Speech Path & Hearing Imp Child Final
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
Normal hearing range
-10-15
Slight hearing loss range
16-25
mild hearing loss range
26-40
moderate hearing loss range
41-55
moderately severe hearing loss range
56-70
severe hearing loss range
71-90
profound hearing loss range
91 and up
What is the normal hearing range for children?
-10-15 dB HL
What is the normal hearing range for adults?
-10-20 dB HL
Borderline normal hearing can be up to ____
25 dB HL
What is the soft conversational level?
35-45 dB HL
What is the normal conversational level?
55-65 dB HL
What is the loud conversational level?
75 dB HL and greater
minimal/slight degree of hearing loss 16 dB HL to 25 dB HL and its impact on speech
not hearing endings of words
mild degree of hearing loss 26 dB HL to 40 dB HL and its impact on speech
can miss 25% to 40% of a speech signal
difficulty in reading skills
moderate degree of hearing loss 41 dB HL to 55 dB HL and its impact on speech
can miss up to 80% of average-level conversational speech
flat speech
moderately severe degree of hearing loss 56 dB HL to 70 dB HL and its impact on speech
miss 100% of average conversational speech
severe/profound degree of hearing loss and its impact on speech
can miss 100% of ALL speech
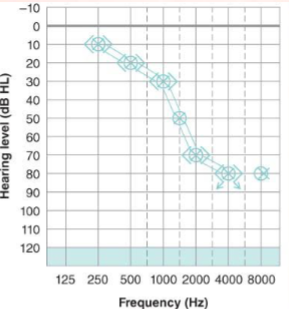
What is a high-frequency sensorineural hearing loss?
greater loss in higher frequencies than in lower
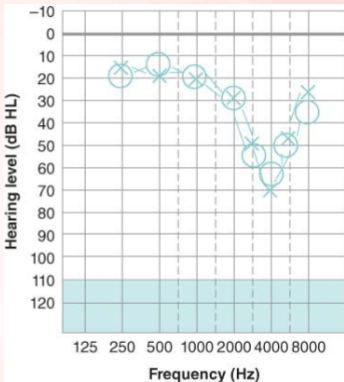
What is a noise-notch hearing loss?
high-frequency hearing loss that is classically associated with an individual who has been exposed to high-intensity noise
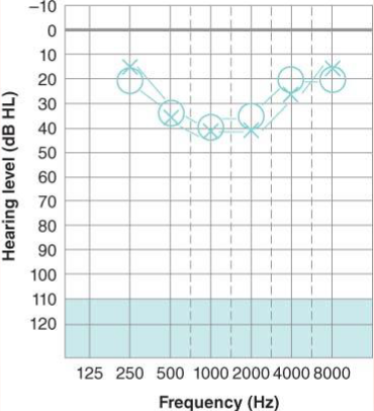
What is a “cookie-bite” pattern of hearing loss?
a midfrequency sensorineural loss
HL in 1000-3000 Hz range
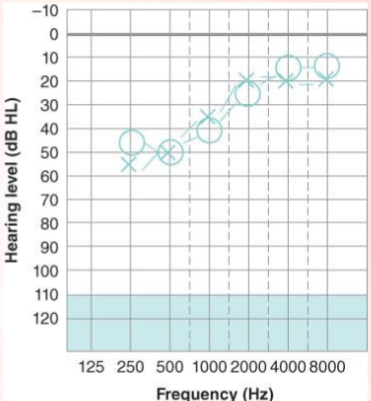
What is a reverse curve pattern of hearing loss?
a hearing loss in lower frequencies
What is a progressive hearing loss?
loss of hearing over a period of time
What is a conductive hearing loss?
a hearing loss where air conduction is abnormal and bone conduction is normal
presence of an air-bone gap
result of damage to outer/middle ear
What is a sensorineural hearing loss?
hearing loss where both air conduction and bone conduction are abnormal
no air-bone gap
damage to inner ear/auditory nerve
What is a common characteristic of a sensorineural hearing loss?
ability to hear in lower frequencies better than higher
What is a mixed hearing loss?
a combination of conductive and sensorineural components
there is an air-bone gap, but both are abnormal
What is speech audiometry?
measures and qualifies a person’s ability to recognize and understand the content of a speech signal
speech reception threshold (SRT)
repeating of specific words with accuracy
Digital ear level devices do things like
noise suppression
frequency shifting
feedback control
What characterizes the behind-the-ear (BTE) style hearing aid?
it utilizes an earmold coupled to the body of the hearing aid or receiver in the canal
usually for profound hearing losses
processing of acoustic sound occurs in the body of the hearing aid and sits behind the ear
behind the ear style hearing aids are most appropriate for
children
those with neuropathy
long time users of BTE
What is in an in the ear (ITE) and completely in the canal (CIC) style hearing aid?
programming nestled inside the ear canal portion of the hearing aid
usually for mild to moderate degrees of hearing loss due to size constraints
processing sound occurs in the receiver in the earpiece
In the ear and completely in the canal style hearing aids are most appropriate for
adults
The placing of earmolds is important because it
reduces feedback
optimizes sound transduction
provides proper retention
completely in the canal hearing aid

picture in the canal style hearing aid
In the ear style hearing aid
full shell ITE style hearing aid

Half shell ITE style hearing aid

In the canal style hearing aid

What are some hearing aid accessories?
direct audio input cables
FM boot
connectivity device
these are important to connect devices at home or school
What are bone-conduction hearing aids?
headband style
bone anchored
bone conduction hearing devices are used for
single sided deafness
conductive hearing losses
Cochlear implants are used for patients who do not benefit from traditional forms of hearing aids.
true
FM systems are an assistive technology
true
FM systems
can be for classroom use
allows all people to benefit from a boost in signal or directly to students through microphones
What are a few assistive technologies
closed captions
TV amplification systems
induction loops in large meeting spaces
theatres conference halls
Hearing assistive technology includes a variety of devices that help an individual with or without hearing loss communicate more effectively in adverse listening situations
true
Assistive listening devices are prescribed by
audiologist
what is the purpose of assistive listening devices?
to improve signal to noise ratio
Assistive listening devices
a unit with a limited amount of volume that is used for individuals with auditory attention difficulties within the classroom
Auditory training device
a unit designed to train an impaired auditory system
FM systems are used to
transmit a speaker’s voice or a specific sound DIRECTLY to an individual
DM system works similarly to an FM system but
the audio signals are digitized and packaged in very short bursts of code and broadcast several times
frequency transmission for FM device is regulated by the
Federal Communication Commission
FM/DM devices are beneficial when
educational settings are noisy
extraneous talking
AC and heat running
student/teacher movement
FM/DM systems aid in diminishing the effects of background noise
true
FM/DM systems couple directly to the ear via earphones, induction loop, or earbuds or through a HA or CI
true
A “tabletop” listening device provides amplification
in close proximity to the listener
can easily move with student
What is a personal ear-level assistive listening device?
looks similar to a hearing aid
may be used for someone with a slight HL that doesn’t use aids
What is an induction loop device?
it loops around the neck when a person has telecoil circuitry options in their hearing aids
Portable sound field devices (speakers) are designed to increase signal-to-noise ratio throughout a single room.
true
Portable sound field devices benefit all listeners as they distribute sound throughout the room.
true
What is remote hearing technology?
hearing amplification devices that are often bluetooth compatible and allow the user to connect to other bluetooth devices
Closed captioning and telecommunication devices for the deaf are supportive technologies.
true
In a school system, what is the role of an SLP for a child with hearing impairments?
check devices
troubleshoot issues
work with manufacturer
In school or private therapy, what is the role of an SLP for a child with hearing impairments?
to work towards age-appropriate self-advocacy in the classroom
devices working
ensuring usage of devices
build skills to communicate
The audiogram
provides a scaled graphic description of a person’s hearing perceptibility
What are the components of an audiogram?
Frequency (pitch)
measure in Hz
Intensity (loudness)
measured in HL
Air conduction tests the entire system such as the outer, middle, and inner ear.
true
What transducers are used to test air conduction?
headphones
insert earphones
soundfield testing
Bonce conduction only tests the inner and neural parts of the system.
true
What type of transducer is used to test bone conduction?
an oscillator placed on mastoid process
When testing masked bone conduction what transducers are used?
oscillator, insert earphones, or headphones
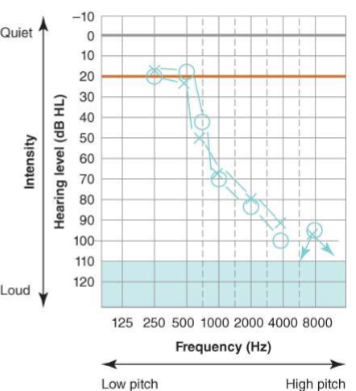
What is a ski slope type of hearing loss?
characterized by a rapid decrease in threshold response after 250-500 HZ
What is speech detection/awareness threshold (SDT)?
when a patient indicates the detection of a words at barely audible level
What is word discrimination testing?
this tests the understandability above SDT
an assessment of clarification
Tympanometry is not a hearing test, cannot tell us whether a person has normal or impaired hearing.
true
What does tympanometry test?
how the conductive mechanism (middle ear) is physically functioning
ear canal volume/ TM mobility
What is otoacoustic emissions used for?
an indirect measure of hearing
elicits brief stimulation to the cochlea
cannot rule out mild HL
What is auditory brainstem response?
where there is an auditory response to an electronic stimulation
most commonly used at newborn screening
pure tone audiometry
determines the loudness threshold in dB HL at which a person begins to hear sound
Otoscopy includes procedures like
choosing the speculum
positioning otoscope
positioning pinna
What does an otoscopy monitor?
the external health of the ear
Is it within the practice of an audiologist or SLP to diagnose otitis media?
no
The middle ear test battery
evaluates the physical properties of the ear
rules out inner/outer ear pathologies that may contribute to hearing loss
Acoustic reflexes
involuntary muscle contraction in the middle ear cavity
Speech audiometry tests the person’s ability to detect and understand speech signals.
true
After air conduction testing, if a loss is present, what should happen?
further testing must be completed to determine conductive and sensorineural pathology
air conduction cannot localize site of damage
Behavioral observation audiometry
6-7 months
responses are reflexive like blinks, startles
Visual reinforcement audiometry
6-7 months
based on child’s natural instinct to turn for an interesting sound when it is heard
child gets rewarded
conditioned play audiometry
2.5 - 5 years of age
make audiometry into a game
What is the purpose of audiology screening?
to identify those who need further testing
After a visual inspection/otoscopy, you should make note of any obvious signs of abnormality or concern.
true
you do not reach conclusions you just refer
After pure tone screening, when results are received you can
retest and refer
After an otoacoustic screening what recommendations should be made?
immediate referral for any failures or any concerns
Otoacoustic emissions (indirect form of hearing sensitivity)
a sound is sent into the ear and in response, the ear produces a sound and sends it back
evoked responses from cochlea
The presence of otoacoustic emissions does not mean normal hearing sensitivity.
true
ABR should never be used in isolation to identify hearing loss.
true