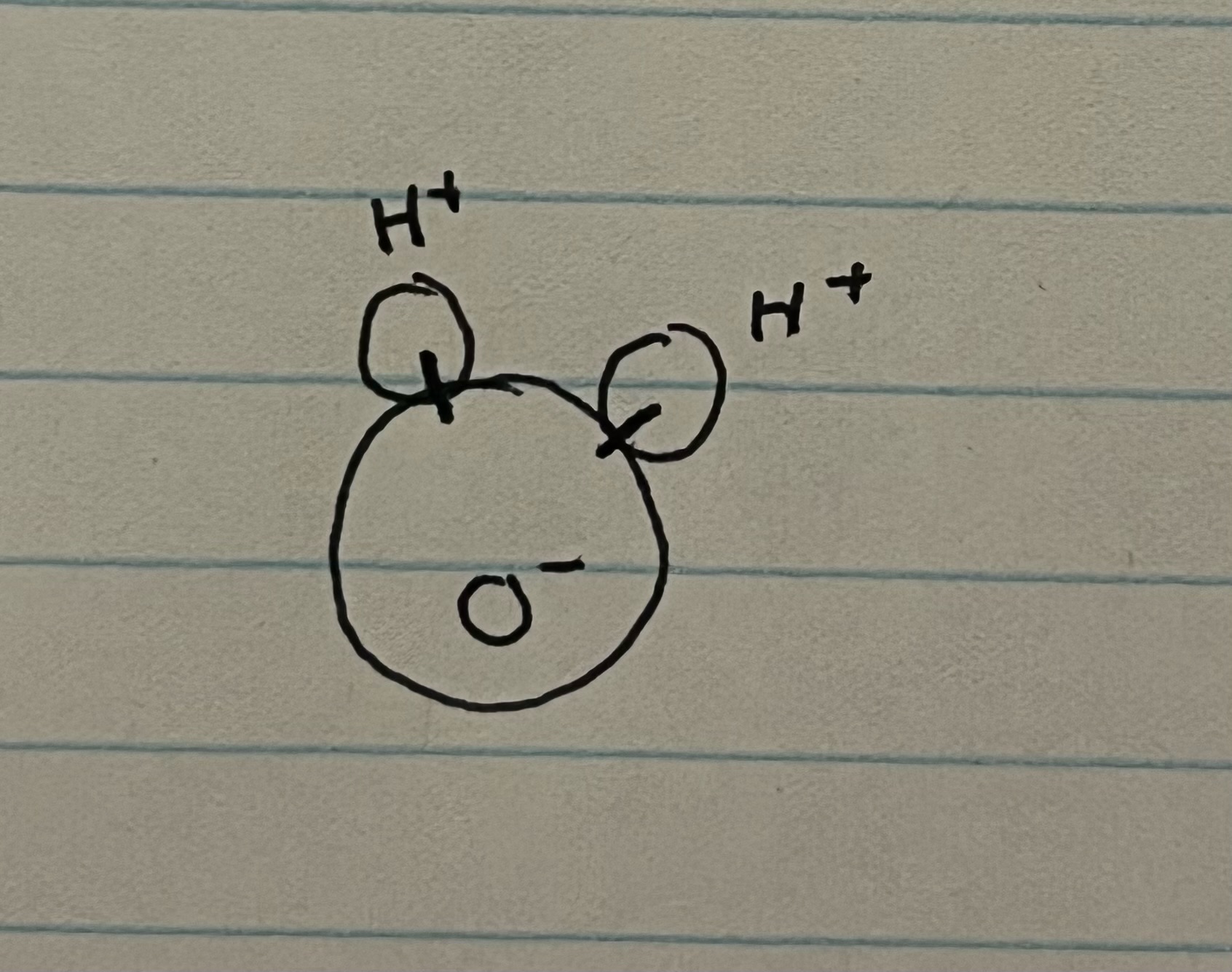
covalent bonding (intramolecular)
* unequal sharing of electrons between H + O atoms
* unequal sharing of electrons between H + O atoms
91
New cards
what does it mean when water has weak attraction between water molecules?
water has some special properties
92
New cards
what are the properties of water?
1. universal solvent
2. temperature regulator
3. lubricant
93
New cards
how is water a universal solvent? examples?
* b/c water is polar, it can dissociate or dissolve ionic compounds into separate ions
* dissolves other polar molecules like sugar and alcohol
* crucial for life to separate ions
eg. potassium (nerve conduction)
sodium, calcium (nerve + muscle conduction)
* dissolves other polar molecules like sugar and alcohol
* crucial for life to separate ions
eg. potassium (nerve conduction)
sodium, calcium (nerve + muscle conduction)
94
New cards
how is water temperature regulator?
* water has high specific heat/heat capacity
* takes a great amount of nrg to heat water 1°C
* therefore, water buffers changes in temp.
* helps keep body temp. @37°C (cooling effect of sweating)
* takes a great amount of nrg to heat water 1°C
* therefore, water buffers changes in temp.
* helps keep body temp. @37°C (cooling effect of sweating)
95
New cards
how is water a lubricant?
reduces friction between 2 surfaces
eg. joints - synovial fluids
eg. joints - synovial fluids
96
New cards
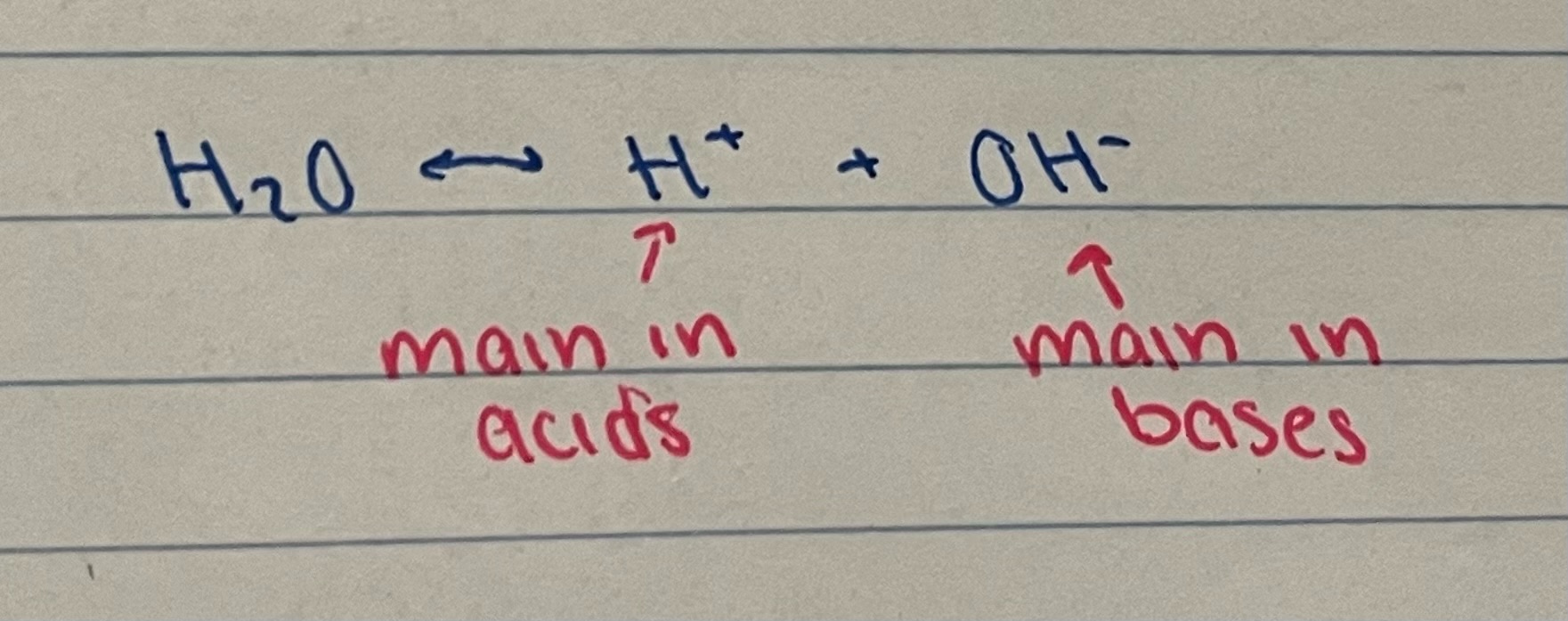
although water is a covalent molecule, it occasionally dissociates into ions
97
New cards
how are the ions in pure water?
H and OH ions are balanced
98
New cards
what is the pH of pure water?
pH 7 (neutral)
99
New cards
what is the pH of blood?
pH 7.4
100
New cards
what is the relation between pH + living organisms?
* biological systems are extremely sensitive to pH
* biochemical molecules (proteins can change structure - denature - with even small changes in pH
* enzymes (proteins) functions best within narrow pH range
* biochemical molecules (proteins can change structure - denature - with even small changes in pH
* enzymes (proteins) functions best within narrow pH range