GEO 110 - Lecture 10: Intro to Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary and concepts from the lecture on weathering, erosion, and deposition.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Weathering
The breakup of rock through mechanical or chemical processes.
Mechanical Weathering
Physical breakup of rocks without changing their chemical composition.
Chemical Weathering
Alteration of minerals in rocks through chemical reactions.
Erosion
The process of moving soil and rock from one location to another. Not part of lithification. It involves the action of wind, water, or ice that transports these materials.
Deposition
The accumulation of sediment in a new location after being transported. 1st step of lithification. When friction and gravity overcome the forces driving sediment transport, sediments accumulate.This process leads to the formation of sedimentary layers and can occur in various environments, such as riverbanks, deltas, or ocean floors.
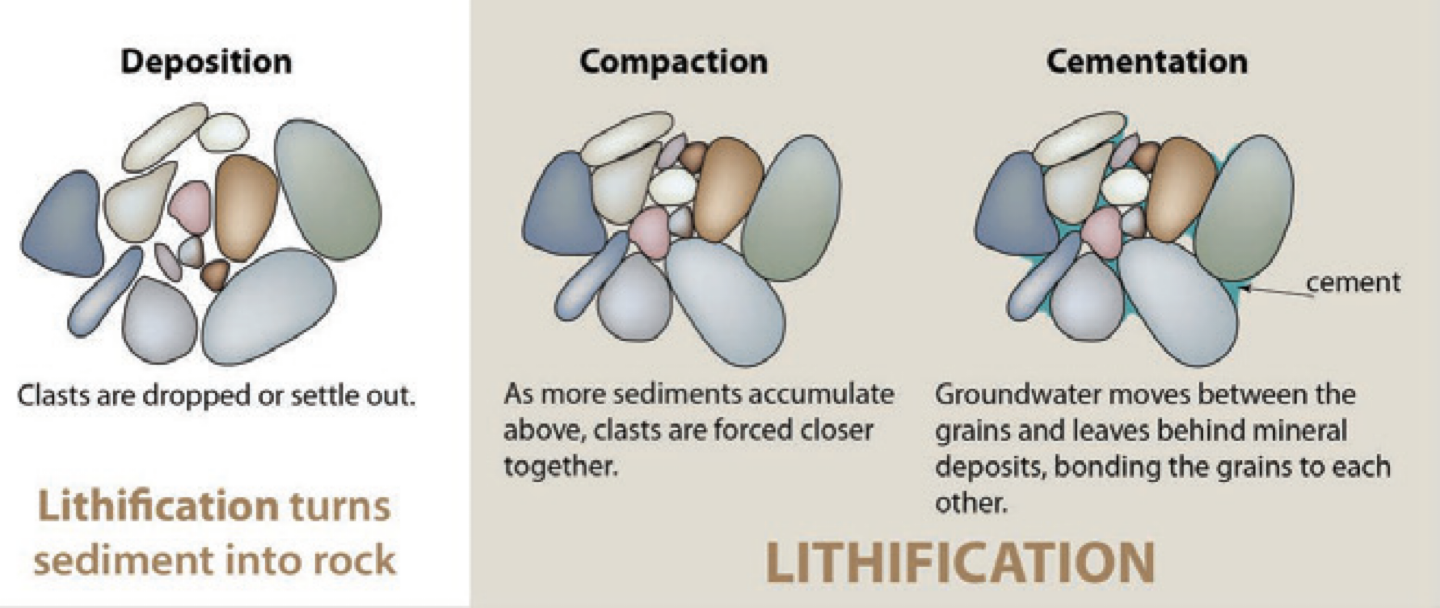
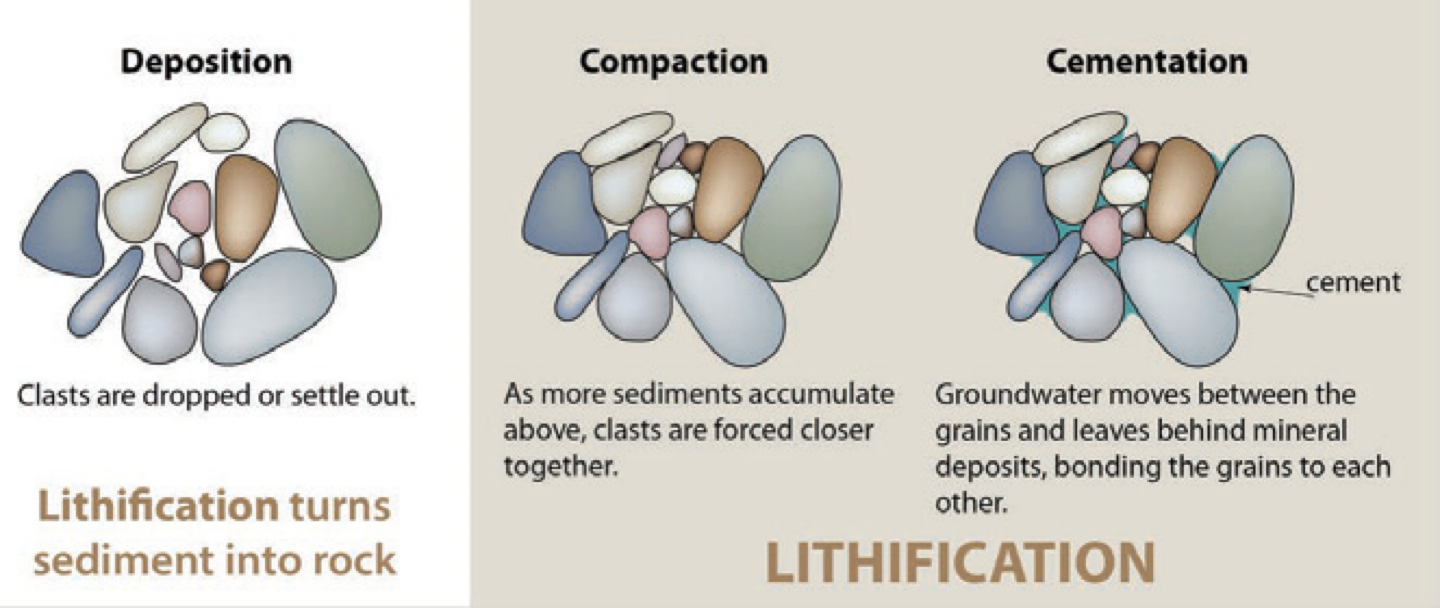
Lithification
The process of turning sediment into rock through compaction and cementation. Process of taking sediments and making them into a rock.
Glaciogenic Sediment
Sediment transported and deposited by ice.
Calcareous Sediments
Sedimentary particles composed of calcium carbonate.
Siliceous Sediments
Sedimentary particles composed of silica.
Terrigenous Sediments
Sediments sourced from land, often carried to oceans.
Hydrolysis
A chemical weathering process where minerals react with water.
Oxidation
A chemical reaction involving the loss of electrons, often resulting in rust.
Frost Wedging
A mechanical weathering process where water freezes in cracks and expands.
Salt Wedging
A mechanical weathering process where salt crystallizes in rock cracks, forcing them apart.
Cementation
The process of binding sediment particles together to form rock. Process of individual grains in a rock being glued together by the precipitation of minerals from water.
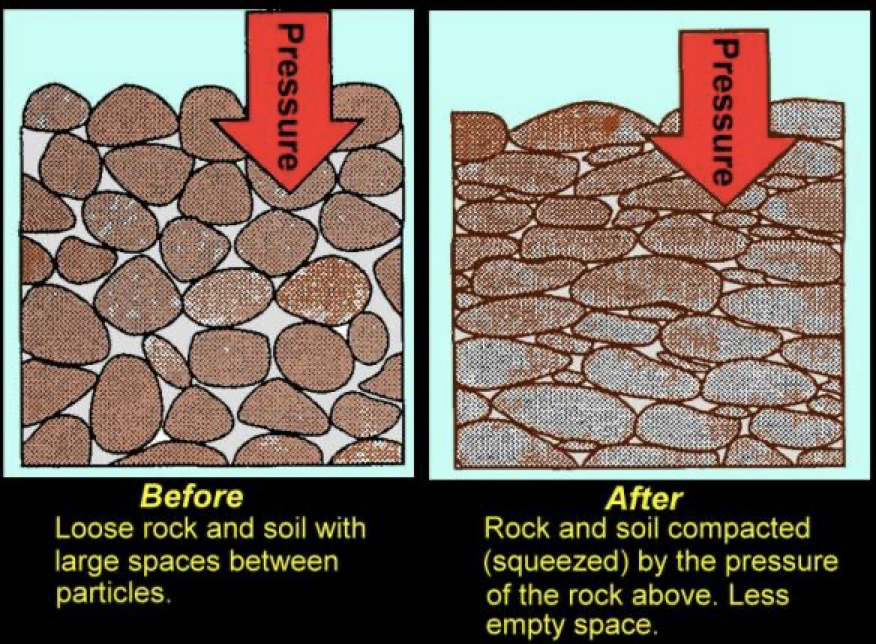
Compaction
The process that reduces the volume of sediment through pressure. Occurs when material continues to accumulate on top of the sediment layer, squeezing the grains together and driving out water.
Clastic sedimentary rocks
Characterized for their predominant grain size. Formed from the accumulation and lithification of sediment fragments, such as sand, silt, and clay.
What does grain size say about a clast?
Grain size indicates the velocity of erosion that sediment was subjected to before it deposition.
Sorting
Refers to the distribution of grain sizes within a sedimentary deposit, indicating energy of transporting medium.
Clast rounding
Describes the smoothness or angularity of a clast's edges, indicating the distance and duration of transport. Rounded clasts indicate longer transport and more erosion, whereas angular clasts indicate minimal transport.
Porosity
Refers to the volume of pore spaces within a sedimentary rock or soil, affecting its ability to hold water and other fluids.
Composition
Refers to the mineral components and chemical makeup of a sediment or rock, which influences its physical properties and behavior in geological processes.
Provenance
The type of source rock (mineral, composition, type of fossils, and textural features). It provides information about the original location and geological history of sediments or rocks, contributing to the understanding of their transport and deposition.
Type of sedimentary rocks
Clastic, chemical/biochemical, and organic
clastic
A type of sedimentary rock. Composed of fragments of other rocks or minerals formed through mechanical weathering. Composed of solid material that has been transported, deposited, and then cemented.
Chemical/biochemical
A type of sedimentary rock. Formed by ions that have transported in solution and precipitated with, or without the aid of life.
Organic
A type of sedimentary rock formed from the accumulation of plant or animal debris, often resulting in coal or certain types of limestone. Contains a large amount of organic matter (plant leaves or tree bark)