EXAM 2
1/198
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
199 Terms
Cytokines
Signaling molecules produced by antigen-presenting cells (APCs) during infection that regulate the differentiation of T cells.
Adaptive immune response
The immune response that occurs after the establishment of infection, characterized by the activation and differentiation of T and B cells.
Innate response
The non-specific immune response that targets pathogens non-specifically, such as through the breakage of skin.
Antigen presenting cells (APCs)
Cells that encounter pathogens, pick them up, and present them to lymphocytes (T or B cells) to stimulate an immune response.
T helper cells
Mature effector cells that differentiate from naive CD4 cells and play a role in the adaptive immune response.
Plasma cells
Mature effector cells that differentiate from B cells and produce antibodies.
Dendritic cells
APCs that produce different cytokines depending on their activation status, such as TGF beta when not fully activated and IL6 and IL-23 when activated.
Naive CD4 T cells
CD4 T cells that have not yet encountered a pathogen and can differentiate into different subsets (TH1, TH2, TH17) depending on the cytokines present.
TH17 cells
Subset of CD4 T cells that differentiate in response to high levels of IL6 and TGF beta during the early phase of infection.
TH1 cells
Subset of CD4 T cells that differentiate in response to IL12 produced by dendritic cells during infection with viruses or bacteria.
TH2 cells
Subset of CD4 T cells that differentiate in response to IL4 produced by NK cells during infection with parasites.
Treg cells
Regulatory T cells that produce TGF beta and inhibit the differentiation of other CD4 T cell subsets.
L-selectin
A molecule that mediates the homing of naive T cells to the lymph nodes.
VLA 4
An integrin molecule that binds to VCAM1 and ICAM-1 on peripheral vascular endothelium.
LFA-1
An integrin molecule that binds to VCAM1 and ICAM-1.
Primary antibody
Antibodies produced by plasma cells that are more general and have relatively low affinity and few somatic mutations.
Secondary antibody
Antibodies produced by memory B cells that are more specific, undergo clonal expansion, and have high affinity for the antigen.
Memory B/T cells
Cells that remember pathogens and provide a quicker and more specific response upon re-infection.
Mucosal immune system
The immune system that protects the internal surfaces of the body, with lymphoid organs associated with various mucosal tissues.
Commensal microorganisms
Microorganisms that reside on the surface of the body or at mucosa without harming human health and provide essential functions like aiding in digestion and educating the immune system.
Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissues (GALT)
Organized secondary lymphoid tissues in the gut, including Peyer's patches and isolated lymphoid follicles.
Waldeyer's Ring
A ring of lymphoid organs that surround the entrance to the intestine and respiratory tract, including adenoids, palatine tonsils, and lingual tonsils.
Peyer's patches
Lymphoid tissues in the small intestine that contain T cells and B cells and are separated from the intestinal lumen by a single layer of epithelium.
Effector cells
Lymphocytes that are scattered throughout the mucosa and are involved in the immune response, such as effector T cells and antibody-secreting plasma cells.
M cells
Specialized cells found in the follicle associated epithelium of Peyer's patch in the small intestine.
Mechanism of M cell uptake and transport of antigens
M cells take up antigens through endocytosis and phagocytosis, transport them across the cell in vesicles, and release them at the basal surface. The antigens are then bound by dendritic cells, which activate T cells.
Transcytosis
The name of the mechanism by which antigens are transported across cells, specifically referring to the transport of antigens by M cells.
Mononuclear cells
Cells located in the lamina propria of the small intestine that capture antigens from the intestinal lumen.
Enterocytes
Cells in the surface epithelium of the small intestine that capture and internalize antigens through antibody complexes. They transport the antigens across the epithelium by transcytosis.
T-cells in the lamina propria of the small intestine
express the integrin α4:β7 and the chemokine receptor CCR9, which attracts them into the tissue from the bloodstream.
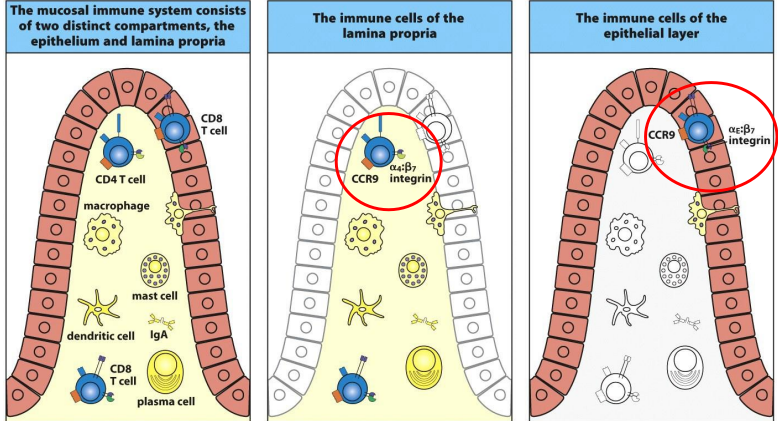
Difference between CD4 T cells and CD 8 T cells:
CD4 T-cells predominate in the lamina propria, whereas CD8 T-cells predominate in the epithelium.
What are the M cells found in the small intestine?
found in the the follicle-associated epithelium of the Peyer’s patch
What’s are the distinct phases of infection
establishment of infection
induction of adaptive response
adaptive immune response
immunological memory
describe the course of the immune response
Innate response- target pathogens non specifically
Breakage of skin, pathogens come in antigen presenting cells encounter pathogens = pick them up and go to lymphonide to present to lymphocytes (T or B) and stimulated, once becomes stimulated become mature effector cells = T helper cells (no longer naive) B cells (plasma cells)
Phase 2 of the infection, what is happening in the induction of adaptive response?
# of pathogens continue to grow
Growth took off
in the course of the immune response, what happens in phase 4?
Infection = cleared + dose of antigen falls below threshold- response ceases
Provide lasting protection against reinfection
What are the cytokines made by the APCs during infection and their effects?
When dendritic cells not not fully activated = TGF beta
activated= IL6, IL-23=produces naive CD4 cells into TH17
Naive CD4= IL-12 + IFN gamma ≠TH2 but does =TH1
TLR drives dendritic cells =IL-12
Naive CD4+IL4=TH2
Is TGF beta present when there is an infection? Or what is present when infection is present?
TGF beta when no infection (main cytokine) or early stage of infection = see Treg cells or TH17 cells
T17= 1st to respond/come out
Treg = suppress activity
When infection doesn’t want inhibition
TH3
involved in mucosal immunity and protecting mucosal surfaces in the gut from nonpathogenic non-self antigens.
mediate this non-inflammatory environment by secreting TGF-beta and IL-10.
What cytokines made in the earliest phase of an infection influenced the differentiation of CD4 T17 subset?
When infections
High level of IL6 + TGF beta = naive CD4 T cells responds by expressing ROR gamma T= TH17 cells
encountering of a pathogen the earliest response of dendritic cells is to synthesize: IL-6 and TGF-, these two cytokines induce naïve CD4 T-cells to differentiate into TH17 which leave the lymph node and migrate to distant sites of infection
Are lymphocytes active when there is no infection? Are they when there is an infection?
When lymphocytes are inactive. Don’t want swelling. When infection comes in want inhibition from Treg to be lyfted= want lymphocytes to do work |
What cytokines made in the later stages of an infection influenced the differentiation of CD4 T cells towards the TH1 or TH2?
Parasite
IL4 (interleukin) by NK cells= naive CD4 tells activated= TH2 cells
virus/bacteria
Induce IL 12 by dendritic cells= Nk cells=IFN gama= TH1
how subset of CD4 T cell regulate each other’s differentiation?
No infection
TGF beta produced by Treg cells=naive T cells
Naive T cells inhibit TH17, TH1, or TH2
During infection
TH17 1st response due to IL6 produced from dendritic cells
TH17 develops regulatory t cell (downgraded) + TH 17 (decrease in environment)
TH 1 or TH2 ≠ TH17
TH2=IL(interleukins) 10 =macrophages
Macrophages ≠ TH 1
By blocking macrophages IL-12 synthesis and TGF beta= acts directly on TH1 cell to inhibit growth
TH1 make IFN gamma=blocks growth of TH2
IL 6 evelated= switch point = produce TH 17
Tgbeta decreases as T reg isn’t as high
TH1 + 2 inhibit TH17
Distinct subset of CD4 T cells can regulate each others differentiation:
what are L selectin?
Mediates homing to the lymphnodes
Expressed in naive T Cells
What’s VLA 4?
Bind to VCAM1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule 1) and ICAM-1 on peripheral vascular endothelium
Integrin
What’s LFA-1?
Bind to VCAM 1- and ICAM- 1
Integrin
Differences between VLA 4 and LFA
Effector T cells don’t express VLA 4
Different set of adhesion molecules
Primary Antibody:
ANTIBODY MADE BY PLASMA CELLS
More General - precursor B cells specific for specific different epitopes of antigens and with receptors with range of affinities for the antigen
Relatively low affinity
Few somatic mutations
initial rapid production of IgM
Mild IgG
Secondary Antibody:
More specific- more limited population
Undergo significant clonal expansion
High affinity for antigen
Extensive somatic mutation
large amounts of IgG
small amounts of IgA and IgE
Describe the survival requirements for naive t-cells and memory cells.
Survival naive T-cells + memory B/T cells
Stimulation with:
IL7, I15
They don’t need contact with self peptide: self MHC complex but will for proliferation
Naive T cells
Stimulation with:
IL7, I15
Self-peptide: self MHC complex
Describe the original antigeic skin phenomenon
Make antibodies only against epitopes present on the initial virus
Only recognize the 1st antigen
Try one approach and then adapt when it doesn’t work (2… time)
Gets reinfected with different variant/ type and memory cells don’t have knowledge
Get more IgM
B cells will be activated
New memory cells will be made
responds to epitopes shared with original virus, add the subnormal response to new epitopes is retained
description of mucosal immune system:
Protect the internal surface of the body
Antamically defined compartment and scattered through muscol tissues
Large # of effector lymphocytes
Controlled by tissue-specific adhesion molecules + chemokines receptors
What lymphoid organs is the mucosal immune system associated with?
Intestines, respiratory tract, urogential tract, oral cavity, pharynx, salivary glands, lachrymal glands, digestive system, lactating breast.
Opening to the outside (similarities )
Communicating with outside pathogens
Innate immunity
Contain white blood ____
Facts about the mucosal immune system II
Priming of Lymphocytes in one mucosal tissue can induce protective immunity at other mucosal surfaces.
Unique populations of dendritic cells control mucosal immune responses.
secretory IgA class of antibody associated with mucosal immune system
IgA deficiency is common in humans but may be compensated for by secretory IgM.
What are commensal microorganisms (microbiota)?
Reside on the surface of the body or at mucosa without harming human health
(live symbiosis with host)
Non pathogenic
Don’t cause problems
Why
Non cell
Beneficial as they don’t allow other bacteria to grow
Why?
Competition / fight for resources
Keep suppress bad bacteria
why are microbiota there?
supply the host with essential nutrients and defend the host against opportunistic pathogens
where do microbiota live?
Mouth
Esophagus
Skin
Stomach
Vagina
Colon
Examples of microbiota
Lactobacillus spp. (Firmicutes),
Bifidobacterium spp. (Actinobacteria),
Bacteroides fragilis (Bacteroidetes)
Escherichia coli (Proteobacteria)
What are Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissues(GALT) and Walderyer’s Ring?
Galt
Comprises:
the peyer’s patches, isolated lumpoid follicles, palatine tonsils, adenoid and lingual tonsils
Organized secondary lymphoid tissues
Waldeyer’s Ring
Ring of lymphoid organs that surround the entrance to the intestine and respiratory tract
Comprises:
Adenoids, palatine tonsils, and lingual tonsils
describe the lymphocyte population distribution in the small intestine
Found in compartment in the intestine:
Peyer’s patches + isolated lympod follicles (GALT)
Separated from the content fo the intestinal lumen by tsingle layer of epithelium
Peyer’s pathes and mesenteirc lymph nodes
Contain desciste T cells and isolated follicles comprise mainly B cells
Lymphocytes found scattered throughout the mucosa outside the organized lymphoid tissues: these are effector cells
effector T-cells and antibody-secreting plasma cells
Found in
lamina propria (floating around are effector)
Peyer’s patch
Follicles
what are part of the discrete lymphoid compartment?
lamina propria
epithelium
what’s lamina Propria?
contains a heterogeneous mixture of IgA-producing plasma cells, lymphocytes with a ‘memory' phenotype, conventional CD4 and CD8 effector T-cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, and mast cell
what’s the difference between CD4 T cells and CD 8 T-cells?
CD4 T-cells predominate in the lamina propria, whereas CD8 T-cells predominate in the epithelium.
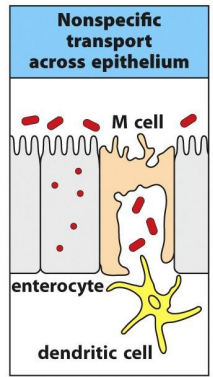
Describe the mechanism that M cells uptake and transport antigens
Mechanism
M cells take up antigens by endocytosis and phagocytosis
Antigen is transported across the M cells in vesicles and released at the basal surface
Antigen is bound by dendritic cells which activate T cells
Transport across cell mechanism name:
Transcytosis
How mononuclear cells located in the lamina propria capture antigens from the intestinal lumen? (step 1)
Soluble antigens get transported across or between enterocytes where M cells might be in the surface epithelium outside Peyer’s patches
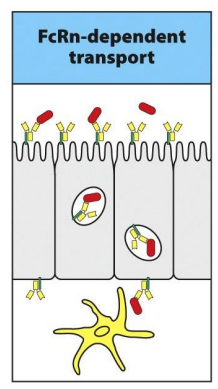
How mononuclear cells located in the lamina propria capture antigens from the intestinal lumen? (step 2)
Enterocyctes capture and internalize antigens though antibody complex
FcRn on their surface and transport them across the epithelium by transcytosis
At the basal face of the epithelium, lamina propria dendritic cells expressing FcRn and other Fc receptors pick up and internalize the complexes.
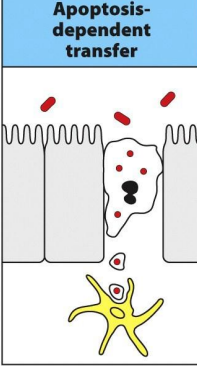
How mononuclear cells located in the lamina propria capture antigens from the intestinal lumen? (step 3)
an enterocyte infected with an intracellular pathogen undergoes apoptosis and its remains are phagocytosed by the dendritic cell
How mononuclear cells located in the lamina propria capture antigens from the intestinal lumen? (step 4)
mononuclear cells have been seen extending processes between the cells of the epithelium without disturbing its integrity. The cell process could pick up and internalize antigen from the gut lumen and then retract
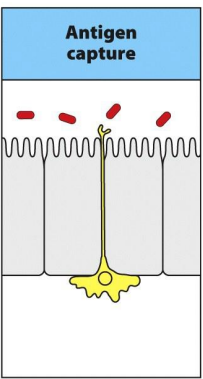
Examples of leukocytes
NK
dendritic cells
monocytes
leukocytes
What is the “type a” intraepithelial lymphocyte (IEL)?
CD8 cryptic T cells
Recognize Peptides derived from virus
Triggered by MHC I
What is the “type b” intraepithelial lymphocyte (IEL)?
T cells actives by IEL
Stressed epithelial
How do IgA antibodies get to be sereted into the gut lumen ?
mediated by polymeric Ig receptor (pIgR)
What can IgA do at the epithelial surface?
Neutralize pathogens + toxins= prevents access to tissues + inhibit their functions
How:
IgA absorbs on the layer of mucus covering the epithelium
Neutralize antigens internalized in endosome
How
Antigens internalized by the epithelial cells can meet
IgA can export toxins and pathogens form the lamina propria while being secreted
describe the protective response to intestinal helminths
Induce CD 4 T cells
TH2 induce B cells in order to switch to IgE (protective response)
TH1 produces inflammatory reaction. Generated when activating dendritic cells express I
what do TH3 cells do?
Secrete TGF-beta and IL-10
Inhibit TH1 and TH2 responses
Differentiation is enhanced by TGF Beta IL 4, and IL 10
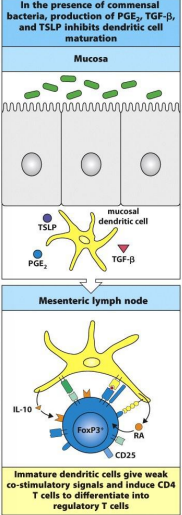
how mucosal dendritic cells regulate the induction of tolerance and immunity in the intestine? (under normal condition)
dendritic cells present in the mucosa underlying the epithelium and can acquire antigens or commensal organism
take antigens to the draining lymph node- present them to naive CD 4 T cells
constitutive production by epithelia cells and mesenchymal cells:
TGF beta, TSLP, PGE2
maintain the local dendritic cells in quiescent state w/ low levels of co-stimulatory molecules
when present antigen to naive CD 4 t cells, reg T cells generated
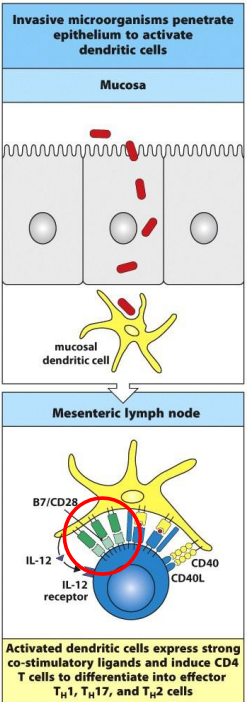
how mucosal dendritic cells regulate the induction of tolerance and immunity in the intestine? (invasion by pathogen)
full activation of local dendritic cells and their expression of co-stimulatory molecules and pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL12)
presentation of antigen to naive CD4 T cells in mesenteric lymph nodes by dendritic cells cause differentiation into effector TH1 and TH2 cells
Protective Immunity with invasive bacteria, virus, toxins:
primary Ig Production:
Intestinal IgA
specific Ab present in serum
Primary T cell response
local and systemic effector and memory T cells
Response to antigen reexposure:
enhanced memory response
mucosal tolerance w/ food proteins
primary Ig production:
some local IgA
low or no antibody in serum
Primary T response:
no local effector T cell response
Response to antigen reexposure:
low or no response
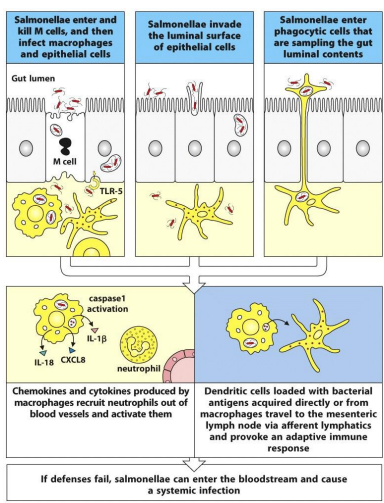
what are the three route of entry for Salmonella
enters and kills M cells and then infects macrophages and epithelial cells
invades the luminal surface of epithelial cells
enters phagocytic cells that are sampling the gut luminal contents
Discuss the infections from salmonella
Enters M cells and causes apoptosis
Penetrates the epithelium and infects macrophages and gut epithelial cells
Epithelial cells express TLR 5= bind flagellin on the salmonella flagella= activating an inflammatory response via the NFkB pathway
Induces Caspase 1 activation= promoting production of IL 1 Beta and Il 18
CXCL 8 is produced by infected macrophages and recruit and activate neutrophils
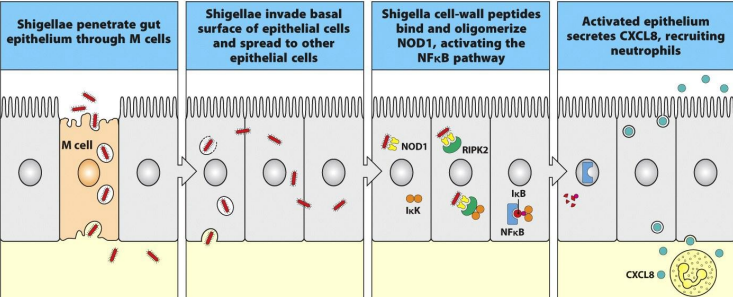
Discuss the infections from shigella flexneri
Binds to M cells and is translocated benearth the gut epithelium
Bacteria infects intestinal epithelial cells from their basal surface and are released ino the cytoplasm.
Murmamy tripeptide containing diaminopimelic acid in the cells walls of shigella bind to and oligomerize the protein of NOD1
Oligomerized NOD1 binds to serine/thronine kinase RIPK2= trigs activation of NFkB pathways= leading to the transportation of genes for chemokines and cytokines
activated epithelial cells release the chemokine CXCL8= acts a neutrophil chemoattractant.
IkB inhibitor of NFkB; IkK, IkB kinase
chemokine CXCL8
Acts a neutrophil chemoattractant
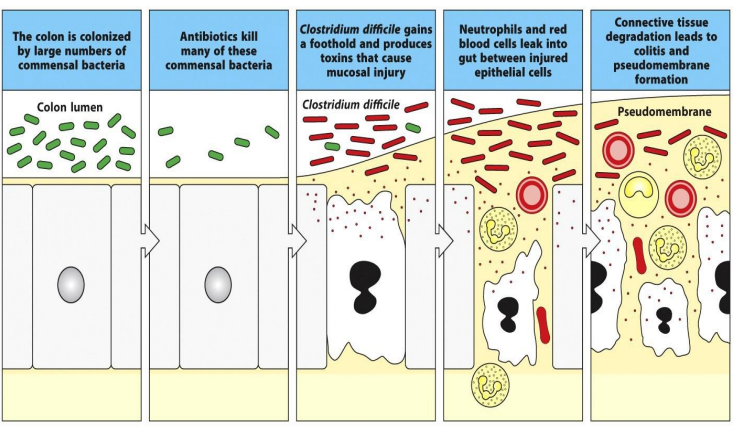
Discuss the infections from C. Diff
colon is colonized by large # of commensal bacteria
antibiotics kill many of these commensal bacteria
C.Diff gains a foothold and produces toxins that cause mucosal injury
neutrophils and red blood cells leak into gut btw injured epithelial cells
connective tissue degraded lead to colitis and pseudomembranous formation
Describe the crucial role the epithelial cells have in the innate defense against pathogens.
TLRs +NODs activate the NFkB pathway= generate pro=inflammatory response by epithelial cells
production of:
CXCL8, CXCL1 (GROalpha), CCL1, CCL2
attract neutrophils and macrophages
CCL20 + beta defense’s
attract immature dendritic cells
cytokines IL 1 +IL 6
activate macrophages
epithelial cells express MIC-1 + MIC B
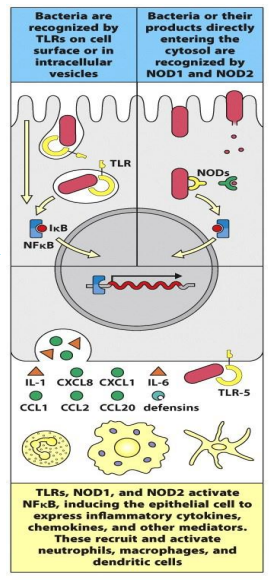
NOD1 and NOD2 pattern recognition receptors
found in the cytoplasm and recognize cell wall peptides from bacteria
TLR 5
recognize flagellin
TLRs
present in intracellular vesicles or on the basolateral or apical surfaces of epithelial cells, where they recognize different components of invading bacteria
TLRs + NODs activate ____
NFkB pathway
NFkB pathway
lead to the generation of pro-inflammatory responses by epithelial cells
discuss the immediate response in allergic reaction
IgE-mediated mast cell activation
Due to the activity of histamine, prostaglandin = rapid increase in vascular permeability and contraction
Mass cells
Prostagladin
Inflammation
discuss the late-phase response in allergic reaction
Caused by
Induce synthesis and release mediators including prostaglandins, leukotrienes, chemokines, and cytokines such as IL-5 and IL-13 from activated mast cells and basophils. These recruit other leukocytes to the site of inflammation.
associated with a second phase of smooth muscle contraction mediated by T-cells, with sustained edema and with tissue remodeling such as smooth muscle hypertrophy (an increase in size due to cell growth) and hyperplasia (an increase in the number of cells
Fluid leaking = swelling =edema
Histamine increases the permeability of blood vessels= allowing leukocytes to bring to the site and go inside blood tissue
Permeability = allows to escape
Allows fluid to escape
Thus allowing fluid to be released into the tissue
Allows lymph drainage to take pathogen to lymphoid
Describe the type I of hypersensitivity reactions
Mediated:
IgE Ab-mediated
effector mechanism
mast cell activation
antigen
soluble antigen
Describe the type II of hypersensitivity reactions
mediator
IgG Ab
effector mechanism
complement
phagocytic
antigen
cell surface antigen
matrix antigen
Describe the type III of hypersensitivity reactions
mediated
IgG Ab
effector mechanism
complement
phagocytic
antigen
soluble antigen
Describe the type IV of hypersensitivity reactions
mediated
T lymphocytes
effector mechanism
Macrophage activation by T H 1
Eosinophil activation by T H 2
cytotoxicity via CD8 TC
antigen
soluble antigen
cell-associated Antigen
Give an overview of the IgE–mediated reactions to extrinsic antigens.
IgE is produced by plasma cells in lymph nodes
binds to mast cells via FcERI receptor (high–affinity IgE receptor) which causes mast – cells to release their granules which causes allergic symptoms
high permeability – things can leave blood vessels to go to tissue
Describe the process of sensitization to an inhaled allergen (respiratory tract)
Antigen invades mucous membrane by breaking down occluding – interacts w/dendritic cells, the dendritic cells pick up the Ag and present it to naïve T cells in lymph nodes
How B–lymphocytes get triggered for class switching to IgE
IgE bound to a high – affinity Fc receptor on mast cell cross–links to Ag express CD40 ligand