EXAM 2- Austin (copy)
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Antimicrobials may be
a. natural
b. synthetic
c. both (semi-synthetic)
d. all of the above
d
What’s the difference between antimicrobials and antibacterials, antifungals, antivirals, and antiprotozoals?
“antimicrobials” is a broad term that includes any substance that kills or inhibits the growth of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, viruses, and protozoa.
What are the 3 ways of selectively targeting a pathogen?
(i bet there’s a test question on this topic/ LO)
UNIQUE- targets completely unique to pathogen, absent in host
SELECTIVE- targets that are similar but not identical to the host
COMMON- targets that are shared, but differ in relative importance
PRACTICE:
For EACH of the following identify the type of selective targeting (unique, selective, or common):
folic acid in pyrimidine synthesis
bacterial ribosome
cell wall
cell membrane
folic acid in pyrimidine synthesis- common
bacterial ribosome- selective
cell wall- unique
cell membrane- selective
What are the major targets of antibacterials? (LO)
cell wall synthesis
protein synthesis
nucleic acid homeostasis
metabolism
cell membrane
What’s the difference between bacterioSTATIC and bacteriCIDAL? (LO)
bacteriostatic—> agents that INHIBIT bacterial growth WITHOUT causing cell death
bactericidal—> agents that cause bacterial death
ANYTHING that inhibits cell walls is _____________.
a. bacteriostatic
b. bactericidal
b.
Most protein synthesis inhibitors are ___________.
a. bacteriostatic
b. bactericidal
a
When antibacterials are combined, they can either be synergistic, additive, or antagonistic. Describe what each of those mean:
synergistic- combo does MUCH better than each individually
additive- only slightly different than best drug (hard to see)
antagonistic- combo does WORSE than each individually
What are the 3 kinds of bacterial cell walls?
gram +
gram -
mycobacteria (atypicals)
Describe gram + cell walls:
thick/thin?
contains what?
outer membrane?
LPS?
(LO)
thick wall with teichoic and lipoteichoic acid
no outer membrane or LPS
Describe gram - cell walls:
thick/thin?
contains what?
outer membrane?
LPS?
(LO)
thin walls with LPS
contain porins in outer membrane
Describe the cell walls of mycobacteria:
thick/thin?
contains what?
outer membrane?
LPS?
(LO)
thin wall
outer membrane contains mycolic acids
also known as acid-fast
Peptidoglycan is also known as __________.
murein
What are the MAIN steps in bacterial cell wall synthesis? Which steps can be targets for antibacterials? (LO)
murein/peptidoglycan monomer synthesis
polymerization (stick monomers together)
cross-linking
each of these steps can be targets!!!!!!!!!!
Where does EACH step of cell wall synthesis take place/occur? What enzymes facilitate EACH step (if applicable)? (LO)
murein/peptidoglycan monomer synthesis- CYTOPLASM
polymerization- outside the cell
facilitated by PGT/ peptidoglycan glycosyltransferase enzymes
cross-linking- outside the cell
facilitated by TP/TRANSPEPTIDASES (also called PBP/ penicillin-binding proteins)
What antibacterials act by inhibition of murein monomer synthesis?
bacitracin
fosfomycin
Mycobacteria cell wall synthesis differs in the fact that myolic acid is used to form a large waxy outer membrane. How is mycolic acid synthesized? (LO)
by fatty acid synthetases 1 and 2
What is the importance of gram staining?
to highlight the physical and chemical differences between cell walls
determine drug therapy
split bacteria into 2 large groups (+ or -)
Describe the actual process of gram staining:
(just focus on 2 main staining agents) (LO)
apply primary stain (CRYSTAL VIOLET)
add iodide
decolorize
counterstain (SAFRANIN)
How do each of the following stain in a gram stain test?
(for the millionth time)
gram +
gram -
atypicals
gram + = PURPLE
gram - = PINK
atypicals = doesn’t stain or random staining
Antibacterials can also target DNA replication, transcription, and translation. What enzymes on bacteria are targeted during each? (LO)
replication: DNA gyrase, and Top IV
transcription: RNA polymerase
translation: 30S and 50S subunits
Antibacterials that target DNA replication, transcription, and translation use what mechanism?
a. unique
b. selective
c. common
b
Describe an antibacterial with a narrow spectrum:
active against ONLY a single species/small group of bacteria (ex: antibacterial that only limited to gram +)
Describe an antibacterial with a broad spectrum:
active against many or most species of bacteria
Describe an antibacterial with an extended spectrum:
“intermediate”
started as narrow spectrum and then add more coverage
What’s the difference between empiric and definitive therapy?
empiric- “we’re guessing”
tx based on educated guess like symptoms, usually broad spectrum
definitive- “we know”
we know exactly what’s causing the infection and how to treat it
What is MIC or EC90?
lowest concentration of an agent that inhibits visible growth of the organism after 18-24hrs
(basically what’s the least amount of abx I can give to inhibit the bacteria)
For measuring the MIC of an abx what 2 tests can be used?
broth-dilution
disk-diffusion
Describe broth-dilution:
fill a bunch of test tubes with equal amounts of microorganism
in each test tube, add a different conc of abx
after 18-24 look at the test tubes
the LOWEST concentration of an abx that results in the inhibition of visible growth of the organism is your MIC
For disk-diffusion, the larger the zone of inhibition, the _______ the MIC of the abx for the organism tested.
a. higher
b. lower
b
Minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) is the lowest concentration of an abx that…
kills 99.9% of the bacteria
Antibiotics are generally considered bactericidal if MBC ≤ ___ MIC
MBC ≤ 4x MIC
Optimally effective abx doses achieves IC___ to IC___ at the site of infection.
IC80 to IC90
Once the pathogen is known, what 2 components heavily influence what abx we select?
(not that important)
susceptibility testing
pharmacokinetics
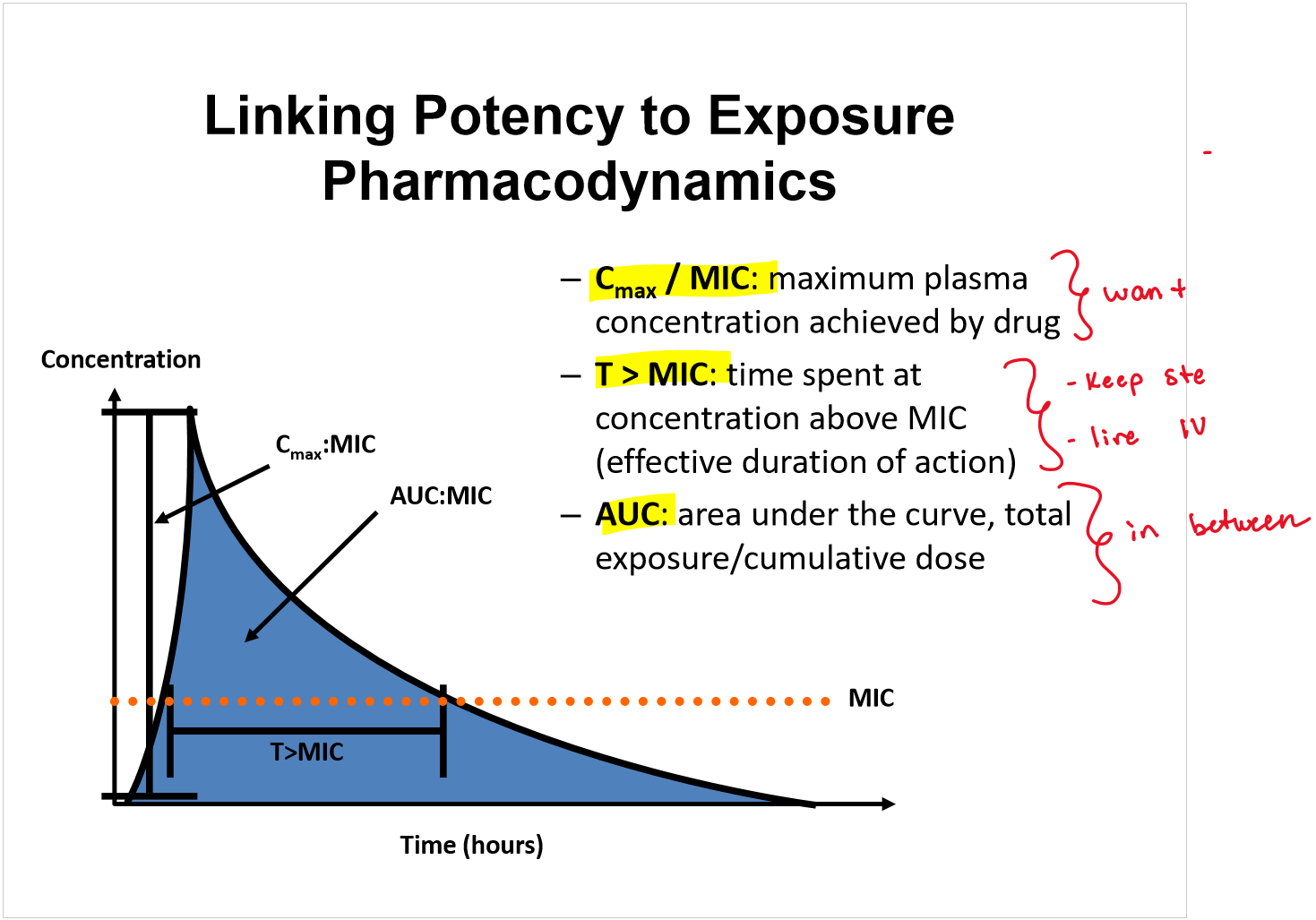
Can’t think of how to write a card on this—> just know EACH
Can’t think of how to write a card on this—> just know EACH
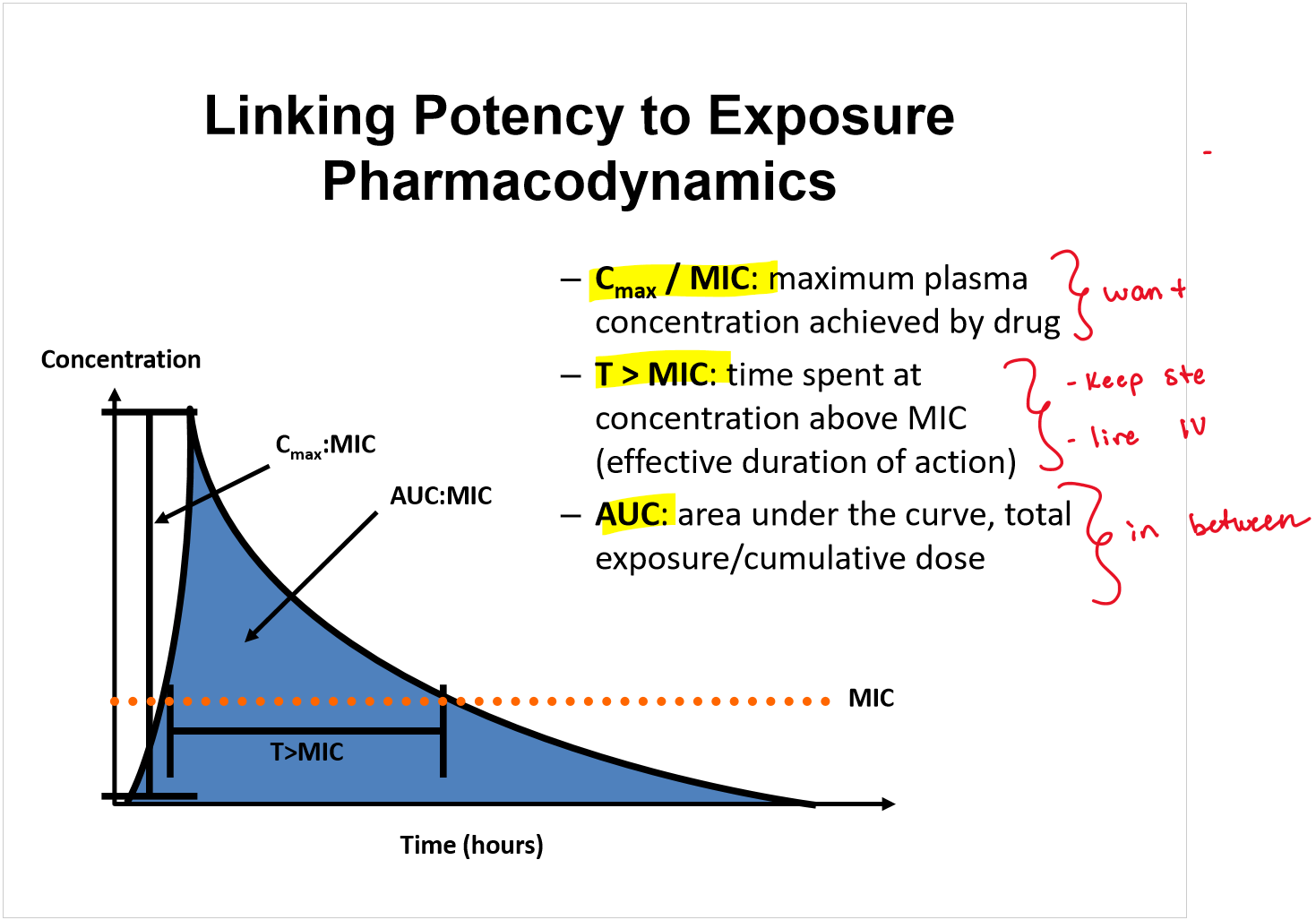
When antibiotics continue to suppress bacterial growth after concentrations fall below the MIC it is called…
post-antibiotic effect
Antimicrobial stewardship is…
ensuring proper use of antimicrobials
What are some mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance?
reduced entry of
increased export of
release of
alteration of antimicrobial…
alteration of proteins…
development of…
reduced entry of abx into pathogen
increased export of abx by efflux pumps
release of enzymes that destroy abx
alteration of antimicrobial targets
alteration of proteins required to take prodrugs—>drugs
development of alternative pathways to those inhibited by abx
How are low level mechanisms of resistance, like porins and efflux pumps, countered?
increased dose or cell permeability
How are higher level mechanisms of resistance, like target site mod and enzyme inactivation, countered?
target site—> drug modification, novel MOAs
enzyme inactivation—> countered inhibitors
A clinical breakpoint is…
concentration above which treatment is unlikely
What are the pros and cons of combination therapy?
pros: may decrease/slow resistance, treat mixed infections or life-threatening infections
cons: toxicity, cost, increase abx exposure to pathogen, risk of superinfections
What’s a superinfection?
a new infection that is caused by overgrowth of highly resistant or opportunistic organisms
Describe each of the following about prokaryotes:
nucleus?
smaller or larger ribosomes?
cell wall composition?
how do they reproduce?
motility?
no true nucleus—> nucleoid
smaller ribosomes
peptidoglycan cell wall
reproduce by binary fission
some motility—> flagella
Whether a bacteria is aerobic or anaerobic is based on whether they have what enzymes?
catalase and superoxide dismutase
For each of the following bacteria, list their oxygen requirements:
obligate aerobes
facultative anaerobes
obligate anaerobes
(“austin said test question dealing with these!!!!!!)
obligate aerobes- require O2 to live/generate ATP
facultative anaerobes- can live with/without O2
obligate anaerobes- unable to grow in presence of O2
Remember that LPS is an endotoxin found in the outer membrane of gram - bacteria. In some causes it can be the direct cause of…
symptoms of disease such as fever and shock
What is the structure of LPS? Which component is responsible for toxic effect?
Lipid A- responsible for toxic effect
Core polysaccharide
outer polysaccharide
Match the virulence factor to its definition:
gelatinous layer covering the entire bacteria | |
slime layer polysaccharide coating of some bacteria | |
resistant structures formed in response to adverse conditions | |
long, whip-like structures | |
shorter filaments that mediate attachment |
Word Bank: Pili, Glycocalyx, Spores, Flagella, Capsule
Capsule | gelatinous layer covering the entire bacteria |
Glycocalyx | slime layer polysaccharide coating of some bacteria |
Spores | resistant structures formed in response to adverse conditions |
Flagella | long, whip-like structures |
Pili | shorter filaments that mediate attachment |
What is the function of a capsule?
limits phagocytosis
aid in adhesion
antigen components in some vaccines (ex: PPV-23)
What is the function of a flagella?
facilitate chemotaxis (movement of a bacteria in response to certain chemicals)
Motile bacteria are common causes of _____.
UTIs
What is the function of a glycocalyx?
covers surfaces like a film
component of biofilms
adhesion
Spores are important for what species of bacteria?
gram + rods Bacillus and Clostridium
Bacteria colonize and thrive in human tissue with the help of enzymes. What are these enzymes, and what do they do?
collagenase & hyaluronidase- break down connective tissue
coagulase- formation of fibrin clot—> immune cells can’t get to bacteria
IgA protease- adherence to mucous membranes
leukocidins- destroy WBCs
Bacteria need iron to survive. How do they get it? By producing what?
HEMOLYSIS—> produce hemolysins= destroy RBC= IRON
Match the hemolytic pattern with its type?
partial hemolysis | |
complete hemolysis | |
minimal/no hemolysis |
word bank: α, β, γ
α | partial hemolysis |
β | complete hemolysis |
γ | minimal/no hemolysis |
What are exotoxins? are they toxic?
substances that are produced and secreted by bacteria (not a structural component like endotoxins)
may be extremely toxic
What is the structure of exotoxins? What does each DETERMINE?
A subunit- active subunit
determines EFFECT of toxicity
B subunit- binding subunit
determines LOCATION of toxicity
What are the 3 shapes of bacteria?
cocci- spheres
bacilli- rods
spirals
What are the IMPORTANT roles of “the normal flora” in human health?
protective host defense mechanisms
indirect—> colonization resistance (ur bacteria resist other bacteria)
direct—> secretion of antibacterials
nutritional functions (help digest food)
may cause disease
How are bacteria classified? Which form is most precise?
phenotypic
analytic
genotypic—> most precise
Which of the following are most common infectious agents?
a. gram + cocci, gram - rods
b. gram - cocci, gram + rods
a
Answer the following about STAPHYLOCOCCI:
Gram + or -
catalase + or -
strains present in normal flora/pathogenic (or both)
disclaimer—> sing says something slightly different
KEY structural components
gram +
catalase +
S. epidermidis- normal flora
S. aureus- normal or pathogenic
S. saprophyticus- pathogenic
Structural components
capsule
teichoic acid
protein A
What are the enzymes and toxins that S. aureus secretes?
enzymes
catalase
coagulase
hyaluronidase
B-lactamase
toxins
a/b-toxin (hemolysins)
leukocidin
superantigen
enterotoxins
exfoliative toxin
The toxins secreted by S. aureus can cause what toxic mediated diseases?
toxic shock syndrome
food poisoning
scaled skin syndrome (SSS)
S. aureus can cause different disease based on the location of infection. List the diseases S. aureus causes based on the following locations:
cutaneous
subcutaneous
deep tissue
cutaneous- impetigo, folliculitis, carbuncles
subcutaneous- cellulitis
deep tissue- bacteremia, pneumonia, endocarditis, osteomyelitis, arthritis
S. saprophyticus can cause ______.
UTIs
What are 3 resistance mechanisms identified in staphylococci that determine the treatment strategy?
MSSA
MRSA
VRSA
Answer the following about STREPTOCOCCI:
Gram + or -
catalase + or -
KEY structural components
Gram +
catalase -
key structural components
capsule
lipoteichoic acid
pili (S. pneumoniae)
M protein
Function of M protein?
adhesion to keratinocytes
inhibition of complement activation
S. pyogenes (group A streptococci) has what enzymes and toxins?
enzymes: streptokinase, hyaluronidase, DNases, proteases
toxins: streptolysins O and S, pyrogenic exotoxins
S. pneumoniae (group A streptococci) has what enzymes and toxins? What does it bind to activate complement?
enzymes: IgA protease, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
toxins: pneumolysin
binds C-reactive protein
Answer the following about Enterococcus:
found in normal flora in…
aerobic/anaerobic?
name the 2 pathogenic strains?
What type of resistance is associated with these strains?
disclaimer: slightly different than sing****
found in noraml flora in GI tract
facultative anaerobe
2 pathogenic enterococcus
E. faecalis and E. faecium
associated with VRE (vancomycin-resistant enterococcus)
Answer the following about Pseudomonas:
Gram +/ -
aerobic/anaerobic?
key structural components?
gram - rods
aerobic
key structural components
flagella
pili
capsule
LPS
What enzymes and toxins do Pseudomonas aeruginosa have?
enzymes: elastase, exoenzymes (S,T,U,Y)
toxins: exotoxin A, pyocyanin
What are exoenzymes?
secreted into host cells by needle-like appendage
Pseudomonas species use Quorum Sensing. What is it and how do Pseudomonas species use it?
Quorum sensing—> a cell-to-cell signaling mechanism bacteria use to coordinate gene expression based on population density
pseudomonas—> once the bacteria population reaches a certain amount—> the bacteria make a BIOFILM = increases resistance
What are some common diseases caused by Pseudomonas disease?
pulmonary infections
common cause of hospital-acquired pneumonia
bacteremia
UTI
especially nosocomial
dermal
What are the key mechanisms of resistance for Pseudomonas?
efflux pumps
decreased porin permeability
drug degrading enzymes
target alteration
biofilms
multidrug resistance