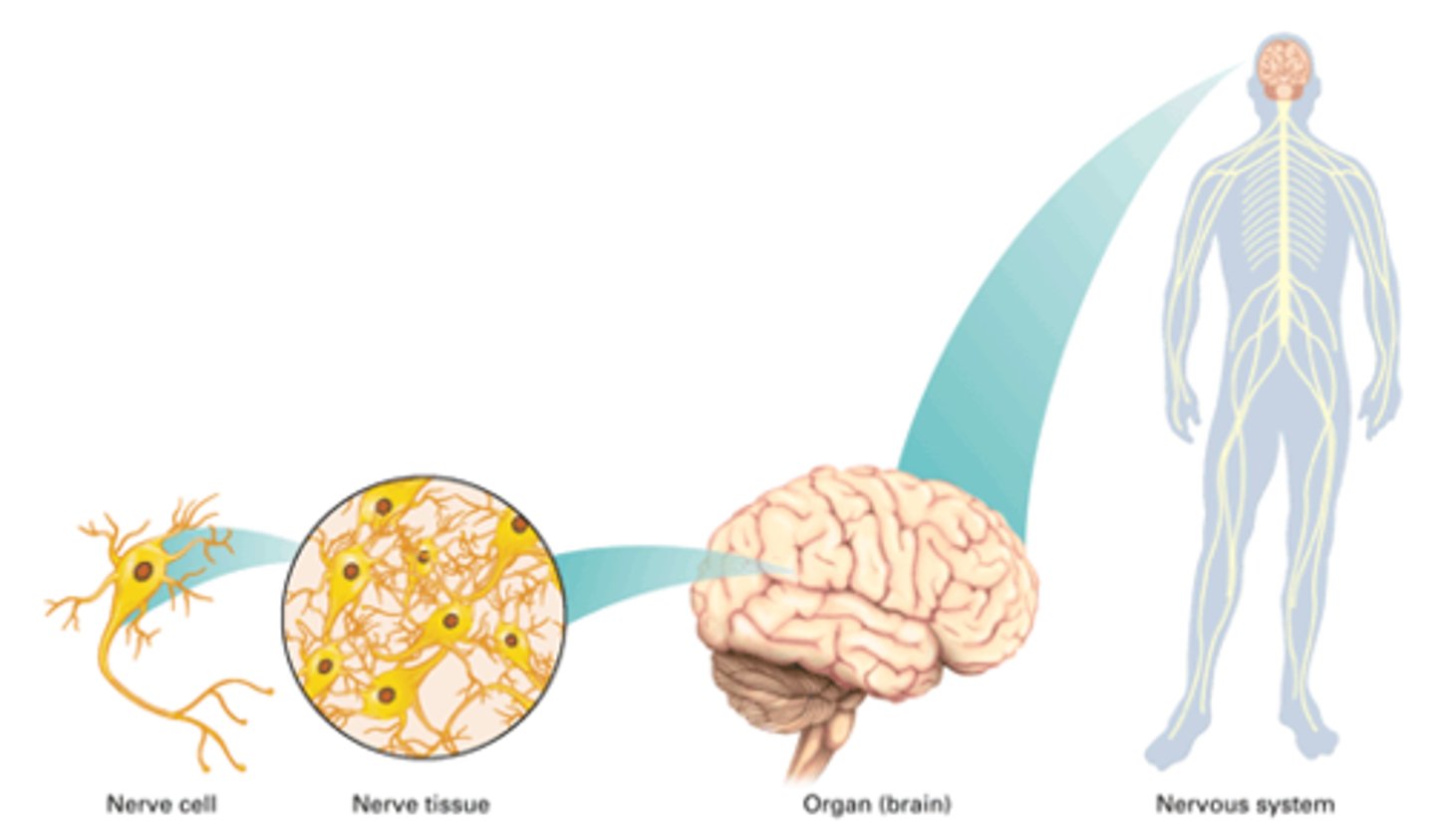
Cell Theory
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Zacharias Janssen
Wanted to help people who couldn't see well. Created the first lens and made a simple microscope.

Robert Hooke
Spent a lot of time studying and drawing specimens under his handmade microscopes. Published a book in 1665 with his drawings. His drawing of "cork cells" is famous. He gave us the word "cell" for use with living things. He discovered cells.
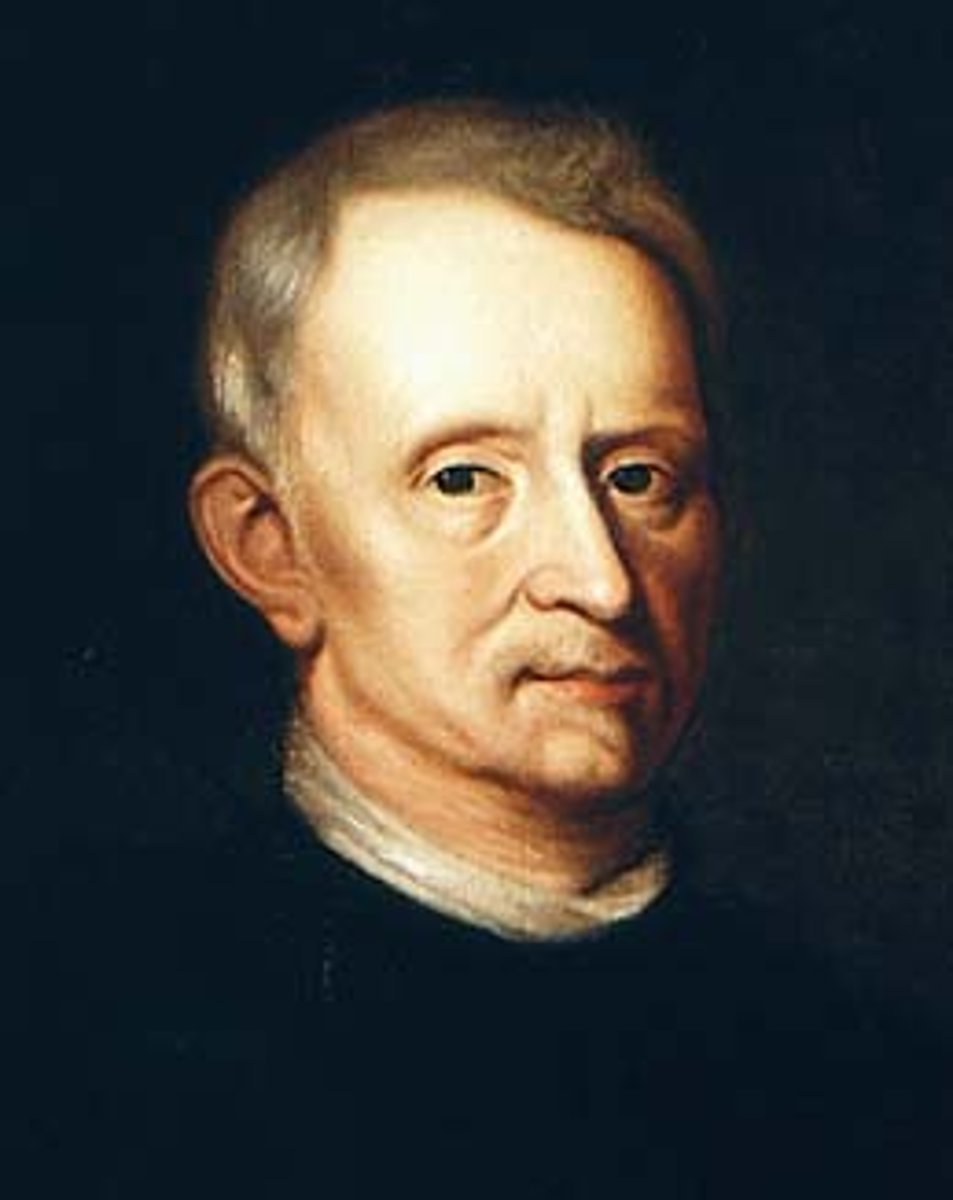

Anton von Leeuwenhoek
Improved the microscope with a secret technique. Made hundreds of microscopes. He saw the first living microorganisms. He is called the "Father of Microscopy".
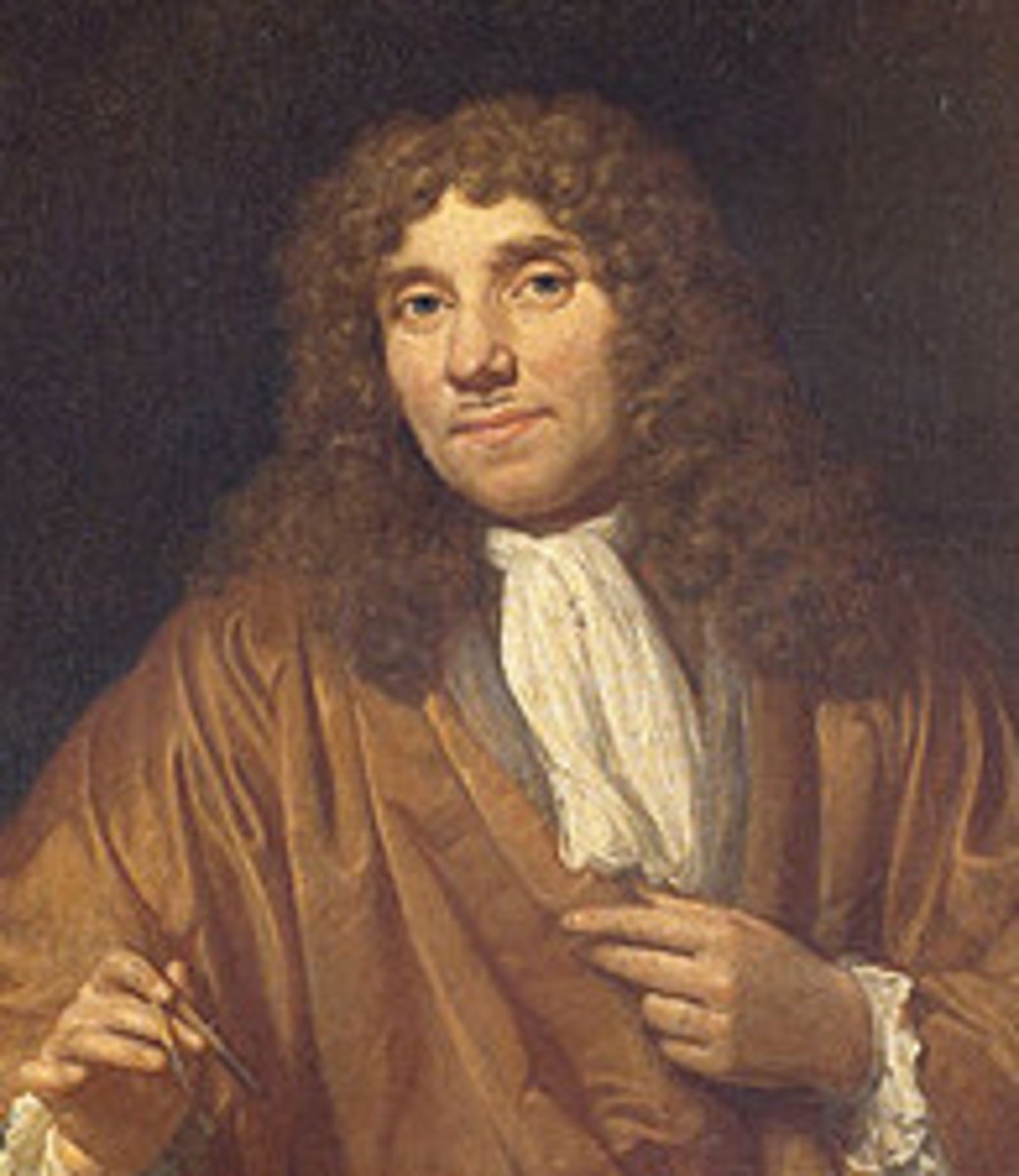

Matthias Schleiden
He studied plants. He looked at lots of plants under the microscope; their leaves, flowers, roots and stems. He decided that "All plants are made of cells".
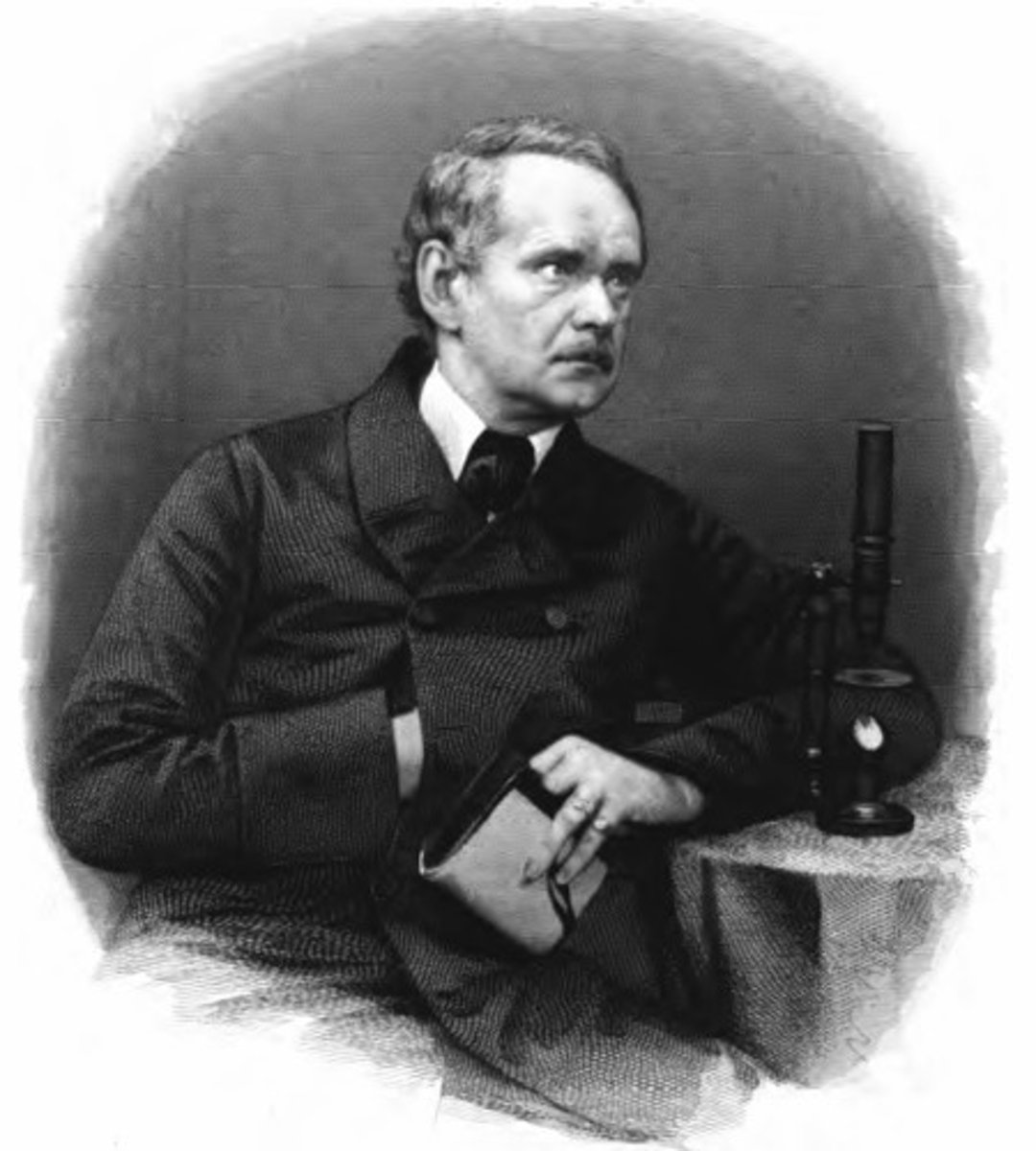

Theodor Schwann
He studied animals. He looked at animal tissues under the microscope and saw cells. He came to the conclusion, "All animals are made of cells".
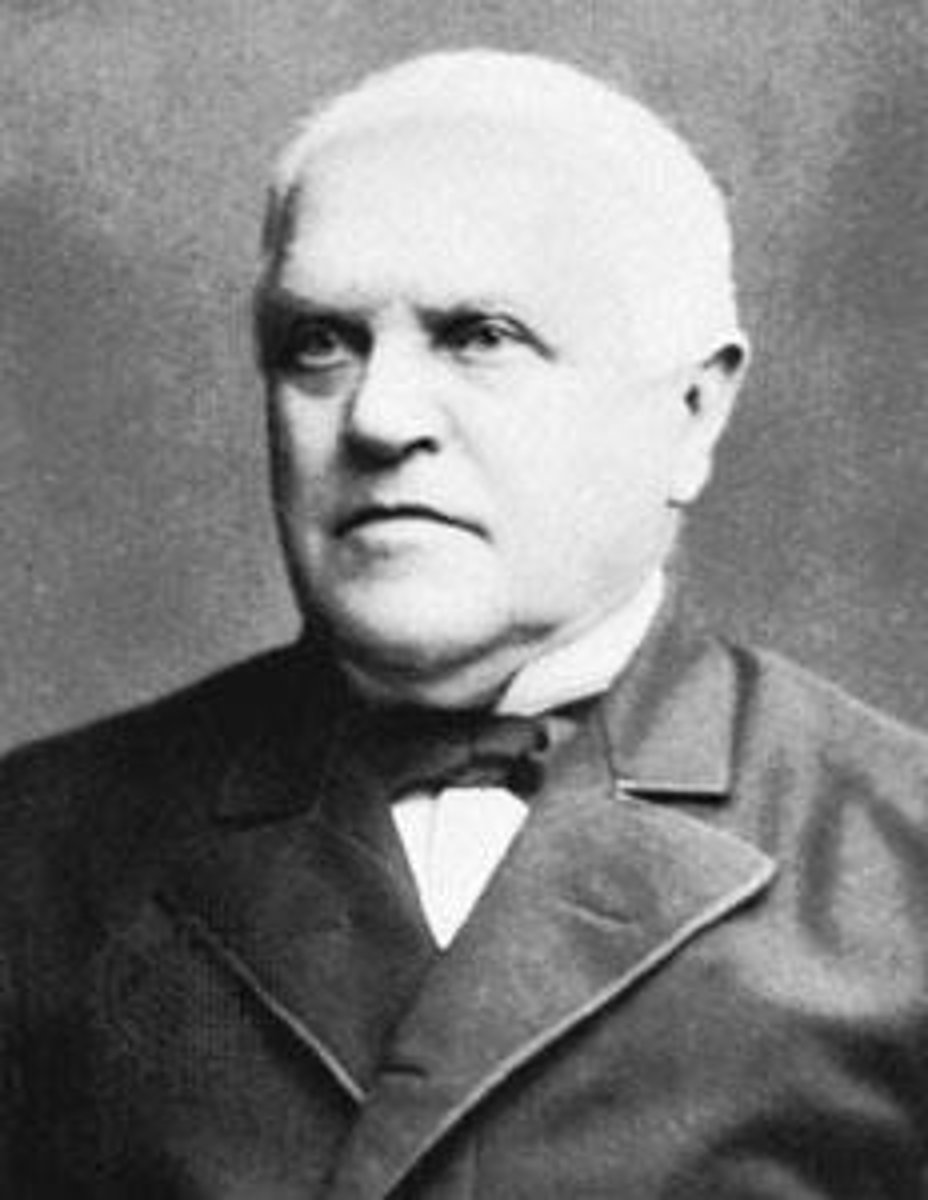

Rudolph Virchow
He was a doctor. He studied human illness and looked at diseased body tissue. He observed living cells dividing into two parts. He came to the conclusion that living cells reproduced and made new living cells.

Cell Theory
A basic theory of biology that describes one of the major characteristics of life. All living things have cells. This theory replaced the theory of Spontaneous Generation.
Microscope
A tool used by biologists to study microscopic (TINY) details of living things.

Lens
A special piece of curved glass that makes things look larger.

All living things are made of cells.
The first part of The Cell Theory based on the work of Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann.
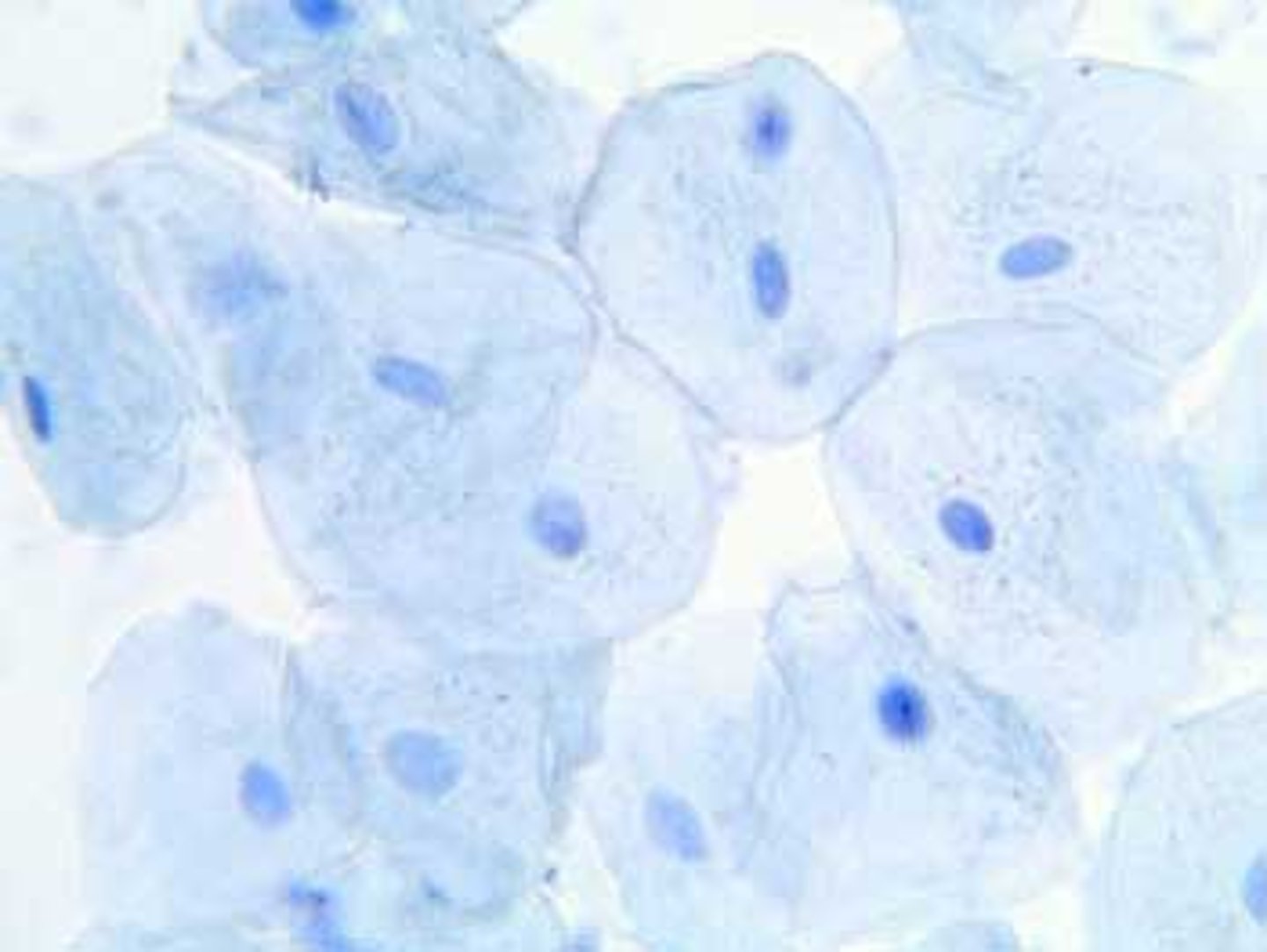
Cells are the basic units of living things.
The second statement of The Cell Theory. It is also based on the work of Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann.

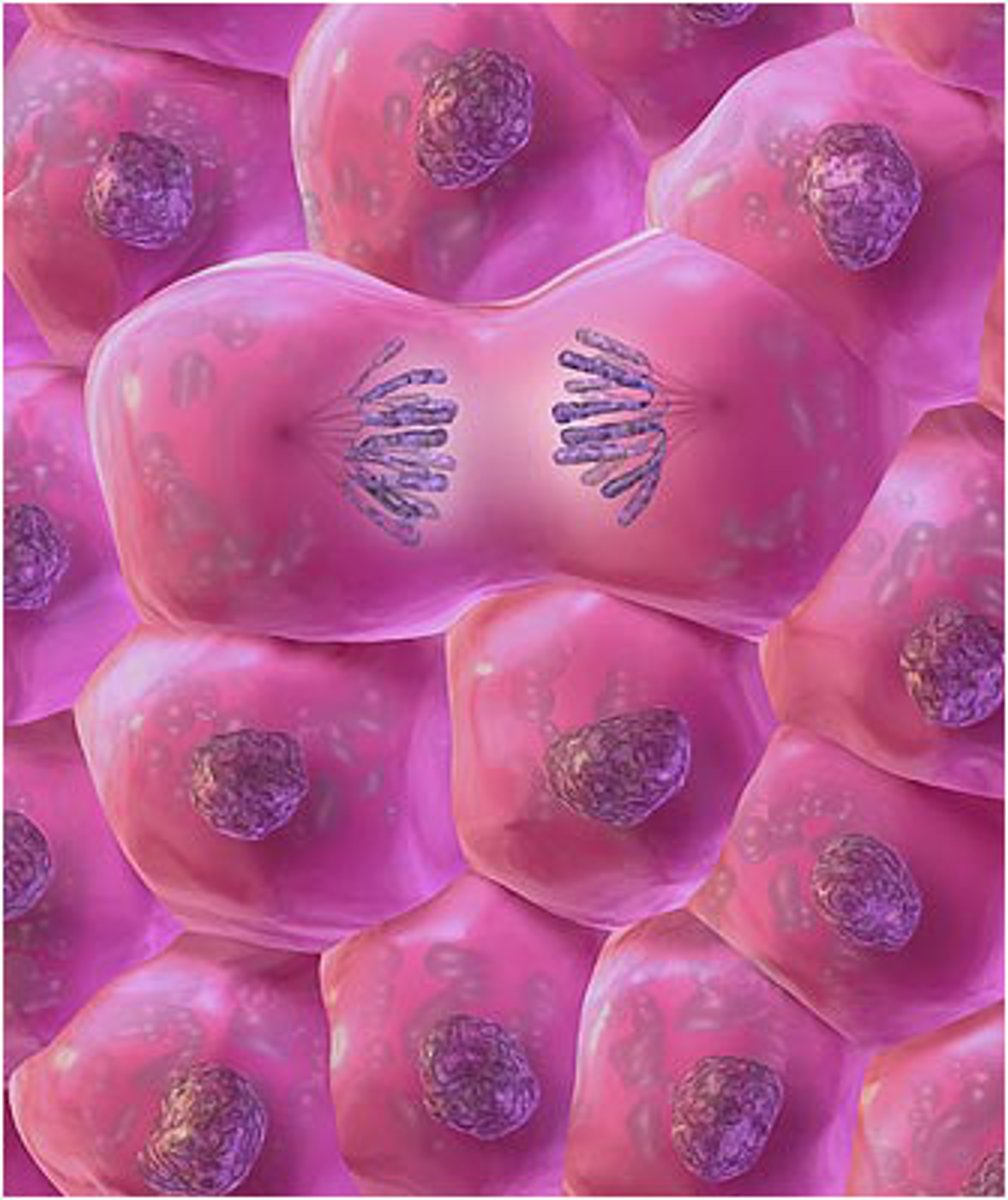
Cells only come from living cells.
The third statement of The Cell Theory. This is based on Rudolf Virchow's observation of living cells reproducing.
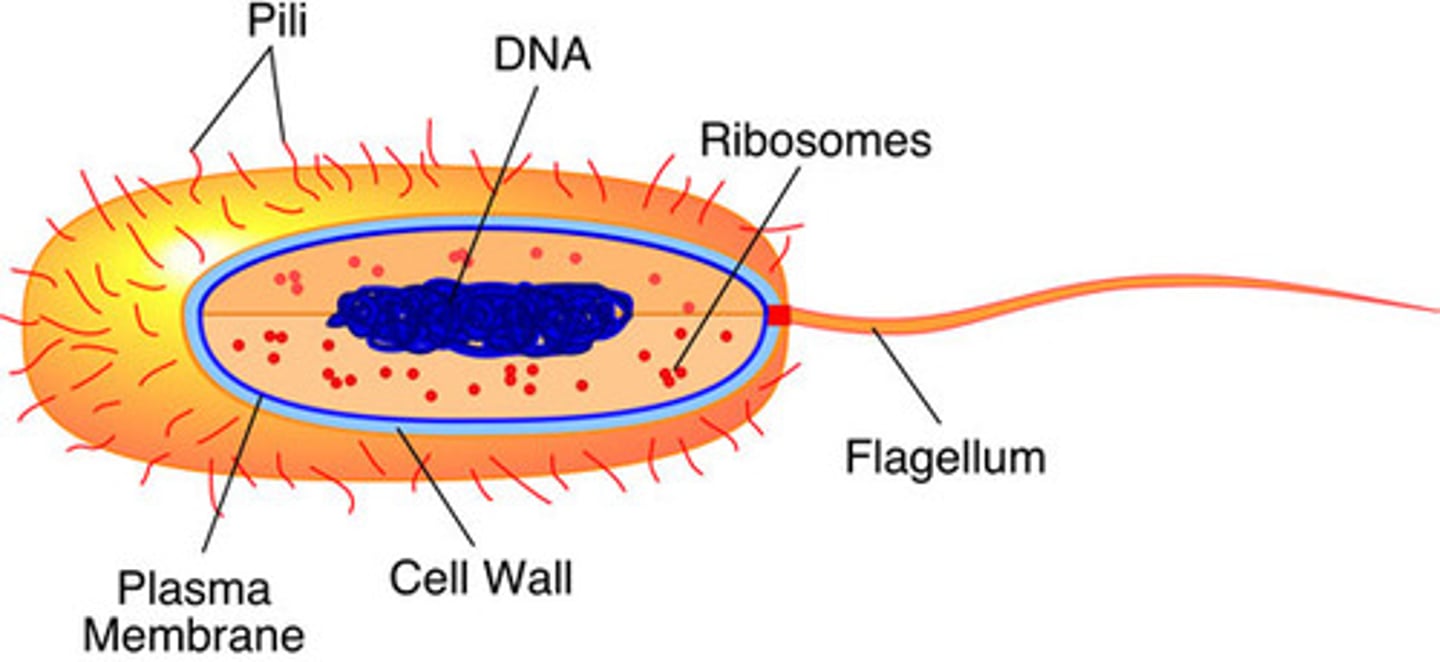
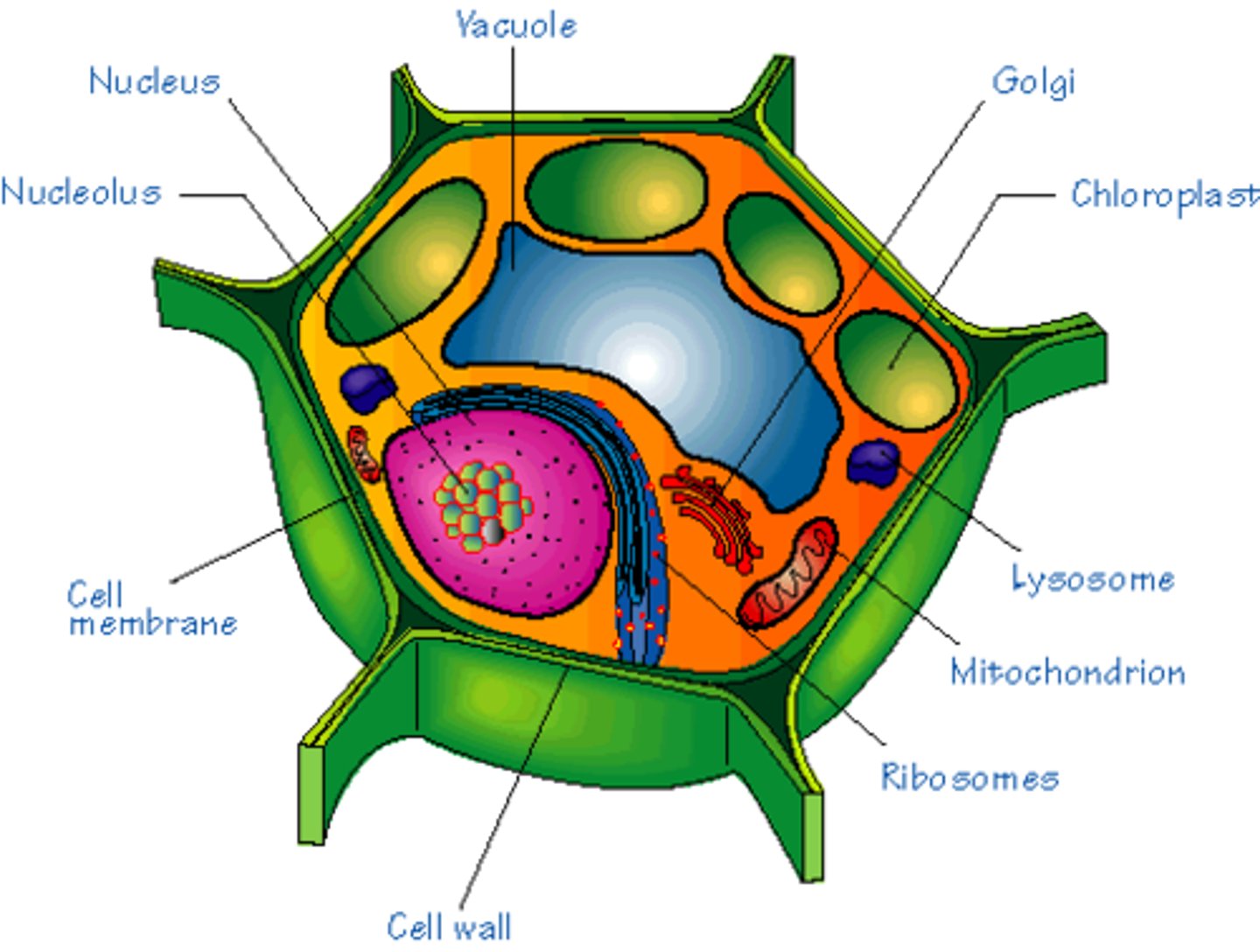
Prokaryote
A cell that does NOT have a nucleus. The Eubacteria and Archaebacteria have prokaryotic cells. They are simple, small cells.
Eukaryote
A cell that has a nucleus. Animals, plants, fungi, and protists have eukaryotic cells. They are complex and larger than prokaryotic cells.
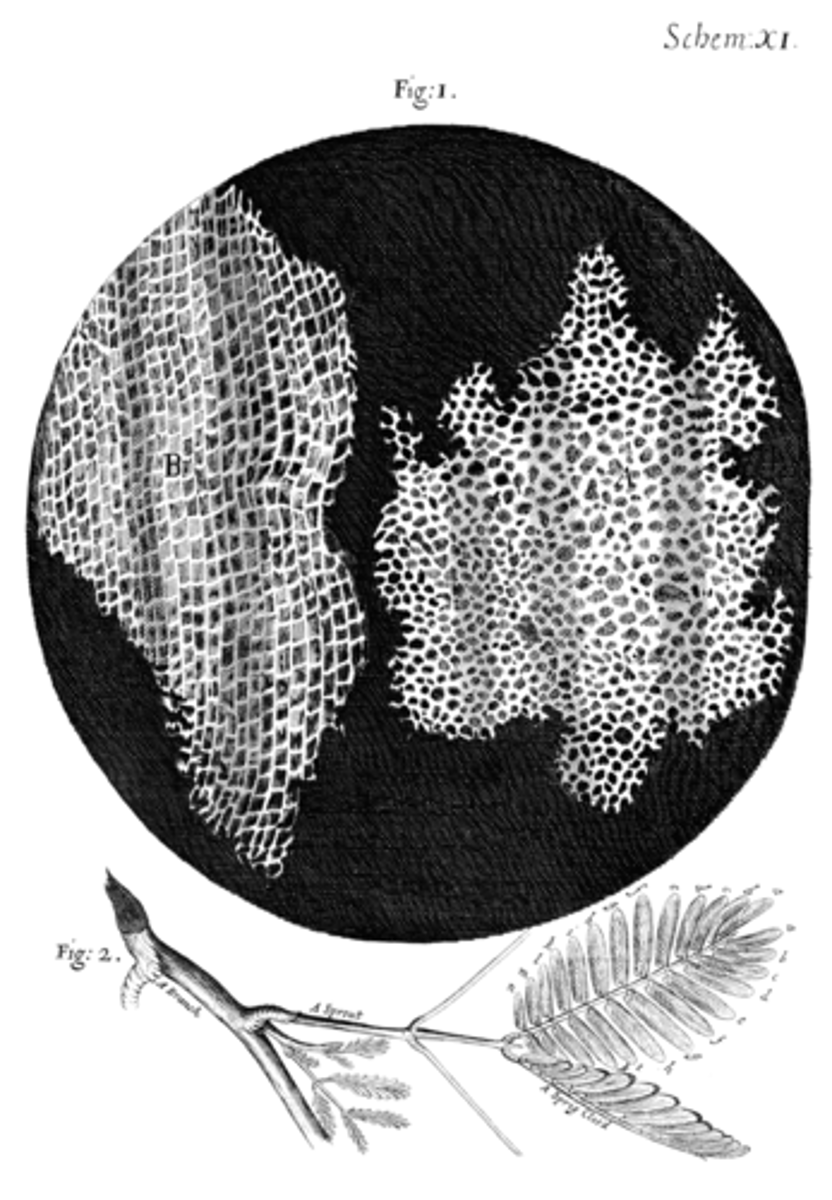
Hooke's Famous Drawing
This drawing from Robert Hooke's book "Micrographia" is in most Biology textbooks. Robert Hooke looked at thin slices of cork tree bark and saw "cells" for the first time.
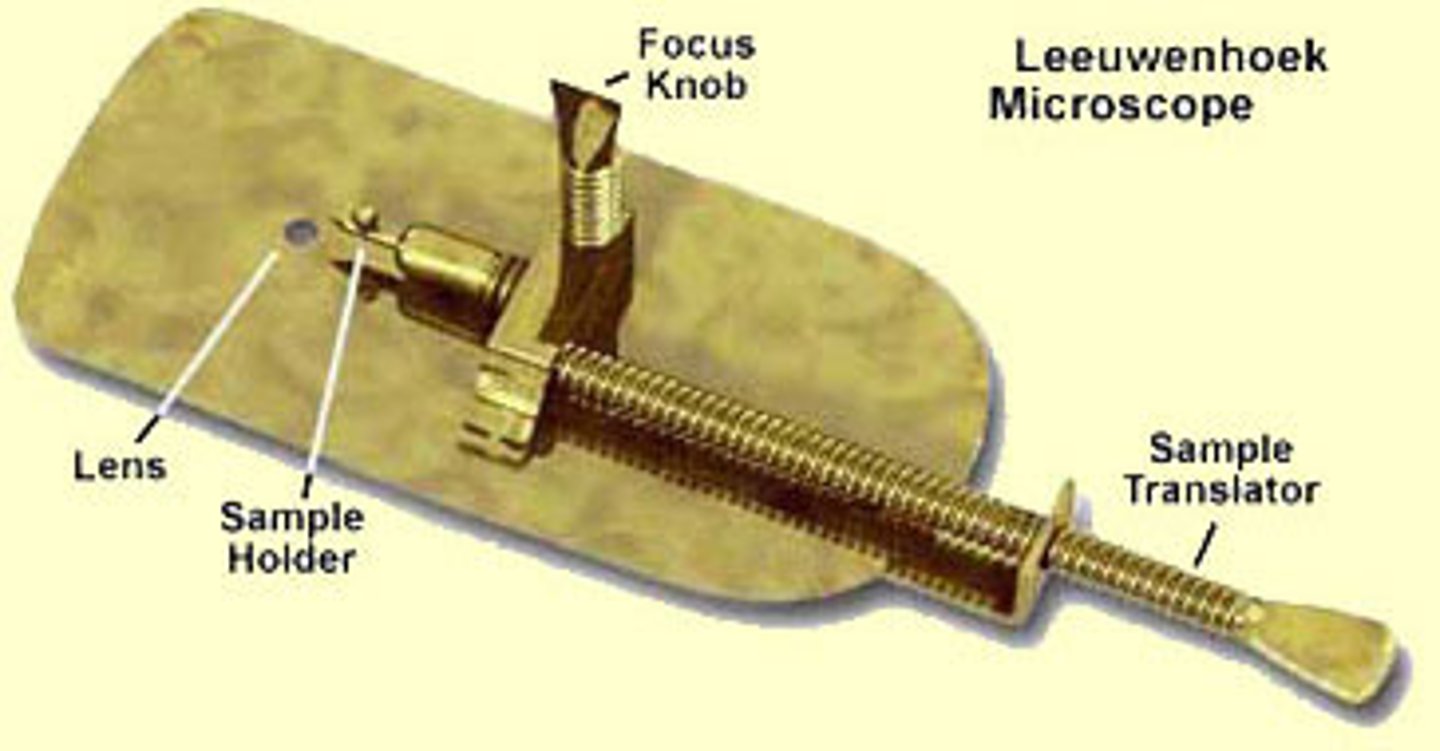
Leeuwenhoek's Microscope
Leeuwenhoek made hundreds of these microscopes using his "secret" technique. He made a new microscope every time he wanted to look at another specimen.
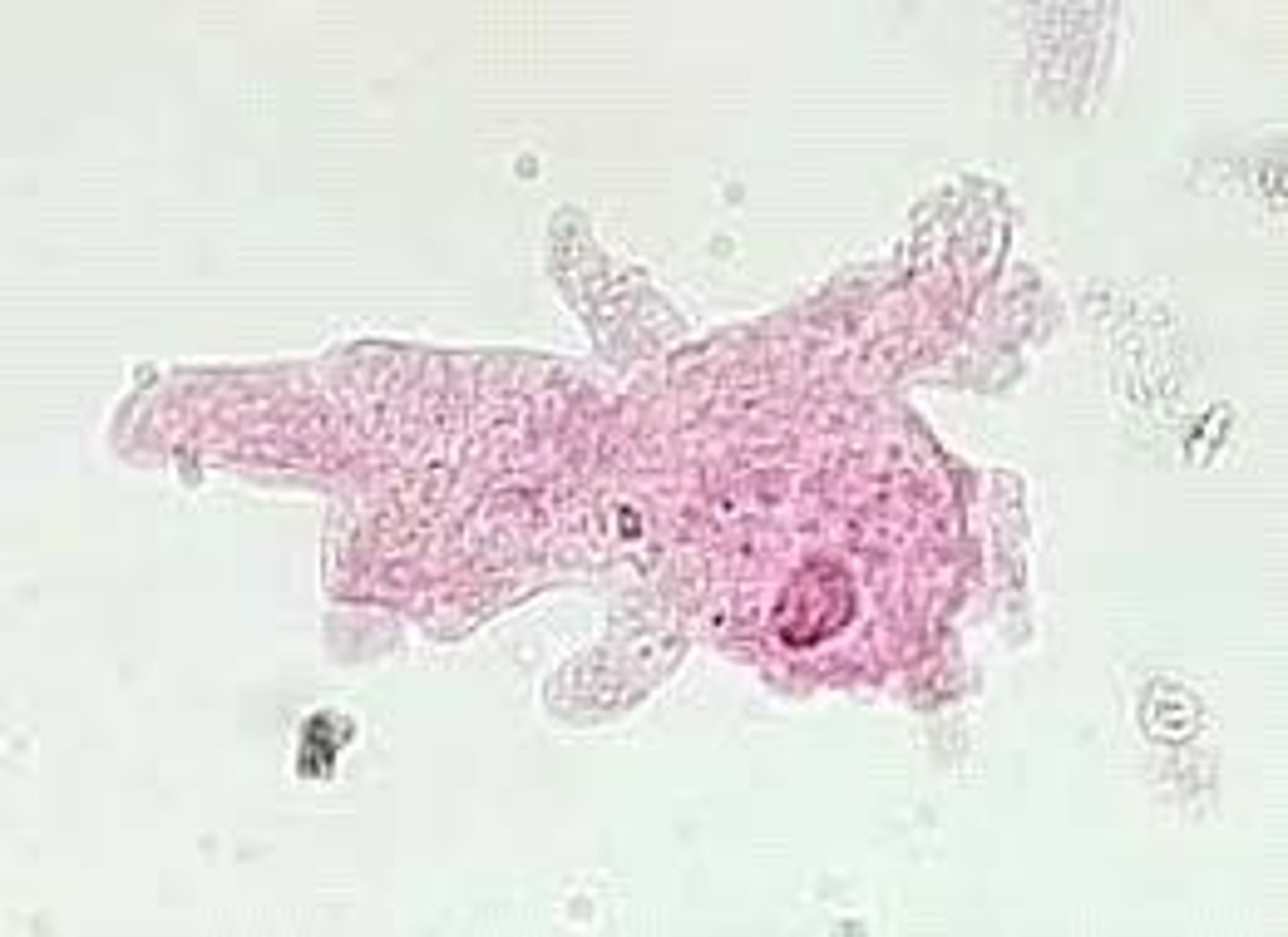
Unicellular
What type of organism is this Amoeba?
Cells
What are the tiny boxes Robert Hooke saw in this drawing?
