Sensation & Perception TASTE, SMELL, TOUCH, HEARING (Psychology)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Frequency:
wavelength of sound wave (we can detect from 20 - 20,000 Hz)
Pitch
perceived frequency of a sound (higher frequency = higher pitch)
Amplitude:
height of sound wave
Loudness:
degree of sound volume (larger waves = louder)
Decibel:
unit of relative loudness (human can comfortably hear up to 80dB ~ prolonged exposure to above that = hearing loss)
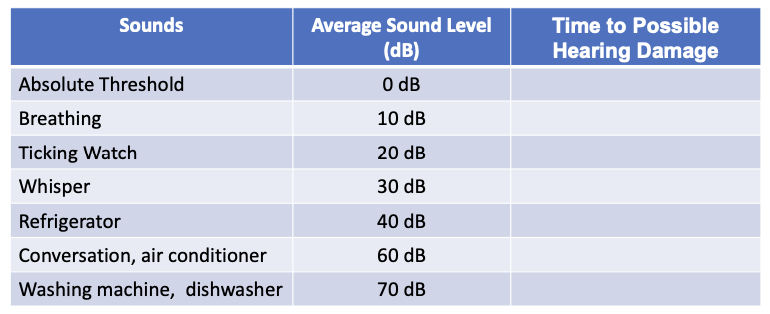
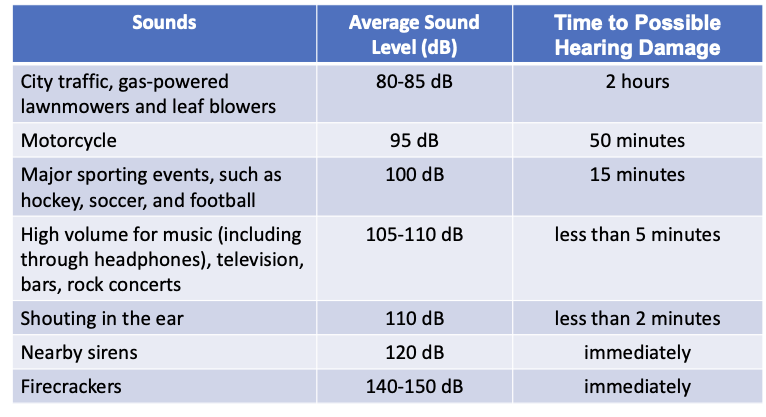
Possible hearing damage:
Place theory of hearing:
different areas of cochlea respond to different frequencies (higher tones excite areas near opening/oval window; lower tones excite areas near tip of cochlea)
Frequency theory of hearing:
whatever pitch of the sound wave, nerve impulses of a corresponding frequency are sent to the auditory nerve
Conductive hearing loss:
caused by physical damage to the ear, reducing ability of the ear to transfer vibrations from the outer to the inner ear
Sensorineural hearing loss:
caused by damage to the cilia, the auditory nerve, or the auditory cortex
increases with age; may be from prolonged exposure
Taste & smell are ___________ senses
chemical
5 basic tastes:
sweet
sour
bitter
salty
umami savory
Anosmia:
inability to smell
4 basic touch sensations:
temp
touch
pain
body movement
(skin is LARGEST organ in body ~ the sensory organ a for touch)
Proprioception:
ability to sense the position and movement of our body parts
(accomplished by specialized neurons in the skin, joints, bones, ears, and tendons ~ w/out it we couldn’t stand/walk)
Vestibular system:
set of liquid-filled areas in the inner ear that monitors our head’s position and movement
semicircular canals: rotational movements
vestibular sacs: linear accelerations
Gate control theory of pain:
Pain is determined by two types of nerve fibers in the spinal cord.
small fibers carry pain from body to brain.
larger fibers can open or shut (like a gate) the flow of pain to the brain (activated by massaging painful area)
Olfaction (smelling) process:
transduction occurs when receptors in olfactory membrane detect airborne chemicals that are inhaled through the nostrils (diff chemical molecules fit into different receptor cells = diff smells)
Sensory adaptation:
decreased sensitivity to stimuli after constant & prolonged exposure
Selective attention:
allows us to focus on some sensory experiences while tuning out others
Perceptual constancy:
ability to perceive stimuli as unchanging despite changes in sensation
(car is the same size, even tho it’s getting smaller in the distance)
Synesthesia:
mixing of senses in such a way that experiencing one sensation triggers an experience from a different sense
ex. (seeing colors when u hear music)
Illusions:
occur when the perceptual processes that normally help us correctly perceive the world are fooled by a particular situation so that we see something that does not exist or that is not correct
(our perception of the world may be influenced by our prior knowledge)
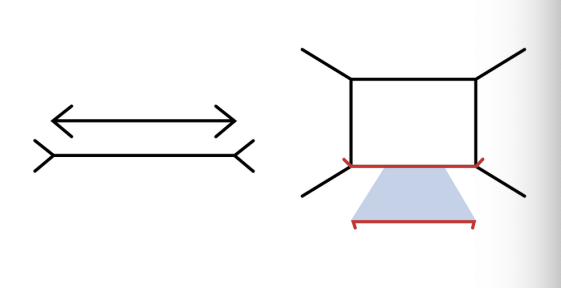
Mueller-Lyer illusion:
Moon illusion:
moon always looks larger on the horizon than when it is high above

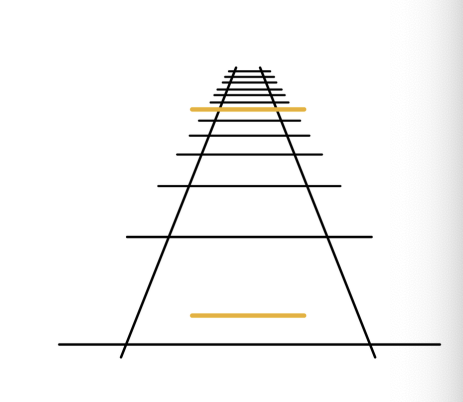
Ponzo illusion:
caused by the monocular depth cue of linear perspective.
Perception is influenced by:
expectation
culture
context
desires
emotions
motivations