Growth Hormone
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
where are red blood cells produced
bone marrow
what substance is important for RBC production
erythropoietin
parts of long bones
shaft, ends (epiphysis)
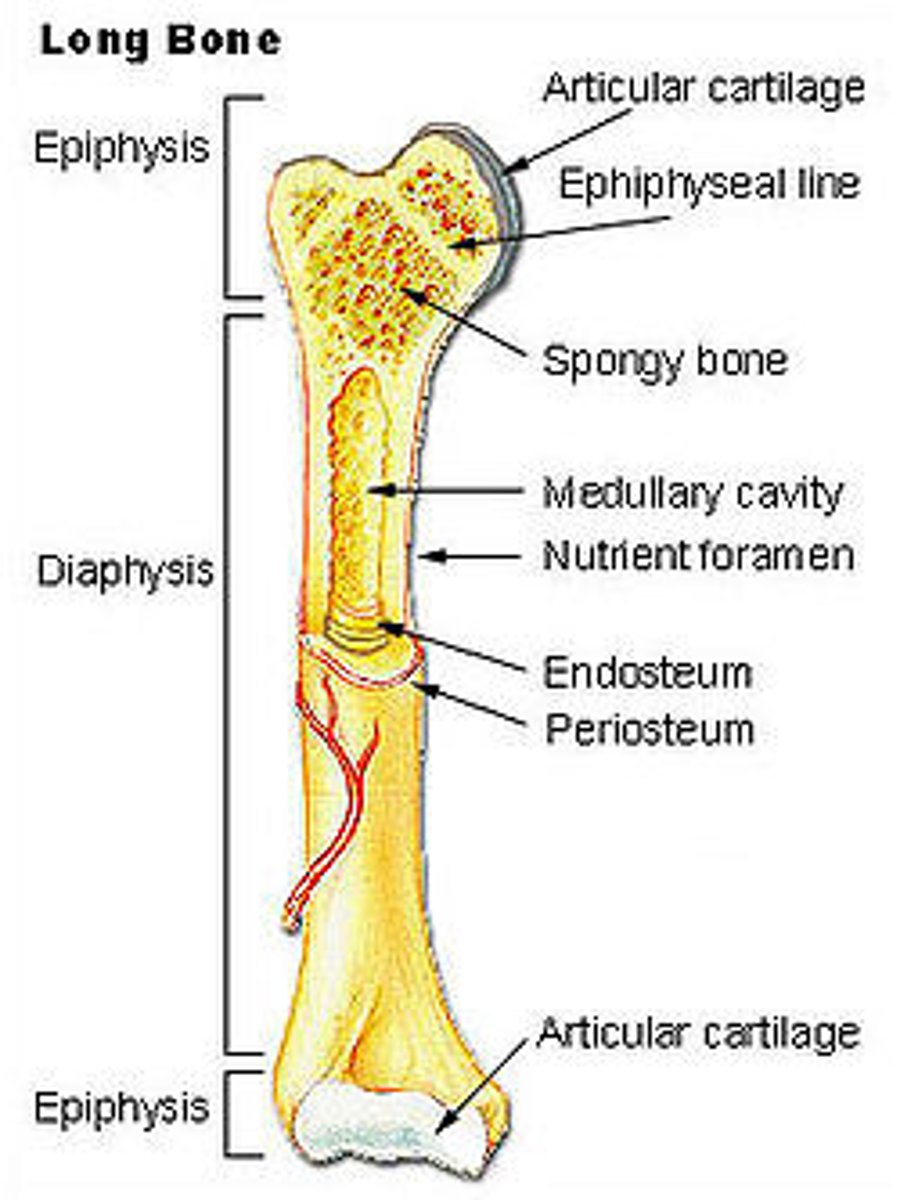
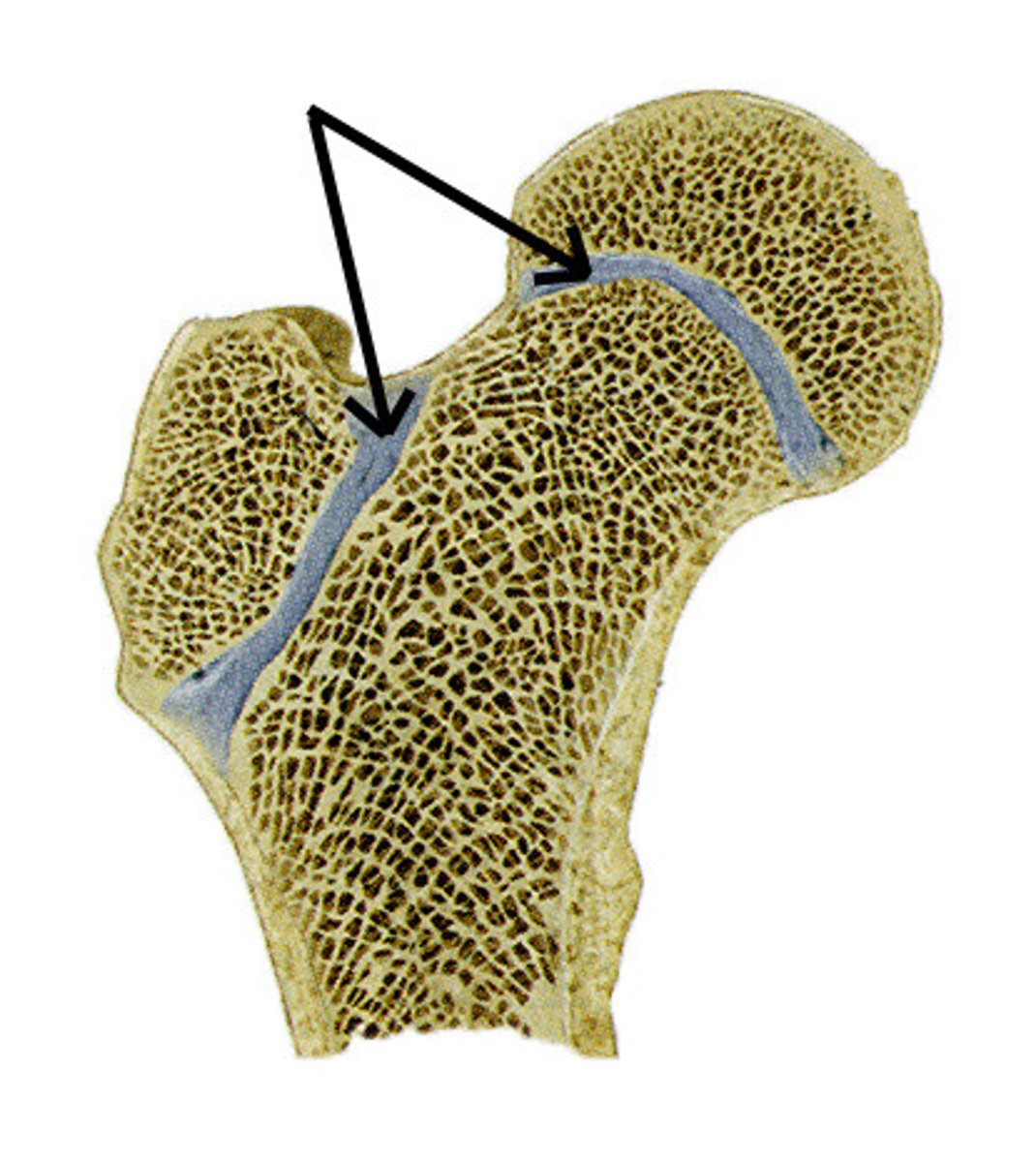
where is the epiphyseal growth plate
between epiphysis and shaft
Hyperplasia
increase in number of cells
hypertrophy
increase in cell size
process of bone growth
1. hyperplasia: chondrocytes undergo cell division (mitosis)
2. hypertrophy: older chondrocytes enlarge and move down toward the shaft
3. osteoblasts in the shaft convert cartilage to bone
processes involved in bone growth are influenced by
local paracrine agents and circulating hormones
chondrocytes
cartilage cells
osteoblasts
convert cartilage to bone
BUILDERS
brain growth
rapid growth in first year of life
eventually stops when the skull fuses (nowhere for brain to expand)
total body height growth
two growth spurts (early in life and then again during puberty)
reproductive organ growth
do not start growing until puberty
environmental factors that influence growth
-adequate nutrition (esp. protein)
-freedom of chronic illness/disease
-freedom from chronic psychological stress (high cortisol = stunted growth)
-sleep
**also hormones
Hormones that influence growth
1. GH
2. IGF
3. insulin
4. thyroid hormone
5. testosterone
6. estrogen/ DHEA
7. cortisol
how does insulin effect growth
stimulates glucose and amino acid uptake into cells, favoring protein synthesis and growth; stimulates IGF-1 secretion
thyroid hormone effect on growth
permissive--> stimulates GH synthesis and directly affects bone by stimulating growth factors, chondrocytes, and blood vessels
important for CNS development
testosterone effect on growth
stimulates GH and IGF-1 secretion, esp. during puberty
prolonged exposure can cause closure of epiphyseal plates, stimulates protein synthesis
estrogen/DHEA effect on growth
stimulates GH and IGF-1 secretion esp. in puberty
prolonged exposure usually causes closure of epiphyseal plate
Cortisol effect on growth
exerts anti-growth effects such as protein catabolism, decalcification of bone, and it inhibits IGF-1 and GH
high GH + low cortisol =
growth
High GH + High Cortisol =
fuel mobilization, no growth
pathways controlling GH and IGF-1
hypothalamus--> GHRH --> AP --> increase GH --> liver and other cells--> increase IGF-1
hypothalamus --> SST --> AP --> decrease GH --> liver and other cells --> decrease IGF-1
GHRH
growth hormone regulating hormone
positive tropic effect on GH
released by hypothalamus
SST
somatostatin
negative tropic effect on GH
released by hypothalamus
IGF-1 negative feedback on SST and GHRH
SST: negative feedback tells SST to increase secretion to decrease GH and IGF-1
GHRH: negative feedback tells GHRH to decrease secretion to decrease GH and IGF-1
long loop negative feedback IGF-1
IGF-1 singles for hypothalamus and anterior pituitary to reduce secretions
short loop negative feedback GH
GH tells SST to increase secretion and GHRH to decrease secretion
Functions of GH
promotes postnatal growth
metabolic effects
functions of GH: promote postnatal growth
-stimulate cell differentiation and division (bone and other tissue)
-stimulate protein synthesis (muscle)
-stimulate secretion of IGF-1
functions of GH: metabolic effects
-mobilize glucose for energy (prevent storage)
-mobilize fatty acids for energy (fat breakdown)
Functions of IGF-1
promote postnatal growth
-stimulates cell division (hyperplasia)
-stimulates protein synthesis (hypertrophy)
end results of GH and IGF-1
enhances body protein
burns fat
prevents glucose storage
promotes bone and organ growth
Hormone abnormalities: GH and IGF-1
-genetic mutations
-destructive tumors
-hypersecreting tumors
-receptor insensitivity
-mimic antibodies
growth abnormalities may lead to
short stature
most common cause of excess growth hormone
hyper-secreting tumor of the anterior pituitary
acromegaly
too much GH after epiphyseal plates close
thickening bones in hands, feet, and face
other organs also enlarge (heart)
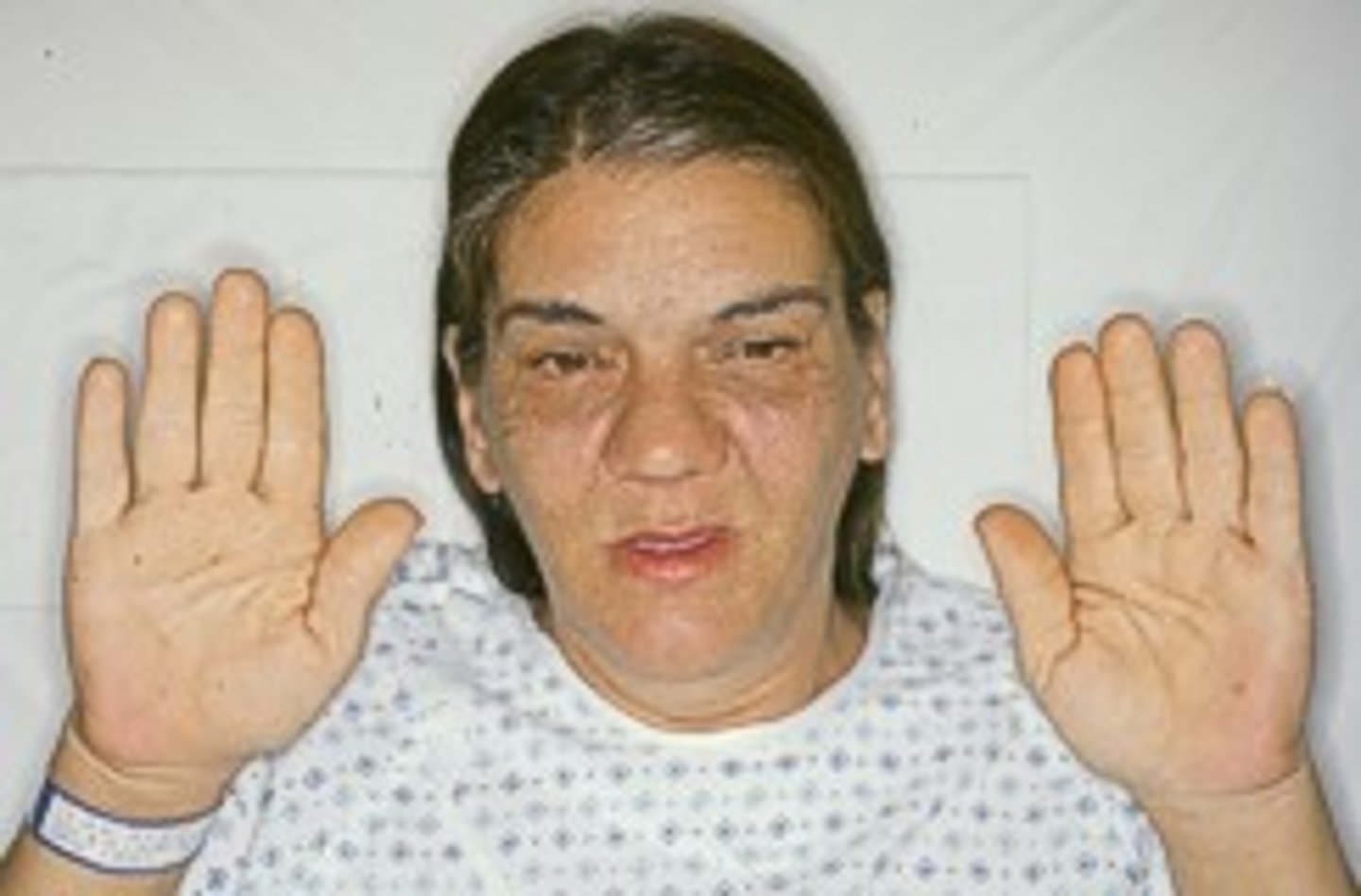
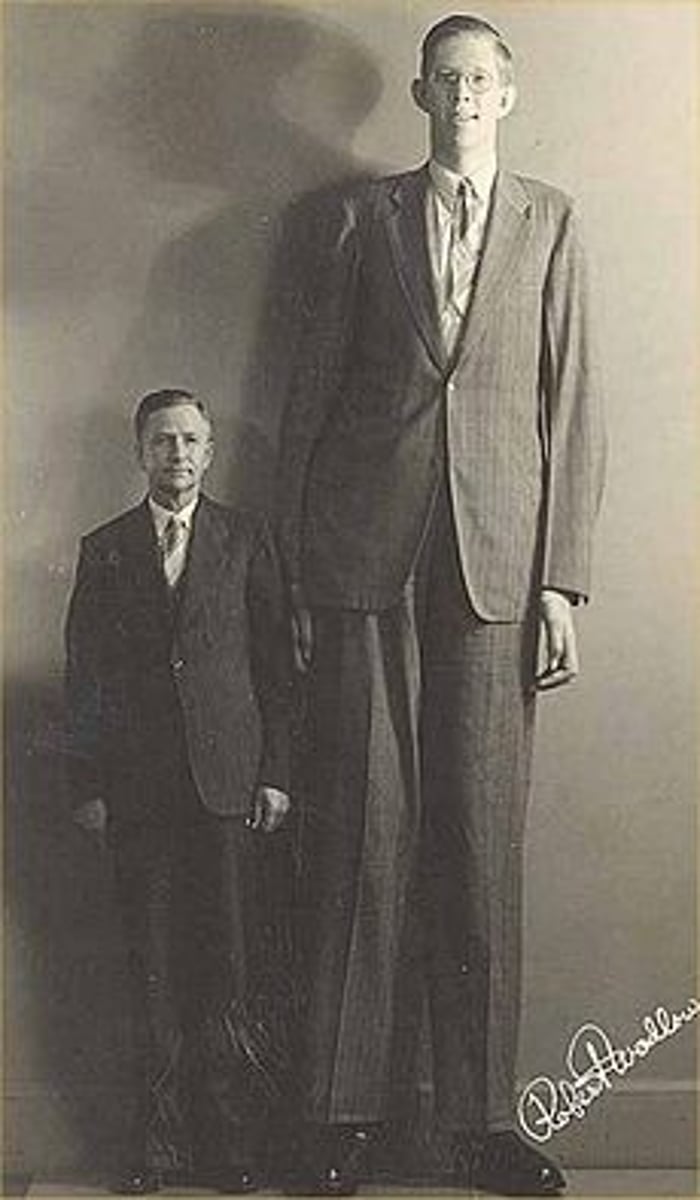
Gigantism
too much GH before growth plate closes
