CNA ch.1
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
providers
people or organizations that provide health care, including doctors, nurses, clinics, and agencies
facilities
places where health care is delivered or administered, including hospitals, long term care facilities, and treatment centers
payers
people or organizations paying for healthcare services
long term care (LTC)
care given in long term facilities for people who need 24 hour skilled care
skilled care
medically necessary care given by a skilled nurse or therapist
length of stay
the number of days a person stays in a healthcare facility
terminal illness
a disease or condition that will eventually cause death
chronic illness
a disease or condition that is long term or long lasting and requires management of symptoms
home health care
care that is provided in a person’s home
diagnoses
medical conditions determined by a doctor
assisted living
residences for people who do not need 24 hour skilled care, but do require some help with daily care
dementia
general term referring to a serious, progressive loss of mental abilities such as thinking, remembering, reasoning, and communicating
adult day services
care for people who need some assistance or supervision during certain hours, but who do not live in the facility where care is given
acute care
24 hour skilled care given in hospitals and ambulatory surgical centers for people who require short term, immediate care for illnesses and injuries
subacute care
care given in a hospital or in a long term care facility for people who need less care than for an acute illness, but more care than for a chronic illness
outpatient care
care given to people who have had treatments, procedures, or surgeries and need short term skilled care
rehabilitation
care given by specialists to help restore or improve function after an illness or injury
hospice care
holistic, compassionate care given to people who have approximately six months or less to live
managed care
a system or strategy of managing health care in a way that controls costs
health maintenance organizations (HMOs)
a form of health insurance in which the cost of care is covered only when a person uses a particulare doctor or group of doctors except in case of emergency; seeing specialists generaly requires referrals from the primary doctor
preferred provider organizations (PPOs)
a form of health insurance in which patients are encouraged to recieve care from a network of approved providers, but can see other providers at an additional cost; patients cant usually choose their providers, including specialists, without being referred by another doctor
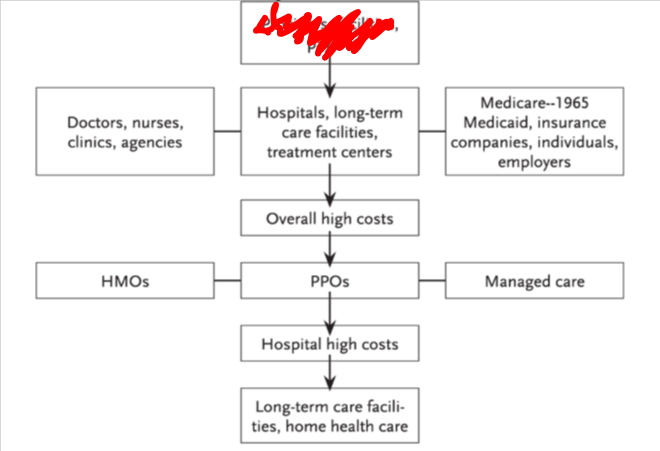
what is inked in red in this diagram
providers, facilities, payers
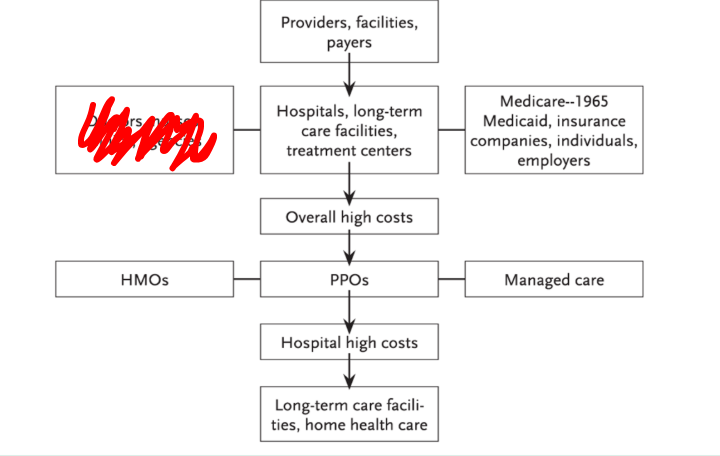
what is blocked in red in this diagram
doctors, nurses, clinics, agencies
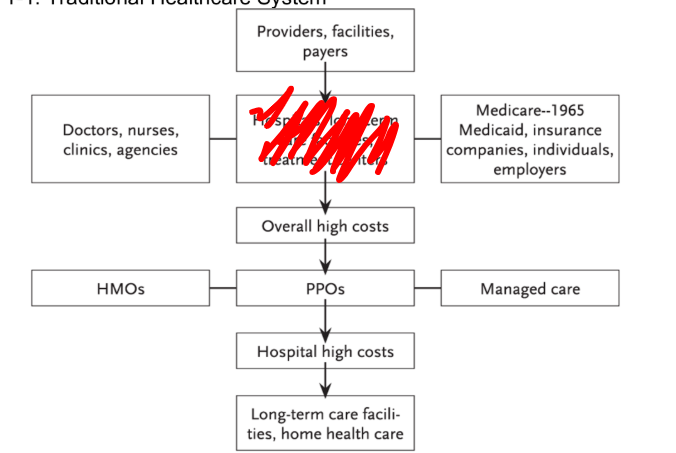
what is blocked in red in this diagram
hospitals, long term care facilities, treatment centers
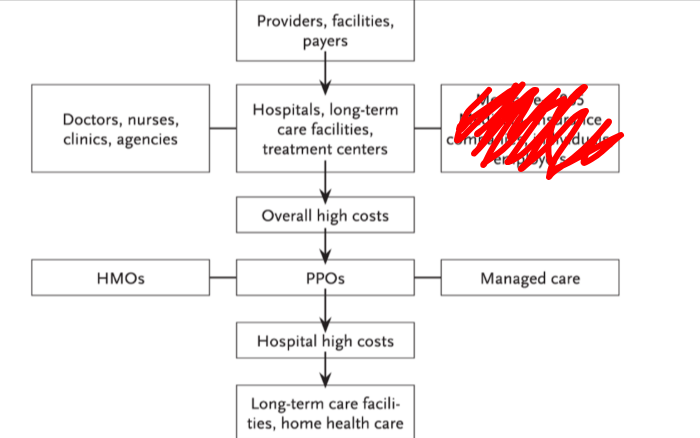
what is blocked in red in this diagram
medicare, medicaid, insurance compancies, individuals, employers
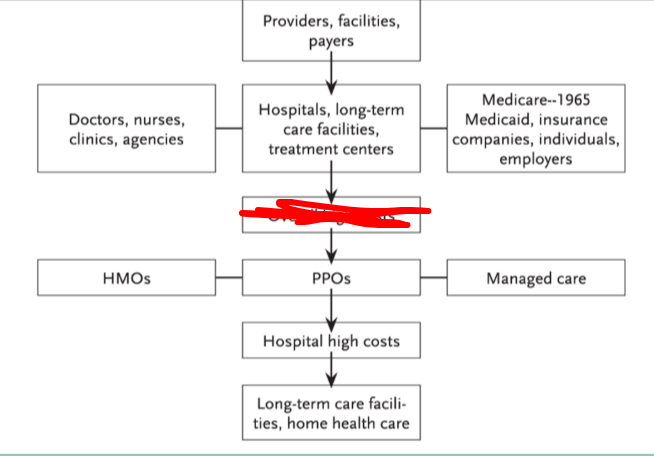
what is blocked
overall high costs
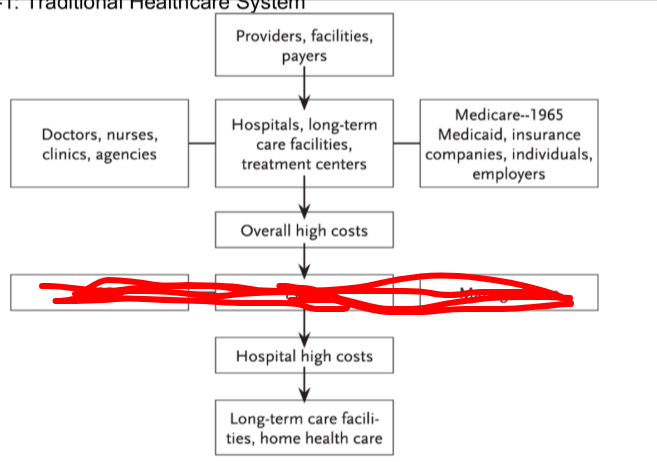
what is blocked in red
HMOs, PPOs, managed care
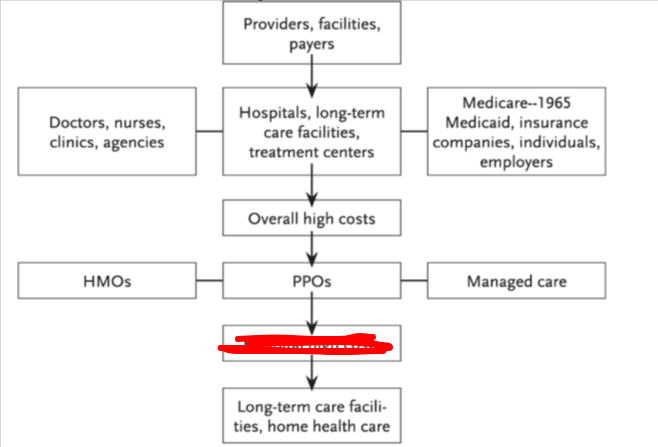
what is blocked in red
hospital high costs
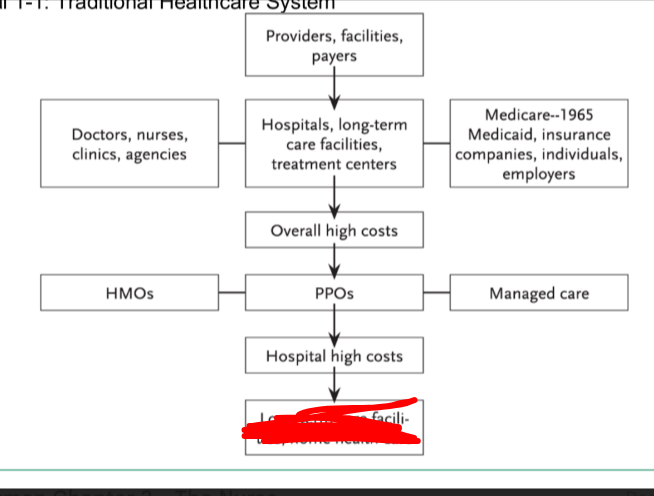
what is blocked in red
long term care facilities, home health care
what are the major changes that have a serious impact on how health care is provided
increased use of expensive tech
rising costs of healthcare
new ways to control costs of care
activities of daily living (ADLs)
daily personal care tasks: bathing, skin, nails, hair care, mouth care, walking, eating, drinking, dressing, transferring, and elimination
catheter
a think tube inserted in the body to drain fluids or inject fluids
what percentage of residents in LTC facilities are over the age of 65
83.5%
what percentage of residents in LTC facilities are female
68%
what percentage of residents in LTC facilities are white and non hispanic
75%
what statistic of residents in LTC facilities are from a private residence
1/3
what percentage of residents in LTC facilities come from a hospital or other facility
50%
what percentage of residents in LTC facilities have dementia
48%
residents with a length stay of six months or more make up how many of total residents
2/3
residents with a length stay of six months require what type of care
24 hour care
residents with a length stay of six months have what reason for staying
did not have caregivers able to give enough care at home
residents with a length stay of six months or more have what type of disability
developmental disabilities
the group with the ____ average stay is made up of people who are developmentally disabled
longest
residents with a stay of less than six months may be admitted for what type of care
terminal care (will die in facility)
residents with a stay of less than six months may be admitted for what type of reason
rehabilitation or temporary illness (will recover and return to community)
many residents lack ___ support. This means it is very important to care for the ____ person - addressing ____ and ____ needs as well as ___ needs
outside, whole, social, emotional, physical
policy
a course of action that should be taken every time certain situation occurs
procedure
a method or a way of doing something
according to common policies and procedures in long-term care facilities: what type of information is confidential
all resident info
according to common policies and procedures in long-term care facilities: what care plan must be followed
resident’s care plan
according to common policies and procedures in long-term care facilities: what type of tasks can be performed
tasks in job descriptions
according to common policies and procedures in long-term care facilities: who do NA’s report to
a nurse
according to common policies and procedures in long-term care facilities: what types of problems can NAs discuss with residents or families
no discussion of personal problems
according to common policies and procedures in long-term care facilities: what can NAs not accept from residents or families
money or gifts
according to common policies and procedures in long-term care facilities: what is expected of NAs when attending work
must be on time and dependable
what steps should be taken if an NA is unsure about policies or procedures
ask questions or review procedure manual
cite
in a long term care facility, to find a problem through a survey
joint commission
an independent, not for profit organization that evaluates and accredits healthcare organizations
what are surveys
regular inspections performed in facilities to make sure they are following state and federal regulations at least every three years
surveys conducted to the join commission are not affiliated with ___ inspections. facilities participate in joint commission surveys are on a ___ basis
state, voluntary
surveyors use these methods to study residents’ care and determine how their needs are being met:
interview residents and their families
observe staff interactions with residents and care given
review residents’ charts
observe residents’ meals
centers for medicare and medicaid services (CMS)
a federal agency within the US department of health and human services that is responsible for medicare and medicaid, among many other responsibilties
medicare
federal health insurance program for people who are 65 and older, have certain disabilities or permanent kidney failure, or are ill and cannot work
medicaid
a medical assistance program for people who have low income, as well as for people with disabilities
medicare part a - hospial insurance
helps pay for care in a hospital or skilled nursing facility or for care from a home health agency or hospice
medicare part b - medical insurance
helps pay for doctor services and other medical services and equipment
medicare part c - medicare advantage plan
allows for private health insurance companies to provide medicare benefits
part d - prescription drug coverage
helps pay for medications prescribed for treatment
what is an important factor that is set in place for medicare coverage
will only pay for care that it determines to be medically necessary
who funds medicaid
federal government and each state
medicare and medicaid work with long-term care facilities in these ways:
LTC facilities receive a fixed amount for services provided
services are based on the resident’s needs upon admission and throughout the facility stay
culture change
a term given to the process of transforming services for elders so that they are based on values and practices of the person receiving care
what are the core values of culture change
choice
dignity
respect
self-dtermination
purposeful living
person-centered care
a type of care that places the emphasis on the person needing care and his or her individuality and capabilities
description of person-centered care:
emphasized individuality of person who needs care
each person’s background, culture, language, beliefs, and traditions are respected
improving each resident’s quality of life is an important goal
trauma-informed care
an approach to patient care that recognizes that people may have experienced trauma in their lives so trauma, experiences, and preferences should be considered while providing care
what are the four Rs in the TIA approach
realization: understand how trauma can affect the individual
recognize: people in the organization recognizes signs of trauma
responds: the organization or care team responds by applying the principles of TIA approach to all areas of providing care
resist Re-traumatization: seek to resist exposing the individual to re-traumatization