Perfect competition
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What are the four types of market structures?
Perfect competition
monopolistic competition
oligopoly
monopoly
What is the main objective for all firms in all different market structures?
Profit maximisation
What are the characteristics of perfect competition?
Homogenous products, different producers’ products are identical
Perfect knowledge, consumers and producers are full aware of what is being offered
Firms are price takers, as there are so many firms.
What does the SR refer to in perfect competition?
This refers to an equilibrium position that will not last, there is a tendency to change.
What does the LR refer to in perfect competition?
This refers to an equilibrium position that will last ceteris paribus, there is no tendency to change.
How does the market operate?
Firms are price takers, meaning any price above means customers will go elsewhere but any price below will result in reduced revenue. Therefore, results in a horizontal demand curve for the firm, implying there are perfect substitutes.
What does the diagram for short run equilibrium (supernormal profit) look like?
Firms are price takers so they have to accept P1, profit maximisation occurs at MR=MC. The distance between x and z represents the profit per unit.
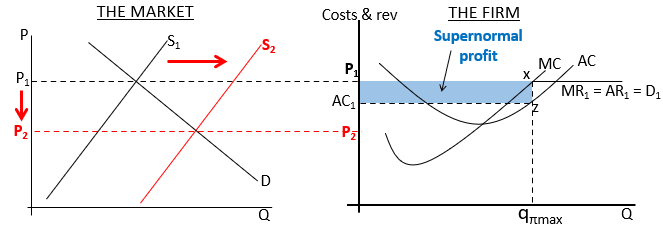
Why is supernormal profit only available in the short run?
Supernormal profits act as a signal for market entry as firms are attracted to the market and therefore the supply shifts to the right leading to a lower market price.
What does the diagram for short run equilibrium (loss) look like?
Market entry shifts the supply curve to S2 leading to a lower market price and a move down the demand curve to D2.
AR curve has fallen below the AC curve, the firm will produce where MC=MR with output Q2 at loss minimising.
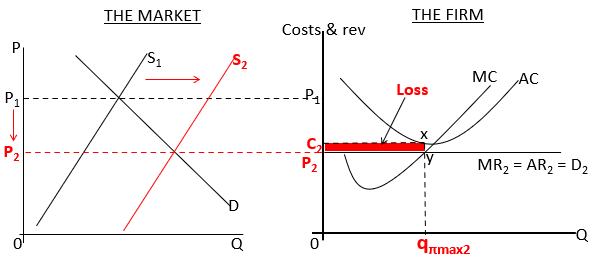
Why will a loss in the short run equilibrium not impact all firms?
It will impact the most inefficient firms, those who have higher costs, the market signal in this case is for firms making a loss to leave.
Why is a short run equilibrium loss always the end result?
When the most inefficient firms exit the market due to losses this will push supply left and prices up again resulting in more firms being attracted to the market and so on.
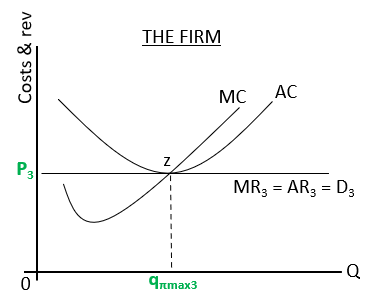
What does the diagram for long run equilibrium (normal profit) look like?
AC=AR therefore the firm will only make a normal profit , at this level there is neither a signal for market entry or exit. Unless market demand or supply changes the market and firm will remain at this level of output.
What are the benefits of perfect competition?
MC=P, allocatively efficient
firms producing at minimum AC, productively efficient
customers get the goods that they want so their welfare is maximised at the lowest unit cost possible
What is allocative efficiency?
Occurs when resources are allocated in such a way that the welfare of society is maximised, MC=P.
What is meant by welfare?
The positive difference between the benefits and costs of an economic activity.
When should a firm close in the short run?
In the SR a firm only needs to make enough revenue to cover its variable costs because its fixed costs have already been covered.
What is the level of output called in which firms are unable to pay its variable costs?
This is referred to as the short run shut down position.
Why are fixed costs referred to as ‘sunk’?
As they are already paid in advance.
How is a shut down of a firm represented in a diagram?
In the SR, market is in equilibrium at P1 with supernormal profit, demand decreases lowering P to P2 but it can still cover AVC
however if demand doesn’t return the firm will eventually shut down because it can no longer afford to cover ATC
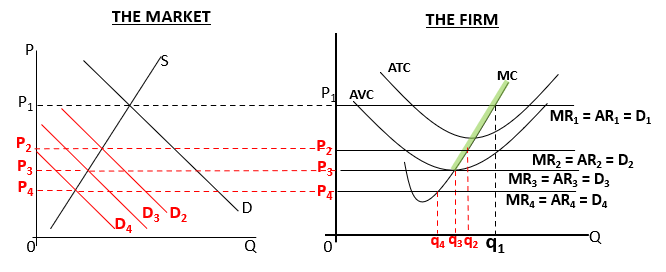
What is the evaluation of shut down price?
If the firm believes that the fall in demand is temporary, firms may prefer to keep producing
If a firm sees AR is smaller than AC then they may cut costs not shut down
What are the advantages of perfect competition?
Consumers receive low prices, increases consumer surplus
Allocative efficiency occurs in SR and LR
Productive efficiency is achieved in the LR, consumers get goods at the lowest possible cost.
What are the disadvantages of perfect competition?
Products are identical, meaning that customers lack meaningful choice
Absence of LR supernormal profits
Firms are productively inefficient in the SR