AP Psych 9.5 - Conformity & Obedience
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Social Norms
the perceived informal, mostly unwritten, rules that define acceptable and appropriate actions within a given group or community, thus guiding human behavior
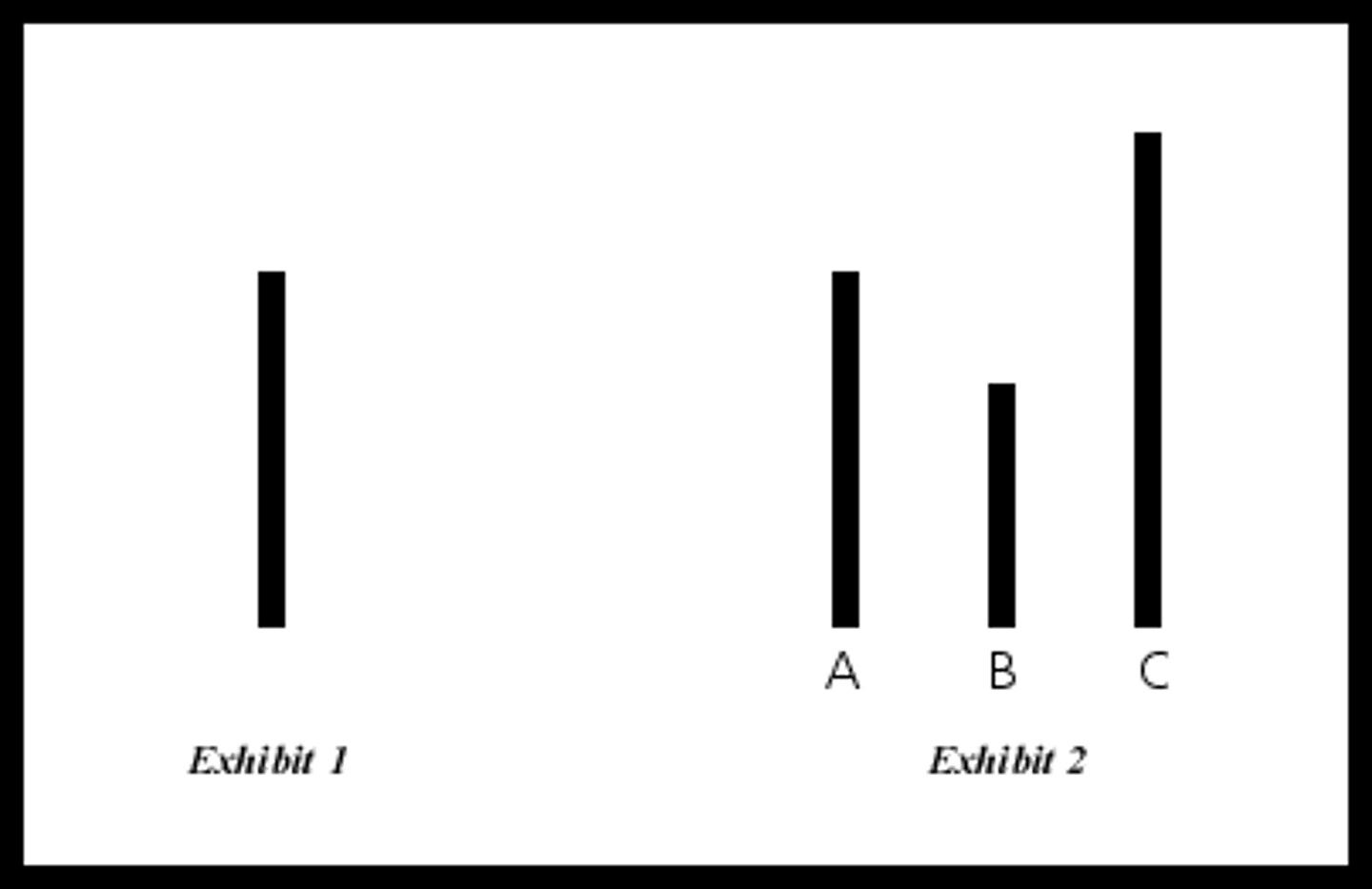
Asch's Conformity Study
asked which line matches original line (left)
each announces choice to group; all but one is an accomplice of the experimenter
accomplices give incorrect answers during multiple trials
37% conformity (on majority of the trials); 75% conformed at least once
Factors That Influence Conformity: Group Size
conformity increases with group size, but only up to a certain point (4-5 people)
Factors That Influence Conformity: Unaniminity
individuals are more likely to conform when everyone in the group agrees, however if just one person disagrees, conformity tends to decrease
Factors That Influence Conformity: Cohesion
the stronger the emotional bonds among group members, the more likely they are to conform to each other
Factors That Influence Conformity: Cultural Differences
conformity is often higher in collectivist cultures (Japan, Hong Kong) where group harmony is valued over individualism
Normative Influence
when people conform to social norms in a group for fear of negative social consequences
(or the desire to fit in/be accepted)
Informational Influence
when you conform to a group in ambiguous situations (because you are unsure what to do); you look to the behaviors of others to see how they behave because you assume they know something you don't
Obedience
form of compliance that occurs when people follow direct commands, usually from someone in a (real or imagined) position of authority
Milgram's Shock Experiment
no Shocks were actually given
participants were told that the study was about impact of punishment on learning
shock generator set up w/descriptions for voltage
script for "learner" to express distress
findings: of 40 participants only 5 quit at 300 volts; only 14 participants defied the experimenter before the full series of shocks was completed; 65% gave all 30 levels of shock
Ethical Concerns of Milgram's Experiment
deception, severe stress, knowledge that capable of harm to innocent victim; Milgram felt it was ethical due to debriefing (which included introduction)
Factors That Influence Obedience: Proximity
authority figure is closer, victim is farther away
Factors That Influence Obedience: Legitimacy
authority figure seems more legitmate, prestigious
Factors That Influence Obedience: Consensus
everyone else is obeying
Factors That Influence Obedience: Collectivism
societies that value the group over the individual