skin, hair, nails, heentt
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
assessment of the skin
reveals the patient’s health status related to oxygenation, circulation, nutrition
skin coloration
cyanosis, jaundice, tanned
skin variations
vitiligo, seborrheic keratosis
inspection
check skin integrity
inspect for lesions
palpation
texture, thickness, moisture
skin
vascularity, edema, lesions
asymmetry
uneven shape
border irregularity
look for edges that are blurred, notched, or ragged
color
look for pigmentation that is not uniform
diameter
look for areas greater than the size of a typical pencil eraser
evolving
changes in size shape symptoms
three types of skin cancer
melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma
basal cell carcinoma
type of skin cancer that most often develops on areas of skin exposed to sun
squamous cell carcinome
type of skin cancer caused by overproduction of squamous cells in your epidermis
melanoma
most serious type of skin cancer, develops in cells that produces melanin
kaposi sarcoma
a disease in which cancer cells are found in the skin or mucous membranes that line the GI tract from mouth to anus.
caused by human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8)
macule
flat lesion less than 1 cm without elevation or depression
patch
flat lesion greater than 1 cm without elevation or depression
plaque
flat, elevated lesion, greater than 1 cm
papule
elevated solid lesion less than 1cm
nodule
elevated solid lesion greater than 1cm
tumor
abnormal mass of tissue may be cancerous or premalignant
bulla
elevated fluid filled lesion
wheal
skin lesion caused by an allergic reaction
cysts
abnormal, fluid-filled sacs that can develop in tissues in any part of the body
erosion
intraepithelial loss of epidermis
lichenification
skin that is thick and leathery
scales
visible peeling or flaking of outer skin layers
crust
dried exudate on the skin surface
ulcer
crater-like, open sore on the skin
fissure
breaks in the skin look likes cuts or cracks
scars
can result from injury to the skin through disease and trauma
tinea corporis
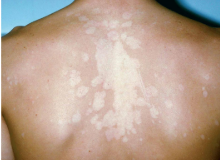
measles (rubeola)
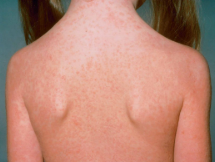
german measles
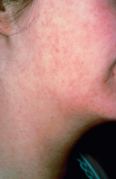
chickenpox (varicella)
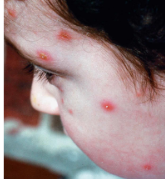
herpes simplex
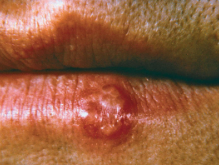
herpes zoster (shingles)
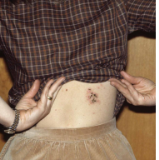
psoriasis
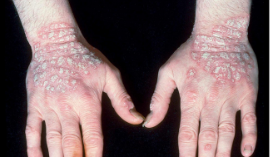
contact dermatitis
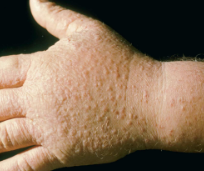
eczema
impetigo
hirsutism
furuncle
folliculitis
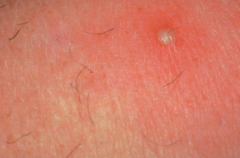
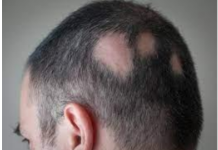
alopecia areata
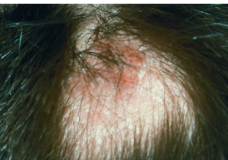
tinea capitis (scalp ringworm)
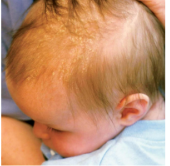
seborrheic dermatitis (cradle cap)
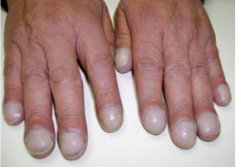
clubbing
bulbous, club-like deformation of the distal portion of fingers and toes

raynaud disease
when blood vessels in your fingers and toes temporarily overreact to low temperature or stress
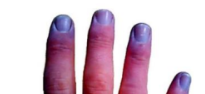
acute digital ischemia
may cause blue nails
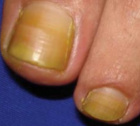
lymphoedema
yellow nail syndrome
chronic paronychia
most often on the hands in person repeatedly exposed to moist environment prolonged and repeated contact with irritants
housekeepers, dishwashers, bartenders, swimmers
ingrown nail
nail as a foreign body - inflammatory response - erythema, edema, focal at the nail fold and nail plate junction
gastrointestinal disease
malabsorption leading to malnutrition, discoloration, lunula may be absent
renal disease
half-and-half nails, about 30% of dialysis patients have no lunula
nystagmus
extraocular movements
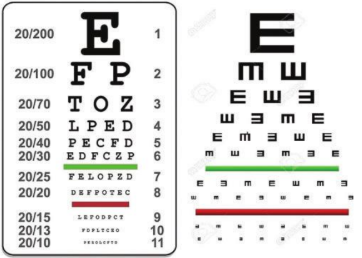
snellen chart and e chart
perrla
pupils, equal, round, reactive to light, and accommodation
cover test
measurement of eye posture
performed at distance (6cm) and near (40cm)
tuning fork
if a hearing loss is present, test the hearing using a __
weber’s test
hold fork at base and tap it lightly against heel of palm
rinne test
place stem of vibrating tuning fork against patient’s mastoid process
romberg’s test
pt stand w feet together
vision can compensate for loss of position sense
nose
assess by inspection and palpation
sinuses
assess by palpation
assess for tenderness
lips
color
texture
hydration
mouth and pharynx
buccal mucosa
gums
teeth
palate
hard
soft
pharynx
examine to rule out infection, inflammation
inspect the uvula, soft, palate
head and neck
inspect the head noting the position size shape
neck
anterior posterior triangle
lymph nodes
inspection, palpation