41. Cardiovascular System: Anatomy, Heart Failure, & Congenital Cardiac Defects
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What are the functions of the cardiovascular system?
M
F
maintain an adequate and steady supply of nutrients to all organs and tissues of the body
facilitate removal of waste products from organs and tissues
a progressive clinical syndrome of impaired pumping of the heart that decreases ventricular ejection thus impeding venous return
heart failure
decreased pumping that results in an inability to maintain arterial pressure
low output heart failure
inability to empty venous reservoirs
congestive heart failure
True or false: There can be a combination of both low output heart failure and congestive heart failure.
true
Heart failure can be either ________ or ________.
acute; chronic
True or false: Congestive heart failure is a clinical syndrome that can be right sided, left sided, or both.
true
What are clinical signs associated with right sided congestive heart failure?
C
A
H
M
S
P
chronic hepatic passive congestion “nutmeg liver”
ascites
hydroperitoneum
modified transudate (protein rich) peritoneal effusion
subcutaneous edema
pleural effusion (in small animals, this is a sign of biventricular CHF)
What clinical sign is associated with left sided congestive heart failure?
pulmonary edema
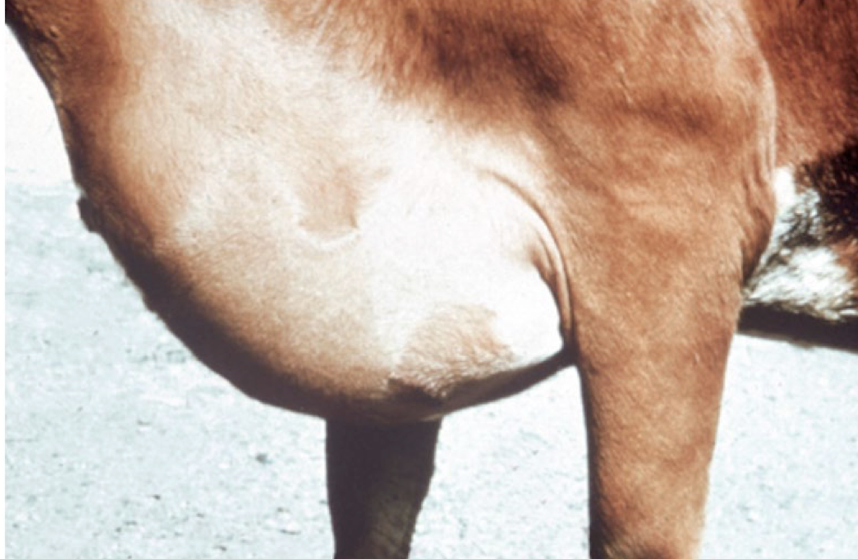
This is typically associated with what clinical syndrome?
right sided heart failure
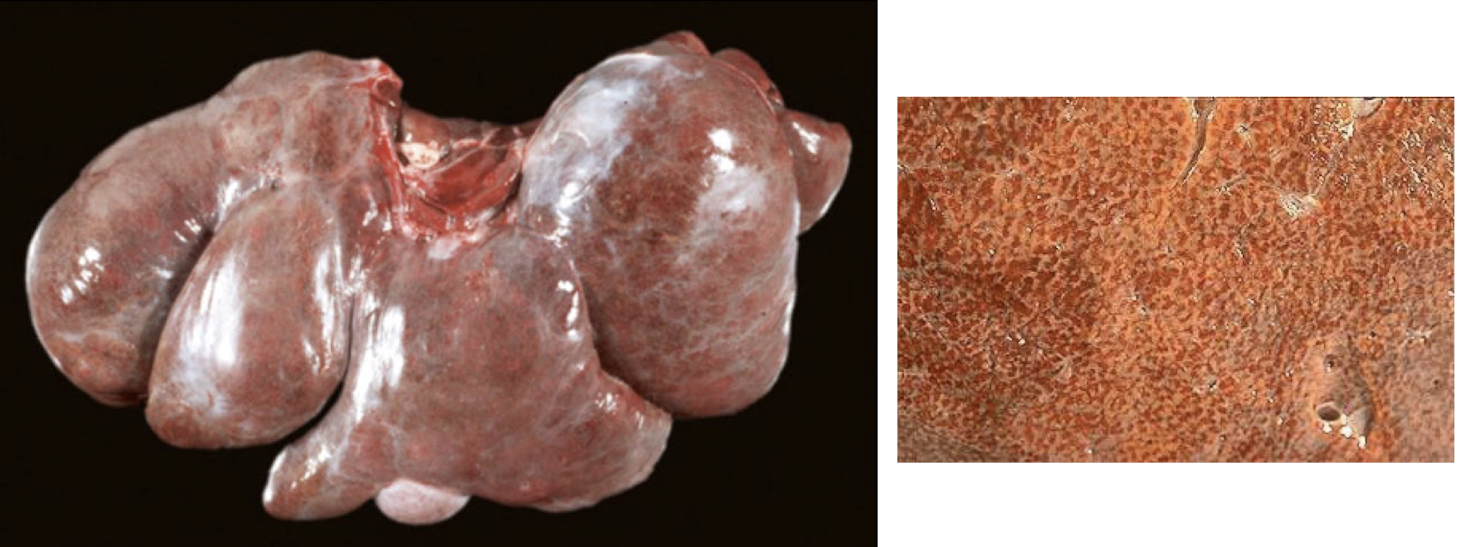
What clinical syndrome is this typically associated with?
right sided heart failure
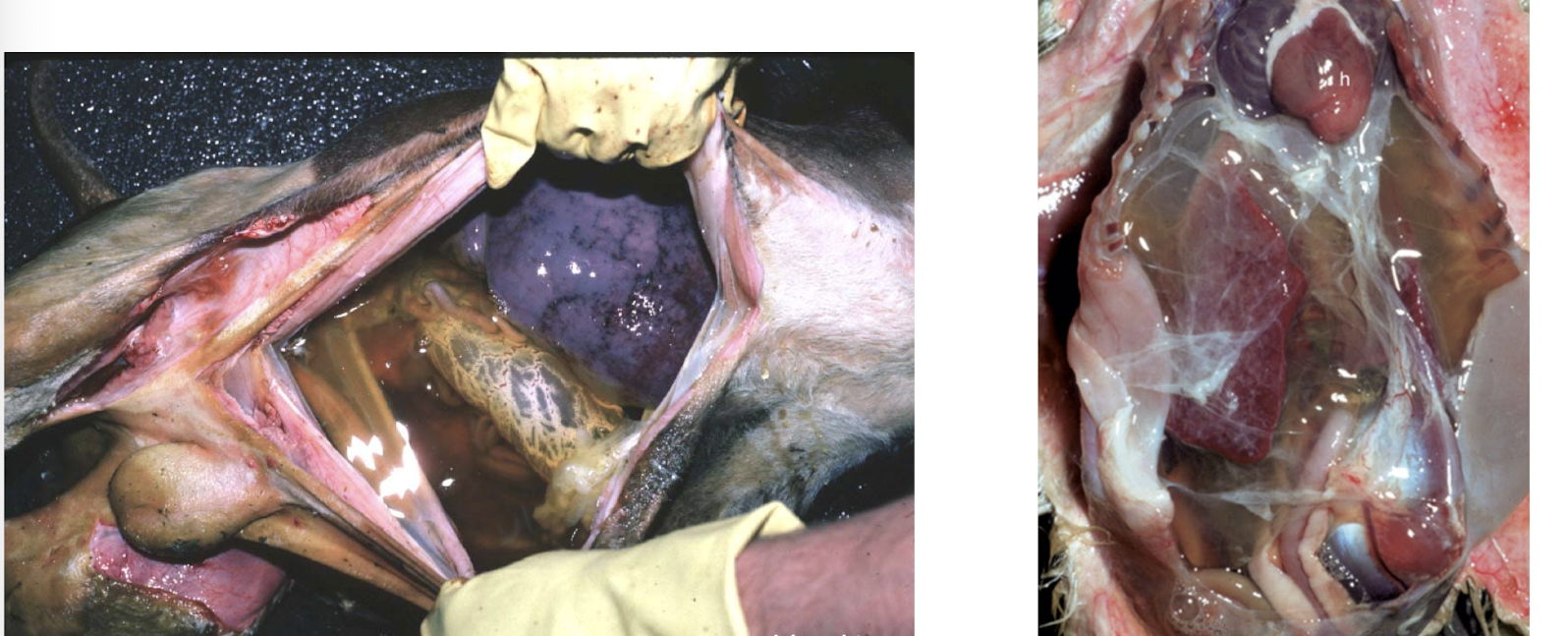
This symptom is commonly associated with what clinical syndrome?
right sided heart failure
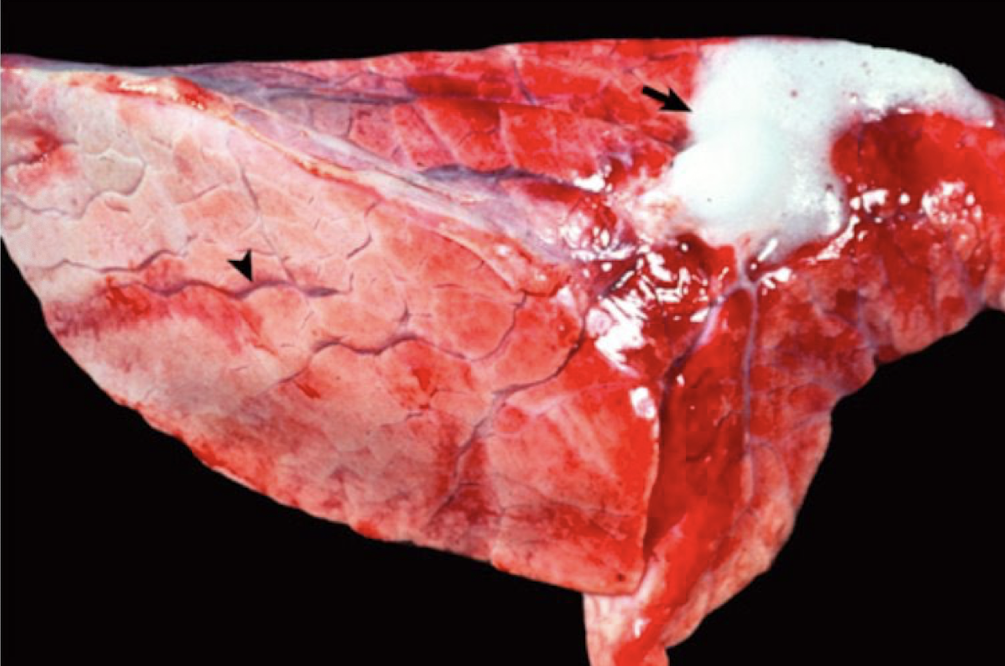
What clinical syndrome is this associated with?
left sided heart failure
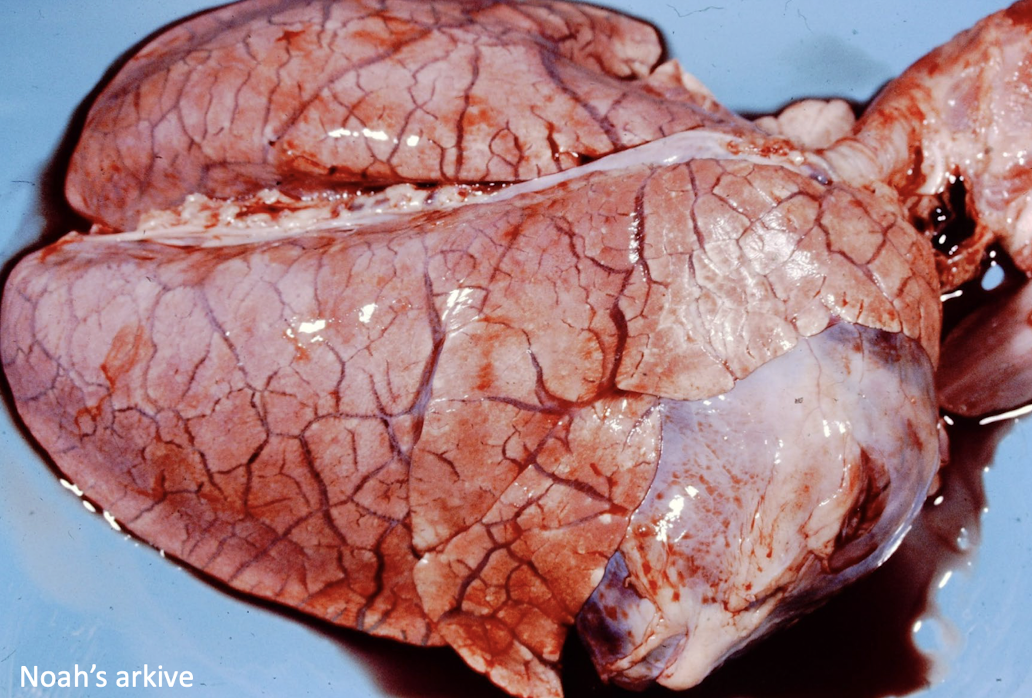
This is associated with what clinical syndrome?
left sided heart failure
What is a sign of bilateral (right and left sided) congestive heart failure in small animals?
pleural effusion
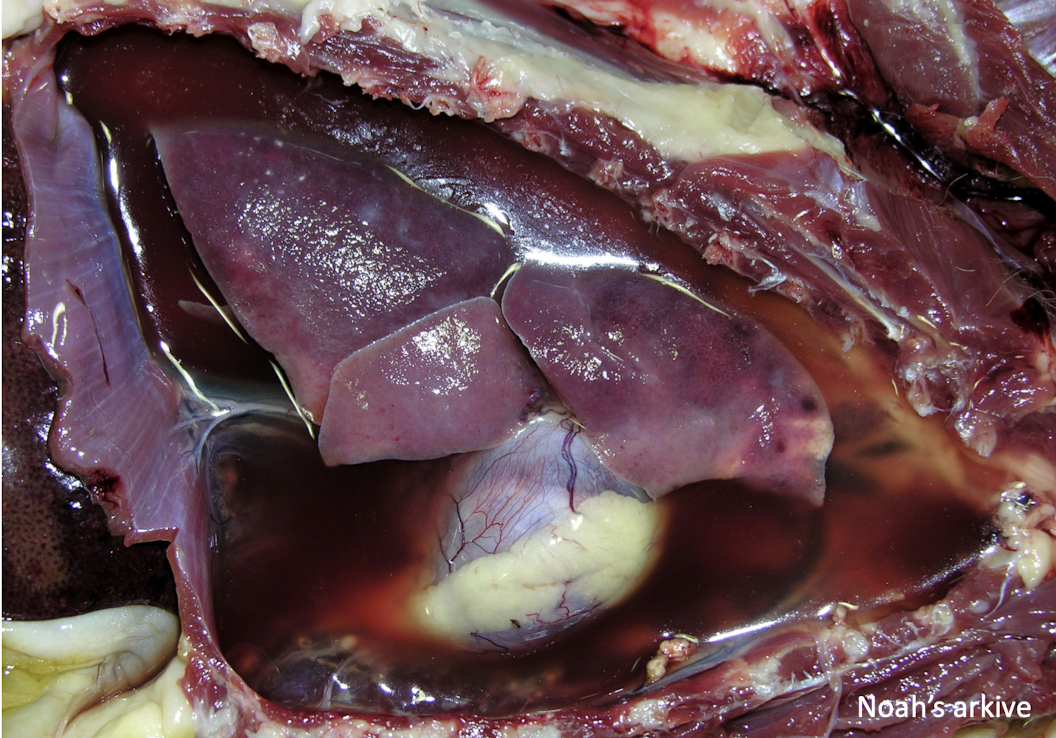
This is typically associated with what clinical syndrome?
bilateral congestive heart failure
increase in muscle mass due to increased size of cardiac muscle cells
myocardial hypertrophy
What are the two forms of myocardial hypertrophy?
C
E
concentric hypertrophy
eccentric hypertrophy
form of myocardial hypertrophy in which the myocardium thickens, narrowing the ventricular lumen
concentric hypertrophy
In concentric hypertrophy, what is the hypertrophied ventricle prone to? What does this lead to?
ischemia; fibrosis
Concentric hypertrophy occurs with what?
pressure overload
form of myocardial hypertrophy in which there is an increase in the length of the myofibers
eccentric hypertrophy
What will eccentric hypertrophy result in?
ventricular dilation with normal to decreased wall thickness
What does eccentric hypertrophy occur with?
volume overload
What are the two main causes for congen
What are other causes for congenital cardiac malformations?
D
X
F
M
drug or toxic compound induced
x-irradiation
fetal hypoxia
maternal nutritional imbalances
What are common drugs/toxins that can cause congenital cardiac malformations?
salicylates (in aspirin) and griseofulvin
What is a specific maternal nutritional imbalance that can lead to congenital cardiac malformations?
vitamin A deficiency/excess
What results in volume overload of the pulmonary circuit? What will this lead to?
left to right shunting; left atrial and ventricular eccentric hypertrophy
Which congenital cardiac malformations result in volume overload?
V
P
P
A
ventricular septal defect
patent foramen ovale
patent ductus arteriosus
atrial septal defect
What is the most common congenital cardiac defect of cattle and horses?
ventricular septal defect
What are the two types of ventricular septal defects?
high and low
ventricular septal defect that is located just below the aortic semilunar valves and is most common
high defect
ventricular septal defect that is closer to the apex of the heart
low defect
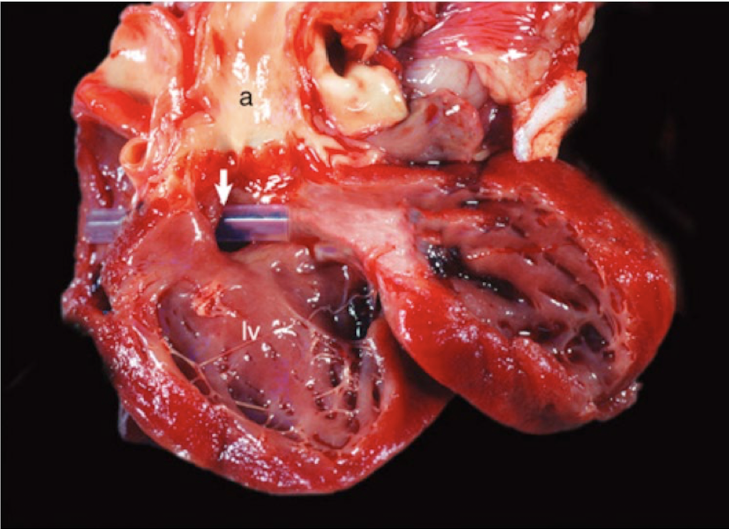
What is this showing?
ventricular septal defect
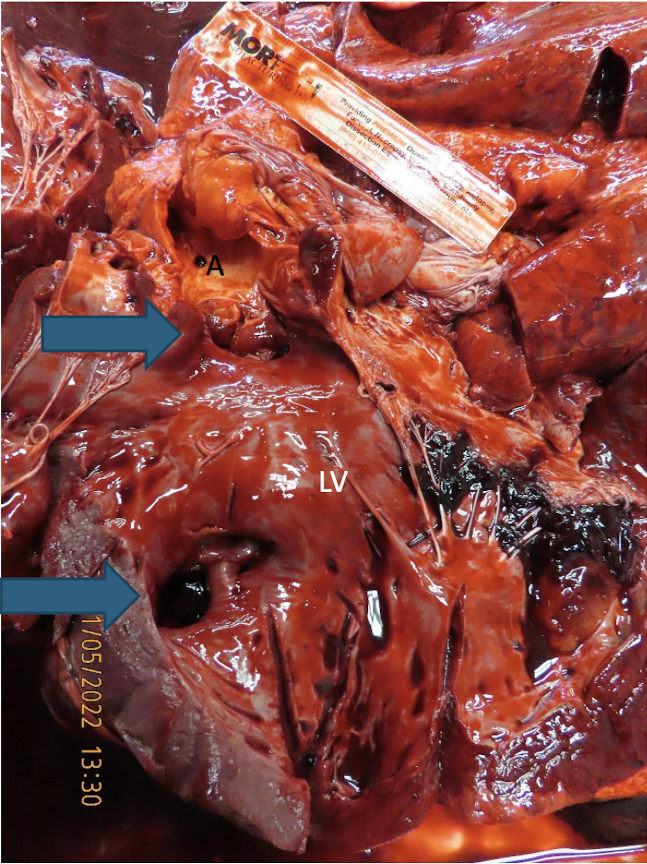
What is this showing?
high and low ventricular septal defect
What is the most common congenital cardiac defect in small ruminants?
patent foramen ovale
one of the two pulmonary bypases in a fetus that connects the right atrium to the left atrium and is best visualized by opening the caudal vena cava ostia that closes after birth with a small flap of connective tissue, which covers the opening due to the pressure change of taking a first breath
foramen ovale
What is this showing?
patent foramen ovale
What is the most common congenital cardiac defect in dogs?
patent ductus arteriosus
the second pulmonic fetal bypass to the lungs that connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta
ductus arteriosus
failure of the closure of the ductus arteriosus
patent ductus arteriosus
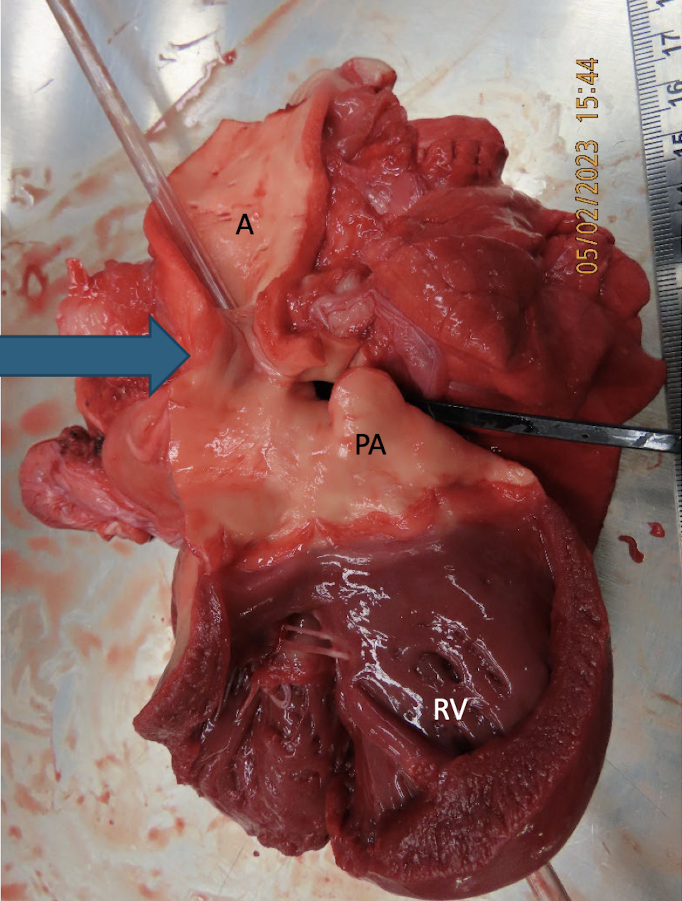
What is this showing?
patent ductus arteriosus
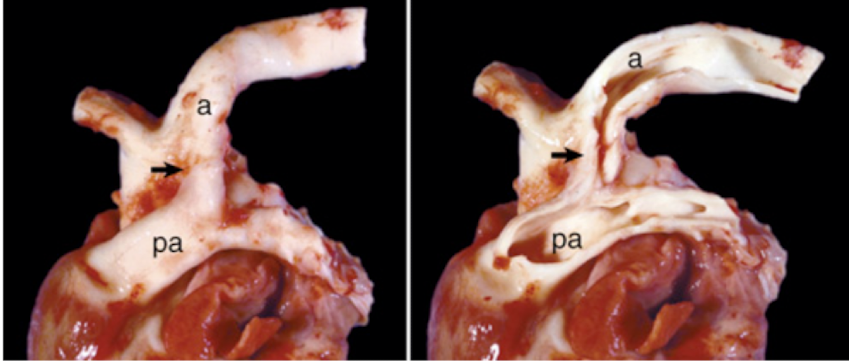
What is this showing?
patent ductus arteriosus
What is the second most common septal defect in cattle
atrial septal defect
What are the two types of atrial septal defects? Which is most common?
septum primum and septum secundum; septum secundum
atrial septal defect that is adjacent to the foramen ovale
septum primum
atrial septal defect that is in the mid atrial septum
septum secundum
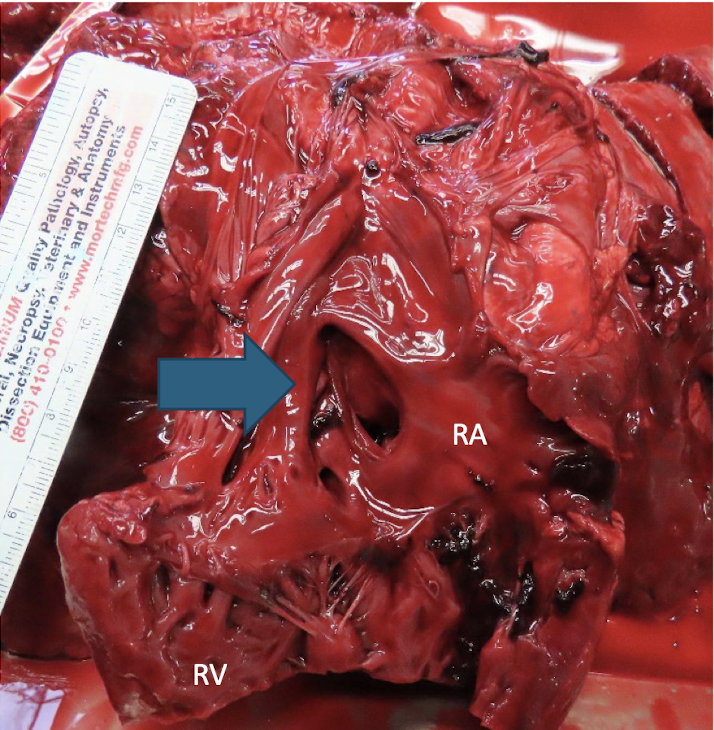
What is this showing?
atrial septal defect
In congenital cardiac malformations that result in pressure overload, what will ventricular outflow obstruction lead to? This will then lead to what?
progressive increase in intraventricular pressure; concentric ventricular hypertrophy
What are the congenital cardiac malformations that result in pressure overload?
P
S
pulmonic stenosis
subaortic stenosis
What is the second most common congenital cardiac malformation in dogs?
pulmonic stenosis
development of a dense band of fibrous muscular tissue below the pulmonic semilunar valves with or without malformation of the valve
pulmonic stenosis or subaortic stenosis
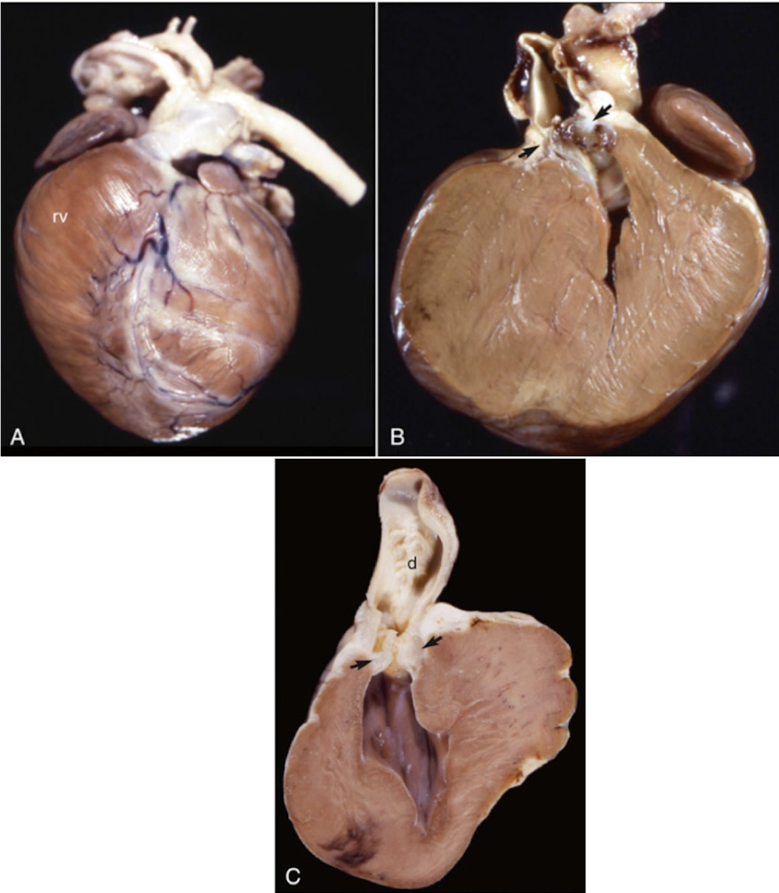
What is this showing?
pulmonic stenosis
What is the most common congenital cardiac malformation in the pig and the third most common malformation in the dog?
subaortic stenosis
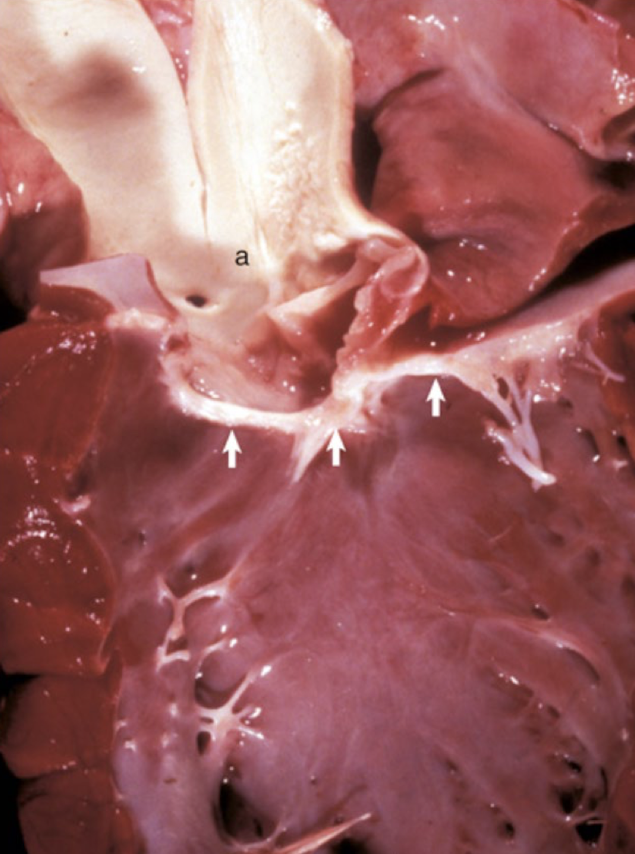
What is this showing?
subaortic stenosis
What congenital cardiac diseases result in cyanosis and collapse due to reduced cardiac output?
T
T
tricuspid/mitral valvular dysplasia
tetralogy of fallot
What is the most common congenital cardiac defect in cats and is also frequently seen in pigs?
tricuspid/mitral valvular dysplasia
Is mitral or tricuspid valvular dysplasia more common?
tricuspid
Valvular dysplasia can be a combination of what?
S
I
E
D
A
shortened, rolled, or notched valves
incomplete separation of the valve leaflets from the wall
elongation, shortening, fusion, or thickening of the chordae tendinae
direct insertion of the valve into a papillary muscle
atrophy, fusion, or malpositioning of the papillary muscles
True or false: Valvular dysplasia can be seen in conjunction with septal defects.
true
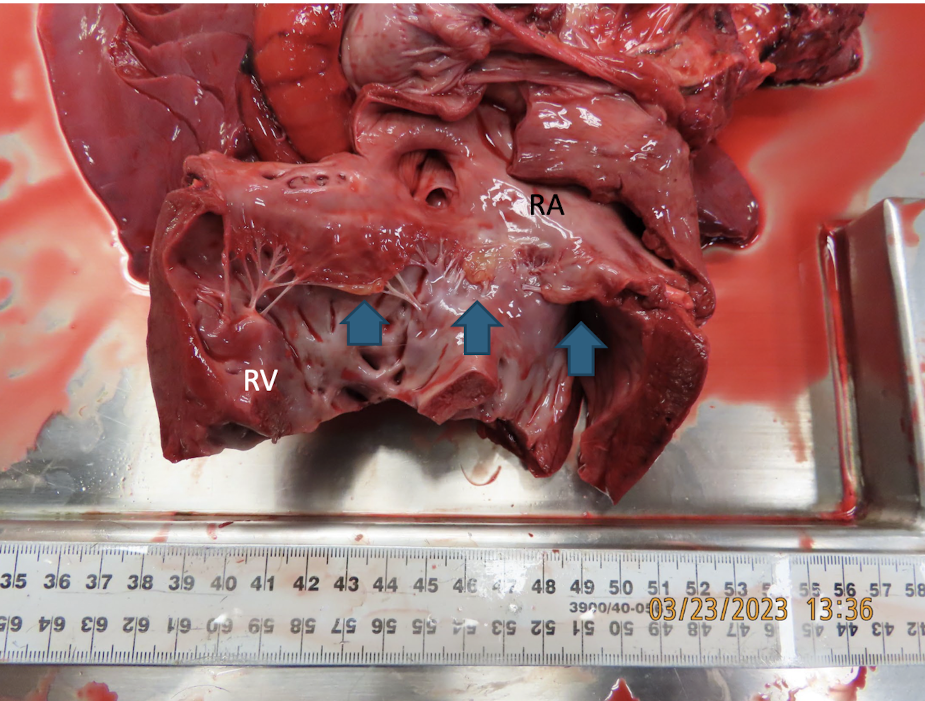
What is this showing?
tricuspid/mitral valvular dysplasia
Tetralogy of fallot is ________ in all species and comprises ________ lesions.
uncommon; four
What are the four lesions that comprise tetralogy of fallot?
H
D
P
R
high VSD
dextroposition of the aorta (aorta connecting to RV outflow tract)
pulmonic stenosis
right ventricular hypertrophy
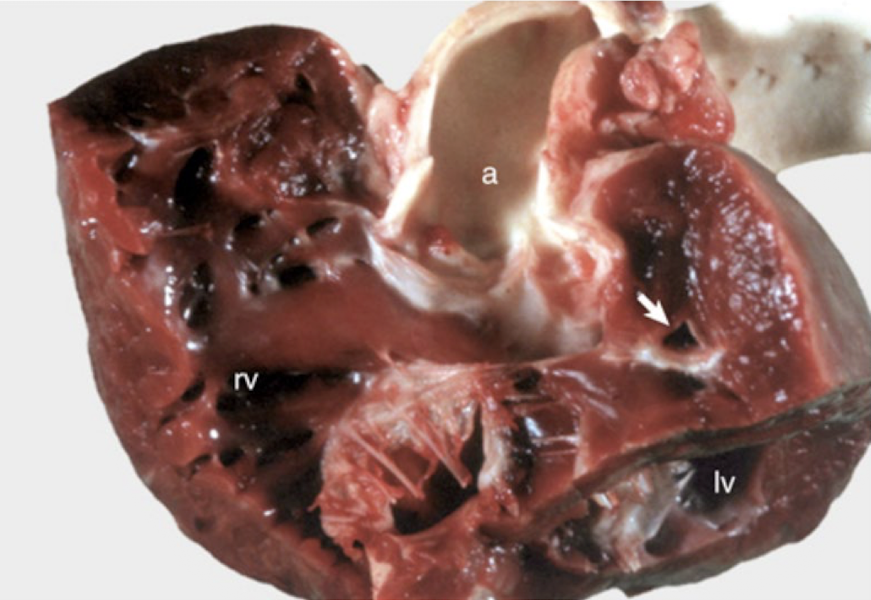
What is this showing?
tetralogy of fallot
vascular ring anomaly that is a failure of regression during fetal development
persistent right aortic arch (PRAA)
With a persistent right aortic arch (PRAA), what is there entrapment of? What does this cause? This will then lead to what? Ultimately, what does this result in?
esophagus and trachea; megaesophagus; regurgitation; aspiration pneumonia
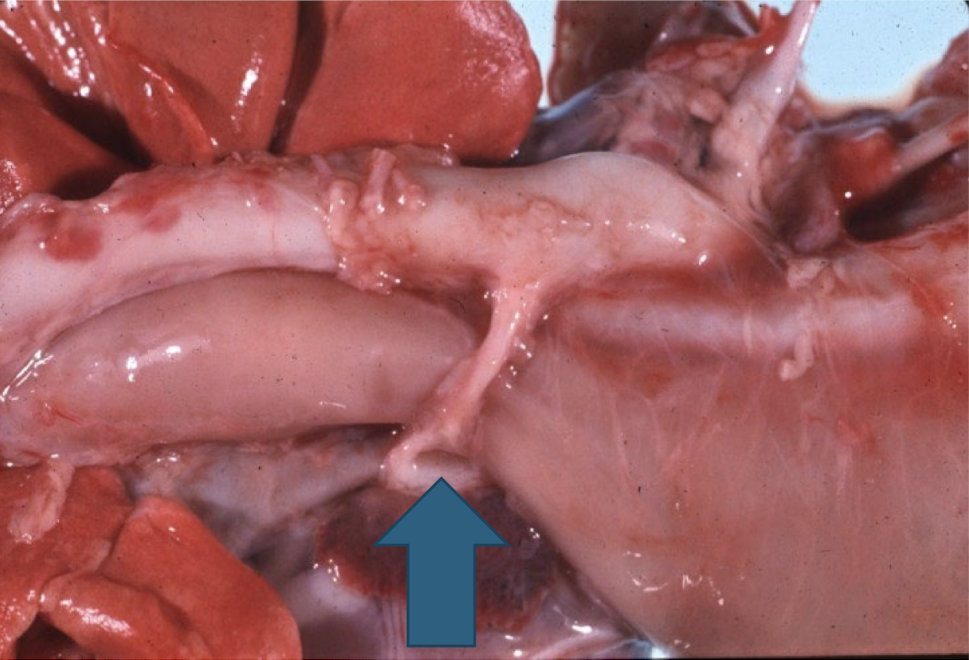
What is this showing?
persistent right aortic arch (PRAA)