Breeding Management - Equine Therio
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Mare Reproductive tract
image
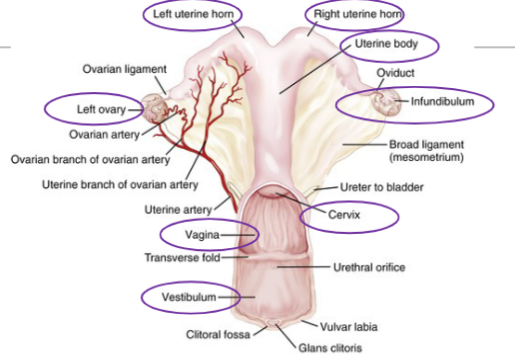
Mares are seasonally polyestrous
Breeding season is spring and summer (long day breeders)
Multiple ovulations per year
Optimal birth season for foals
maximum survival occurs with birth in late spring and summer
4 seasons for the mare
Winter anestrus
Vernal transition period
Physiologic breeding season
Autumnal transition period
Winter anestrus
Centers around the winter solstice: December 21-22
Vernal transition period
Centers around vernal equinox: March 21-22
Physiologic breeding season
Centers around summer solstice: June 21-22
Autumnal transition period
Centers around autumnal equinox: September 21-22
Use of lights to increase day length early in spring
Vernal Transition and estrus occur sooner
Especially helpful when breeding in the northern parts of the northern hemisphere
When early foals are desired for production or racing reasons
!6 hours total daylight daily - adding stall lights timed on from 6pm to midnight
Mare puberty
First ovulation
occurs between 15-24 months - second summer of life
Estrous Cycle
The length of one ovulation to the next
average cycle length is 21 days (range 18-24)
2 phases of estrous cycle
Estrus and Diestrus
Estrus
FOLLICULAR phase
Mare is receptive to stallion during the 4-7 days prior to ovulation
Diestrus
LUTEAL phase
Mare is not receptive to stallion from ovulation to beginning of estrus phase
reproductive tract prepares for pregnancy
Reasons for Mare BSE
early estrus
Determine if mare is fit to breed
Maximizes chances of pregnancy and healthy foal
Especially important with maiden mares, barren mares, older mares, mares with a history of loss
Mare BSE includes
Identification - name, number
Complete history - previous breeding? Any losses, previous pregnancy?
Examination
Cardiothoracic auscultation?
Lameness?
Osteoarthritis?
Temperament?
Conformation
Perineal inspection
Vaginal exam
Trans-rectal Palpation and ultrasound
Uterine culture and cytology
Uterine Biopsy
Mare - Perineal Inspection
Vulva close to vertical
Closely apposed
No discharge, scars
No gaping with gentle pressure on either side
Mare - Vaginal Exam
Speculum exam
Visualize vestibule, vagina, external cervical os
Direct (digital) exam
Evaluation of tears or adhesions
Evaluation of fibrosis or incomplete dilation
Mare - Trans-rectal Palpation and Ultrasound
Vagina (masses, air)
Cervix (position, cysts, masses)
Uterus (tone, size, fluid, cysts, pregnancy)
Ovaries (size, shape, follicles, CL, cysts, masses)
Mare - Uterine culture and cytology
Sterile swab of uterine endometrium (lining)
Submit for bacterial culture
Examine cells for cytology
Mare - Uterine Biopsy
Informative with barren, multiparous, older mares
Category I, IIa, IIb, III
Uterine biopsy category I
> 70% pregnancy
Uterine biopsy category II
30-70% pregnancy
Uterine biopsy category III
<10% pregnancy
Stallions of Seasonal long day breeders
20-50% more spermatozoa produced May-August than September-April
Artificially advance the onset of long day photoperiod
What time of year do Stallions produce more spermatozoa?
May to August
Stallion - Puberty
Occurs in the stallion by 18 months, may be as early as 12 months
Increased muscle mass, increased jowl size, and male behaviors
Sperm count increases with testicular size in mature stallion
Testicular Descent
Typically at birth or just after
May be delayed until 2-6 months of age (still normal)
Can descend between 6-24 months of age: cryptorchid
Cryptorchid
Where one or both of the testes fail to descend from the abdomen into the scrotum
Spermatogenesis
Hormonal control trough testicles, hypothalamus, and pituitary gland
Occurs in cycles/waves
57 days to create a mature spermatozoon
57 days
Days to create a mature spermatozoon
Thermoregulation of testes
Function of scrotum and spermatic cord
Fever over 104.9 leads to decreased concentration and morphology
occurs from 40×70 days after temperature elevation
Prolonged exposure - 3 months to return to normal
Stallion BSE
Identification
Complete history
Physical exam
Heart, eyes, lameness
External genitalia
Caution with tranquilizers
Wash penis and prepuce
Examine for masses
Bacteriologic culture
Other STD testing (EVA)
Stallion - External genitalia exam
Scrotal width, consistency
Penis - erect examination
Acepromazine
Tranquillizer not typically used with Stallions
Semen Evaluation
Volume
Motility (total progressive)
Velocity
Concentration
Morphology
Longevity studies in extenders
Stallion on-site breeding
Pasture Breeding
Hand breeding
Serial
Veterinary
Pasture Breeding
Turn out mare and stallion together
limited information
Hand Breeding - Serial
Breed every other day from Day 2 estrus
Hand Breeding - Veterinary
Breed prior to ovulation
Stallion off-site breeding
Stallions are collected every other day
Semen is extended, cooled and shipped
Mare is monitored via ultrasound examination
Insemination
Post-Breeding examination
Ovulation
Fluid clearance
When should insemination occur?
Between 12 hours prior and 48 hours post-ovulation; ideally within 12 hours of ovulation
Day of first ultrasound
14-16 days post-ovulation
Ultrasound exams
14-16 days - looking for twins
25-30 days - heartbeat
45-60 days - sexing
Pregnant Mare Housing
Separated
Moderate exercise
Routine care
Pregnant Mare vaccinations
Rhinopneumonitis (months 3, 5, 7, 9)
All spring vaccines boostered at 4-6 weeks pre-foaling
Pregnant Mare Deworming
Safe, administer based on FEC, exposure, and at foaling
Pregnant Mare Nutrition
65% foal birth weight gained in last 3 months of gestation
Lactation - highest nutritional requirements
Do not let clients overfeed!
Routine Care for Pregnant mares
Ultrasound exams
Housing
Vaccinations
Deworming
Nutrition
Preparing for Parturition
Suitable location for foaling
Udder cleansed with mild detergent
Wash perineal region
Caslicks removal
Suitable location for foaling
4-6 weeks prior to due date
Clean, dry, protection against elements
14 ×16 foot stall with straw over shavings
Caslicks
Surgical procedure where the upper part of a mares, vulvar lips are partially stitched closed to create a tight seal, preventing air and fecal cntamination from entering the reproductive tract.
This must be cut open before foaling!
Post-Partum changes
Waxing of teats
Milk Secretions
Vulvar and pelvic ligament laxity
Udder enlargement
Waxing of teats
Early colostrum formation
Typically 1-4 days prior to foaling
Milk Secretions
Milk changes from thin straw-colored to milky white
Yellow-orange as colostrum forms
Udder enlargement
Typically significant growth in final 2 weeks
Monitoring Parturition
Sleep in the barn
Video
Sound monitors
Various foal alert systems
foal-alert system
birth-alarm system
Stage 1 of Parturition
30 minutes to 4 hours
Restlessness and signs of colic
Uterine contractions
Fetal repositioning
Proper fetal position
Anterior longitudinal dorsalsacral with head resting on extended metacarpals
Stage 1 - Preparation of the Mare
Clean udder
Tail wrapped
Perineal area scrubbed
Remove extraneous people - helps mare relax
Stage 2 of parturition
Fetus passes into birth canal
Mare lays down, strains in lateral recumbency
Rupture of the chorioallantoic membrane
20-30 minutes for this stage
steady progression
Maximum time - 70 minutes
Rupture of the chorioallantoic membrane
Embryonic membrane
Order:
Extended legs
Nose
Head and shoulders
followed by hips
The three P’s
Presentation
Position
Posture
Presentation
Relationship of the long axis of the foal to the long axis of the mare
(longitudinal)
Position
Relationship of the dorsum of the fetus to the maternal pelvis
(dorsosacral)
Posture
Relationship of the fetal extremities to the fetal body
(had resting on extended metacarpals)
Stage 3 of parturition
Delivery of the placenta/fetal membranes
30 minutes to 3 hours
Tie up above mare’s hocks
Beginnings of uterine involution
Decrease in uterine size occurs within 12-24 hours
Uterine fluid mostly expelled by 24-48 hours
Uterine Involution
Shrinkage of the uterus back to its normal size after birth
Post-Partum exam - Mare
Cleanse udder
Ensure adequate milk production
Colostrum
Examine perineal area
ensure vulva and anus intact
Evaluation bruising and edema
Rectovaginal fistula
Post-Partum exam - Placenta
Lay out on clean floor
Examine inside-out and right-side in
Can fill with water
Critical that entire placenta, including tips of horns, is present
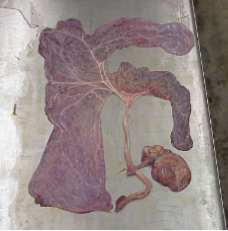
What is this?
An intact placenta
Foaling complications
Red Bag
Dystocia
Retained placenta
Red Bag
Premature placental separation
Chorio-allantois must be ruptured immediately
Assisted delivery — foal will rapidly become hypoxic and anoxic
Associated with placentitis, twinning, inappropriate induction methods, unknown causes

Dystocia
Lack of progression in first or second stages
Medical emergency
Fetal cause of Dystocia
Typically some sort of malpresentation
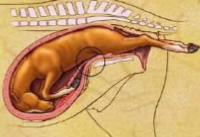
Maternal causes of dystocia
Inadequate pelvic size or pelvic abnormality
Rupture of prepubic tendon
Abdominal hernia
Uterine inertia
Uterine torsion
Cervical scarring
Uterine inertia
Failure of uterus to contract effectively during foaling, leading to prolonged labor or failure to pass the foal
Retained placenta
Fetal membranes not expelled within 3 hours
Most common post-partum complication
Complications of Retained placenta
Metritis
Septicemia
Laminitis
Mare death
3 Function genital seals of the Mare
The vulva
The vulvo-vaginal constriction (vestibular seal)
The cervix