Basal Cell Carcinoma
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
BCC: What is the pathophysiolgy?
Originates from basal keratinocytes
DNA damage due to UV radiation
Most common skin cancer
BCC: What is the classification?
Nodular→ most common, shiny pink nodule
Sclerosing→ firm, scar-like plaque
Superficial→ scaly red patches (mistaken for eczema or psoriasis)
BCC: What are the symptoms?
Very slow growing
Local destruction can occur
Usually painless and ulcerates
Flesh coloured nodules with central depression, pearly surface, rolled edge, and telangiectasia
They can can necrose and ulcerate in the centre ('rodent ulcer)
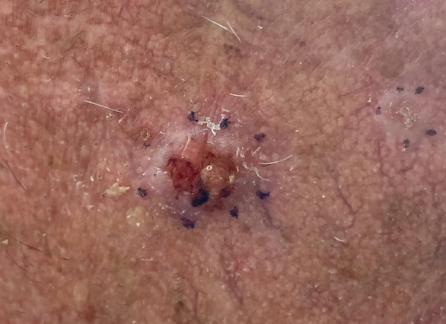
BCC: What are the investigations?
Excision biopsy with 4mm margin
If lesion is 2cm diameter or on ear/lip/face/genitals/hand/feet etc or patient is immunocompromised or had BCC before→ excision biopsy with 6mm margin
BCC: What is the treatment?
Almost always treated surgically with excision using a 4mm margin (6mm for high-risk lesions)
Micrographic surgery for poorly-defined areas
Radiotherapy
Other options: curettage and cautery, topical 5-fluorouracil, topical imiquimod, cryotherapy for low-risk lesions