T5:Energy Changes
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What happens to the energy chemical reactions?
Energy is conserved in chemical reactions.
The amount of energy in the universe at the end of a chemical reaction….
..is the same as before the reaction takes place.
What must be true in a reaction?
If energy is transferred to the surroundings, the products have less energy than the reactants.
What is an exothermic reaction?
An exothermic reaction is one that transfers energy to the surroundings so the temperature of the surroundings increases
What are three examples of exothermic reactions?
Combustion
Many oxidation reactions
Neutralisation
What are everyday uses of exothermic reactions?
Self-heating cans and hand warmers.
What is an endothermic reaction?
An endothermic reaction is a reaction that takes in energy from the surroundings so the temperature of the surroundings decreases.
What are two examples of endothermic reactions?
Thermal decomposition
Reaction of citric acid and sodium hydrogencarbonate.
What is an everyday use of an endothermic reaction?
Sports injury packs.
When is the only time that chemical reactions can occur?
Chemical reactions can occur only when reacting particles collide with each other with sufficient energy.
What is minimum amount of energy that particles must have to react called?
The activation energy.
What do energy profile diagrams represent?
They represent the energy changes that take place in reactions.
Draw the reaction profile for an exothermic reaction:
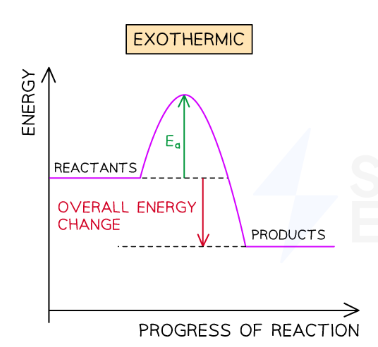
In an exothermic reactions products have less energy…
Than the reactants because energy has been transferred from the reaction to the surroundings.
What does the difference between the energy of the reactants and energy of the products tell us?
The energy that has been transferred to the surroundings.
Draw the reaction profile for an endothermic reaction:
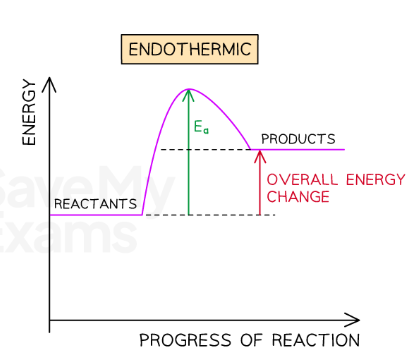
In endothermic reactions the products have more energy…
Than the reactants because energy has been taken in from the surroundings.
What does the difference between the energy of the reactants and energy of the products tell us?
The amount of energy that has been taken in by the reaction.
During a chemical reaction,energy must be supplied to….
Break bonds in the reactants (endothermic).
During a chemical reaction,energy is released when bonds …….
In the products are formed(exothermic).
What reaction is it if a)the enrgy change is positiv and b)the enrgy change is negative?
Negative=exothermic
Positive=endothermic
What is the overall energy change of a reaction?
The overall energy change is the difference between energy needed to break reactant bonds and energy released when product bonds form.
What is the relationship between bonds and energy in an exothermic reaction?
In an exothermic reaction, the energy released from forming new bonds is greater than the energy needed to break existing bonds.
What is the relationship between bonds and energy in an endothermic reaction?
In an endothermic reaction, the energy needed to break existing bonds is greater than the energy released from forming new bonds
What is the non-official formula to calculate the overall energy change of a reaction?
Overall energy change=bonds broken-bonds formed
Do you use the big numbers in bond energy calculations?
No.
What do cells contain?
Cells contain two different metals in an electrolyte which react to produce electricity.
What 2 things is the voltage produced by a cell dependent on?
The type of electrode
The electrolyte
How can a simple cell be made?
A simple cell can be made by connecting two different metals in contact with an electrolyte.
What are batteries?
Batteries consist of two or more cells connected together in series to provide a greater voltage.
How do you know what the more reactive element is in an electrochemical cell?
It is the negative element.
What happens in a non-rechargeable battery?
In non-rechargeable cells and batteries the chemical reactions stop when one of the reactants has been used up.
What is an example of a non-rechargeable battery?
An alkaline battery.
Why are they non-rechargeable?
There is no way for us to reverse the chemical reaction.
Why can rechargeable cells and batteries be reacharged?
They can be recharged because the chemical reactions are reversed when an external electrical current is supplied.
What are fuel cells supplied by?
Fuel cells are supplied by an external source of fuel (eg hydrogen) and oxygen or air.
What happens to the fuel within the fuel cell?
The fuel is oxidised electrochemically within the fuel cell to produce a potential difference.
What does the overall reaction in an hydrogen fuel cell involve?
The overall reaction in a hydrogen fuel cell involves the oxidation of hydrogen to produce water.
What can hydrogen fuel cells offer?
Hydrogen fuel cells offer a potential alternative to rechargeable cells and batteries
What is the balanced half equation for a hydrogen feul cell at the Cathode?

What is the balanced half equation for a hydrogen feul cell at the Anode?

What is the equation for the overall reaction in a hydrogen fuel cell?

What are some advantages of hydrogen fuel cells?
Don’t produce as much pollutants as other fuels.
The only waste products are water and heat.
Fuel cells are less expensive than batteries.
Fuel cells store more energy than batteries.
Hydorgen fuel cells do not get less efficient the longer they run.
What are some disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cells?
Hydrogen is a gas so takes up more space to store
Hydrogen is hard to store safely as it is explosive when mixed with air
Hydrogen fuel cells produce a relatively low pd sop several are needed together.