Chap 13 Host Repsonse PART 1
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Inflammatory Response
Activated by immune system in response to offending agent or injury
Traps offending agents or starts healing injured tissue
Not meant to be activated for long time
When tissue does not go through resolution phase, result is chronic inflammation—destruction of the periodontum (when something should not be there REBOUST), tissue can NOT repair or resolve
Periodontal Disease
Biofilm-induced infection that precipitates complex immunoinflammatory response, Multiple factors can cause disease, Biofilm alone can not cause the disease,
Presence of periodontal pathogens alone insufficient to cause tissue destruction seen in periodontitis
Host immunoinflammatory response, triggered by presence of microbial biofilm, is direct cause of nearly all destruction seen in periodontal disease
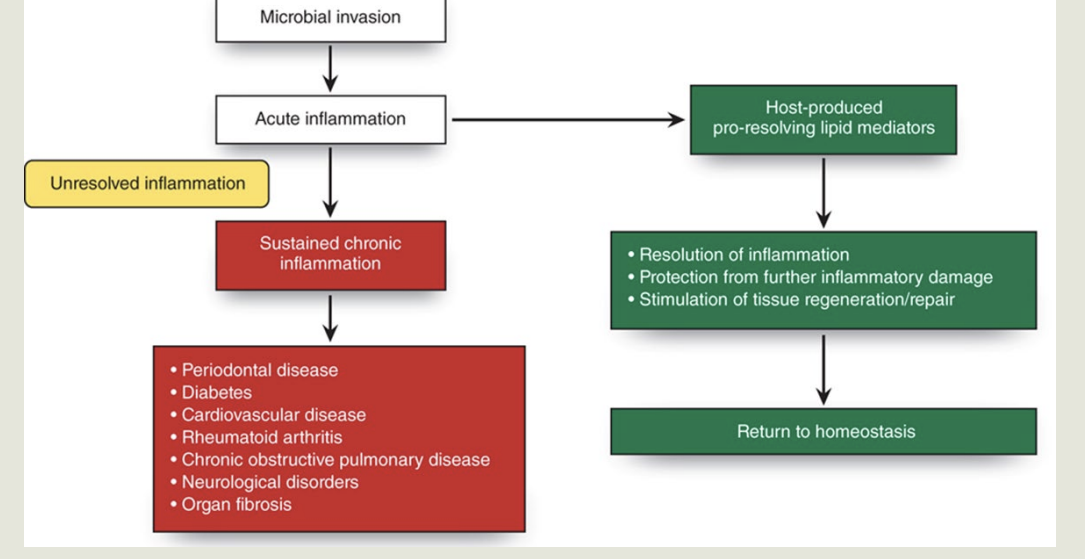
Inflammatory Response and Resolution: image
Image: 2 pathways
Biofilm microbial invasion to the host and triggers - Acute inflammation( reversable
Chronic inflammation- permanent tissue damage
Factors Enhancing the Microbial Challenge:
Virulence Factor?
Primary Factor (3)
Virulence factor ?
Mechanisms that enable biofilm bacteria to colonize and damage tissues of periodontium- how pathogenic colonizing
Factors Can be Proteins on cell membrane, Toxins substances called endotoxins
Primary virulence factors:
KNOW*** Presence of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (Activation of the complement pathway get immune system involved and go after the bacteria)
BECAUSE OF Gram negative bacteria in mature is a lot more pathogenic because of LPS( endotoxin) it can initate the inflammtion process
Ability to invade host tissues, allow bacteria to escape this host defense
Ability to produce enzymes(collagene)
Factors Modulating the Host Immunoinflammatory Response
Genetic factors?
Ex?
Genetic factors
Affect formation of biochemical mediators >> impact host’s susceptibility to periodontal disease
Example: Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome (genetic origin)
Factors Modulating the Host Immunoinflammatory Response
Acquired factor?
Decreases?
Increases ?
Acquired factors
Example: diabetes mellitus: known risk factor for periodontal disease >>significant effect on the immune & inflammatory responses
Decreases PMNs
Increases TNF-a, IL-1b & PGE levels
Environmental factors?
Example: tobacco smoking: known risk factor for periodontal disease >> significant effect on the immune & inflammatory responses
Decreases PMNs phagocytic activity
Decreases vascularity
Microbial shift to pathologic bacteria
Acute Inflammation (6 Types of cells involve) ?
Host response to microbes involves cells including:
Inflammatory cells
PMNs
Antigen-presenting cells
T- and B- lymphocytes
Fibroblasts
Epithelial cells
Acute inflammation has host-protective effect: 4 effects?
Must dampen after microbial challenge eliminated
First line of defense against microbial invasion
Eliminates harmful stimuli
Replaces injurious host cells
Creates environment favorable to tissue repair
Resolution of Acute Inflammation Following Removal of Microbial Challenge:
Effectiveness?
Acute inflammation and resolution must work together
Effectiveness of acute inflammation determines whether inflammation favor or detrimental
Recent studies indicate resolution of inflammation and return to noninflammatory state is actively regulated biologic process
Catabasis?
It is what?
Proinflammation mediators in periodontitis ex?
Return to homeostasis after inflammatory process
Thought to be biologic process just as complicated as onset of inflammation
Proinflammation mediators in periodontitis:
Prostaglandins, thromboxanes, prostacyclins, and leukotrienes
Catabasis:
Periodontitis lipid mediators associated with?
Over-recruitment or overactivity of PMNs can?
Periodontitis lipid mediators associated with:
Recruitment of PMNs
Destruction of connective tissue matrix
Resorption of alveolar bone
Over-recruitment or overactivity of PMNs can amplify inflammatory process
If host unable to tamp down inflammation then its called?
Can have pathologic effects on?
If host unable to tamp down inflammation soon after removal of microbial challenge:
Acute inflammation progresses to uncontrolled, unresolved chronic inflammation
Can have pathologic effects on host tissue
Inflammatory Biochemical Mediators of the Host Response:
“Middlemen” sent by?
Important biochemical mediators (3)?
Def
In response to bacterial challenge, host immune cells secrete biologically active compounds >> activate the body’s inflammatory response
“Middlemen” sent by host cells to activate inflammatory response
Important biochemical mediators:
Cytokines
Prostaglandins (PG)
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)
Cytokines:
what is it?
Released by?
2 main things it does?
Produced by (6)
What is it: Powerful regulatory proteins released by host immune cells that influence behavior of other cells
Transmit information or signals between cells
Alert and activate immune system for help
Produced by
PMNs,
macrophages,
B-cells,
epithelial cells,
gingival fibroblasts,
osteoblasts
Cytokines Functions & Key Periodontist
4 functions?
Key cytokines in periodontitis- 4 Types
Function to:
Recruits cells (PMNs and macrophages) to infection site
Bind to specific cell surface receptors on target cells
Increase vascular permeability – increases movement of immune cells of site of infection
Can initiate and perpetuate irreversible tissue destruction and bone loss in chronic inflammatory diseases
Key cytokines in periodontitis:
Interleukin-1 (IL-1β)
Interleukin-6 (IL-6)
IL-8
Tumor Necrosis Factor – (TNF-α)
Prostaglandins:
What is?
Important prostaglandins- ( start from d…6 letters)
Prostaglandins of E series play huge role in?
Macrophage: major source of PGEs
Def:
Powerful biochemical mediators derived from fatty acids expressed on surface of most cells
Important prostaglandins:
Prostaglandins D, E, F, G, H, and I
Prostaglandins of E series :
(PGEs) play important role in bone destruction in periodontitis
Macrophage a major source of PGEs
Also produced by PMNs and gingival fibroblasts
Prostaglandins Functions:
Increase?
Trigger?
Promote?
Functions:
Increase permeability and dilation of blood vessels
Trigger osteoclasts to destroy alveolar bone
Can promote overproduction of destructive MMP enzymes
Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs)
Proteolytic enzymes breaksdown:
Produced by (4):
Major source of MMPs in Periodontitis:
MMPS IS:
Family of at least 12 proteolytic enzymes that breakdown connective tissue matrix
Produced by
PMNs
macrophages,
gingival fibroblasts
junctional epithelial cells
Major source of MMPs in Periodontitis
PMNs
Gingival fibroblasts
MMPs Effects in Health and Chronic Infection:
In Health
Facilitate
Overactivity of MMPs tightly regulated by?
MMP-TIMP balance helps the?
Health
Facilitate normal turnover of periodontal connective tissue matrix
Overactivity of MMPs tightly regulated by host-derived tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases (TIMP)
MMP-TIMP: balance helps maintain integrity and health of connective tissue
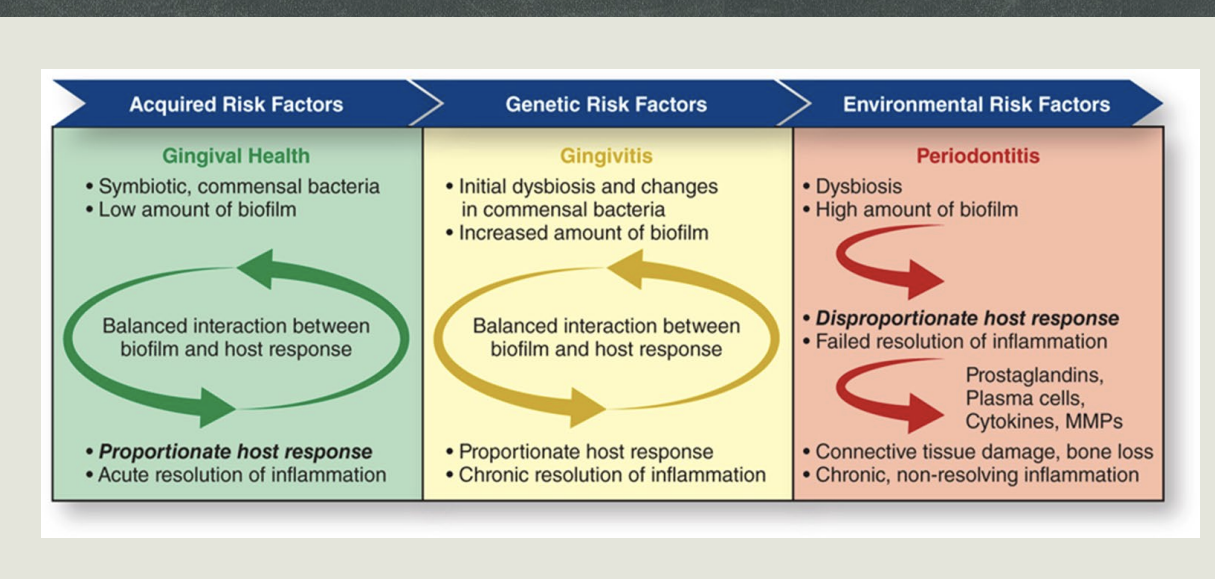
Current Theory of Pathogenesis Image
Gingival health associated with symbiotic biofilm
Mediated by proportionate immunoinflammatory response
Traditional pathogenic bacteria accumulate when bacterial biofilm not disturbed
Interferes with normal tissue function and host response
Balance remains stable in people not susceptible
In susceptible individuals, dysbiotic biofilm activates host response to produce excessive cytokines, reactive oxygen species, and MMPS, leading to:
Collagen breakdown
Bone resorption
Periodontal tissue damage
Current Theory of Pathogenesis
Removal of bacterial biofilm,
Risk factor- Alter host, Impacts what?
Removal of bacterial biofilm can help reestablish health-promoting biofilm
Risk factors are associated with dysbiotic dental biofilm communities and can:
Alter host immuno-inflammatory response to biofilm
Impact individual’s susceptibility to periodontal disease