WGU C213 ACCOUNTING FOR DECISION MAKERS ULTIMATE 2025 KEY POINTS & EXAM STUDY GUIDE | 300+ ESSENTIAL CONCEPTS WITH MEMORIZATION TECHNIQUES | MASTER FINANCIAL STATEMENTS, RATIO ANALYSIS & COST ACCOUNTING | GUARANTEED OA SUCCESS
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Debt Ratio
Total Liabilities/Total Assets
Current Ratio
Current Assets/Current Liabilities. Only need a balance sheet.
Return on Sales
Net Income/Sales. Only need income statement
Asset Turnover
Sales/Total Assets
Return on Equity
Net Income/Stockholder's equity. Balance and Income Statements used.
Price-Earnings Ratio (PE)
Market Value fo Shares/Net Income
Accounting is
the recording of the day-to-day financial activities of a company and the organization of that information into summary reports used to evaluate the company's financial status.
Bookeeping is
the preservation of a systematic, quantitative record of an activity. Without bookkeeping, good business is impossible. An accounting system is used by a business to handle routine bookkeeping tasks and to structure the information so it can be used to evaluate the performance and financial status of the business. Accounting information is intended to be useful in making decisions about the future.
The focus of financial accounting is
the three primary financial statements: the balance sheet, the income statement, and the statement of cash flows.
Financial accounting information is
provided for, and used by, external users. Managerial accounting is the name given to accounting systems designed for internal users. The information provided by financial accounting is summarized in the financial statements:
The balance sheet reports a company's assets, liabilities, and owners' equity.
The income statement reports the amount of net income earned by a company during a period. Net income is the excess of a company's revenues over its expenses.
The statement of cash flows reports the amount of cash collected and paid out by a company in the following three types of activities: operating, investing, and financing.
Among the users of financial accounting information are
lenders, investors, company management, suppliers, customers, employees, competitors, government agencies, politicians, and the press.
Financial accounting information helps
lenders evaluate the cash flows a business can be expected to generate in the future in order to repay loans. Investors use the same type of information to assess the attractiveness of companies as investments. Managers use financial accounting data to formulate company goals, to compute bonuses for employees, and to illuminate company weaknesses. Suppliers, customers, and employees use financial statements to tell them about the long-run prospects of a company. Competitors use financial accounting information to reveal strategic opportunities within their industry. Government agencies and politicians use financial statement data to bolster political and regulatory positions for and against companies. Reporters use financial accounting data as background information and to indicate which companies are undergoing significant changes in financial status.
The practice of accounting involves adherence to
he established accounting rules as well as the use of judgment. U.S. accounting rules are established by the FASB.
FASB is
a group that sets accounting standards. The XXXX is not a government agency; it is a private body established and supported by the joint efforts of the U.S. business community, financial analysts, and practicing accountants.
The FASB has
no legal power to enforce the accounting standards it sets but maintains its influence by carefully protecting its prestige and reputation.
SEC
regulates U.S. stock exchanges and seeks to create a fair information environment in which investors can buy and sell stocks without fear that companies are hiding or manipulating financial data.
The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) is
the professional organization of certified public accountants (CPAs) in the United States. A CPA is someone who has taken a minimum number of college-level accounting classes, has passed the CPA exam, and has met other requirements set by his or her state. A CPA firm is a company that provides freelance business advice, particularly in connection with accounting issues.
The Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB)
inspects the audit practices of registered audit firms and has statutory authority to investigate questionable audit practices and to impose sanctions such as barring an audit firm from auditing SEC-registered companies.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS)
establishes rules to define exactly when income should be taxed. It has no role in setting financial accounting rules; and a company's financial statements are not used in determining how much tax the company must pay.
The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB)
was formed to develop a common set of worldwide accounting standards. IASB standards are increasingly accepted worldwide, but FASB rules are still the standard in the United States.
Three factors have combined to make right now a time of significant change in accounting. The three factors are
the rapid advance in information technology, the international integration of worldwide business, and the increased scrutiny associated with the large corporate accounting scandals.
SOX
was created in response to wave of accounting scandals starting in 2001 and which increases U.S. federal government scrutiny of the production of financial statements.
Liabilities are
formally defined as "probable future sacrifices of economic benefits arising from present obligations of a particular entity to transfer assets or provide services to other entities in the future as a result of past transactions or events.
By increasing the information available about a company,
financial statements make it easier for a company to attract investors, lenders, and other parties interested in the company's financial status.
The balance sheet
reports a company's financial position at a specified point in time and lists the company's resources (assets), obligations (liabilities), and net ownership interest (owners' equity).
Assets are
probable future economic benefits obtained or controlled by a company as a result of past transactions or events. Liabilities are probable future sacrifices of economic benefits arising from present obligations of a company to transfer assets or provide services in the future as a result of past transactions or events. Owners' equity is the residual interest in the assets of a company that remains after deducting its liabilities. By definition, Assets = Liabilities + Owners' Equity; this relationship is called the accounting equation.
For a corporation, owners' equity is called
tockholders' equity. Stockholders can invest in a corporation in two ways. First, they can directly invest cash or other assets as paid-in capital. Second, they can allow the corporation to keep a portion of the profits for reinvestment in the business; these profits are called retained earnings.
Assets are usually listed in
a balance sheet in order of liquidity, with the most liquid asset—cash—shown first and the least liquid assets—intangible assets—shown last. Liabilities are separated into those to be paid soon (current liabilities) and those to be paid later (long-term liabilities). Balance sheets are usually presented in a comparative format with at least two years of data provided.
The entity concept states that
the financial results of an economic entity should be reported separately from the financial results of other entities, even though all those entities may be controlled by the same person. With large corporations, identifying the extent of the economic "entity" can be quite difficult. Accountants frequently report assets at their historical cost rather than their current value, resulting in companies' reported accounting values often being less than their market values. Accountants assume that a company is a going concern, so assets don't have to be reported in the balance sheet at liquidation value.
The income statement describes
a company's financial performance for a period of time. A company's expenses are subtracted from its revenues in computing net income.
Revenues are
the amount of assets generated in the normal course of business; expenses are the amount of assets consumed in doing business. An income statement also reports gains and losses that result from activities outside a company's normal business operations. An additional number reported in the income statement is earnings per share, which is the amount of net income divided by the number of shares of stock outstanding.
Revenue recognition is
the accounting process used to determine when revenue should be reported in the income statement. Revenue should be recognized when work has been done and when collectibility of cash is reasonably assured.
The statement of cash flows details
how a company obtained and spent cash during a certain period of time. All of a company's cash transactions are categorized as either operating, investing, or financing activities.
Operating activities are
those activities that comprise the day-to-day operations of a business. Investing activities are the purchase and sale of long-term assets such as land and equipment. Financing activities are those activities through which cash is obtained from, or repaid to, creditors and investors.
The notes to financial statements provide
information on the accounting assumptions used in preparing the statements and also provide supplemental information not included in the statements themselves. Notes are an integral part of financial statements.
Financial statement notes are of four general types
a summary of accounting policies, additional information about summary totals in the statements, disclosure of important information not in the statements, and supplemental disclosure required by the FASB or SEC.
An audit performed by accountants from outside a company
increases the reliance that users can place on the information in the company's financial statements.
A key trade-off in the preparation of useful accounting information is
between relevance and reliability. Other concepts underlying the practice of accounting are comparability, conservatism, materiality, and articulation.
Comparability makes
financial statement information more useful because it allows a company's financial statements to be analyzed in light of the company's own performance in prior years or other companies' performance.
Relevant information is
information that is provided on a timely basis and can be used to assess the past and to project the future for decision making.
Conservatism is
the practice of recognizing all losses but not recognizing gains until they are certain.
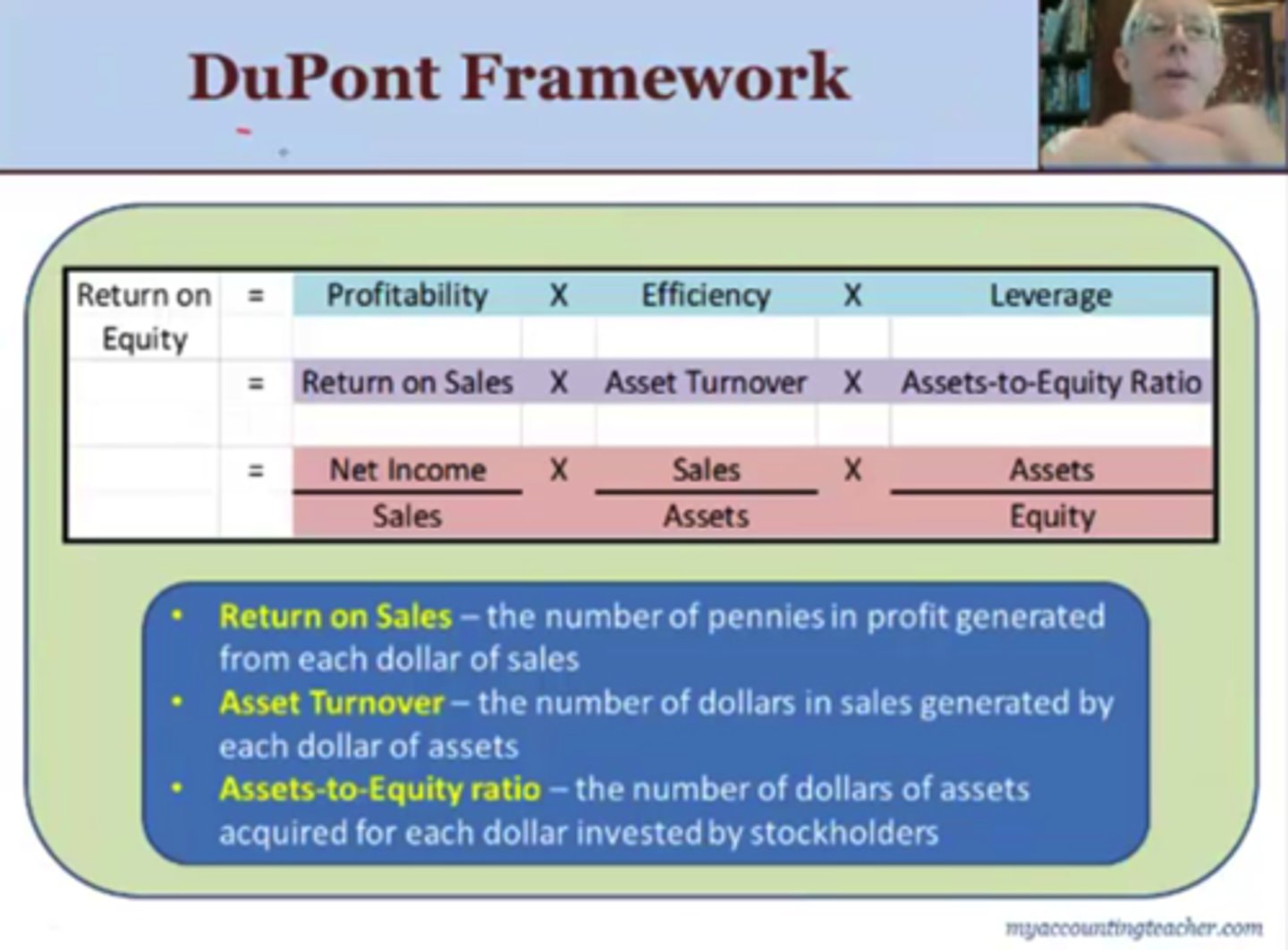
DuPont Framework
Return on sales is computed as net income divided by sales and is interpreted as the number of pennies in profit generated from each dollar of sales.
Asset turnover is computed as sales divided by assets and is interpreted as the number of dollars in sales generated by each dollar of assets.
Assets-to-equity ratio is computed as assets divided by equity and is interpreted as the number of dollars of assets acquired for each dollar invested by stockholders.
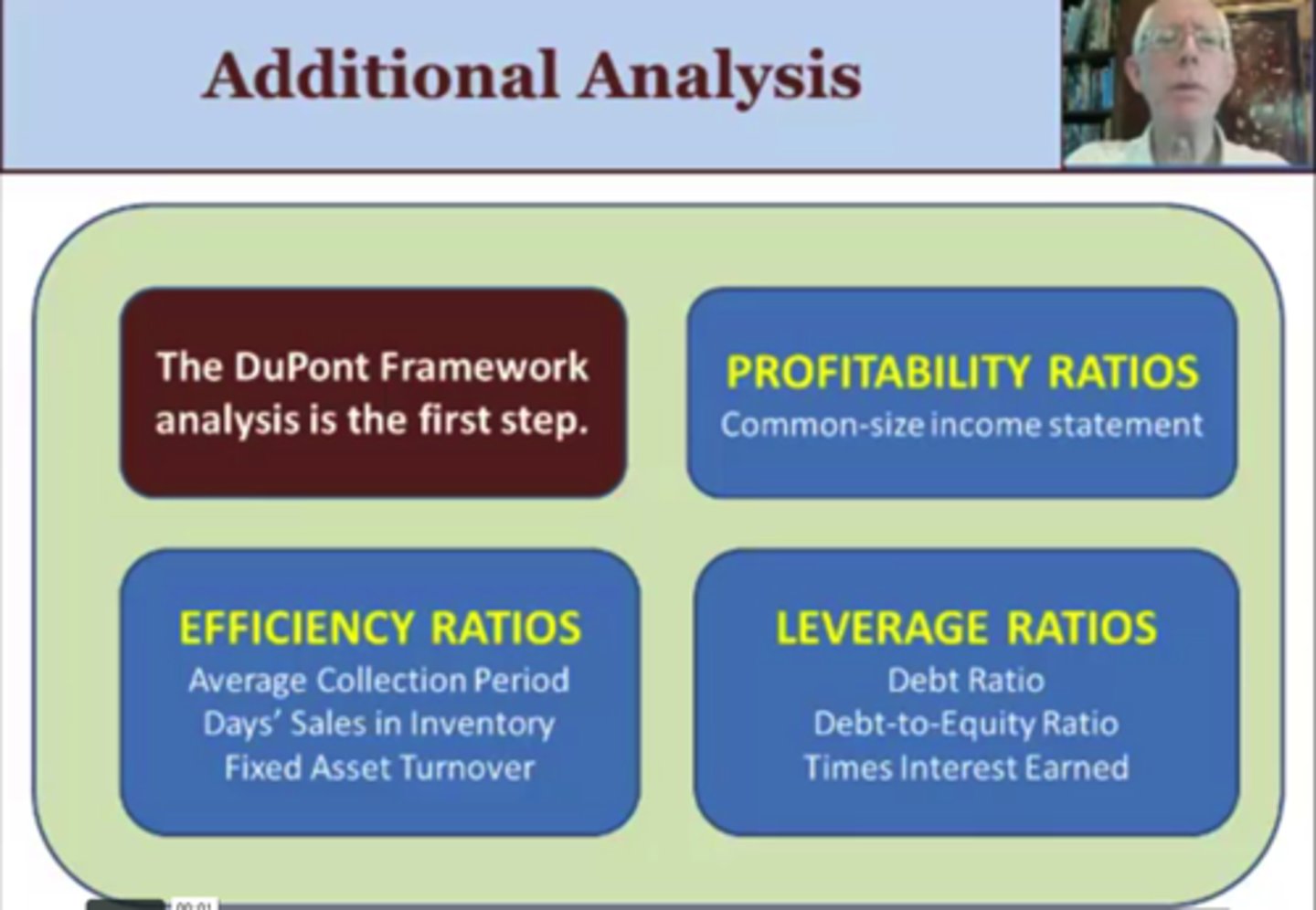
Other than DuPont Framework, additional analysis includes
Five key measures of income are
Gross profit: the difference between the selling price of a product and the cost of the product.
Operating income: gross profit minus all other expenses except for interest and taxes. Operating income measures the performance of the fundamental business operations conducted by a company.
Income from continuing operations: operating income minus interest expense, minus income tax expense, and plus or minus other miscellaneous revenue and expense items, and gains and losses from peripheral transactions and events. Income from continuing operations is the best baseline from which to forecast a company's income for the following year.
Net income: income from continuing operations plus or minus the results of discontinued operations and extraordinary items, net of their respective income tax effects. Net income includes all revenues, expenses, gains, and losses.
Comprehensive income: net income plus or minus adjustments for changes in company wealth stemming from changes in certain exchange rates, interest rates, or financial instruments' values.
The primary categories of income statement items are
revenues, expenses, gains, and losses
Income statement items that do not relate to a company's continuing operations are
income from discontinued operations and extraordinary items.
One useful format is the multiple-step income statement and
emphasizes the presentation of gross profit and operating income.
Revenue should be recognized when
value has been delivered to customers which is typically only after the required work has been performed and after the collection of cash is reasonably assured.
The matching concept has traditionally been
used to decide when to recognize expenses.
Individual transactions impacting income can be analyzed using the expanded accounting equation which is:
Assets = Liabilities + Paid-in Capital + (Revenues - Expenses - Dividends)
An important use of an income statement is
to forecast income in future periods