CHEM 102L Final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:07 PM on 4/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
189 Terms
1
New cards
LAB SAFETY
2
New cards
Which of the following precautions is important when using a Bunsen burner or Meker burner? Select all that apply.
\
Choice 1 of 6:Set up your work space so that wires and cables cannot accidentally make contact with the flame or hot glassware and melt.
\
Choice 2 of 6:Always tie back hair, even long bangs, that might accidentally come in contact with the flame.
\
Choice 3 of 6:Set up the work space so that flammable materials - notebooks, paper towels, other reagents, etc. - are far away from the burner to prevent them coming in contact with the hot surface.
\
Choice 4 of 6:Set up your work space with the burner in a secure location away from the edge of the bench so that you won't accidentally bump it and spill hot liquids.
\
Choice 5 of 6:Remember that any glassware heated by the burner will look the same when hot as cold, and will not cool down until well after the burner has been shut off.
\
Choice 6 of 6:Never leave an open flame unattended, even for a brief time.
\
Choice 1 of 6:Set up your work space so that wires and cables cannot accidentally make contact with the flame or hot glassware and melt.
\
Choice 2 of 6:Always tie back hair, even long bangs, that might accidentally come in contact with the flame.
\
Choice 3 of 6:Set up the work space so that flammable materials - notebooks, paper towels, other reagents, etc. - are far away from the burner to prevent them coming in contact with the hot surface.
\
Choice 4 of 6:Set up your work space with the burner in a secure location away from the edge of the bench so that you won't accidentally bump it and spill hot liquids.
\
Choice 5 of 6:Remember that any glassware heated by the burner will look the same when hot as cold, and will not cool down until well after the burner has been shut off.
\
Choice 6 of 6:Never leave an open flame unattended, even for a brief time.
all of the above
3
New cards
In some circumstances, materials that are being heated in the lab could catch fire. If a flammable substance in a beaker should catch fire while you are working but the flames are relatively contained, what is a simple method for extinguishing the flame?
\
Choice 1 of 3:Turn off the heat source immediately, and use a watch glass to cover the beaker and minimize the oxygen around the flame.
\
Choice 2 of 3:Use the chemical fire extinguisher located in the lab. Pull the pin, aim the nozzle into the beaker, and pull the lever.
\
Choice 3 of 3:Use water from the sink nearest the bench to douse the flames.
\
Choice 1 of 3:Turn off the heat source immediately, and use a watch glass to cover the beaker and minimize the oxygen around the flame.
\
Choice 2 of 3:Use the chemical fire extinguisher located in the lab. Pull the pin, aim the nozzle into the beaker, and pull the lever.
\
Choice 3 of 3:Use water from the sink nearest the bench to douse the flames.
Choice 1 of 3:Turn off the heat source immediately, and use a watch glass to cover the beaker and minimize the oxygen around the flame.
4
New cards
What is your BEST resource for understanding the nature of the chemical hazards of materials you work with in lab?
\
Choice 1 of 3:Your TA, or your instructor you visit during office hours.
\
Choice 2 of 3:The label on the reagent bottles found in the fume hood.
\
Choice 3 of 3:Safety Data Sheets (SDS) that should be consulted before coming to lab each week.
\
Choice 1 of 3:Your TA, or your instructor you visit during office hours.
\
Choice 2 of 3:The label on the reagent bottles found in the fume hood.
\
Choice 3 of 3:Safety Data Sheets (SDS) that should be consulted before coming to lab each week.
Choice 3 of 3:Safety Data Sheets (SDS) that should be consulted before coming to lab each week.
5
New cards
When reading the label on a reagent container, what are the three most important pieces of information?
\
Choice 1 of 6:Chemical formula
\
Choice 2 of 6:Concentration
\
Choice 3 of 6:CAS Number
\
Choice 4 of 6:Hazard warning(s)
\
Choice 5 of 6:Color
\
Choice 6 of 6:Name
\
Choice 1 of 6:Chemical formula
\
Choice 2 of 6:Concentration
\
Choice 3 of 6:CAS Number
\
Choice 4 of 6:Hazard warning(s)
\
Choice 5 of 6:Color
\
Choice 6 of 6:Name
choice 1, 4, 6
6
New cards

This is appropriate for lab. (Assuming proper PPE will be worn)
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
Choice 2 of 2:False
7
New cards
Your lab partner accidentally spills some acid on his wrist and watchband. You should: Select all that apply.
\
Choice 1 of 4:Take him to the safety shower, and make sure he stands under it for at least 15 minutes to be sure all hazardous material has been washed away.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Let the TA inspect his wrist to see if it is okay.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Remove the watch and watchband immediately, and rinse his wrist for at least 15 minutes to be sure all hazardous material has been washed away.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Rinse the watch band before allowing him to put it back on.
\
Choice 1 of 4:Take him to the safety shower, and make sure he stands under it for at least 15 minutes to be sure all hazardous material has been washed away.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Let the TA inspect his wrist to see if it is okay.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Remove the watch and watchband immediately, and rinse his wrist for at least 15 minutes to be sure all hazardous material has been washed away.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Rinse the watch band before allowing him to put it back on.
choice 2, 3, 4
8
New cards

This is appropriate for lab. (Assuming proper PPE will be worn)
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
Choice 2 of 2:False
9
New cards
When the procedure calls for making a more dilute solution of an acid, or mixing an acid with other solutions, what is the correct order of steps?
\
Choice 1 of 3:Always Add Acid - Either add all of the water or non-acid component first, or add a significant portion, before adding the acid to the mixture. This helps to minimize the heat generated, which could otherwise create dangerous fumes or reactions.
\
Choice 2 of 3:Always Add Acid - the acid should be added first and then the other materials to prevent a dangerous reaction.
\
Choice 3 of 3:Neither of these methods is safe.
\
Choice 1 of 3:Always Add Acid - Either add all of the water or non-acid component first, or add a significant portion, before adding the acid to the mixture. This helps to minimize the heat generated, which could otherwise create dangerous fumes or reactions.
\
Choice 2 of 3:Always Add Acid - the acid should be added first and then the other materials to prevent a dangerous reaction.
\
Choice 3 of 3:Neither of these methods is safe.
Choice 1 of 3:Always Add Acid - Either add all of the water or non-acid component first, or add a significant portion, before adding the acid to the mixture. This helps to minimize the heat generated, which could otherwise create dangerous fumes or reactions.
10
New cards
Suppose a beaker of solid reagent drops onto the bench and cracks. Which of the following represents the correct disposal:
\
Choice 1 of 3:To minimize the risk of injury, all materials should be added to the glass waste.
\
Choice 2 of 3:To the extent possible, solid reagent should be added to the solid waste container and broken glass should be added to the glass waste. Hazardous materials should never be added to the glass waste, and broken glass should only be allowed in the solid waste with the TA's approval.
\
Choice 3 of 3:To maximize the correct disposal of hazardous material, all materials should be added to the chemical solid waste.
\
Choice 1 of 3:To minimize the risk of injury, all materials should be added to the glass waste.
\
Choice 2 of 3:To the extent possible, solid reagent should be added to the solid waste container and broken glass should be added to the glass waste. Hazardous materials should never be added to the glass waste, and broken glass should only be allowed in the solid waste with the TA's approval.
\
Choice 3 of 3:To maximize the correct disposal of hazardous material, all materials should be added to the chemical solid waste.
Choice 2 of 3:To the extent possible, solid reagent should be added to the solid waste container and broken glass should be added to the glass waste. Hazardous materials should never be added to the glass waste, and broken glass should only be allowed in the solid waste with the TA's approval.
11
New cards
If you choose to wear loose clothing, large or dangling jewelry, or contact lenses to lab, which of the following statements best represents how you should proceed?
\
Choice 1 of 4:Make sure all loose clothing or jewelry can be confined by the lab coat
\
Choice 2 of 4:Make sure to wear your goggles securely over your contact lenses and check with your lab manual and TA to be sure you will not be working with any volatile or fume-producing reagents.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Make sure none of the jewelry will catch on your clothing or accidentally cut your gloves, and don't wear anything too valuable.
\
Choice 4 of 4:All of these statements are reasonable compromises if you MUST wear these items to lab, but the best and safest practice is to leave them at home and dress for lab intentionally.
\
Choice 1 of 4:Make sure all loose clothing or jewelry can be confined by the lab coat
\
Choice 2 of 4:Make sure to wear your goggles securely over your contact lenses and check with your lab manual and TA to be sure you will not be working with any volatile or fume-producing reagents.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Make sure none of the jewelry will catch on your clothing or accidentally cut your gloves, and don't wear anything too valuable.
\
Choice 4 of 4:All of these statements are reasonable compromises if you MUST wear these items to lab, but the best and safest practice is to leave them at home and dress for lab intentionally.
Choice 4 of 4:All of these statements are reasonable compromises if you MUST wear these items to lab, but the best and safest practice is to leave them at home and dress for lab intentionally.
12
New cards
When should you be sure to wear full PPE (proper attire, lab coat, goggles) in the laboratory? (Check all that apply.)
\
Choice 1 of 4:While cleaning up after experimental work is done.
\
Choice 2 of 4:While waiting in the lab room for a friend to finish.
\
Choice 3 of 4:As soon as you enter the lab, and until you are ready to walk out the door.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Once the experimental work has begun.
\
Choice 1 of 4:While cleaning up after experimental work is done.
\
Choice 2 of 4:While waiting in the lab room for a friend to finish.
\
Choice 3 of 4:As soon as you enter the lab, and until you are ready to walk out the door.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Once the experimental work has begun.
all of the above
13
New cards
What is the most important consideration to preserve safety when it is necessary to feed glass tubing, thermometers, or other apparatus through a rubber stopper?
\
Choice 1 of 4:Using sufficient vacuum grease that the apparatus slides smoothly.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Using sufficient force that the apparatus will slide through the stopper.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Letting your TA handle the procedure for you.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Using the correct hand position so that if something goes wrong you can avoid coming into contact with broken or sharp ends.
\
Choice 1 of 4:Using sufficient vacuum grease that the apparatus slides smoothly.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Using sufficient force that the apparatus will slide through the stopper.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Letting your TA handle the procedure for you.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Using the correct hand position so that if something goes wrong you can avoid coming into contact with broken or sharp ends.
Choice 4 of 4:Using the correct hand position so that if something goes wrong you can avoid coming into contact with broken or sharp ends.
14
New cards
Which of the following must be completed before the pre-lab lecture in lab? Select all that apply.
\
Choice 1 of 4:Put on your lab coat.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Store your backpack, cell phone, jacket, and all other nonessential items in designated storage areas.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Tie back long hair.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Put on your goggles.
\
Choice 1 of 4:Put on your lab coat.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Store your backpack, cell phone, jacket, and all other nonessential items in designated storage areas.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Tie back long hair.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Put on your goggles.
all of the above
15
New cards

This footwear is appropriate for lab.
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
Choice 2 of 2:False
16
New cards
When should you inspect the glassware in your lab drawer for chips, cracks, or chemical residues?
\
Choice 1 of 3:During an experiment, before using any piece of glassware.
\
Choice 2 of 3:Before beginning every experiment.
\
Choice 3 of 3:Glassware should be inspected at all of these times to prevent accidents, injuries, or unwanted complications during experimental work.
\
Choice 1 of 3:During an experiment, before using any piece of glassware.
\
Choice 2 of 3:Before beginning every experiment.
\
Choice 3 of 3:Glassware should be inspected at all of these times to prevent accidents, injuries, or unwanted complications during experimental work.
Choice 3 of 3:Glassware should be inspected at all of these times to prevent accidents, injuries, or unwanted complications during experimental work.
17
New cards

This is appropriate for lab. (Assuming you will wear the proper PPE)
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
Choice 2 of 2:False
18
New cards
When should you immediately turn off the gas valve for a Bunsen or Meker burner? Check all that apply.
\
Choice 1 of 4:If you must leave the open flame unattended and there is no one else to monitor it.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Only at the end of lab when everyone has completed the experiment.
\
Choice 3 of 4:If you smell gas in the room.
\
Choice 4 of 4:If the flame suddenly goes out.
\
Choice 1 of 4:If you must leave the open flame unattended and there is no one else to monitor it.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Only at the end of lab when everyone has completed the experiment.
\
Choice 3 of 4:If you smell gas in the room.
\
Choice 4 of 4:If the flame suddenly goes out.
choice 1, 3, 4
19
New cards
Which of the following is the reason backpacks must be stored during lab?
\
Choice 1 of 3:Backpacks on the floor of the lab or on the benches may be exposed to hazardous materials, which might then lead to student exposure outside the lab.
\
Choice 2 of 3:Backpacks on the floor present a tripping hazard to students in lab, which may lead to spills and other incidents.
\
Choice 3 of 3:Both of these are good reasons to keep nonessential items stored properly.
\
Choice 1 of 3:Backpacks on the floor of the lab or on the benches may be exposed to hazardous materials, which might then lead to student exposure outside the lab.
\
Choice 2 of 3:Backpacks on the floor present a tripping hazard to students in lab, which may lead to spills and other incidents.
\
Choice 3 of 3:Both of these are good reasons to keep nonessential items stored properly.
Choice 3 of 3:Both of these are good reasons to keep nonessential items stored properly.
20
New cards
Everyone should be wearing PPE in the lab.
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
Choice 1 of 2:True
21
New cards
For which of the following situations should you be sure to notify your TA? Check all that apply.
\
Choice 1 of 3:You begin to feel faint and dizzy in lab because you had to skip lunch.
\
Choice 2 of 3:You accidentally pick up a beaker from the hot plate, not realizing that it was already hot, and the edge of the beaker leaves a small red mark on your thumb.
\
Choice 3 of 3:You arrive in lab, but realize that your cold medicine is making you feel groggy.
\
Choice 1 of 3:You begin to feel faint and dizzy in lab because you had to skip lunch.
\
Choice 2 of 3:You accidentally pick up a beaker from the hot plate, not realizing that it was already hot, and the edge of the beaker leaves a small red mark on your thumb.
\
Choice 3 of 3:You arrive in lab, but realize that your cold medicine is making you feel groggy.
all of the above
22
New cards
Your lab partner accidentally gets a mist of your solution in her eye. You immediately help her to the eye wash to rinse it. After about a minute, she feels better and is ready to get back to work. You should still do the following before the TA fills out the incident report:
\
Choice 1 of 4:Keep her in the eye wash for at least 5 minutes and then let the TA decide if she can continue working.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Keep her in the eye wash for at least 15 minutes, and then make sure she goes to student health, just to be sure.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Check to see if her eye is still red. If not, hurry so that you can finish the experiment.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Let the TA inspect her eye to see if it is okay.
\
Choice 1 of 4:Keep her in the eye wash for at least 5 minutes and then let the TA decide if she can continue working.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Keep her in the eye wash for at least 15 minutes, and then make sure she goes to student health, just to be sure.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Check to see if her eye is still red. If not, hurry so that you can finish the experiment.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Let the TA inspect her eye to see if it is okay.
Choice 2 of 4:Keep her in the eye wash for at least 15 minutes, and then make sure she goes to student health, just to be sure.
23
New cards
Which of the following is NOT a behavior that can pose a safety risk in the laboratory environment?
\
Choice 1 of 4:Leaving your lab drawer open while you set up your apparatus and obtain your reagents.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Staying focused on your own experiment and not being distracted by what nearby groups are doing.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Moving rapidly around the lab to be sure to finish the experiment in time.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Looking away from your work to answer a question from your TA or lab partner.
\
Choice 1 of 4:Leaving your lab drawer open while you set up your apparatus and obtain your reagents.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Staying focused on your own experiment and not being distracted by what nearby groups are doing.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Moving rapidly around the lab to be sure to finish the experiment in time.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Looking away from your work to answer a question from your TA or lab partner.
Choice 2 of 4:Staying focused on your own experiment and not being distracted by what nearby groups are doing.
24
New cards
If you need to work with a flammable or volatile solvent, which piece of lab equipment should you be sure to use?
\
Choice 1 of 5:Bunsen or Meker burner, or anything with an open flame.
\
Choice 2 of 5:Hot plate.
\
Choice 3 of 5:Heating mantle.
\
Choice 4 of 5:Fume hood with good ventilation.
\
Choice 5 of 5:Volumetric flask.
\
Choice 1 of 5:Bunsen or Meker burner, or anything with an open flame.
\
Choice 2 of 5:Hot plate.
\
Choice 3 of 5:Heating mantle.
\
Choice 4 of 5:Fume hood with good ventilation.
\
Choice 5 of 5:Volumetric flask.
Choice 4 of 5:Fume hood with good ventilation.
25
New cards
Double gloving can provide additional protection against hazardous chemicals.
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
Choice 1 of 2:True
26
New cards
If ankle is exposed, socks should be worn to cover the bare skin.
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
Choice 1 of 2:True
27
New cards
When should you NEVER use a sealed container ?
\
Choice 1 of 3:When transporting materials from one lab room to another.
\
Choice 2 of 3:When transporting materials from the hood to the bench.
\
Choice 3 of 3:When heating a solution over a hot plate, burner, or heating mantle.
\
Choice 1 of 3:When transporting materials from one lab room to another.
\
Choice 2 of 3:When transporting materials from the hood to the bench.
\
Choice 3 of 3:When heating a solution over a hot plate, burner, or heating mantle.
Choice 3 of 3:When heating a solution over a hot plate, burner, or heating mantle.
28
New cards

This is appropriate clothing attire for lab.
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
Choice 1 of 2:True
29
New cards

This mesh shoe (contains holes) is appropriate for lab.
\
Choice 1 of 2:False
\
Choice 2 of 2:True
\
Choice 1 of 2:False
\
Choice 2 of 2:True
Choice 1 of 2:False
30
New cards
The proper process(es) for disposing of liquid waste containing hazardous material could be:
\
Choice 1 of 3:Bring the waste to the liquid waste bottle in the fume hood. Check the liquid level in the waste bottle. If the level is within 2" of the neck of the bottle, notify your TA so that the bottle won't be overfilled.
\
Choice 2 of 3:Bring the liquid waste bottle and funnel to your bench. Check the liquid level in the waste bottle. As long as the liquid is not yet into the funnel, proceed.
\
Choice 3 of 3:Open the latch, lift the funnel cover out of the way, and pour the waste material into the funnel. Close the funnel lid most of the way. It is okay to leave it unlatched if other students will soon be using the waste container.
\
Choice 1 of 3:Bring the waste to the liquid waste bottle in the fume hood. Check the liquid level in the waste bottle. If the level is within 2" of the neck of the bottle, notify your TA so that the bottle won't be overfilled.
\
Choice 2 of 3:Bring the liquid waste bottle and funnel to your bench. Check the liquid level in the waste bottle. As long as the liquid is not yet into the funnel, proceed.
\
Choice 3 of 3:Open the latch, lift the funnel cover out of the way, and pour the waste material into the funnel. Close the funnel lid most of the way. It is okay to leave it unlatched if other students will soon be using the waste container.
choice 1, 2
31
New cards
Your lab partner accidentally trips and douses the front of your lab coat and shirt with a hazardous material. The TA immediately takes you to the safety shower, since the spill has soaked into your clothing. What do you need to do at this point? Check all that apply.
\
Choice 1 of 3:Stay under the shower for at least 15 minutes.
\
Choice 2 of 3:Remove your shirt and any other clothing that were in contact with the chemical.
\
Choice 3 of 3:Stay under the shower until the shirt has been completely rinsed.
\
Choice 1 of 3:Stay under the shower for at least 15 minutes.
\
Choice 2 of 3:Remove your shirt and any other clothing that were in contact with the chemical.
\
Choice 3 of 3:Stay under the shower until the shirt has been completely rinsed.
choice 1, 2
32
New cards
What should you do if you get chemicals on your gloves or they appear stained?
\
Choice 1 of 4:Carry on with the experiment and dispose of them in solid waste at the end of the period, unless your skin is irritated
\
Choice 2 of 4:Put on another pair of gloves over the gloves you are wearing to protect yourself from the chemicals you are working with since one layer of gloves doesn’t appear to be enough
\
Choice 3 of 4:Be sure to touch every surface in the lab
\
Choice 4 of 4:Dispose of the dirty gloves and replace them with new ones, rinsing your hands and telling your TA if you think something particularly hazardous has permeated them or if you feel any irritation
\
Choice 1 of 4:Carry on with the experiment and dispose of them in solid waste at the end of the period, unless your skin is irritated
\
Choice 2 of 4:Put on another pair of gloves over the gloves you are wearing to protect yourself from the chemicals you are working with since one layer of gloves doesn’t appear to be enough
\
Choice 3 of 4:Be sure to touch every surface in the lab
\
Choice 4 of 4:Dispose of the dirty gloves and replace them with new ones, rinsing your hands and telling your TA if you think something particularly hazardous has permeated them or if you feel any irritation
Choice 4 of 4:Dispose of the dirty gloves and replace them with new ones, rinsing your hands and telling your TA if you think something particularly hazardous has permeated them or if you feel any irritation
33
New cards
It is important to know the location of the safety equipment.
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
Choice 1 of 2:True
34
New cards
My most important role in lab is
\
Choice 1 of 4:working safely.
\
Choice 2 of 4:learning all the techniques.
\
Choice 3 of 4:writing excellent lab reports.
\
Choice 4 of 4:arriving to lab on time.
\
Choice 1 of 4:working safely.
\
Choice 2 of 4:learning all the techniques.
\
Choice 3 of 4:writing excellent lab reports.
\
Choice 4 of 4:arriving to lab on time.
Choice 1 of 4:working safely.
35
New cards
If you need to leave the lab to go to the restroom, you should
\
Choice 1 of 6:Remove your gloves and recycle.
\
Choice 2 of 6:Remove your lab coat and hang it on the coat rack by the door.
\
Choice 3 of 6:Ask a lab partner to watch your experiment.
\
Choice 4 of 6:Notify your TA of your plans to momentarily leave the room.
\
Choice 5 of 6:All of the above
\
Choice 6 of 6:Only A and B
\
Choice 1 of 6:Remove your gloves and recycle.
\
Choice 2 of 6:Remove your lab coat and hang it on the coat rack by the door.
\
Choice 3 of 6:Ask a lab partner to watch your experiment.
\
Choice 4 of 6:Notify your TA of your plans to momentarily leave the room.
\
Choice 5 of 6:All of the above
\
Choice 6 of 6:Only A and B
Choice 5 of 6:All of the above
36
New cards
If any chemical makes contact with your hand, you should
\
Choice 1 of 4:Remove your glove.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Put your hand under running cold water for 15 minutes.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Contact your TA.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Fill out an incident report.
\
Choice 1 of 4:Remove your glove.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Put your hand under running cold water for 15 minutes.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Contact your TA.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Fill out an incident report.
all of the above
37
New cards
After disposing of a material into a hazardous waste container, always
\
Choice 1 of 1:close the lid.
\
Choice 1 of 1:close the lid.
Choice 1 of 1:close the lid.
38
New cards
While weighing out a reagent for use in an experiment, a student finds he has leftover reagent. The student should
\
Choice 1 of 4:Return the excess reagent to the stock bottle to minimize the amount of waste generated.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Place the excess reagent in the appropriate solid or liquid waste container to prevent contamination of the stock reagent.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Notify the TA immediately.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Leave the dispensed material out on the bench so that another group can use it, which will minimize the waste generated.
\
Choice 1 of 4:Return the excess reagent to the stock bottle to minimize the amount of waste generated.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Place the excess reagent in the appropriate solid or liquid waste container to prevent contamination of the stock reagent.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Notify the TA immediately.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Leave the dispensed material out on the bench so that another group can use it, which will minimize the waste generated.
Choice 2 of 4:Place the excess reagent in the appropriate solid or liquid waste container to prevent contamination of the stock reagent.
39
New cards
Which of the following statements is FALSE when it comes to working with hot glassware?
\
Choice 1 of 4:When handling hot glassware, be sure to use the silicone or rubber "hot hand" provided to prevent burns.
\
Choice 2 of 4:If you receive a small burn on your hand, you should immediately notify your TA and run cold water of the burn.
\
Choice 3 of 4:To check if a piece of equipment is hot, quickly touch it, but do not hold your finger in place to prevent burns.
\
Choice 4 of 4:NEVER TOUCH HOT GLASSWARE!
\
Choice 1 of 4:When handling hot glassware, be sure to use the silicone or rubber "hot hand" provided to prevent burns.
\
Choice 2 of 4:If you receive a small burn on your hand, you should immediately notify your TA and run cold water of the burn.
\
Choice 3 of 4:To check if a piece of equipment is hot, quickly touch it, but do not hold your finger in place to prevent burns.
\
Choice 4 of 4:NEVER TOUCH HOT GLASSWARE!
Choice 3 of 4:To check if a piece of equipment is hot, quickly touch it, but do not hold your finger in place to prevent burns.
40
New cards
When dealing with hazardous materials generated in the lab, select all the guidelines that are applicable:
\
Choice 1 of 4:Collect ALL hazardous material for proper disposal.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Organize the experiment to generate the least amount of hazardous material possible.
\
Choice 3 of 4:When in doubt, dispose of materials as though they are the most hazardous type to be safe.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Materials used in General Chemistry are generally nonhazardous, so most can go in the normal trash.
\
Choice 1 of 4:Collect ALL hazardous material for proper disposal.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Organize the experiment to generate the least amount of hazardous material possible.
\
Choice 3 of 4:When in doubt, dispose of materials as though they are the most hazardous type to be safe.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Materials used in General Chemistry are generally nonhazardous, so most can go in the normal trash.
choice 1, 2, 3
41
New cards
When working in the lab, you should always remove your gloves when:
I. Typing on your laptop keyboard
II. Leaving the laboratory
III. Picking up your pen to record observations in the lab notebook
IV. Using the doorknob
V. Using the laboratory phone
\
\n Choice 1 of 4:Only I. and II. are correct
\
Choice 2 of 4:All but III. are correct
\
Choice 3 of 4:All of these are cases when you should first remove your gloves
\
Choice 4 of 4:Only II. is correct
I. Typing on your laptop keyboard
II. Leaving the laboratory
III. Picking up your pen to record observations in the lab notebook
IV. Using the doorknob
V. Using the laboratory phone
\
\n Choice 1 of 4:Only I. and II. are correct
\
Choice 2 of 4:All but III. are correct
\
Choice 3 of 4:All of these are cases when you should first remove your gloves
\
Choice 4 of 4:Only II. is correct
Choice 3 of 4:All of these are cases when you should first remove your gloves
42
New cards
elements of a Safety Data sheet
General overview:
* Hazardous ingredients
* Physical and chemical characteristics
* Effect on human health
* Chemicals with which it can adversely react
* Handling precautions
* Measures to control exposure
* Emergency and first aid procedures
* Methods to contain a spill
\
Specifics:
* Properties of each chemical:
* Chemical name, formula, and structure
* Physical state, color, and odor
* Health hazards:
* Toxicity, carcinogenicity, and mutagenicity
* Routes of exposure and symptoms of exposure
* Environmental hazards:
* Ecotoxicity, persistence, and bioaccumulation
* Disposal considerations and spill response procedures
* Protective measures:
* Personal protective equipment (PPE)
* Engineering controls and ventilation
* Safety precautions:
* Handling, storing, and transporting procedures
* Emergency response procedures and first aid measures
* Hazardous ingredients
* Physical and chemical characteristics
* Effect on human health
* Chemicals with which it can adversely react
* Handling precautions
* Measures to control exposure
* Emergency and first aid procedures
* Methods to contain a spill
\
Specifics:
* Properties of each chemical:
* Chemical name, formula, and structure
* Physical state, color, and odor
* Health hazards:
* Toxicity, carcinogenicity, and mutagenicity
* Routes of exposure and symptoms of exposure
* Environmental hazards:
* Ecotoxicity, persistence, and bioaccumulation
* Disposal considerations and spill response procedures
* Protective measures:
* Personal protective equipment (PPE)
* Engineering controls and ventilation
* Safety precautions:
* Handling, storing, and transporting procedures
* Emergency response procedures and first aid measures
43
New cards
EXPERIMENT 10
44
New cards
endothermic vs exothermic reactions
endothermic: heat absorbed (heat as a reactant)
\
exothermic: heat released (heat as a product)
\
exothermic: heat released (heat as a product)
45
New cards
different ways to calculate heat change (thermal energy)
heat change = thermal energy = q
\
**q = mcΔT**
* q represents the amount of heat transferred
* m represents the mass of the substance
* c represents the specific heat capacity of the substance
* ΔT represents the change in temperature of the substance
\
**ΔHºrxn = ∑nΔHºf (products) - ∑nΔHºf (reactants**)
* ΔHºrxn is the change in enthalpy for a chemical reaction at constant pressure.
* It is calculated using the standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHºf) values for the reactants and products.
* The standard enthalpy of formation is the enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements in their standard states.
* The ΔHºf values for elements in their standard states are defined as zero.
* The ΔHºrxn value is positive for endothermic reactions and negative for exothermic reactions.
* The stoichiometric coefficients (n) in the balanced chemical equation are used to determine the number of moles of reactants and products involved in the reaction.
\
**ΔHºrxn = ∑ΔHbond breaking - ∑ΔHbond forming**
* ΔHºrxn: Change in enthalpy of a chemical reaction
* ∑ΔHbond breaking: Sum of energy required to break all bonds in reactants
* ∑ΔHbond forming: Sum of energy released when new bonds are formed in products
* ΔHbond = n(bonds) × BE(avg)
* n: mol of bonds (of that same avg BE) breaking/forming
* BE(avg): avg bond energy (kJ/mol)
* ΔHbond: enthalpy change of bond breaking/forming
* ΔHbond > 0 for bond breaking
* ΔHbond < 0 for bond forming (but this is factored in with the minus sign)
* Follows reactants minus products format bc BE is in terms of breaking REACTANTS’ bonds
\
**q = mcΔT**
* q represents the amount of heat transferred
* m represents the mass of the substance
* c represents the specific heat capacity of the substance
* ΔT represents the change in temperature of the substance
\
**ΔHºrxn = ∑nΔHºf (products) - ∑nΔHºf (reactants**)
* ΔHºrxn is the change in enthalpy for a chemical reaction at constant pressure.
* It is calculated using the standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHºf) values for the reactants and products.
* The standard enthalpy of formation is the enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements in their standard states.
* The ΔHºf values for elements in their standard states are defined as zero.
* The ΔHºrxn value is positive for endothermic reactions and negative for exothermic reactions.
* The stoichiometric coefficients (n) in the balanced chemical equation are used to determine the number of moles of reactants and products involved in the reaction.
\
**ΔHºrxn = ∑ΔHbond breaking - ∑ΔHbond forming**
* ΔHºrxn: Change in enthalpy of a chemical reaction
* ∑ΔHbond breaking: Sum of energy required to break all bonds in reactants
* ∑ΔHbond forming: Sum of energy released when new bonds are formed in products
* ΔHbond = n(bonds) × BE(avg)
* n: mol of bonds (of that same avg BE) breaking/forming
* BE(avg): avg bond energy (kJ/mol)
* ΔHbond: enthalpy change of bond breaking/forming
* ΔHbond > 0 for bond breaking
* ΔHbond < 0 for bond forming (but this is factored in with the minus sign)
* Follows reactants minus products format bc BE is in terms of breaking REACTANTS’ bonds
46
New cards
Hess’s Law
the overall enthalpy change in a reaction is equal to the sum of enthalpy changes for the individual steps in the process
\
the principle that the enthalpy of rxn (ΔH(rxn)) for a process that is the sum of 2 or more reactions is equal to the sum of the ΔH(rxn) values for each of the individual reactions
\
* Hess's law states that the enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of the pathway between the initial and final states.
* Enthalpy is a STATE FUNCTION, meaning it only depends on the initial and final states of a system.
* Hess's law can be used to calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction by summing the enthalpy changes of a series of reactions that add up to the overall reaction.
* Hess's law is based on the first law of thermodynamics, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or converted from one form to another.
* Hess's law is useful in determining the enthalpy change of reactions that cannot be directly measured.
\
the principle that the enthalpy of rxn (ΔH(rxn)) for a process that is the sum of 2 or more reactions is equal to the sum of the ΔH(rxn) values for each of the individual reactions
\
* Hess's law states that the enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of the pathway between the initial and final states.
* Enthalpy is a STATE FUNCTION, meaning it only depends on the initial and final states of a system.
* Hess's law can be used to calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction by summing the enthalpy changes of a series of reactions that add up to the overall reaction.
* Hess's law is based on the first law of thermodynamics, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or converted from one form to another.
* Hess's law is useful in determining the enthalpy change of reactions that cannot be directly measured.
47
New cards
Select all that apply.
Learning objectives of Experiment 10 include:
\
Choice 1 of 5:Demonstrating concepts, terms, and calculations of thermochemistry.
\
Choice 2 of 5:Demonstrating Newton's Law of Heating and Cooling.
\
Choice 3 of 5:Illustrating the concept of a state function for heats of reaction.
\
Choice 4 of 5:Using calorimetry to relate measured temperature changes in chemical reactions to the reactions' thermochemical properties.
\
Choice 5 of 5:Observing the reaction of NaOH solid with a 1.25 M solution of citric acid.
Learning objectives of Experiment 10 include:
\
Choice 1 of 5:Demonstrating concepts, terms, and calculations of thermochemistry.
\
Choice 2 of 5:Demonstrating Newton's Law of Heating and Cooling.
\
Choice 3 of 5:Illustrating the concept of a state function for heats of reaction.
\
Choice 4 of 5:Using calorimetry to relate measured temperature changes in chemical reactions to the reactions' thermochemical properties.
\
Choice 5 of 5:Observing the reaction of NaOH solid with a 1.25 M solution of citric acid.
choice 1, 3, 4
48
New cards
In an exothermic reaction, will the enthalpy change be positive or negative? Why?
\
Choice 1 of 4:Enthalpy change will be negative; the energy of the starting materials is lower than the energy of the products.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Enthalpy change will be positive; the energy of the starting materials is lower than the energy of the products.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Enthalpy change will be negative; the energy of the starting material is higher than the energy of the products.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Enthalpy change will be positive; the energy of the starting material is higher than the energy of the products.
\
Choice 1 of 4:Enthalpy change will be negative; the energy of the starting materials is lower than the energy of the products.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Enthalpy change will be positive; the energy of the starting materials is lower than the energy of the products.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Enthalpy change will be negative; the energy of the starting material is higher than the energy of the products.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Enthalpy change will be positive; the energy of the starting material is higher than the energy of the products.
Choice 3 of 4:Enthalpy change will be negative; the energy of the starting material is higher than the energy of the products.
49
New cards
True or false: Hess's Law states that if a reaction can be written as the sum of two or more other reactions, the Δ*H* for the overall process must be the sum of the Δ*H* values of the constituent reactions.
\
Choice 1 of 2:A. True
\
Choice 2 of 2:B. False
\
Choice 1 of 2:A. True
\
Choice 2 of 2:B. False
Choice 1 of 2:A. True
50
New cards
True or false: enthalpy change (Δ*H*) is referred to as a "path function" because it is dependent on the specific mechanism of reaction, or pathway.
\
Choice 1 of 2:A. True
\
Choice 2 of 2:B. False
\
Choice 1 of 2:A. True
\
Choice 2 of 2:B. False
Choice 2 of 2:B. False
51
New cards
Google the SDS for sodium hydroxide pellets. What should you do if you get sodium hydroxide on your skin/clothes?
\
Choice 1 of 4:Wipe it off with a paper towel or Kimwipe.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Neutralize it with HCl.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Use soap to clean the affected area.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Flush skin with water for 15 minutes and let your TA know.
\
Choice 1 of 4:Wipe it off with a paper towel or Kimwipe.
\
Choice 2 of 4:Neutralize it with HCl.
\
Choice 3 of 4:Use soap to clean the affected area.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Flush skin with water for 15 minutes and let your TA know.
Choice 4 of 4:Flush skin with water for 15 minutes and let your TA know.
52
New cards
According to the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for hydrochloric acid (*HCl*), which of the following statements are listed as hazard statements?
\
Choice 1 of 4:A. may be corrosive to metals.
\
Choice 2 of 4:B. may cause respiratory irritation.
\
Choice 3 of 4:C. causes severe skin burns and eye damage.
\
Choice 4 of 4:D. All of the above.
\
Choice 1 of 4:A. may be corrosive to metals.
\
Choice 2 of 4:B. may cause respiratory irritation.
\
Choice 3 of 4:C. causes severe skin burns and eye damage.
\
Choice 4 of 4:D. All of the above.
Choice 4 of 4:D. All of the above.
53
New cards
Why do you weigh the solid NaOH by difference instead of directly weighing it on a weigh boat?
\
Choice 1 of 3:The mass of the weigh boat would lead to a less precise measurement.
\
Choice 2 of 3:Sodium hydroxide absorbs *CO*2 from the air and will cause the mass to be inaccurate.
\
Choice 3 of 3:Sodium hydroxide is hygroscopic and will absorb water from the air, making it difficult to get an accurate mass.
\
Choice 1 of 3:The mass of the weigh boat would lead to a less precise measurement.
\
Choice 2 of 3:Sodium hydroxide absorbs *CO*2 from the air and will cause the mass to be inaccurate.
\
Choice 3 of 3:Sodium hydroxide is hygroscopic and will absorb water from the air, making it difficult to get an accurate mass.
Choice 3 of 3:Sodium hydroxide is hygroscopic and will absorb water from the air, making it difficult to get an accurate mass.
54
New cards
What is the balanced chemical reaction and the net ionic reaction for reaction 3, NaOH solid in HCl?
balanced: NaOH(s) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
\
net ionic: NaOH(s) + H+(aq) → Na+(aq) + H2O(l)
\
net ionic: NaOH(s) + H+(aq) → Na+(aq) + H2O(l)
55
New cards
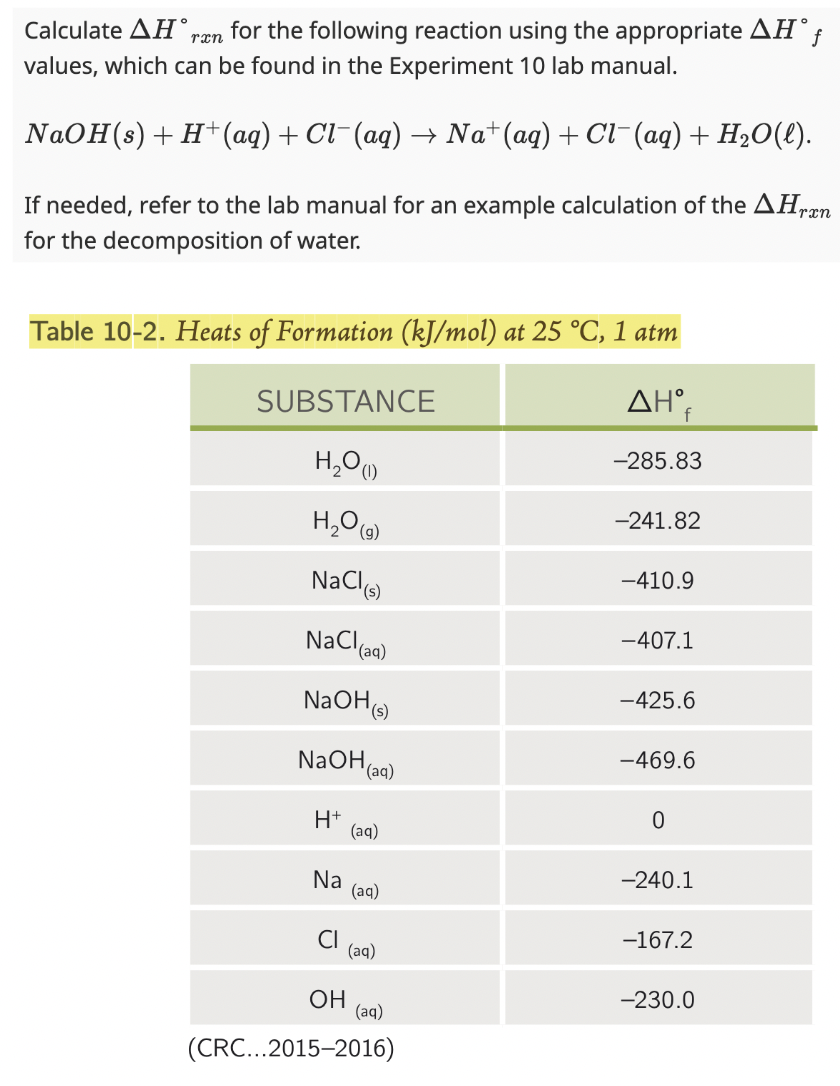
(question in image)
\-100.33 kJ/mol
56
New cards
Select all that apply.
Important PPE for Experiment 10 lab includes:
\
Choice 1 of 5:Goggles (to be worn at all times in the lab space)
\
Choice 2 of 5:Lab coat
\
Choice 3 of 5:Gloves (to be worn at all times manipulating the experimental set-up)
\
Choice 4 of 5:Gloves (to be worn at all times, even on a computer)
\
Choice 5 of 5:Fully enclosed shoes, clothes covering entire torso/midriff/shoulders and entire lower body
Important PPE for Experiment 10 lab includes:
\
Choice 1 of 5:Goggles (to be worn at all times in the lab space)
\
Choice 2 of 5:Lab coat
\
Choice 3 of 5:Gloves (to be worn at all times manipulating the experimental set-up)
\
Choice 4 of 5:Gloves (to be worn at all times, even on a computer)
\
Choice 5 of 5:Fully enclosed shoes, clothes covering entire torso/midriff/shoulders and entire lower body
choice 1, 2, 3, 5
57
New cards
write the balanced and net ionic reaction of citric acid with sodium bicarbonate
balanced: 3NaHCO3(s) + H3C6H5O7(aq) → Na3C6H5O7(aq) + 3CO2(g) + 3H2O(l)
\
net ionic: 3NaHCO3(s) + H3C6H5O7(aq) → 3Na+(aq) + C6H5O7 3-(aq) + 3CO2(g) + 3H2O(l)
\
net ionic: 3NaHCO3(s) + H3C6H5O7(aq) → 3Na+(aq) + C6H5O7 3-(aq) + 3CO2(g) + 3H2O(l)
58
New cards
__*Temperature Calculations*__ __for Solid Sodium Bicarbonate with a Citric Acid Solution__*: The initial temperature, Ti, of the water before addition and the maximum temperature, Tmax, reached during the addition of solid sodium bicarbonate to a citric acid solution is most accurately determined by using linear extrapolation. F*ollow the examples and descriptions in the lab manual on Hayden-McNeil. *Considering the relevant data for* Ti *and* Tmax*, extrapolated values for each can be determined b*y extending the linear trendlines to the time of addition of sodium bicarbonate. 3 Points
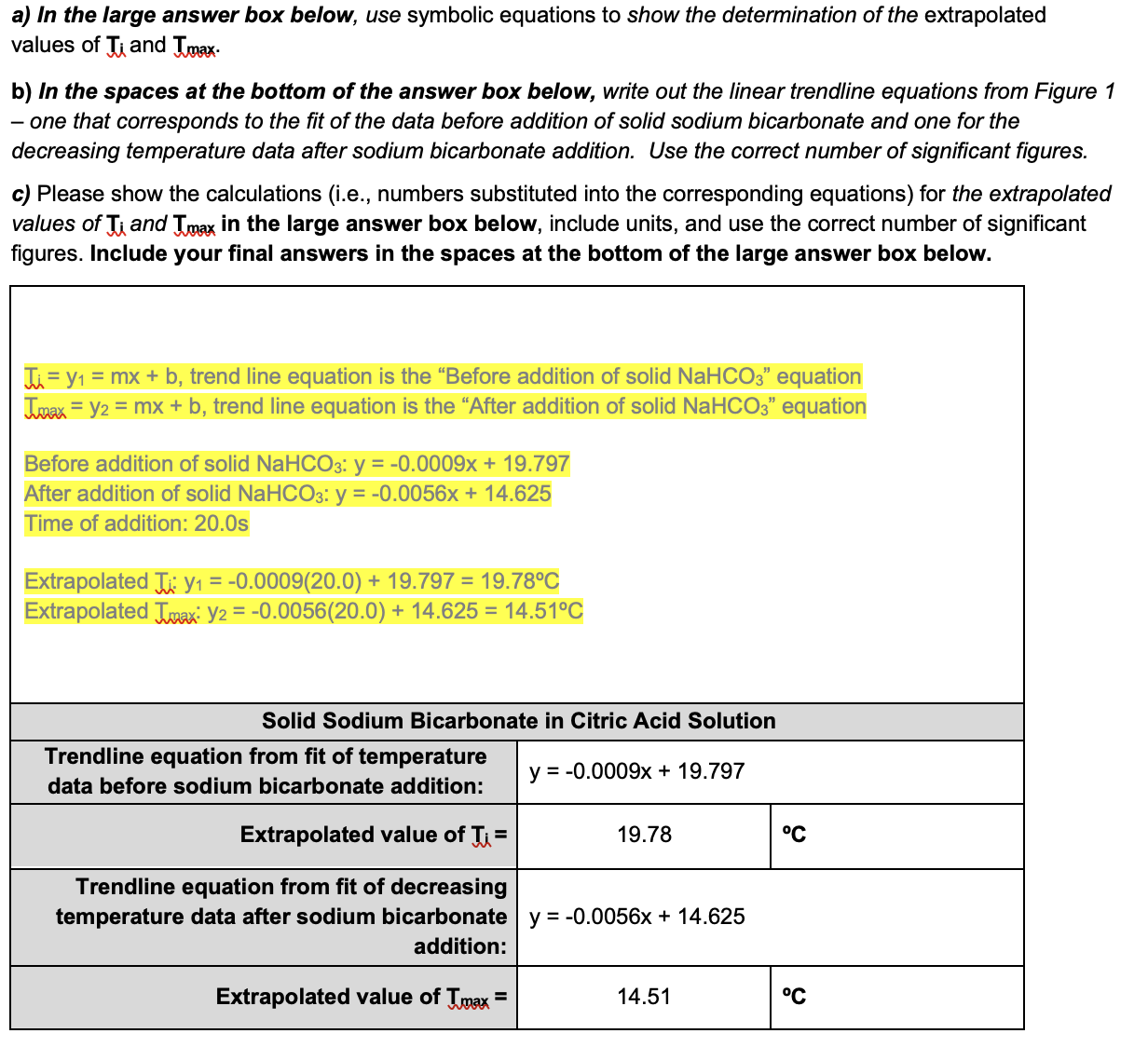
59
New cards
write the balanced and net ionic reaction of solid sodium hydroxide with water
balanced: NaOH(s) + H2O(l) → H2O(l) + NaOH(aq)
\
net ionic: NaOH(s) + H2O(l) → H2O(l) + Na+(aq) + OH-(aq)
\
net ionic: NaOH(s) + H2O(l) → H2O(l) + Na+(aq) + OH-(aq)
60
New cards
ERROR ANALYSIS
61
New cards
1\. 2 Points In your own words, define accuracy and precision. (2 sentences)
Accuracy is how close the experimentally-measured value is to the actual value, but precision is how close your measurements are to each other.
62
New cards
2\. 5 points In your own words, define systematic and random uncertainties. What is the main difference between these types of uncertainty? (2-4 sentences)
Systematic uncertainties are based on problems with experimental equipment, so these are consistent/uniform errors throughout all data. Random uncertainties are due to uncontrolled variables and are thus not consistent errors because they are not due to issues with experimental setup or equipment used to collect all data and can thus be detected by reproducing the experiment.
63
New cards
3\. 5 points Label each of the following situations as systematic or random uncertainty.
\
A. A 25-mL transfer pipette consistently delivers 24.984 ± 0.007 mL
\
B. A 10-mL burette consistently delivers 2.01 ± 0.02 mL when drained from 0.01 mL to 2.01 mL and consistently delivers 1.94 ± 0.03 mL when drained from 2.01 mL to 4.01 mL
\
C. A 10-mL graduated cylinder delivered 4.926 g of water when filled to the 5 mL mark. The next time I used the graduated cylinder, it delivered 4.9859 g of water when filled to the 5 mL mark
\
D. The same sample of sodium bicarbonate was measured on a tared (zeroed) analytical balance three times. The masses displayed were 0.255-, 0.261-, and 0.254-g
\
A. A 25-mL transfer pipette consistently delivers 24.984 ± 0.007 mL
\
B. A 10-mL burette consistently delivers 2.01 ± 0.02 mL when drained from 0.01 mL to 2.01 mL and consistently delivers 1.94 ± 0.03 mL when drained from 2.01 mL to 4.01 mL
\
C. A 10-mL graduated cylinder delivered 4.926 g of water when filled to the 5 mL mark. The next time I used the graduated cylinder, it delivered 4.9859 g of water when filled to the 5 mL mark
\
D. The same sample of sodium bicarbonate was measured on a tared (zeroed) analytical balance three times. The masses displayed were 0.255-, 0.261-, and 0.254-g
A. Systematic
\
B. Systematic
\
C. Random
\
D. Random
\
B. Systematic
\
C. Random
\
D. Random
64
New cards
4\. 4 points Which type of error predominantly influences accuracy? In what way(s) can you minimize or remove its influence? (2-5 Sentences)
Issues with accuracy generally result from systematic fluctuations (issues with experiment equipment and/or setup). You can minimize this influence through experimentation with positive and negative controls, which test that your equipment is functioning properly.
65
New cards
5\. 4 points Which type of error predominantly influences precision? In what way(s) can you minimize or remove its influence? (2-5 Sentences)
Issues with precision typically result from random fluctuations (issues with uncontrolled variables impacting the experimental variables). Solutions like increasing sample size can reduce standard deviation or reproducing the experiment multiple times can minimize the influence of uncontrolled variables in creating random fluctuations.
66
New cards
how to calculate average
add all values up and divide by the total number of values addedho
67
New cards
how to calculate standard deviation
* Calculate the mean of the data set
* Subtract the mean from each data point
* Square each result
* Sum the squared results
* Divide the sum by the number of data points minus one
* Take the square root of the result to get the standard deviation
* Subtract the mean from each data point
* Square each result
* Sum the squared results
* Divide the sum by the number of data points minus one
* Take the square root of the result to get the standard deviation
68
New cards
how to calculate percent error
* Subtract the actual value from the experimental value
* Divide the absolute value of the difference by the actual value
* Multiply the result by 100 to get the percent error
* Divide the absolute value of the difference by the actual value
* Multiply the result by 100 to get the percent error
69
New cards
sig figs for average ± standard deviation
STDEV always 1 sig fig & averages only have the number of decimals allowed by STDEV
70
New cards
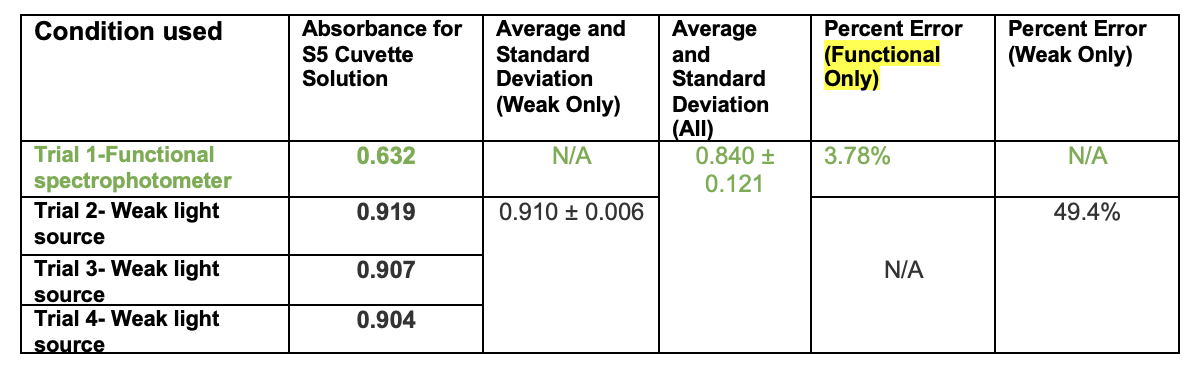
7\. 2 points Considering trials: a) 1, b) 2-4, and c) 1-4, would you describe each set as accurate, precise, both accurate and precise, or neither accurate nor precise? Explain (1-2 sentences).
Trial 1 is accurate but not precise (low percent error but no data to compare trial 1 to determine its precision), trials 2-4 are precise but not accurate (high percent error but now standard deviation), and trials 1-4 are neither accurate nor precise (higher average than the expected 0.609 and high standard deviation).
71
New cards
8\. 4 points In Experiment 10, coffee cup calorimetry was used to determine the molar enthalpy for several different reactions. In these reactions, a base (sodium bicarbonate or NaOH) was added to a solution in a coffee cup, and the temperature was measured over time. Unfortunately, the specific lid you were using was old and had a couple holes on the top. 1) describe how this would impact your temperature data compared to someone using a lid without holes, and 2) classify the type of error. (3-6 Sentences)
Having a hole in the cup lid would result in release of some heat to the environment around the cup. This would impact temperature data because it would create a systematic uncertainty. Therefore, there would be uncertainty in accuracy throughout all temperature data as compared to someone without a hole in their lid.
72
New cards
9\. 5 points 1) Think back to how you calculated __molar enthalpy__ in Experiment 10. Would the value calculated using the coffee cup with the holey lid be different than that obtained using a fully functional coffee cup calorimeter? If so, how? In your calculations, the heat loss to the calorimeter was accounted for using a calorimeter constant. 2) If you had used a calorimeter constant calculated from data using the holey lid, how would this influence your accuracy? Would it impact your precision? (3-6 Sentences)
Yes, the molar enthalpy in the coffee cup with the hole would be different than that obtained from a fully functional coffee cup calorimeter because the hole would result in a faster cool-down period of the solution’s temperature after the initial temperature shoots up in the exothermic reaction when the two reactants react, thus *increasing* the change in temperature, which would result in an overestimation of heat transferred in the reaction. This would lead to an overestimation in the molar enthalpy if the lid has a hole in it.
If you calculated the calorimeter constant with data from the lid with the hole, you would not have an accurate calorimeter constant because some of the heat, that in theory would have been transferred to the calorimeter, would also have escaped outside the calorimeter to the environment. However, your precision would not be affected by this error because it is a uniform error across the experiment.
If you calculated the calorimeter constant with data from the lid with the hole, you would not have an accurate calorimeter constant because some of the heat, that in theory would have been transferred to the calorimeter, would also have escaped outside the calorimeter to the environment. However, your precision would not be affected by this error because it is a uniform error across the experiment.
73
New cards
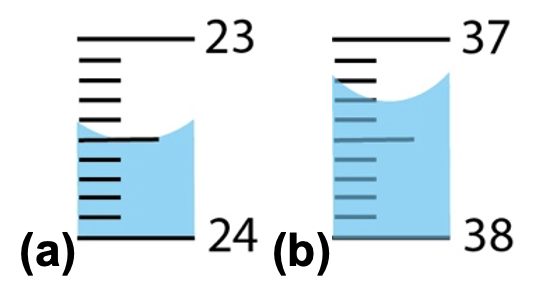
10\. Suppose you are performing a titration of KHP to standardize a 0.1 M NaOH solution. After filling the burette with NaOH solution, you and your partner measure the initial volume from the bottom up, which looks like (a). After reaching the equivalence point of the titration, you again measure the volume from the bottom up, which looks like (b). You then use these values to calculate the volume of titrant used and find it to be 14.2 mL. This data is used to determine the actual concentration of the NaOH solution.
\
a. 2 points In the scenario above, did any errors occur? If so, what was it and what type was it?
\
b. 4 points If any errors occurred, how would the recorded volume compare to the "true" volume you measured out? If no error occurred, say “no error.”
\
c. 4 points If any errors occurred, how would this influence the concentration of NaOH standard solution? Hints: refer to Experiment 16.1 to support your reasoning.
\
a. 2 points In the scenario above, did any errors occur? If so, what was it and what type was it?
\
b. 4 points If any errors occurred, how would the recorded volume compare to the "true" volume you measured out? If no error occurred, say “no error.”
\
c. 4 points If any errors occurred, how would this influence the concentration of NaOH standard solution? Hints: refer to Experiment 16.1 to support your reasoning.
a. Systematic errors occurred because the person is reading the buret wrong consistently.
\
b. The recorded volume is more than the true volume. The person measured bottom-up but should actually be reading a buret from top-down. Thus, they should get (a) is 23.5 mL and (b) 37.3 mL. Thus, the true volume is 13.8 mL, not 14.7 mL.
\
c. This would decrease the concentration of NaOH. This is because we know moles of KHP, and at the equivalence point, moles of KHP = moles of NaOH. Then, solving for Molarity of NaOH, we divide the moles of NaOH by the *misread* (larger) volume of NaOH, and consequently, the *calculated* molarity of NaOH is *smaller* than the true molarity of NaOH.
\
b. The recorded volume is more than the true volume. The person measured bottom-up but should actually be reading a buret from top-down. Thus, they should get (a) is 23.5 mL and (b) 37.3 mL. Thus, the true volume is 13.8 mL, not 14.7 mL.
\
c. This would decrease the concentration of NaOH. This is because we know moles of KHP, and at the equivalence point, moles of KHP = moles of NaOH. Then, solving for Molarity of NaOH, we divide the moles of NaOH by the *misread* (larger) volume of NaOH, and consequently, the *calculated* molarity of NaOH is *smaller* than the true molarity of NaOH.
74
New cards
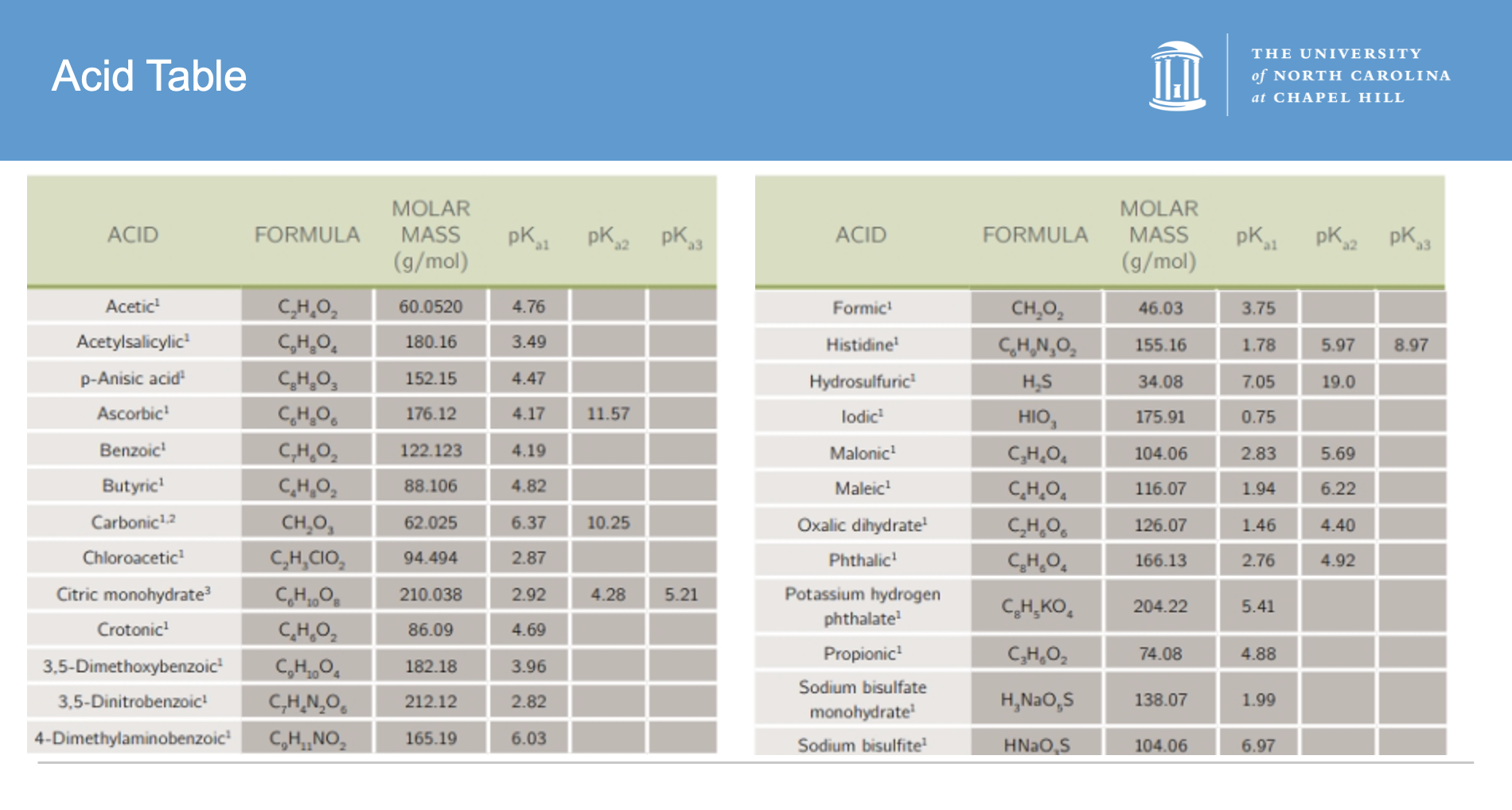
11\. Suppose you were using a correctly standardized NaOH solution to determine the identity of an unknown acid (monoprotic in this example). With the titration curve you measure, you create a first derivative plot to determine the inflection point giving you the equivalence point. You repeat this process as directed for a total of three times and using the half equivalence point you determine the pKa1 from each trial to be 4.67, 4.71, and 4.79. With the equivalence points and masses of unknown acid, you calculate the molar mass from each trial to be 85.44 g/mol, 71.81 g/mol, and 63.70 g/mol.
\
a. 2 points Using Error PPT Slide 34 and the average pKa1 from the three trials, identify the unknown monoprotic acid. Then, using the same table and the average molar mass, identify the monoprotic acid.
\
b. 4 points Determine the relative standard deviations for both the pKa and the molar mass. Based on these values, do you think there was more error in determining the pKa or the molar mass values? What do you think the true identity of the unknown acid is?
\
c. 3 points What type of error led to these different measurements? What are examples of this type of error that could have influenced the results?
\
a. 2 points Using Error PPT Slide 34 and the average pKa1 from the three trials, identify the unknown monoprotic acid. Then, using the same table and the average molar mass, identify the monoprotic acid.
\
b. 4 points Determine the relative standard deviations for both the pKa and the molar mass. Based on these values, do you think there was more error in determining the pKa or the molar mass values? What do you think the true identity of the unknown acid is?
\
c. 3 points What type of error led to these different measurements? What are examples of this type of error that could have influenced the results?
a. Average pKa1 = (4.67 + 4.71 + 4.79) / 3 = 4.72. This average is closest to Crotonic acid’s pKa1 value.
Average molar mass = (85.44g/mol + 71.81g/mol + 63.70g/mol) / 3 = 73.65. This average is closest to Propionic acid’s molar mass.
\
b. The relative standard deviation for the pKa1 is 0.013 = 1.3%. The relative standard deviation for the molar mass is 0.149 = 14.9%. Based on these values, I think there was more error in determining the molar mass. Thus, I think the true identity of the acid is Crotonic acid.
\
c. Random error must have led to these different measurements because the measured values are not precise but they are accurate. Examples of random errors are having air bubbles in the buret in trials 2 and 3 but not trial 1, resulting in trial 1 having a more accurate volume (and thus mass) used to titrate while air bubbles resulted in an inaccurate representation of volume (and thus mass).
Average molar mass = (85.44g/mol + 71.81g/mol + 63.70g/mol) / 3 = 73.65. This average is closest to Propionic acid’s molar mass.
\
b. The relative standard deviation for the pKa1 is 0.013 = 1.3%. The relative standard deviation for the molar mass is 0.149 = 14.9%. Based on these values, I think there was more error in determining the molar mass. Thus, I think the true identity of the acid is Crotonic acid.
\
c. Random error must have led to these different measurements because the measured values are not precise but they are accurate. Examples of random errors are having air bubbles in the buret in trials 2 and 3 but not trial 1, resulting in trial 1 having a more accurate volume (and thus mass) used to titrate while air bubbles resulted in an inaccurate representation of volume (and thus mass).
75
New cards
EXPERIMENT 13
76
New cards
The main purpose for Experiment 13: Colligative Properties is to
\
Choice 1 of 4:experimentally determine what the definition of molality is
\
Choice 2 of 4:to identify an unknown acid dissolved in stearic acid through the colligative property of freezing point depression
\
Choice 3 of 4:define what a colligative property is
\
Choice 4 of 4:Navigate through the procedure and collect data
\
Choice 1 of 4:experimentally determine what the definition of molality is
\
Choice 2 of 4:to identify an unknown acid dissolved in stearic acid through the colligative property of freezing point depression
\
Choice 3 of 4:define what a colligative property is
\
Choice 4 of 4:Navigate through the procedure and collect data
Choice 2 of 4:to identify an unknown acid dissolved in stearic acid through the colligative property of freezing point depression
77
New cards
True or False: A colligative property depends upon the number of solute molecules present and is not dependent upon the specific chemical identity.
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
\
Choice 1 of 2:True
\
Choice 2 of 2:False
Choice 1 of 2:True
78
New cards
The following freezing temperatures will be recorded in this lab.
\
Choice 1 of 6:The pure solvent, water
\
Choice 2 of 6:The pure solvent, stearic acid
\
Choice 3 of 6:The solution of stearic acid with water
\
Choice 4 of 6:The pure solvent, unknown acid
\
Choice 5 of 6:The solution of stearic acid with an unknown fatty acid
\
Choice 6 of 6:The solution of unknown fatty acid with water
\
Choice 1 of 6:The pure solvent, water
\
Choice 2 of 6:The pure solvent, stearic acid
\
Choice 3 of 6:The solution of stearic acid with water
\
Choice 4 of 6:The pure solvent, unknown acid
\
Choice 5 of 6:The solution of stearic acid with an unknown fatty acid
\
Choice 6 of 6:The solution of unknown fatty acid with water
choice 2, 5
79
New cards
Describe the expected experimental apparatus you will use to determine the freezing point of the fatty acid samples.
\
Choice 1 of 5:Large test tube and a small test tube were clamped over a beaker that have boiling water. The alcohol thermometer was placed in the water to monitor temperature.
\
Choice 2 of 5:The smaller test tube was required to be wrapped around with a paper towel and fit into the larger test tube. The large test tube was secured on the ring stand using a clamp and it was positioned over the hot plate. A Vernier temperature probe will be placed inside the smaller test tube to record the temperature.
\
Choice 3 of 5:The smaller test tube was required to be wrapped around with a paper towel and fit into the larger test tube. The large test tube was secured on the ring stand using a clamp and it was positioned over the hot plate that contained a water beaker. A Vernier temperature probe will be placed inside the beaker to record the temperature of the water.
\
Choice 4 of 5:The larger test tube was required to be wrapped around with a paper towel and fit beside the smaller test tube. The large test tube was secured on the ring stand using a clamp and both tubes were positioned over the hot plate that contained a water beaker. An alcohol thermometer was placed inside the beaker to record the temperature.
\
Choice 5 of 5:The smaller test tube was required to be wrapped around with a paper towel and fit into the larger test tube. The large test tube was secured on the ring stand using a clamp and it was positioned over the hot plate that contained a water beaker. An alcohol thermometer will be placed in the small test tube to monitor the temperature.
\
Choice 1 of 5:Large test tube and a small test tube were clamped over a beaker that have boiling water. The alcohol thermometer was placed in the water to monitor temperature.
\
Choice 2 of 5:The smaller test tube was required to be wrapped around with a paper towel and fit into the larger test tube. The large test tube was secured on the ring stand using a clamp and it was positioned over the hot plate. A Vernier temperature probe will be placed inside the smaller test tube to record the temperature.
\
Choice 3 of 5:The smaller test tube was required to be wrapped around with a paper towel and fit into the larger test tube. The large test tube was secured on the ring stand using a clamp and it was positioned over the hot plate that contained a water beaker. A Vernier temperature probe will be placed inside the beaker to record the temperature of the water.
\
Choice 4 of 5:The larger test tube was required to be wrapped around with a paper towel and fit beside the smaller test tube. The large test tube was secured on the ring stand using a clamp and both tubes were positioned over the hot plate that contained a water beaker. An alcohol thermometer was placed inside the beaker to record the temperature.
\
Choice 5 of 5:The smaller test tube was required to be wrapped around with a paper towel and fit into the larger test tube. The large test tube was secured on the ring stand using a clamp and it was positioned over the hot plate that contained a water beaker. An alcohol thermometer will be placed in the small test tube to monitor the temperature.
choice 5
80
New cards
True or False: The unknown was added to the same stearic acid sample used in Part C.
\
Choice 1 of 2:False
\
Choice 2 of 2:True
\
Choice 1 of 2:False
\
Choice 2 of 2:True
Choice 2 of 2:True
81
New cards
At different elevations, compounds can have different van't hoff factors.
Choice 1 of 4:Yes! Pressure effects the ability for solute to dissolve in water.
\
Choice 2 of 4:No, it depends on the identity of the solute.
\
Choice 3 of 4:No, van't hoff factors are only dependent on the quantity of solute particles.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Yes! The smaller the boiling point, the more likely ions will dissolve.
Choice 1 of 4:Yes! Pressure effects the ability for solute to dissolve in water.
\
Choice 2 of 4:No, it depends on the identity of the solute.
\
Choice 3 of 4:No, van't hoff factors are only dependent on the quantity of solute particles.
\
Choice 4 of 4:Yes! The smaller the boiling point, the more likely ions will dissolve.
Choice 2 of 4:No, it depends on the identity of the solute.
82
New cards
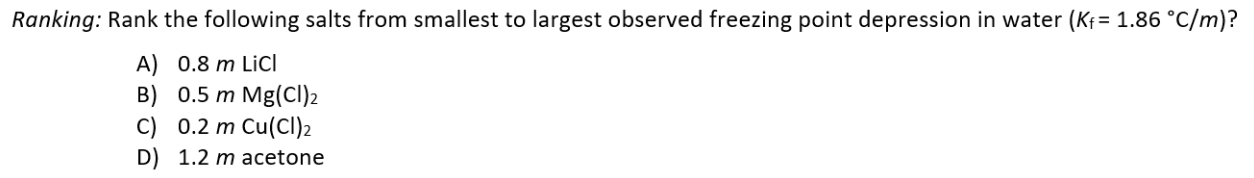
Choice 1 of 5:A
Choice 4 of 5:C
83
New cards
A solution containing 20.0 g of an unknown non-electrolyte liquid and 110.0 g water has a freezing point of -1.32 °C. Given Kf = 1.86°C/m for water, the molar mass of the unknown liquid is **____**g/mol.
256
84
New cards
Important PPE for this lab includes
Choice 1 of 5:Goggles (to be worn at all times in the lab space)
\
Choice 2 of 5:Lab coat
\
Choice 3 of 5:Gloves (to be worn at all times manipulating the experimental set-up)
\
Choice 4 of 5:Gloves (to be worn at all times even on a computer)
\
Choice 5 of 5:Close-toed shoes
Choice 1 of 5:Goggles (to be worn at all times in the lab space)
\
Choice 2 of 5:Lab coat
\
Choice 3 of 5:Gloves (to be worn at all times manipulating the experimental set-up)
\
Choice 4 of 5:Gloves (to be worn at all times even on a computer)
\
Choice 5 of 5:Close-toed shoes
choice 1, 2, 3, 5
85
New cards
freezing point depression
* Freezing point depression occurs when a solute is added to a solvent, lowering the freezing point of the solution compared to the pure solvent
* This phenomenon is used in antifreeze solutions for cars and in the preservation of food by freezing it with salt or sugar added to the water
* This phenomenon is used in antifreeze solutions for cars and in the preservation of food by freezing it with salt or sugar added to the water
86
New cards
molality
Molality is the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent.
87
New cards
freezing point depression formula
The freezing point depression formula is ΔTf = -i Kf m
* ΔTf represents the change in freezing point
* i is the Van’t Hoff factor
* Kf is the cryoscopic constant, which is specific to the solvent
* m is the molality of the solute in the solution
* ΔTf represents the change in freezing point
* i is the Van’t Hoff factor
* Kf is the cryoscopic constant, which is specific to the solvent
* m is the molality of the solute in the solution
88
New cards
boiling point elevation
Boiling point elevation is the difference between the boiling point of a pure solvent and the boiling point of a solution.
\
The molal boiling point elevation constant is a characteristic property of the solvent and is dependent on the solvent's identity and temperature.
\
The molal boiling point elevation constant is a characteristic property of the solvent and is dependent on the solvent's identity and temperature.
89
New cards
boiling point elevation formula
Formula for boiling point elevation is ΔTb = Kb \* m \* i, where ΔTb is the boiling point elevation, Kb is the molal boiling point elevation constant, m is the molality of the solution, and i is the van't Hoff factor.
\
The van't Hoff factor is a measure of the number of particles into which a solute dissociates in solution.
\
The van't Hoff factor is a measure of the number of particles into which a solute dissociates in solution.
90
New cards
vapor pressure lowering
* The vapor-pressure lowering formula is a colligative property, meaning it depends only on the number of solute particles in the solution, not their identity.
* The formula assumes ideal behavior of both the solvent and solute, meaning they do not interact with each other and follow the laws of thermodynamics.
* The vapor-pressure lowering formula is commonly used in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering.
* The formula assumes ideal behavior of both the solvent and solute, meaning they do not interact with each other and follow the laws of thermodynamics.
* The vapor-pressure lowering formula is commonly used in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering.
91
New cards
vapor-pressure lowering formula
The vapor-pressure lowering formula is ΔP = X₂P₀, where ΔP is the change in vapor pressure, X₂ is the mole fraction of the solute, and P₀ is the vapor pressure of the pure solvent.
\
The formula is used to calculate the decrease in vapor pressure of a solvent when a non-volatile solute is added to it.
\
The formula is used to calculate the decrease in vapor pressure of a solvent when a non-volatile solute is added to it.
92
New cards
osmotic pressure
Osmotic pressure is the pressure required to prevent the flow of solvent across a semipermeable membrane.
\
The osmotic pressure is directly proportional to the concentration of solute particles in solution.
\
Osmotic pressure is an important factor in many biological and industrial processes, such as kidney function and water purification.
\
The osmotic pressure is directly proportional to the concentration of solute particles in solution.
\
Osmotic pressure is an important factor in many biological and industrial processes, such as kidney function and water purification.
93
New cards
osmotic pressure formula
The formula for osmotic pressure is π = iMRT, where π is the osmotic pressure, i is the van't Hoff factor, M is the molar concentration of solute particles, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
* The van't Hoff factor is the number of particles into which a solute dissociates in solution.
* The van't Hoff factor is the number of particles into which a solute dissociates in solution.
94
New cards
how to calculate an unknown solute’s molar mass based on its van’t Hoff factor, the known solvent’s given molal-freezing-point-depression constant, and its calculated molality (mols solute/kgs solvent) in solution.
* Determine the van't Hoff factor of the solute
* Obtain the molal-freezing-point-depression constant of the solvent
* Calculate the freezing point depression of the solution
* Convert the freezing point depression to molality
* Calculate the number of moles of solute in the solution
* Divide the mass of solute by the number of moles to obtain the molar mass of the solute
\
1. ΔTf = ΔTf solvent+solute – ΔTf pure solvent, ΔTf pure solvent = avg. freezing point of stearic acid = 69.8ºC
2. ΔTf = -i Kf m, m = molsolute / kgsolvent, i = 1, Kf = 4.5 ºC/m, kgsolvent = 8.007g \* (1 kg / 1000g) = 0.008007 kg
3. m = molsolute / kgsolvent, kgsolvent = 8.007g \* (1 kg / 1000g) = 0.008007 kg = molsolute = 0.467m \* 0.008007kg = 0.00373 molsolute = molar mass of solute = 0.760gsolute / 0.00373molsolute = 203g/mol solute
* Obtain the molal-freezing-point-depression constant of the solvent
* Calculate the freezing point depression of the solution
* Convert the freezing point depression to molality
* Calculate the number of moles of solute in the solution
* Divide the mass of solute by the number of moles to obtain the molar mass of the solute
\
1. ΔTf = ΔTf solvent+solute – ΔTf pure solvent, ΔTf pure solvent = avg. freezing point of stearic acid = 69.8ºC
2. ΔTf = -i Kf m, m = molsolute / kgsolvent, i = 1, Kf = 4.5 ºC/m, kgsolvent = 8.007g \* (1 kg / 1000g) = 0.008007 kg
3. m = molsolute / kgsolvent, kgsolvent = 8.007g \* (1 kg / 1000g) = 0.008007 kg = molsolute = 0.467m \* 0.008007kg = 0.00373 molsolute = molar mass of solute = 0.760gsolute / 0.00373molsolute = 203g/mol solute
95
New cards
how to interpret a plotted warming or cooling curve to identify freezing point or boiling point
96
New cards
1\. 10 Points *Discuss the Concept*: Give a concise but descriptive definition of what a colligative property is. Explain how Van’t Hoff factors and/or solubility determine the extent of colligative properties. You may need to reference your chemistry textbook, the lab manual or your 102 lecture notes. (5-7 Sentences)
In a solution of solvent + some amount of solute, a colligative property is a property of a solvent that changes depending on *how much* solute(s) there is in the solution but NOT on the *identity* of the solute(s) (what the solute is). The Van’t Hoff factor is the number of *particles* that a solute naturally dissolves into in a solution (the number of ions a compound forms when dissolved in solution). If the Van’t Hoff factor is greater, more moles of particles result from 1 mol of initial solute particle, and more non-solvent particles in a solution more dramatically affect colligative properties. Similarly, solubility means the extent to which a solute can dissolve in a solvent. If a solute is more soluble (more able to dissolve) in the solvent, more particles will be dissolved in solution and thus the effect of solute on changing the properties of pure solvent (colligative properties) will be greater.
97
New cards
3\. 10 Points *Discuss the Concept/Expand Understanding*: Describe possible errors in this experiment. Use language from the Error and Error Analysis workshop for full credit (6-8 Sentences). - EXPERIMENT 13
One error was that not all the weighed stearic acid or unknown acid made it into the test tube, affecting overall precision. Specific to trial 1, where our data was the least accurate and consequently caused our overall data to not be precise, this was likely the error. This type of error is a random fluctuation because it was an error with our uncontrolled variables and not an error repeated consistently via faulty equipment. Another random fluctuation that might have affected our precision as well was that maybe we didn’t correctly determine the temperature reading from the thermometer. Again, this would not affect our accuracy because it was not an error repeated consistently but instead would have affected precision if in some trials we misread the thermometer. Although our data was fairly accurate, judging by the low percent errors, one issue that might have affected our accuracy could have been an issue with our equipment. If our thermometer was just a little bit off, we would have consistently recorded data with errors, thus affecting overall accuracy.
98
New cards
EXPERIMENT 15.1
99
New cards
how to standardize samples of stock solutions to a known concentration
use M1 V1 = M2 V2
100
New cards
The main purpose for Experiment 15.1 is to
\
Choice 1 of 5:Run a reaction
\
Choice 2 of 5:Determine the relationship between the concentration of Fe(NCS)2+ and the absorbance to collect the value of molar absorption coefficient
\
Choice 3 of 5:Collect absorbances and discuss the chemical equilibrium
\
Choice 4 of 5:Solve the K value of the reaction
\
Choice 5 of 5:To use Beer's Law to calculate the wavelength needed for spectrophotometry
\
Choice 1 of 5:Run a reaction
\
Choice 2 of 5:Determine the relationship between the concentration of Fe(NCS)2+ and the absorbance to collect the value of molar absorption coefficient
\
Choice 3 of 5:Collect absorbances and discuss the chemical equilibrium
\
Choice 4 of 5:Solve the K value of the reaction
\
Choice 5 of 5:To use Beer's Law to calculate the wavelength needed for spectrophotometry
Choice 2 of 5:Determine the relationship between the concentration of Fe(NCS)2+ and the absorbance to collect the value of molar absorption coefficient