A&P II Respiratory System Exam 1
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Pulmonary ventilation
movement of air into and out of lungs (ventilation of lungs, breathing)
External Respiration
O2 and CO2 exchange between the air in the lungs and blood in the capillaries
Internal respiration
O2 and CO2 exchange between the blood and the cells, O2 utilization and CO2 production by cell metabolism (cellular respiration)
upper
nose and pharynx are part of the ________ respiratory system
lower
larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs are part of the _______ respiratory system
conducting zone
moves air (no gas exchange) from mouth/nose to bronchioles
superior external
nasal and parts of the maxillae and frontal bones are part of the _____ _____ nose
inferior external
cartilage plates held by CT are part of the _____ _____ nose
nasal cavity
extends from the external nares to the nasopharynx posteriorly
nasal septum
nasal cavity is divided by the _____ into rt and lt chambers
cartilage
anterior nasal septum is made up of ______
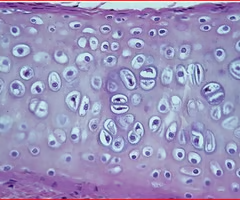
ethmoid and vomer bone
posterior nasal septum is made up of _____________
nasal roof
cribriform plate of ethmoid bone
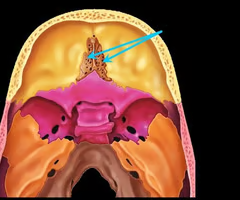
lateral walls
3 bony projections from each wall
superior, middle, and inferior Conchae
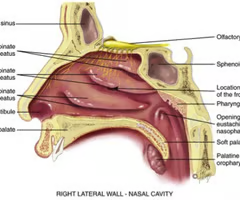
meatuses
between each conchae are recesses
Superior, middle, and inferior _______
nasal cavity floor
formed by bony hard palate + soft palate
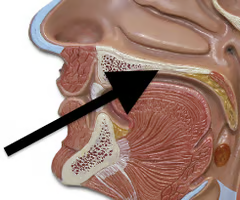
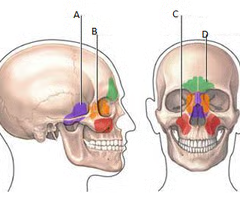
paranasal sinuses
air spaces located in bones of skull which open into the meatuses
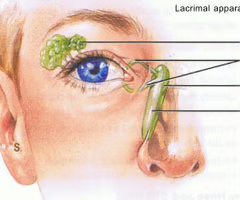
nasolacrimal ducts
drain tears into the nasal cavity
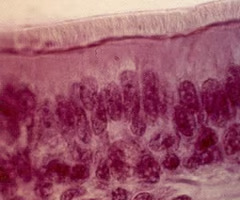
mucous membrane
lining of the nasal cavity + paranasal sinuses
contains large # of mucus secreting goblet cells and ciliated cells
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
type of cells that line the nasal cavity (make up the mucous membrane)
warms, saturates, traps, antibacterial
the function of mucous membrane:
_____ inhaled air (bv)
_____ inhaled air with water
_____ small particles
used as _____ agents: nerve endings → sneeze
paranasal sinuses
mucous membrane inflammation leads to this being mucus filled, less resonant voice, more pressure (headaches)
Eyes
This mucous membrane covering is via nasolacrimal duct → red watery eyes
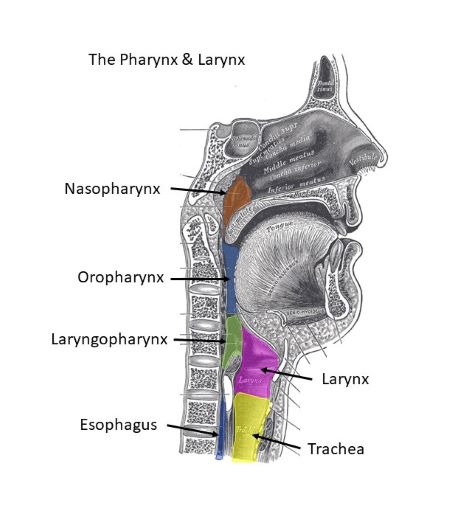
pharynx
divided into bronchi or eustachian tubes
In mucous membrane inflammation, coughing or bronchitis in bronchi, stuffed up in eustachian tubes
pharynx
muscular tube used by both the digestive system and the respiratory system
nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
pharynx divided into these three regions
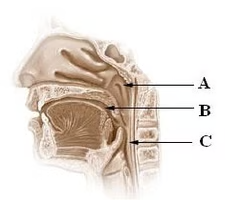
internal nares
The nasopharynx is continuous with the nasal cavity through the ______ _______
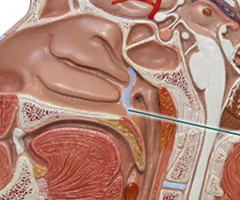
eustacian
The nasopharynx connects with the middle ear via the ______ tubes on the lateral wallsThe nasopharynx connects with the middle ear via the ______ tubes on the lateral walls
tubal tonsil
lymphoid tissue near the eustacian tube openings
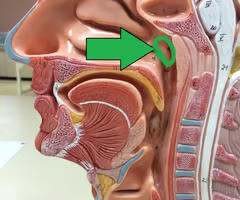
pharyngeal tonsil
in posterior wall of nasopharynx
when enlarged, termed adenoids
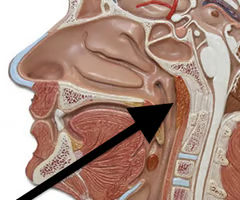
soft palate
oropharynx extends from the ___ ______ to the beginning of the larynopharynx
oral
oropharynx communicates with the ____ cavity
stratified squamous epithelium
type of epithelium lining oropharynx
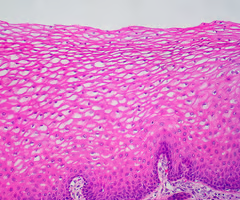
esophagus
laryngopharynx extends from oropharynx above the larynx and the ______ below
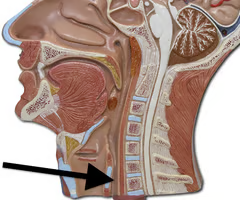
larynx
connects the laryngopharynx with the trachea; sound production
6, 3
Larynx is formed by 9 cartilages:
__ paired, __ unpaired
ligaments and muscles
hold the cartilages of the larynx together (intrinsic muscles) + attach them to the hyoid bone (extrinsic muscle)
hyoid bone
What is this structure?
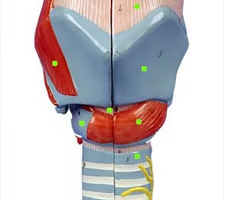
thyroid cartilage
What is this structure?
formed by the joining of 2 broad plates of cartilage (“adams” apple = laryngeal prominence: anterior angle)
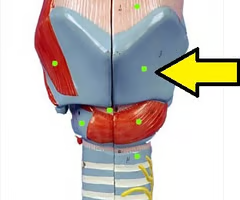
cricothyroid ligament
What is this structure?
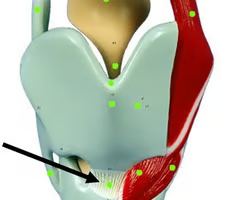
cricotracheal ligament
What is this structure?
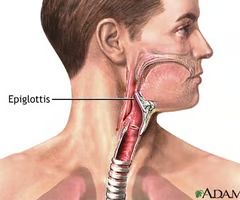
epiglottis
What is this structure?
leaf-shaped; attached to the thyroid inner surface
Acts like a flap which alllows air to enter the larynx but during swallowing in blocks the opening of the larynx
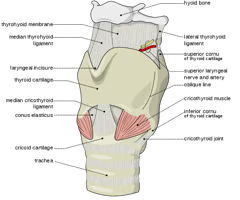
thyroihyoid membrane
What is this structure?
cuneiform cartilage
What is this structure?
corniculate cartilage
What is this structure?
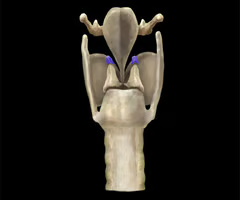
arytenoid cartilage
What is this structure?
most important of the paired cartilages
small, pyramidal, rest on the superior-posterior border of the cricoid cartilage
movement of these → varying tension on the cord
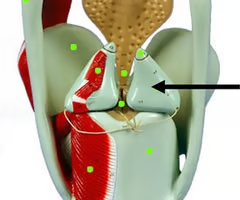
cricoid cartilage
What is this structure?
ring-shaped; anchored to the thyroid cartilage above + trachea below
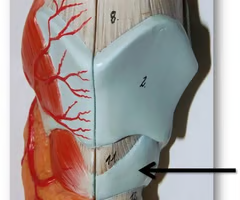
laryngeal cartilage
hyaline cartilage (except epiglottis = elastic cartilage)
ventricular folds
another name for false vocal cords
the superior pair of folds
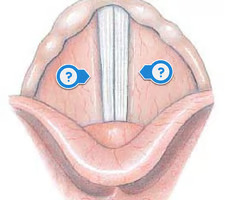
true vocal cords
inferior pair of vocal folds
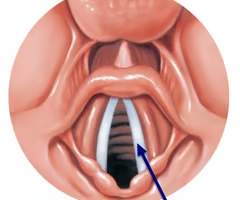
glottis
opening between the vocal folds (rima glottidis) + vocal folds
within vocal folds are bands of elastic ligaments
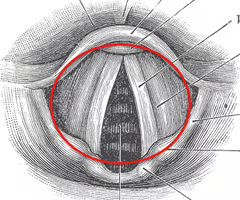
glottis
air passing through the ______ will cause vocal cord vibration which will lead to sound
pitch
you can change this by changing vocal fold tension → changing vocal cord vibration frequency
deeper
longer and thicker vocal cords mean a ________ voice
laryngitis
irritation or inflammation of the mucous membrane covering the larynx
→ swelling → interference with fold vibration → hoarseness
2.5, 1
the trachea is __cm or _in in diameter
12, 5
the trachea is __cm or _in long
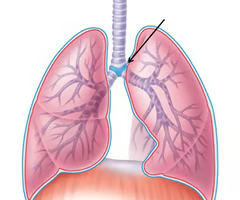
carina
extends from larynx to T(5-7) level where it divides into the right and left primary bronchi
esophagus
trachea lies anterior to the ________
hyaline cartilages
trachea is surrounded by a series of C-shaped _________ which prevent it from collapsing
elastic CT
With the trachealis muscle, it joins C-shaped tracheal rings posteriorly.
pseudostratified ciliated columnar
trachea contains mucosa lining with this type of epithelium with goblet cells
cilia
smoking causes a decrease in these structures in the trachea
coughing would be only way to prevent mucus from accumulating in lungs
cartilage rings
walls of the primary bronchi supported by incomplete _______________
vertical
right primary bronchus is more _________
3,2
the right lung has __ secondary bronchi and the left lung has _ secondary bronchi.
smooth muscle
walls of the cartilage do not contain cartilage, rather, they are completely surrounded by ________
spasm
asthmatic attack connurs in terminal bronchiole due to sm. muscle _____ → airways squeezed shut (since no cartilage support) → breathing difficulties
dilation
sympathetic NS → sm. muscle relaxation → bronchiole ________
constriction
parasympathetic NS → sm. muscle contraction → bronchiole ________