7. Organic Chemistry
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
What are Alkanes?
Saturated Hydrocarbons
General formula CnH2n+2
What do hydrocarbons contain?
Only carbon and Hydrogen
What does saturated mean?
Contains only single bonds
What are the first four alkanes?
Methane, Ethane, Propane, Butane (Monkeys Eat Peanut Butter)
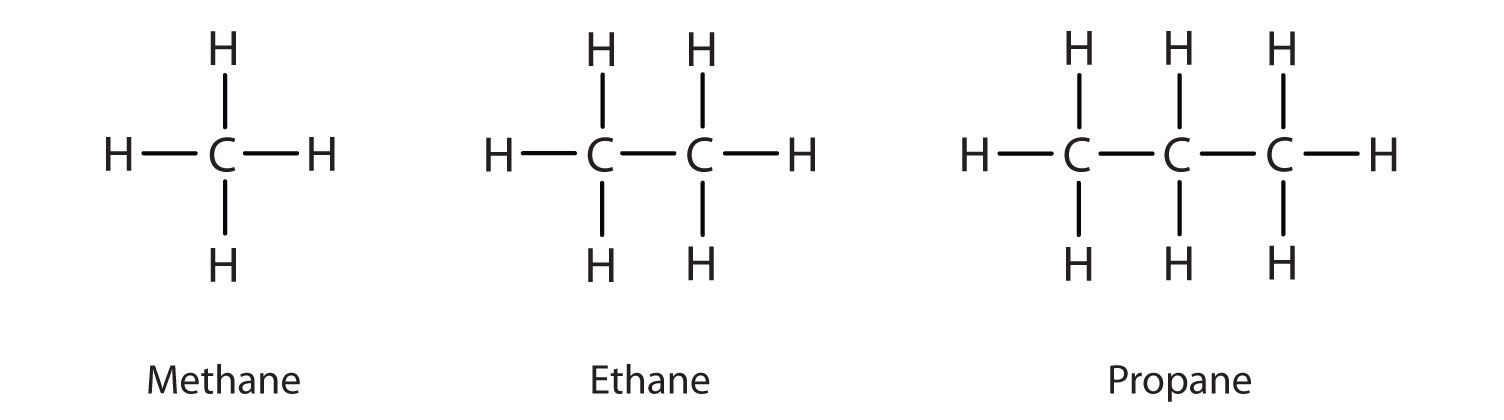
How can alkane molecules be represented?
Molecular Formula e.g Methane CH4
Displayed (structural) formula (picture)
Uses of fractions and trends
Small molecules - Low bpt, very volatile, low viscocity, flammable
Large molecules - high bpt, not very volatile, high viscocity, ignites poorly
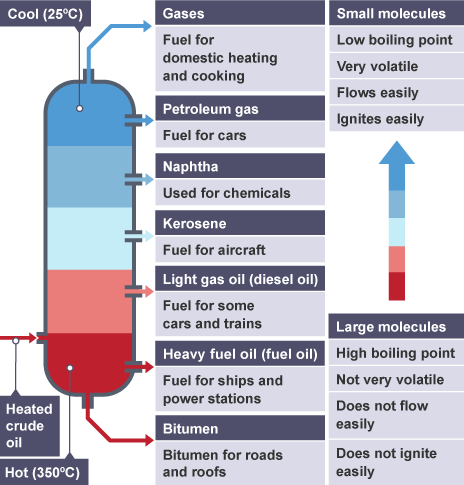
Use of gas (LPG)
Fuel for domestic heating and cooking
Use for petrol
Fuel for cars
Use for kerosene
Fuel for aircraft
Use for diesel
Fuel for some cars and trains
Use for fuel oil
Fuel for ships and power stations
Use for bitumen
Material for roads and roofs
What is a homologous series?
Same:
General formula
Functional groups
Similar Chem. properties
What is crude oil?
Mixture of compounds; fossil fuel consisting of the remains of ancient biomass
Finite resource
What does incomplete/complete combustion of Hydrocarbons produce?
Complete combustion produces CO2 + H2O (carbon and hydrogen atoms are completely oxidised)
Incomplete combustion produces C or CO + H2O
Is combustion of hydrocarbons endo or exo
Exothermic and occurs when hydrocarbons are reacted with oxygen
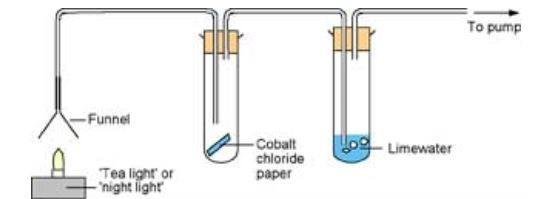
How can we detect the products of complete combustion of hydrocarbon fuels/ alkanes?
Using this apparatus
Limewater turns cloudy - CO2 produced
Anydrous copper sulphate turns from white to blue & Cobalt chloride paper turns from blue to pink - H2O produced by fuel burning
Physical properties of alkanes - states
-First few = gases, then liquids, then solids
Physical properties of alkanes - BPTs and Vicsocity
increase as molecules get bigger
Physical properties of alkanes - tendency to change
Decreases as molecules get bigger
Physical properties of alkanes - reactivity
Poor reactivity
Fractional distillation of crude oil
-Heat the crude oil to vaporise most of the hydrocarbons
-Vapours rise up the column
-Column is cooler at the top
-Most vapours cool and condense at different heights due to different bpts
-V. Low boiling fractions removed as gases
-V. High boiling fractions removed as gases
What is cracking?
When large hydrocarbons are thermally broken down into smaller and useful molecules
Breaking down long alkane molecules into smaller alkanes and also alkenes
What type of reaction is cracking?
Thermal decomposition (evidence: one reactant forms two or more products)
What are the conditions for cracking?
Reactant heated to vapor
Passed over a hot catalyst (catalytic cracking) or heated to vapour, mixed with steam and heated to high temperatures (steam cracking)
How are the products of cracking used?
Products = Alkanes and Alkenes
Used as polymers
used as starting materials for synthesis
some products are useful as fuels since they have shorter chains than alkanes you started with = more flammable = better fuel
What is an alkene?
Unsaturated hydrocarbon
Contains a C=C bond
General formula = CnH2n
What is the test for alkenes?
Add bromine water
Colour change occurs from orange to colourless
Describe combustion of alkenes
burn with smoky flames due to incomplete combustion
Why does crude oil have limited uses?
It is a mixture of many different alkane hydrocarbons
Contains so many substances
How is crude oil formed?
Plankton buried and compressed in mud
Over millions of years
Under high temp and pressure
How do we make crude oil more useful?
It is separated into fractions (groups of hydrocarbon molecules of similar size and bpts)
Each fraction has a range of bpts because they contain a range of molecules
Seperated by fractional distillation
Why do bpts increase?
Molecules are larger
More energy needed to break
Stronger intermolecular forces
Why are fractions with smaller molecules (petrol, kerosene) good fuels?
All very flammable
Liquid flows easily
Why are fractions with big molecules (bitumen) bad fuels?
Very viscous (don’t flow well)
Not flammable
How is CO2 produced when burning fuels and what are it’s effects?
Complete combustion
Global Warming
How is CO produced when burning fuels and what are it’s effects?
Incomplete Combustion
Toxic / Killer - Stops red blood cells transporting oxygen
How is C produced when burning fuels and what are it’s effects?
Incomplete combustion
Global Dimming, Asthma/Lungs, Global Cooling
How is SO2 produced when burning fuels and what are it’s effects?
S impurities burn in oxygen
Acid Rain
How is NOx produced when burning fuels and what are it’s effects?
N2 + O2 increase in temp
Acid Rain
Conditions needed for industrial cat. cracking
High temp (to give molecules activation energy)
Catalyst (speeds up reaction without being used up)
Absence of air (prevent hydrocarbons burning in O2)
How to carry out industrial cat. cracking
Heat the alkane to vaporise it
And pass vapours over a hot catalyst (aluminium oxide)
Conditions for industrial steam cracking
High temp
Steam
Absence of air
How to carry out industrial steam cracking
Heat the alkane to vaporise it
And mix vapours with steam
Why is cracking done?
-meet demand for good fuels
-make polymers and plastics from alkenes
Cracking Equations
-Same no. of carbons and hydrogens on each side (same as any eqtn.)
-Bigger molecule to 2 smaller molecules
How + why are the products of cracking seperated?
seperated by fractional distillation because they have different bpts
Advantages of cracking
Provides fuels: to meet high demand
Makes alkenes: used to make polymers
Disadvantages of cracking
Uses fossil fuels to provide energy for cracking: they are non-renewable
Burning fuels: CO2 emissions global warming, SO2 + NOx emissions acid rain
Chemicals for cracking come from crude oil: non-renewable
Products of cracking require f.d which uses non-renewable fossil fuels
What are alkenes?
Unsaturated hydrocarbons (contains a double bond)
What is the general formula for alkenes?
CnH2n
Why is there no ‘methene’?
2 carbons are needed to make a double bond
‘meth’ means 1 C
Why are alkenes more reactive than alkanes?
They have a double bond which breaks open
What is alkenes functional group?
C=C
What is hydrogenation?
When alkenes react with hydrogen to form alkanes
Double bond breaks
What is halogenation?
When alkenes react with halogens to form alkanes
Double bond breaks
How do alkenes form alcohols?
React with steam (H2O)
Why are alkene reactions addition reactions?
Double bond breaks
Other atoms add on
What are polymers?
Very long molecules formed by combining many small molecules
What are addition polymers?
Formed from many alkene molecules (or alkene ‘type’ molecules)
What does ethene form when it’s an addition polymer?
Polyethene:
C=C breaks
Many molecules combine
To form a very long chain
What is needed in a repeat unit?
Bracket
^That cuts through lines
‘n’ to show repeating
What are polymers and plastics made from?
Alkenes
First four alkenes
ethene, propene, butene, pentene
How do alkenes react with oxygen?
In the same way as other hydrocarbons: in combustion reactions
However, they tend to burn in air with smoky flames because of incomplete combustion (carbon or carbon monoxide formed (CO))
Alkenes reaction with hydrogen, water and the halogens
Reaction by the addition of atoms across the carbon-carbon double bond so that double bond becomes single carbon-carbon bond
What happens in every alkene reaction with hydrogen, water and halogens?
every reaction works the same for all alkenes
C=C bond breaks to form C-C bond
Compound added splits into two groups and two groups added to 2 carbons in the C=C bond (each group added to either carbon)
e.g H2 Splits into 2 H’s, H2O splits into a H and an OH, Br2 splits into 2 Brs
Alcohol’s functional group
-OH
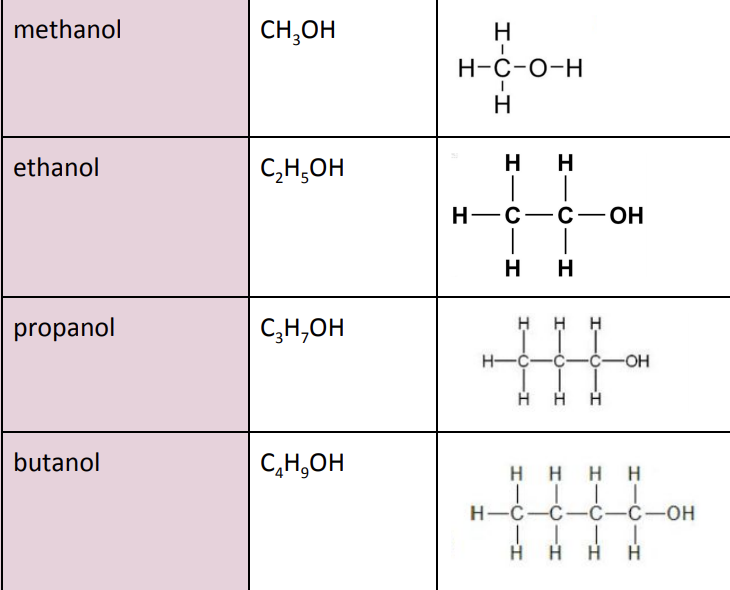
What are the first 4 members of the alcohol series?
Methanol (CH3OH)
Ethanol (C2H5OH)
Propanol (C3H7OH)
Butanol (C4H9OH)
Reactions of methanol, ethanol, propanol and butanol (alcohols)
-Burn in air: produces CO2 and H2O
-Dissolve in water: forms neutral solution (PH = 7)
-React with sodium to produce hydrogen and a salt (e.g C2H5ONa - H given off, Na added)
-React with oxidising agents to form carboxylic acids
Uses of methanol
Chemical feedstock, in anti freeze, to make biodiesel
Uses of ethanol
Main alcohol in alcoholic drinks, used as solvent and fuel
Uses of all 4 (methanol, ethanol, propanol, butanol)
Can be used as fuels
How to produce ethanol
Can be produced by fermentation of sugar with yeast, using renewable sources
Conditions of producing ethanol
about 35 degrees
anaerobic (without oxygen)
yeast enzyme catalyst
Equation of producing ethanol (written)
Sugar → Ethanol + Carbon Dioxide
What is ethanoic acid?
Member of the carboxylic acids
What is the functional group of carboxylic acids?
-COOH
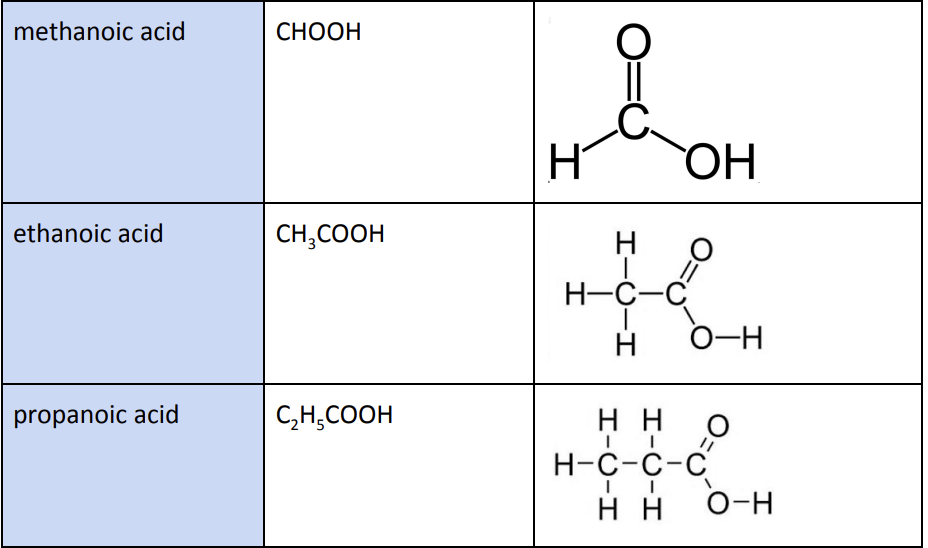
First four members of carboxylic acids
Methanoic Acid (CHOOH)
Ethanoic Acid (CH3COOH)
Propanoic Acid (C2H5COOH)
Butanoic Acid (C3H7COOH)
Reactions of methanoic acid, ethanoic acid, propanoic acid, butanoic acid
Dissolve in water: produce acidic solutions (pH under 7)
React with metal carbonates: produce carbon dioxide (turns limewater cloudy), a salt and a water
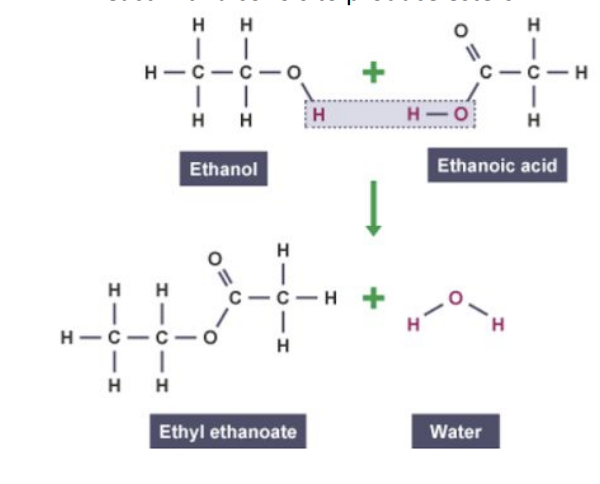
Reacts with alcohols in presence of an acid catalyst: produce esters
Ester we need to know name of
Ethyl ethanoate
Why are carboxylic acids weak acids?
They do not ionise completely in solutions so do not release many H+ ions
This means they have higher pH (less acidic) than solutions of strong acids of the same conc.
What kind of polymers can alkenes be used to make?
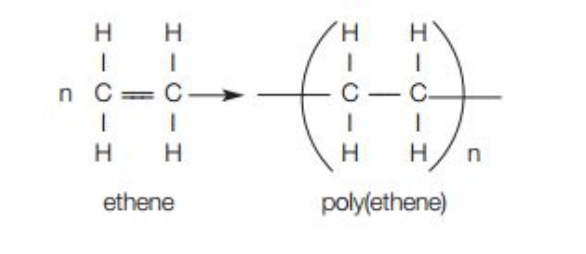
Poly(ethene) and poly(propene) by addition polymerisation
What happens in addition polymerisation?
Many small molecules (monomers) join together to create very large molecules (polymers)
Example of addition polymerisation
Repeat unit has same atoms as monomer because no other molecule is formed in the reaction
What does condensation polymerisation involve?
Monomers with two functional groups
What happens in reaction of condensation polymerisation?
When monomers react, they join together and usually lose small molecules (water)
So reactions are called condensation reactions
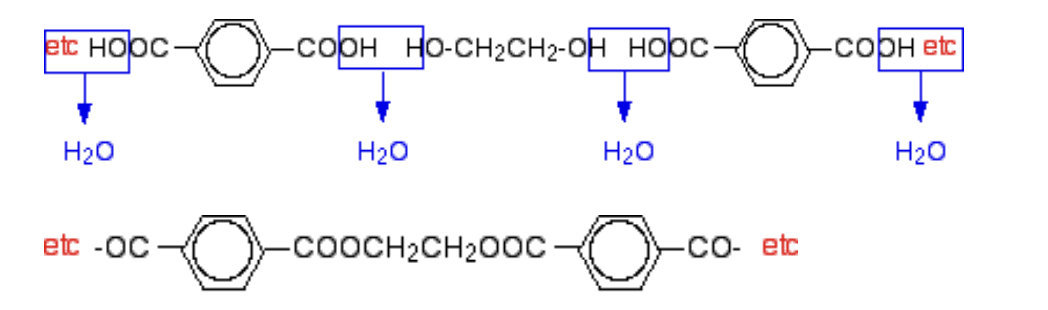
How are simplest polymers produced? (condensation polymerisation)
From two different monomers with two of the same functional groups on each monomer
Example of condensation polymerisation
e.g polyester: 1 monomer with 2 carboxylic acids func groups
1 monomer with 2 alcohol func groups
How many functional groups do amino acids have?
Two different func. groups in a molecule (amine group and carboxylic acid group)
How do amino acids react?
By condensation polymerisation to produce polypeptides
How can different amino acids be combined in the same chain?
To produce proteins
What is DNA?
A large molecule essential for life - encodes genetic instructions for development and functioning of living organisms and viruses
What are most DNA molecules made up of?
two polymer chains made from four different monomers called nucleotides in the form of a doube helix
Other than DNA, what are other naturally occuring polymers important for life?
Proteins (monomer = amino acid)
Starch (monomer = glucose)
Cellulose (monomer = glucose)
What is a monomer?
Molecule that can react with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain