CHEM 43A Midterm 1
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
CAS number
Chemical Abstract Service Number. No chemical significance; no information about structure or properties. Sequentially assigned
GHS
Globally Harmonized System
First digit is either 2, 3, or 4
2 = physical hazard, 3 = health hazard, 4 = environmental hazard
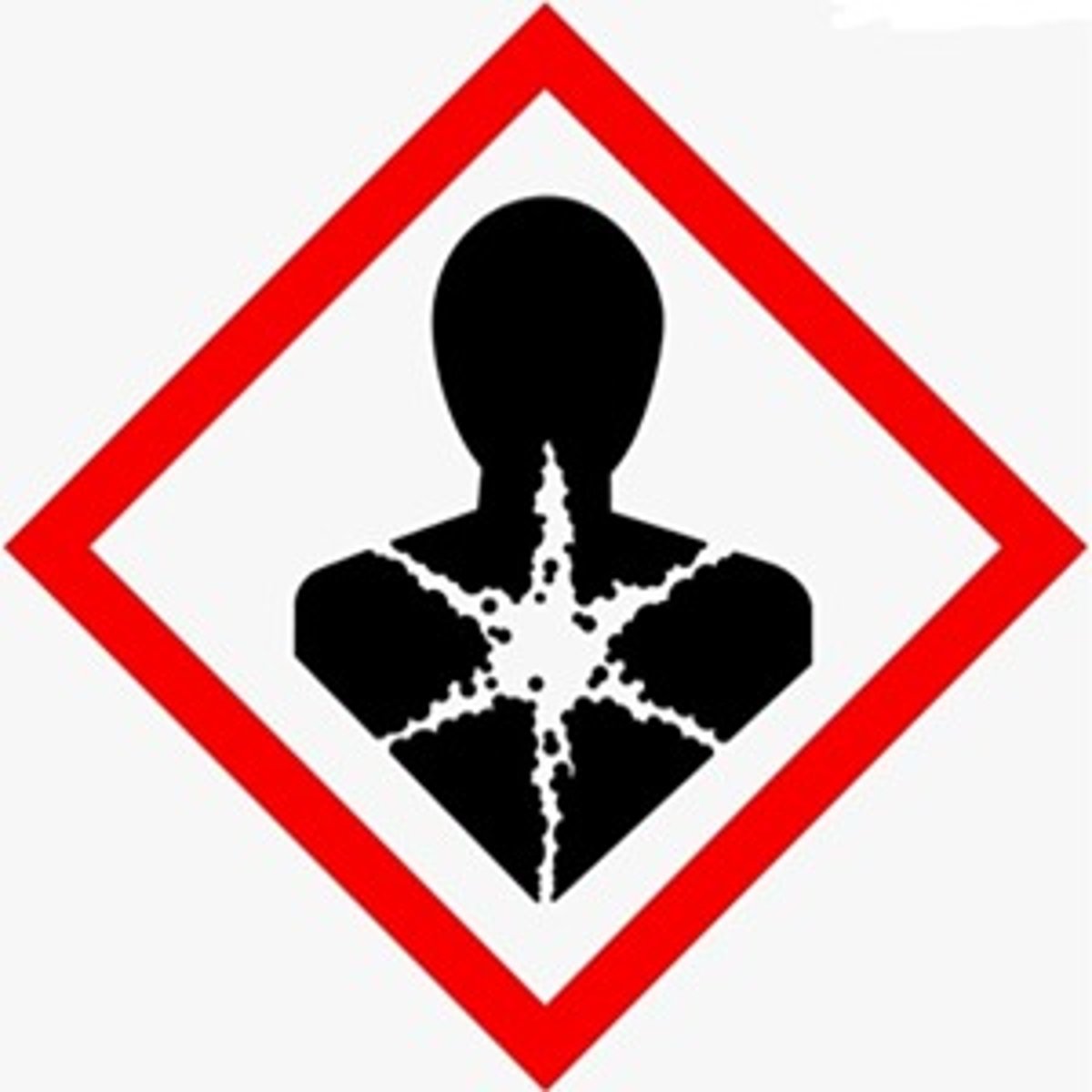
Health Hazard
carcinogen, mutagenicity, reproductive toxicity, respiratory sensitizer, target organ toxicity, aspiration toxicity

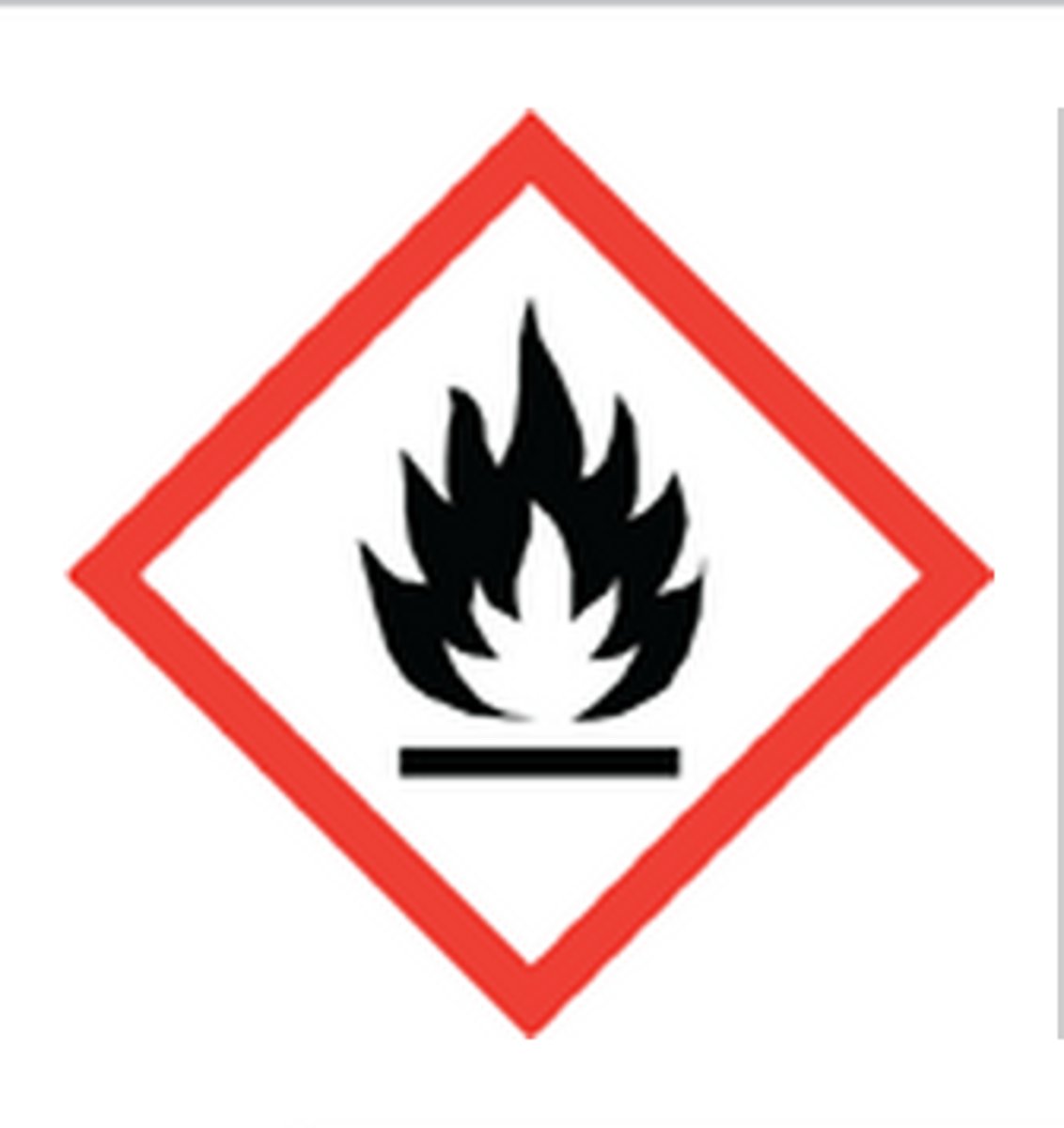
Flame
flammables, pyrophorics, self-heating, emits flammable gas, self-reactives, organic peroxides

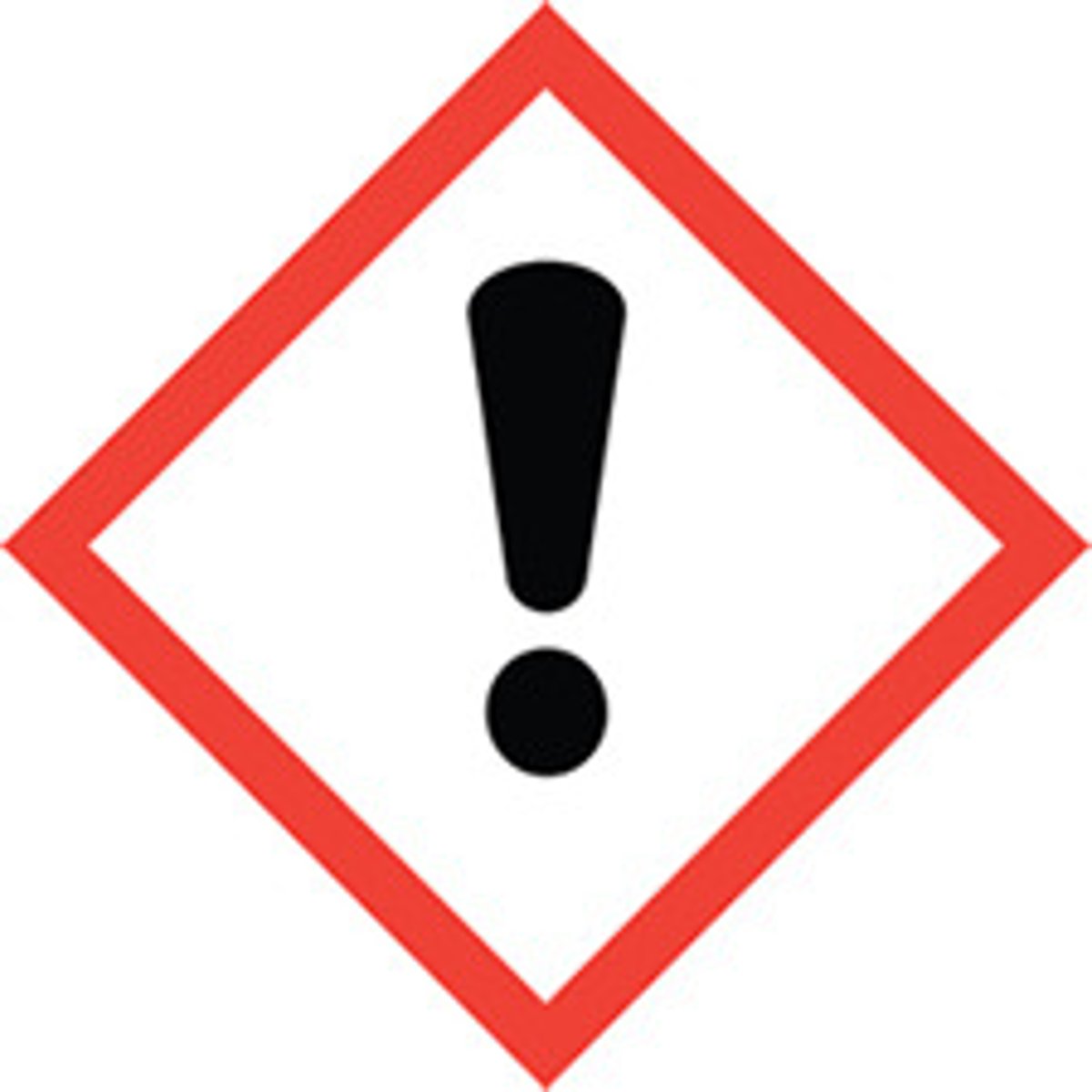
Exclamation mark
irritant (skin and eye), skin sensitizer, acute toxicty, narcotic effects, respiratory tract irritant, hazardous to ozone layer (non-mandatory)

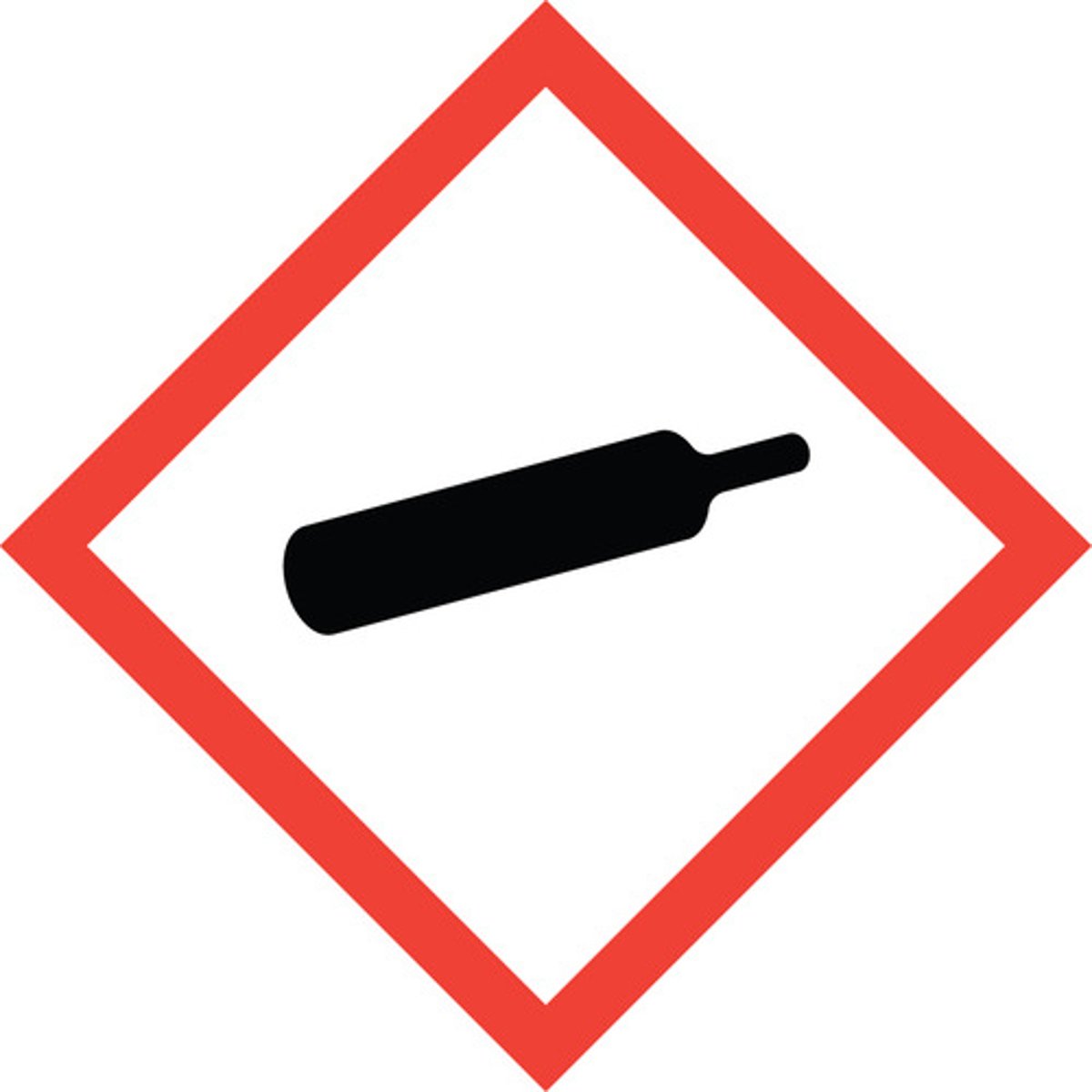
Gas cylinder
gases under pressure

Corrison
skin corrosion/burns, eye damage, corrosive to metals
Exploding bomb
explosives, self-reactives, organic peroxides

Flame over circle
oxidizers

Environmental
Aquatic toxicity

Skull and Crossbones
acute toxicity (fatal or toxic)

Required Lab Clothing
1. chemical splash goggles - not glasses
2. mask covering nose and mouth
3. long hair restrained
4. knee-length, long sleeve lab coat
5. long pants (or equivalent)
6. closed shoes (no exposed skin) - socks must cover ankles
Sig Fig guidelines
Balances and masses - report to the third decimal
Graduated cylinders/pipettes and volumes - report to the tenth of millimeters (1.2 mL)
Thermometers and Temps - mel-temps: report to tenth of a degree; glass thermometers: report to nearest degree
Reaction yields - round to whole percentage
Rf values - report to 2 decimal places
IR wavenumbers - report to whole numbers
Addition and Subtraction - keep the same number of decimals
Multiplication and Division - have the least amount of sig figs in number used
An unknown compound melting at 134 degrees C was suspected to be either aspirin (melting point = 135C) or urea (melting point = 133C). How could you determine whether one of these two suspected compounds was identical to the unknown compound without using any form of spectroscopy?
Using the mixed melting point procedure
Explain this procedure
Pure substances melt over a narrow temperature range. Mixtures melt at a lower temperatures than the pure compounds and over a broader temperature range. If the mixture of the unknown with aspirin shows no depression or expansion of melting point then the unknown is aspirin. If the mixture of the unknown with urea shows no depression or expansion of melting point then the unknown is urea.
SAFETY: When using a melting point apparatus, take care not to burn yourself as the apparatus will get very:
hot
How fast should you heat the melting point sample?
Heat quickly until you get close to the expected temperature
What is the effect of impurities in the sample?
The melting point will be depressed
When adding 7.1 and 6, the result on the calculator is 13.1. Round the answer to the appropriate precision based on the precision of the numbers in the sum.
13
A student is required to perform a recrystallization on an impure sample of biphenyl. The sample weighs 0.5 g, and contains about 5% impurity. Based on their knowledge of solubility, they decide to use benzene as the solvent. Identify the steps that the student must perform, and place them in the correct order.
Step 1: Heat the portion of the benzene solvent
Step 2: Add the minimum amount of hot benzene to dissolve the sample
Step 3: Cool solution, first to room temp, then in an ice-bath water
Step 4: Isolate the biphenyl crystals by vacuum filtration
A student is required to perform a recrystallization on an impure sample of biphenyl. The sample weighs 0.5 g, and contains about 5% impurity. Based on their knowledge of solubility, they decide to use benzene as the solvent. After recrystallization, the final weight of biphenyl is found to be 0.02g. Assume that all steps were carried out correctly, no spillages occurred, and the student lost minimal solid on the glassware or in transfers. Why is the recovery so low?
Biphenyl is highly soluble in both hot and cold benzene
Solvents for recrystallization must be carefully selected so that the compound being purified is soluble in the hot solvent but insoluble in the cold solvent
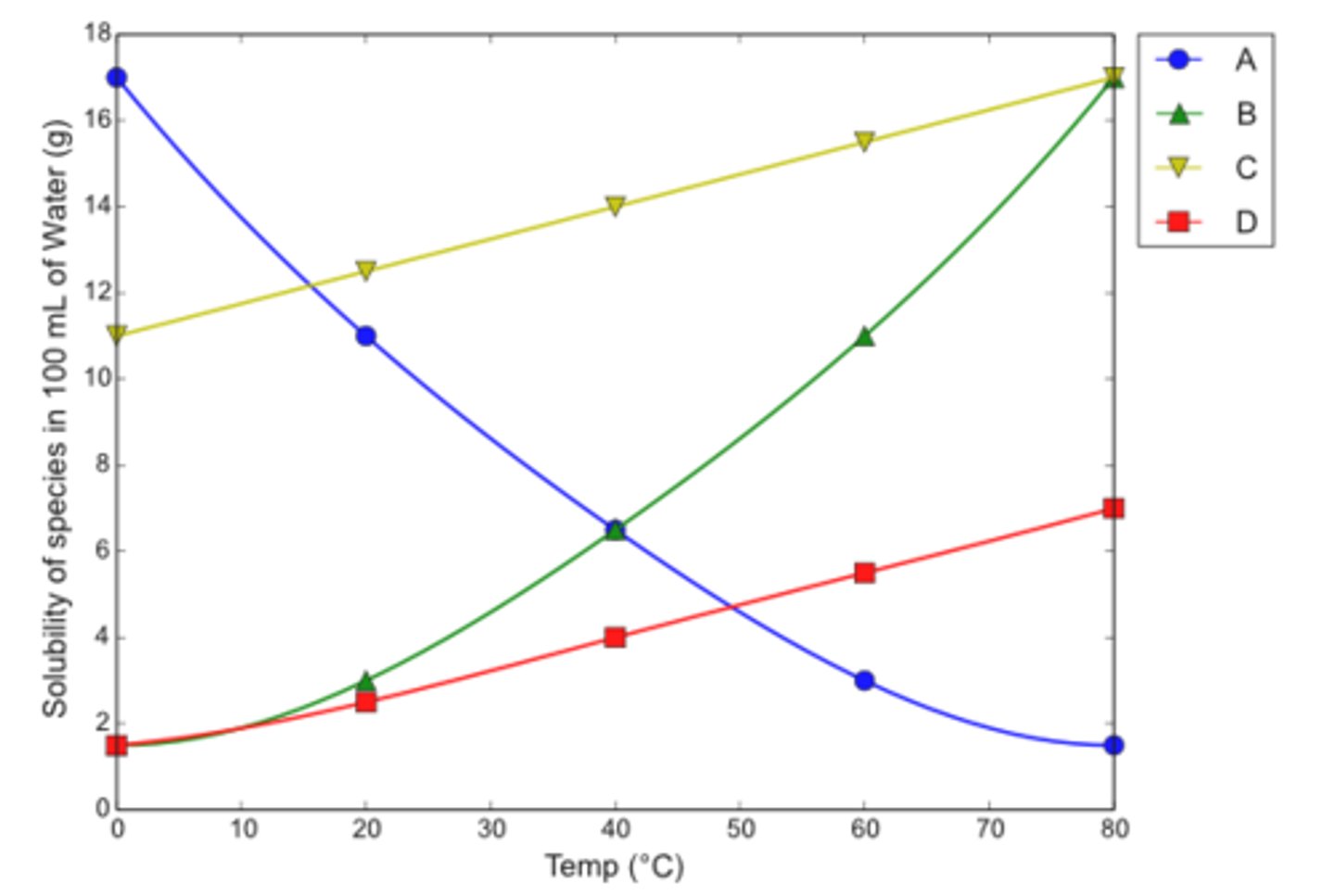
Water was found to be a good solvent for the recrystallization of organic solvent X
a. Which line correctly shows the solubility vs. temperature profile for this substance?
b. Suppose 0.1 g of X and 1.0 mL of water were mixed and heated to 80 C. Would all of substance X dissolve?
c. The solution in (b) is cooled. At what temperature will crystals of X appear?
d. Suppose the cooling described in (c) were continued to 0 C. How many grams of X would come out of solution?
a. B (water is a good solvent choice for the recrystallization of X because X has a low solubility in water at low temperatures, but a high solubility in water at high temperatures)
b. yes (solubility of 17.0 g in 100 mL of water is equivalent to a solubility of 0.17 g in 1 mL of water)
c. 56 C (crystals will start to form when the solubility is reduced to 0.1 g/mL - equivalent to 10 g/100 mL on the graph)
d. 0.085 g
Which of the following statements is true when considering temperature during a recrystallization?
Ideally the hot solvent used will keep the impurities dissolved OR not dissolved them at all
It is important that the sample is dissolved in just enough hot solvent
What is the result of boiling the impure product with too much solvent and then cooling on ice?
No crystals are produced
When too much boiling solvent is used, both the product and the impurities remain in solution. On cooling, the solution will be too dilute to reach saturation, and no crystals will form
Gravity and Vacuum filtration tools
gravity: fluted filter (volumes more than 10 mL), pasteur filter pipets (volumes less than 10 mL)
vacuum: Buchner funnel (volume greater than 10 mL), hirsch funnel (volume less than 10 mL)
Which of the following would be expected to be the most soluble in water?
Ethyl methyl ketone
Like things tend to dissolve like things: non-polar solutes dissolve best in non-polar solvents, and same with polar
Since water is a polar solvent that is capable of hydrogen bonding, it will be a better solvent for polar solutes. Since ethyl methyl ketone has an oxygen bond, that makes it more likely to make hydrogen bonds.
SAFETY: When using a hot plate or other heating device, you need to be aware of hot surfaces that could cause burns: a hot surface will always glow red to let you know it is hot
False
SAFETY: When performing a filtration under vacuum, always make sure that:
the collection flask is securely clamped
SAFETY: When heating a flammable or volatile solvent for a recrystallization, which of these statements are correct?
You should ensure that no one else is using an open flame near your experiment
You should not use an open flame to heat the solvent
In a solvent extraction using a separatory funnel, the densities of the two liquids determine whether the organic solvent is the top layer or the bottom layer. Using the table of densities, determine whether diethyl ether is the top layer or the bottom layer when used with water.
Top layer
The solvent with the greater density is the bottom layer, solvents with the lighter density is the top layer
SAFETY: What is the purpose of venting the separatory funnel?
To relieve built up pressure from gases produced, or solvent vapor formed
When venting a separatory funnel, which of the following statements is correct?
Vent the separatory funnel in a fume hood with the nozzle pointing upwards
When adding drying agent, how do you know when you have added enough?
The powder no longer forms clumps
Solvents: Which of the following are hazards associated with methylene chloride (CH2Cl2)?
Harmful vapor
Causes skin irritation
Suspected carcinogen
When using an extra tube to balance the centrifuge, this should contain either another sample or:
an equal volume of water
Sublimation can be used to purify your product if:
your solid product has a relatively high vapor pressure but the impurities have a low vapor pressure
A substance has one triple point (10C, 650 mmHg). Its melting point and boiling point are 45C and 210C, respectively, at the atmospheric pressure (760 mmHg). Which of the following statements must be true for this substance?
When heated from 0C to 100C at atmospheric pressure (760 mmHg), the substance changes phase from solid to liquid
Which of the following methods would you expect to be most efficient for removing caffeine from coffee beans, while keeping the coffee flavor in the beans? Assume that the flavor comes from high molecular weight water-soluble compounds.
Process the coffee beans with steam to soften them, so liquid can more easily reach inside the beans; extract the moist beans with methylene chloride, then dry the beans
Which of the following would be expected to form hydrogen bonds with water?
Propanal, butanoic acid, and N-methylacetamide
Compounds need an oxygen or nitrogen in order to make hydrogen bonds with water
For each of the following pairs of solutes and solvent, predict whether the solute would be soluble or insoluble.
a. malic acid in water
b. naphthalene in water
c. amphetamine in ethyl alcohol
d. aspirin in water
e. succinic acid in hexane
f. ibuprofen in diethyl ether
g. 1-decanol in water
a. soluble in water
b. insoluble in water
c. soluble in alcohol
d. insoluble in water
e. insoluble in hexane
f. soluble in diethyl ether
g. insoluble in water
Predict whether the following pairs of liquids would be miscible or immiscible
Miscible: water and methyl alcohol, ethyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol, hexane and benzene, and methylene chloride and benzene
Immiscible: water and toluene
Saturated aqueous sodium chloride (d = 1.2 g/mL) is added to the following mixtures in order to dry the organic layer. Which layer is likely to be on the bottom in each case?
a. Sodium chloride layer or a layer containing a high-density organic compound dissolved in methylene chloride (d = 1.4 g/mL)?
b. Sodium chloride layer or a layer containing a low-density organic compound dissolved in methylene chloride (d = 1.1. g/mL)?
a. high-density organic compound dissolved in methylene chloride
b. sodium chloride
Higher density goes to the bottom
Correlate the procedures needed to accomplish the given step (1-6) to separate a mixture containing the following compounds. Benzophenone, benzoic acid, and tributylamine
1. All three compounds are in the organic solution - E. Dissolve the mixture in diethyl ether
2. The salt (C6H5)COONa partitions to the aqueous layer and can be removed - B. Add aqueous NaOH
3. The salt (C4H9)3NHCl partitions to the aqueous layer and can be removed - I. Add aqueous HCl
4. The majority of the water in the diethyl ether moves into the aqueous layer and can be separated - A. Add saturated aqueous NaCl solution
5. The small amount of water remaining in the diethyl ether is taken up by the solid and can be filtered off - G. Dry organic layer over anhydrous sodium sulfate
6. Benzophenone is obtained - D. Evaporate off the diethyl ether
When using a separatory funnel, which layer should be discarded?
It depends on the conditions
the organic layer may be on the top or bottom depending on the densities of the compounds used
SAFETY: The separatory funnel should only be vented once at the start of the procedure when all the reagents have been added.
False