Session 3: The Vertebral Column & Common Injuries
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
Functions of the vertebral column
- Protection = spinal cord, roots of spinal nerves, meninges
- Shock absorption
- Projects weight of body to pelvis and lower limbs
- Segmental innervation of the body
The spinal cord is part of the ___ skeleton
Axial
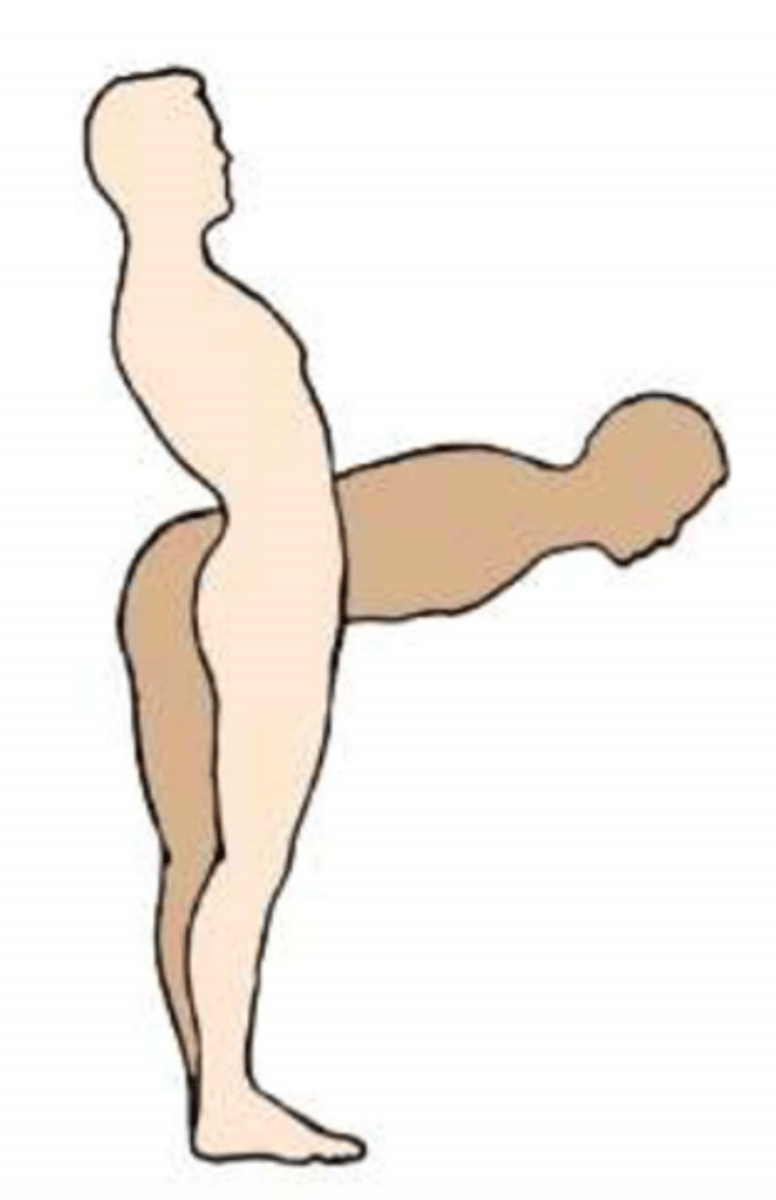
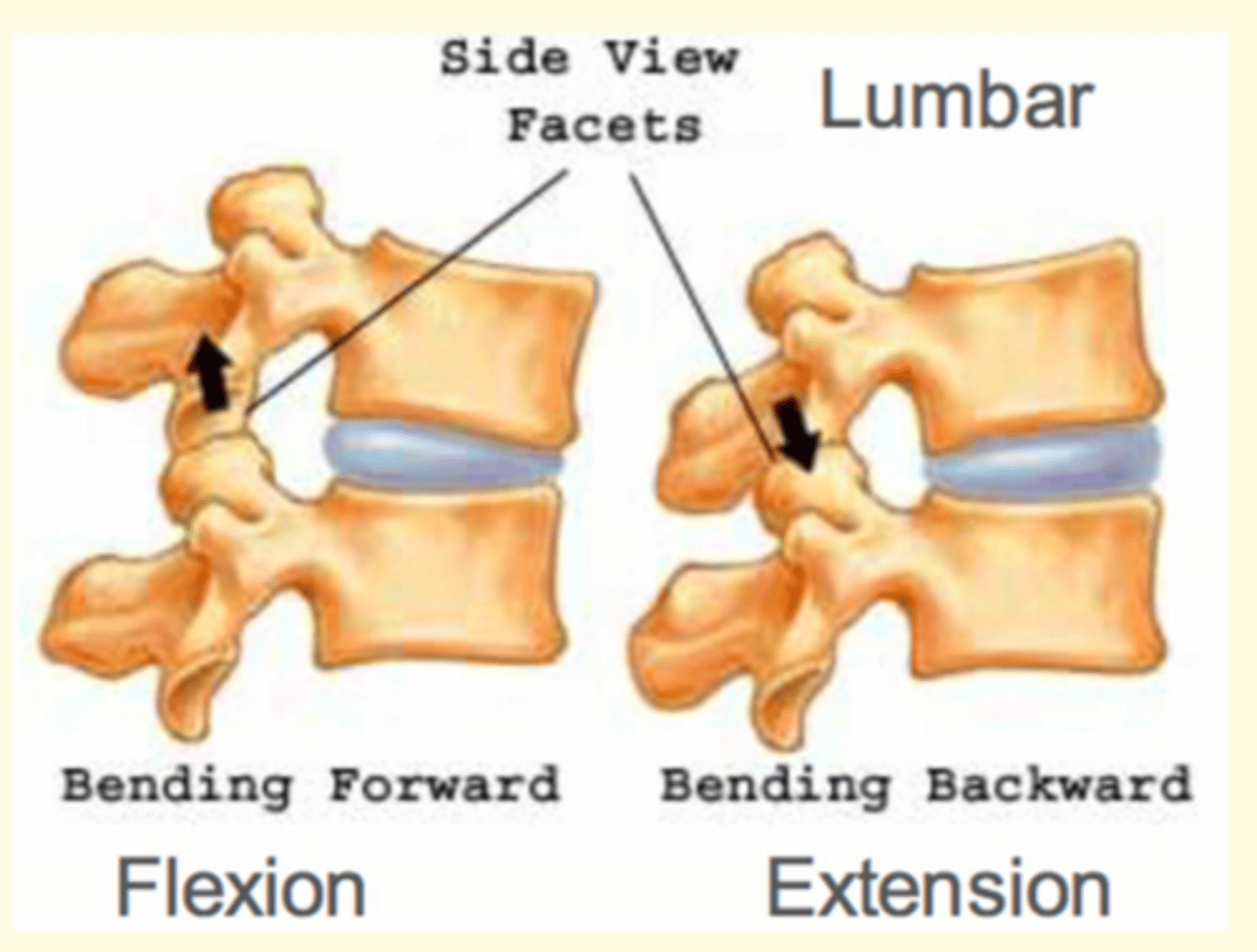
The vertebral column can engage in three types of movement.
This image shows what movement of the vertebral column?
Flexion & Extension of vertebral column
Flexion (bending forward)
Extension (bending backward)

The vertebral column can engage in three types of movement.
This image shows what movement of the vertebral column?
Lateral Flexion of vertebral column
The vertebral column can engage in three types of movement.
This image shows what movement of the vertebral column?
Rotation of vertebral column
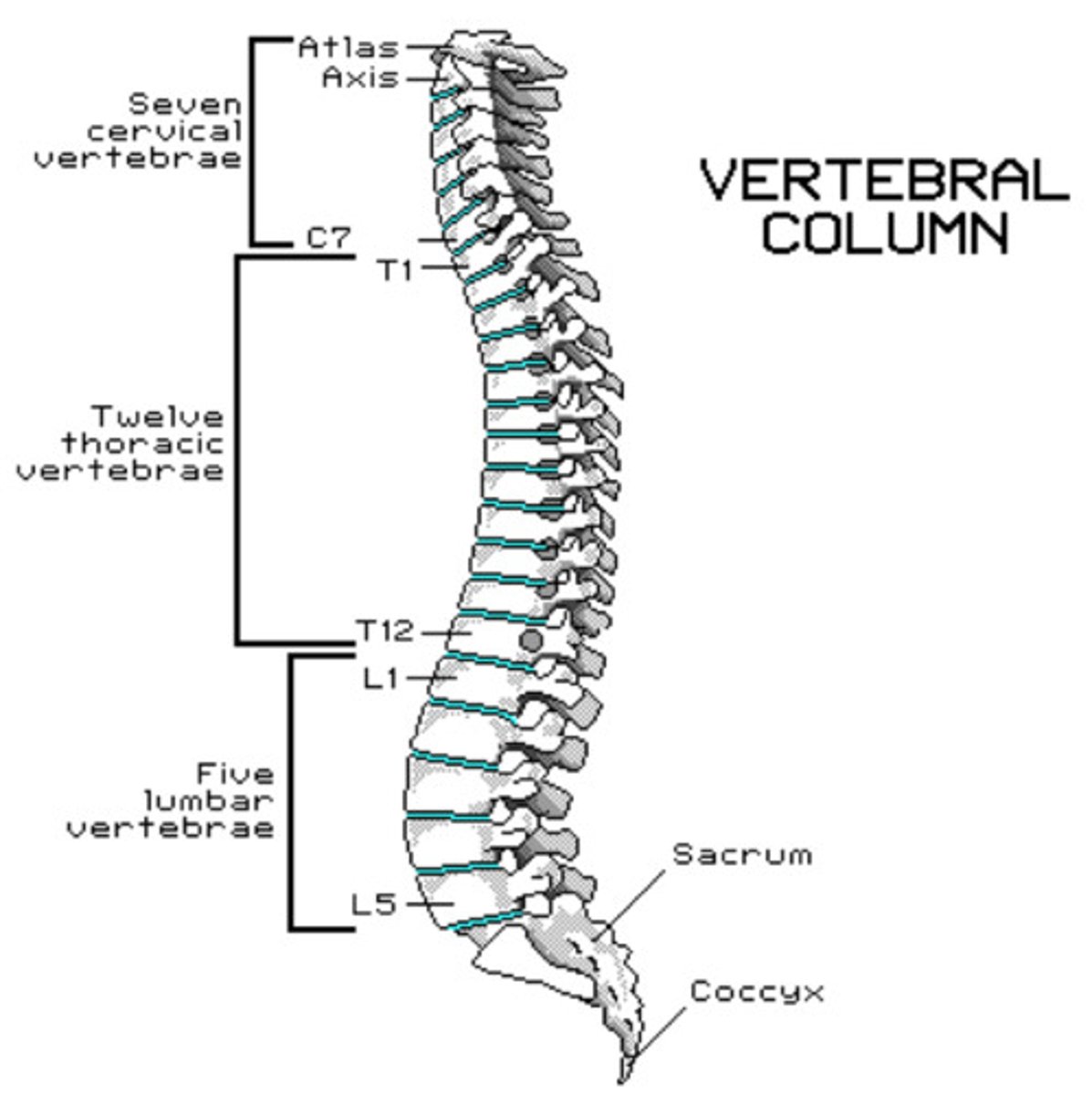
Vertebral column is made up of ___ vertebrae
33 vertebrae
(7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral fused, 4 coccygeal fused)
'Wake up at 7, lunch at 12, go home at 5'
Why do vertebral bodies increase in size inferiorly as compression forces increase?
Transmit weight of body through pelvis to the legs
So sacral vertebrae at bottom of vertebral column are fused, widened and cocaved anteriorly.

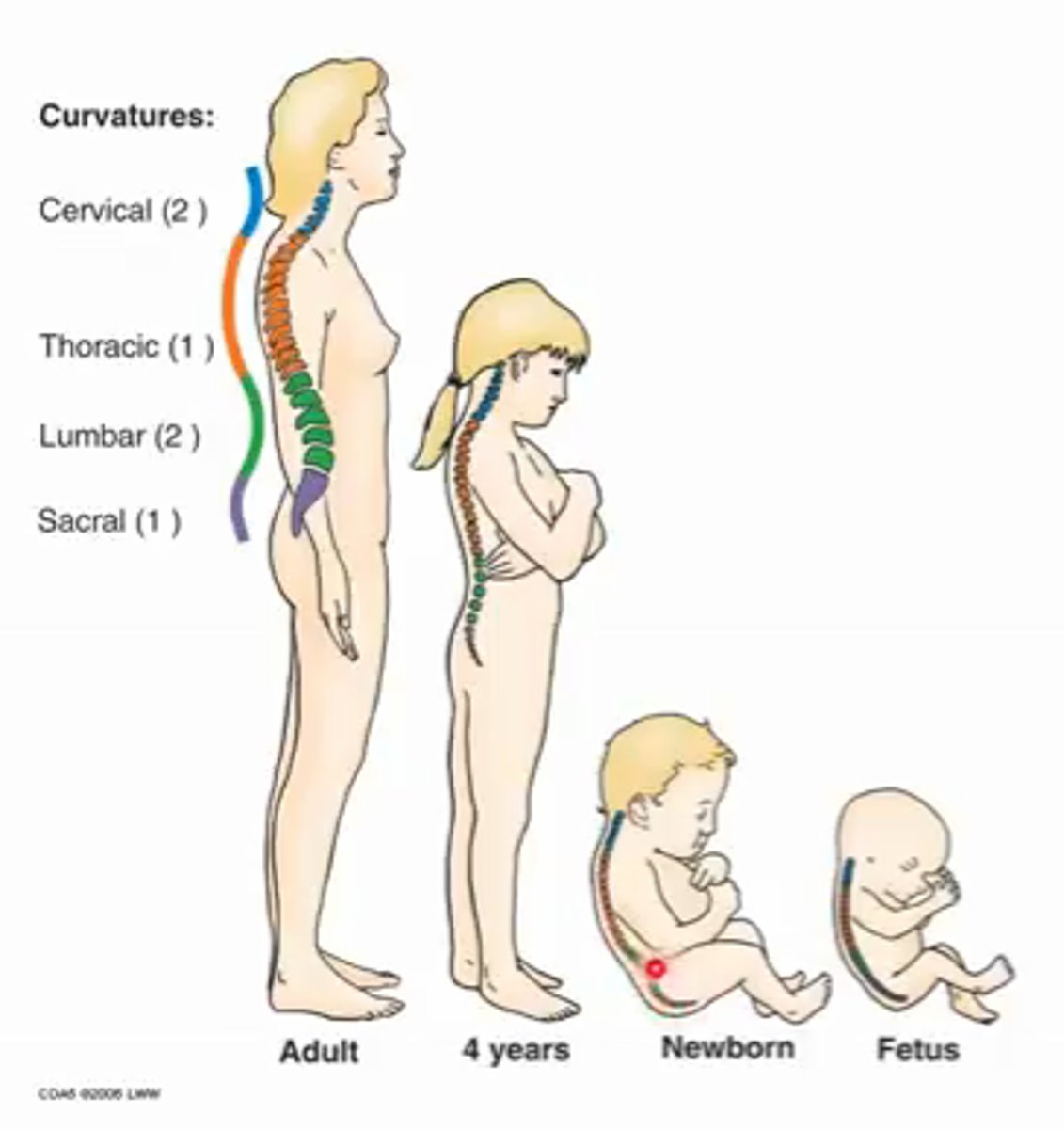
Describe the primary curvature of the vertebral column that occurs in the foetus
Primary = thoracic curvature, also sacral
Flexed in single c-shaped curvature
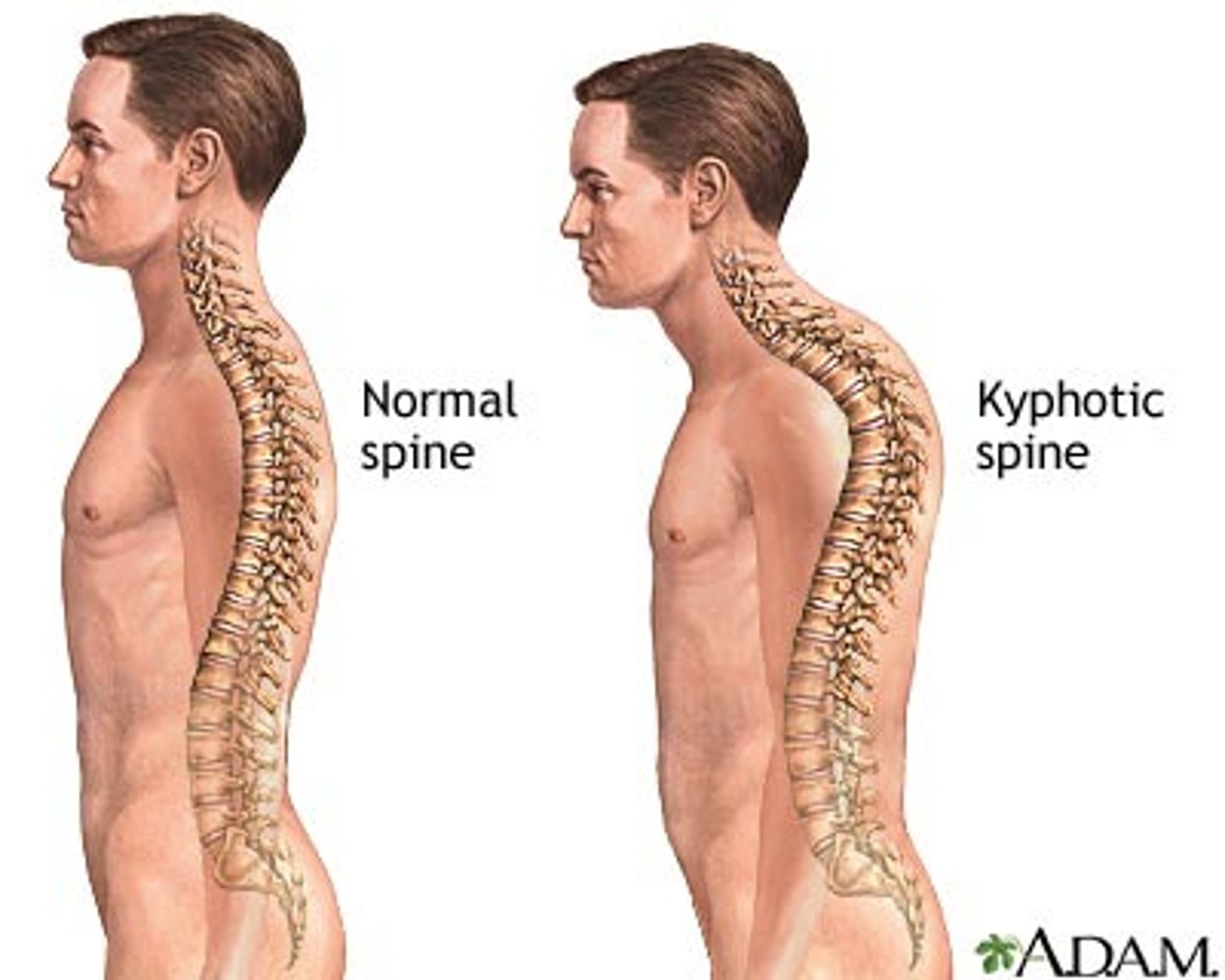
Kyphosis
Kyphosis
Hunchback, exaggerated thoracic curvature
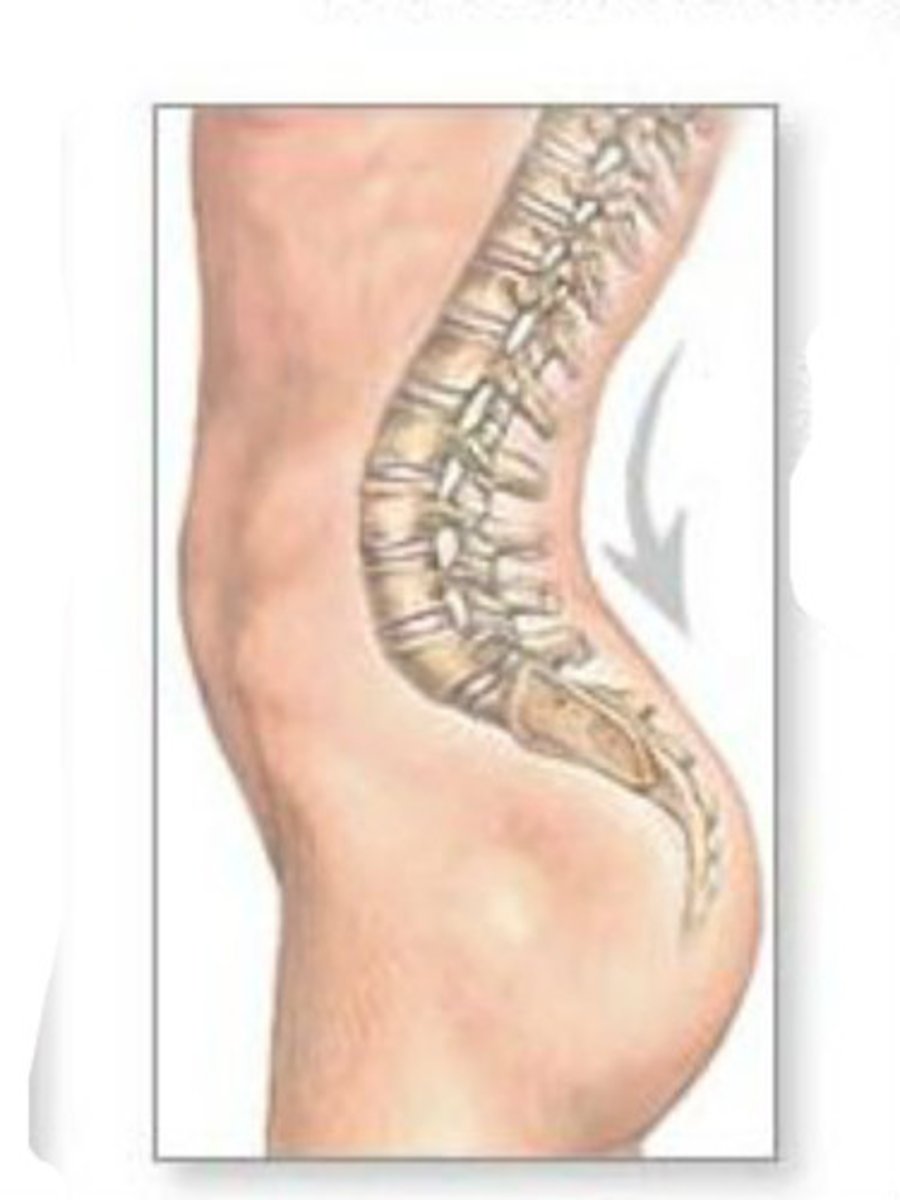
Lordosis
Swayback, increased lumbar curvature
Describe the secondary curvatures of the vertebral column that occurs in childhood
Secondary curvatures...
1) Cervical - lifting head
2) Lumbar - starting to walk (lordosis)
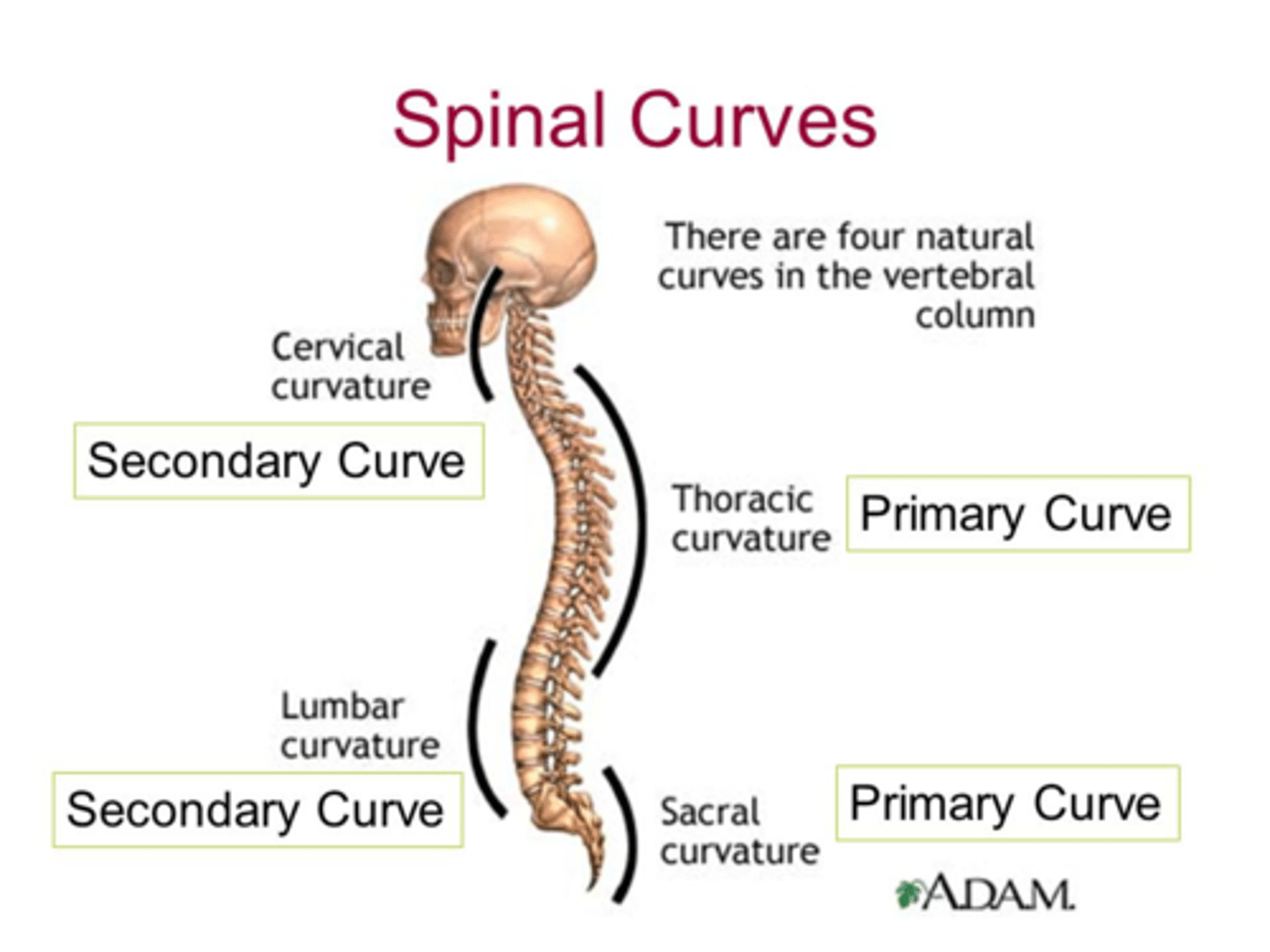
Primary curves of the vertebral column
Thoracic curvature (also sacral)
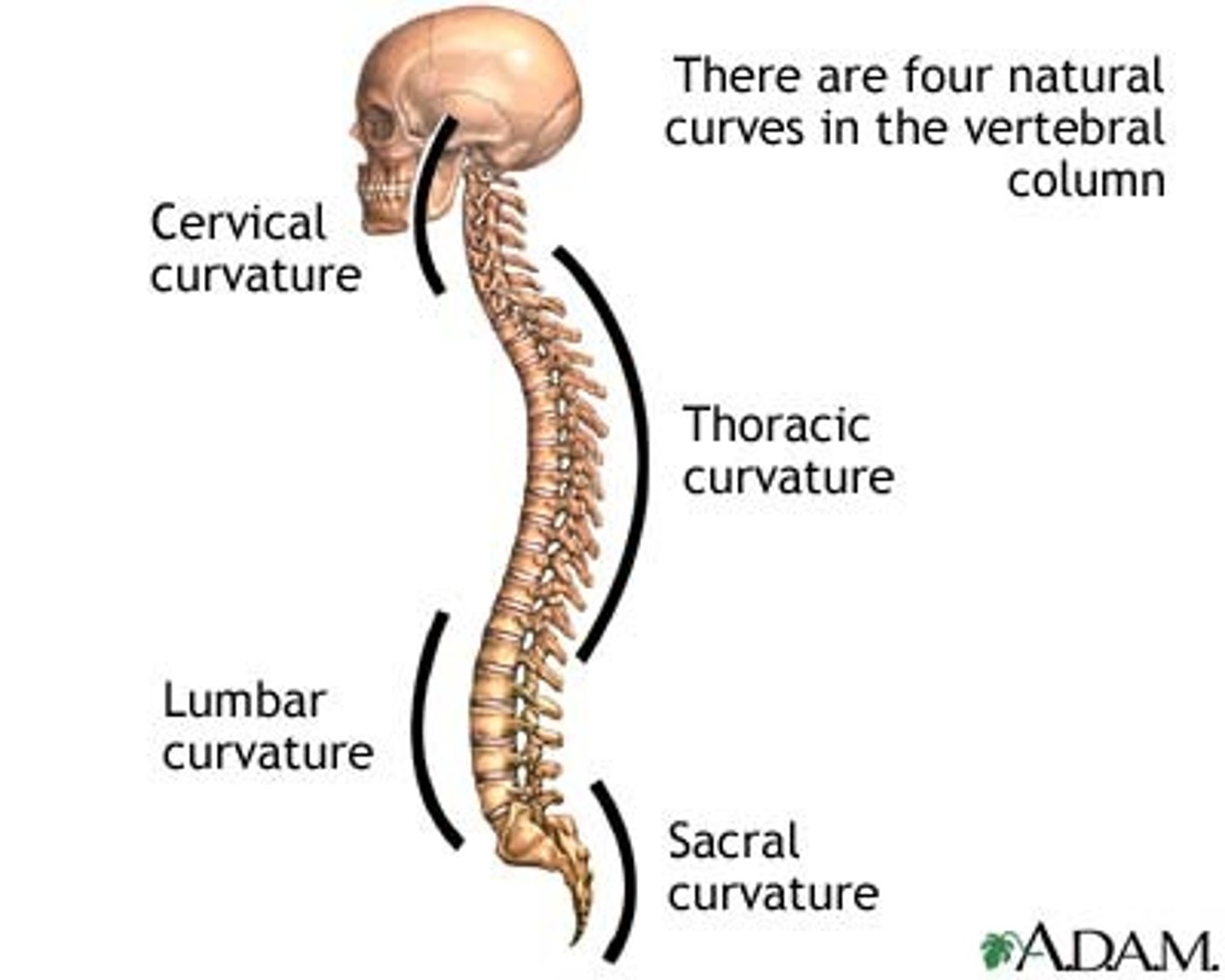
Secondary curves of the vertebral column
Cervical and lumbar curvature
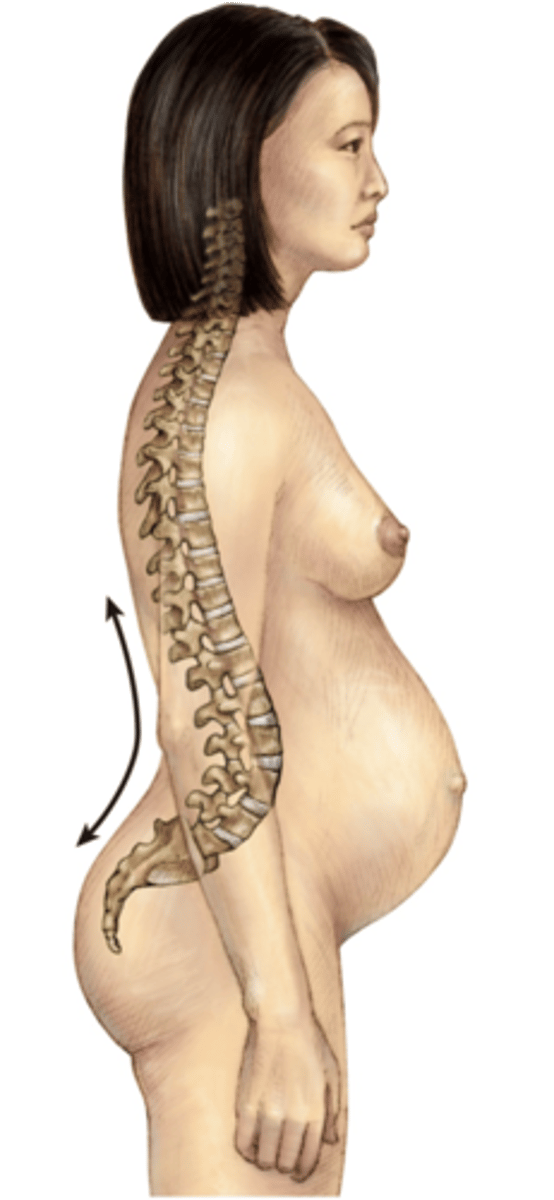
Example of when a lordosis happens naturally (physiological lordosis)
Pregnancy or large central body mass
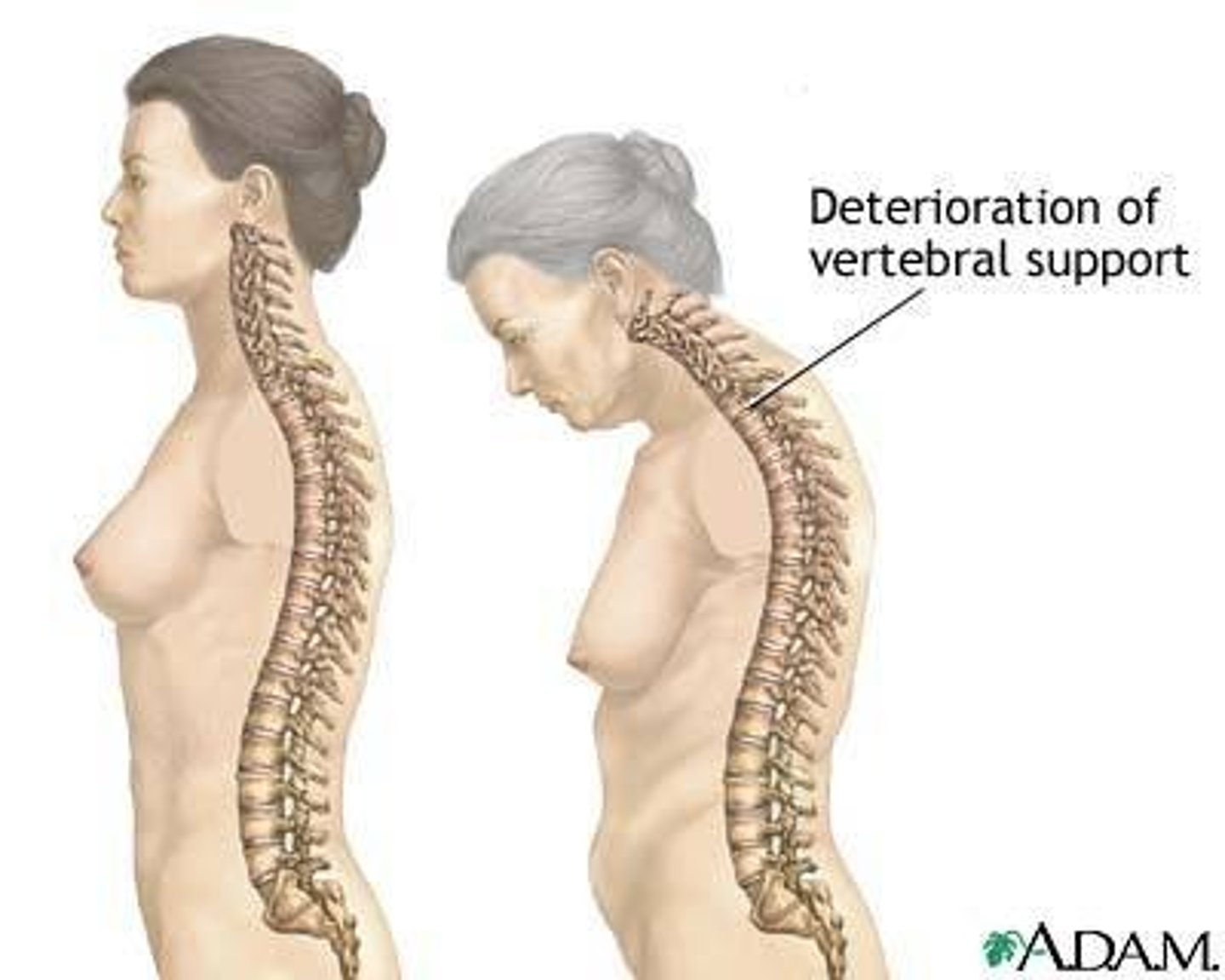
Example of when a kyphosis happens naturally (physiological kyphosis)
Senile kyphosis
With increasing age, secondary curvatures begin to disappear
Example of a pathological curvature of the vertebral column
Scoliosis = abnormal lateral curvature of the spine
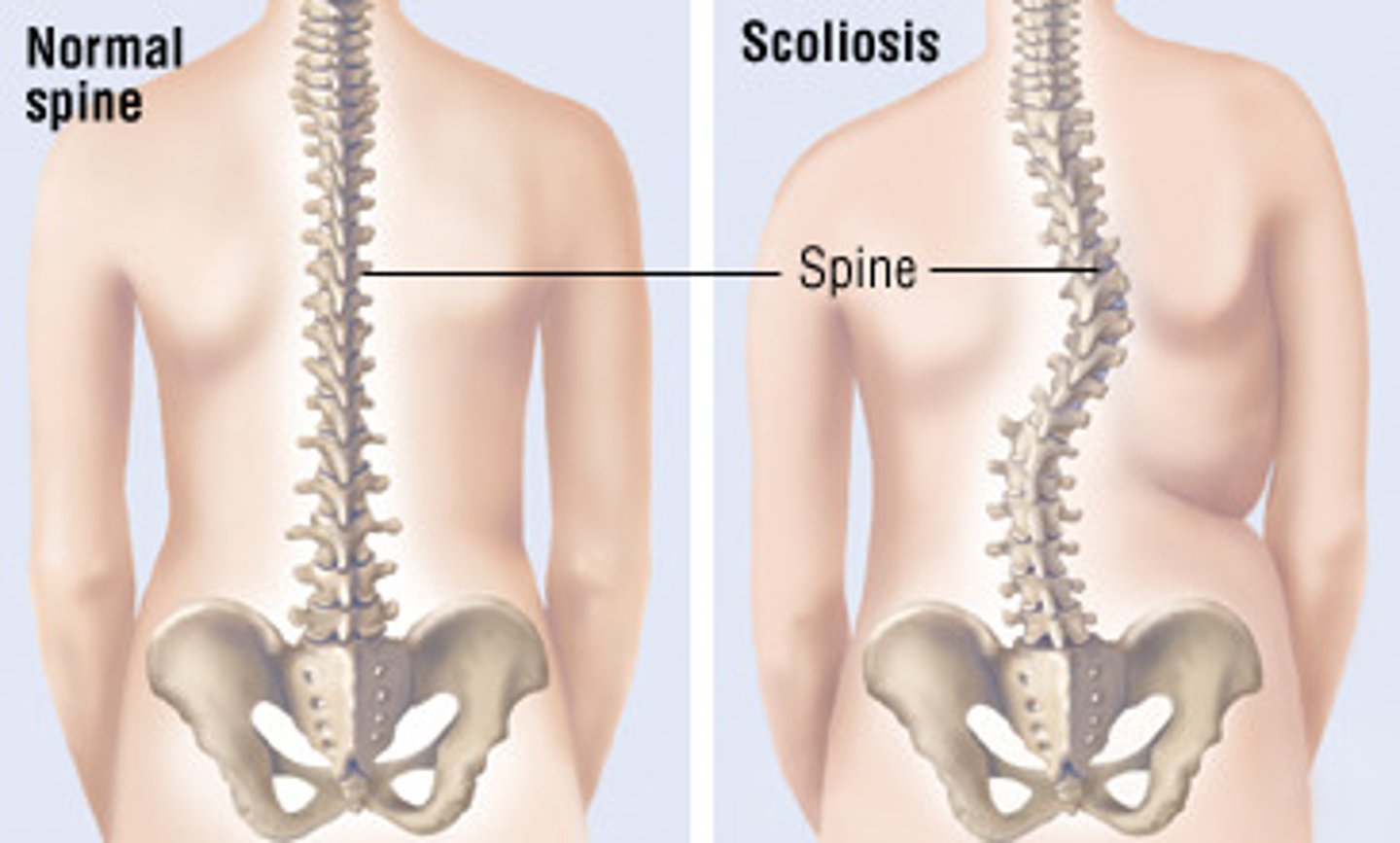
Causes of scoliosis
1) Primary = congenital
2) Idiopathic = any age, unknown
3) Secondary = neuromuscular disease
Scoliosis (the abnormal lateral curvature of the spine) is typically only cosmetic. However, in severe cases of scoliosis, function can be affected. Severe scoliosis can result in...
Decreased lung capacity
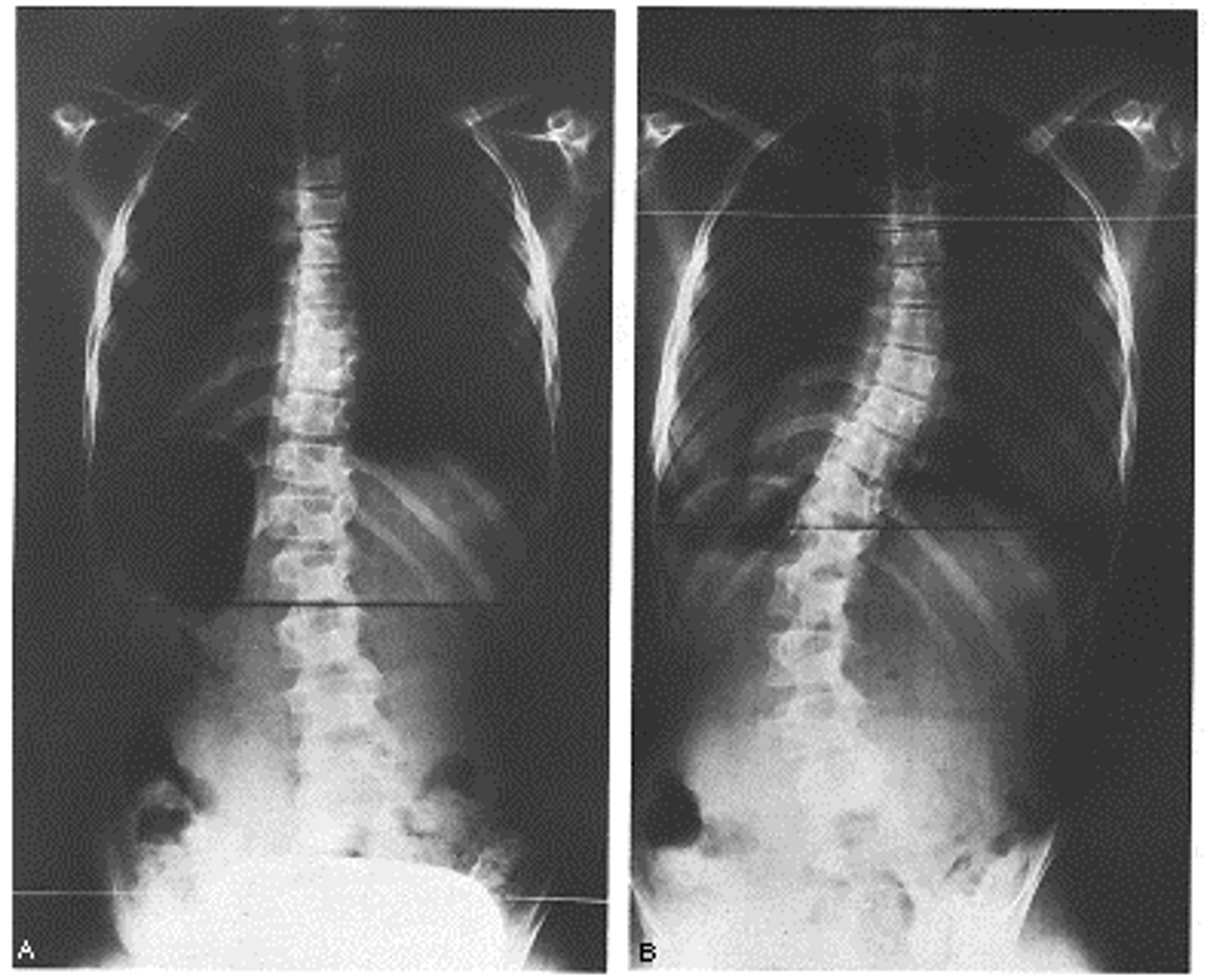
Example of pathological curvature associated with neuromuscular disease e.g., spinal muscular dystrophy
Kyphoscoliosis (kyphosis and scoliosis combined)
Caused by asymmetric weakening of the para-spinal mucles in e.g., spinal muscle dystrophy
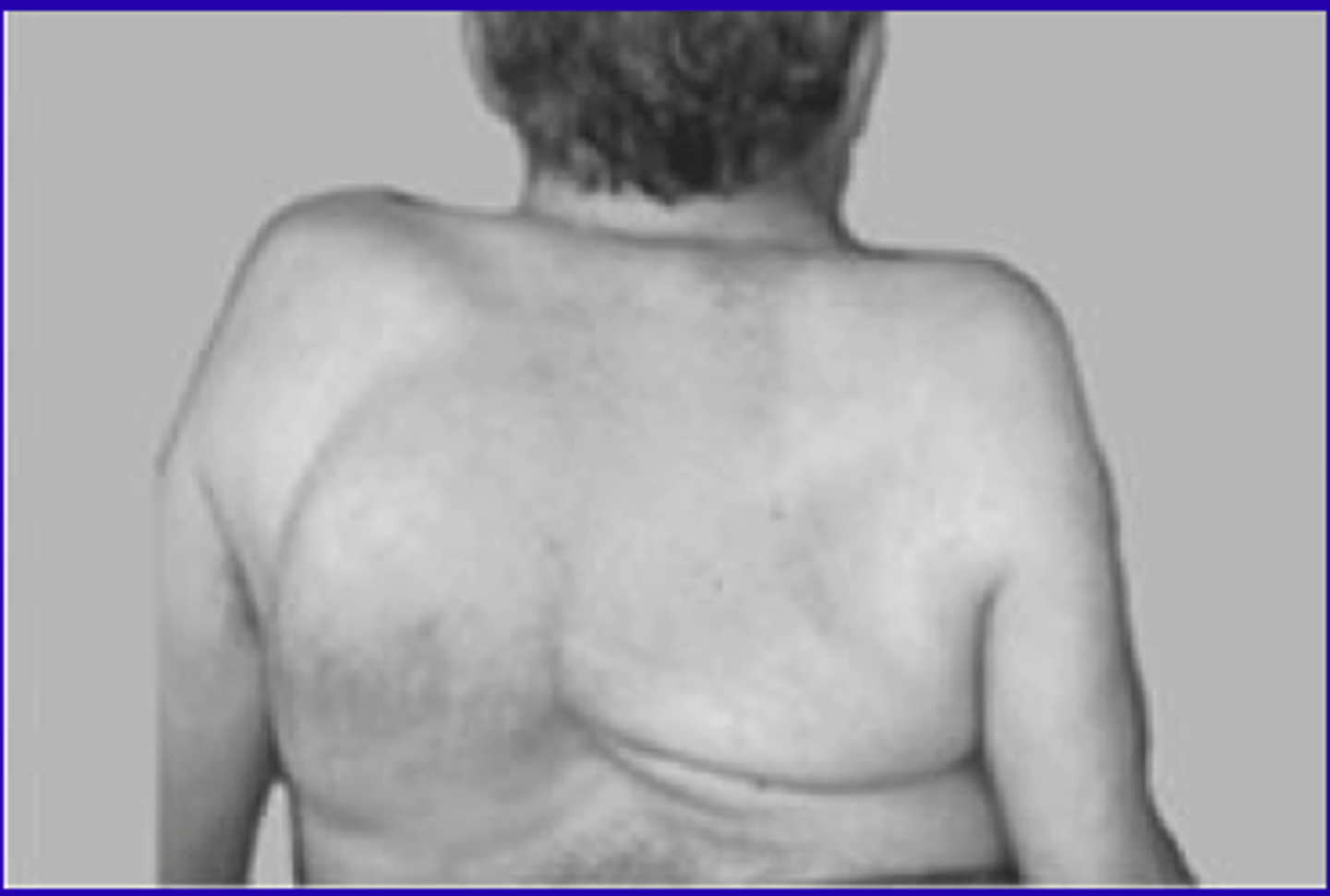
Effects of kyphoscoliosis on function...
1) Reduced lung capacity
2) Pulmonary hypertension
3) Spinal cord compression
The spinal cord ends at ___ in adults
L1
Cauda equina
Collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord (below L1).
Below L1, nerves descend within the subarachnoid space and exit at their respective root levels

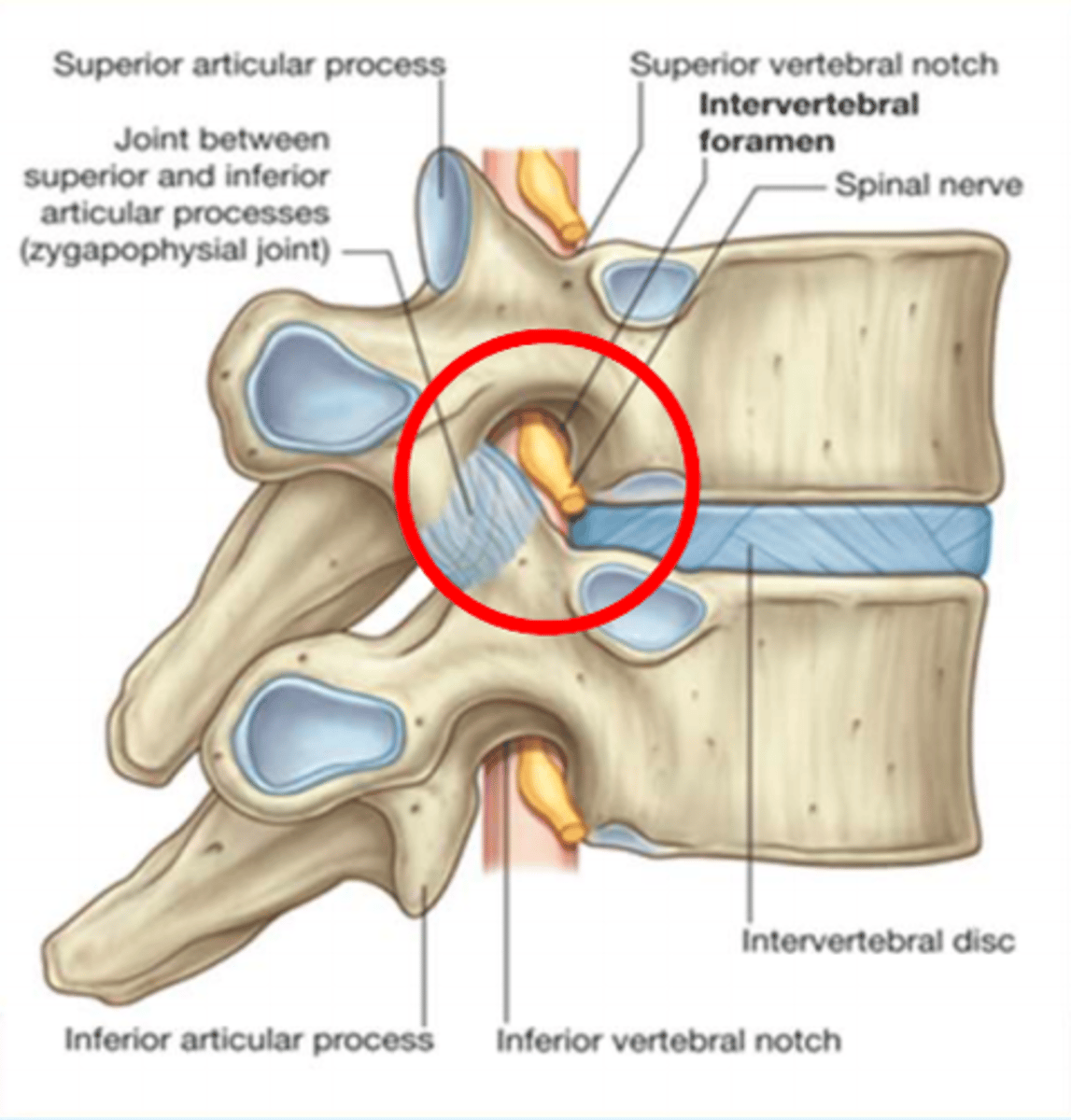
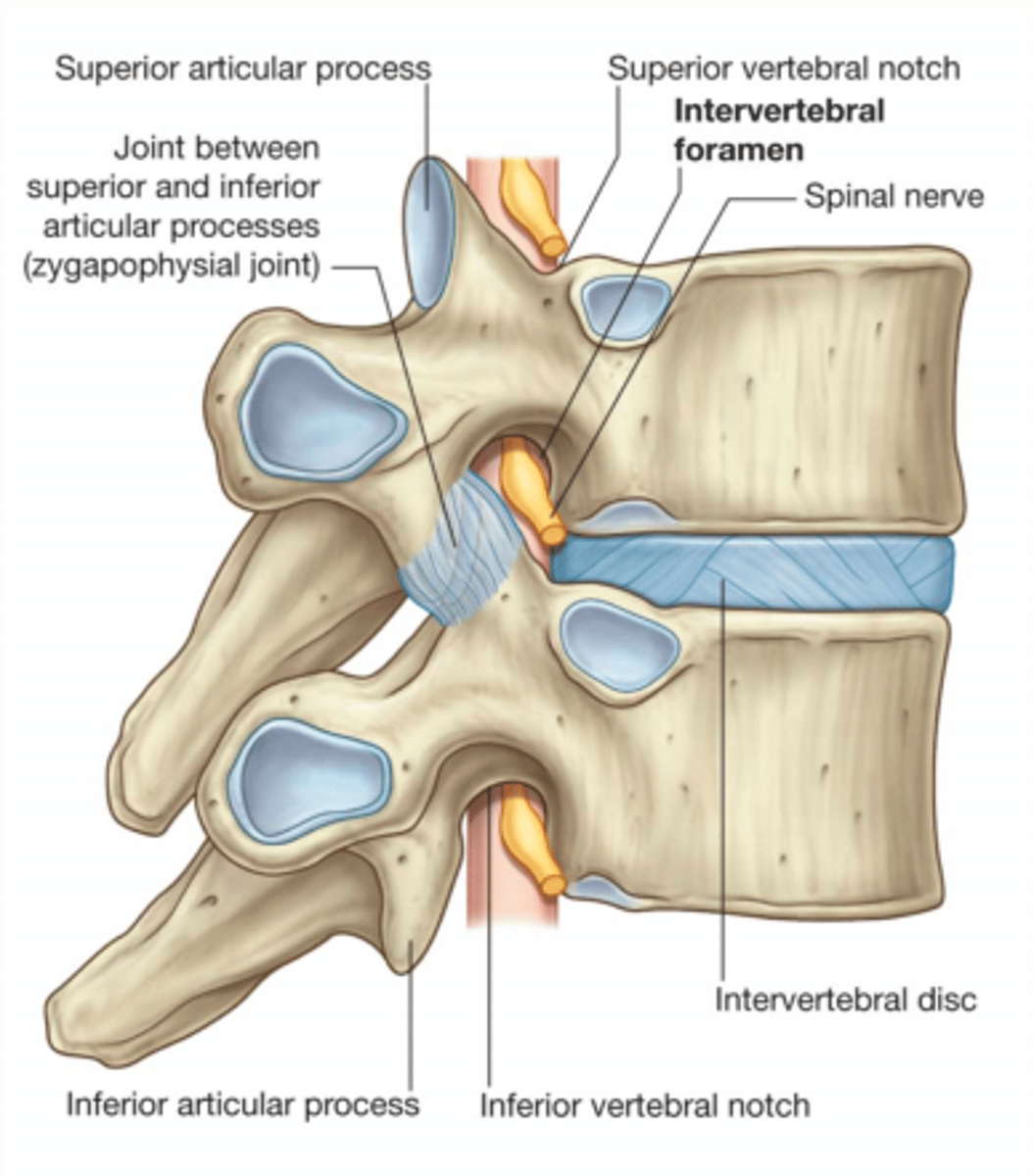
Intravertebral foramen
Carries the nerve roots
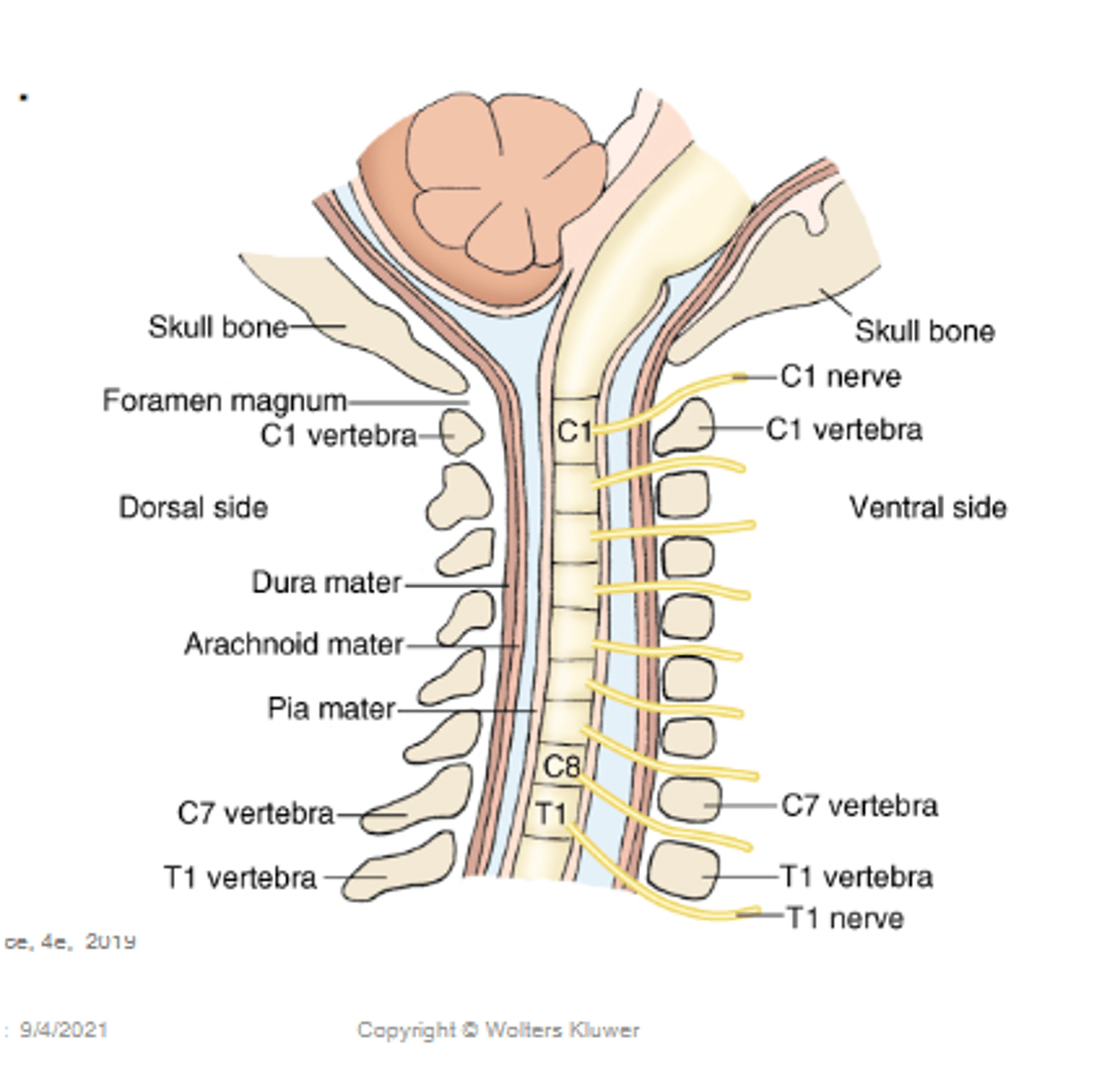
Spinal nerves exit ___ their numbered vertebra (except cervical)
Below
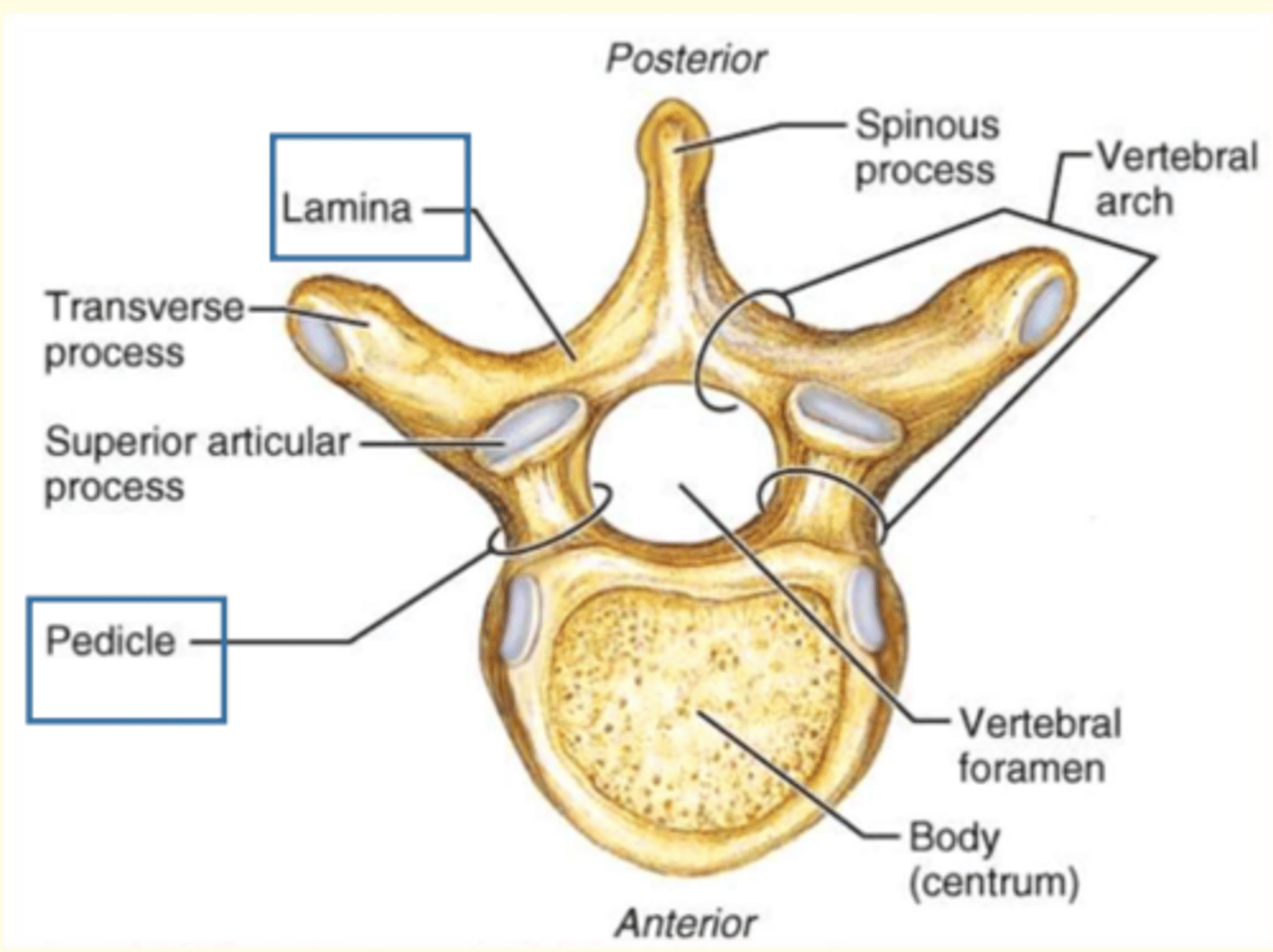
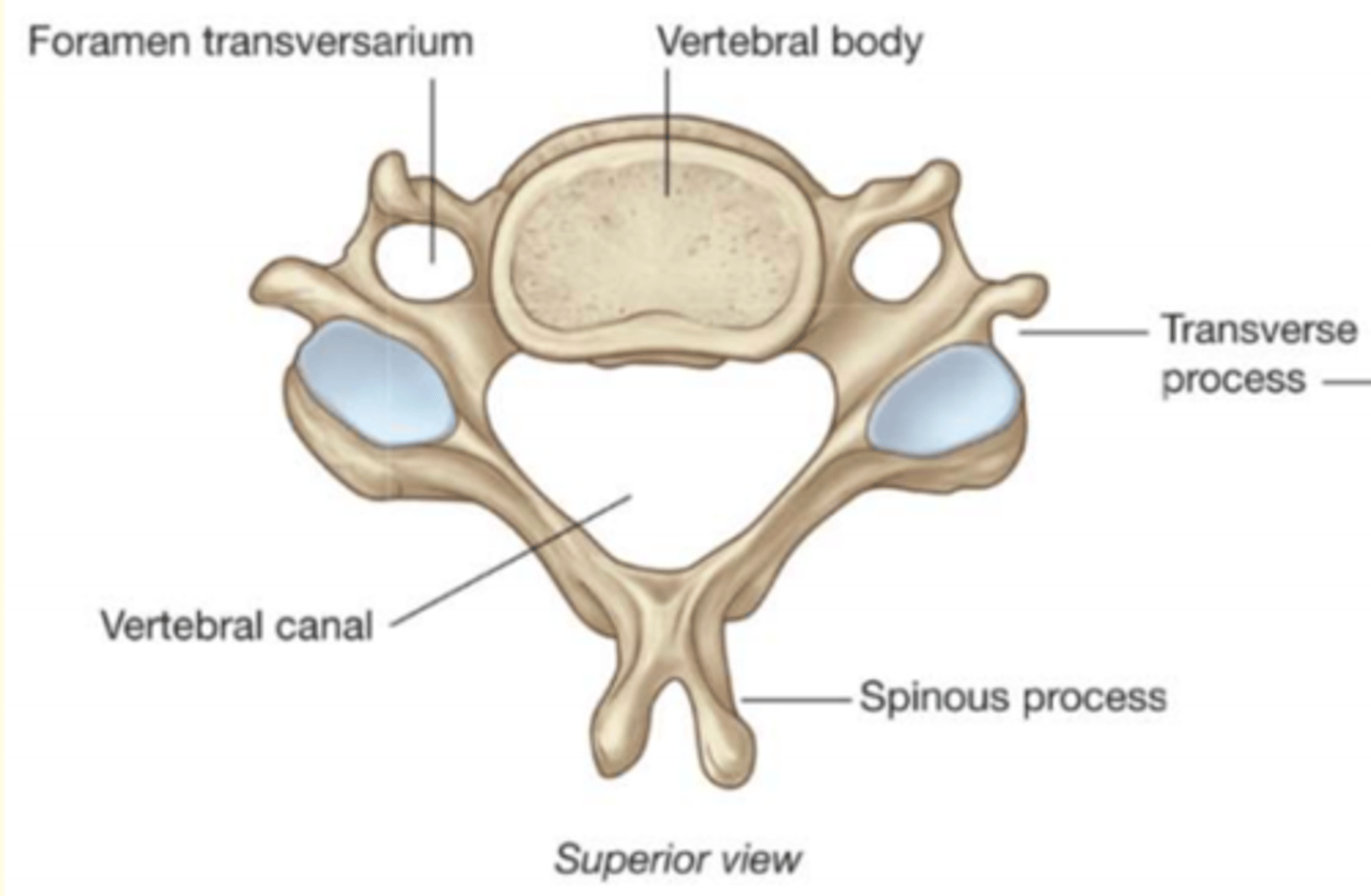
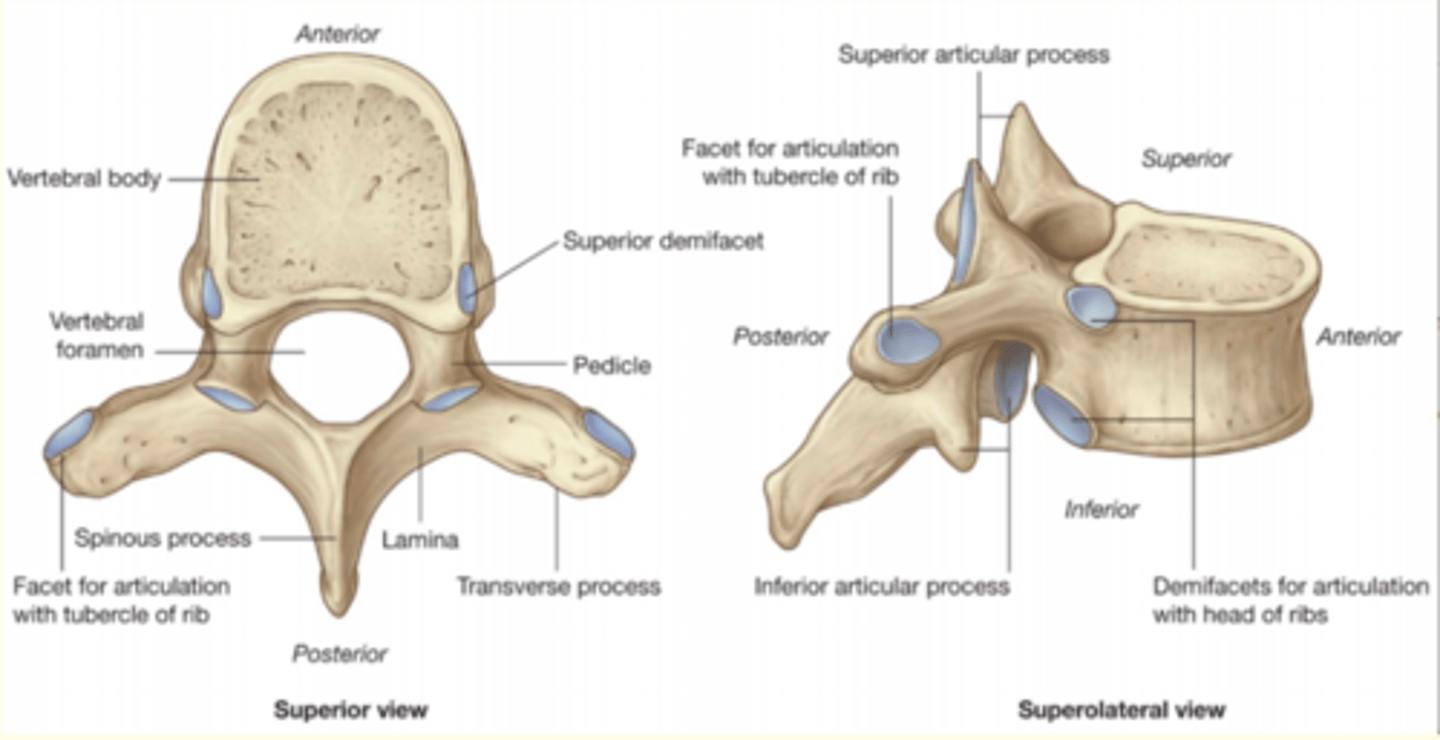
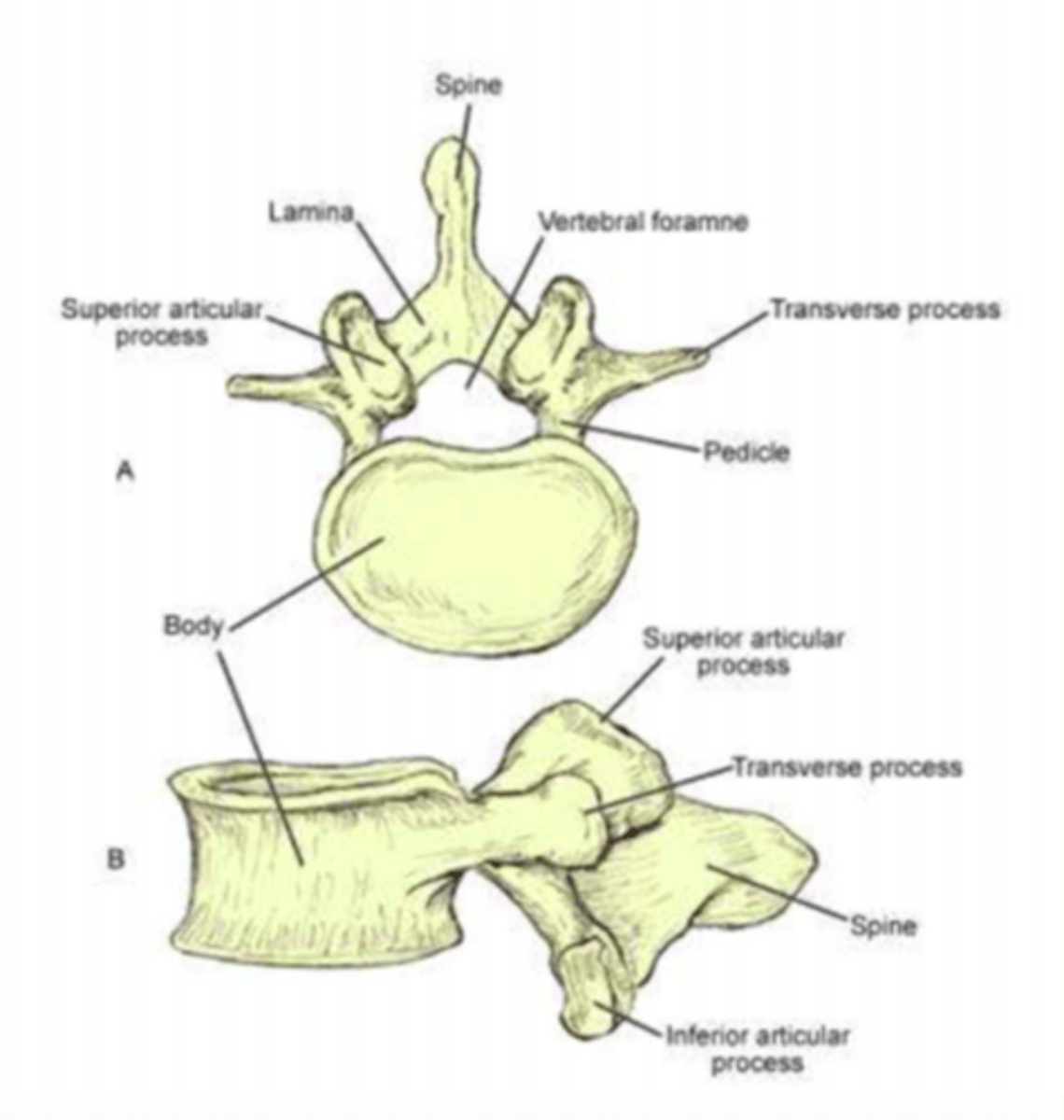
What are the three general characteristics of a typical vertebrae
1) Rounded body anteriorly
2) Vertebral arch posteriorly
3) Vertebral foramen = passageway for spinal cord + meninges
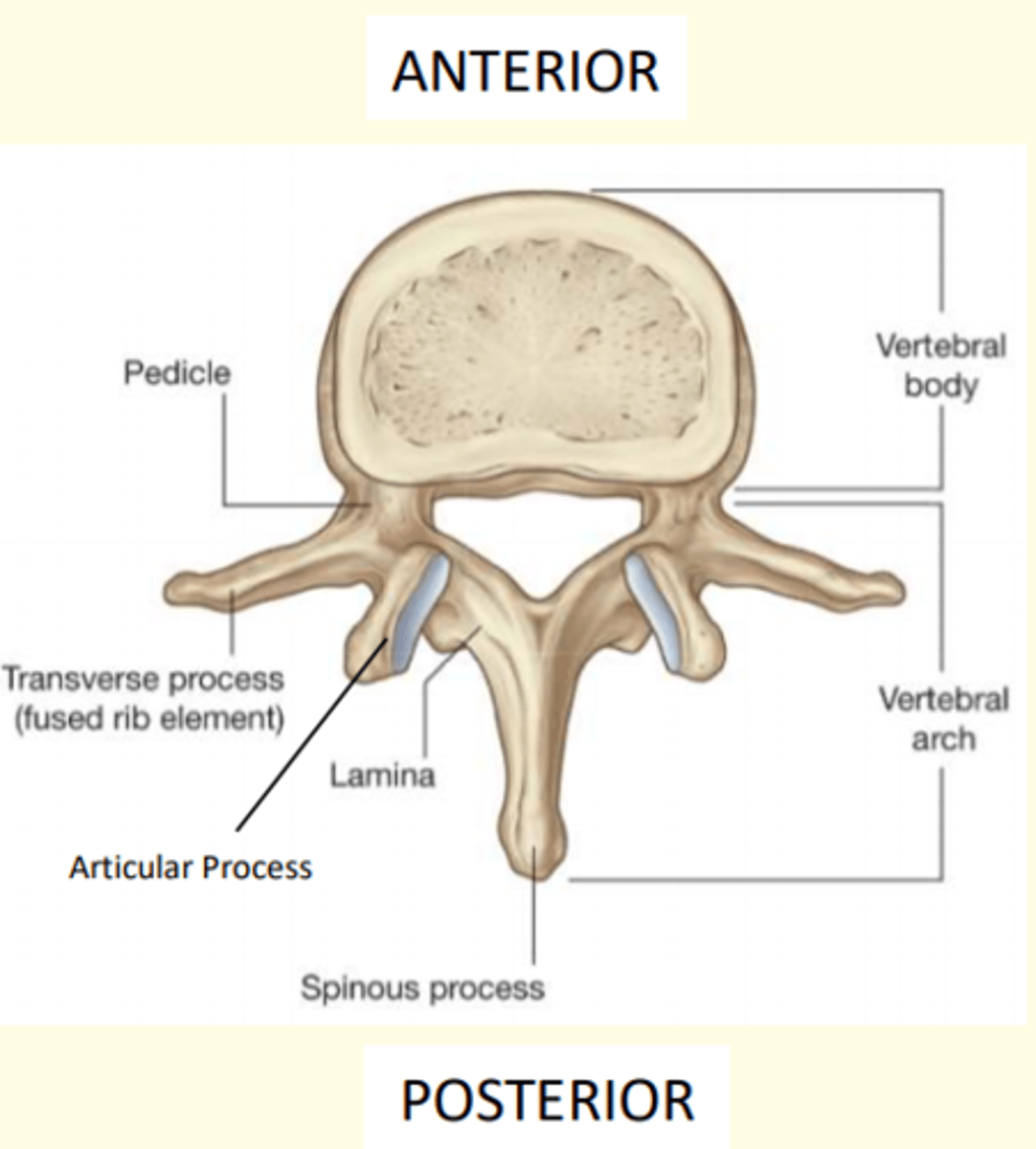
Which part of the vertebra is the largest and weight-bearing part?
Vertebral body
- Largest part of vertebra
- Weight-bearing
- Major site of contact between adjacent vertebra

The vertebral arch has ___ processes
Seven
Name the seven processes of the vertebral arch
1 Spinous process
2 Transverse processes
2 Superior Articular Processes (interlock with vertebra above)
2 Inferior Articular Processes (interlock with vertebra below)
Thoracic vertebrae (rib attachment facets)
The vertebral arch is made up of the lamina and the ___
Pedicle
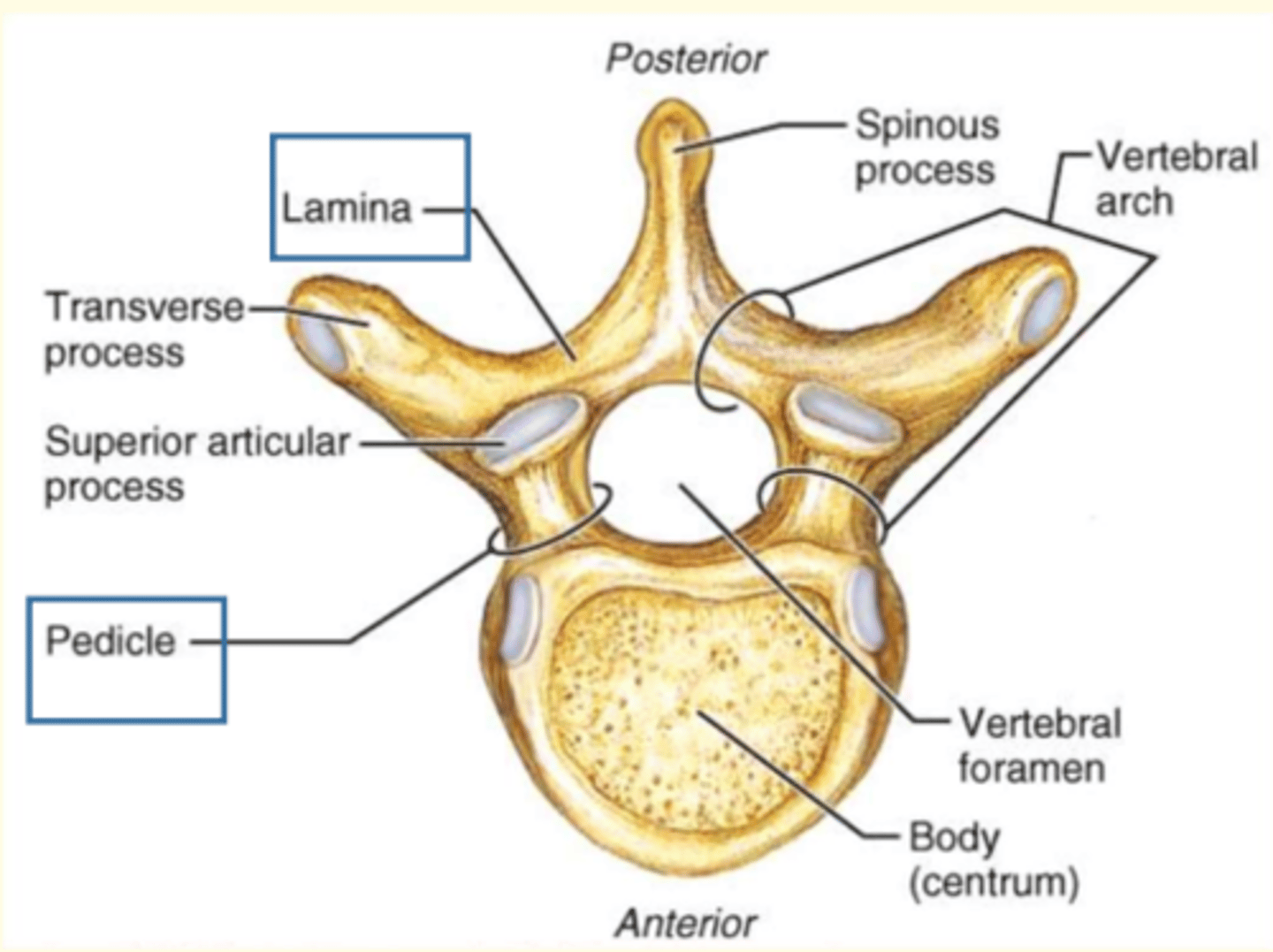
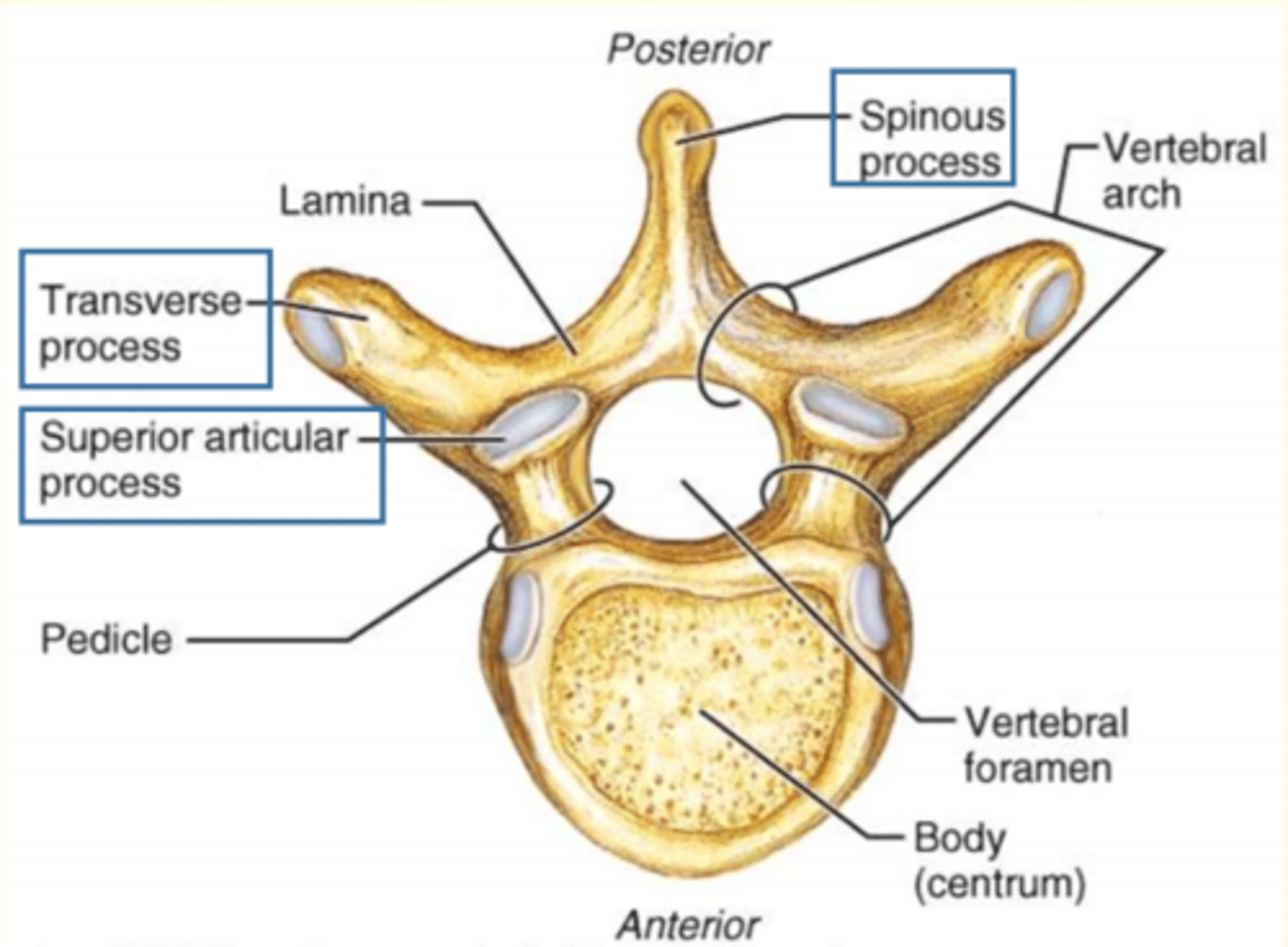
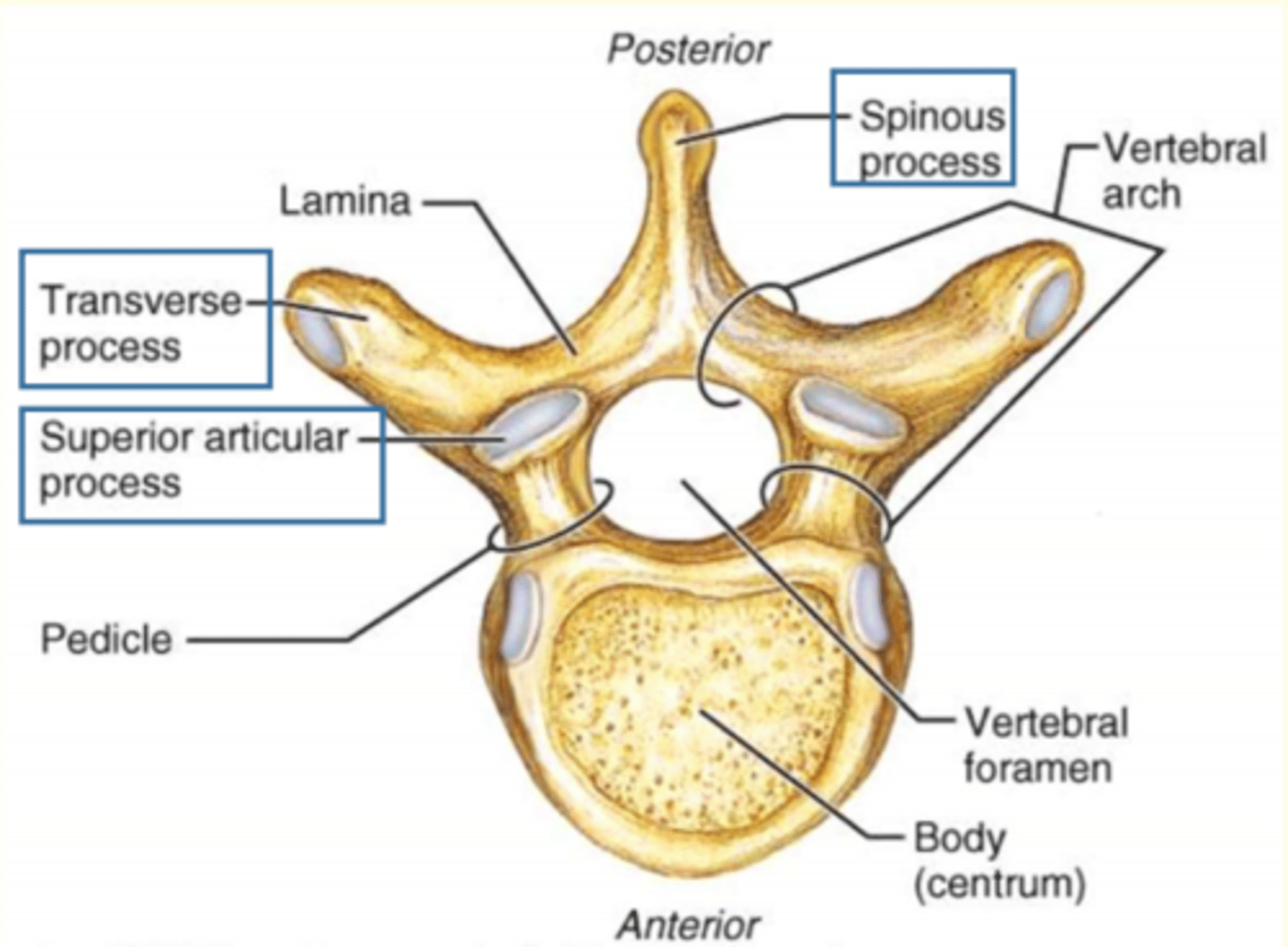
Which vertebral process is this?
2 Transverse processes (R & L)
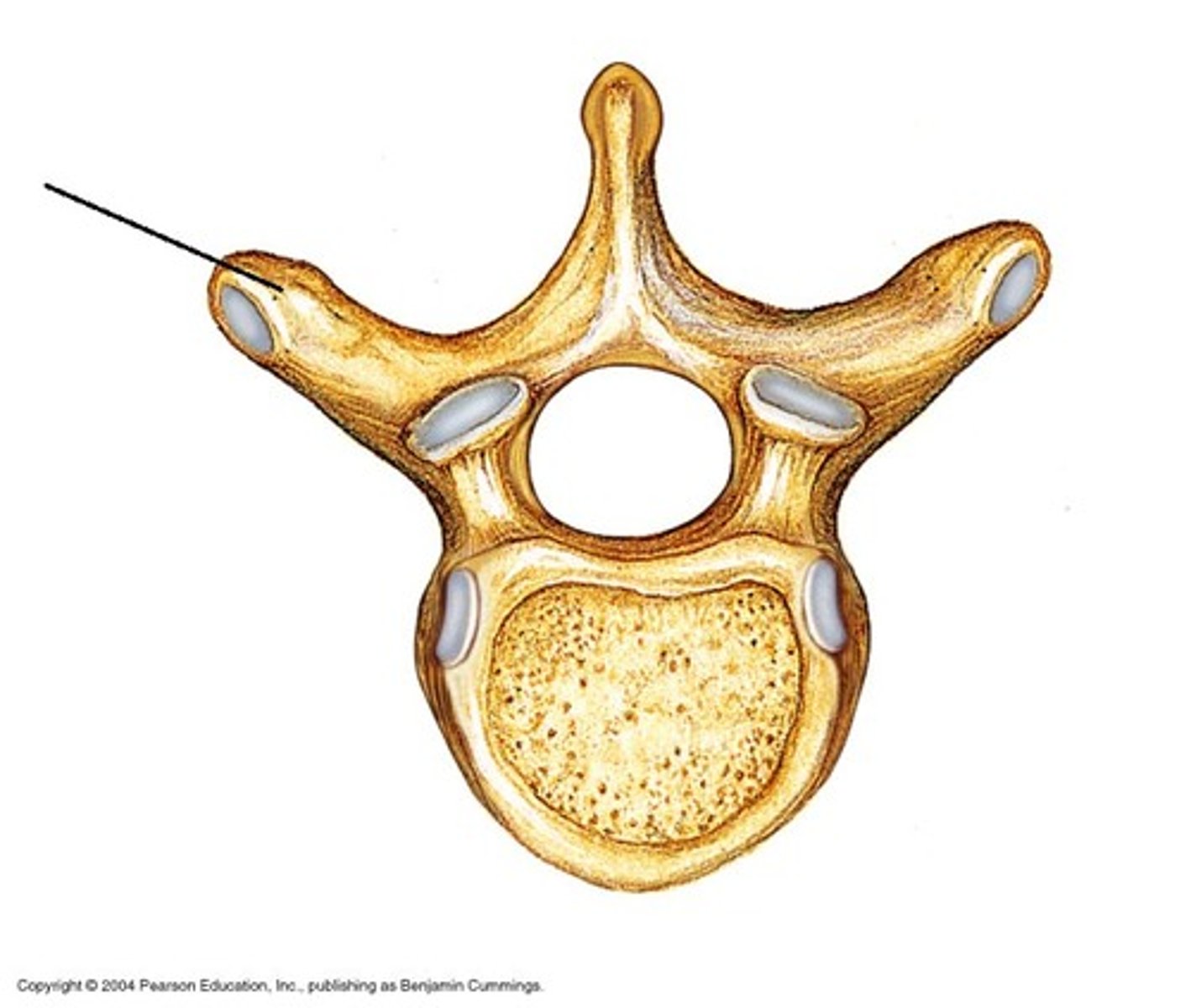
Which vertebral process is this?
1 Spinous process
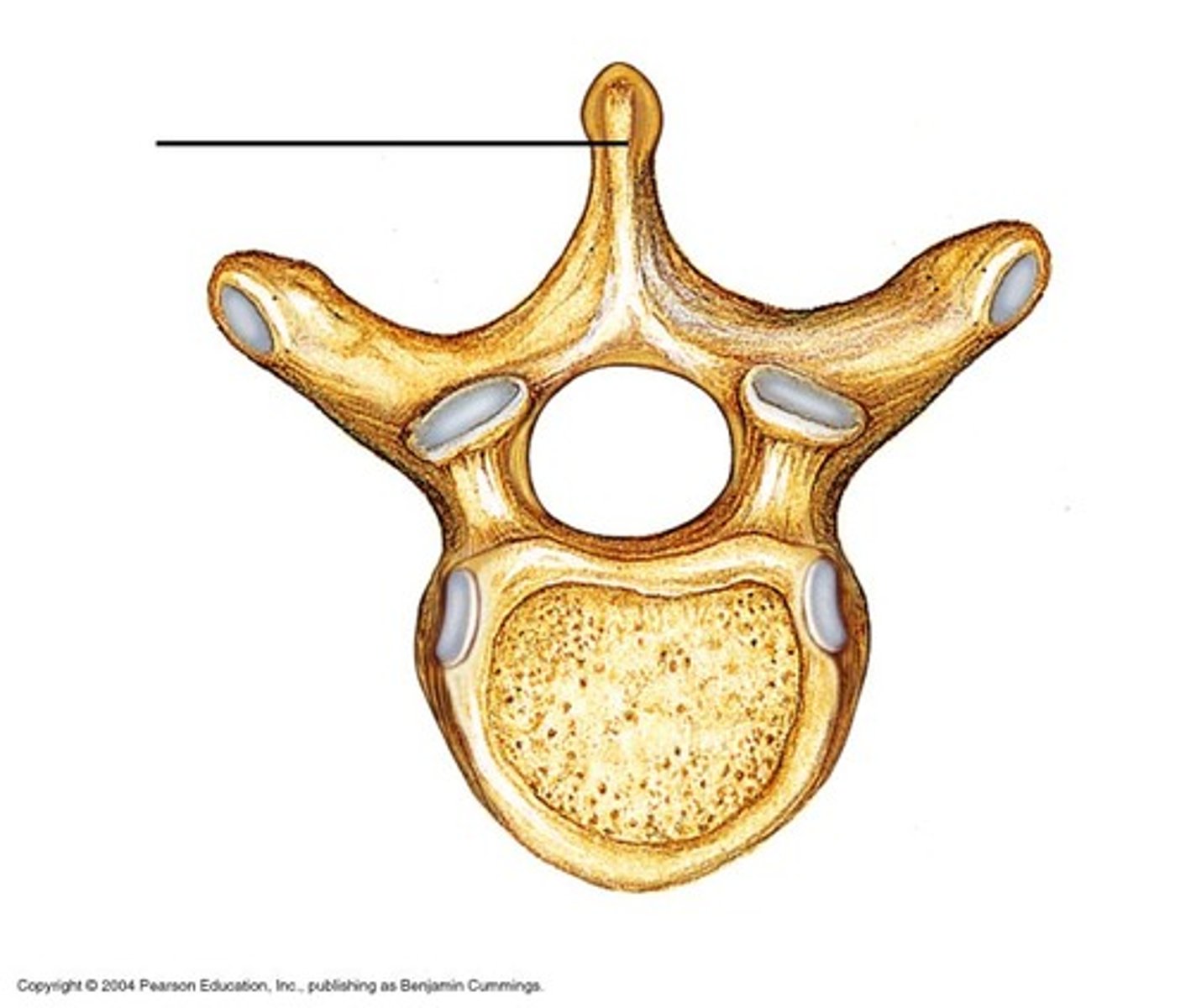
Which vertebral process is this?
2 Superior Articular process (interlock with vertebra above)
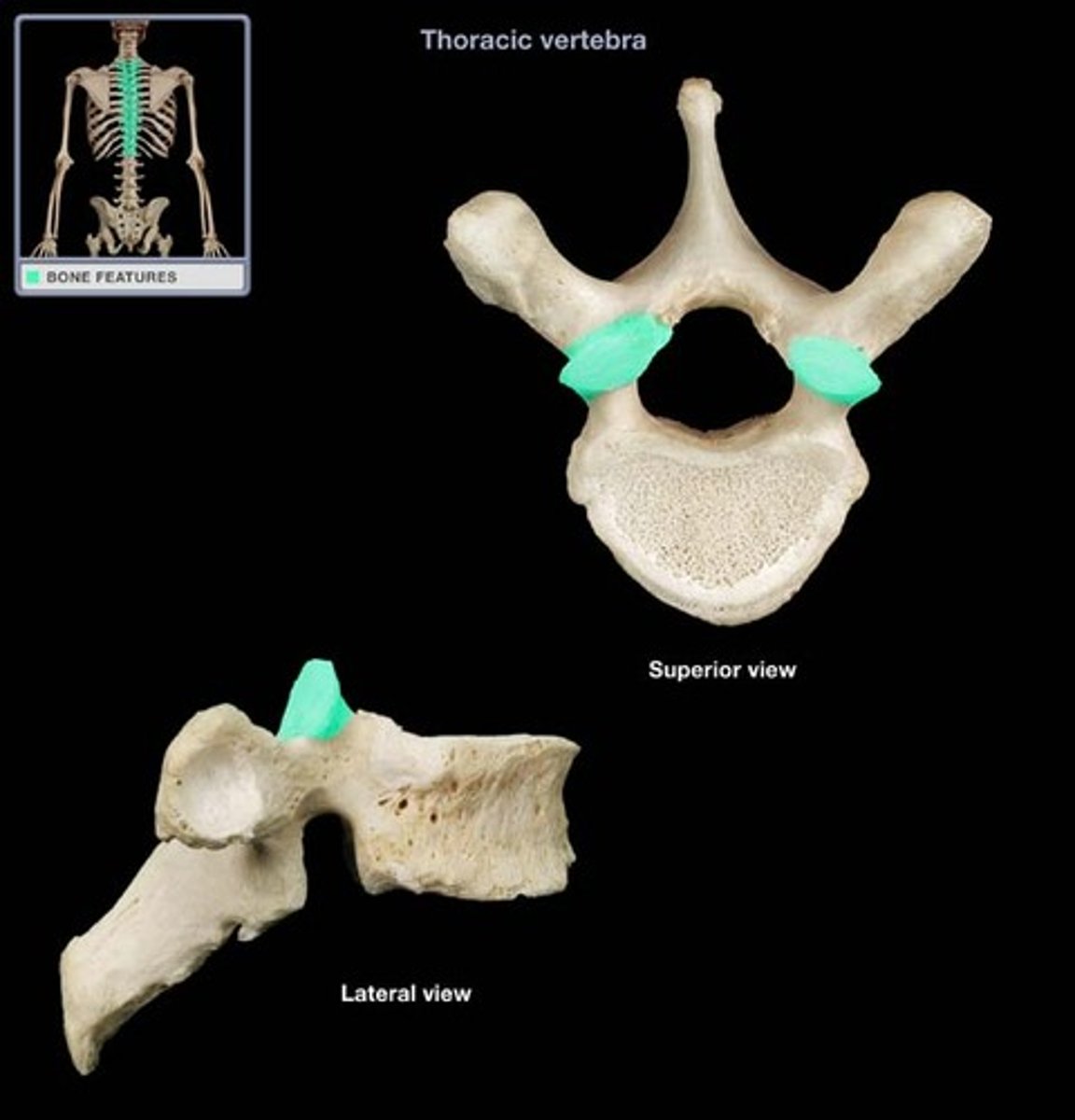
Lamina + pedicle = vertebral arch
Lamina connects...
Lamina connects transverse process to the spinous process
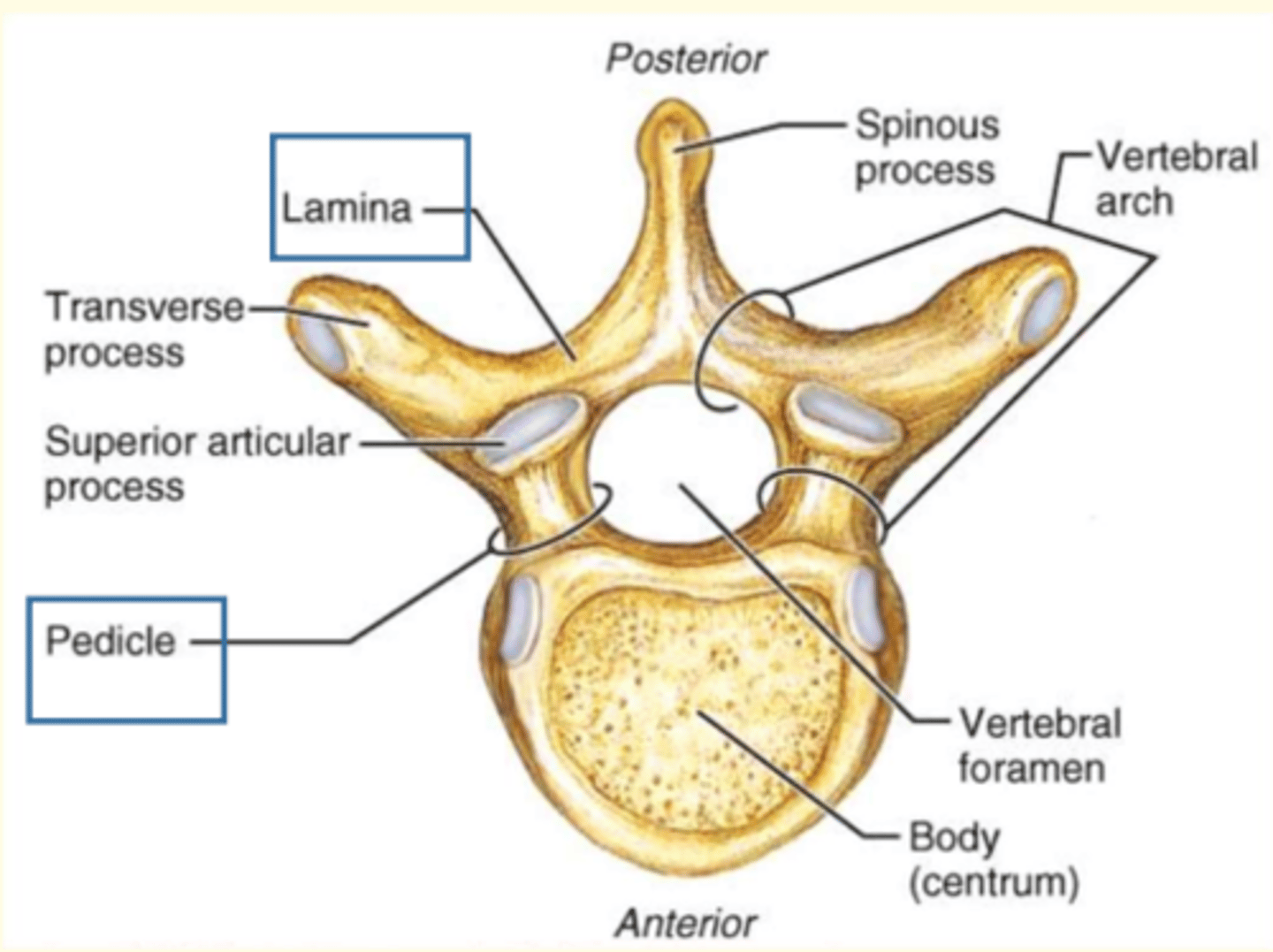
Lamina + pedicle = vertebral arch
Pedicle connects...
Connects transverse process to body of vertebra
The joint found between the superior and inferior articular processes is known as the ___ joint
Zygapophysial joint
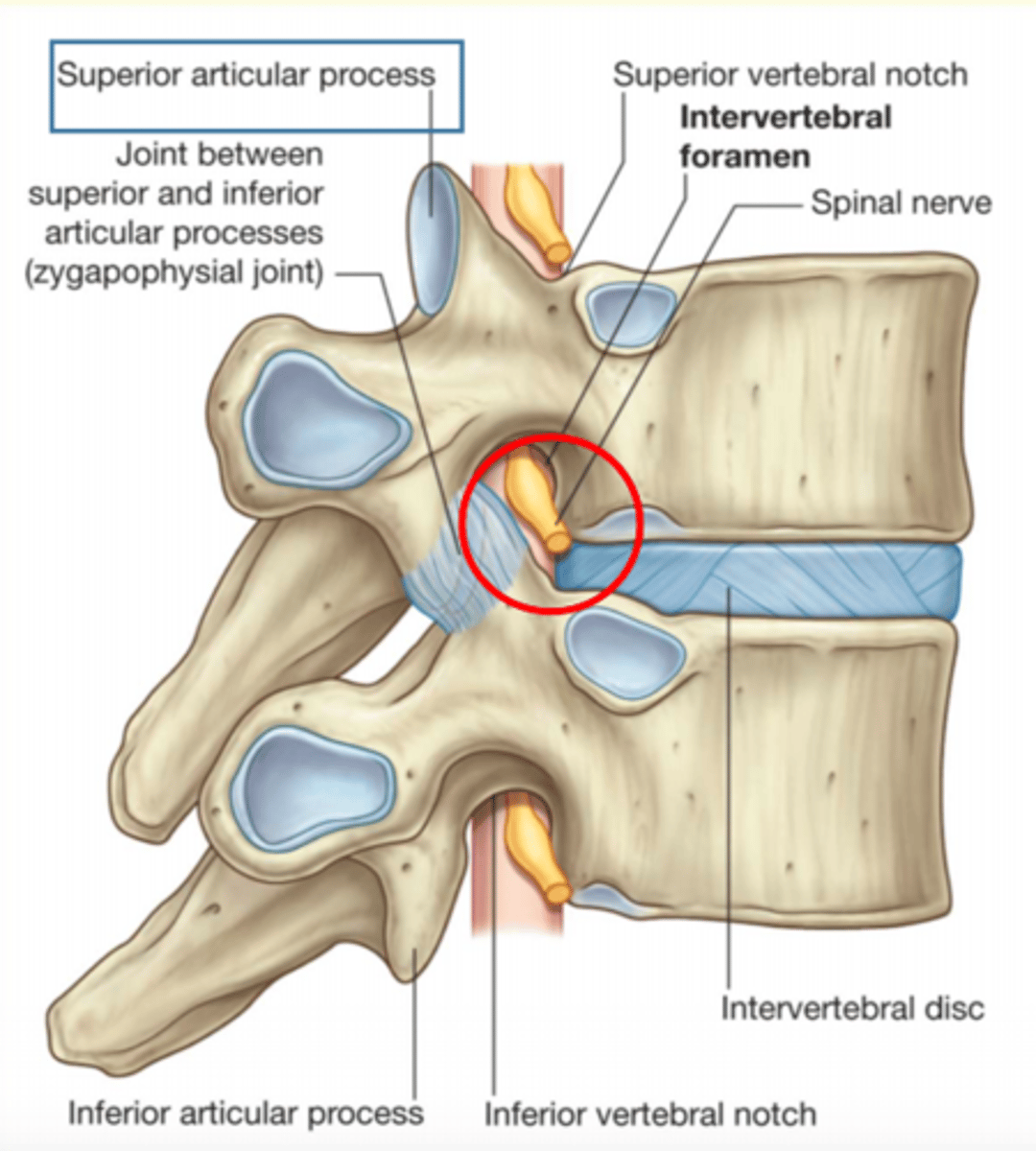
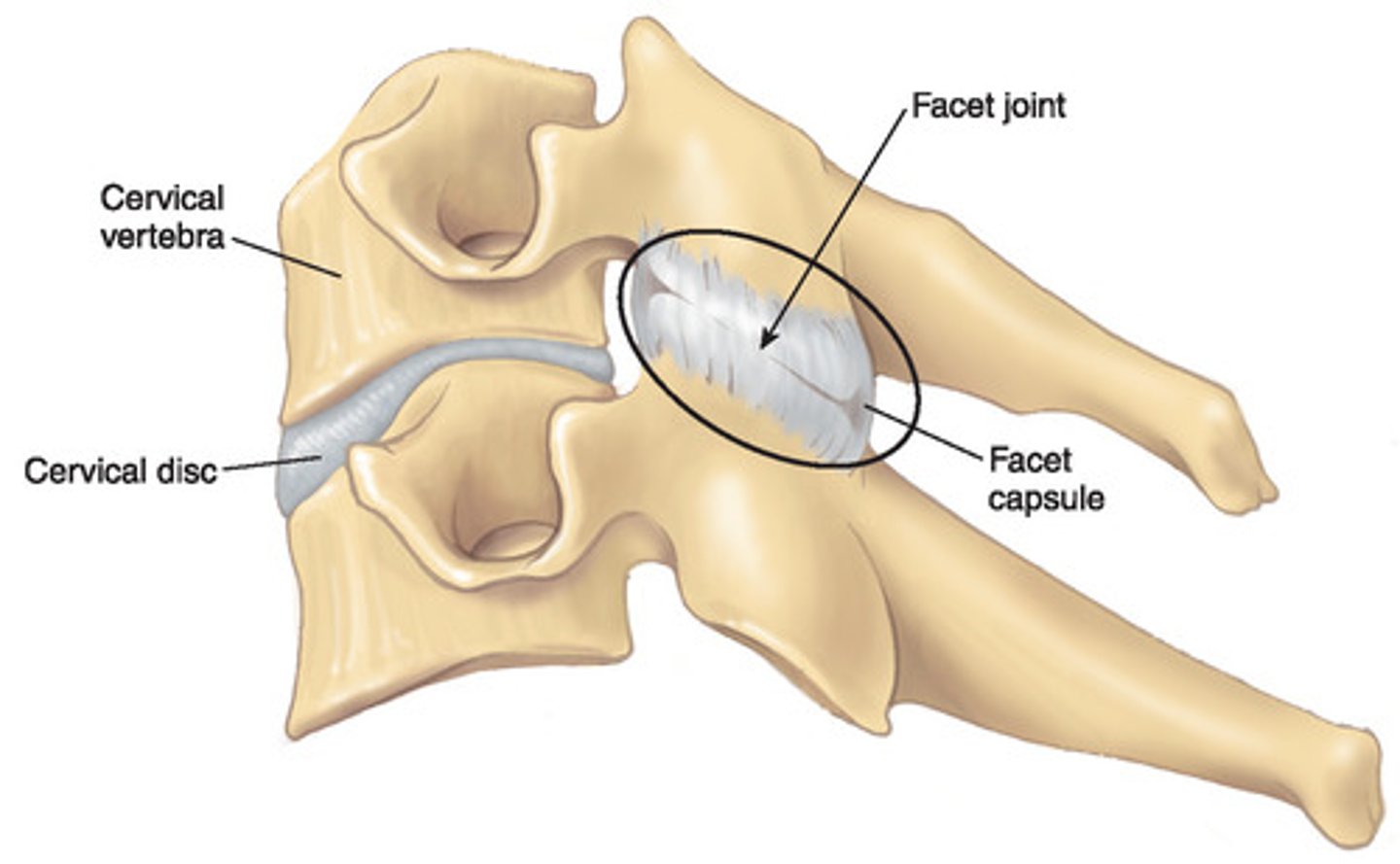
Zygopophysial joints (facet joints)
Plane synovial joints between the superior and inferior articular processes on adjoining vertebrae.
Function
1) Prevent anterior displacement of vertebrae
2) Orientation determines amount of flexion/rotation
Ligamentum flavum
Ligament that connects the laminae of adjacent vertebrae within the vertebral arch - provides strength.
Can deteriorate with age
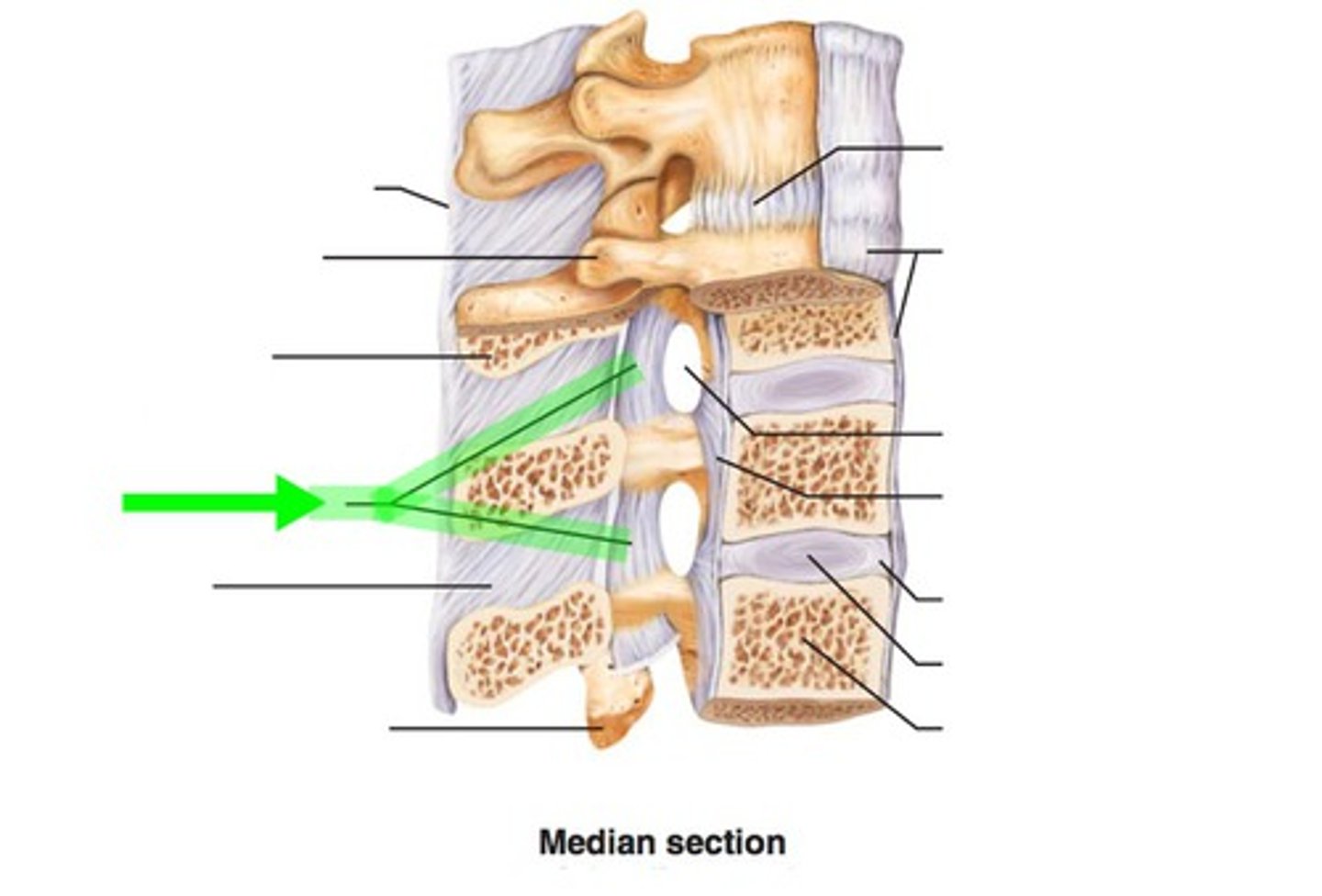
Spinal nerves emerge through IV foramina ___ their numbered vertebra
Below
What is the importance of the interlocking design of the superior and articular processes of the vertebral arch?
Allows for some degree of movement (flexion and extension)
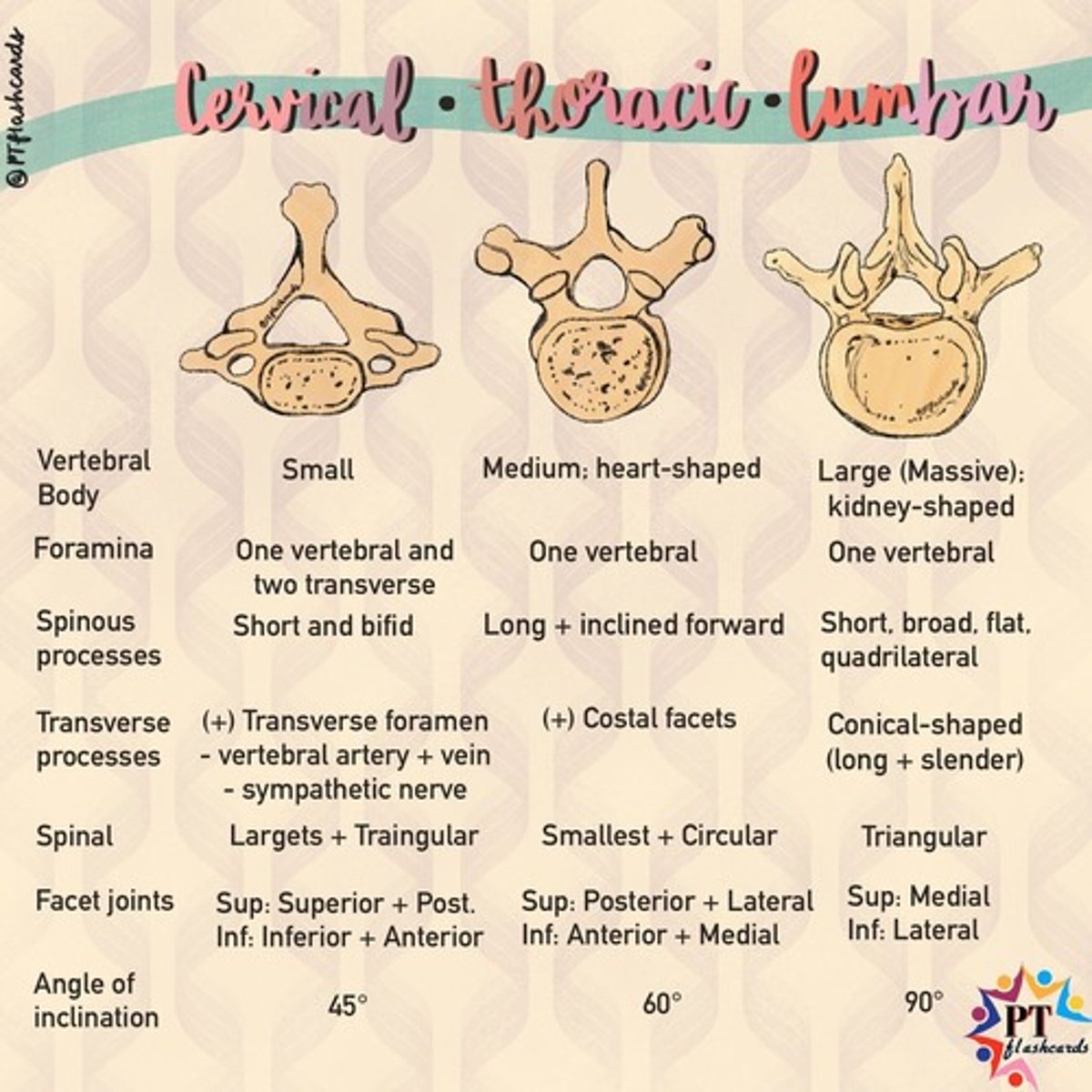
Typical characteristics of a cervical vertebra (C3-C7)
1) Smallest of discrete vertebrae
2) Bifid spinous process
3) 2 Transverse foramen in transverse process
4) Large triangular vertebral foramen
5) Small dome shaped body with edges forming upward facing lips known as the uncinate process
C1
Atlas, supports the head
C2
Axis; dens (odontoid process)
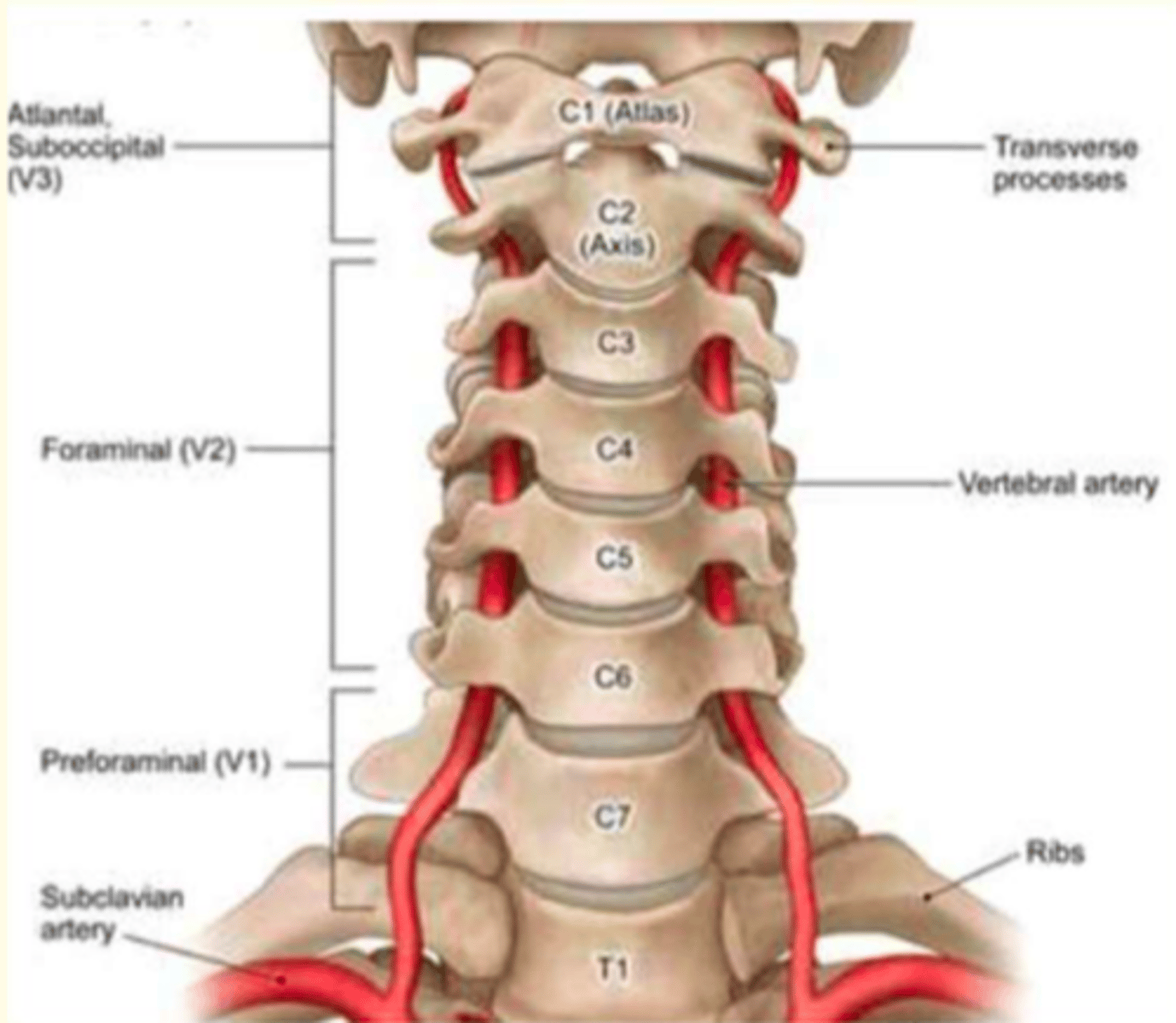
Examples of atypical cervical vertebra
C1 (Atlas), C2 (Axis, Dens) and C7
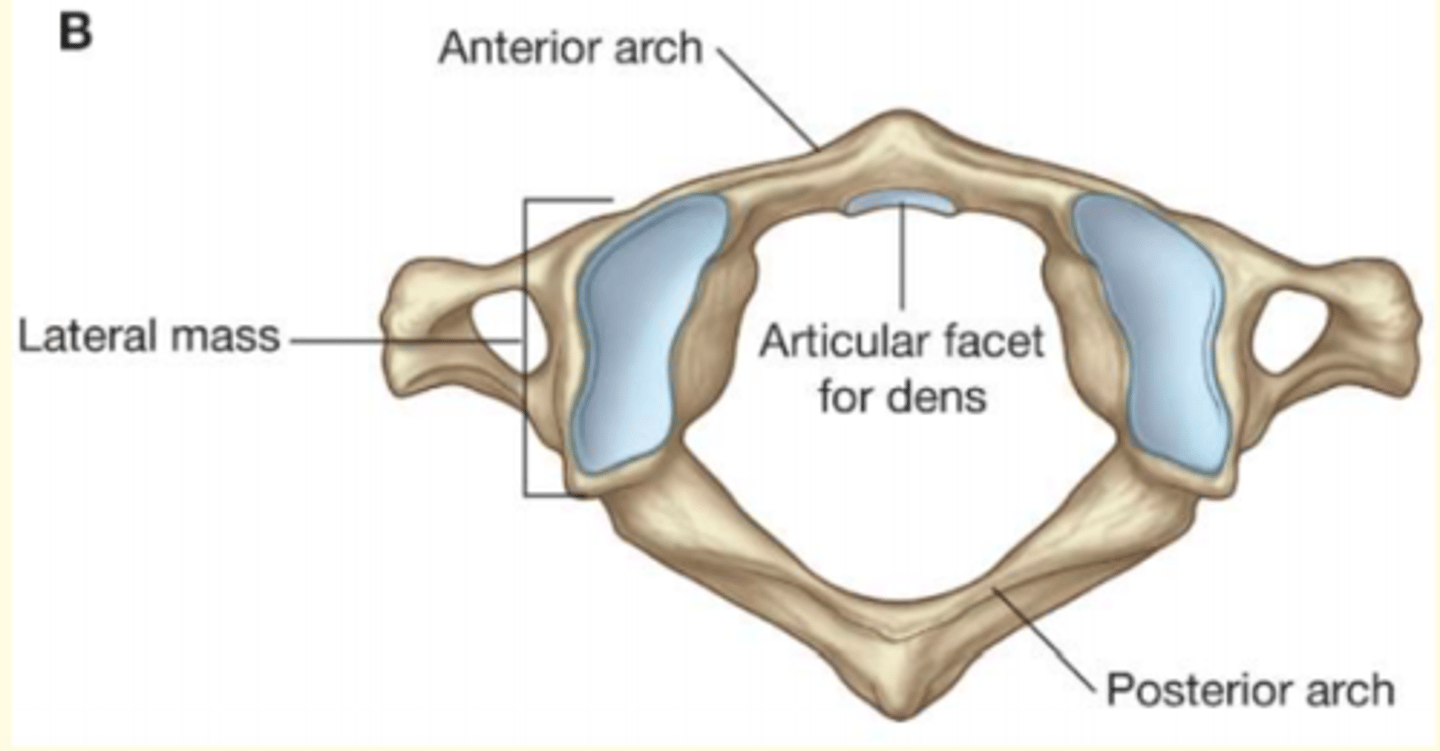
C1 (Atlas) features (atypical cerbical vertebra)
1) Articulates with the skull
2) NO body
3) NO spinous process
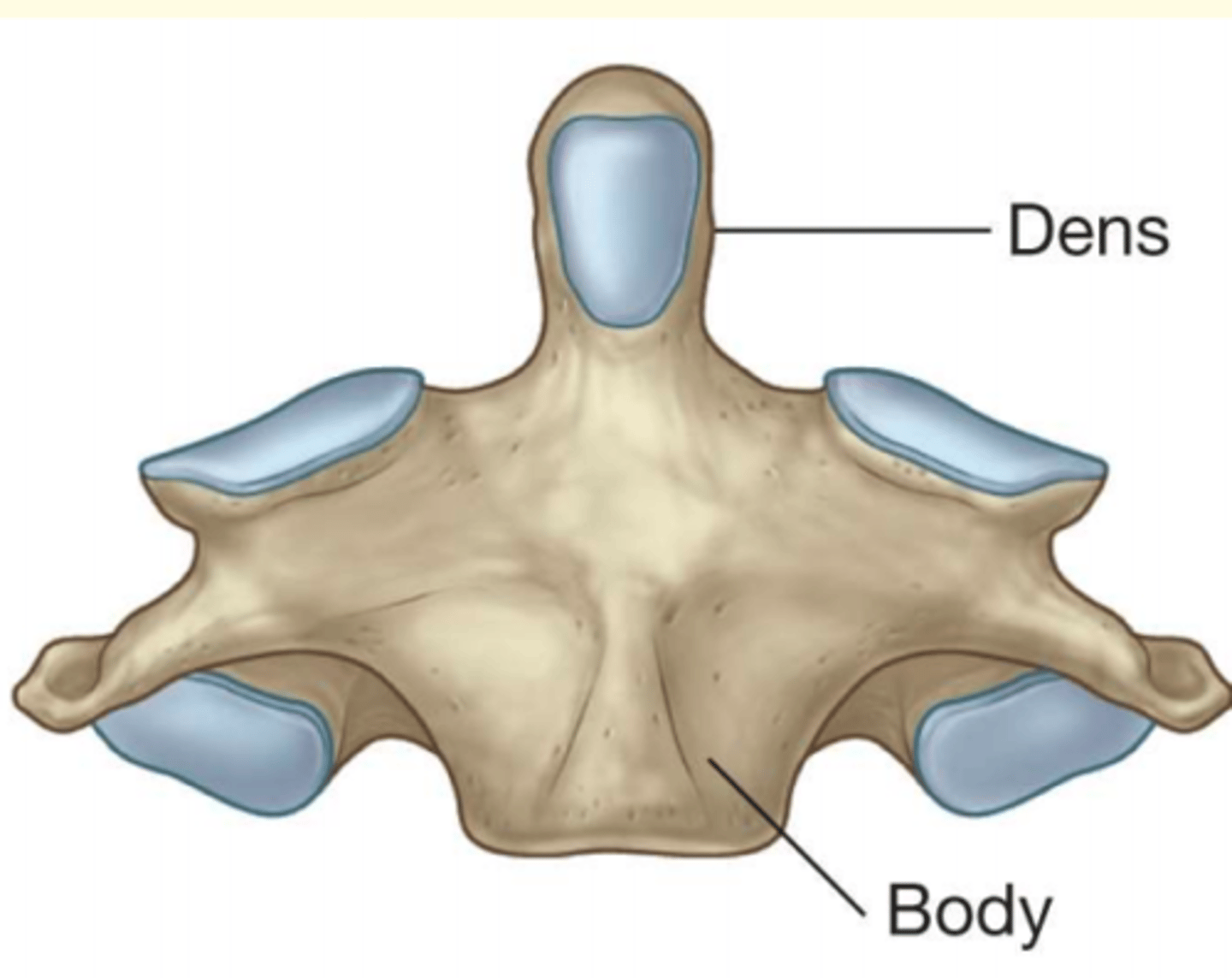
C2 (Axis) features (atypical cervical vertebra)
Odontoid process (Dens)
C7 (no special name) features (atypical cervical vertebra)
No bifid spinous process
Spinous process called the VERTEBRAL PROMINENCE
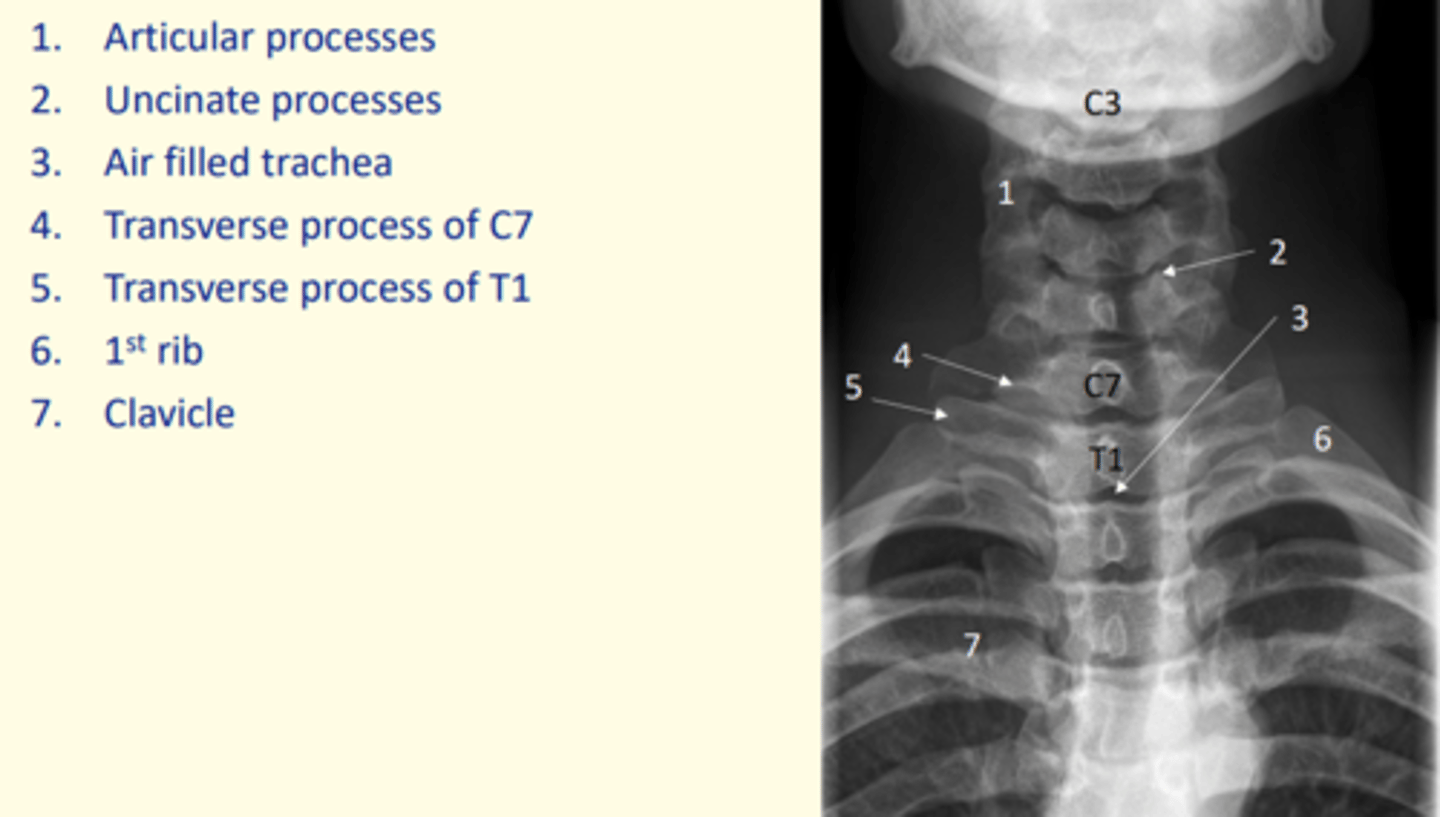
Identify articular processes on this x-ray
1 = Articular processes
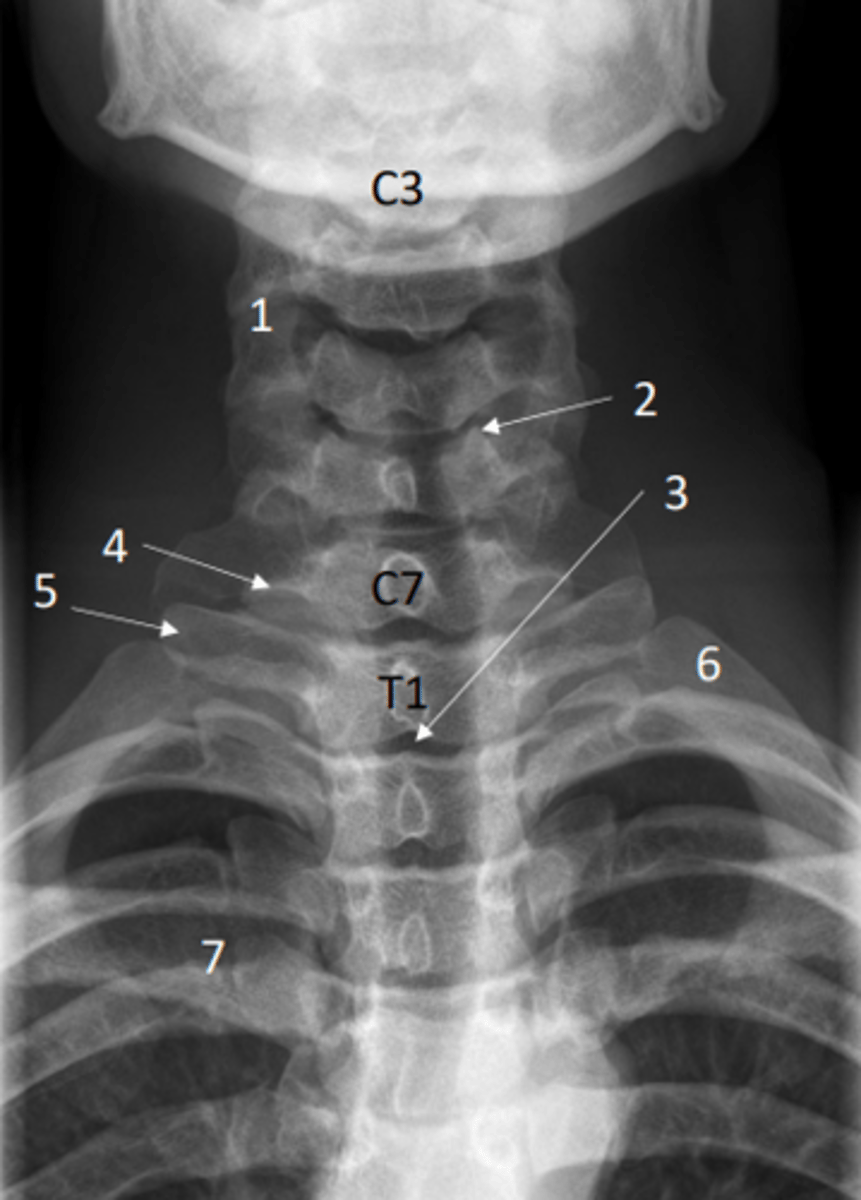
Identify uncinate processes on this x-ray
2 = Uncinate processes
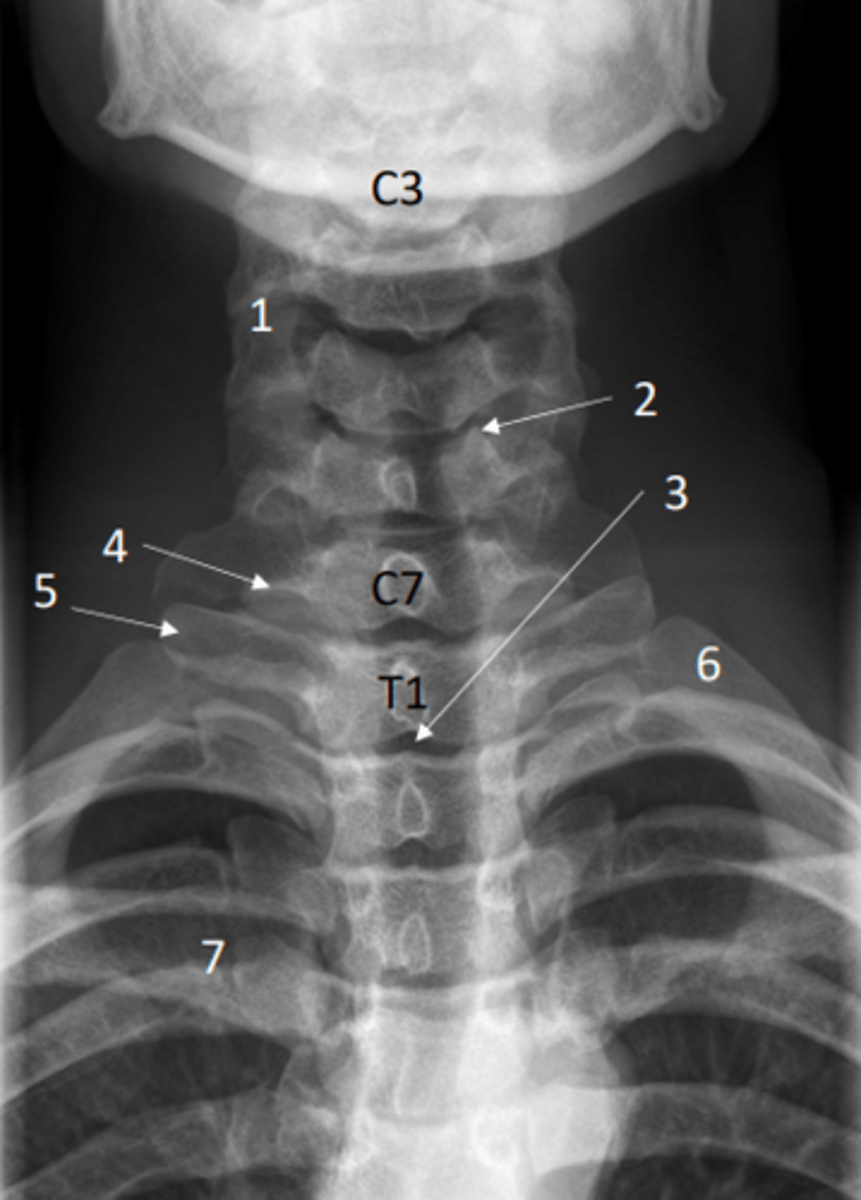
Identify transverse process of C7 on this x-ray
4 = Transverse process of C7
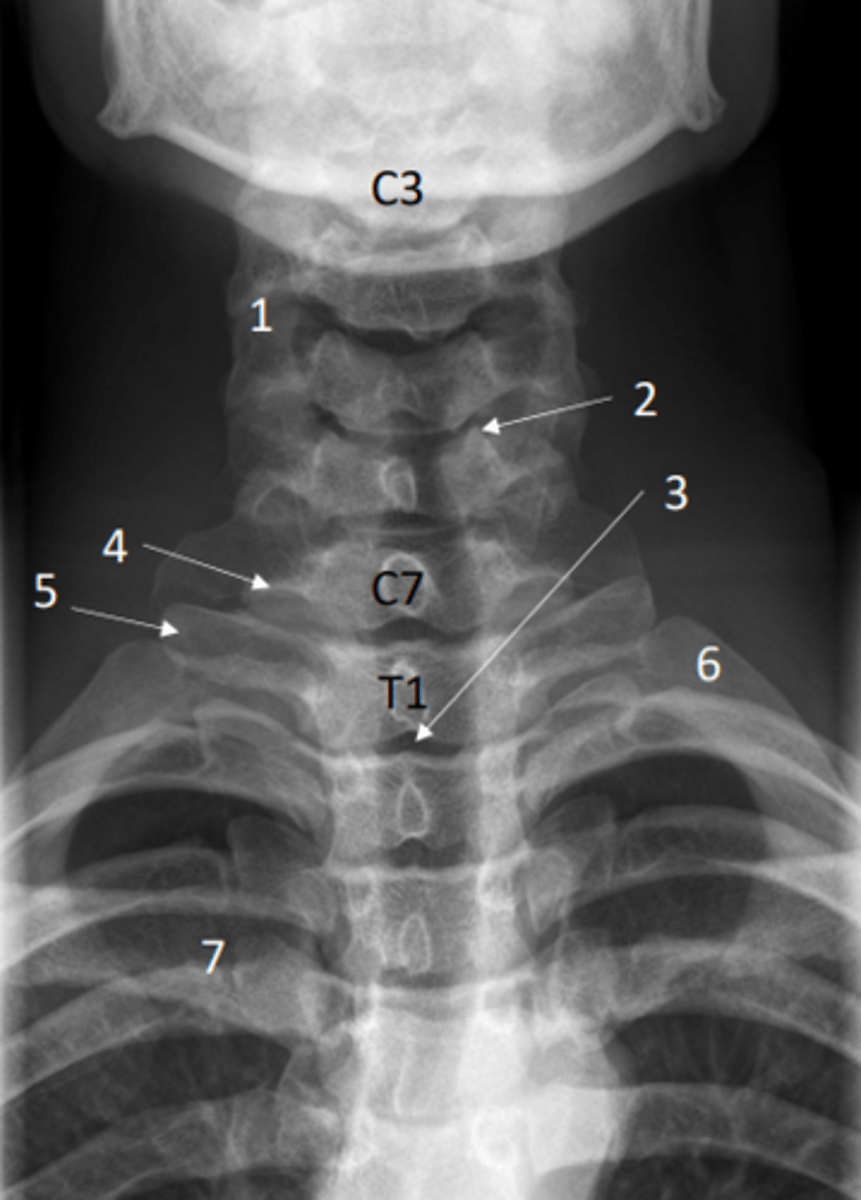
Identify transverse process of T1 on this x-ray
5 = Transverse process of T1
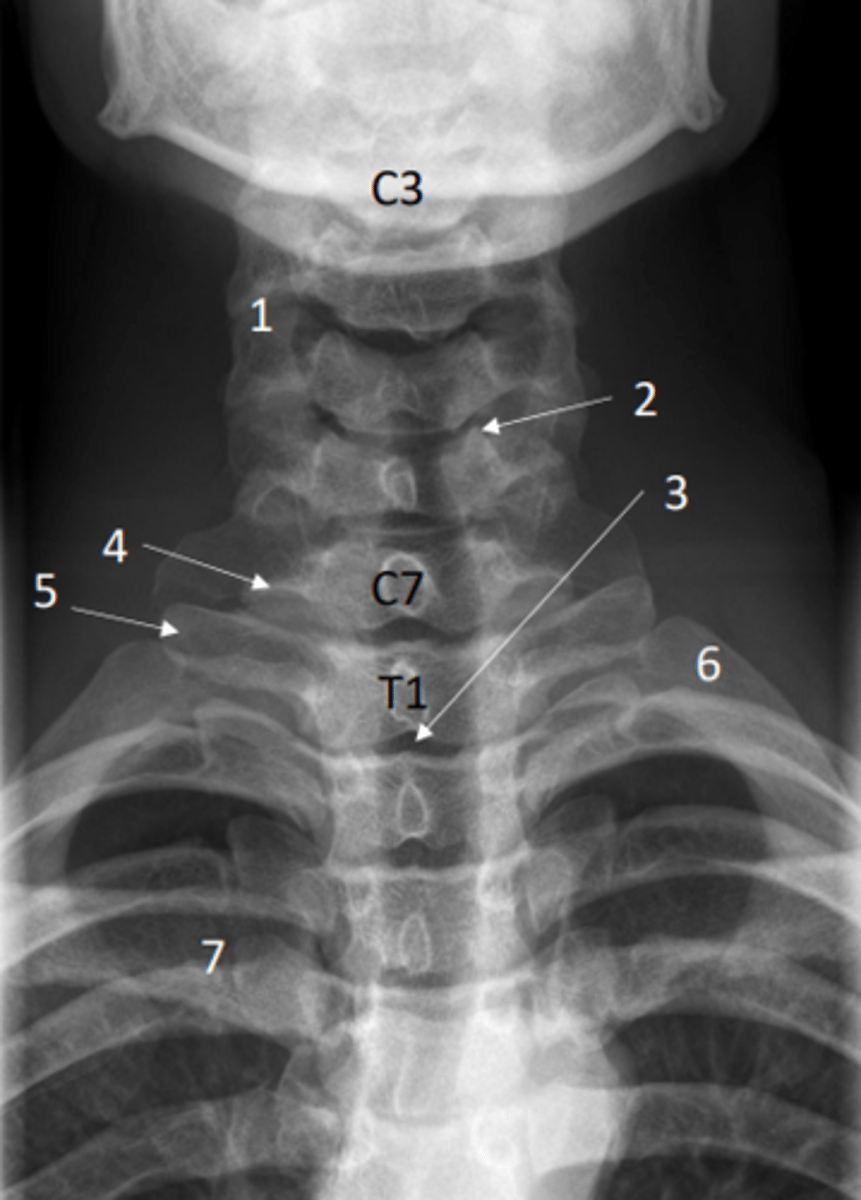
Identify the first rib on this x-ray
6 = First rib
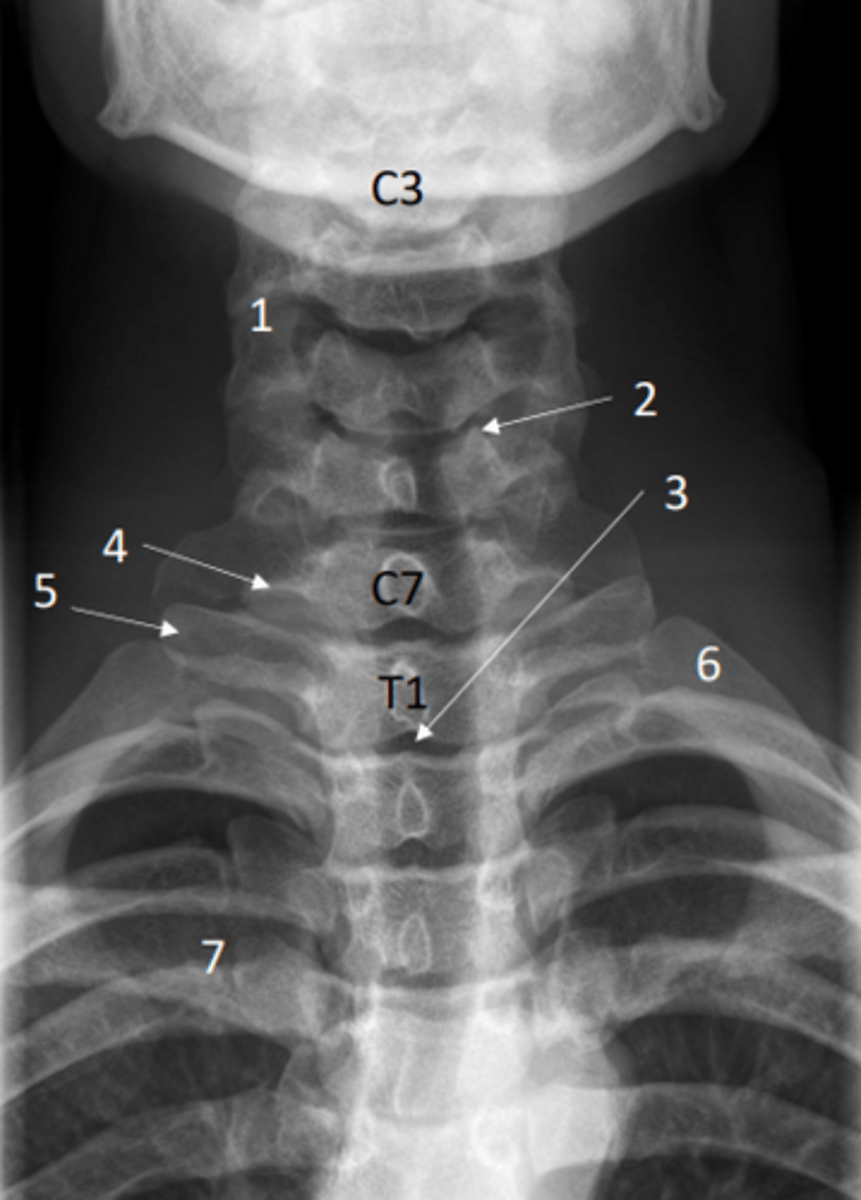
Identify clavicle on this x-ray
7 = Clavicle
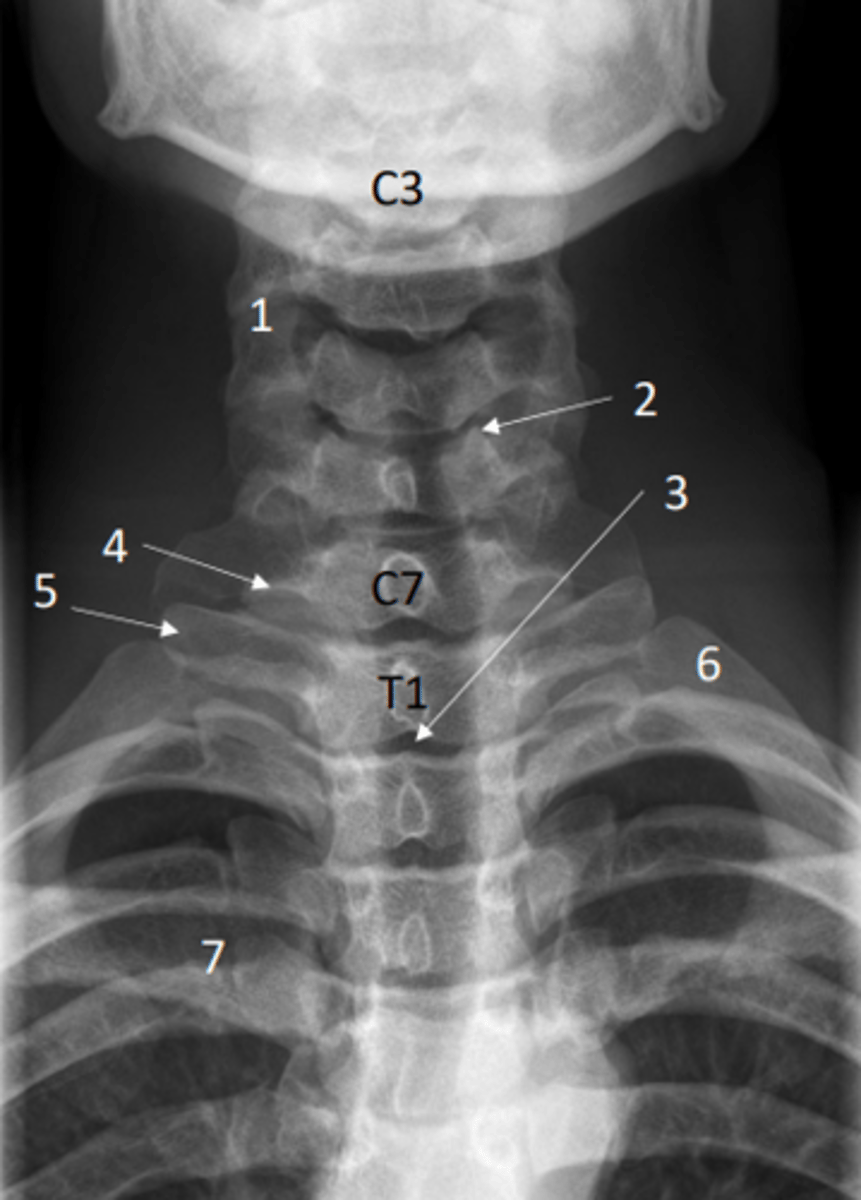
Identify air-filled trachea on this x-ray
3 = Air-filled trachea
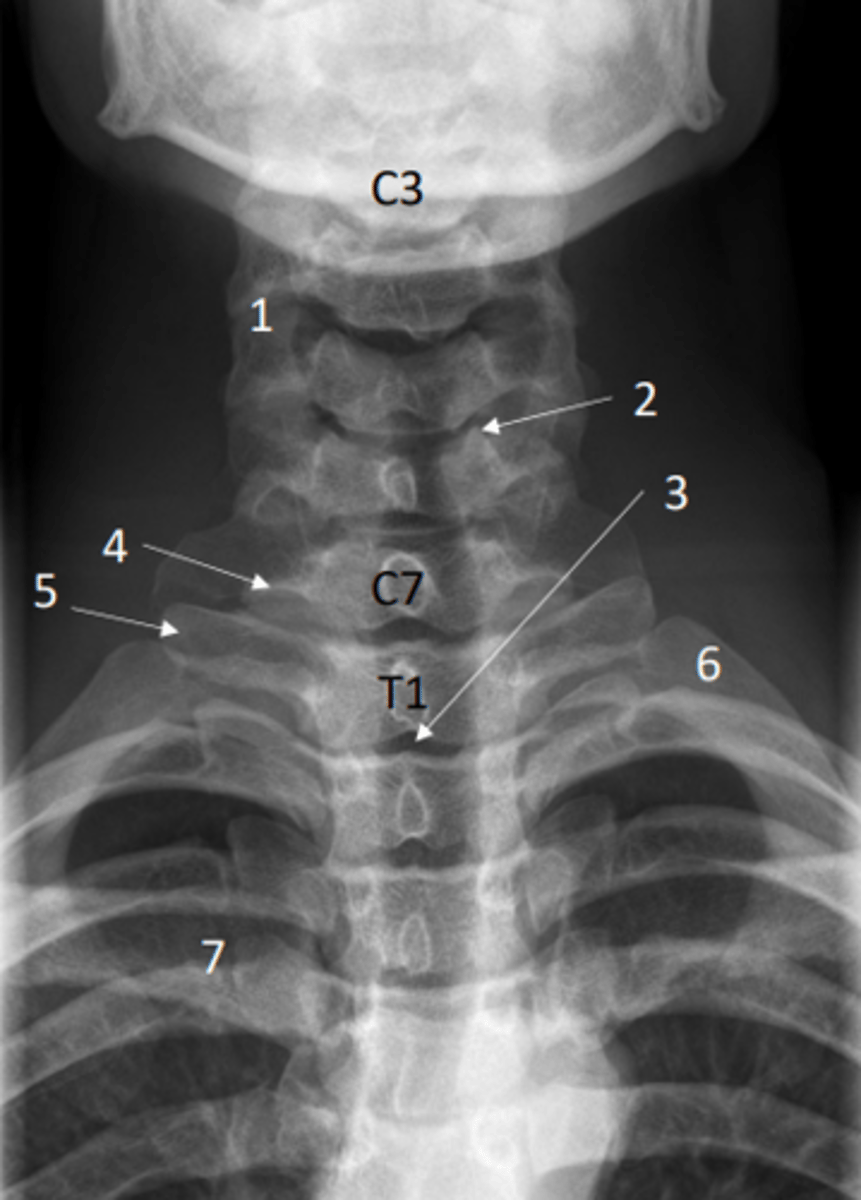
Anterior posterior view of the cervical spine (x-ray)
Lateral view of the cervical spine (x-ray)
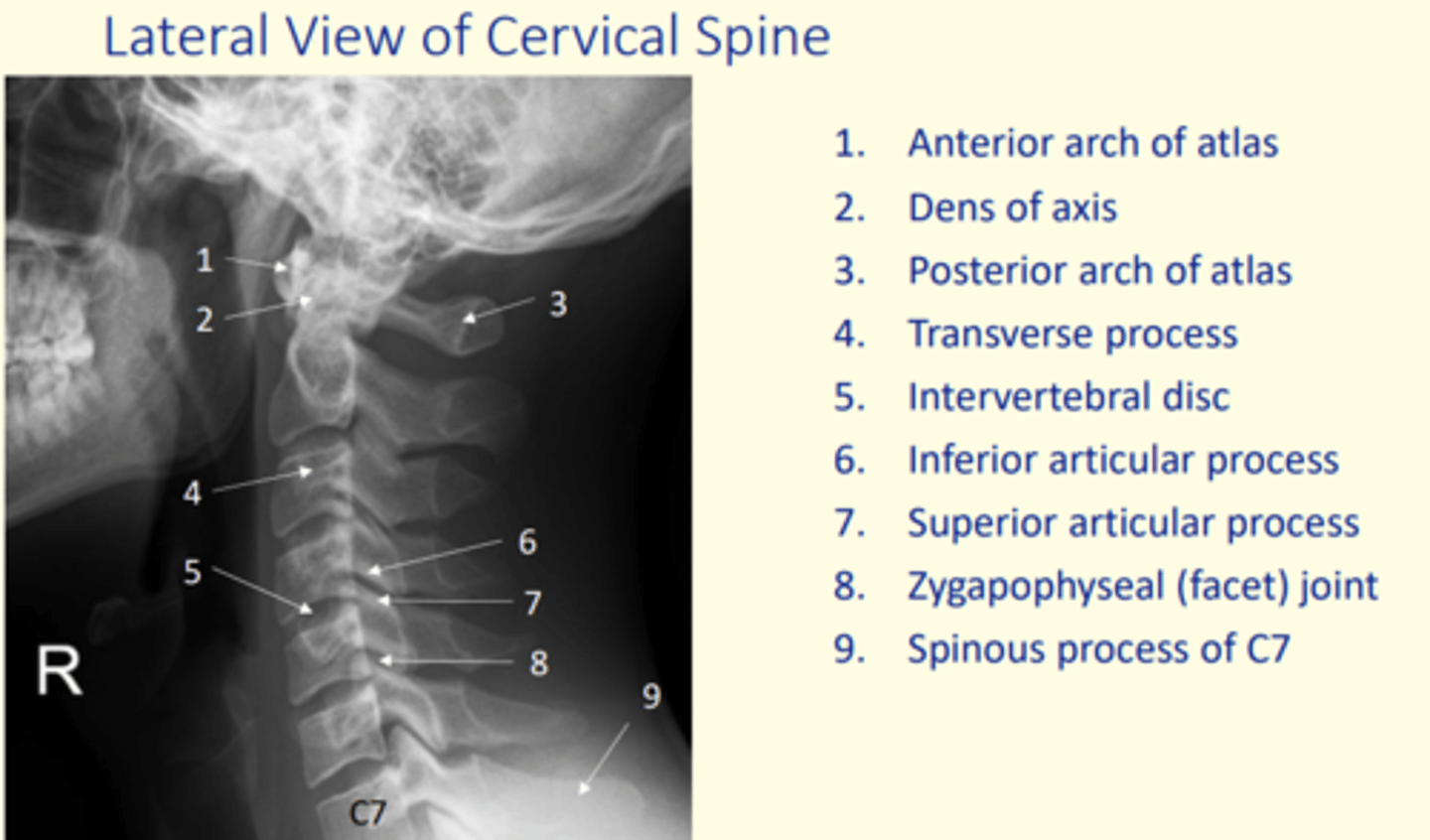
Identify anterior arch of atlas on this x-ray
1
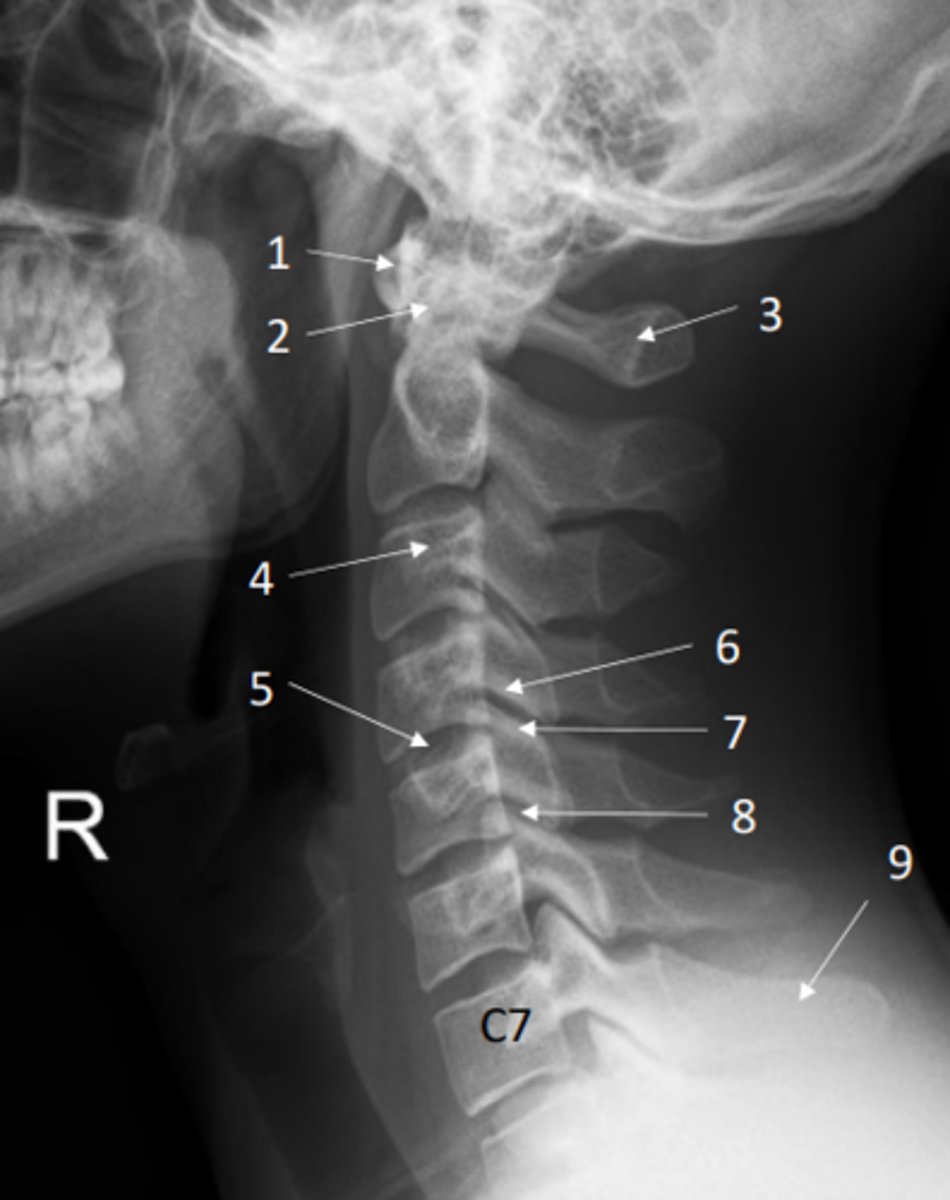
Identify dens of axis on this x-ray
2
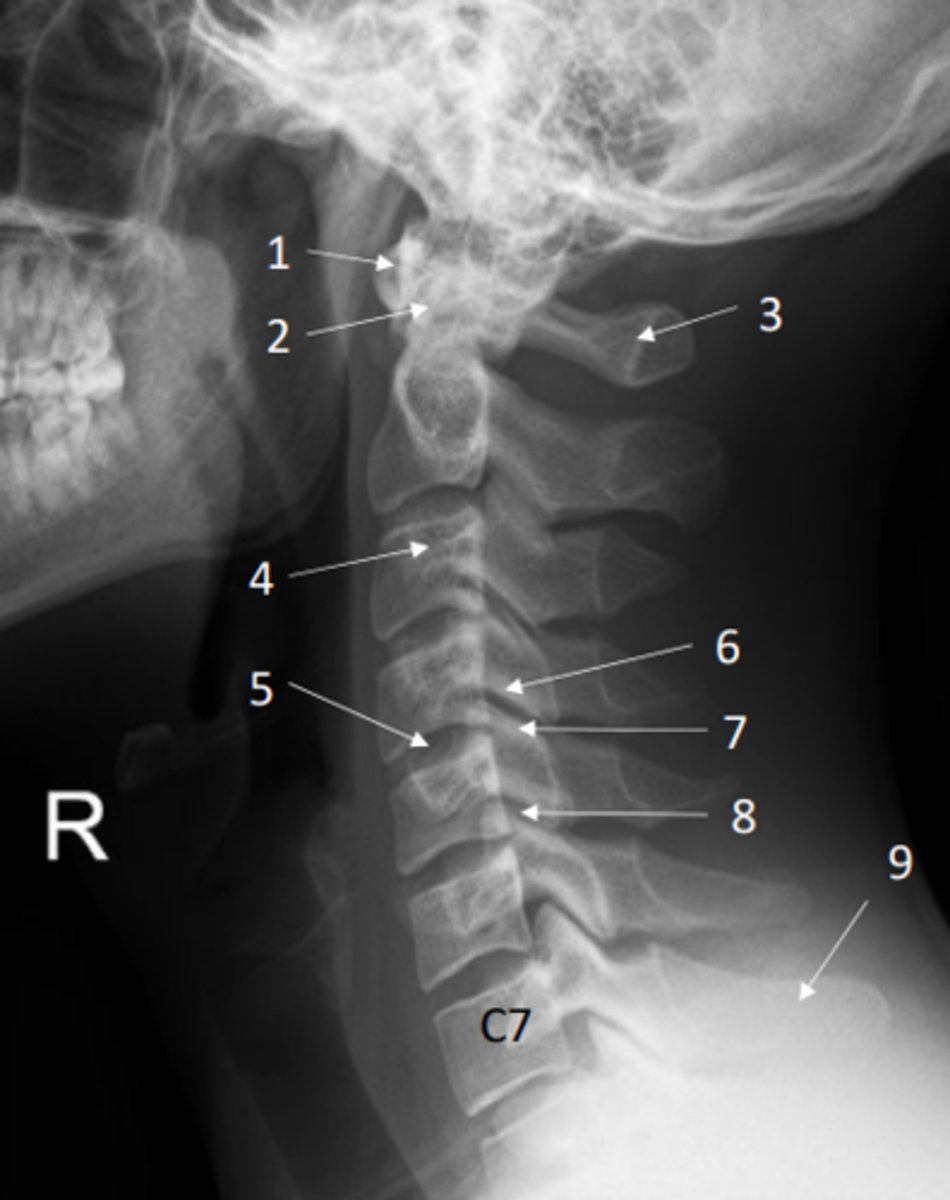
Identify posterior arch of atlas on this x-ray
3
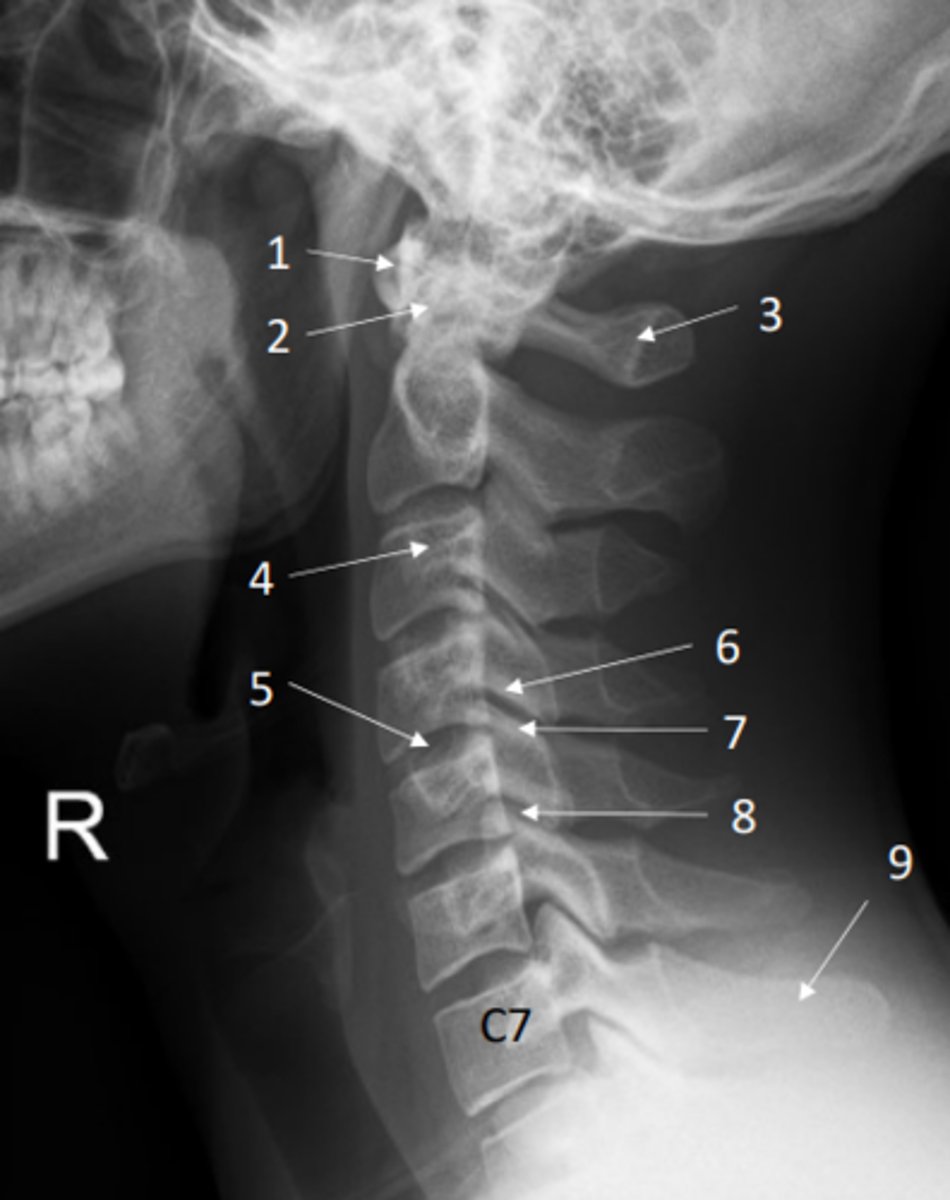
Identify transverse process on this x-ray
4
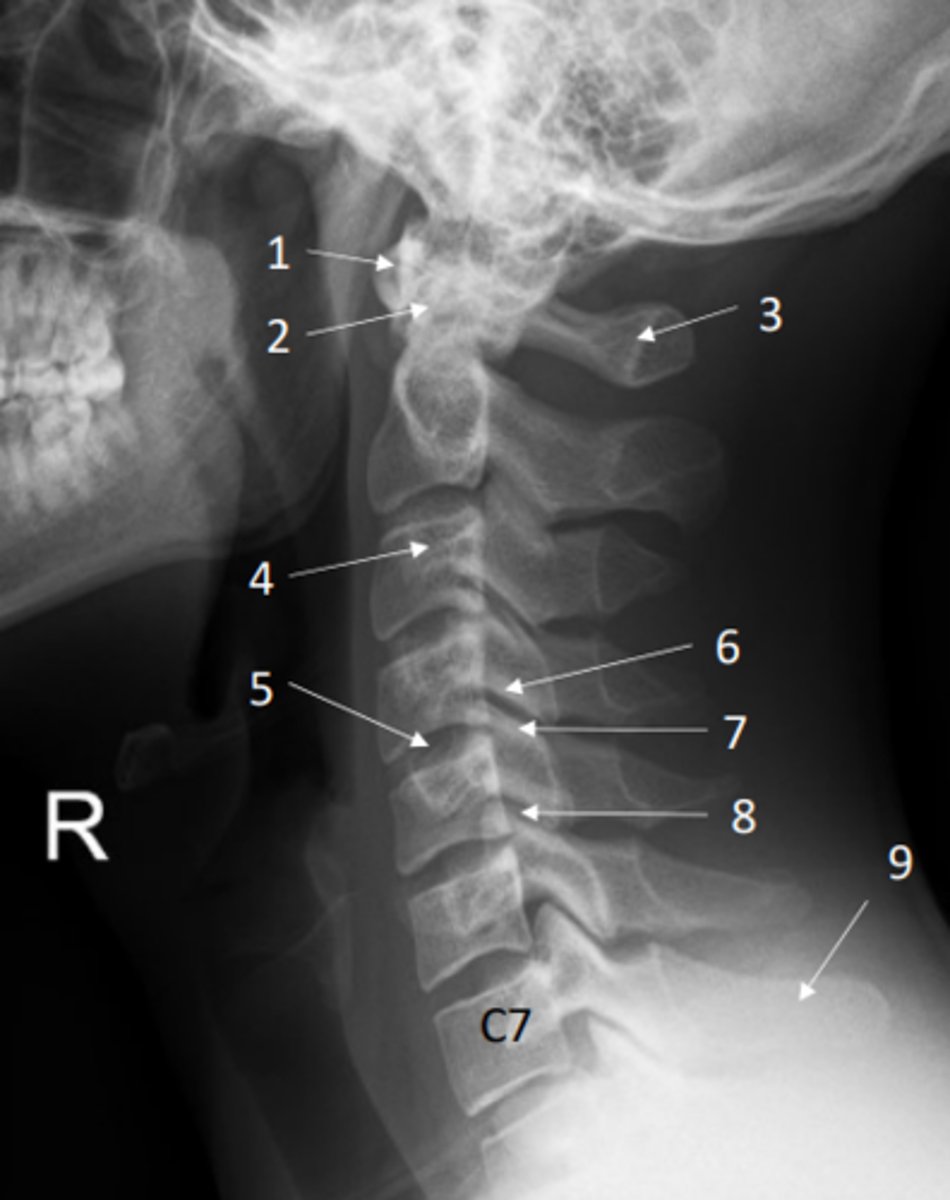
Identify IV disc on this x-ray
5
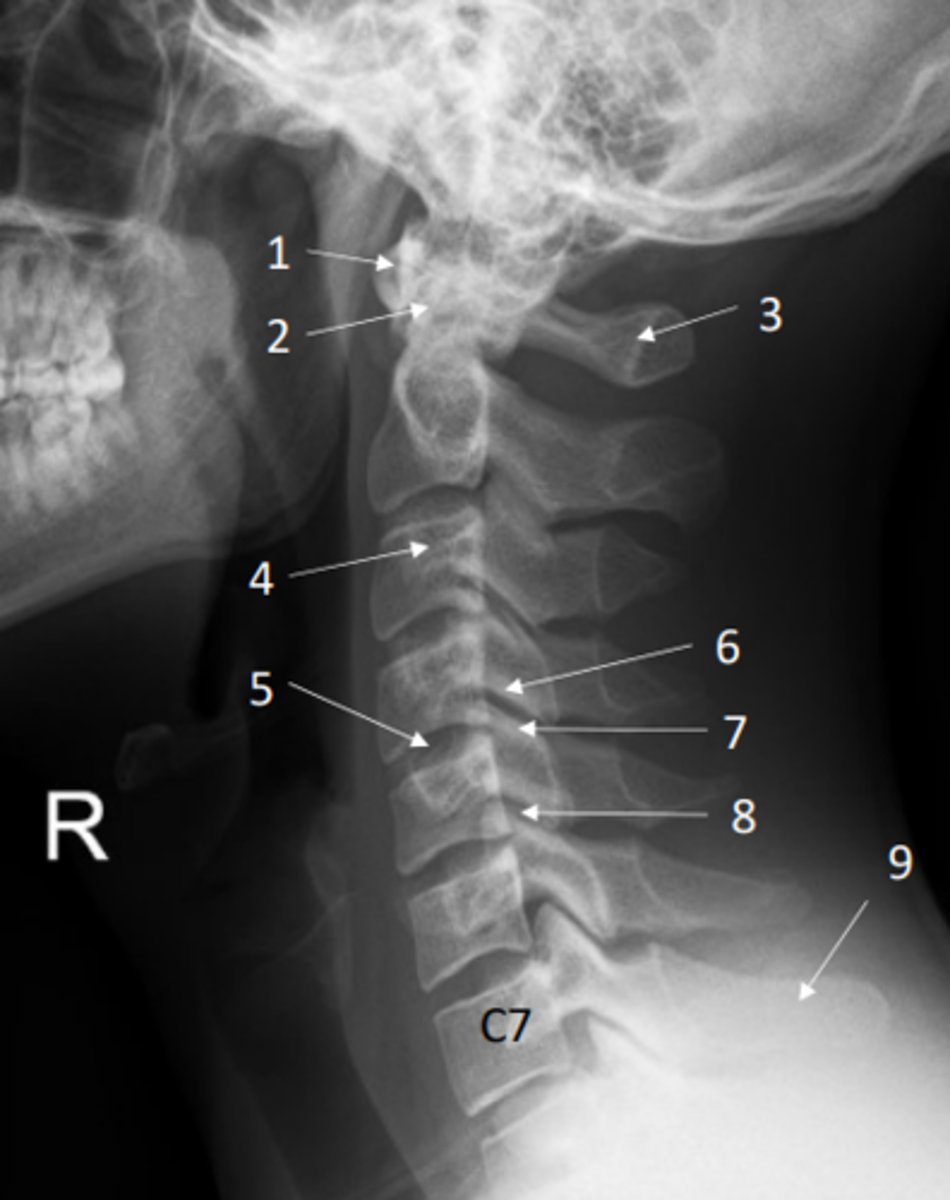
Identify inferior and superior articular processes on this x-ray
Inferior articular process = 6
Superior articular process = 7
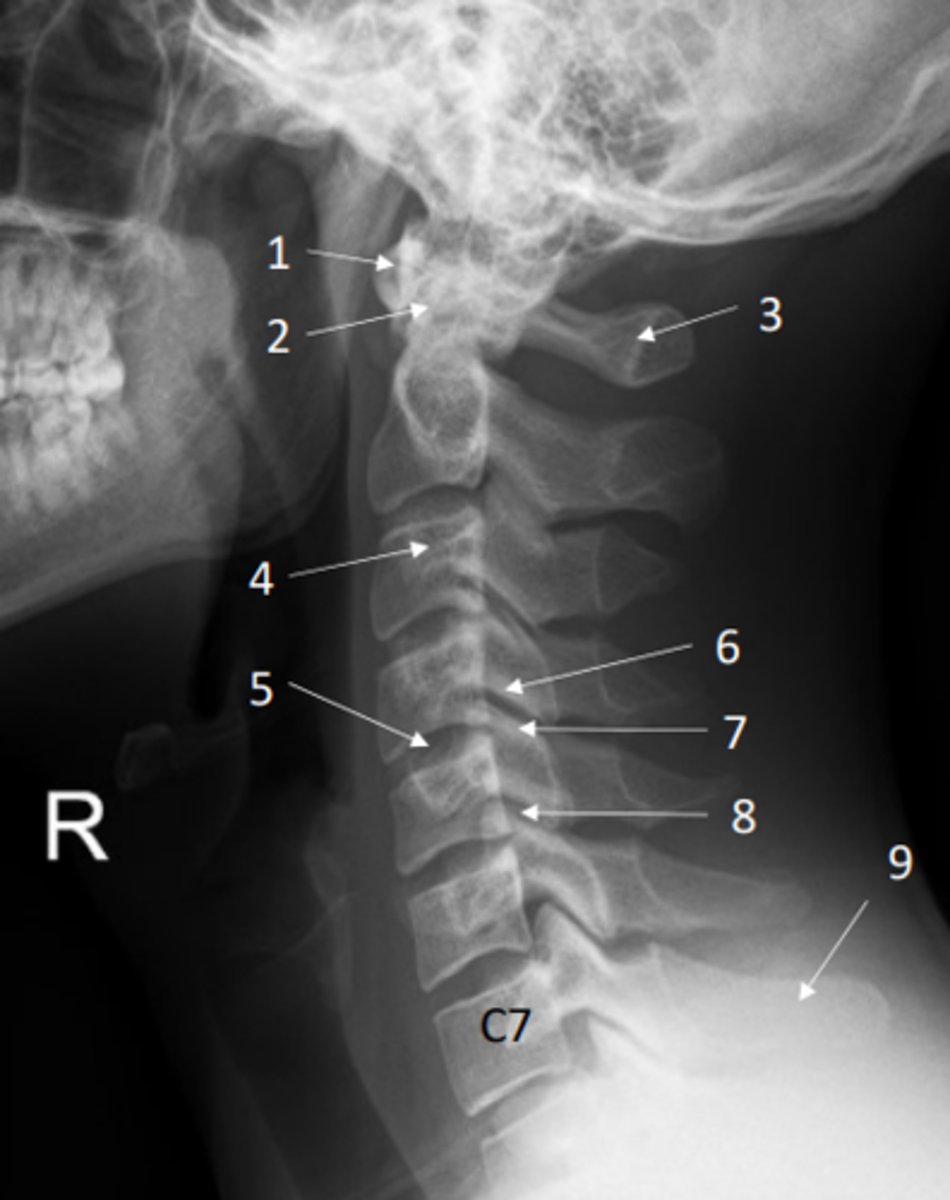
Identify the zygapophyseal (facet) joint on this x-ray
8
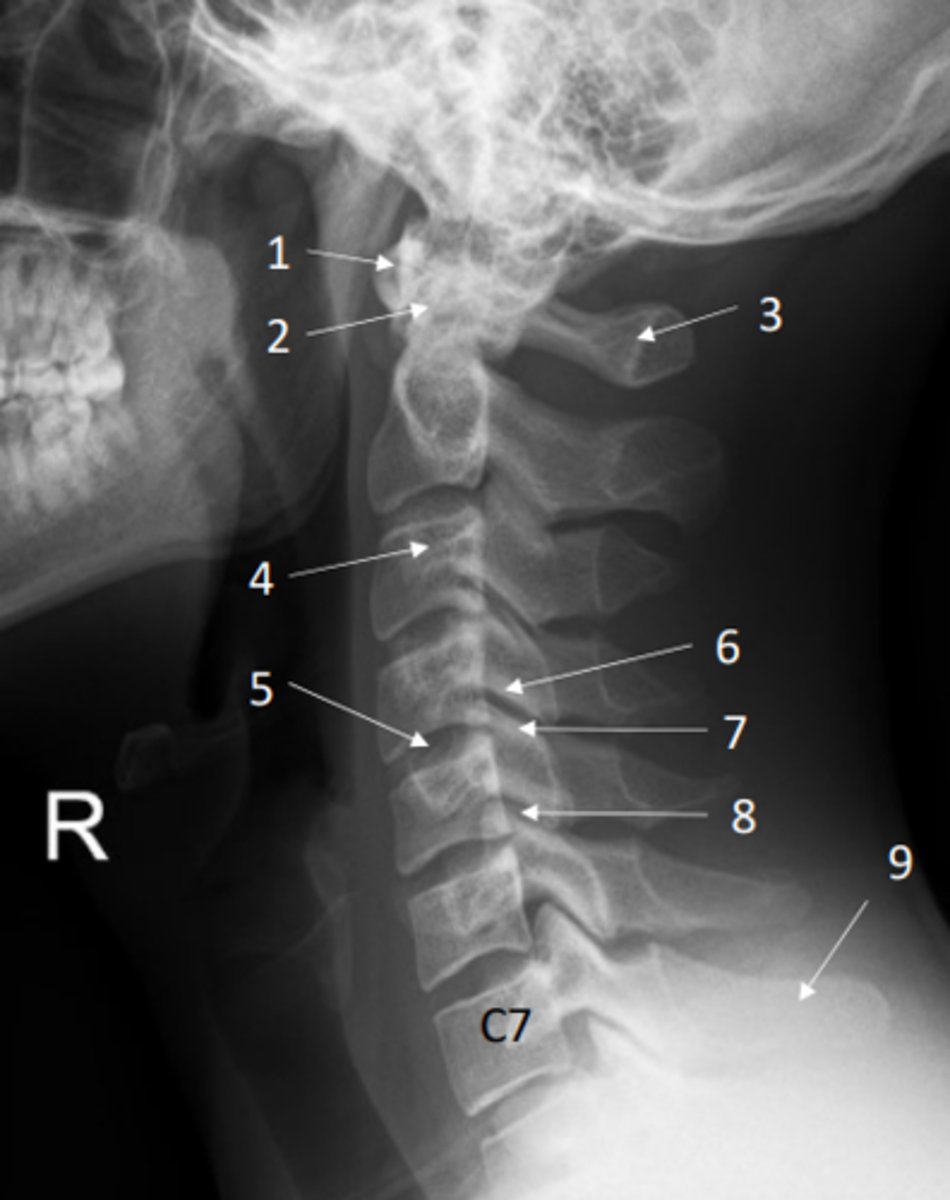
Identify spinous process of C7 on this x-ray
9
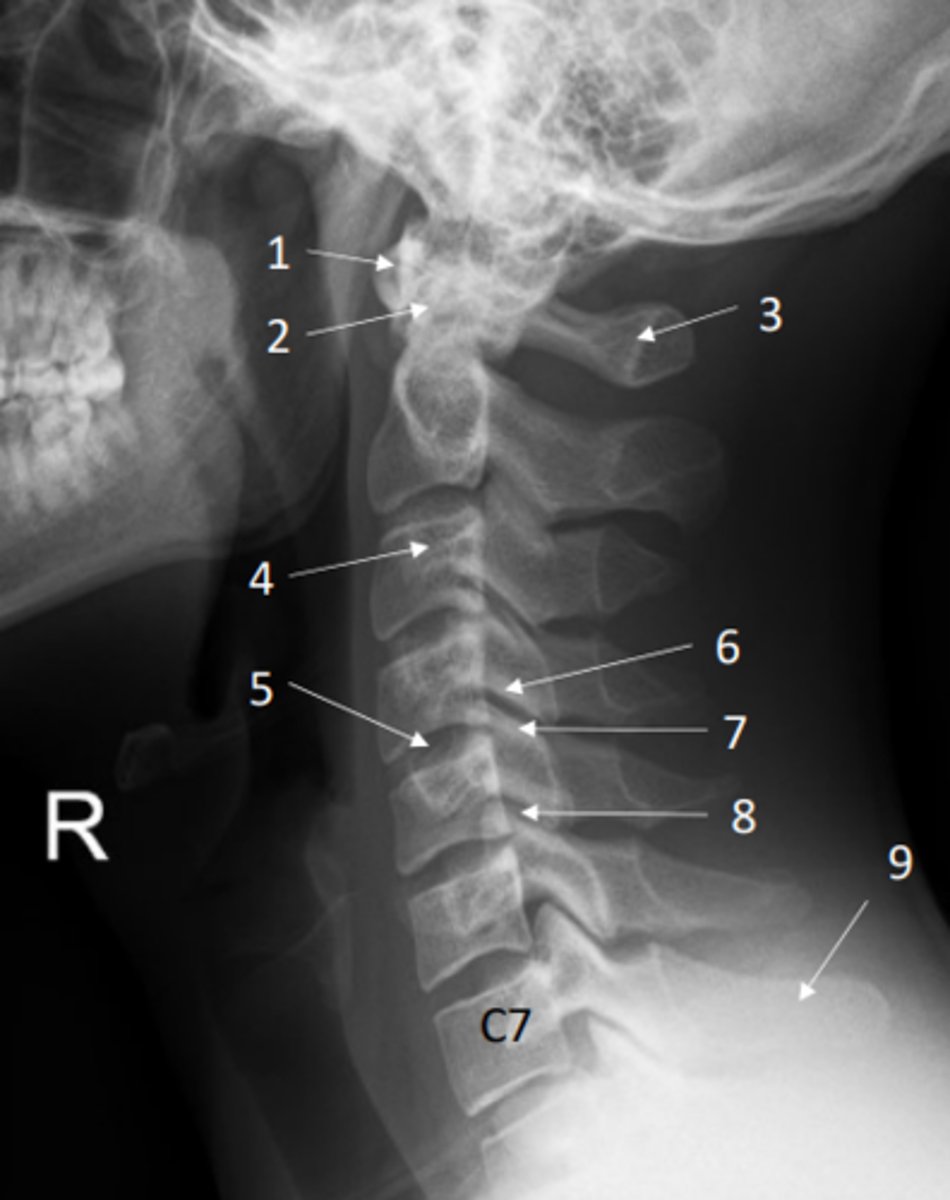
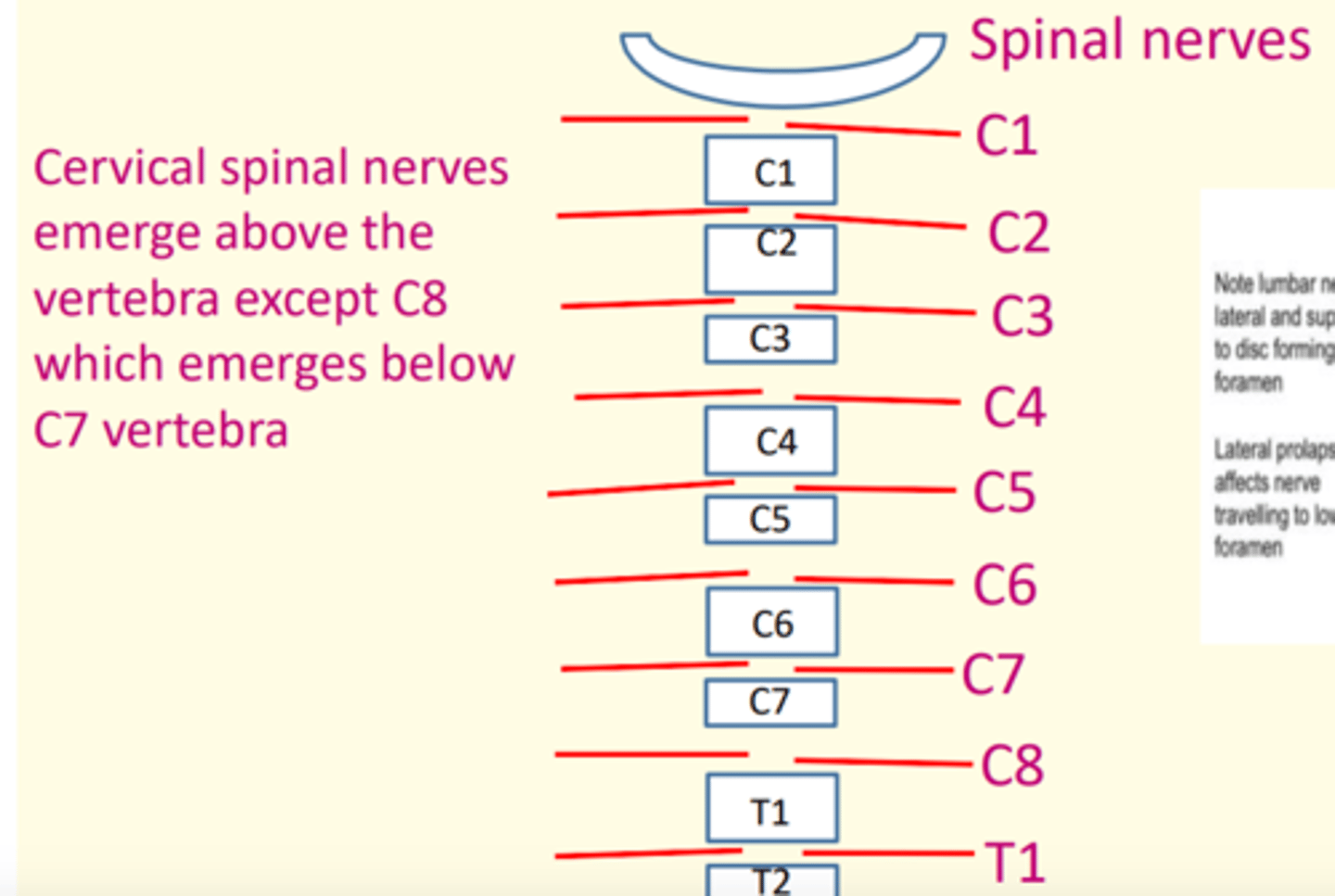
The cervical spinal nerves emerge above the vertebra, except ___ which emerges BELOW ___ vertebra
The cervical spinal nerves emerge above the vertebra, except C8 which emerges BELOW C7 vertebra
This is because there are 7 cervical vertebra but 8 spinal nerves
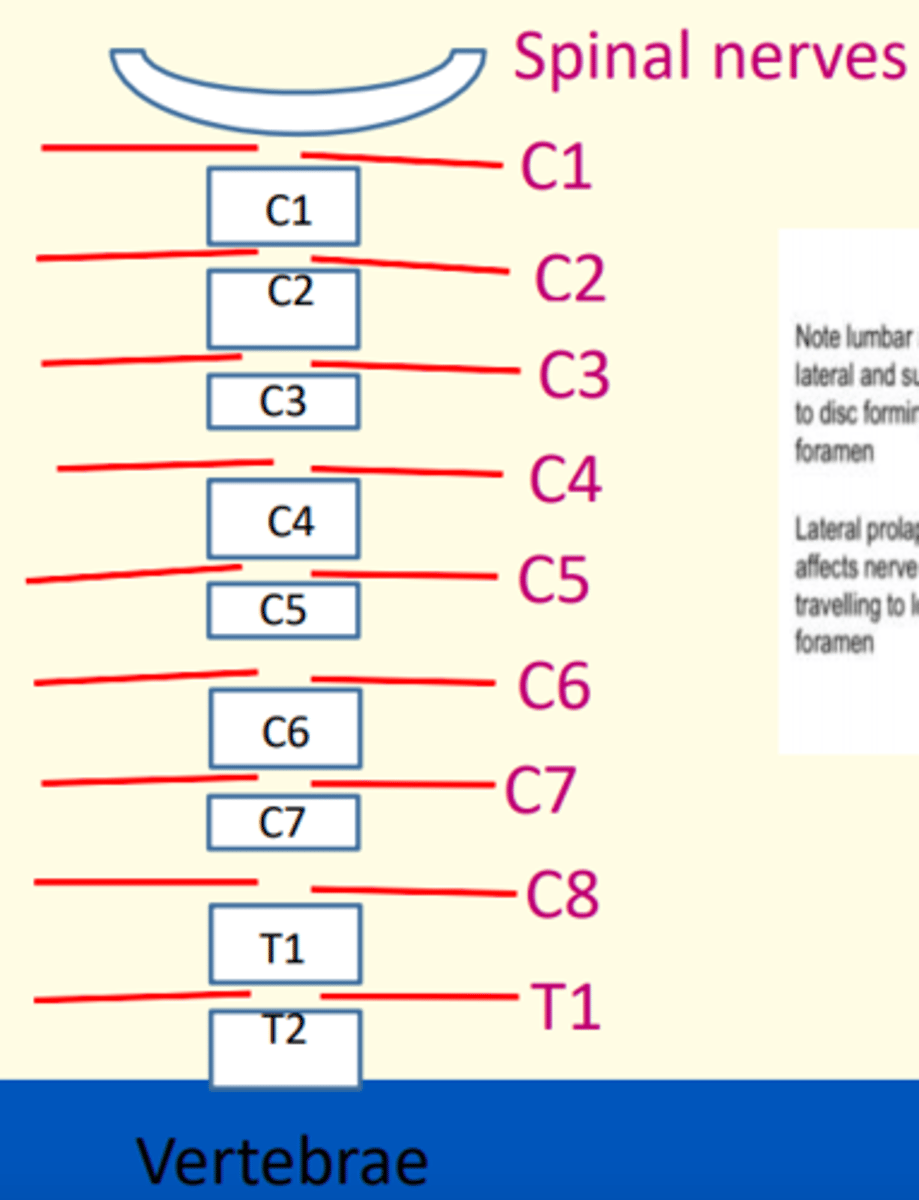
Name two fractures of the cervical spine
1) Fracture of Atlas (C1) = Jefferson's
2) Fracuture of posterior Axis (C2) = Hangman's
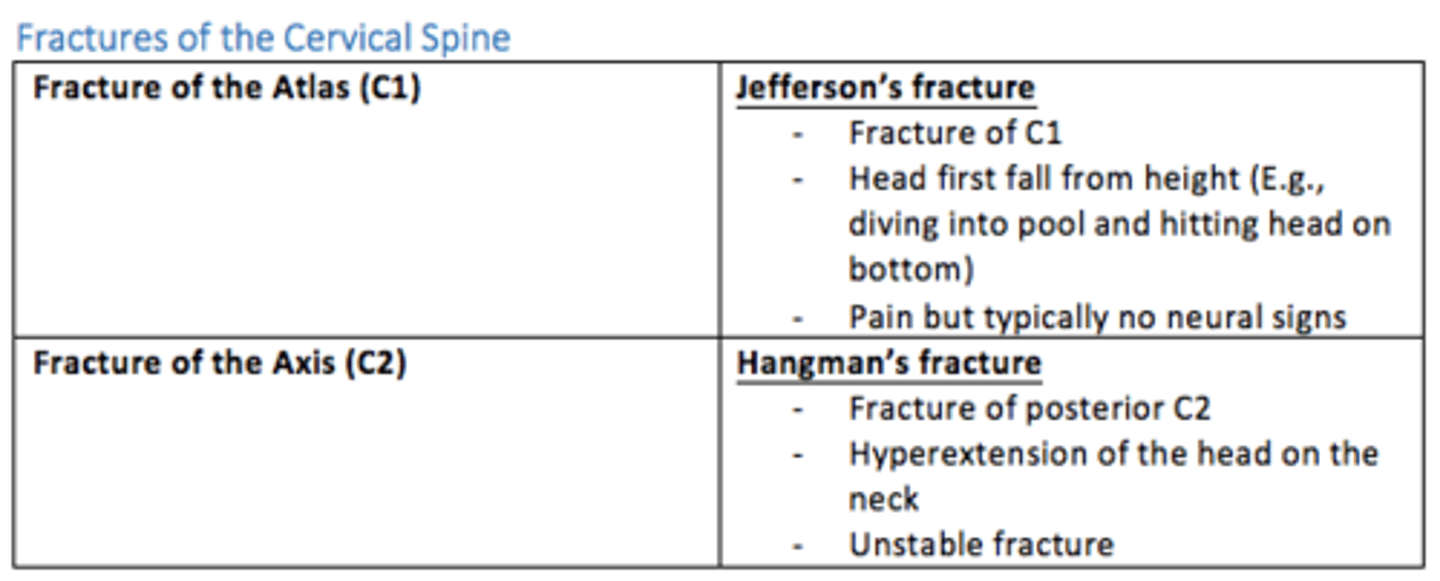
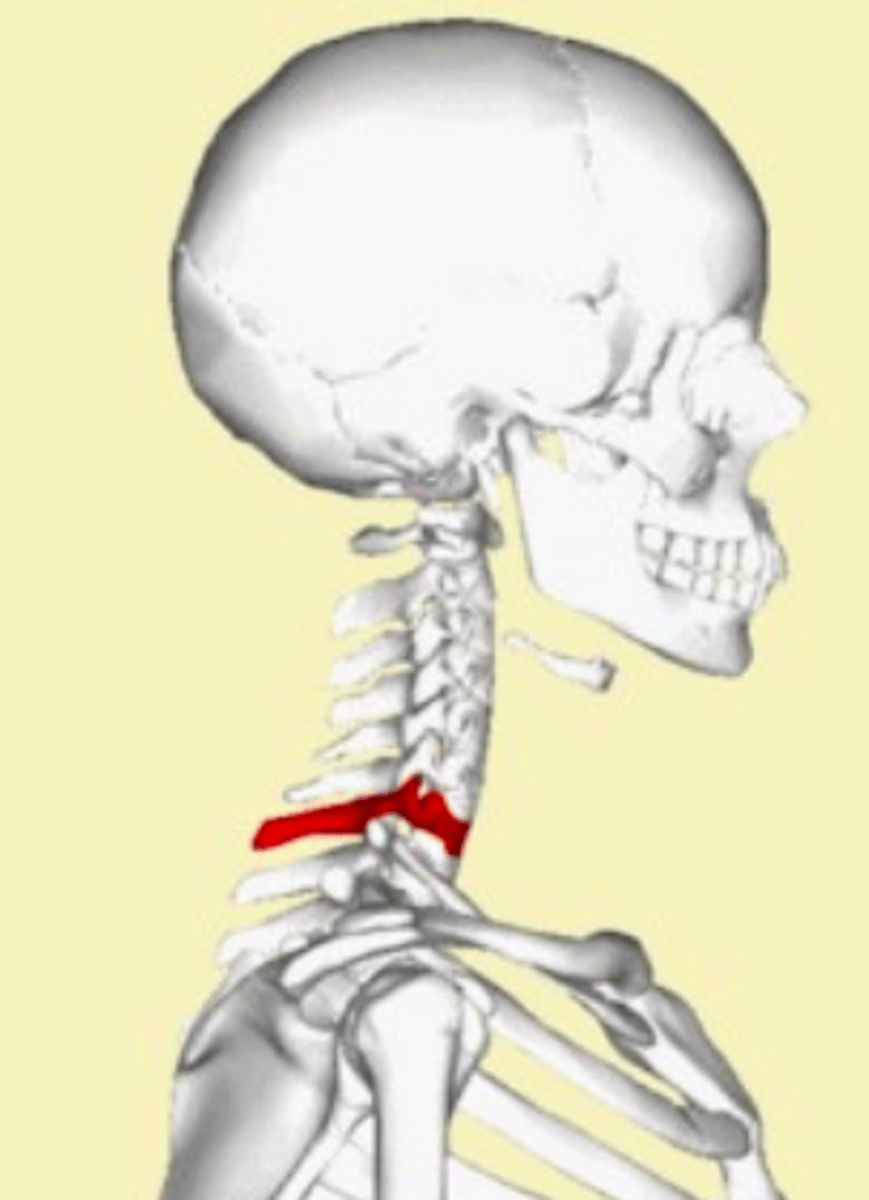
Jefferson's fracture (C1)
- Fracture of C1 (atlas)
- Head first fall from height (e.g., diving into pool, hit head)
- Pain, but typically no neural signs
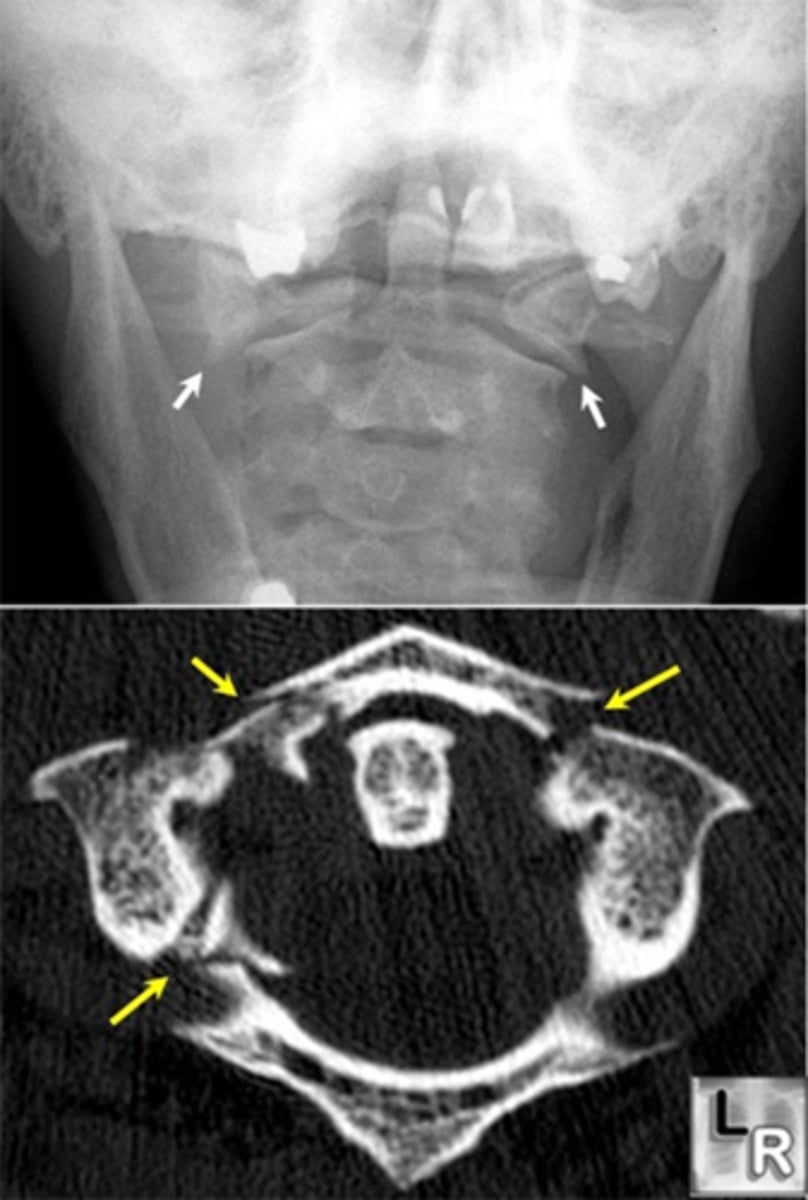
Hangman's fracture (posterior C2)
- Fracture of posterior C2 (axis)
- Hyperextension of the head on the neck
- Unstable
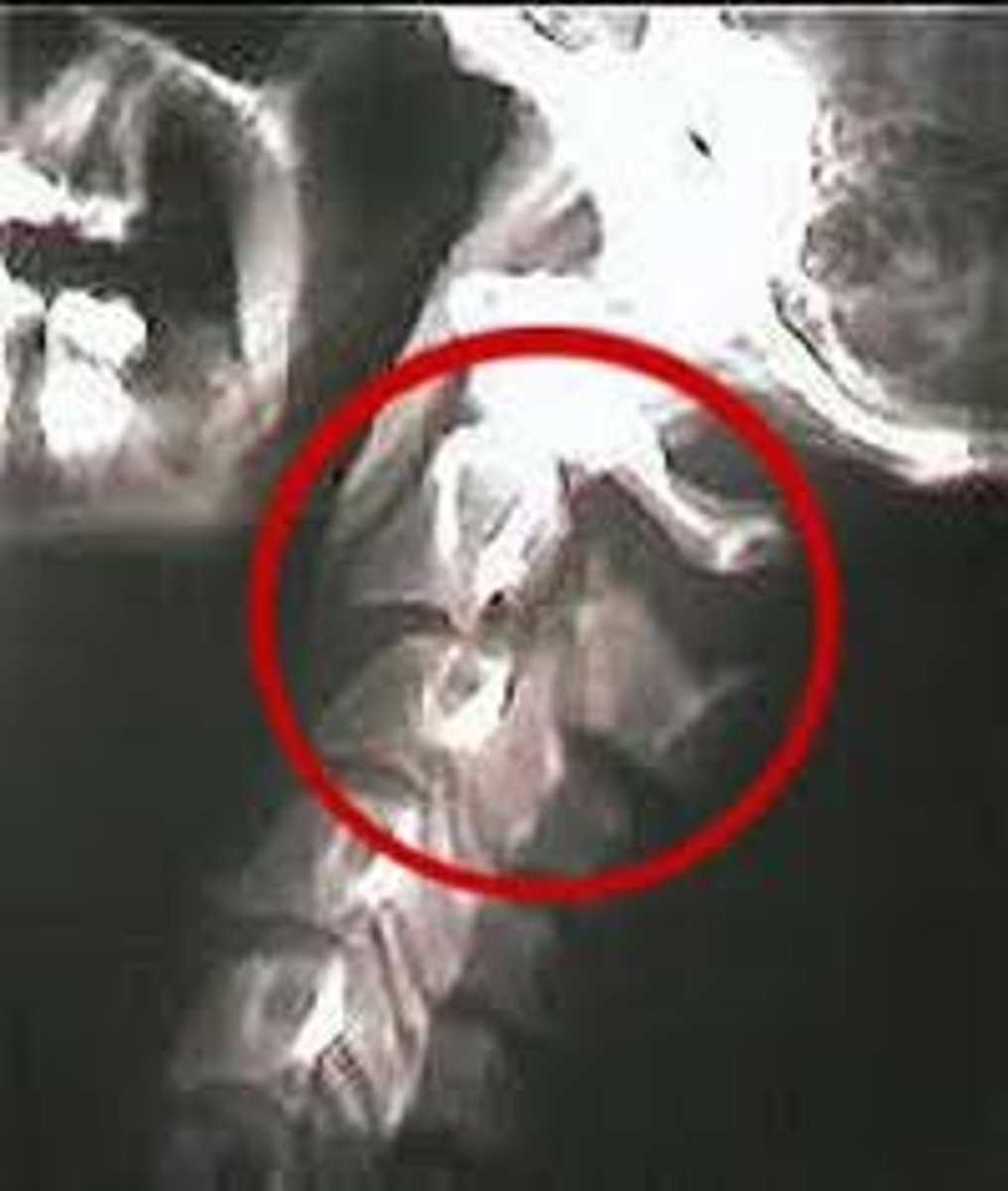
What region of the spine is prone to whiplash?
Cervical region
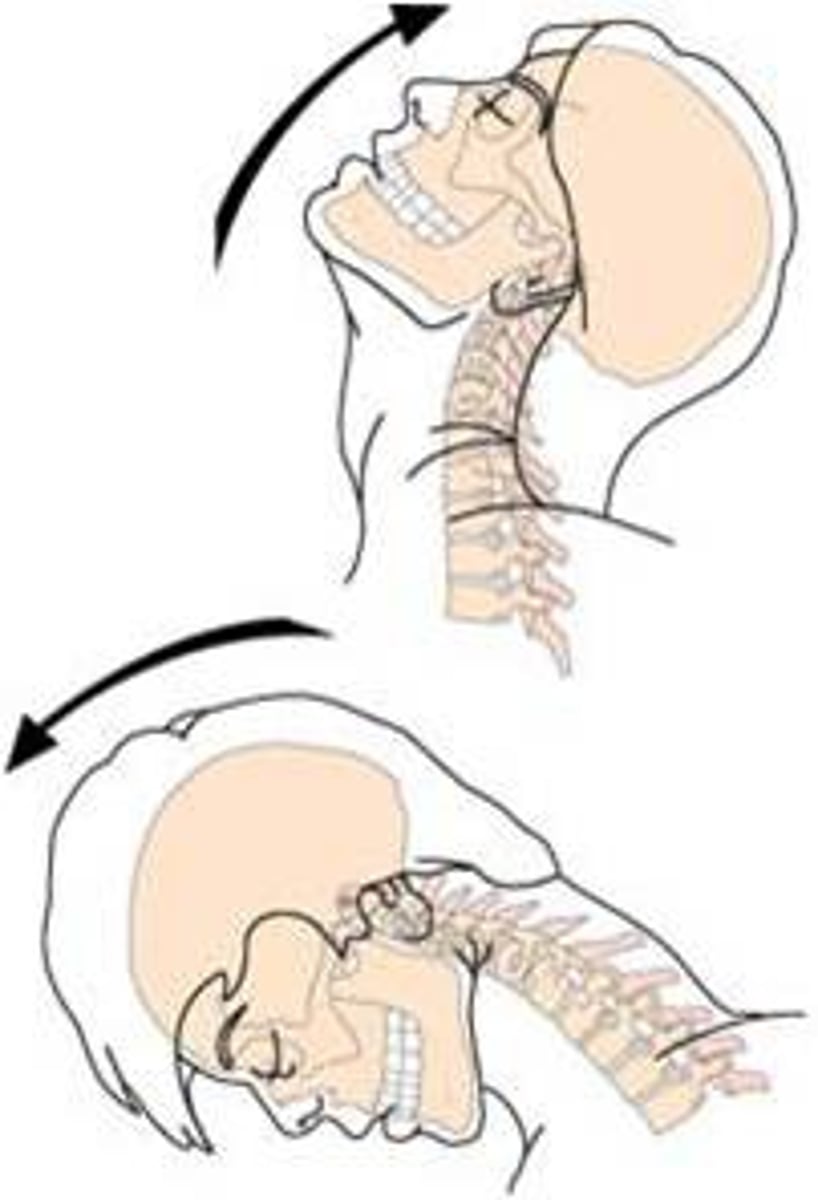
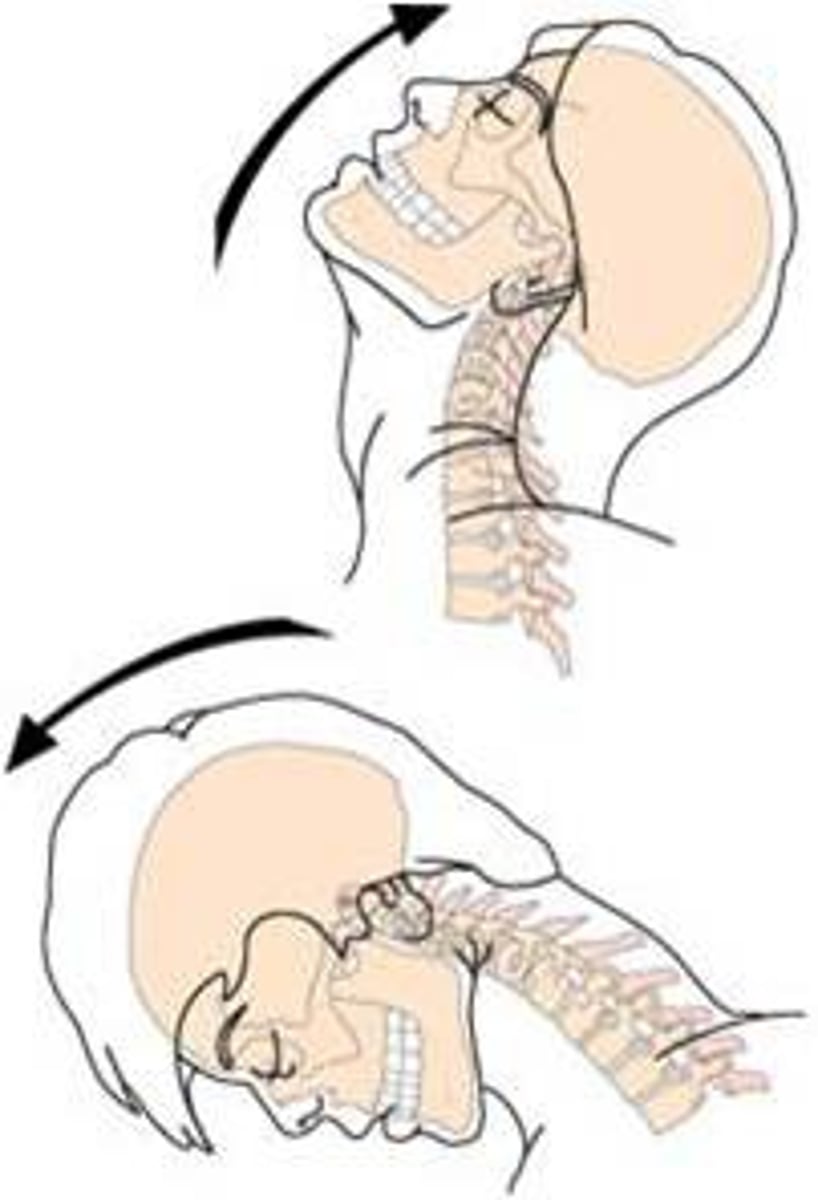
Whiplash injury
Trauma to the cervical vertebrae, usually the result of a car accident (hyperextension and hyperflexion)
Injury to the anterior longitudinal ligament - causing painful muscle spasms
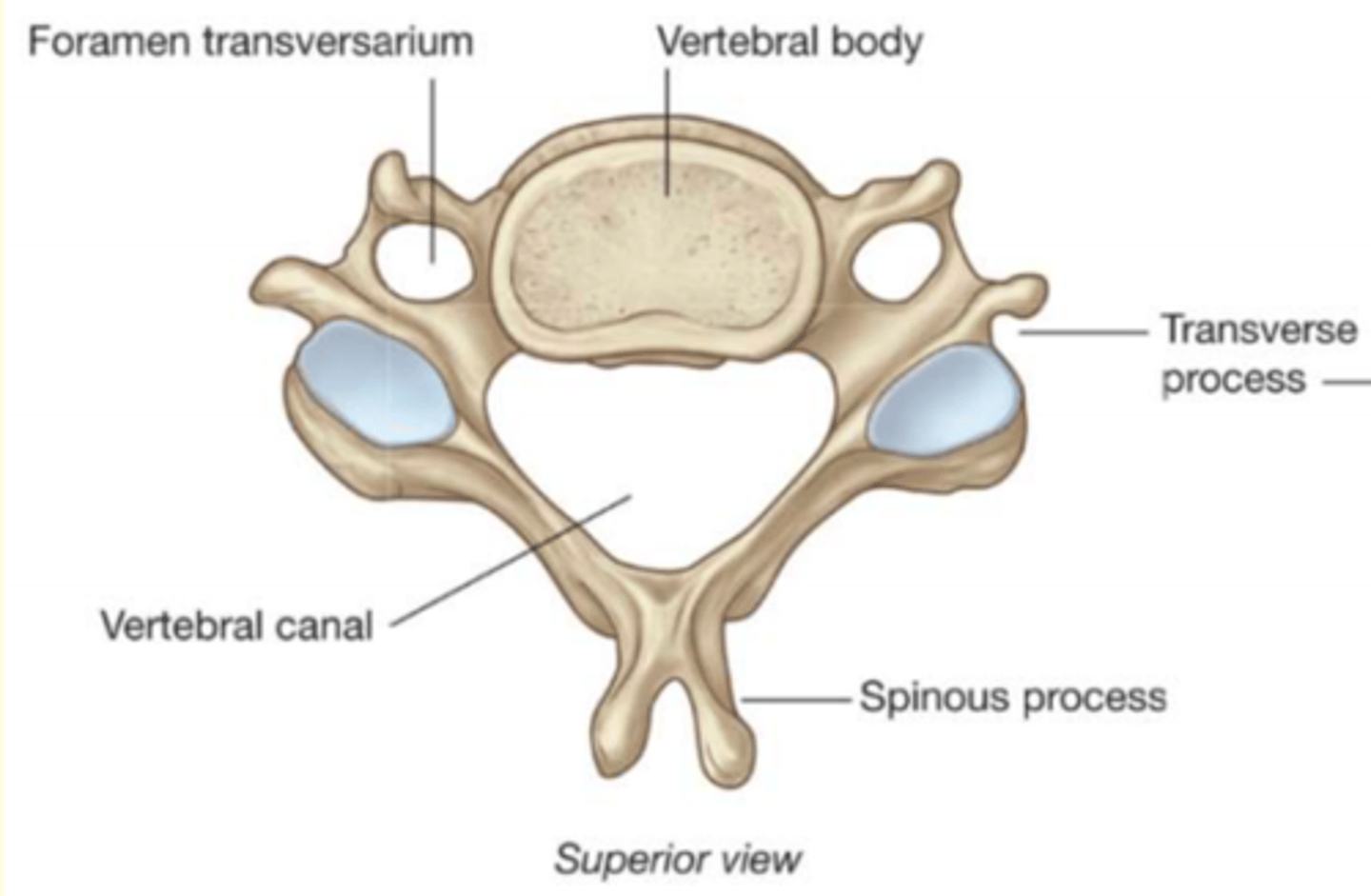
Cervical vertebrae
Up at 7, lunch at 12, home at 5
- C1-C7
- First set of seven bones, forming the neck
- Smallest of the discrete vertebra
- Bifid spinous process
- 2 Transverse foramen in transverse process
- Large triangular vertebral foramen
- Small dome shaped body with edges facing upward lips known as uncinate process
Thoracic vertebrae
Up at 7, lunch at 12, home at 5
- T1-T12
- Second set of 12 vertebrae
- They articulate with the 12 pairs of ribs
- Costal facets on side of vertebral body and transverse processes for articulation of ribs to vertebra
- Vertebral foramen is small and circular
Lumbar vertebrae
Up at 7, lunch at 12, home at 5
- L1-L5
- Third set of five larger vertebrae
- Largest of the vertebra (large body, thick spinous process)
- No foramina or costal facets on transverse processes
- Vertebral foramina is small and triangular
All types of vertebra and their differences (Cervical, Thoracic and Lumbar)
Up at 7, lunch at 12, home at 5
Cervical = C1-C7
Thoracic = T1-T12
Lumbar = L1-L5
All vertebra types
Cervical (left)
Thoracic (middle)
Lumbar (right)
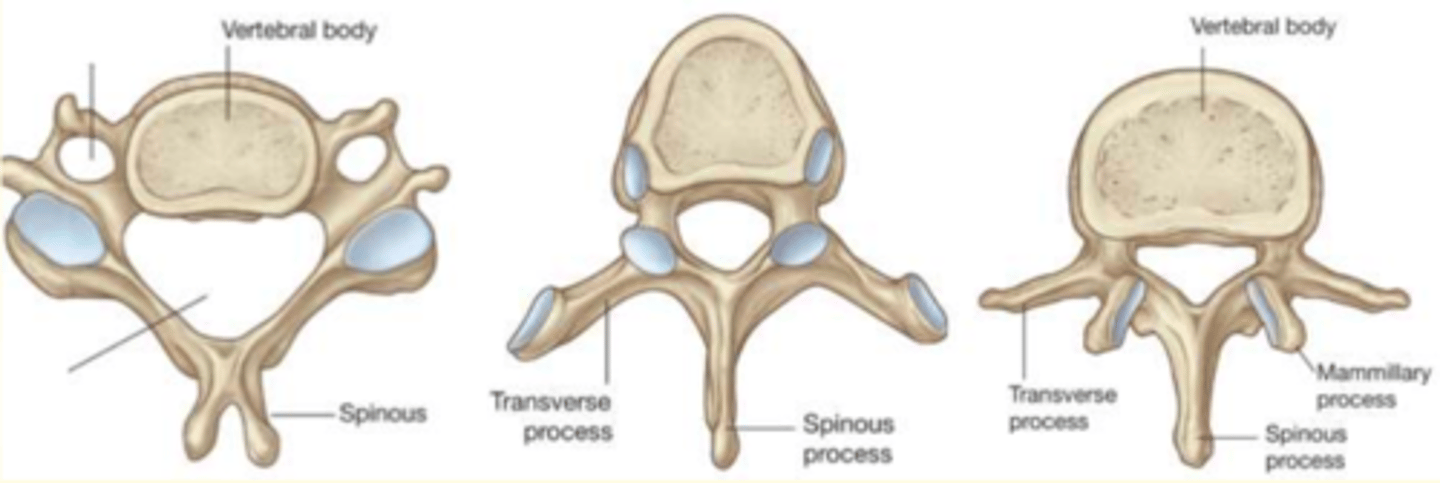
Which vertebra is this?
Cervical
- Small body
- One vertebral and two transverse foramina
- Triangular vertebral foramina
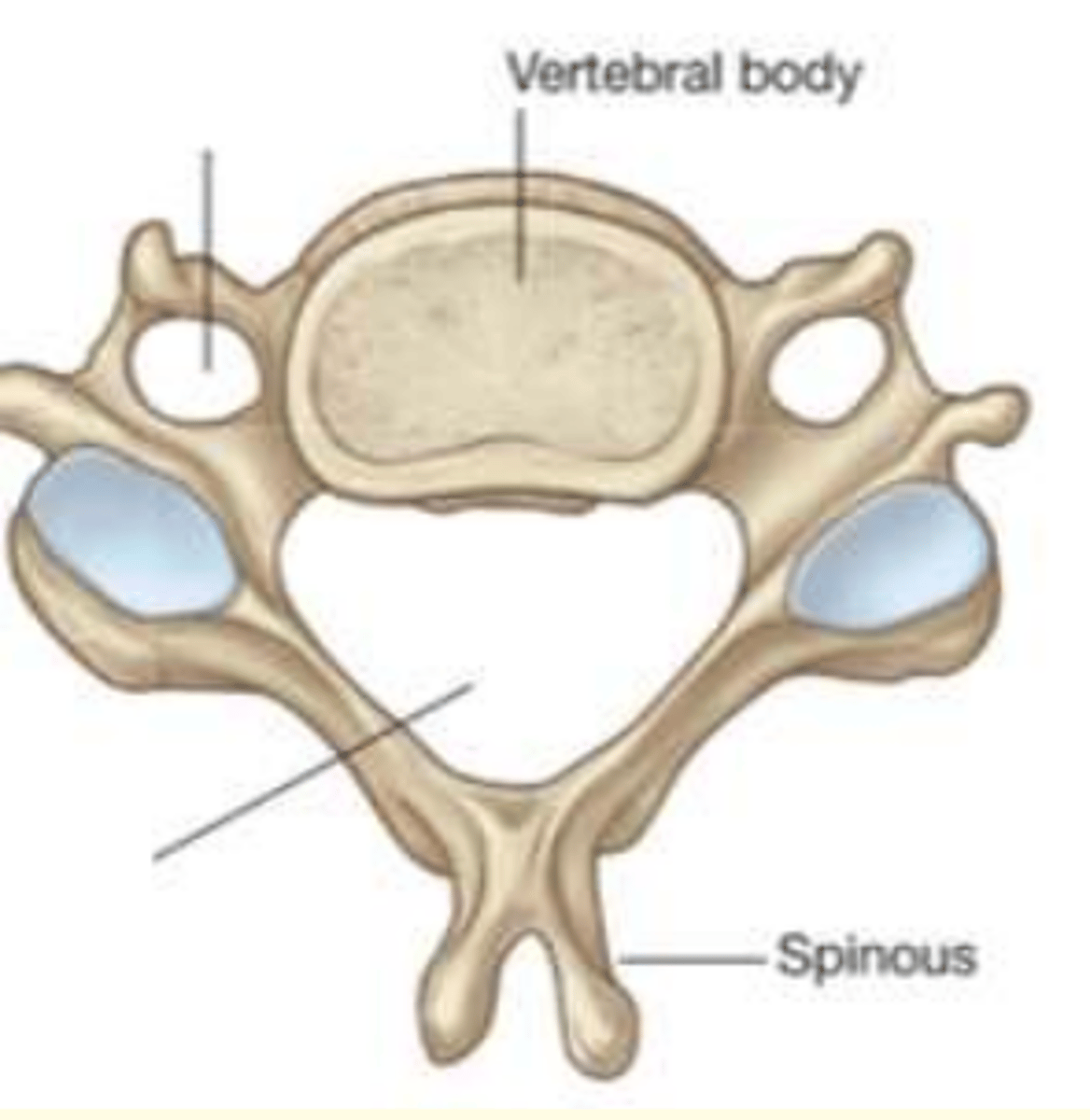
Which vertebra is this?
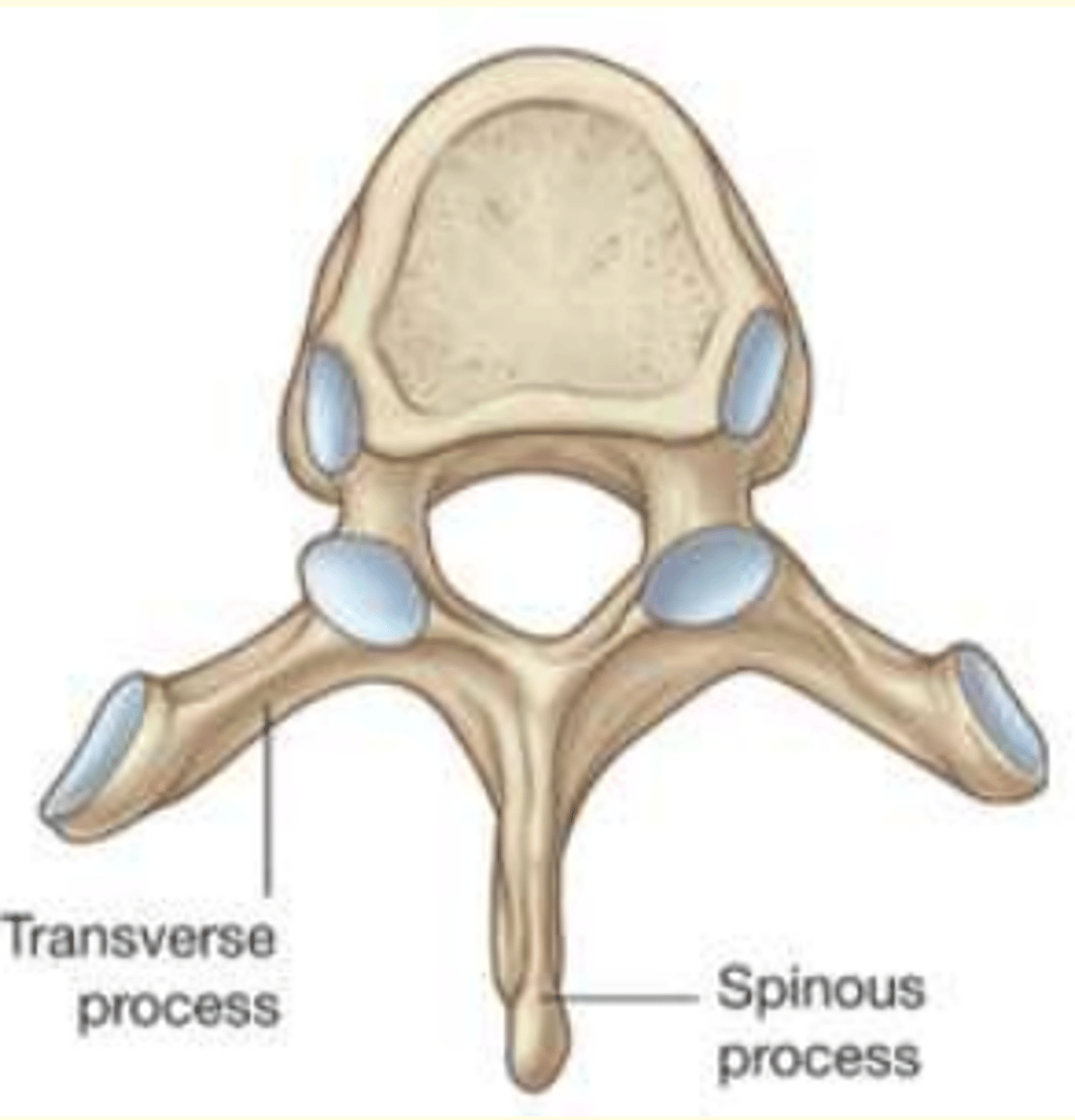
Lumbar
- Largest kidney-shaped body
- One vertebral foramina
- Triangular vertebral foramina
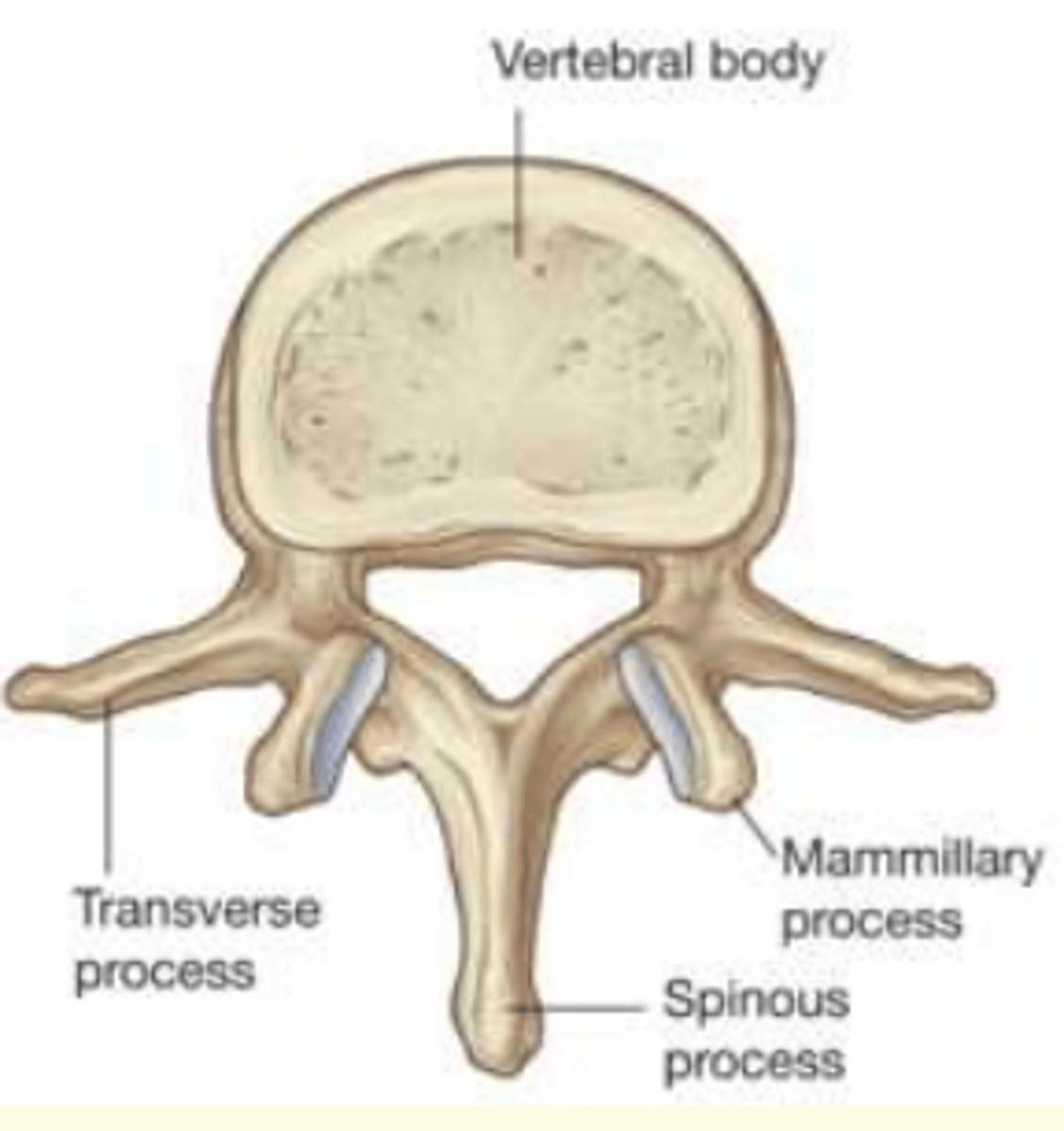
Which vertebra is this?
Thoracic
- Medium heart-shaped body
- One vertebral foramina
- Smallest and circular vertebral foramina
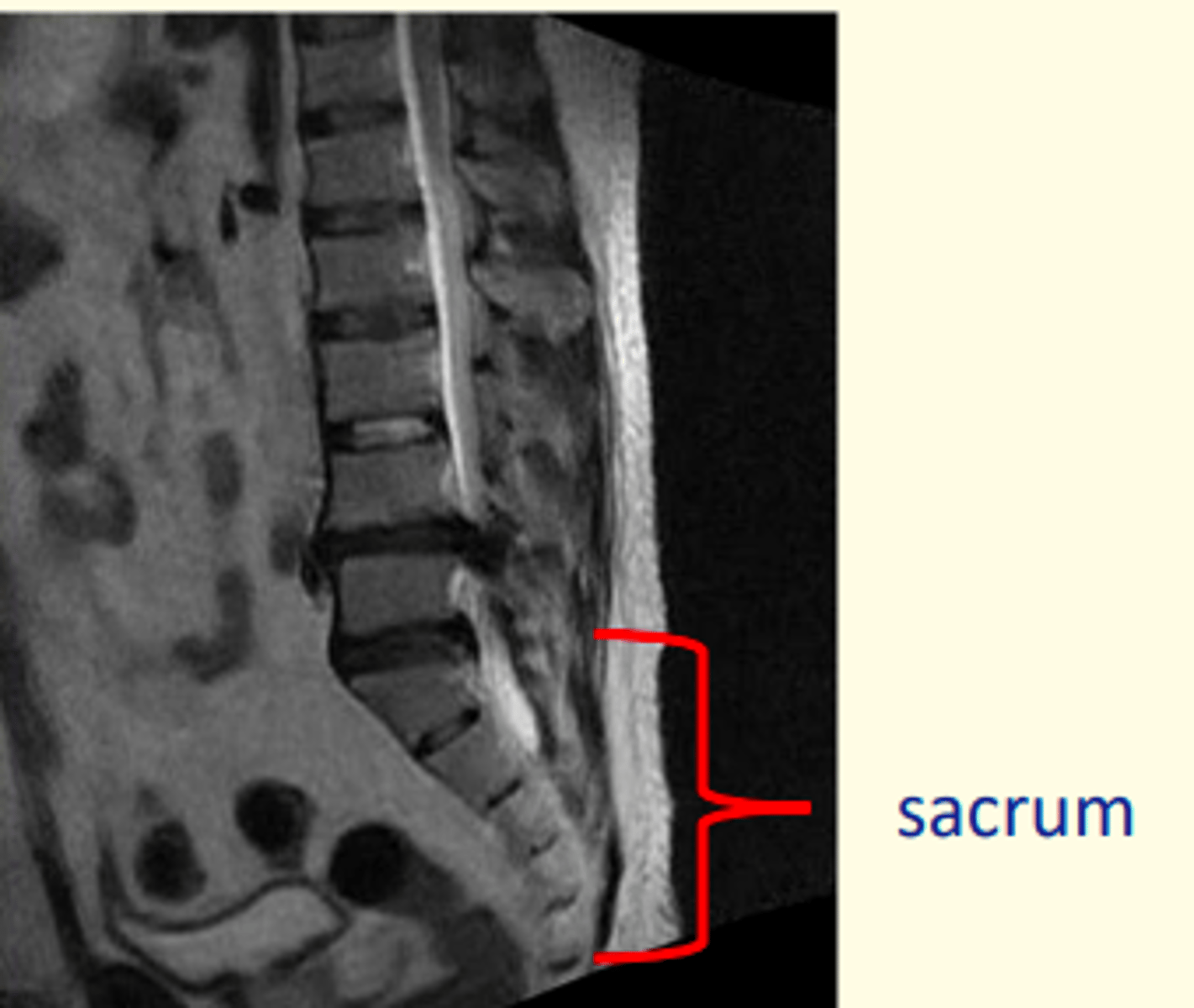
Sacrum
5 fused vertebra at the base of the spine (S1-S5)
Articulates with the pelvis laterally
Coccyx
3-4 fused vertebra which form 'tailbone'
Easily fractured during falls

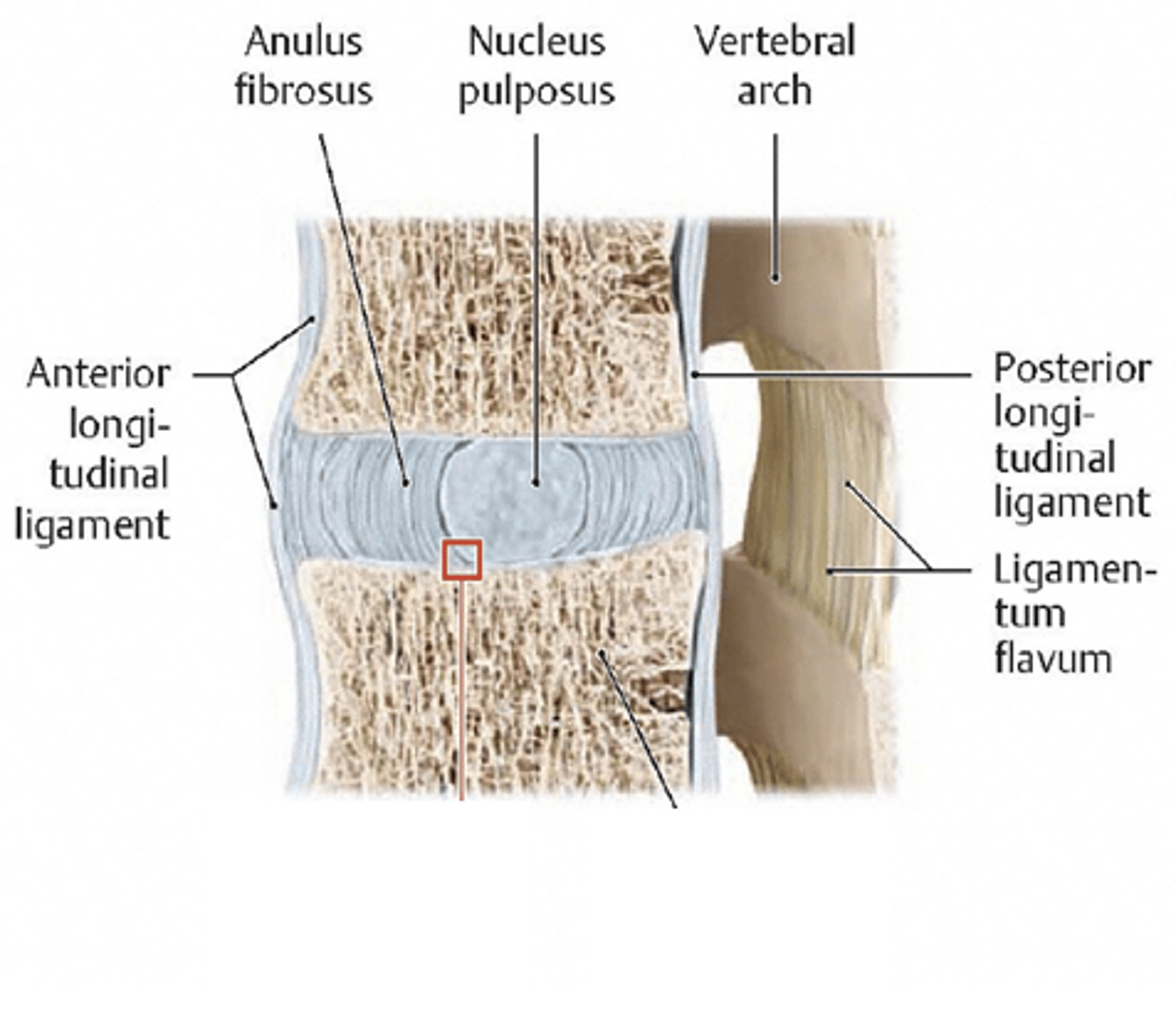
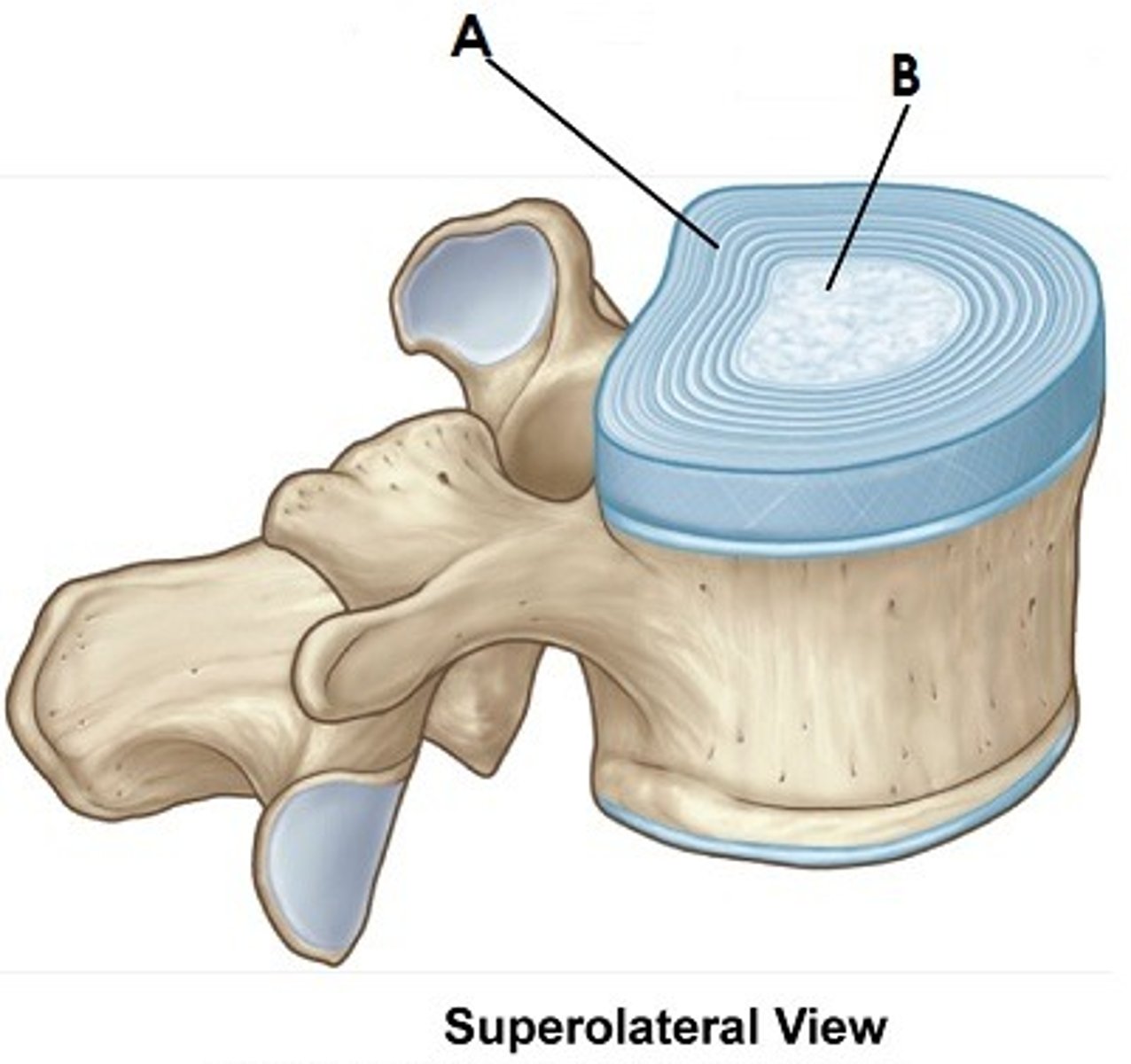
Which part of the vertebral column accounts for 25% of length of vertebral column and has a high water content which keeps them turgid (resilience and resistance)?
Intervertebral discs
Two regions of the Intervertebral (IV) Discs
A) Annulus Fibrosis (peripheral)
B) Nucleus Pulposus (central)
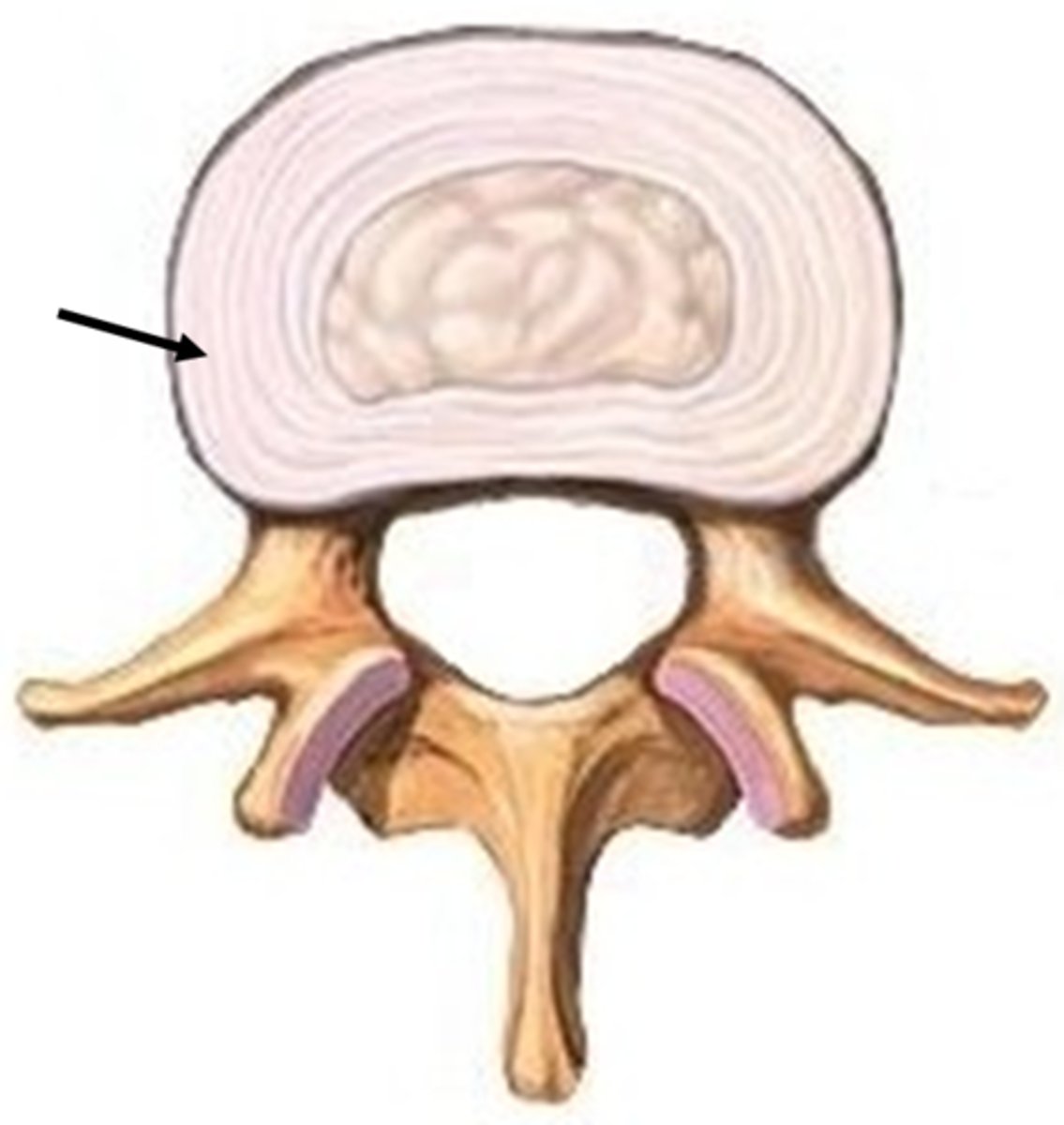
Describe some structural/functional features of the peripheral region of the IV disc (Annulus Fibrosis)
Structure
- Lamellae of annular bands in varying directions
- Avascular, aneural
- Surrounds nucleus pulposus (central)
Function
- Major shock absorber
- Highly resilient under compression (strong)
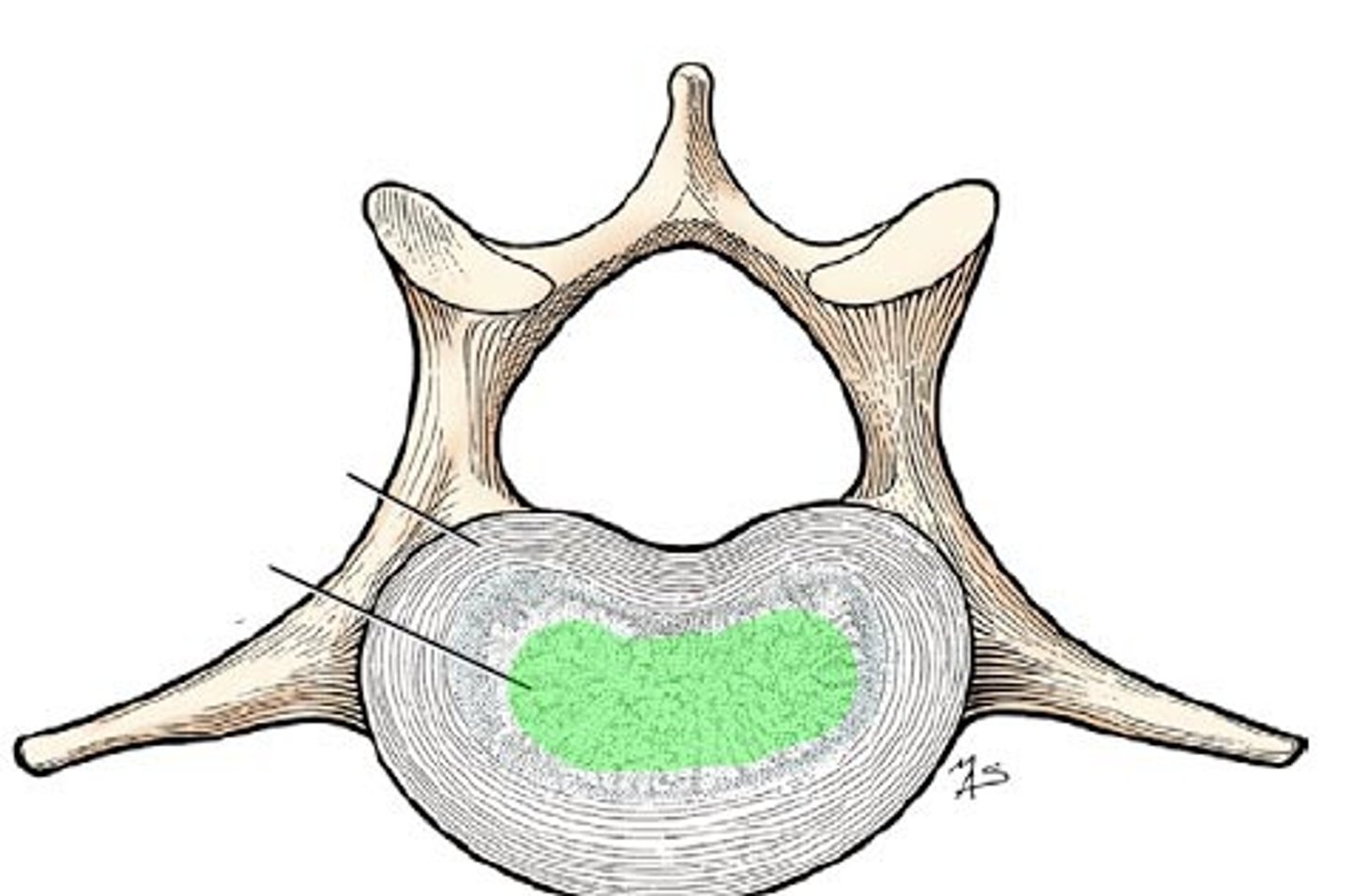
Describe some structural/functional features of the central region of the IV disc (Nucleus Pulposus)
Structure
- Remnant of the notochord
- Gelatinous
- High osmotic pressure
- Changes in size throughout day/with age
- Surrounded by annulus fibrosis
The two main ligaments of the spinal column which provide stability are...
1) Anterior longitudinal ligament (at the front)
2) Posterior longitudinal ligament (at the back)
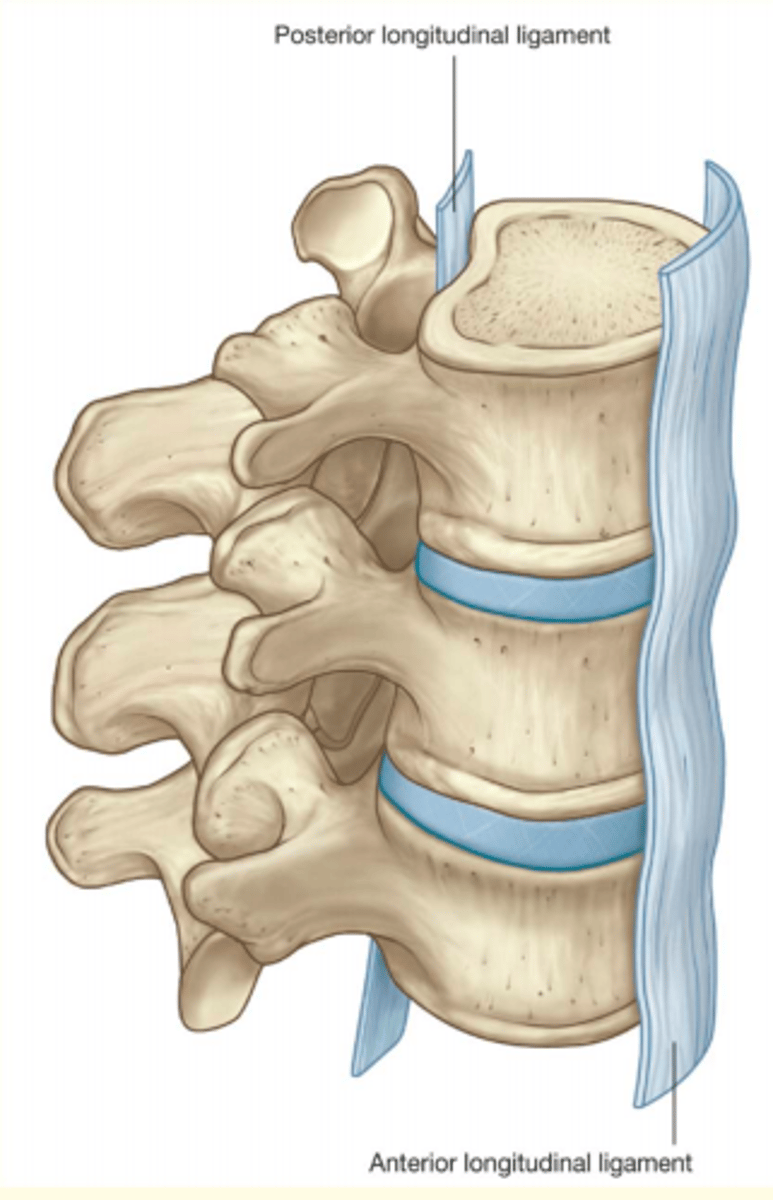
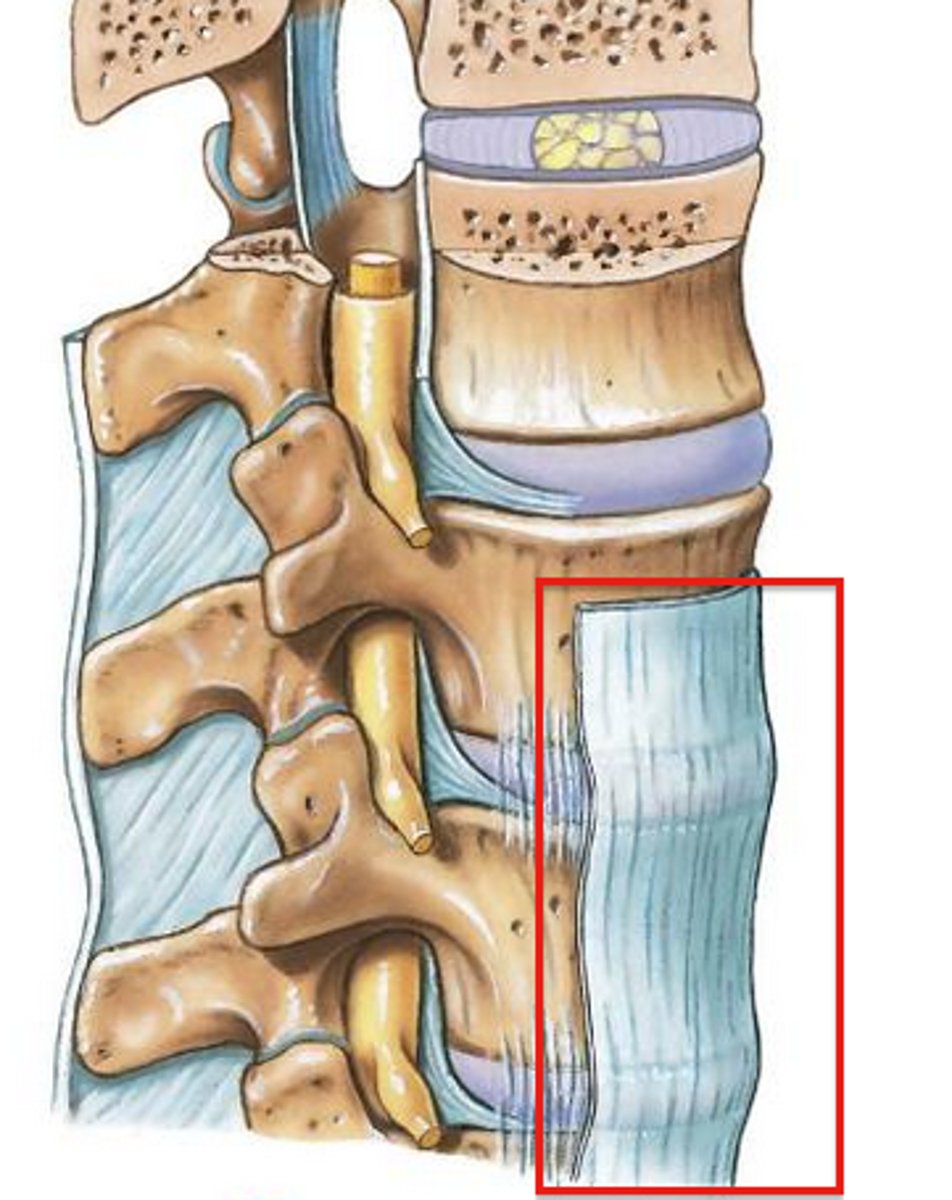
Anterior longitudinal ligament
Stronger
Prevents hyperextension
Posterior longitudinal ligament
Weaker
Prevents hyperflexion
Prevents posterior prolapse of IV disc
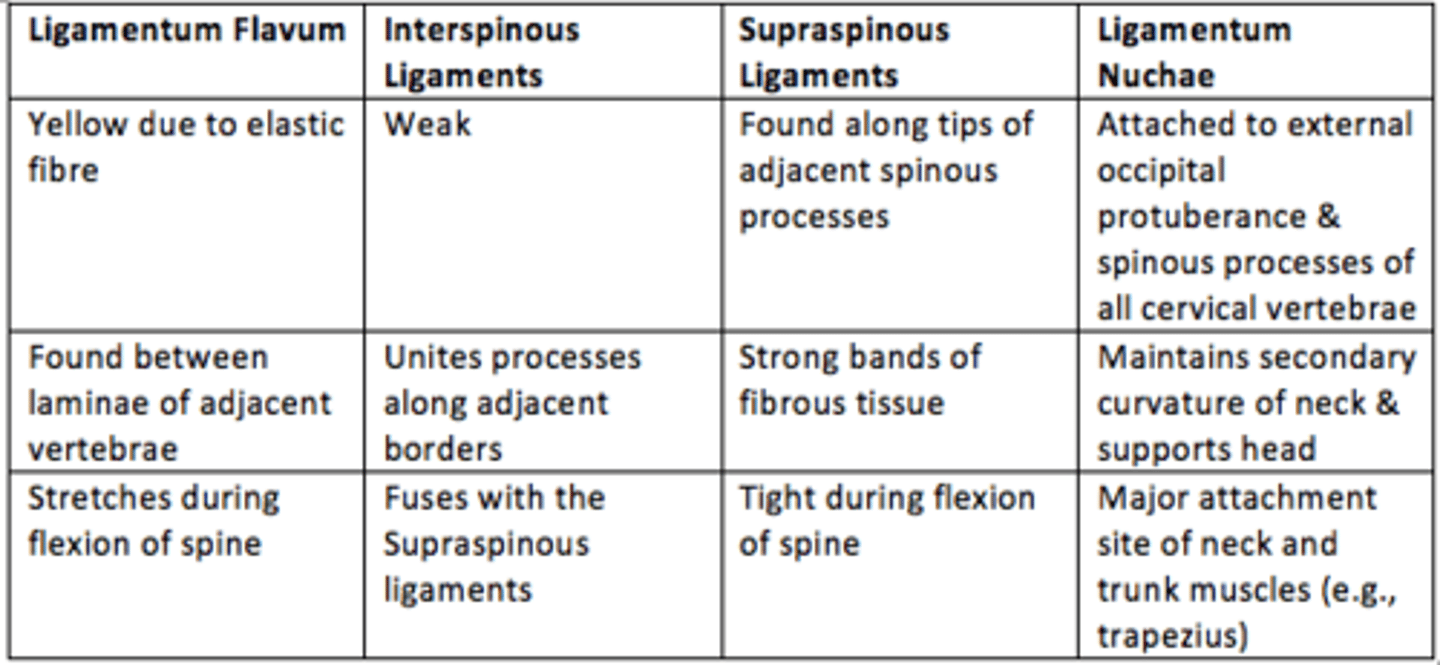
Aside from the two main ligaments of the spinal column - there are an additional four ligaments.
Name these additional four ligaments
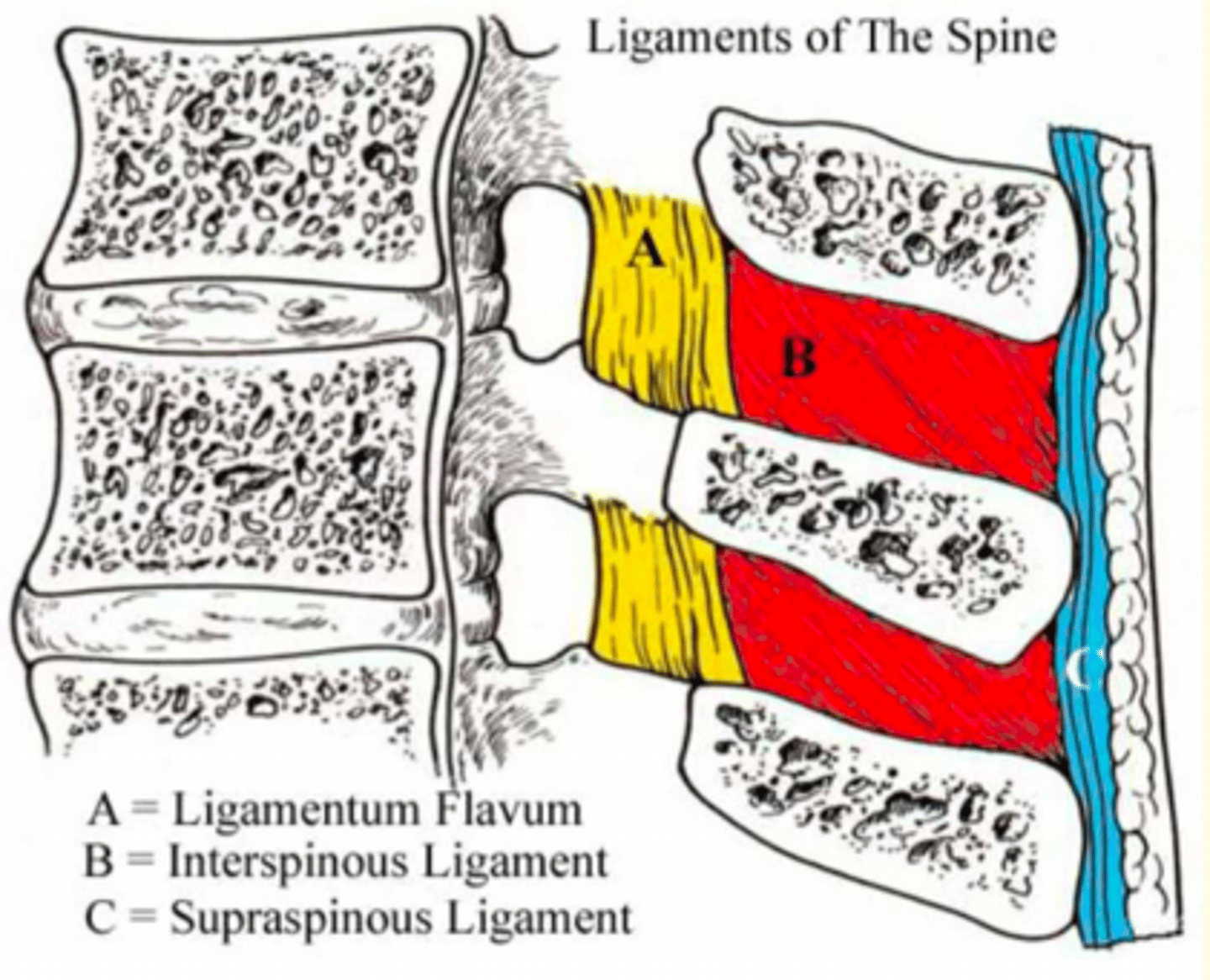
1) Ligamentum Flavum (A)
2) Interspinous Ligaments (B)
3) Supraspinous Ligaments (C)
4) Ligamentum Nuchae
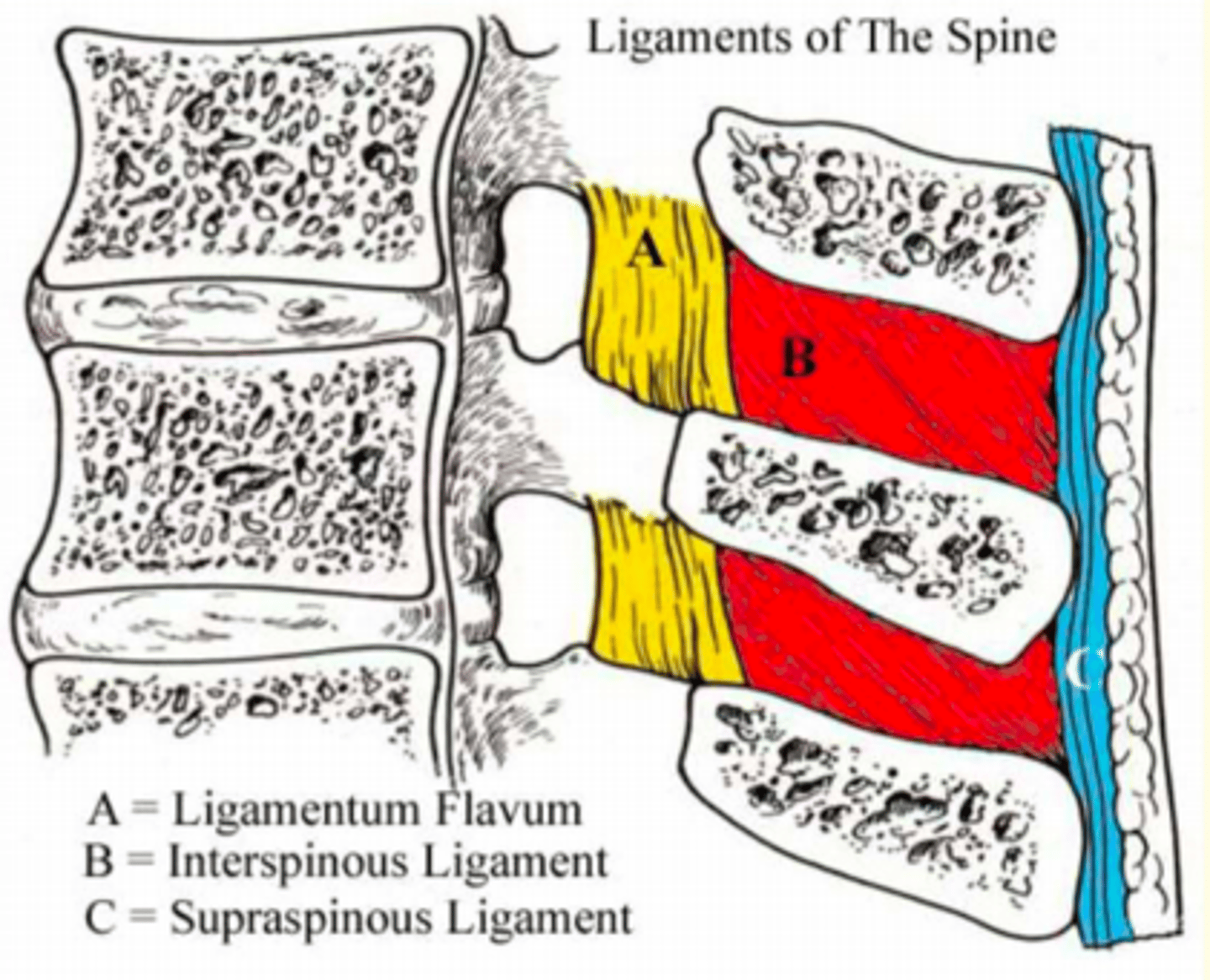
Name the ligament
Yellow in colour due to elastic fibres
Found between laminae of adjacent vertebrae
Stretched during flexion of the spine
Ligamentum Flavum (A)
Name the ligament
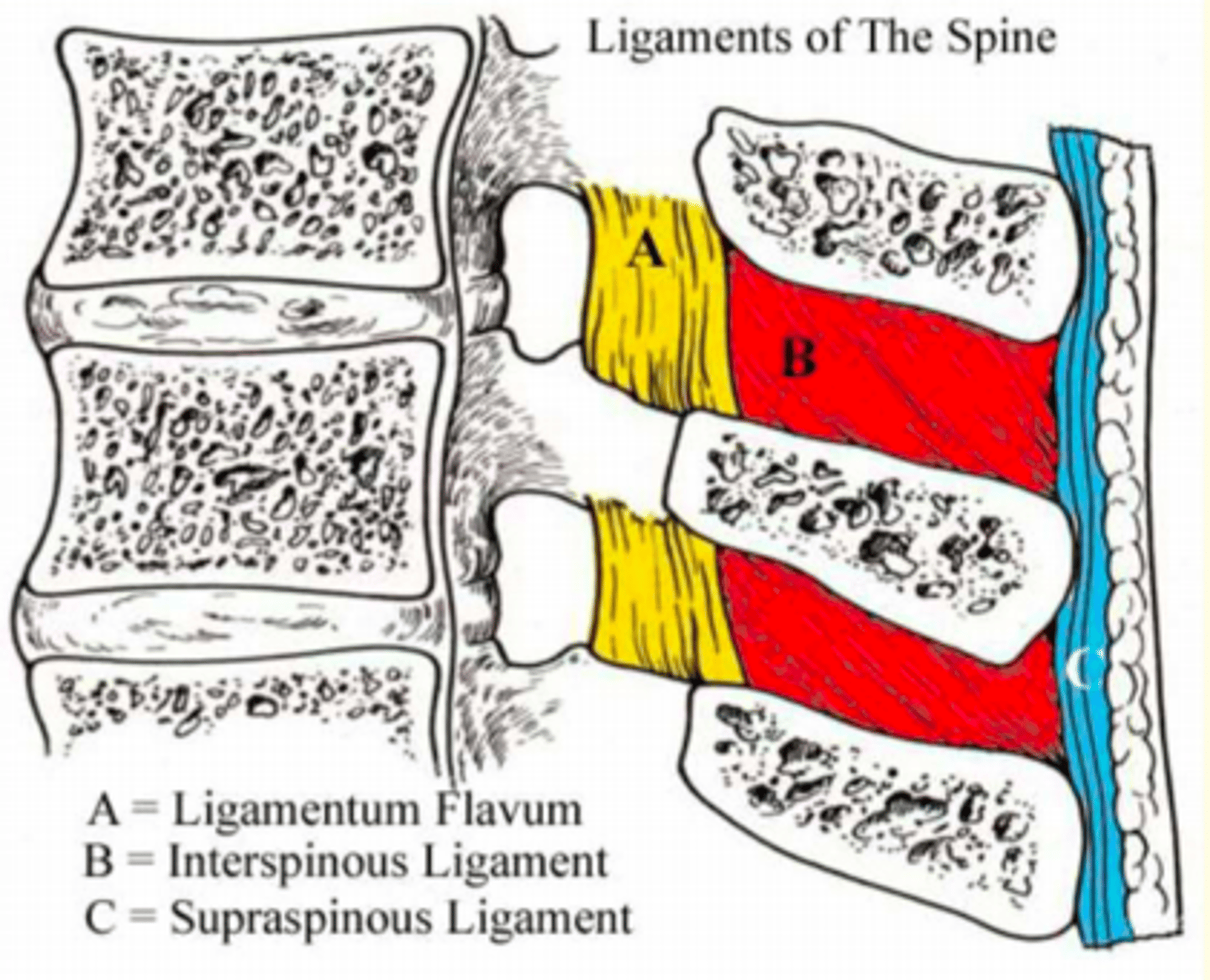
Relatively weak
Unite processes along adjacent borders
Fuses with the Supraspinous ligament
Interspinous Ligaments (B)
Name the ligament
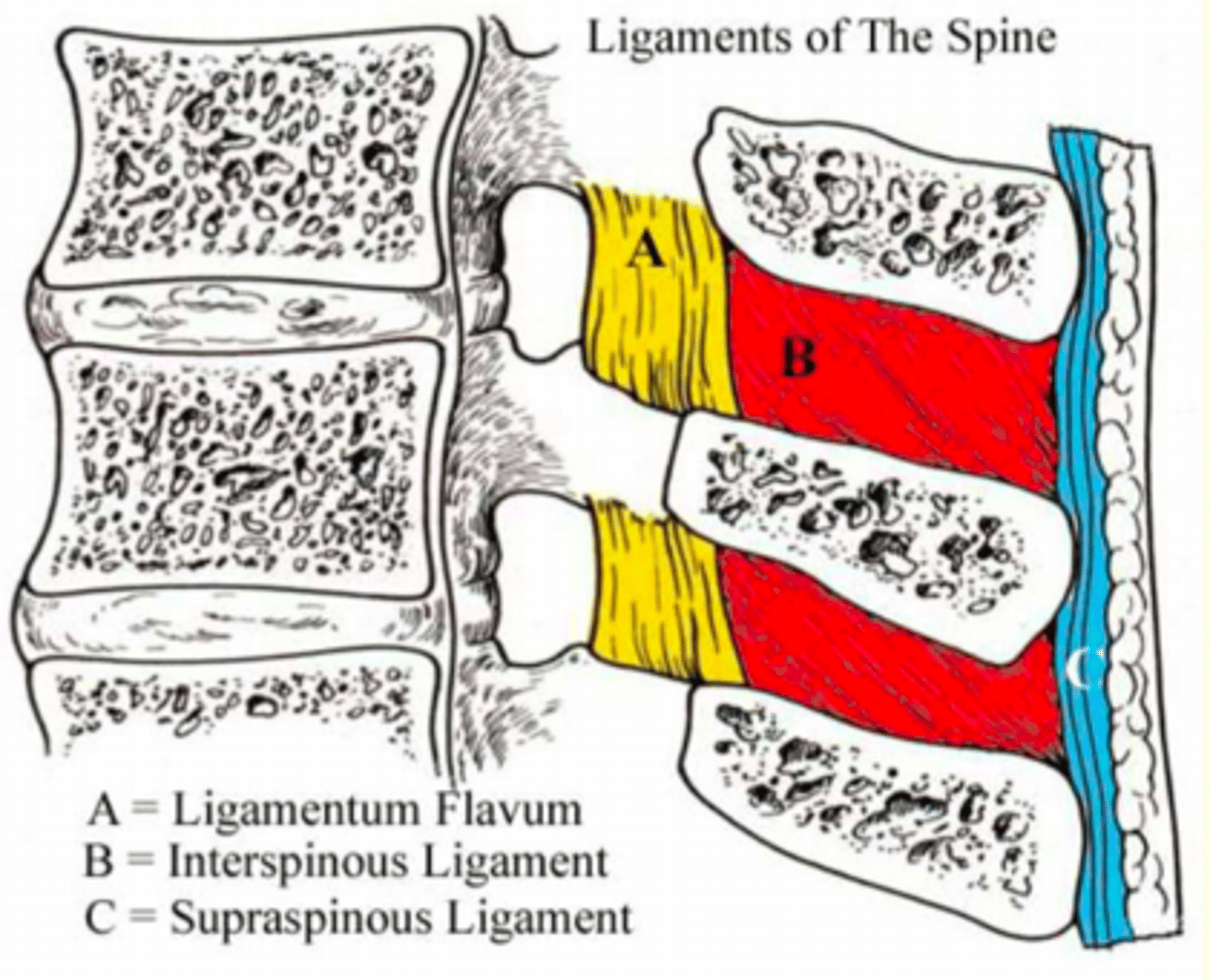
Found along the tips of adjacent spinous processes
Strong bands of fibrous tissue
Tight in flexion
Supraspinous Ligaments (C)
Name the ligament
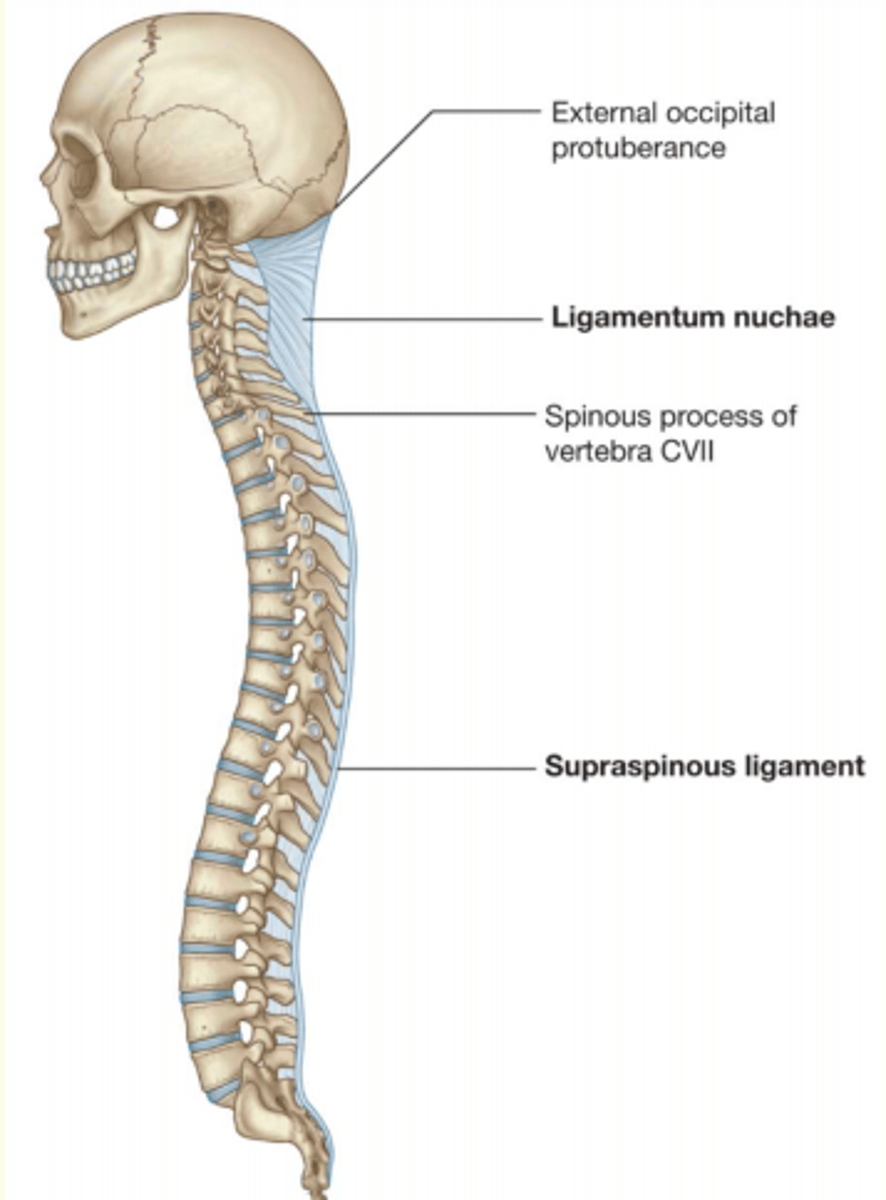
Attached to the external occipital protuberance & spinous processes of all cervical vertebrae
Maintains the secondary curvature of the neck and supports head
Major attachment site of neck & trunk muscles
Ligamentum Nuchae
Summarise the four additional ligaments found in spinal column
Prolapsed intervertebral disc location
Usually occurs at L4/L5 or L5/S1 (or cervical)
Cause of a prolapsed disc
Result of the prolapse of the nucleus pulposus (central part)

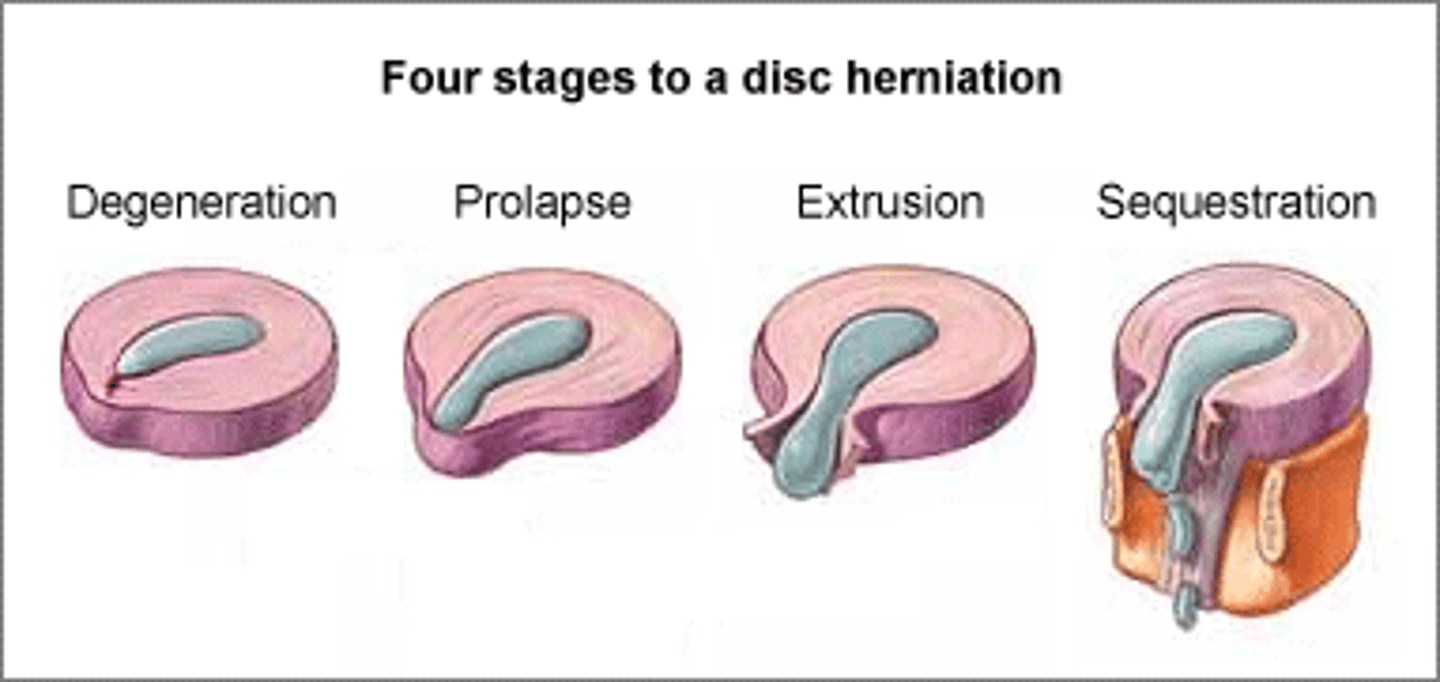
Four stages to disc herniation
1) Degeneration
Chemical change associated with ageing
Causes discs to weaken, but WITHOUT herniation
2) Prolapse
Protrusion of nucleus pulposus
Slight impingement into spinal canal
3) Extrusion
Nucleus pulposus breaks through the annulus fibrosus but remains WITHIN disc space
4) Sequestration
Nucleus pulposus breaks through annulus fibrosus and lies OUTSIDE disc space
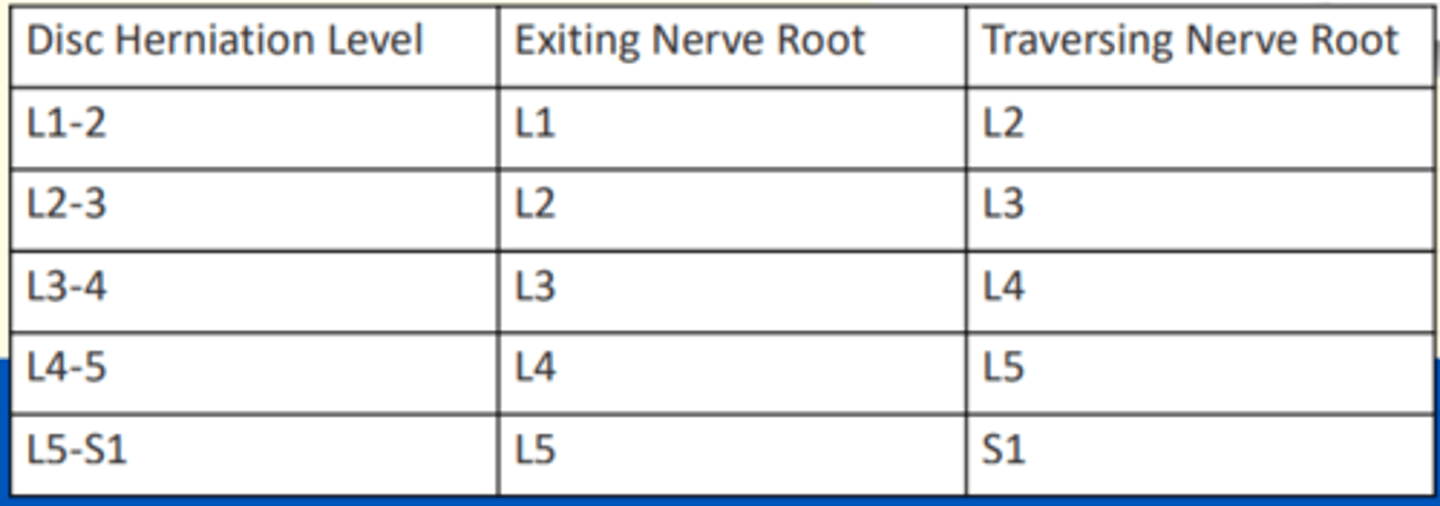
If a disc herniation is in the typical posterolateral position, it will compress the ___ nerve root
If a disc herniation is in the typical posterolateral position, it will compress the traversing nerve root
Exiting nerves = emerge through IV foramina below numbered vertebra
Traversing nerves = crosses over IV disc to exit below its own numbered vertebra (can become compressed in disc herniation)
Cauda Equina Syndrome (neurosurgical emergency) is the result of...
L4/L5 or L5/S1 massive posterior disc herniation
Cauda Equina Syndrome symptoms
- Impaired bladder and/or bowel control
- Loss of sexual sensation/function
- Back pain and referred pain
- 'Saddle' anaesthesia (perineum S2-S4)
This is because Cauda Equina syndrome affects the sacral nerve roots to the perineum, bladder and sphincters

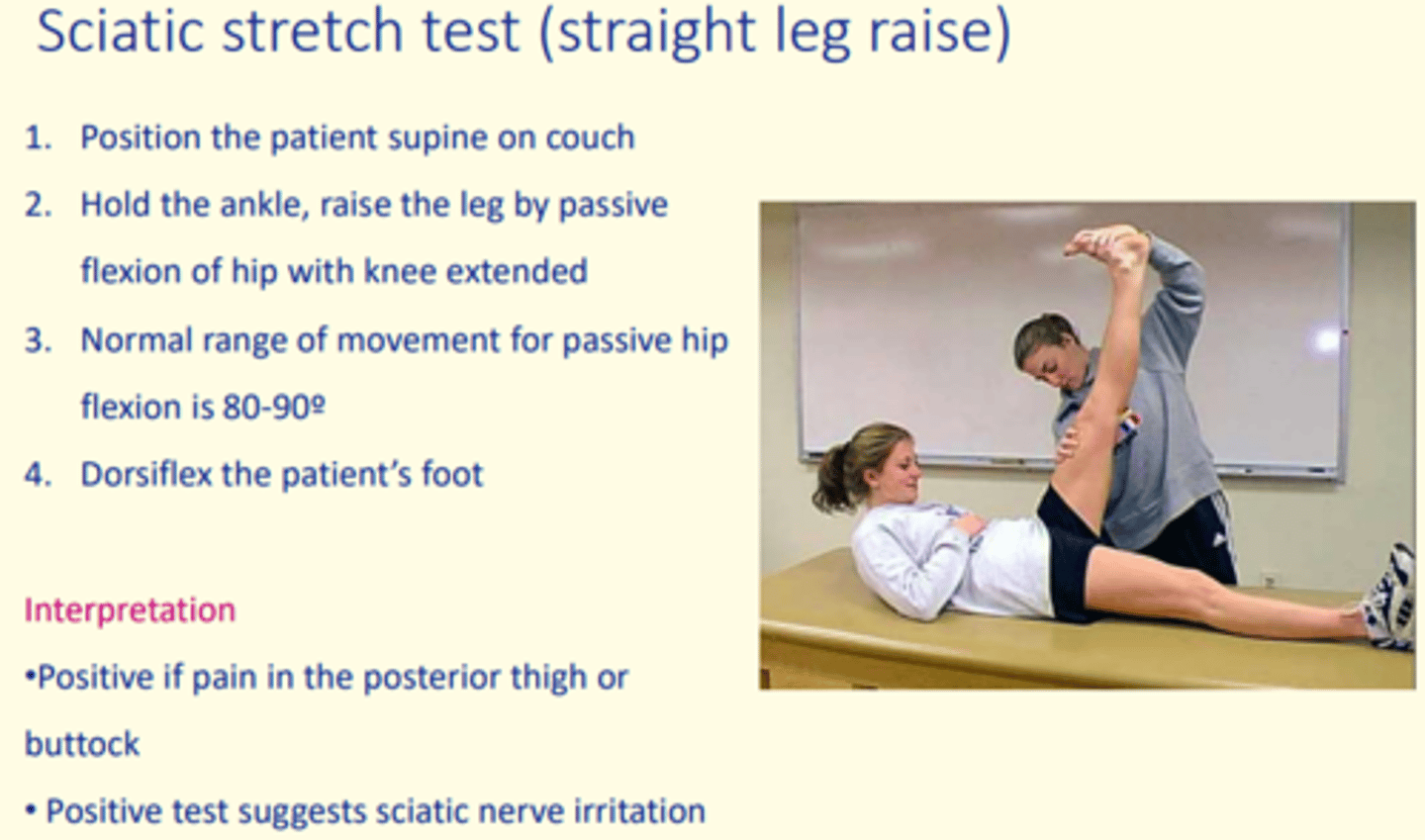
Testing for prolapsed disc
Sciatic stretch test (straight leg rise)
Positive if pain in the posterior thigh or buttock occurs
The nucleus pulposus can dehydrate with ___
The nucleus pulposus can dehydrate with age
This leds to a decrease in the height of IV discs