Econ Exam 1 & 2, Quiz 9 & 10, Homework 5
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
A country’s standard of living is most closely tied to its:
Ability to produce goods and services.
A luxury good will generally have:
A high price elasticity of demand
If an economy is operating on its PPF, what must be true?
Resources are being used efficiently
Country Y requires 8 hours to produce 1 chair and 2 hours to produce 1 table. If Country Z requires 6 hours per chair and 3 hours per table, which country has an absolute advantage in chairs?
Country Z
If the opportunity cost of producing 1 bushel of wheat in Country A is 3 gallons of milk, and in Country B it is 2 gallons of milk, which country should specialize in wheat production?
Country B
If an economy can produce either 500 computers or 1,000 cars, what is the opportunity cost of 1 car?
0.50 computers
Which of the following is true about total revenue when demand is inelastic?
Total revenue increases when price increases
What role do opportunity costs play in trade?
They help countries identify which goods they should import and export
Goods with no close substitutes tend to have highly elastic demand.
False
Which of the following is NOT a determinant of price elasticity of demand?
The cost of production
A country should export the good in which it has the higher opportunity cost.
False
Which of the following would cause the demand curve for cars to shift to the right?
A decrease in interest rates on car loans
At a price of $5, the quantity demanded for a product is 100 units, and the quantity supplied is 150 units. What is the market condition?
Surplus
Which of the following statements is true about absolute and comparative advantage?
A country can have a comparative advantage in producing a good even if it does not have an absolute advantage in producing that good
If the price of laptops decreases due to cost-saving technologies, what happens in the market?
Supply increases, shifting the supply curve right
A product is said to have perfectly inelastic demand when:
Quantity demanded does not change regardless of price changes
If two goods are substitutes, their cross-price elasticity is positive.
True
Which of the following goods is likely to have an inelastic demand?
Insulin for diabetics
If a 30% increase in price results in a 10% increase in quantity supplied, supply is:
Inelastic
If the cross-price elasticity of demand between two goods is negative, the goods are:
Complements
Which of the following is the result of trade between two countries?
Specialization in production based on comparative advantage, increase in global production efficiency, each country consumes beyond its PPF
According to the principle of rational decision-making, when should a person take action?
When the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost
If the price of coffee increases and the demand for tea increases, these two goods are:
Substitues
If the government prints too much money, what is the likely result?
Inflation
If the price of a good rises by 5% and quantity supplied rises by 15%, the price elasticity of supply is:
3
What happens when the price of a complement, like ketchup, increases?
The demand for the complementary good, like fries, decreases
If the price of a necessity good rises by 8% and the quantity demanded falls by only 2%, the price elasticity of demand is:
0.25
A price increase causes total revenue to decrease. What does this imply about demand?
Demand is elastic
Which statement best describes a perfectly elastic demand curve?
Horizontal line
A company raises the price of its product from $50 to $60, and demand falls from 500 units to 450 units. What is the price elasticity of demand?
.57
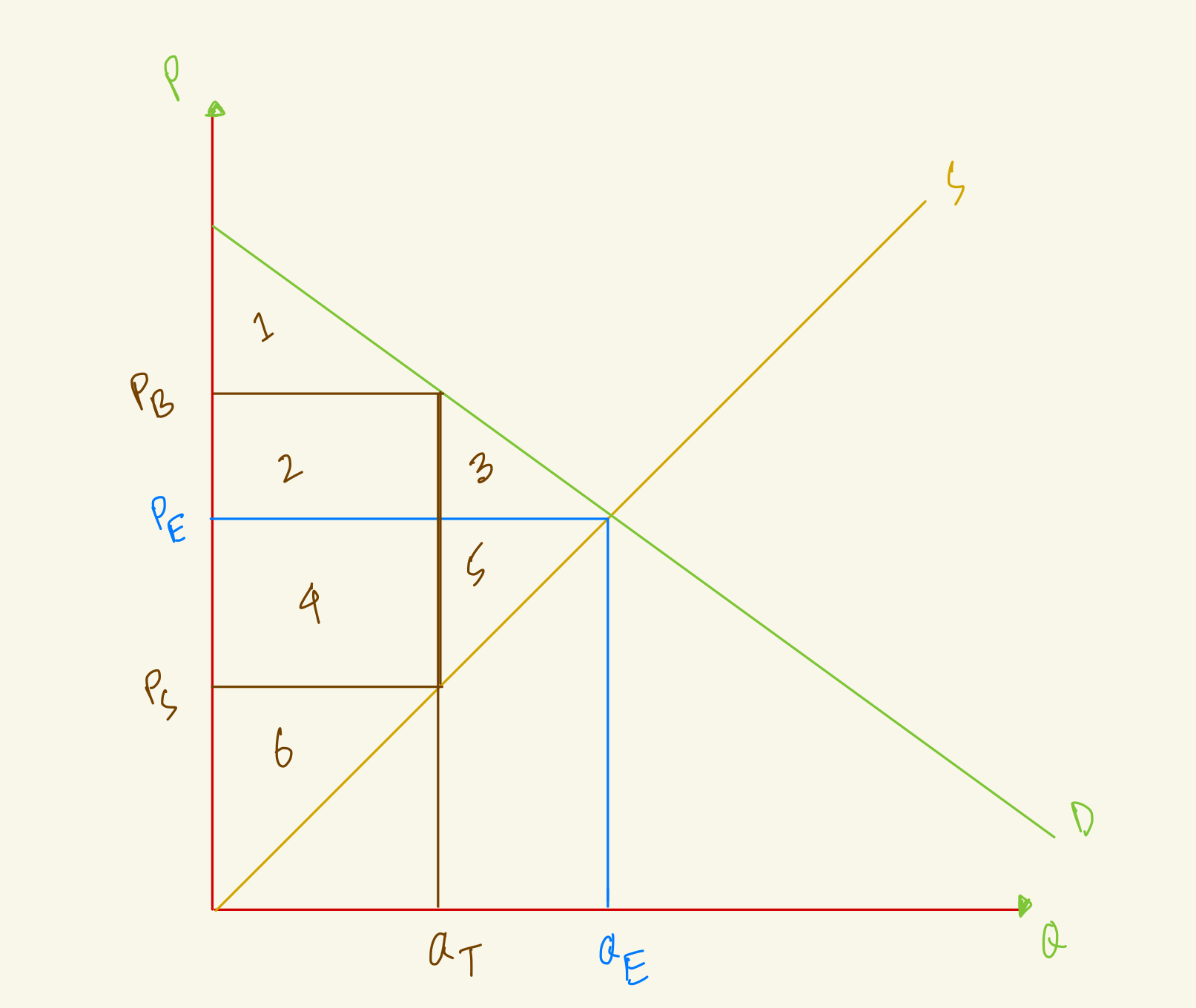
At the equilibrium, price is PE and quantity is QE. After tax, quantity in the market falls to QT, the amount that buyers pay rises to PB and the amount that sellers receive falls to PS. What's the producer surplus in this market with tax?
6
Suppose the government sets a price ceiling on bottled water at $1.50, but the equilibrium price is $2.00. What will likely happen in this market?
Shortage of bottled water
A binding price ceiling will typically result in which of the following outcomes?
A shortage of the good
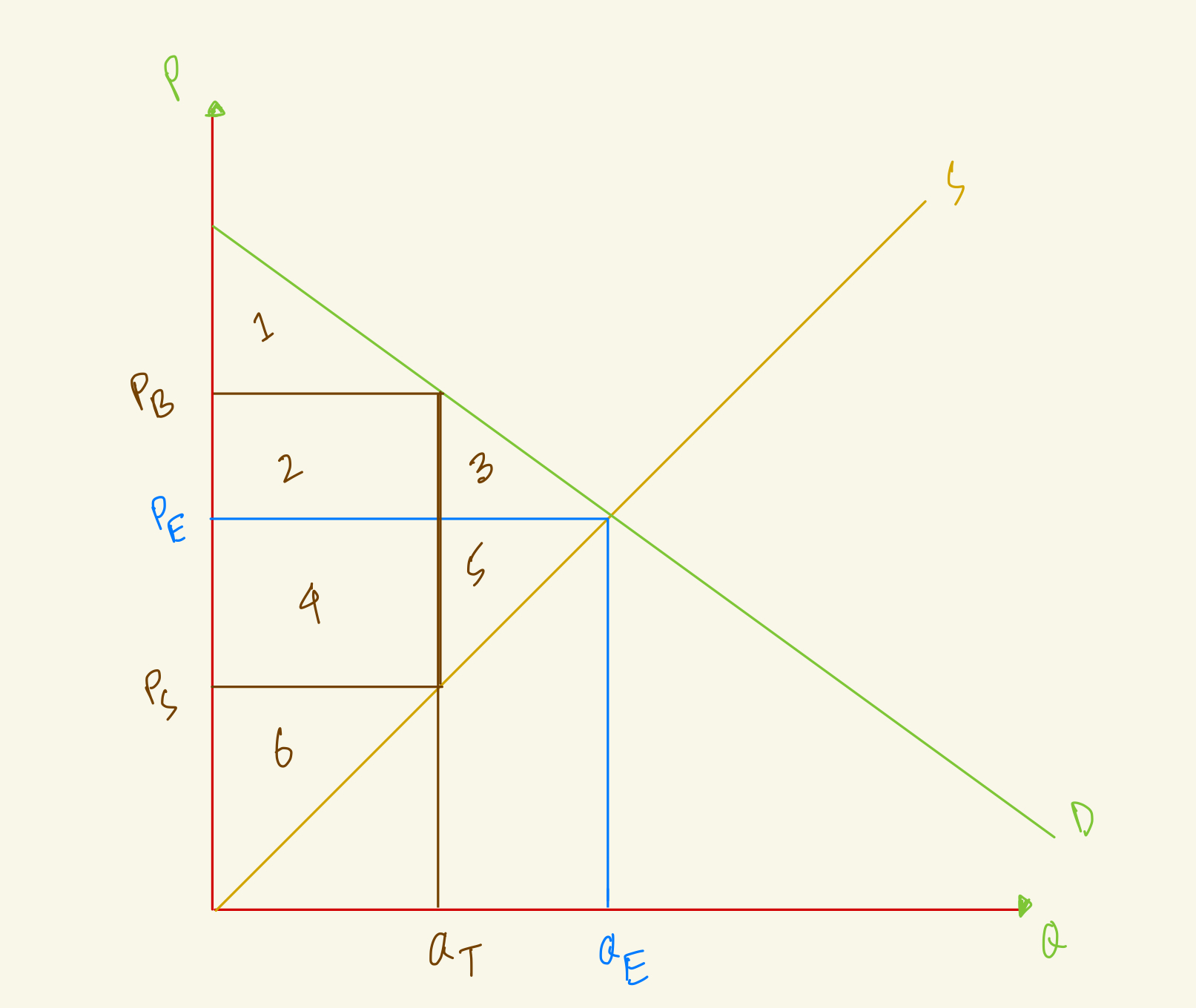
At the equilibrium, price is PE and quantity is QE. After tax, quantity in the market falls to QT, the amount that buyers pay rises to PB and the amount that sellers receive falls to PS. What's the deadweight loss in this market with tax?
3+5
Kurt invested $80,000 in the factory and equipment to start the business last year: $30,000 from savings and borrowed $50,000 (interest 10% for saving and borrowing). Calculate the explicit costs.
$5000
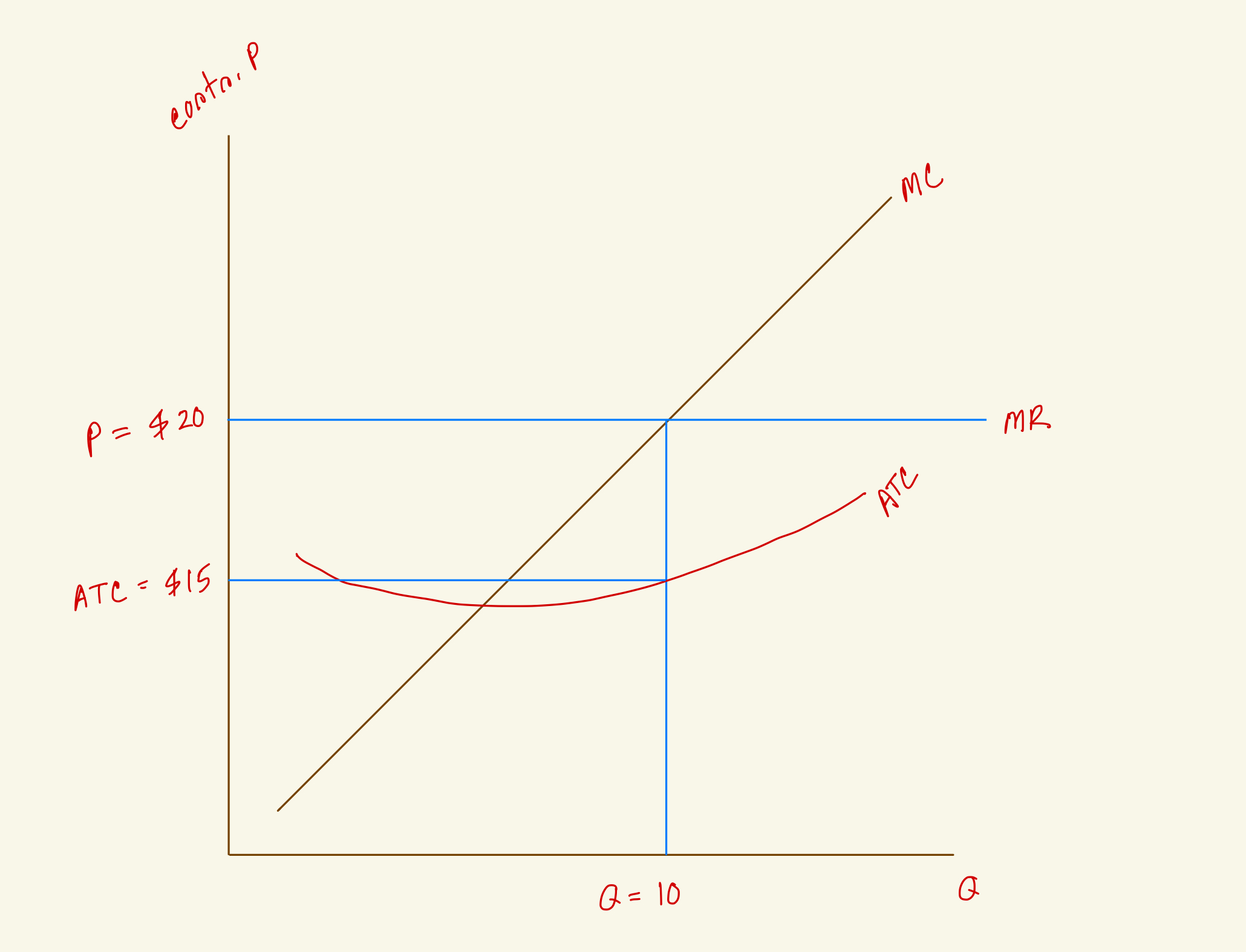
What's the profit for this firm in the diagram?
$50
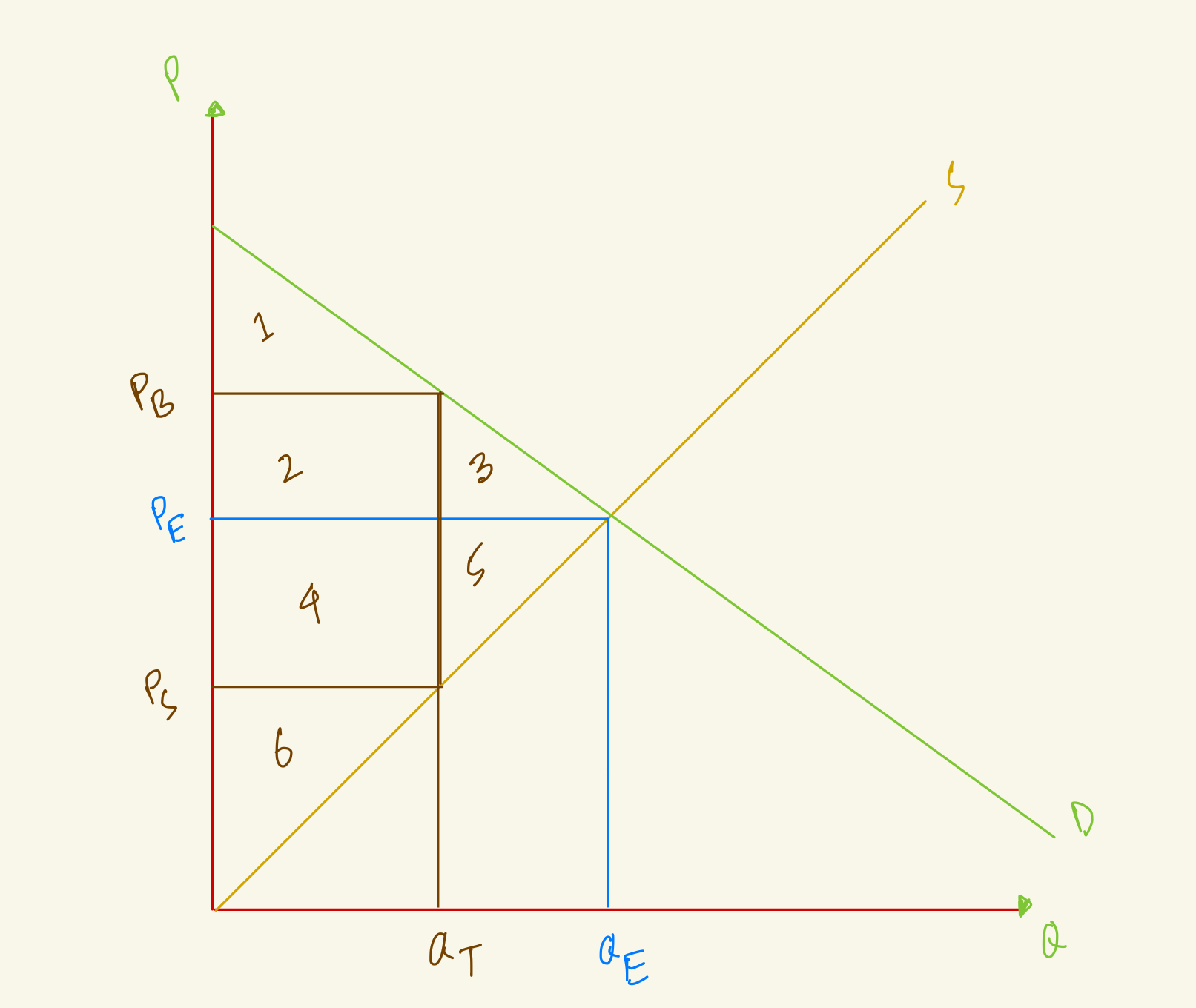
At the equilibrium, price is PE and quantity is QE, what's the producer surplus in this market?
4+5+6
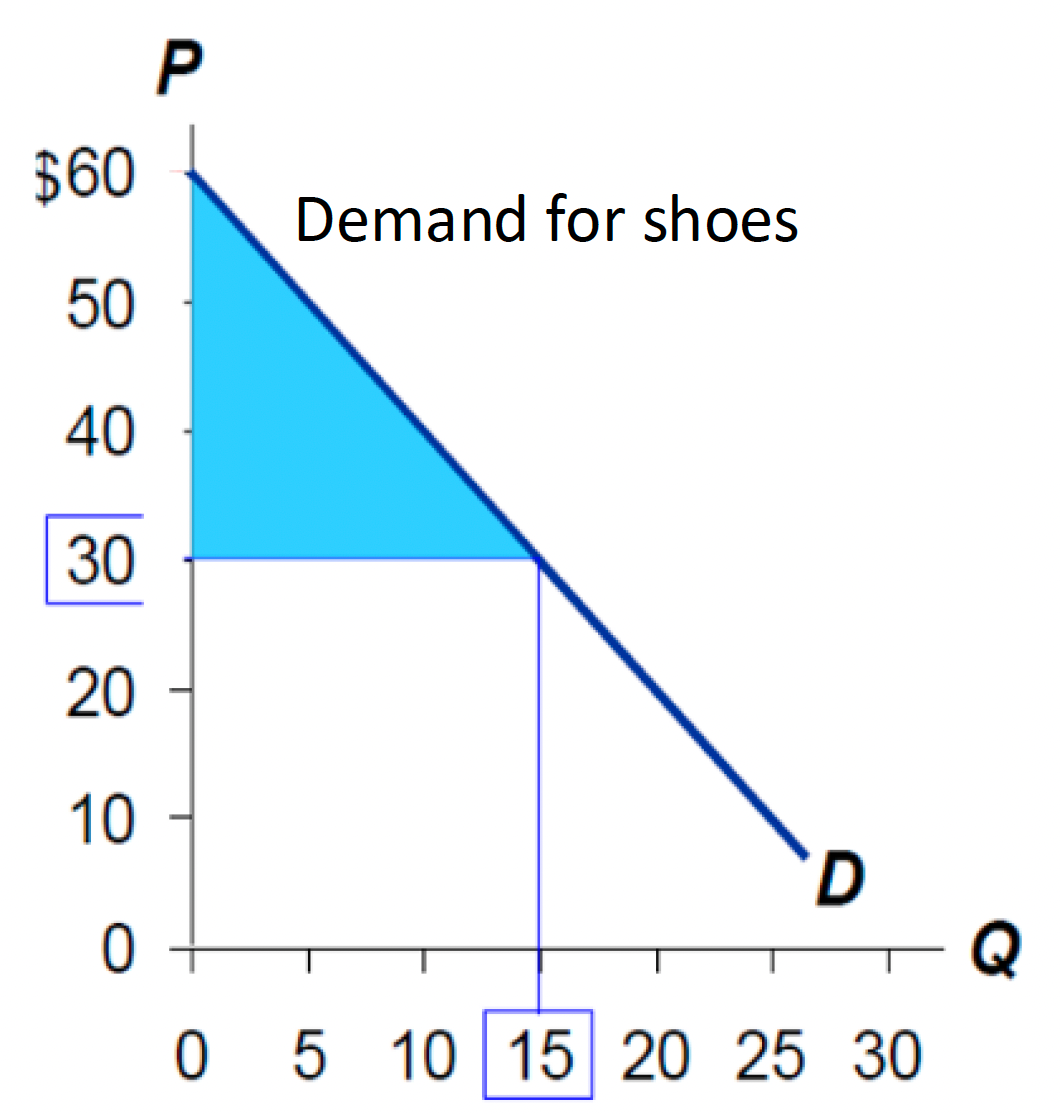
Calculate Consumer Surplus from this diagram if market equilibrium price is $30 and market equilibrium quantity is 15.
$225
Which of the following best defines diminishing marginal product?
Additional input leads to smaller increases in output
The profit-maximizing condition for a competitive firm is:
MR=MC
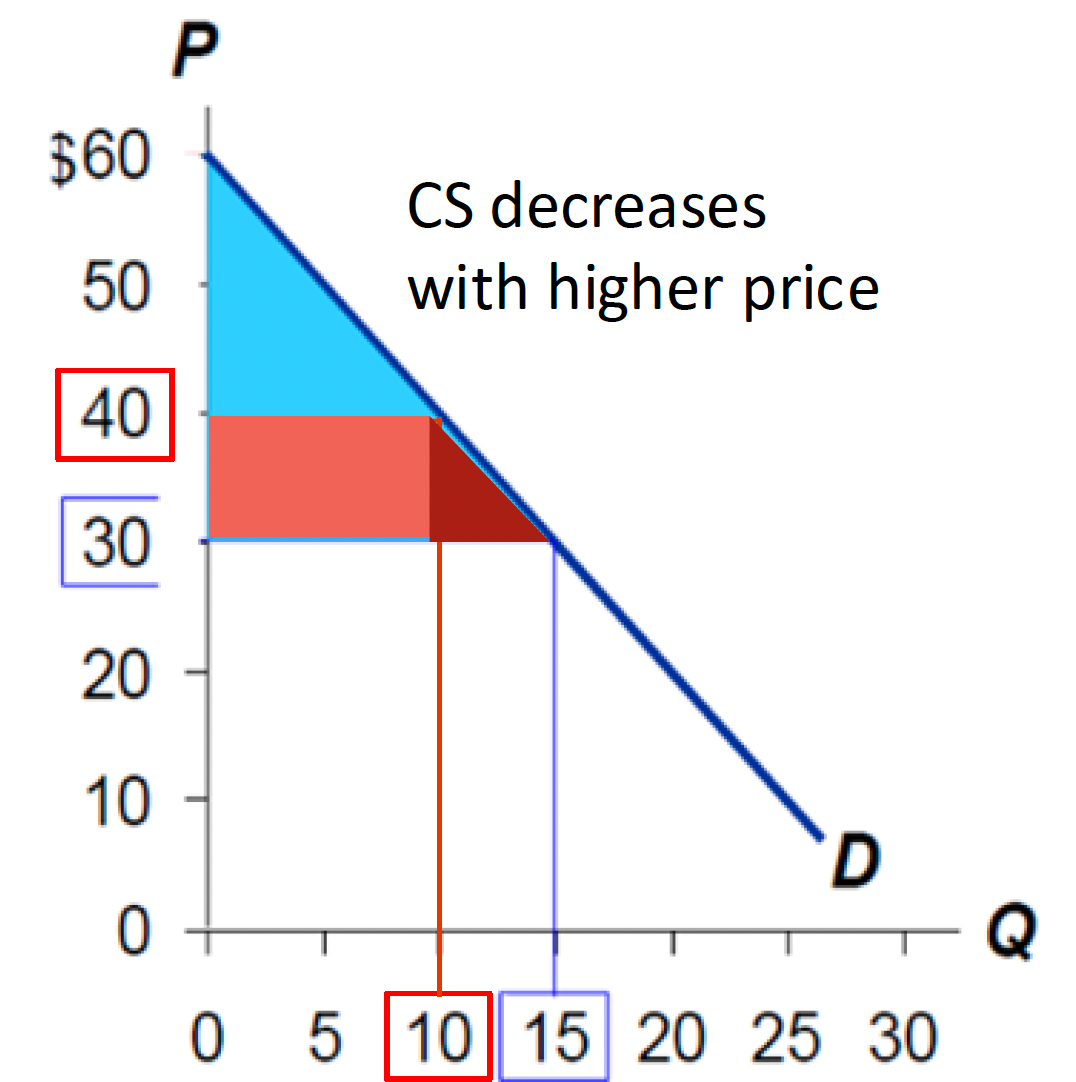
How much do we lose in Consumer Surplus if Price goes up from $30 to $40 and Quantity fall from 15 to 10?
$125
Sunk costs should affect shutdown decisions in the short run.
False
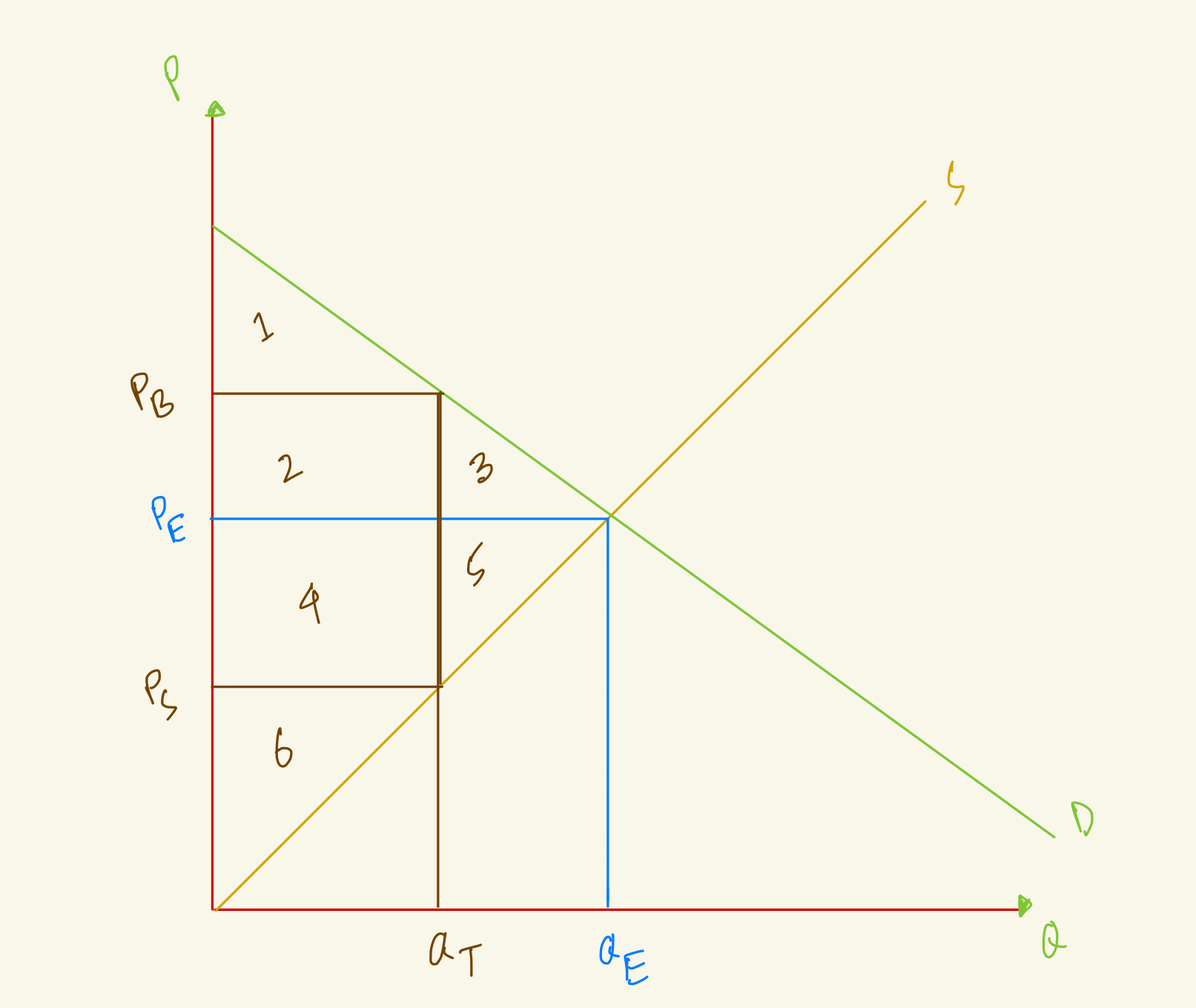
At the equilibrium, price is PE and quantity is QE. After tax, quantity in the market falls to QT, the amount that buyers pay rises to PB and the amount that sellers receive falls to PS. What's the government revenue in this market with tax?
2+4
If demand for a good is more elastic than supply, the majority of the tax burden falls on:
Sellers
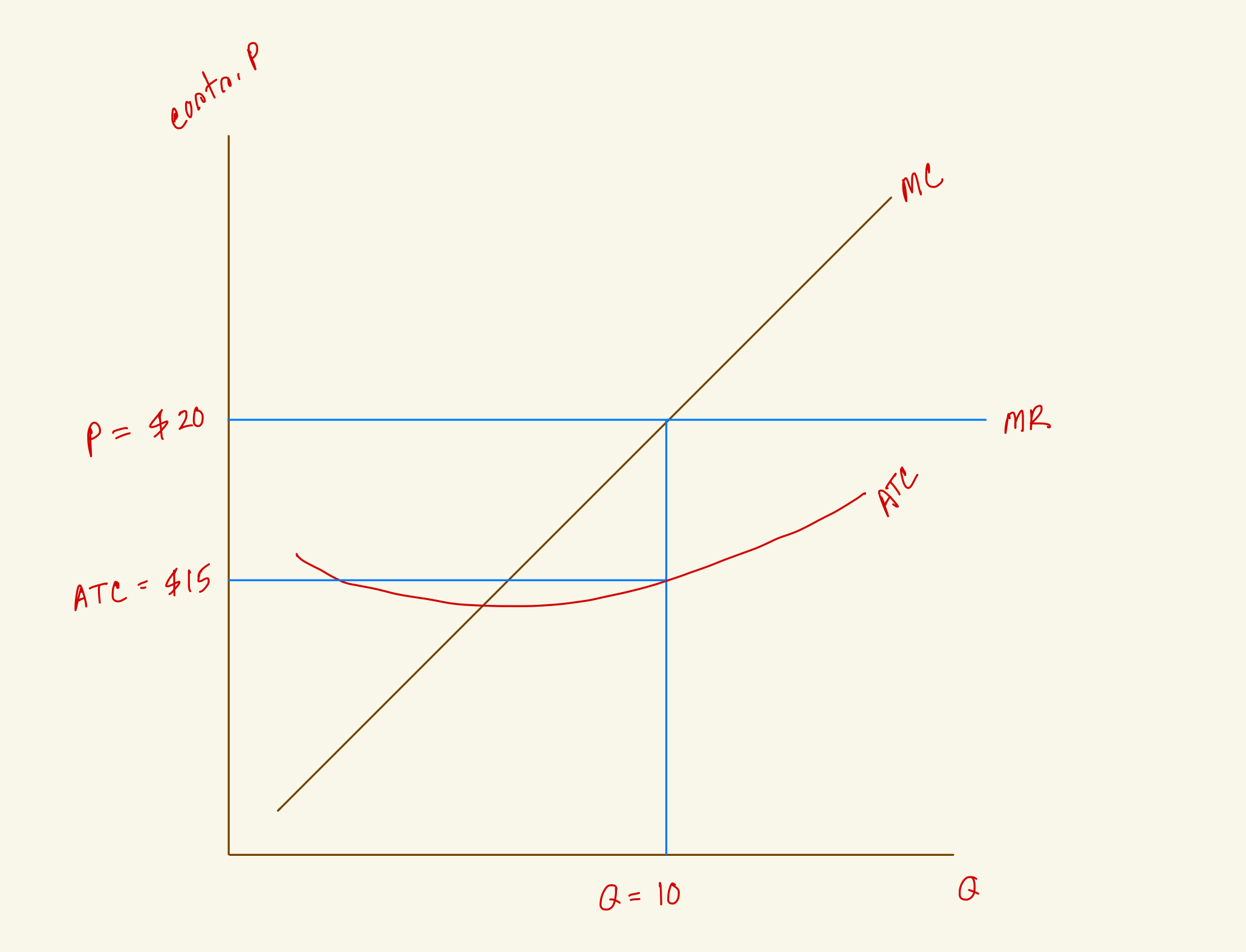
What's the total cost for this firm in the diagram?
$150
When supply is more elastic than demand, which group bears the larger share of the tax burden?
Buyers
Deadweight loss from a tax is the result of:
Transactions that no longer happen due to the tax
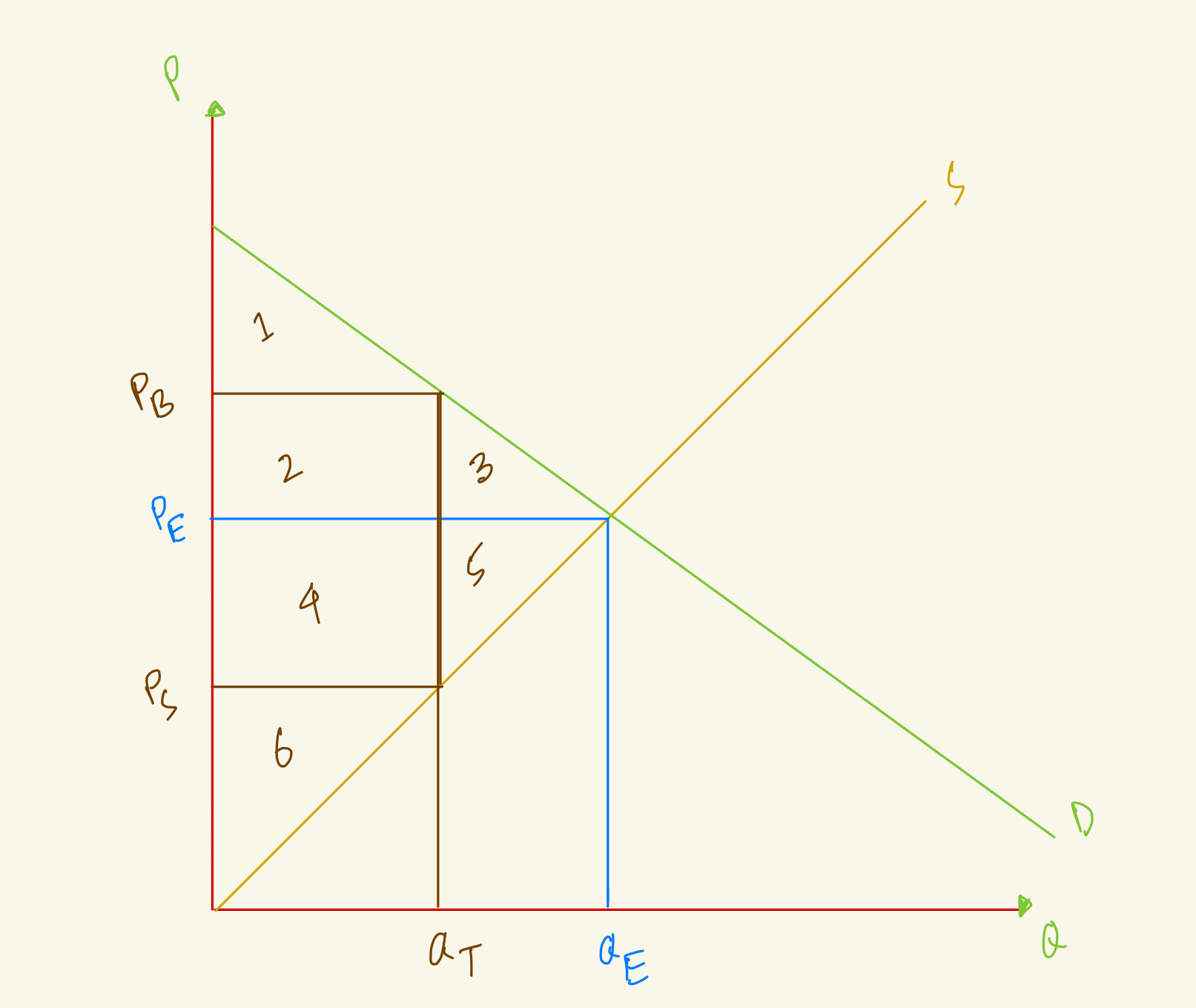
At the equilibrium, price is PE and quantity is QE, what's the total surplus in this market?
1+2+3+4+5+6
If a tax is imposed on a good with perfectly inelastic demand, the deadweight loss will be:
Zero
Accounting profit is always equal to or greater than economic profit.
True
The marginal cost curve intersects the average total cost curve at:
Its lowest point
The firm’s short-run supply curve is:
The marginal cost curve below AVC
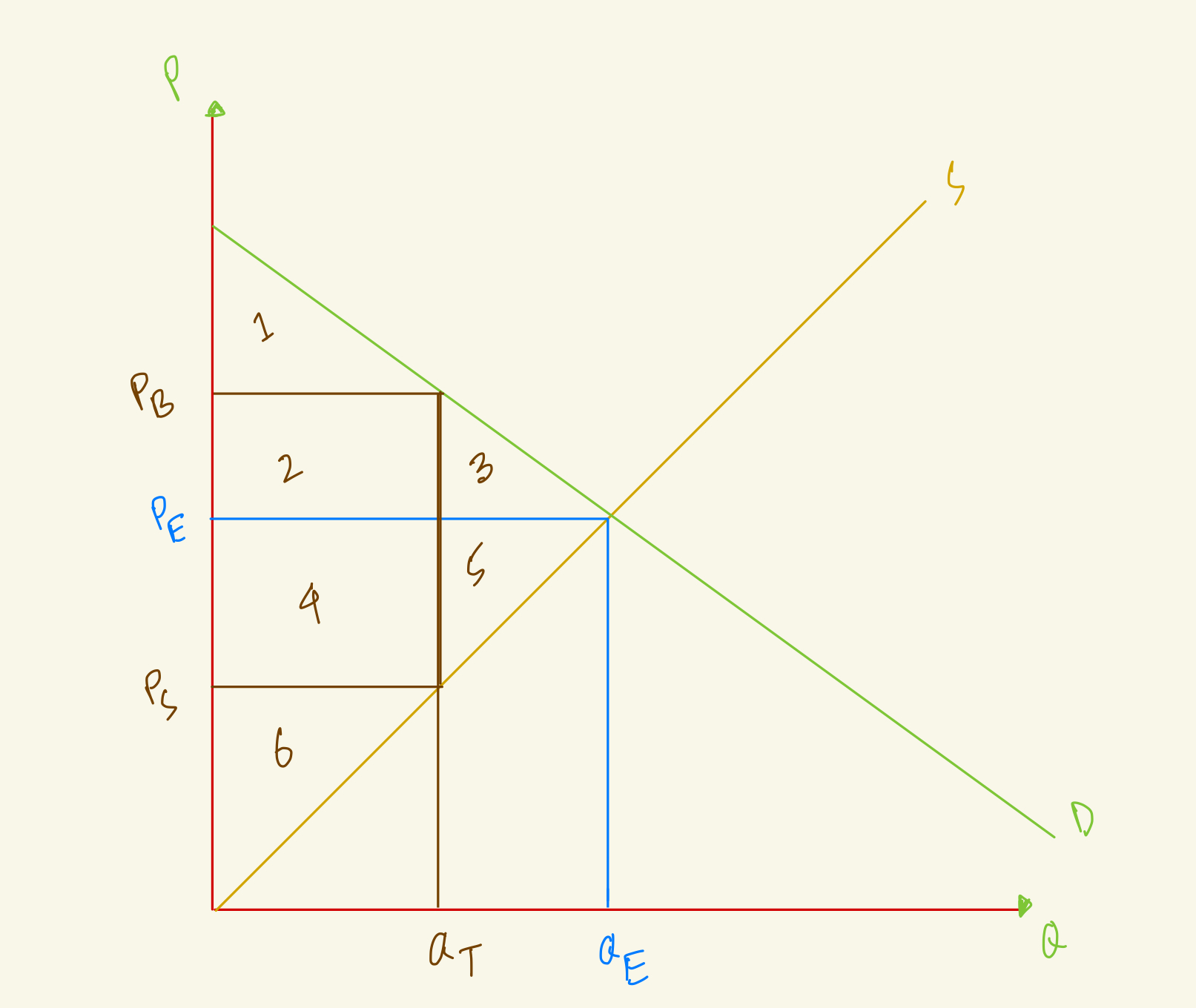
At the equilibrium, price is PE and quantity is QE, what's the consumer surplus in this market?
1+2+3
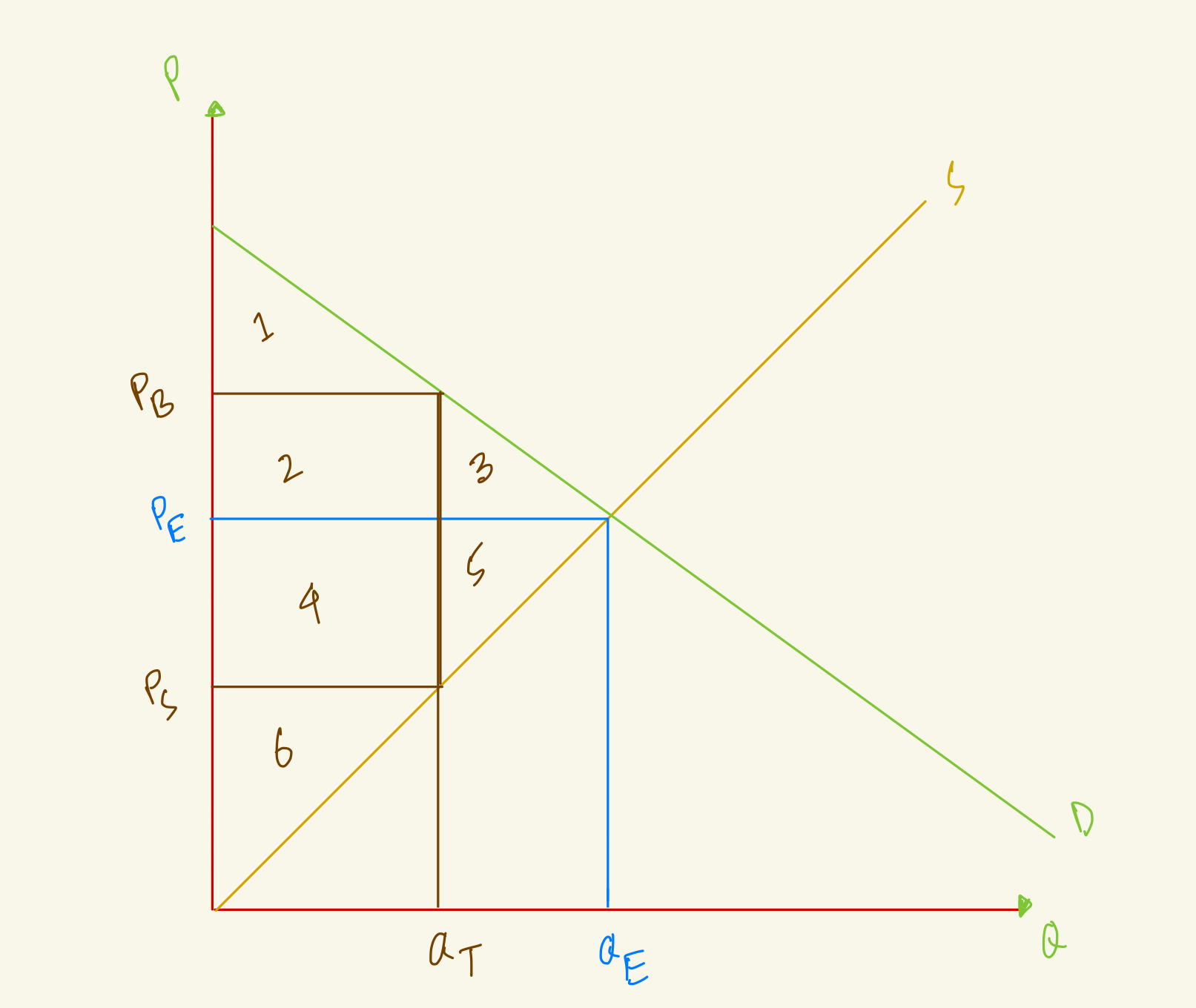
At the equilibrium, price is PE and quantity is QE. After tax, quantity in the market falls to QT, the amount that buyers pay rises to PB and the amount that sellers receive falls to PS. What's the total surplus in this market with tax?
1+2+4+6
A competitive firm shuts down in the short run if:
Price < AVC
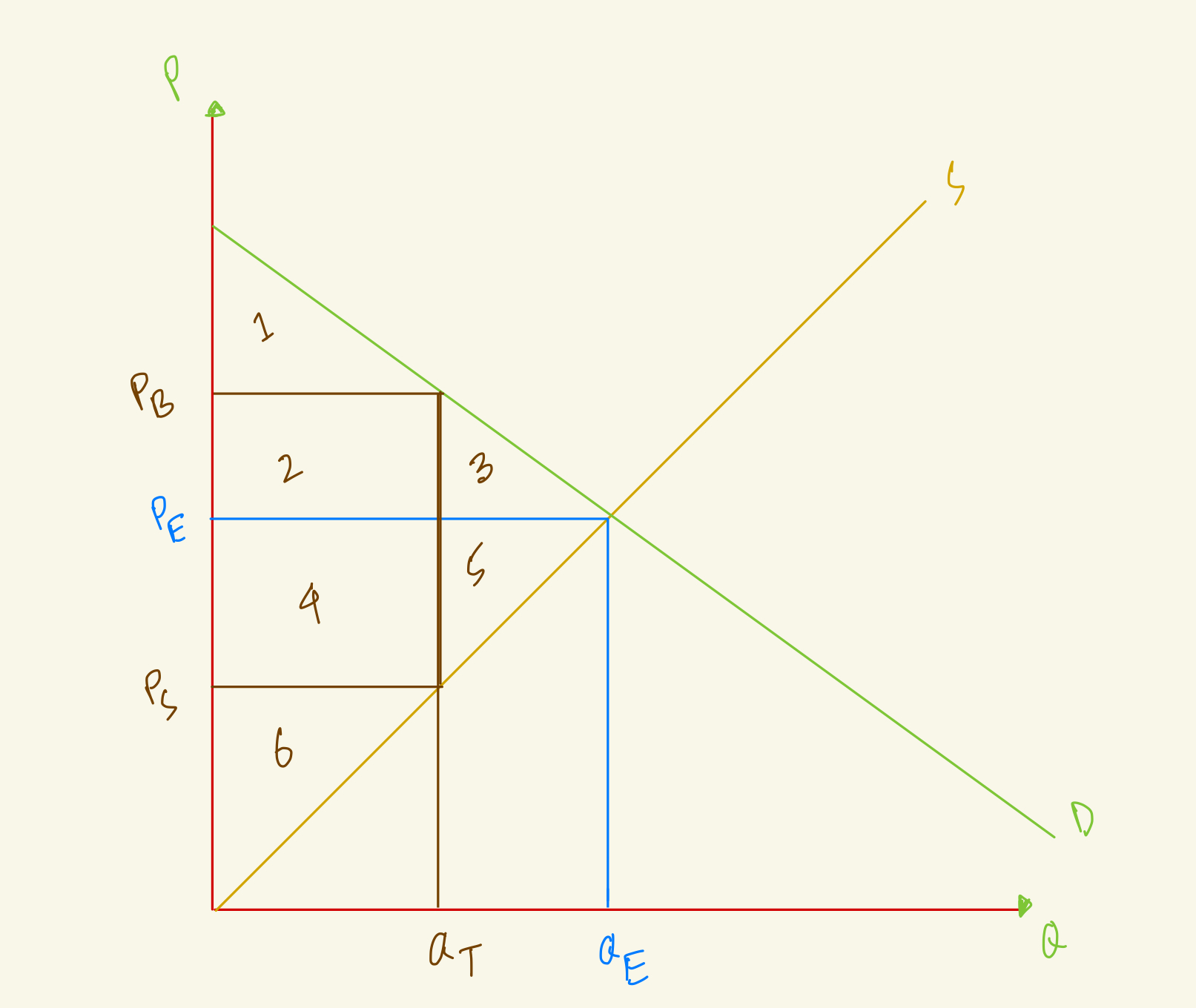
At the equilibrium, price is PE and quantity is QE. After tax, quantity in the market falls to QT, the amount that buyers pay rises to PB and the amount that sellers receive falls to PS. What's the consumer surplus in this market with tax?
1+2+3
Kurt invested $80,000 in the factory and equipment to start the business last year: $30,000 from savings and borrowed $50,000 (interest 10% for saving and borrowing). Calculate the implicit costs.
$3000
A firm exits the market in the long run when:
TR < TC
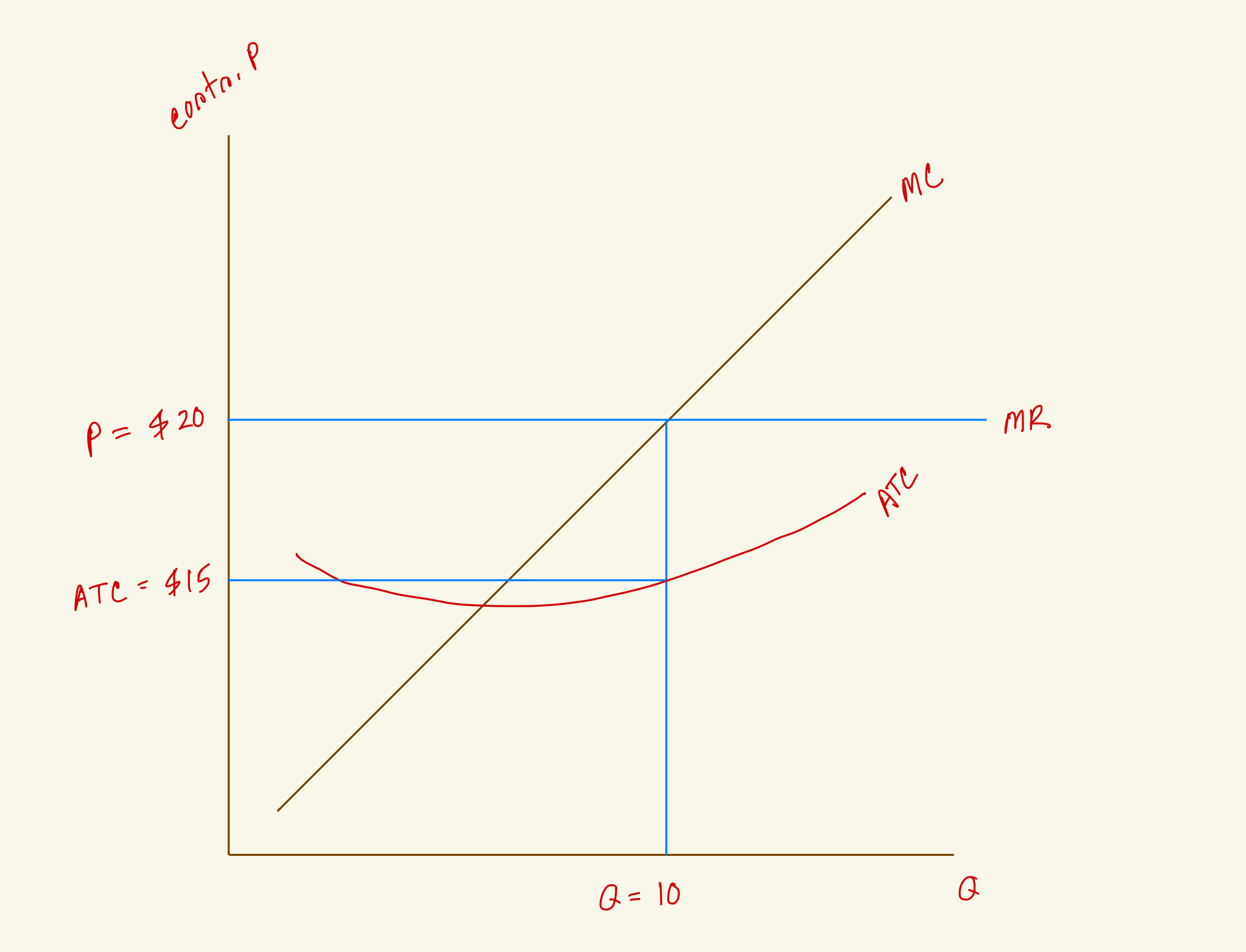
What's the total revenue for this firm in the diagram?
$200
If total cost is $200, fixed cost is $50, and 10 units are produced, what is AVC?
$15
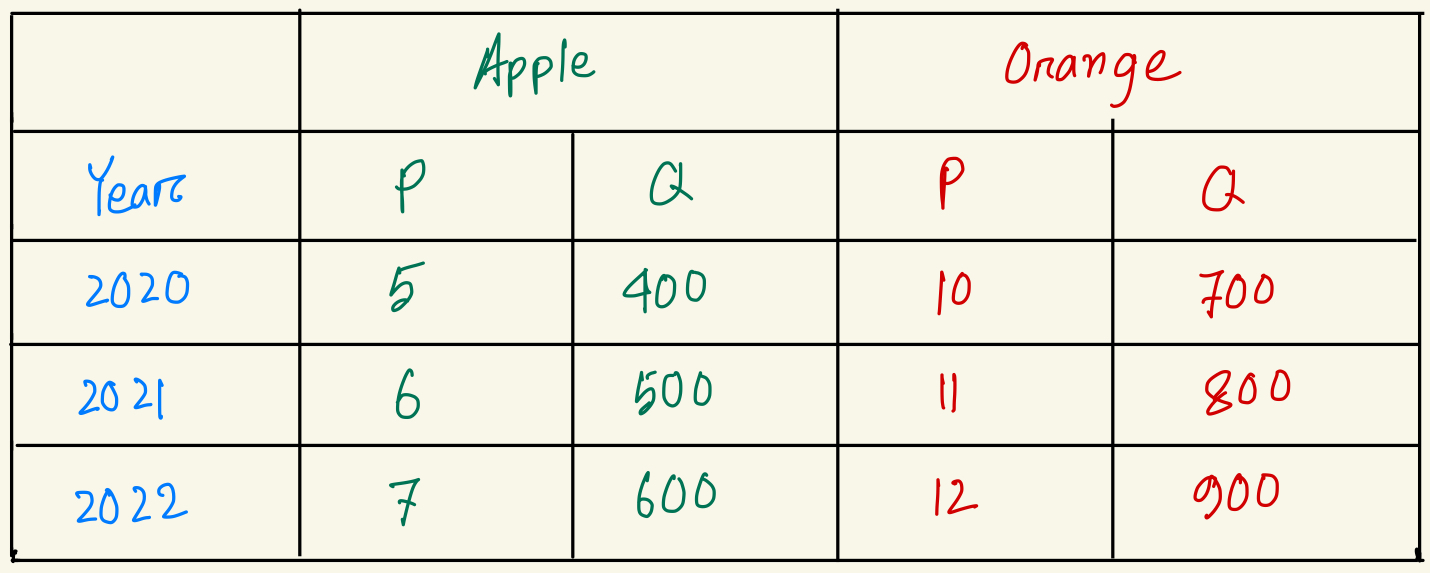
Calculate nominal GDP for year 2020.
$9000
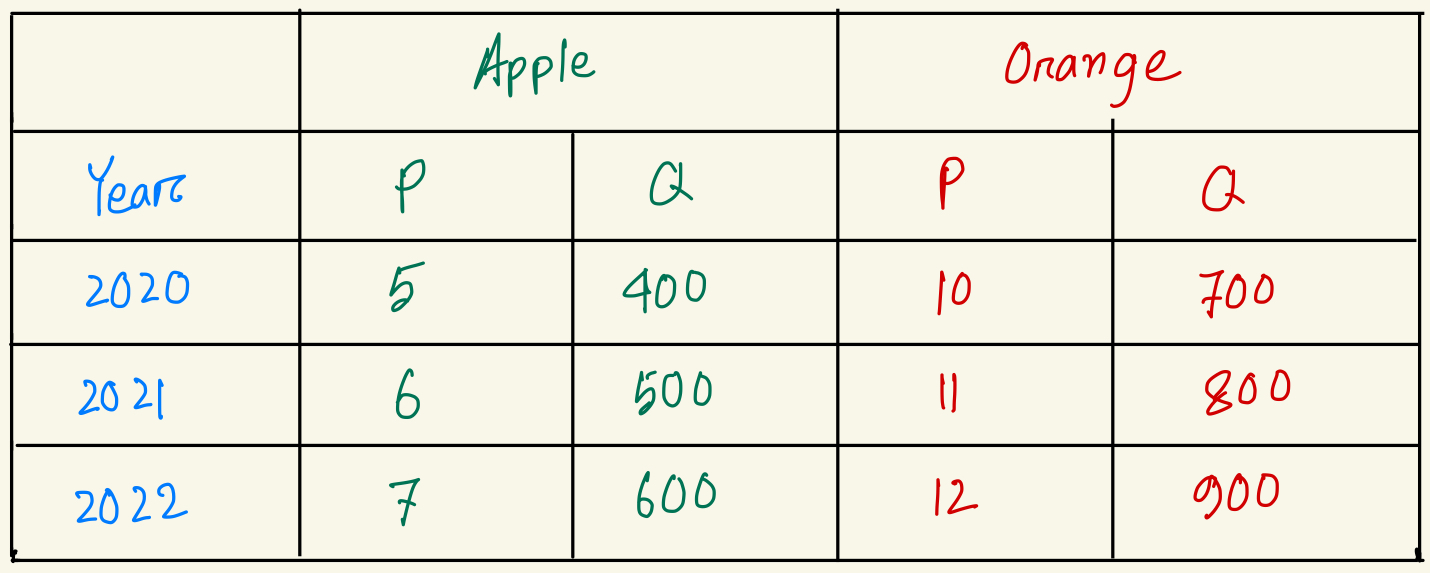
Calculate GDP deflator for year 2020. (base year 2020)
100
A car produced in 2021 and sold in 2022 would be included in 2022 GDP.
False
Calculate GDP deflator for year 2021. (base year 2020)
112.4
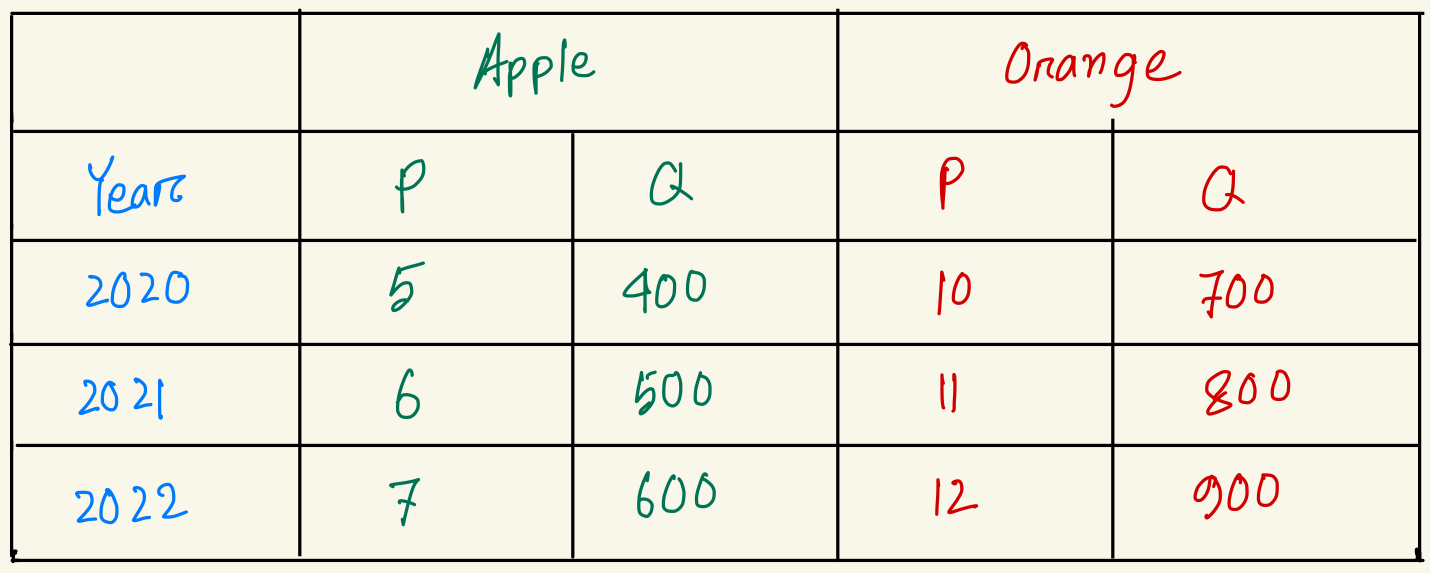
What's the inflation rate from year 2021 to year 2022?
11.21%
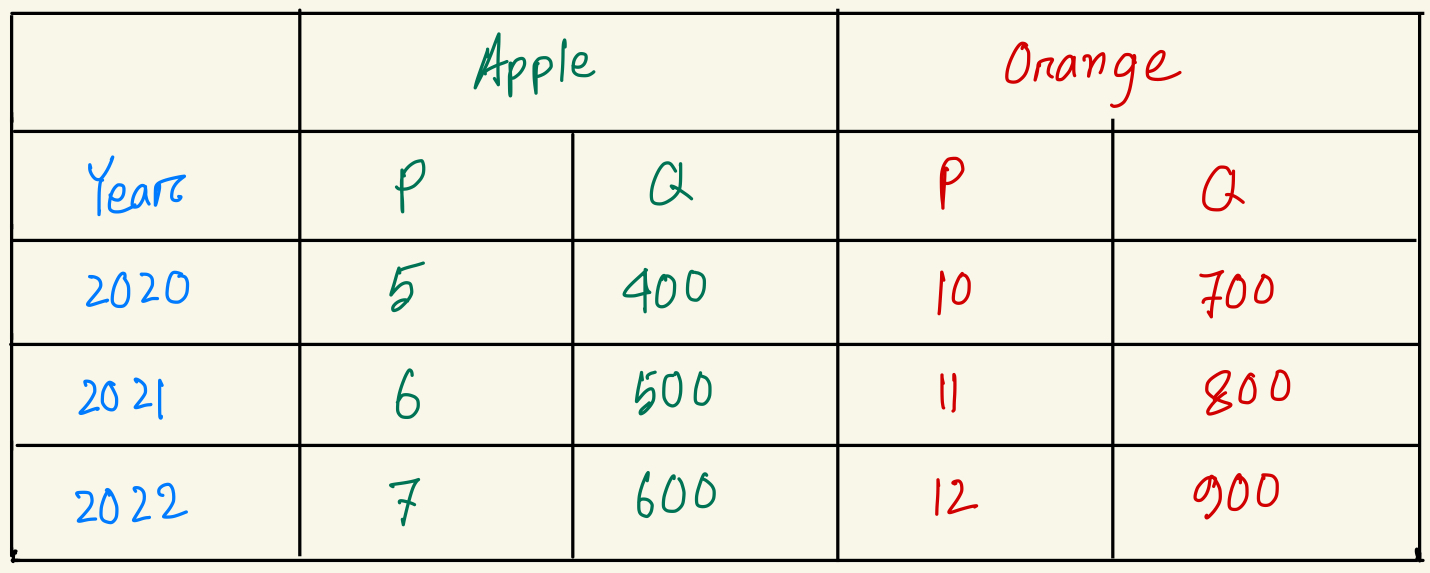
What's the percentage change in real GDP from year 2021 to year 2022? (base year 2020)
14.29% increase
An increase in the GDP deflator indicates rising prices.
True
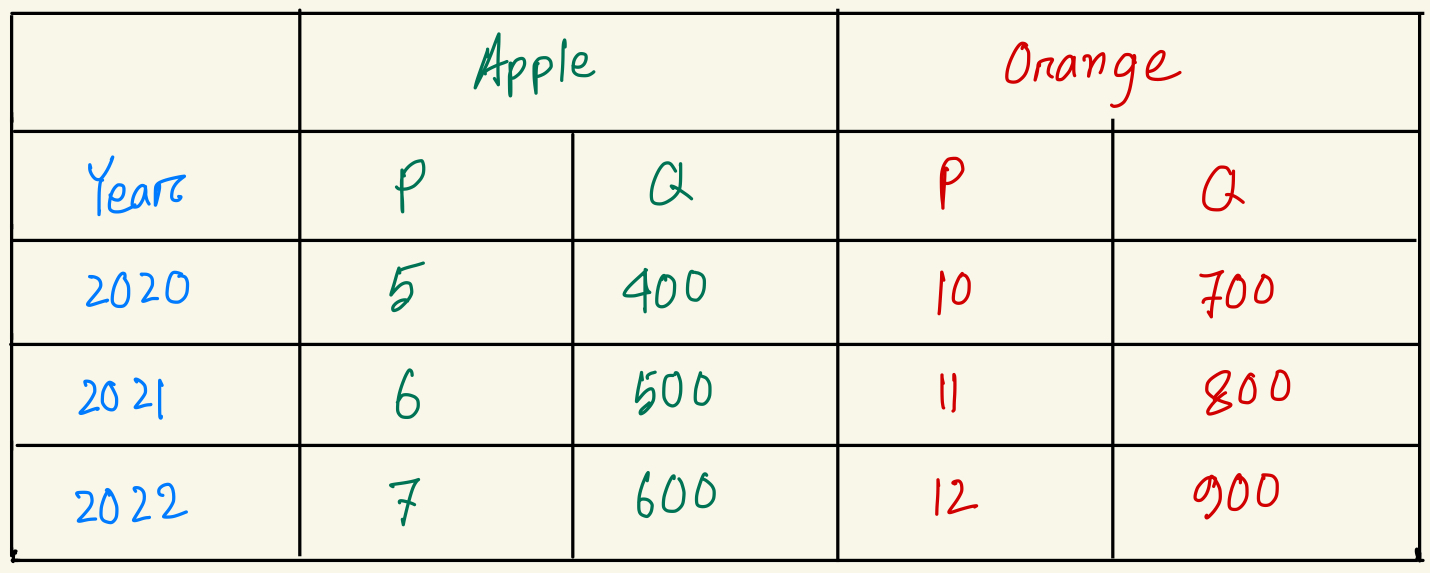
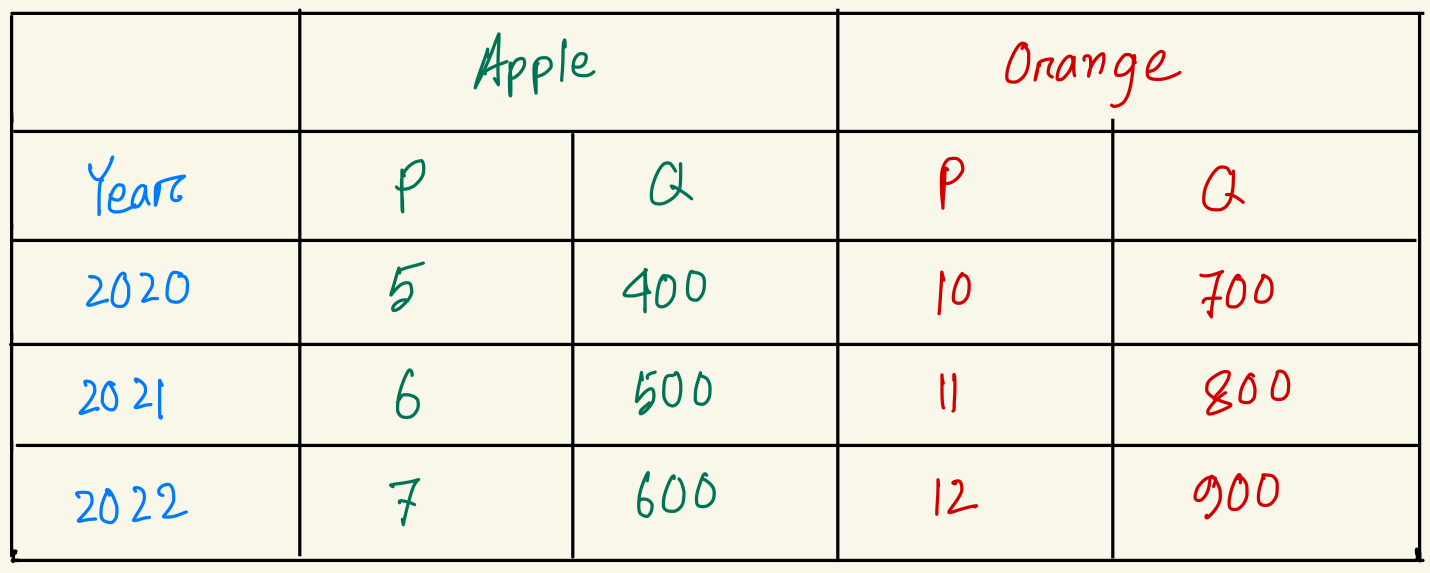
Compute real GDP for year 2022. (base year 2020)
$12000
How does the purchase of a new house affect GDP?
It is included in investment
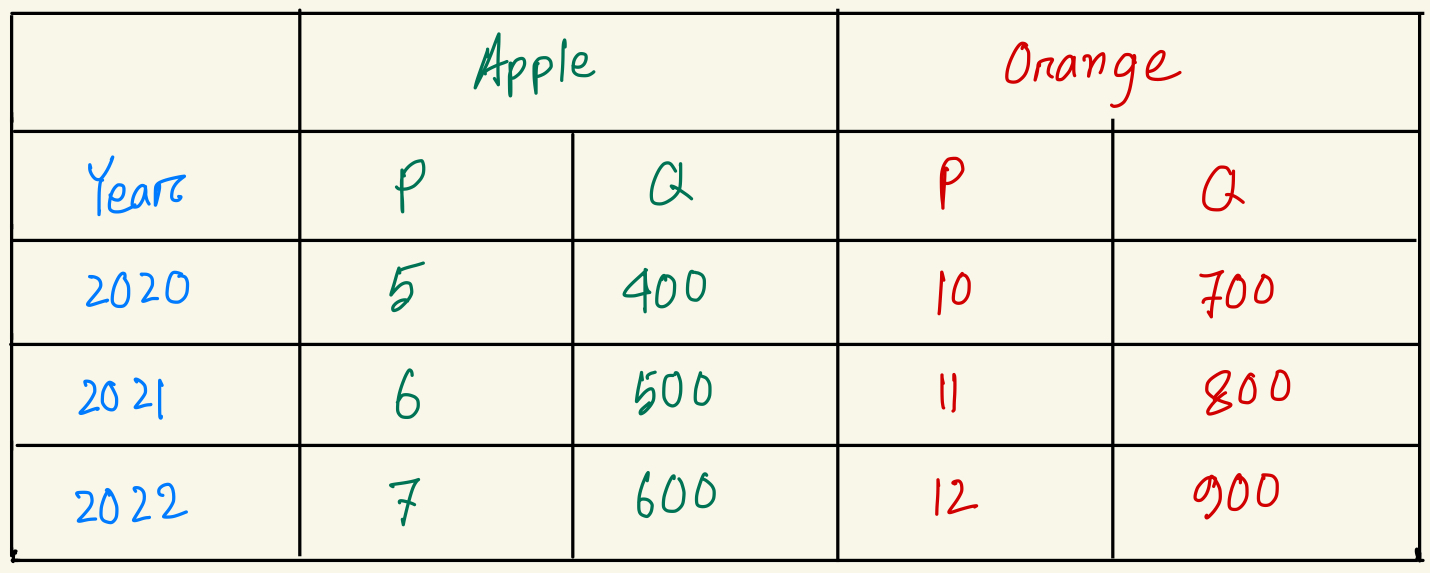
Whats's the percentage change in nominal GDP from year 2021 to year 2022?
27.12% increase
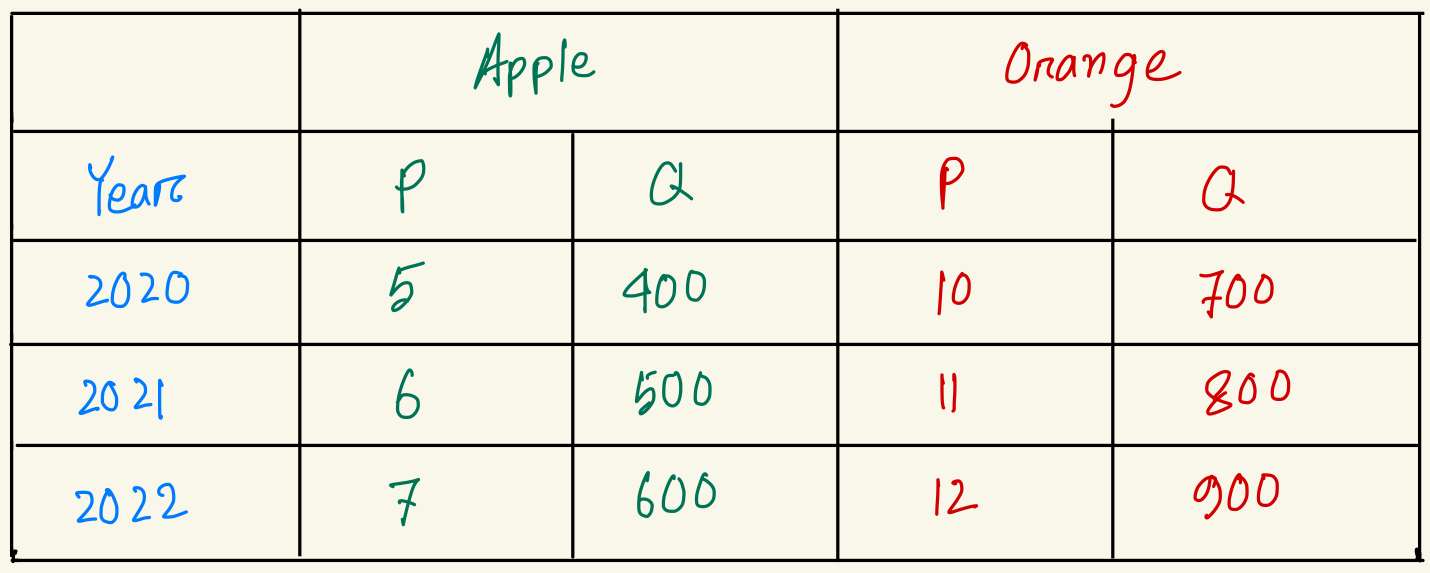
Calculate GDP deflator for year 2022. (base year 2020)
125
You buy $2000 worth of Tesla stock, and hold it for 30 years. If the rate of return is 12%, how long will it take for this investment to double in amount?
5.83
You are thinking about purchasing a lot for $100000. The lot will be worth $150000 in 10 years. You should buy the lot if the market interest rate is 3%.
True
You received $500 from your grandma for your birthday. If you decide to deposit the money in the bank at a 5% interest rate, what will be the future value of this amount after 5 years?
$638.14
What is the future value of $5,000 invested at a 7% annual interest rate for 10 years?
$9835.75
What is the present value of receiving $2,000 in 5 years if the annual interest rate is 6%?
$1494.57
You are thinking about purchasing a lot for $100000. The lot will be worth $150000 in 10 years. You should buy the lot if the market interest rate is 7%.
False
If an investment grows at a rate of 7% per year, how long will it take for the amount to double?
10 years
If you need to have $50000 in 5 years for Grad school and if the market interest rate is 10%, how much do you need to deposit today?
$31046
What is the present value of $1,000 to be received in 3 years at an interest rate of 10%?
$751.31
Nominal GDP is valued at:
Current prices
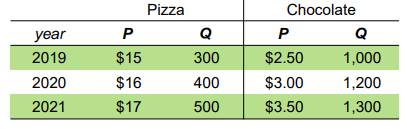
What's the inflation rate from year 2019 to year 2020?
11.1%
A country can have rising nominal GDP but falling real GDP.
True
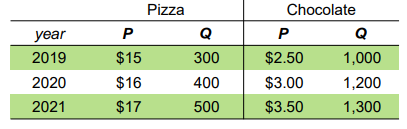
Calculate GDP deflator for year 2020.
111.1
The value of intermediate goods is:
Not counted separately in GDP
If the GDP deflator in 2022 is 105 and in 2023 it is 115, what is the inflation rate?
9.5%
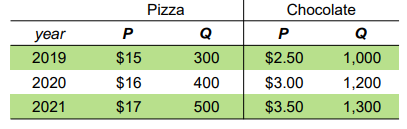
What's the percentage change in real GDP from year 2020 to year 2021? (base year 2019)
19.4% increase
Suppose a country’s GDP increases by 10%, but prices increased by 8%. What happened to real GDP?
Increased by 2%
A new car produced in 2023 but sold in 2024 is counted in GDP of:
2023
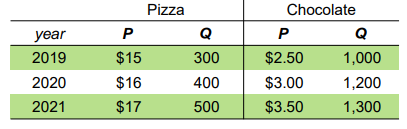
Calculate GDP deflator for year 2021.
121.4
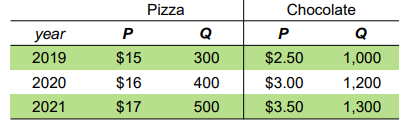
Calculate nominal GDP for year 2019.
$7000
GDP measures:
Total income of everyone in the economy
Total expenditure on the economy’s output
If an Italian company produces shoes in the U.S., the value is:
Part of U.S. GDP
Which of the following is included in GDP?
The purchase of a newly built house
Transfer payments are excluded from GDP because:
They do not reflect current production
In 2023, consumption = $12T, investment = $3T, government purchases = $5T, and net exports = -$1T. What is GDP?
$19T
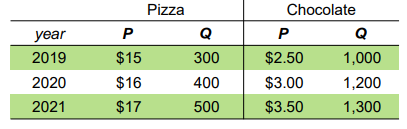
Whats's the percentage change in nominal GDP from year 2020 to year 2021?
30.5% increase
GDP per capita is used to measure:
Standard of living
Suppose in 2023, nominal GDP is $22 trillion and the GDP deflator is 110. What is real GDP?
$20 trillion
Real GDP adjusts for:
Price changes