Chemistry - Level 3 Externals (3.4 and 3.6)
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Trigonal bipyramidal
5,5,0 (Symmetrical)
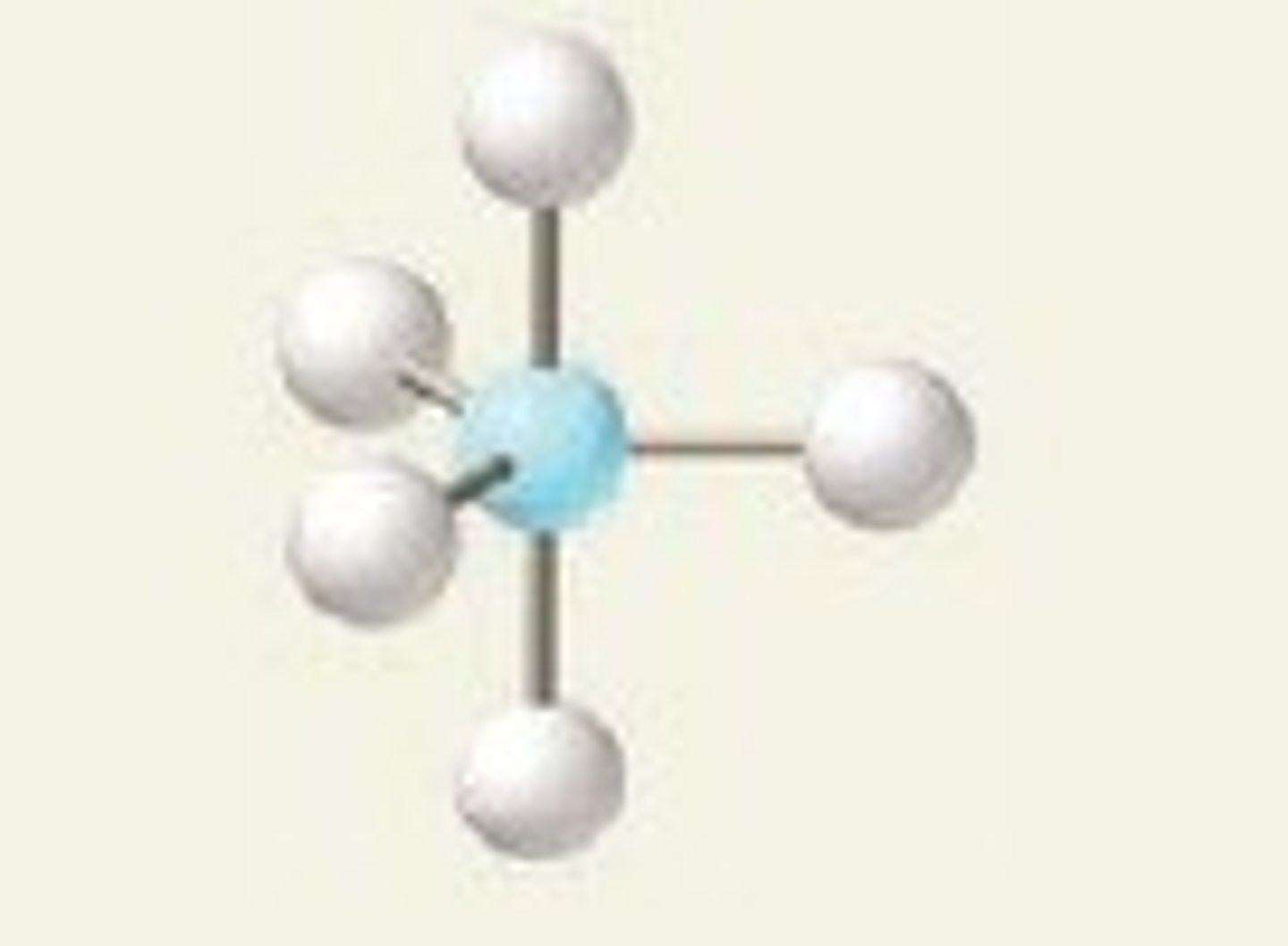
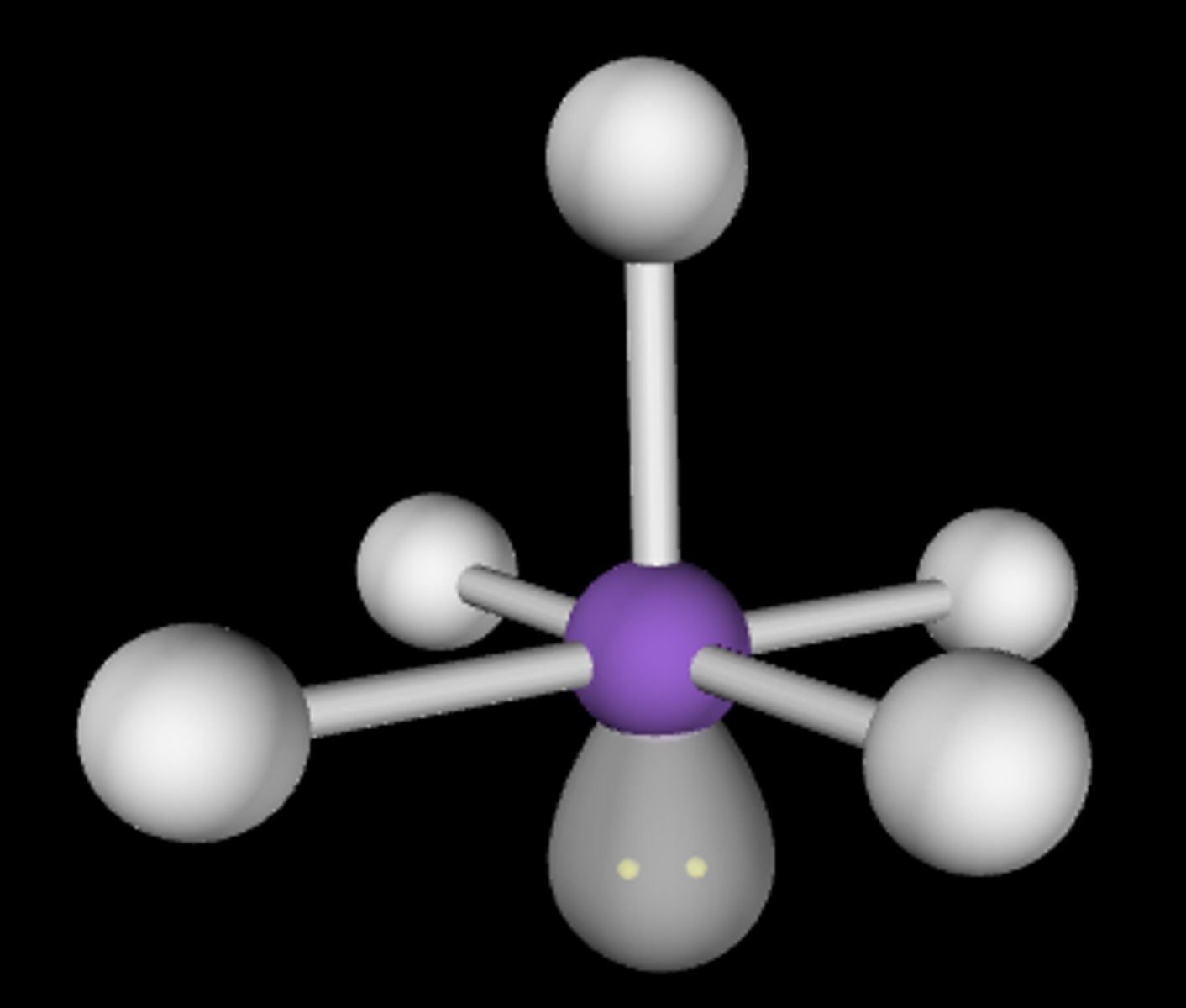
Seesaw
5,4,1 (Unsymmetrical)
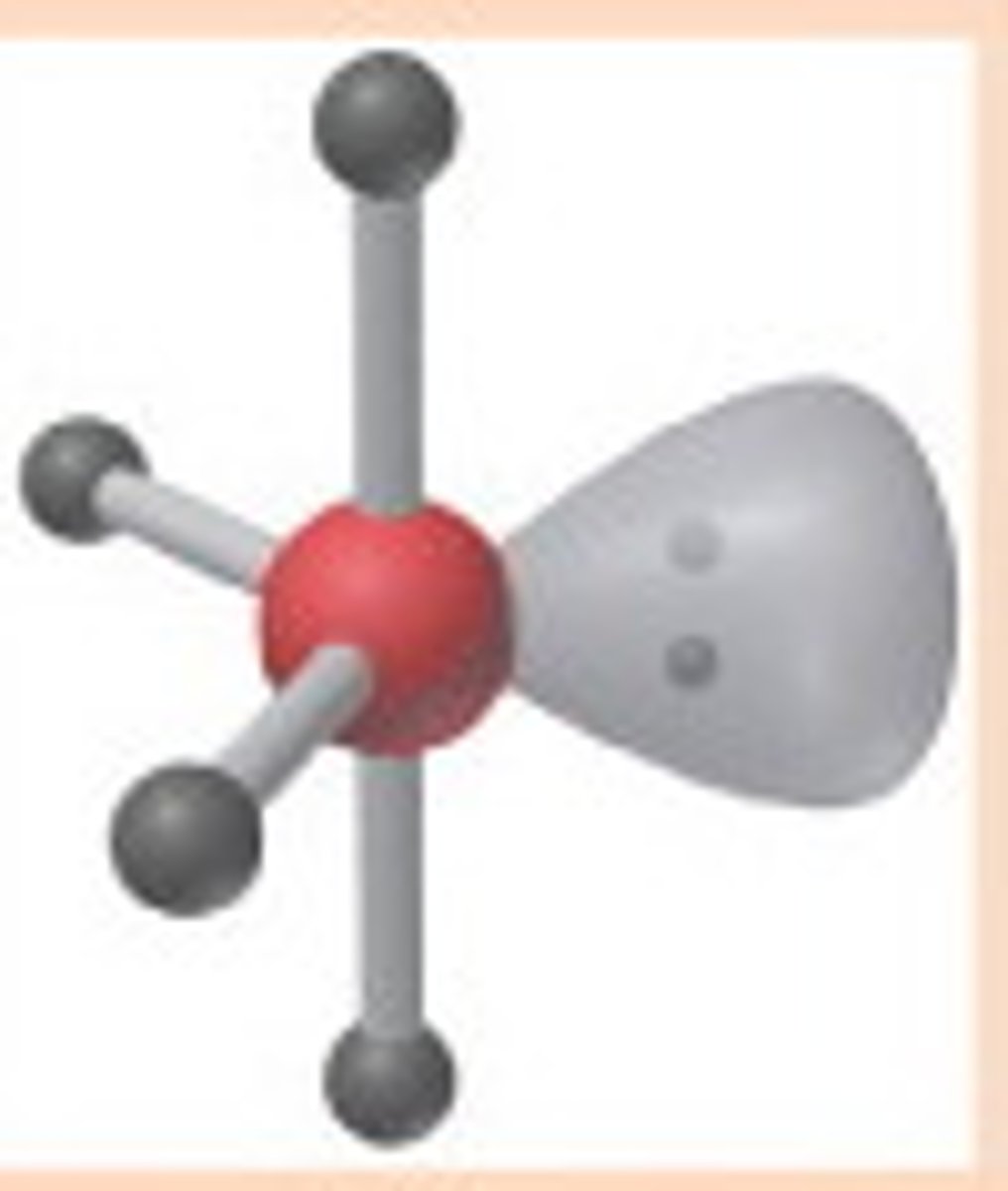
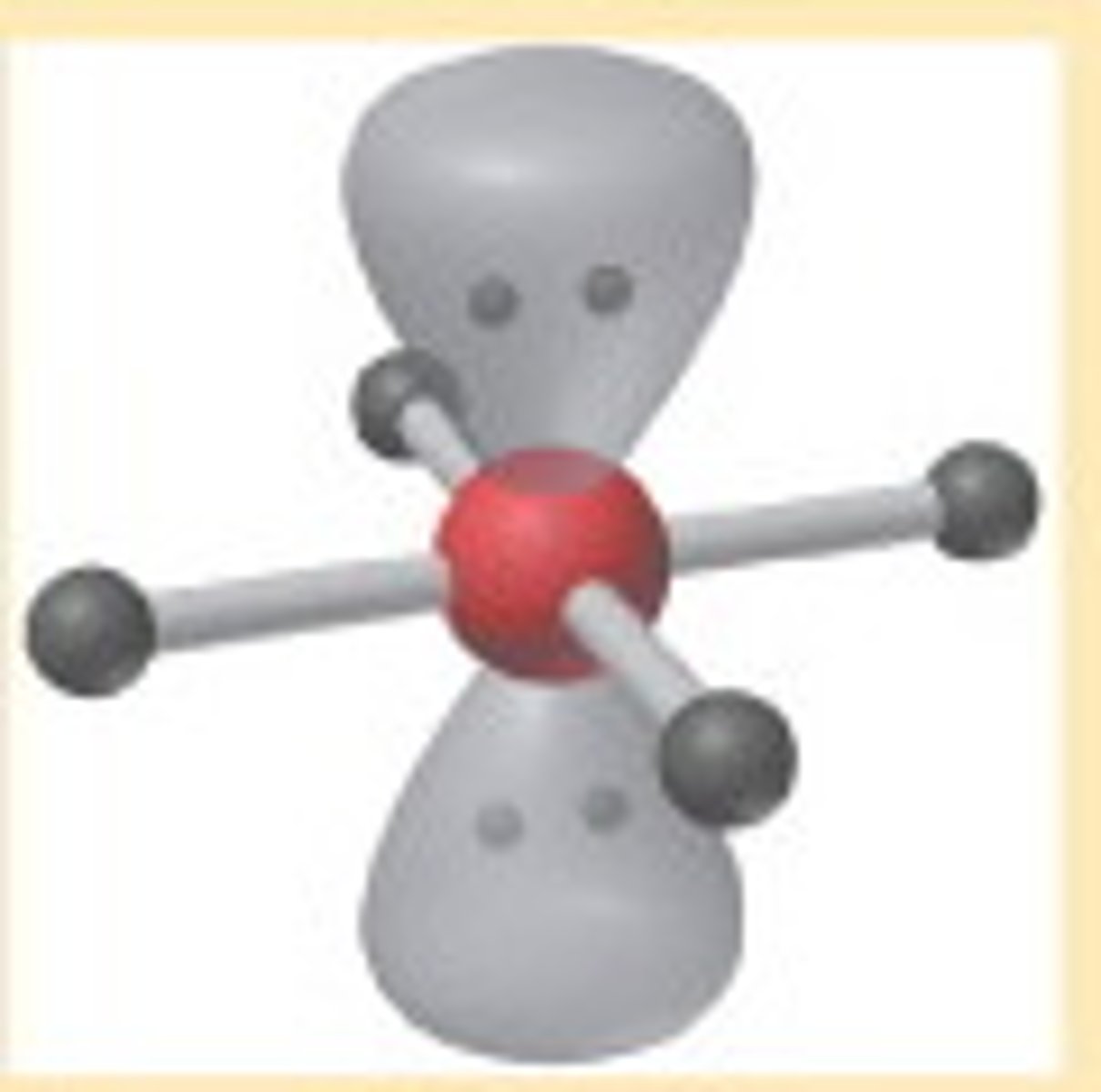
T-shaped
5,3,2 (Unsymmetrical)
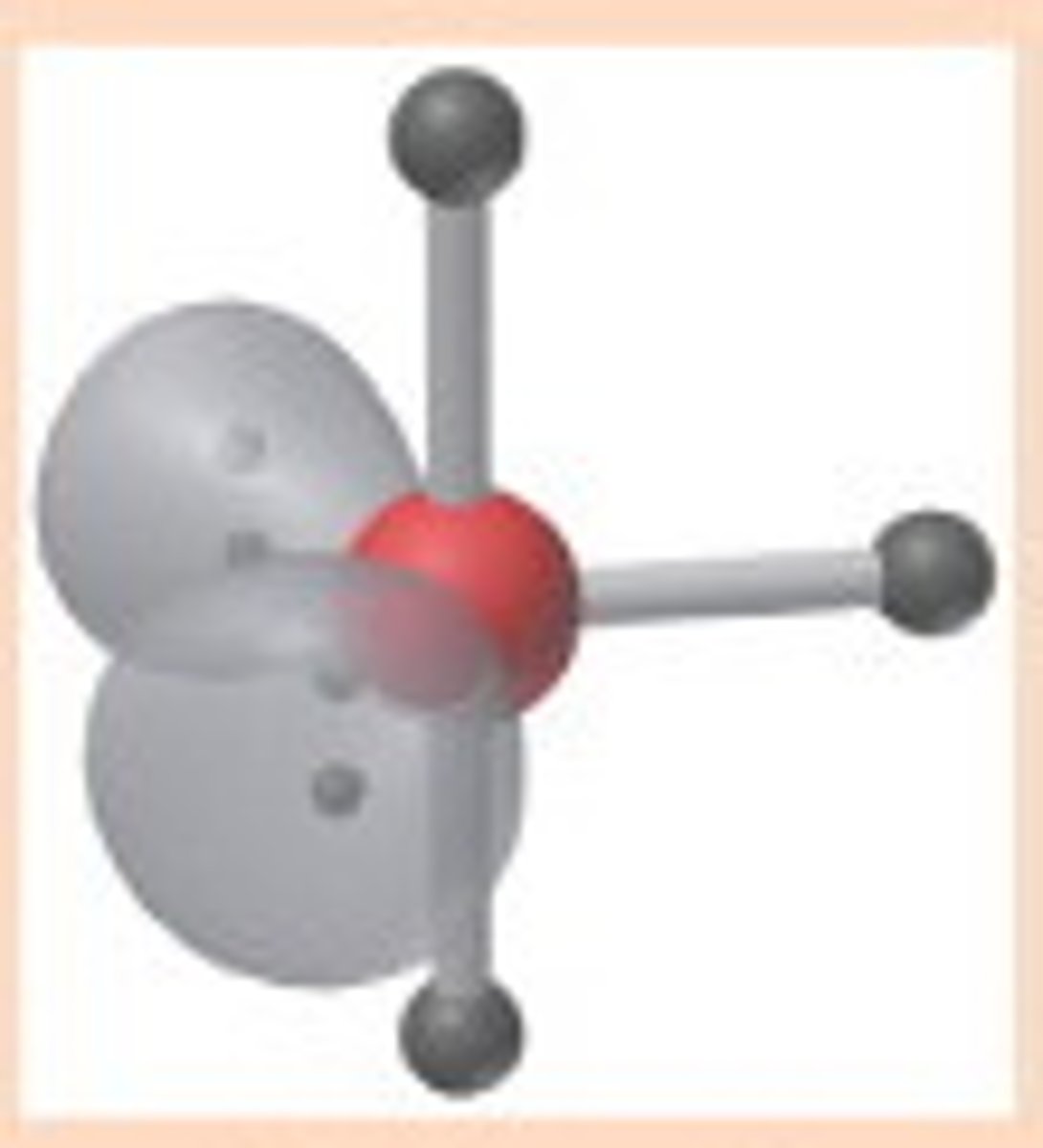
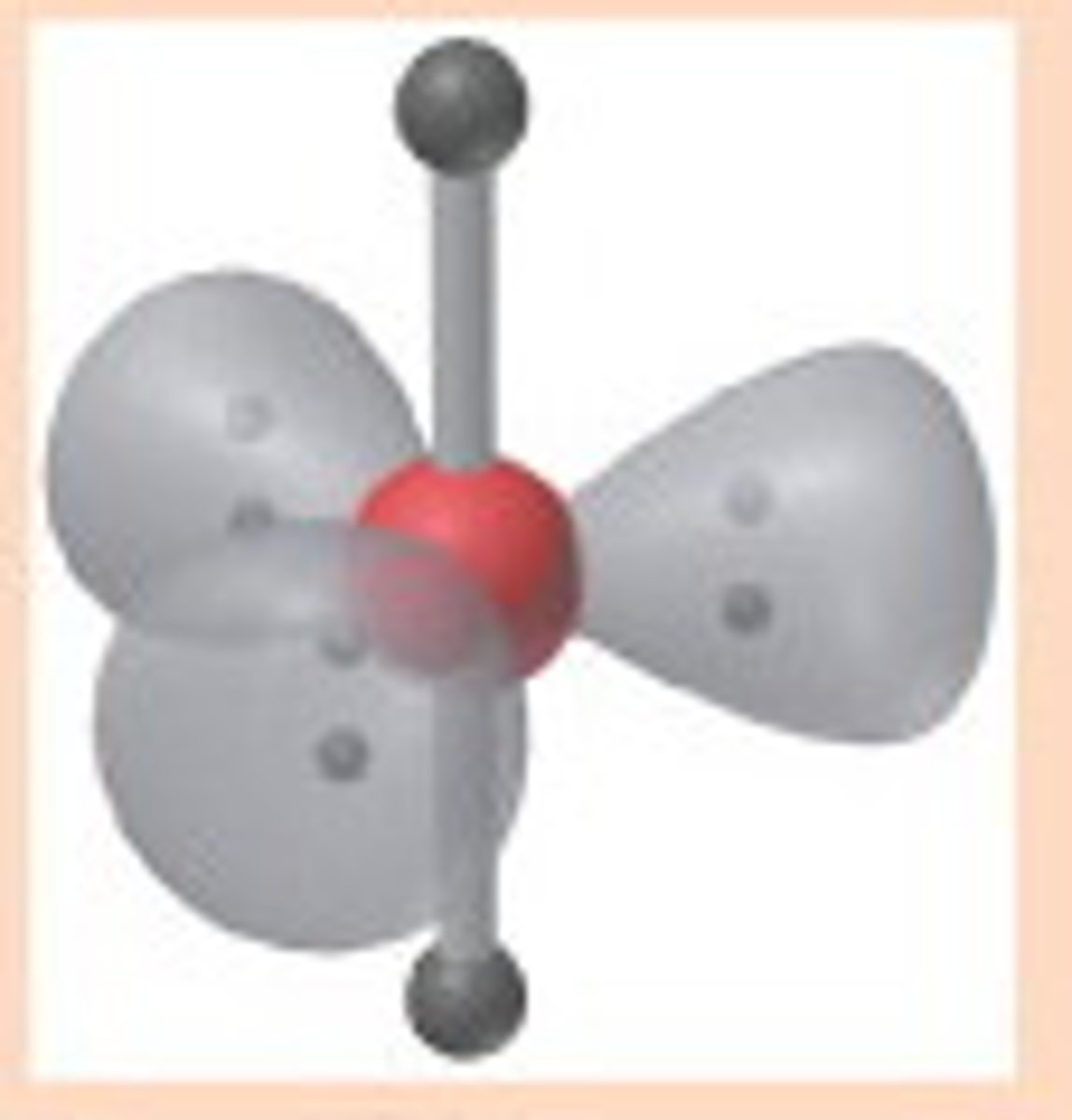
Linear (5)
5,2,3 (Symmetrical)
Octahedral
6,6,0 (Symmetrical)
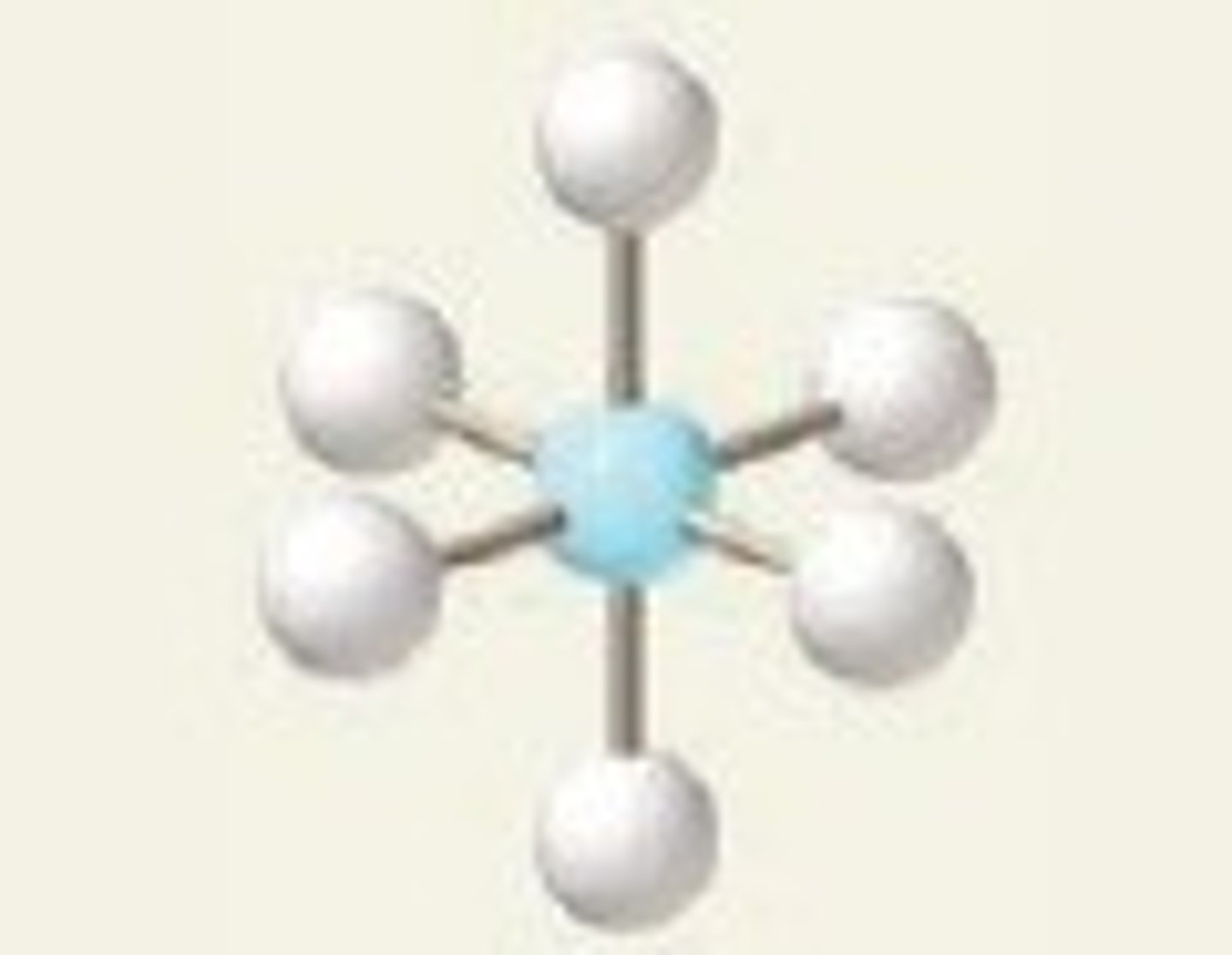
Square-based pyramid
6,5,1 (Unsymmetrical)
Square planar
6,4,2 (Symmetrical)
Repulsion statement
These regions repel to the maximum extent possible, giving a base shape of ___
Why are bonds polar?
Due to a difference in electronegativity
General attractive forces statement
The stronger the total IMF's the more heat energy required to overcome them, and so the higher the bp/ ΔvapHo
H-bonding (between molecules)
Occurs when H is bonded to N/O/F within the molecule causing a large dipole due to the large e-neg difference
pda's
___ is polar so has pda's
tda's
The larger the e- cloud, the stronger the tda's. The larger the surface area, the stronger the tda's.
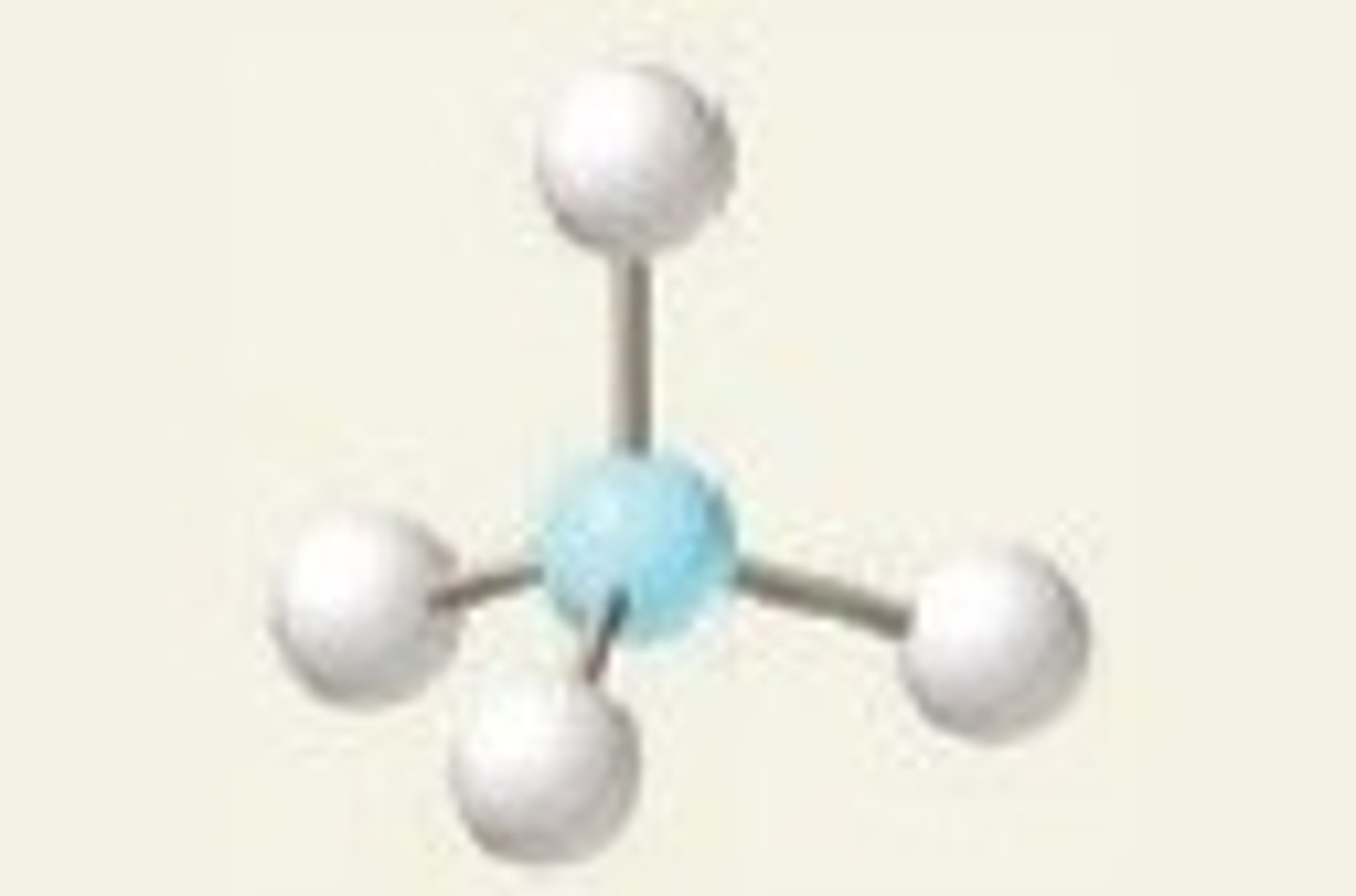
Tetrahedral
4,4,0 (Symmetrical)
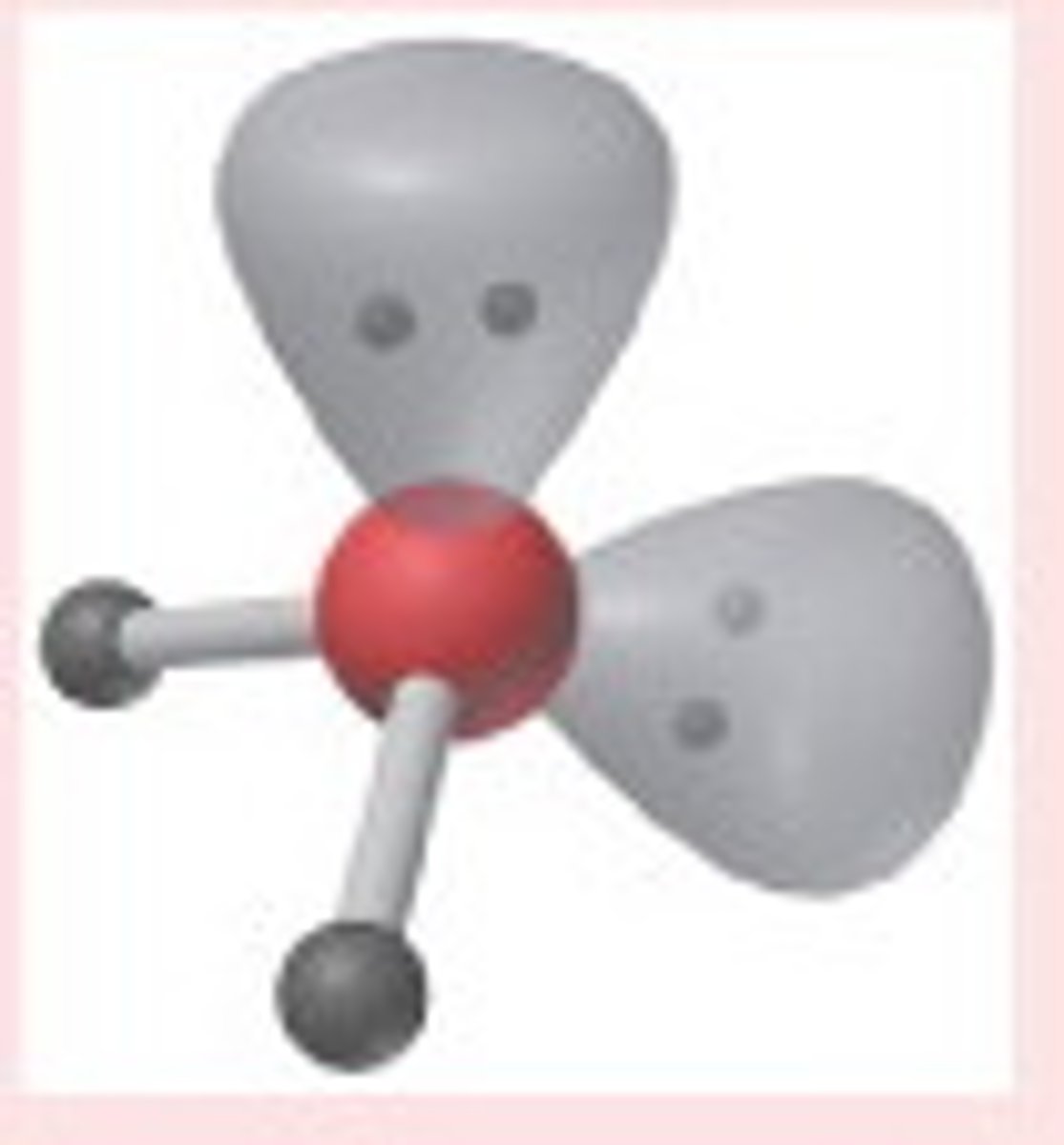
Trigonal pyramidal
4,3,1 (Unsymmetrical)
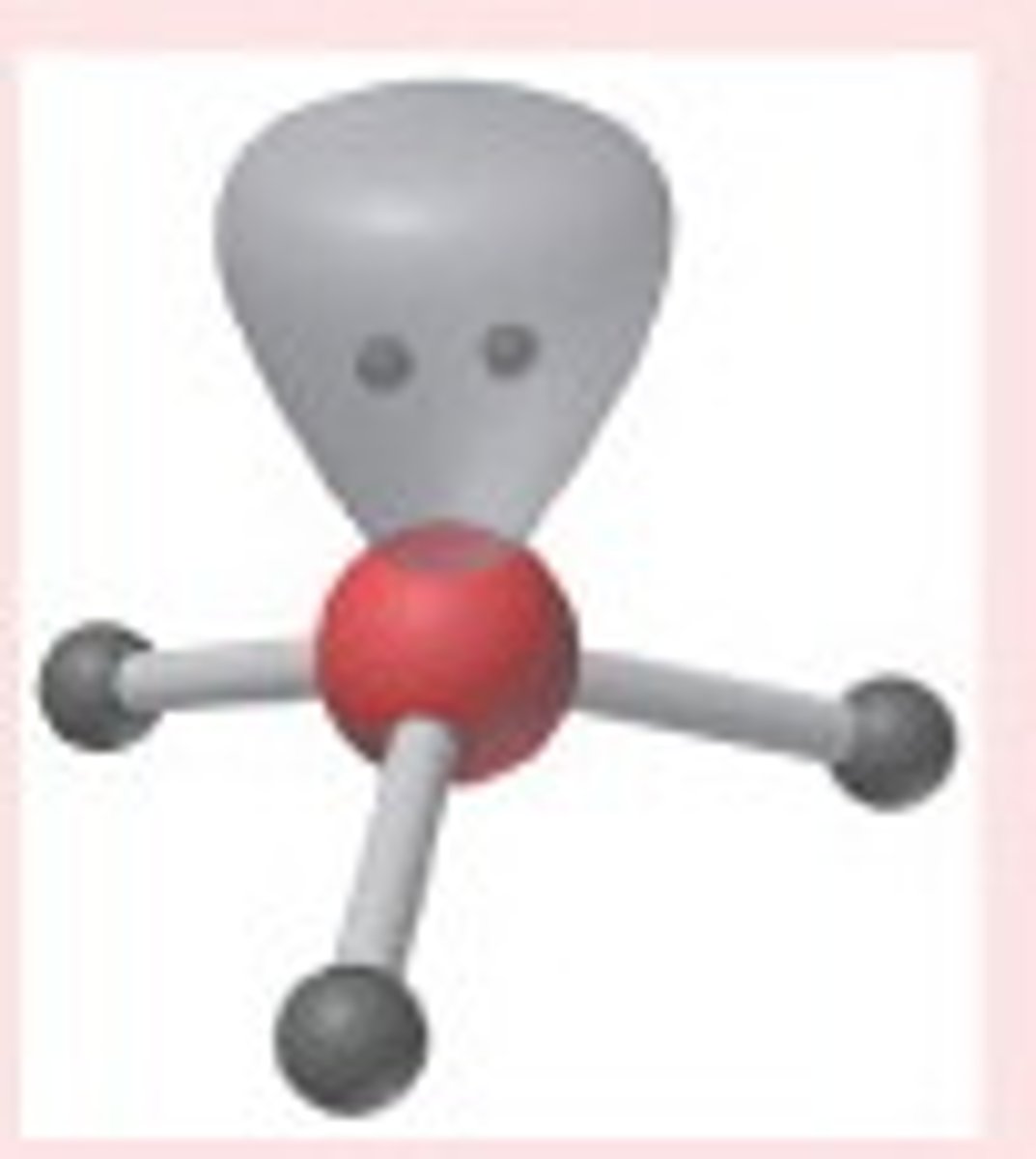
Bent/V-shaped (4)
4,2,2 (Unsymmetrical)
Linear (4)
4,1,3 (Unsymmetrical)
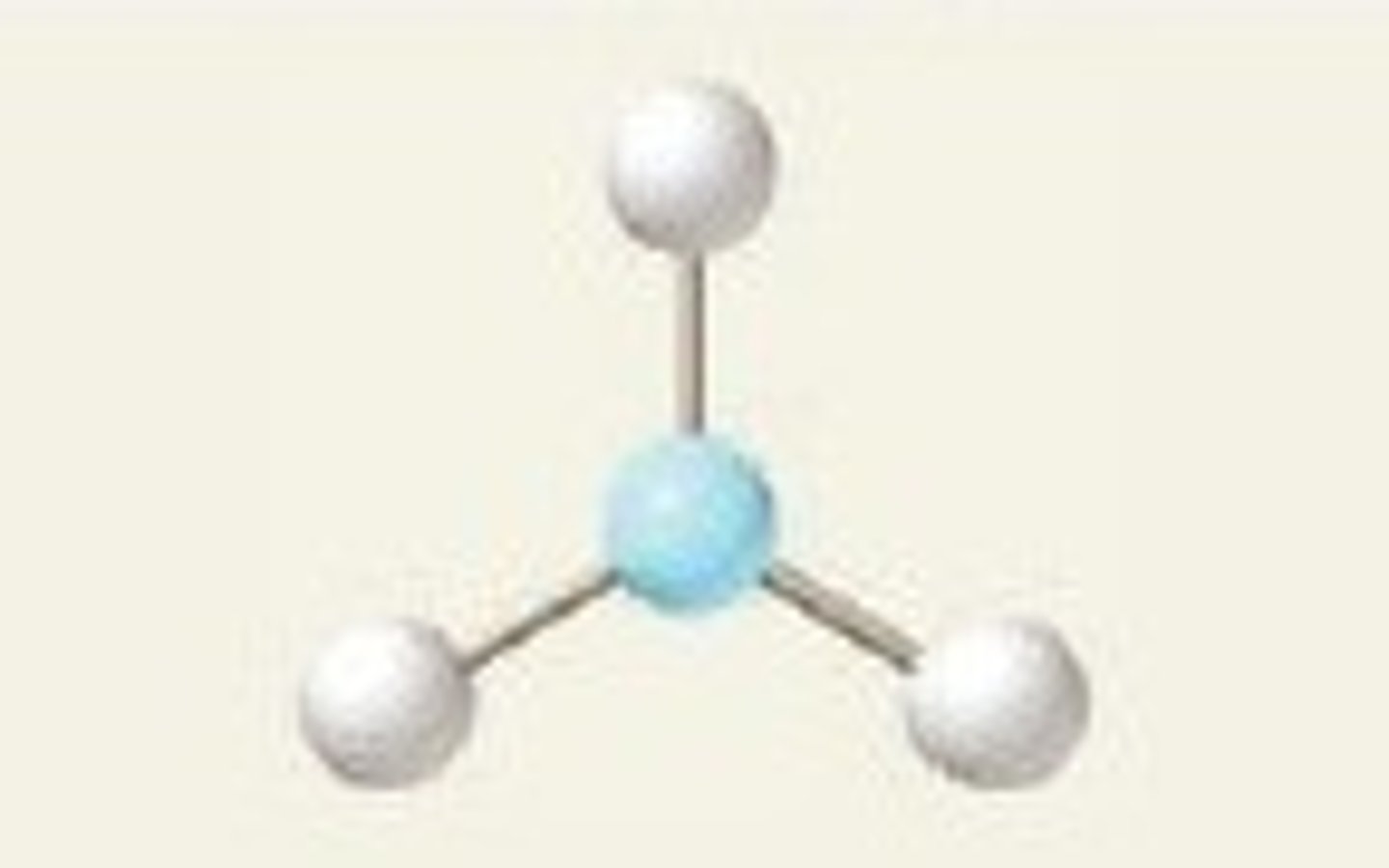
Trigonal planar
3,3,0 (Symmetrical)
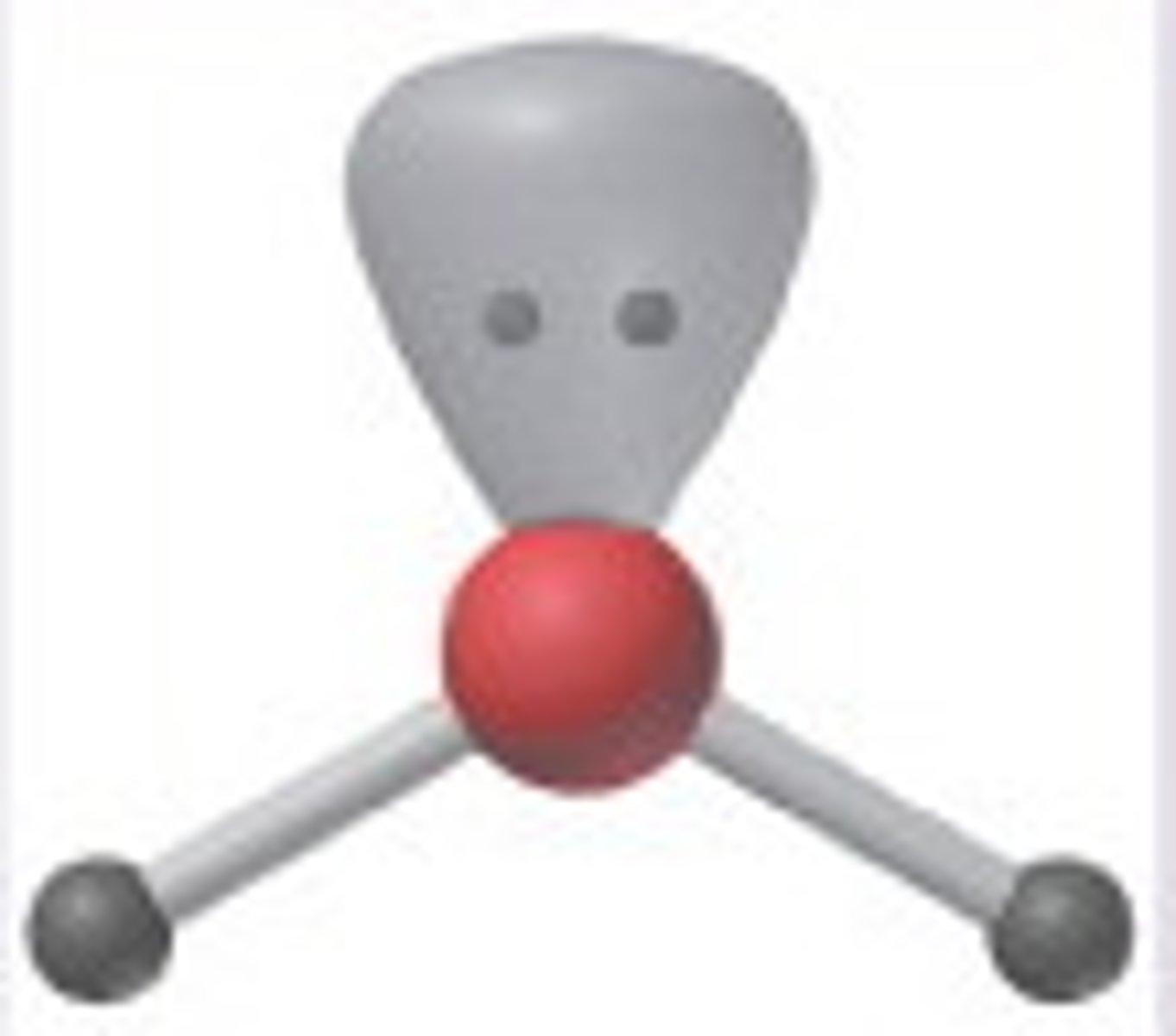
Bent/V-shaped (3)
3,2,1 (Unsymmetrical)
Linear (2)
2,2,0 (Symmetrical)
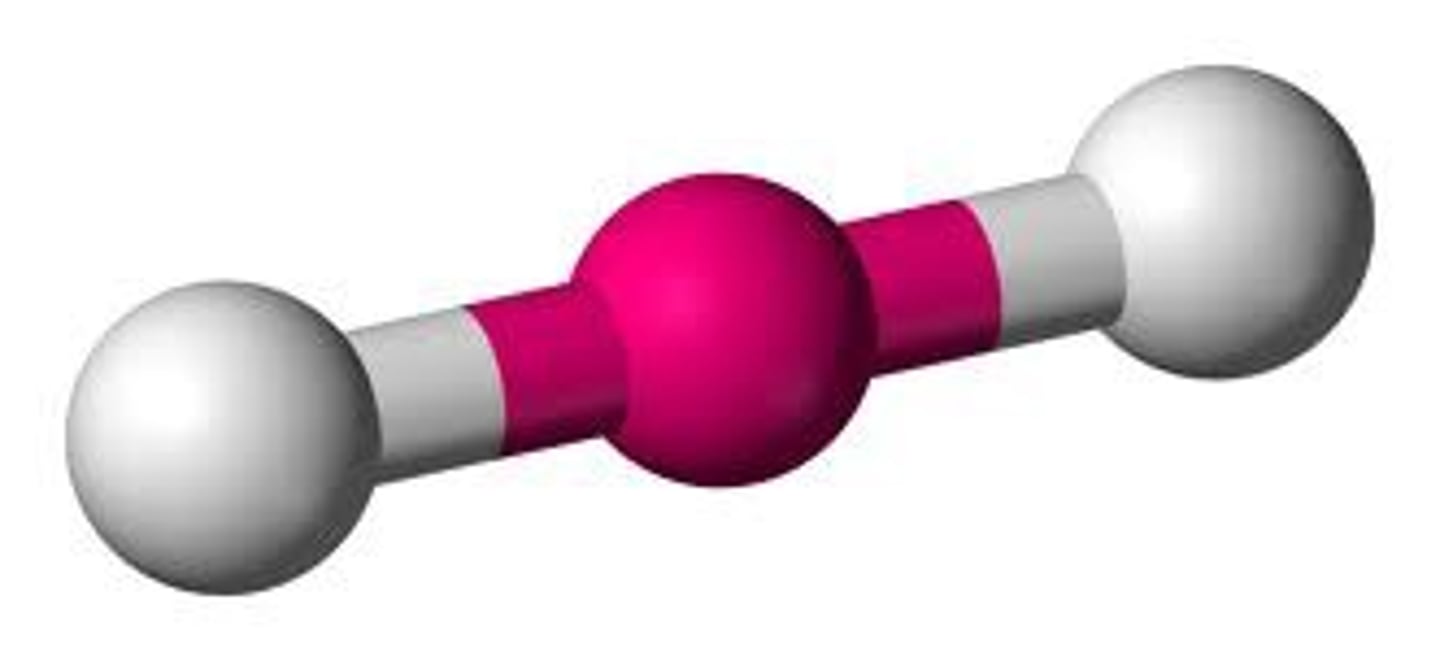
Atomic Radius
The distance between the nucleus and the valence electrons
Electronegativity
The attraction of (the nucleus of) a covalently bonded atom to its bonding electrons
1st Ionisation Energy
The energy required to remove 1 mol of the outermost electrons from 1 mol of gaseous atoms
What factors affect the periodic trends?
The nuclear charge (no. of p+). The no. of e-shells (distance). The no. of inner e-shells (shielding). Which all influence the electrostatic attraction between the nucleus and the relevant electrons.
Shielding (definition)
Repulsions between electron shells
ΔfusHo (standard enthalpy (heat) of fusion)
The energy required to convert 1 mol of solid to 1 mol of liquid at its mp
ΔvapHo (standard enthalpy (heat) of vaporisation)
The energy required to convert 1 mol of liquid to 1 mol of gas at its bp
ΔsubHo (standard enthalpy (heat) of sublimation)
The energy required to convert 1 mol of solid to 1 mol of gas at its sp
Q = m c Δt
Q = heat energy transferred to or from the water m = mass of the water (1mL = 1g) c = specific heat capacity of water Δt = change in temperature of the water
ΔrHo = - Q/n
ΔrHo = the enthalpy change of the reaction - means change sign Q = heat energy transferred to or from the water n = the amount (in moles) of a particular substance
J → kJ NB ΔrHo will be given in kJmol-1 but Q will be calculated in J
Divide by 1000
ΔfHo (standard enthalpy (heat) of formation)
The energy released or absorbed when 1 mol of a substance is formed from its constituent elements at STP
ΔcHo (standard enthalpy (heat) of combustion)
The energy released when 1 mol of a substance burns completely in oxygen at STP
HOFBrINCl
Common elements that exist as diatomic molecules ie H2, O2, F2, Br2, I2, N2, Cl2
ΔfHo (element) = ?
0
Phrases to use with entropy explanations
disorder/ randomness Dispersal of matter & energy
What to look for in entropy of the system
Changes of state Number of particles
Enthalpy vs Entropy
Enthalpy - Energy (heat) Entropy - disorder/ randomness
What to look for in entropy of the surroundings
Whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic
Entropy of surroundings when the reaction is exo
The particles in the surroundings gain kinetic energy so disorder increases
Entropy of surroundings when the reaction is endo
The particles in the surroundings lose kinetic energy so disorder decreases
When is the reaction spontaneous?
When the entropy of the universe (system + surroundings) increases
Word to use when one entropy increases but another decreases
"outweighs"
Silver ion
Ag+
Lead ion
Pb2+
Barium ion
Ba2+
Magnesium ion
Mg2+
Calcium ion
Ca2+
Zinc ion
Zn2+
Nickel ion
Ni2+
Copper ion
Cu2+
Aluminium ion
Al3+
Hydroxide ion
OH-
Fluoride ion
F-
Chloride ion
Cl-
Bromide ion
Br-
Iodide ion
I-
Sulfate ion
SO42-
Chromate ion
CrO42-
Carbonate ion
CO32-
Equation for calculating the new concentration after two solutions have been mixed
cnew = (cold x vold)/vnew
Qs < Ks Will a ppt form?
No
Qs > Ks Will a ppt form?
Yes
When equal volumes of two solutions are combined, what happens to their concentrations?
They are halved.
Which e-'s do we use to calculate the size of the e- cloud for tda's?
All of them (use smaller number next to the element symbol)
NH3
weak base (molecular)
NH3 + H2O ⇌ NH4+ + OH-
HNO3
Strong acid
HNO3 + H2O → H3O+ + NO3-
KOH
Strong base
KOH → K+ + OH-
HCl
Strong acid
HCl + H2O → H3O+ + Cl-
HBr
Strong acid
HBr + H2O → H3O+ + Br-
H2SO4
Strong acid
NaOH
Strong Base
NaOH → Na+ + OH-
NH4+
Weak acid
(Non-neutral salt)
Ch3COO-
Weak base
(Non-neutral salt)
CH3NH3+
Weak acid
(non-neutral salt)
HCO3-
Weak base
(non-neutral salt)
F-
Weak base
(non-neutral salt)
Ch3COOH
Weak acid (molecular)
HF
Weak acid (molecular)
CH3NH2
Weak base (molecular)
Conductivity (str. acid, str. base, salt)
Full dissociation
high [ions]
good conductors
Strong (acid)
Fully dissociates in water
Acids
Proton donor (Increases [H3O+] in water)
Conductivity (wk acid, wk base)
Partially dissociates
Low [ions]
Poor conductors
Proton
H+ or H3O+
Conductivity depends on
[ions]
pH (str. base)
Fully dissociates
High [OH-]
Low [H3O+]
High pH
Amphiprotic
a species that can donate or accept a proton
Weak (acid)
Partially dissociates in H2O
Bases
Proton acceptor
pH (str. acid)
Fully dissociates
High [H3O+]
Low pH
pH (wk. acid)
Partially dissociates
Lower [H3O+]
Higher pH
Conjugate acid/base pairs
Species that differ by 1xH+
Don't include water when...
It's a Salt or a Strong Base