3_2: Clinical Exercise Testing Programing
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are the 2 main parts of the Health Screening and Risk factor analysis?
Exercise Preparticipation Health Screening
Clinical Exercise testing and programming
What are the key steps in exercise participation health screening?
Determine readiness for activity
Identify signs and symptoms of CV, metabolic, renal diseases
Desired exercise intensity
Medical history
Lifestyle history
Informed consent
Health Evaluation: Clinical Tests (6)
Physical examination
Blood chemistry profile
Blood pressure assessment
12-lead ECG
Graded exercise test
Additional lab test
Graded exercise test are recognized for:
detection of coronary artery disease with chest pain syndrome
evaluation of CAD severity
prediction of CV events and all-cause death
evaluation of physical capacity and effort tolerance
assessment of chronotopic competence, arrhythmias, and response to implanted device therapy
assessment of the response to medical intervention
What are some basic recommendations for evaluation of physical functioning?
6 or 8 m gait > 0.6m/s
8 sit to stand reps in 30s
8 arm curls (4kg)
ascend 10 steps under 30 sec
chair sit and reach
True or False? Those basic recommendations for evaluating physical functioning are used to asses health related physical fitness?
False; they are not used to assess health related physical fitness
What are the minimum exercise recommendations when testing is unavailable? (aerobic)
2 to 4 METs
Exercise HR = resting HR + 20 bpm
rate of perceived exertion: 11 to 14
What are the minimum recommendations for activity, when testing is unavailable? (strength)
2 sets of 30s of sit to stand reps
2 sets of 8 arm curls (4kg)
10 step ups 2 times
chair sit and reach hold for 30 sec
What are the 4 intensity levels of physical activity?
light
moderate
vigorous
high
How does breathing change during light intensity PA? What are the MET ranges?
Barely detectable, normal, increased depth
1.5-3 METs
How does breathing change during moderate intensity PA? What are the MET ranges?
Can pass the talk test, slightly heavier breathing
3-6 METs
How does breathing change during vigorous intensity PA? What are the MET ranges?
Can’t pass talk test, deep breathing
6-9 METs
How does breathing change during high intensity PA? What are the MET ranges?
heavy breathing, talking is almost impossible
> 9 METs
Step 1 for exercise programming
assess current health status (medical history, symptoms, restrictions and treatments)
Step 2 for exercise programming
assess current physical activity level
Step 3 for exercise programming
identify symptoms that limit physical activity (objective value, descriptions, recovery time)
Step 4 for exercise programming
evaluate physical function and performance
What are the four levels of physical function and performance?
Mildly impaired to normal
Moderately impaired, low functioning
Severely impaired, very low functioning
Needs aid, debilitated
Step 5 for exercise programming
select physical performance assessments (ADLs)
CHECK HEALTH RELATED FITNESS
List a few tests used for physical functioning
Walking test
Gait speed test
Chair to stand test
Describe the gait speed and placed them into the perspective requirements for various activities
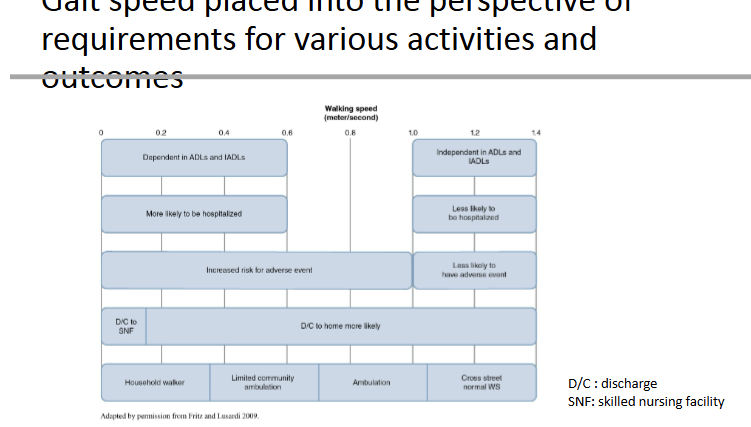
Step 6 for exercise programming
consider formal exercise tolerance training (whether an individual should undergo training before starting an exercise program)
List some types of exercise tolerance tests
Balke or modified naughton protocol (gradual increase)
Low-level constant-increment protocol (small increase in intensity)
Continuous low-level ramping protocol
branching low-level protocol
Step 7 for exercise programming
considerations for program referral
what are the limitations in physical function?
how safe is the exercise?
adherence factors; accessibility
Step 8 for exercise programming
develop a strategy for monitoring progress
track participation and clinical responses