Grignard Synthesis of Triphenylmethanol
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What are Grignard reagents and why are they important?
Highly reactive organomagnesium compounds that form C–C bonds, enabling the construction of larger carbon structures.
How are Grignard reagents prepared?
By reacting alkyl/aryl halides with metallic magnesium in anhydrous ether.
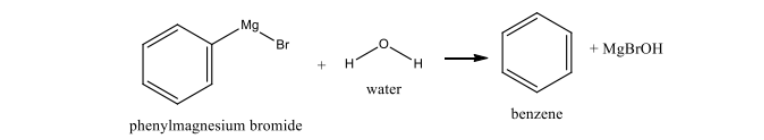
Why must Grignard reactions be dry?
Moisture destroys Grignard reagents, forming benzene and magnesium hydroxide instead.
What was the Grignard reagent we made in lab?
Phenylmagnesium bromide (PhMgBr), from bromobenzene and magnesium in anhydrous ether.
What is the role of anhydrous diethyl ether?
Stabilizes the Grignard reagent by solvating it and protecting it from moisture.
How was the Grignard reaction initiated in lab?
Iodine crystal was added to activate magnesium; bromobenzene/ether was added dropwise with gentle heating.
How is the Grignard reaction controlled once started?
Magnetic stirring, slow addition of reagents, cooling if overheated, maintaining steady reflux.
What type of reaction is Grignard formation?
Autocatalytic and exothermic (self-accelerating and heat-releasing).
What was the main reaction for triphenylmethanol synthesis?
Phenylmagnesium bromide + methyl benzoate → triphenylmethanol after hydrolysis.
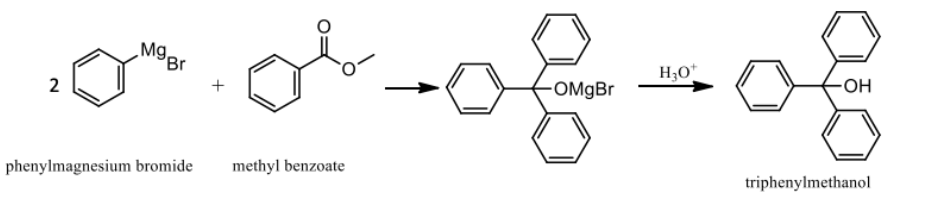
What does sulfuric acid do during the Grignard workup?
Hydrolyzes the magnesium alkoxide to produce the final alcohol (triphenylmethanol).
What is the purpose of a saturated NaCl solution during extraction?
"Salts out" water from the organic layer, aiding in separation.
What is the purpose of anhydrous CaCl₂ pellets?
To dry the organic layer by removing residual water.
Why are hexanes used for recrystallization of triphenylmethanol?
Triphenylmethanol dissolves in hot hexanes but crystallizes out upon cooling; hexanes also dissolve impurities.
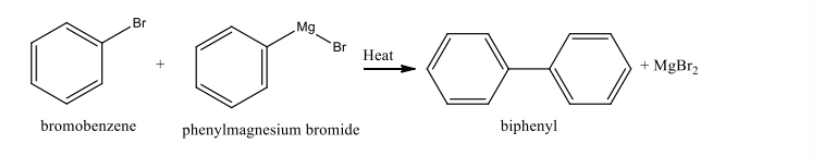
What are common side reactions in Grignard synthesis?
Hydrolysis with water (forms benzene) and biphenyl formation (from Grignard reagent reacting with itself).
Reaction with water
forms the byproduct benzene and MgBrOH
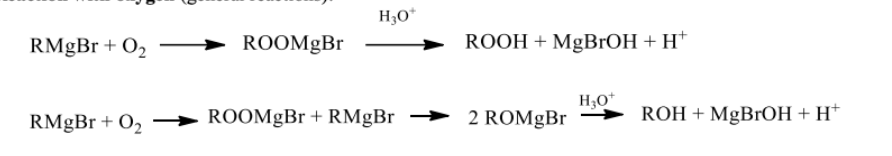
Reaction with Oxygen
can lead to oxidation of the Grignard reagent, producing side products like alkoxides or hydroxides.
Reaction if overheated
can cause decomposition of the Grignard reagent, leading to reduced yields of desired products and potentially forming biphenyl
How do side reactions affect yield and purity?
They lower yield by consuming reagents and reduce purity by introducing contaminants.
Limiting reagent
Methyl benzoate
melting point
160-162°C
Reasons for low % yield in Grignard lab?
Side reactions, incomplete Grignard formation, moisture contamination, losses during transfer/recrystallization.
What happens if moisture is present during Grignard synthesis?
Grignard reagent reacts with water instead of desired reactants, ruining the reaction.
What does the iodine crystal specifically do?
Activates the magnesium surface to help initiate Grignard formation.
What physical signs showed Grignard reaction started?
Color change, bubbling at magnesium surface, warming of mixture.
How is the Product Purified?
Extract organic layer with ether.
Wash with saturated NaCl solution to remove water.
Dry with anhydrous CaCl₂ pellets.
Recrystallize from hexane
Why Are Hexanes Chosen for Recrystallization?
Triphenylmethanol dissolves in hot hexanes but crystallizes on cooling.
Hexanes dissolve impurities better than the product.
Hexanes have a low boiling point, easy to evaporate off.
Why is it important to add bromobenzene slowly to magnesium?
To control the exothermic reaction and prevent violent boiling or overheating.
What structural feature of ethers makes them good solvents for Grignard reactions?
Lone pairs on oxygen atoms stabilize the Grignard reagent by coordination.