VCU DPT - Agents (Compression)
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
_________ is an inward directed mechanical force that increases pressure on body
compression
can compression be...
- static OR intermittent
- applied uniformly OR sequentially to a limb
yes and yes
primary clinical applications for compression (5)
prevent DVT
help venous ulcer healing
residual limb shaping
scar control
peripheral edema control
what 3 pathways does fluid normally move through
circulatory system
lymphatic system
interstitial space between cells
fluid exhcnage at the capillary occurs via ___________ and _______
hydrostatic and osmotic pressure
edema, DVT prevention, venous static ulcers, and lymphedema are all indications for _________
compression
t/f: we treat systemic diseases with compresion
FALSE
we do NOT
we ___(do/do not)______ treat systemic diseases with compression
do not
with normal edema fluid leaks into the _______ but is reabsorbed by ______
with abnormal edema, what are some things that could happen
interstitial space, venous/lymph
venous/lymph insuffieceincy
increased capillary permeability
immobility
increased plasma volume
what are some side effects of edema
decreased ROM and function
delayed healing
pain
collagen deposition
etc
what are three ways to measure edema
anthropometric measurements
- must be taken at reproducible landmarks
volumeter (water)
pitting edema
pitting edema scale:
what is grade for someone who has slight indentation, takes 15 seconds to rebound
2+
pitting edema scale:
what is grade for someone with barely detectable impression when finger pressed into skin
1+
pitting edema scale:
what is grade for someone with deeper indentation, taking 30 seconds to rebound
3+
pitting edema scale:
what is grade for someone with 30+ seconds to rebound
4+
what is pitting edema grade scale from, which is worse
1+, 2+, 3+, 4+
4+ is worst
pitting edema is a ______ issue
venous
80% of patients would develop a DVT without any intervention, largely in part to immobility
what can we do to help
compression!!!
compression for edema can help WHY
we can change the pressure to have an external force increasing osmotic pressure, getting fluid to return into venous/lyphm systems
early mobilization is
CRITICAL
______% of patients undergoing ortho sx will develop a DVt of some kind without interventions
80%
that is a LOT
compression:
a. ____ blood flow
b. _______ venous stasis
c. _______ chance to form clot
a. increase
b. decrease
c. lowers
what happens to create venous insuffeciny
normal and abnormal valves in venous/lympahtic vessels, and relation to backflow
what is the BEST PUMP to return venous/lymph fluids
physical activity with muscular contractions
the best pump to return venous and lymph fluids is
exercise
venous statis ulcers happen due to what
what are some risks (4)
valve incompentence, vein obstruction
immobility
obesity
lack of muscle pump or dysfunction
pregnancy
________ is the cornerstone of venous ulcer treatment
compression
compression can:
1. ____ venous circulation
2. _____ rate of healing venous stasis ulcers
increase
increase
with venous ulcers, compression is best if it is ___(multilayered/single layered)_____
multi
mod-high or low compression recommened for venous ulcer
mod-high (40-60 mmHg)
can static compression be used for limb shaping
yes
after amputation, to reduce and shape residual limb
can also help prepare limb for prosthetic
t/f: static compression helps with hypertrophic scarring
if true: how
if false: what type of scarring does it help with
true
reduces scar formation, increasing collagenase activity
decreases contractures
if using static compression for hypertrophic scarring, how much pressure should be used and for how long per day
20-30 mmHg
23 hours a day
do we treat edema due to congestive heart fai,ure with compression
NO!!! we do not treat systemic diseases
some precautions to compression (4)
recent skin graft
skin infection
impaired sensation
impaired mentation
contraindications to compression (5)
(there are a few others but very similar to this list)
arterial insuffeciency
uncontrolled HTN
DVT
CHF or other systemic issues
fracture
with compression and arterial insuffeciency....
an ABI < 0.06 = _________
an ABI of 0.06 - 0.8 = ___________
an ABI of >0.8 = _________
contraindicated
reducded compression, 27 mmHg or less
full compression allowed
5 potential adverse effects of compression
increased edema
impaired circulation
ischemia
peripheral nn injury
increased cardiac load
potential adverse effects of compression include
- _______ edema
- ________ circulation
- __________
- ___________ nerve injury
- ________ cardiac load
- INCREASED edema
- DECREASED circulation
- ISCHEMIA
- PERIPHERAL nerve injury
- INCREASED cardiac load
what is the issue with stockings for compression
get really bunched up, can make it worse
also difficult to even put on
what device is thought to do the best job at "milking" for compression
sequential intermittent compression devices

____________ throught to provide more effective milking effect than single chamber compression sleeves
sequential intermittment compression devices

describe how a sequential intermittment device works
it starts low, and then will squeeze up your leg
- simiarly to recreating blood flow
"milking" effect
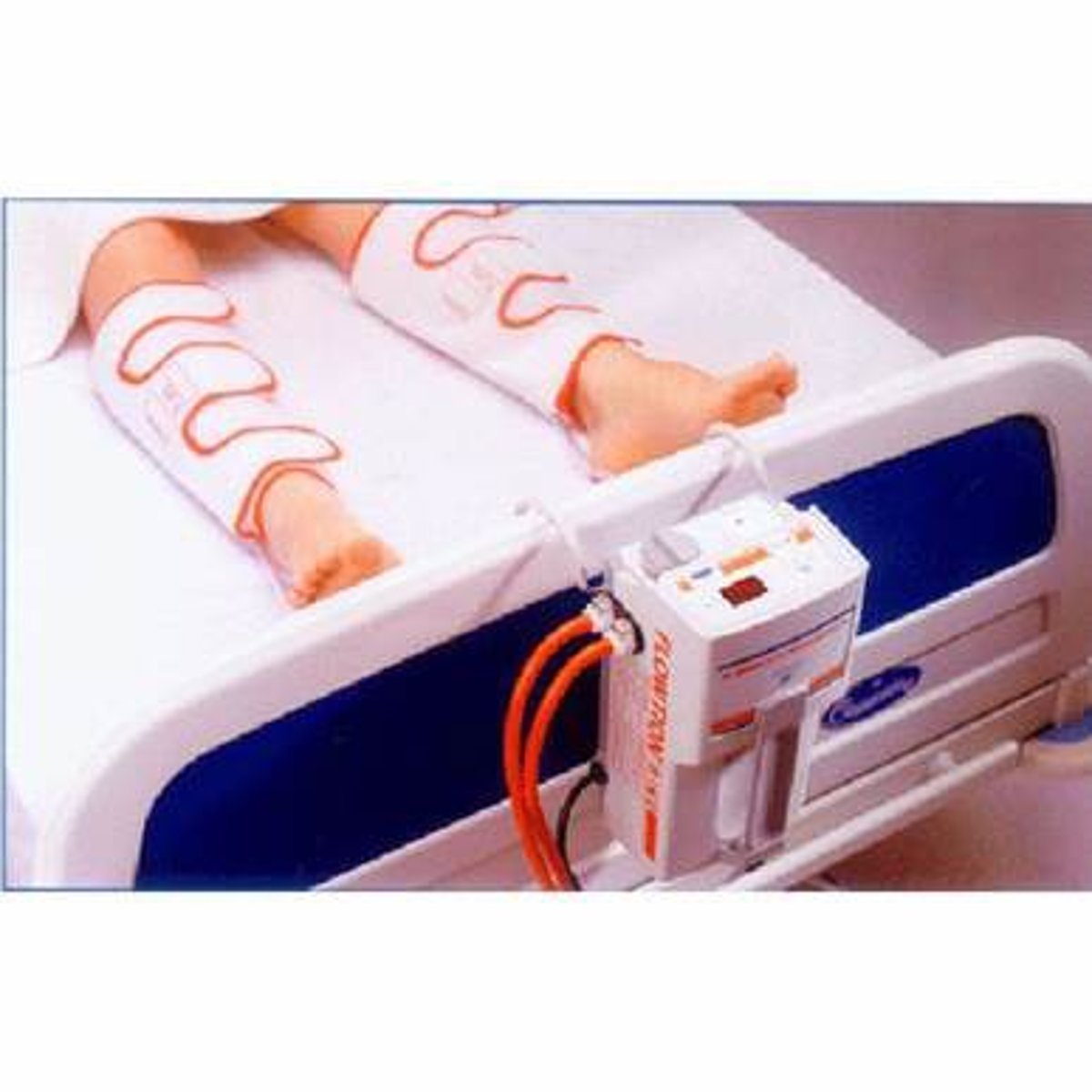
with static compression, bandages apply a _______ or ______ pressure
difference is in type of band you use
working or resting
static compression applies what two types of pressures
which one is made with a elastic band, and which is with an inelastic band
resting pressure (elastic band)
working pressure (inelastic band)
with static compression, describe:
working pressure
resting pressure
working pressure: active muscles squeezing against a INELASTIC bandages
resting pressure: ELASTIC bandages pressing on muscles due to their stretch
______ pressure is provided with static compression because of ELASTIC bandages being put on stretch and squeezing muscles
resting
________ pressure is provided with static compression because of muscles contracting against INELASTIC bandages
working
working pressure only works if patient has _________
some mobility
- need this because it happens with muscles contracting and pushing on bands
for resting pressure, use ___(high/low)_____ stretch bandages
for working pressure, use ___(high/low)_____ stretch bandages
resting:
high
working:
low
why is high stretch bandage not good for giving working pressure
as the muscle contracts and moves, the bandage does too
with resting pressure, you use high stretch bandages
exerts ______ mmHg of pressure
60-70
when you are moving around but want some static compression, should you use high stretch or low stretch
and what pressure does this make
low stretch
working
when you are sitting around by want some static compression, should you use high stretch or low stretch
and what pressure does this make
high stretch
resting
is
a. resting pressure/high stretch
or
b. working pressure/low stretch
best for immobile patients
A
stocking and garments:
what type of pressure do they apply
how long do you wear
is pressure consistent or graded
both working and resting
24 hours a day
graded (more at distal)