Machine Elements
1/35
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
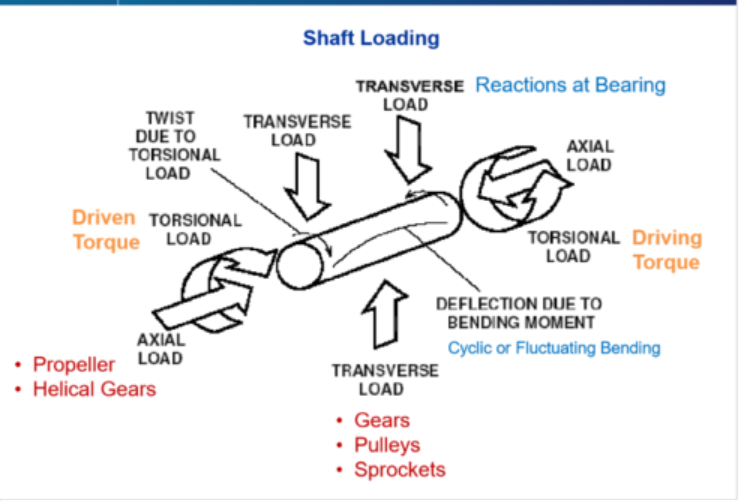
3 Types of shaft loading
Torsion, Axial and transverse
What are the 3 types of shaft misalignments ?
Axial, Parallel and Angular
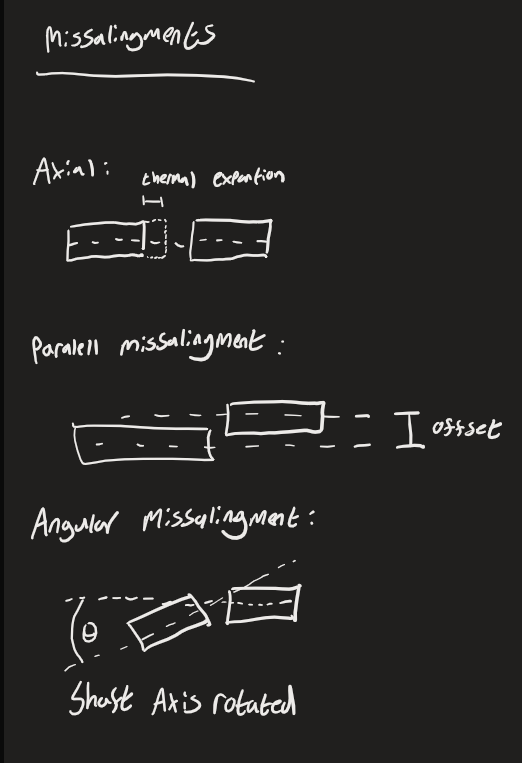
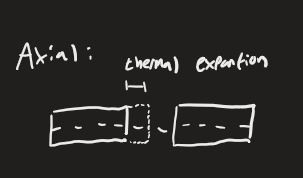
What Type of Misalignment does Thermal expansion cause?
Axial
What type of coupling allows for some misalignment and also provides some damping?
Flexible couplings
Name two types of Rigid Couplings
Flange Coupling
Muff coupling
2 ways the flange coupling secure onto the shafts
Interference fit
Keyed Connection
How does the muff coupling connect onto the shafts?
Tightening the screws on it to clamp onto the shafts
What is the difference between Kinematic and resilient flexible couplings
Kinematic:
Rigid components , no shock damping
Resilient:
Flexible components, provides shock damping
3 types of kinematic flexibility couplings
Claw Coupling
Bellows Coupling
Oldham Coupling

3 types of Resilient flexibility couplings
Flexible Disk Coupling
Flexible Claw Coupling
Rubber Tyre Coupling

4 example of different elements you can put on shafts
Pulley
Gear
Flywheel
Propeller
3 types of posatie drive connections
Pin
Key
Splined shaft ( shaft with build in keys)
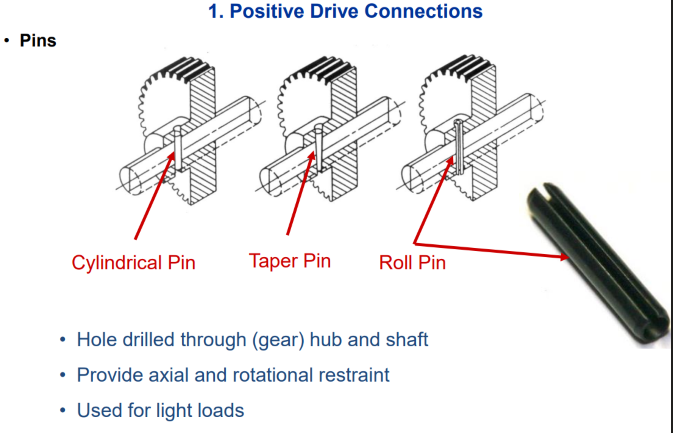
3 Type of pin connections
Cylindrical
Taper
Roller
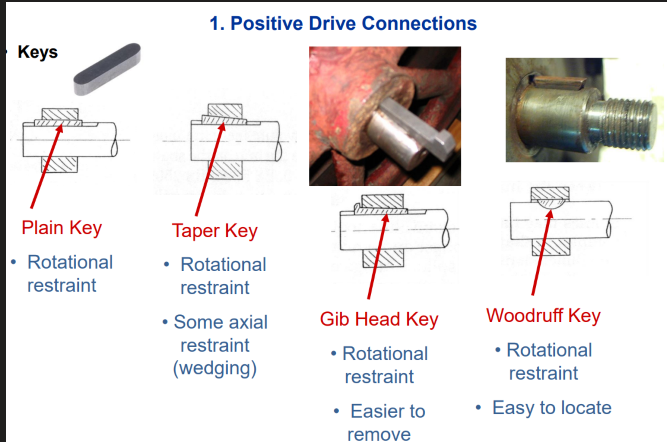
4 Type of Keyed connections
Plain
Taper
Gibhead
Woodruff
3 types of friction Drive connections
Interference
Taper
Clamping
Belt drive vs chain drive ( torque and speed )
Belt drive - High speed , low torque
Chain drive - Low speed , High torque
The 3 main types of drive belts
Flat belt
Vee belt
Toothed / timing belts
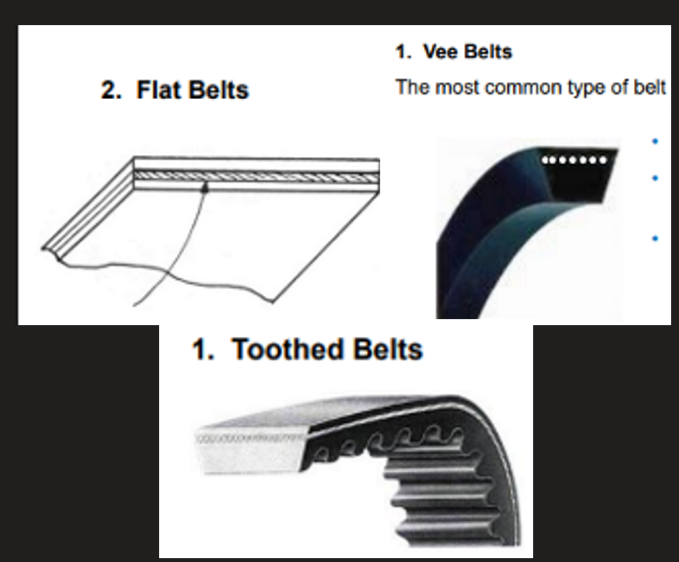
Rank the belts in order of which requires the most pretention
1(most) - Flat belt
2 - Vee belt
3 - Toothed belt
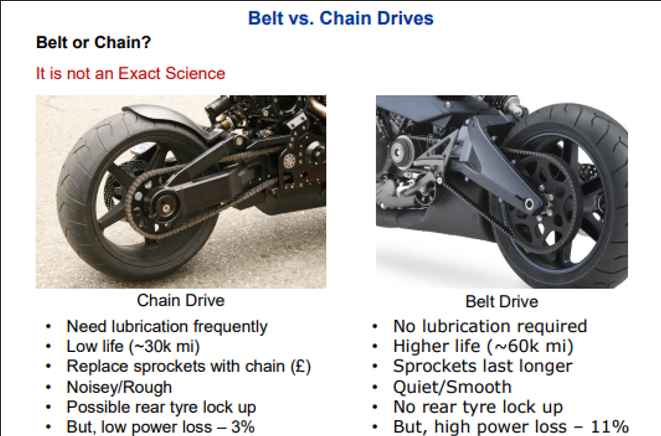
Belt Vs chain drive pros and cons
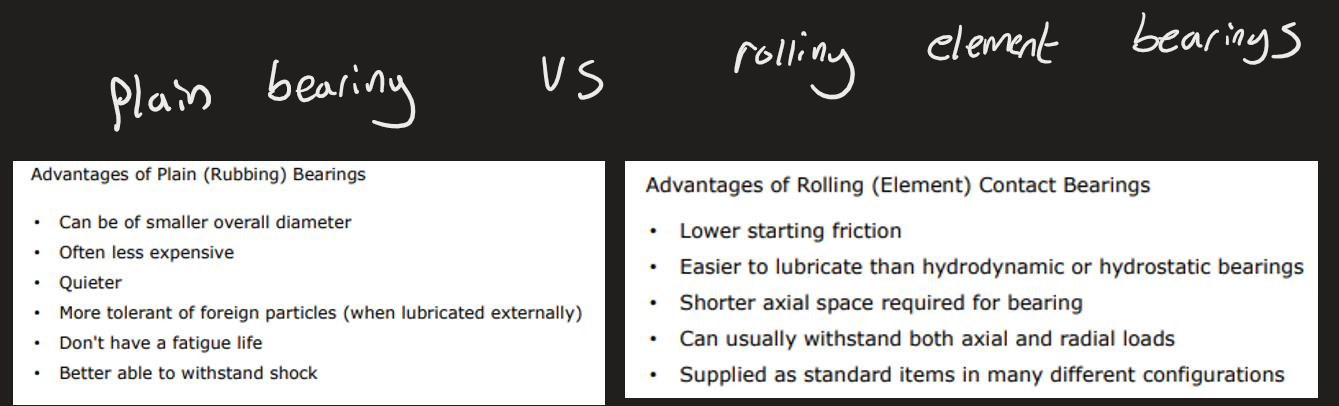
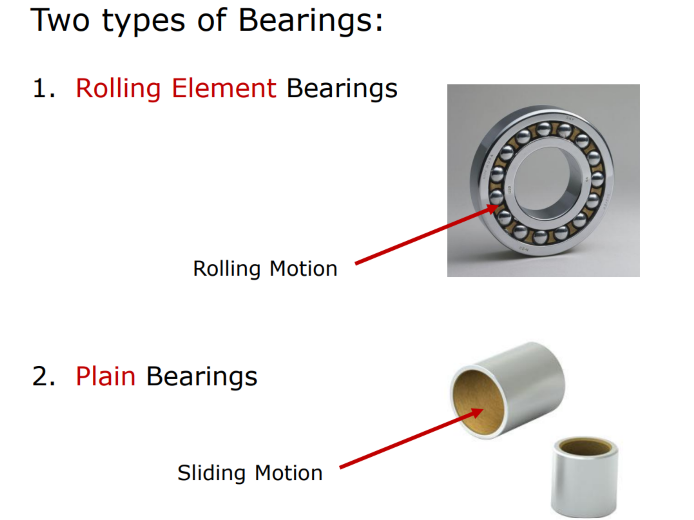
What are the two types of bearings
Rolling Element bearing
Plain bearing
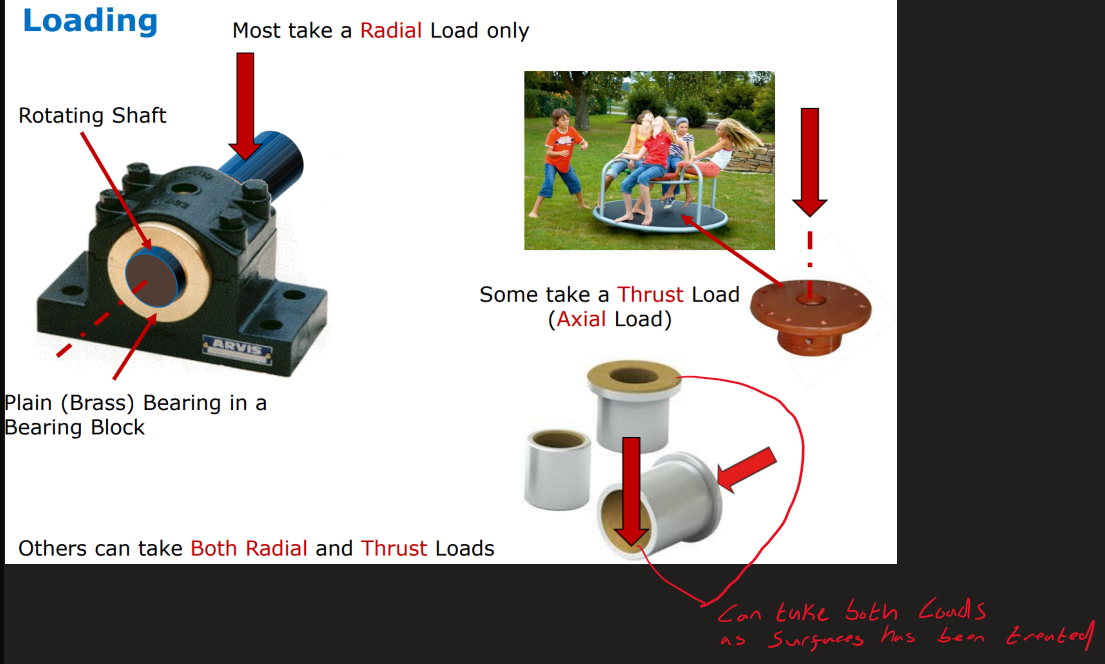
The 2 types of loads on bearings
Radial
Thrust
Types of Lubrication
Partial lubrication :
Boundary - Oil or grease
Dry - Graphite powder
Film Fluid Lubrication ( no contact between shaft and bearing ) :
Hydrostatic
Hydrodynamic
What’s the difference between hydrostatic and hydrodynamic lubrication ?
Hydrostatic uses a pressurized fluid to ensure no contact all the time
Hydrodynamic requires the shaft to rotate at high ish speeds for no contact
Which is typically made out of a harder mateiral, bearings or shaft?
Shafts , typically made from hardened steel
What should the ratio of bearing length to diamiter be
Length should be 1 to 1.5 x the diameter
L = 1.5D
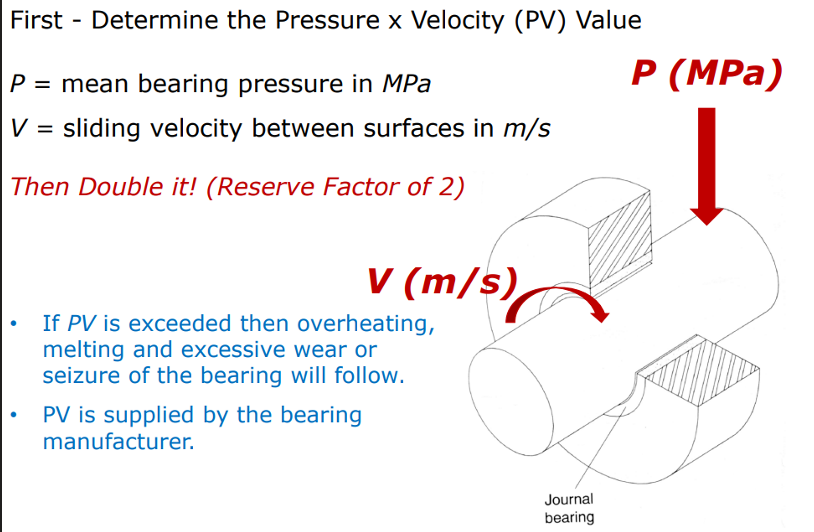
What is the PV value of a bearing and what ‘safety factor’ should be included when choosing a bearing with a PV value
PV value = the pressure x velocity the shaft will experience
Safety factor of x2. E.g. use a bearing of PV value 2x what it requires
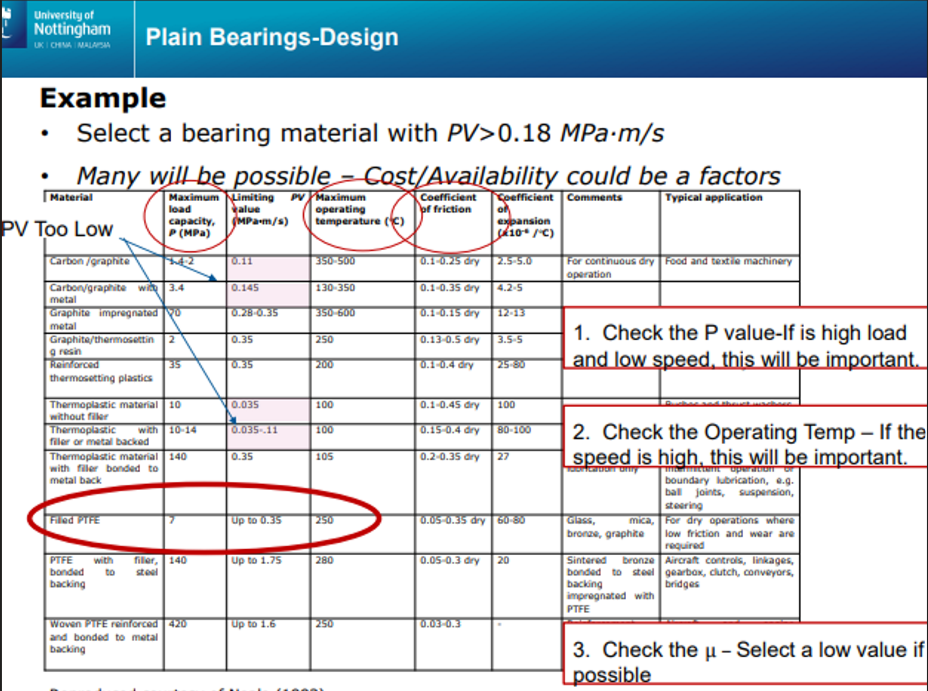
Selecting bearing from PV chart
For a rolling element bearing ( like a ball bearing ) are the contact stresses high or low?
High as force is through a small area
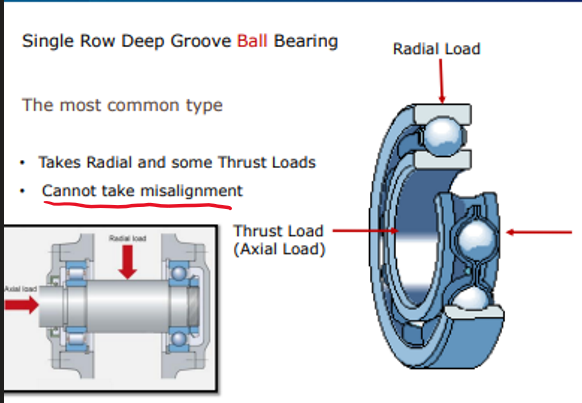
Single row deep groove ball bearing can it take:
Radial Loads?
Axial/thrust Loads?
Misalignment ?
Takes Radical loads
Can take some small Axial loads
Cannot take misalignment - will seize up
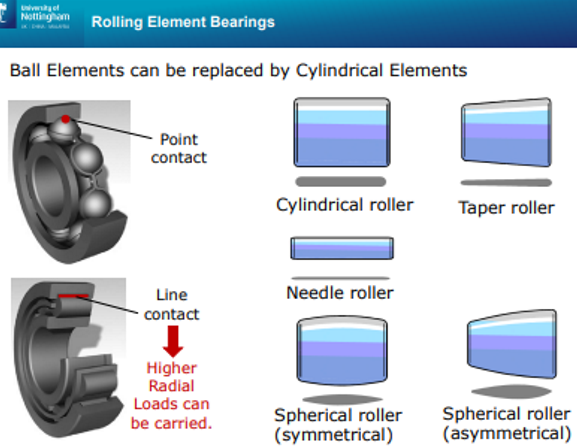
What type of cylindrical rollers are there for bearings?
Cylindrical roller
Taper roller
Needle roller
Spherical roller ( symmetrical and asymmetrical)
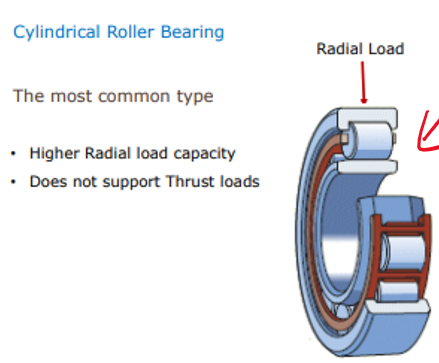
Cylindrical roller bearing ( basic type ) can it take:
High or low radial loads?
Thrust loads?
Can take high radial loads
Cannot take thrust loads
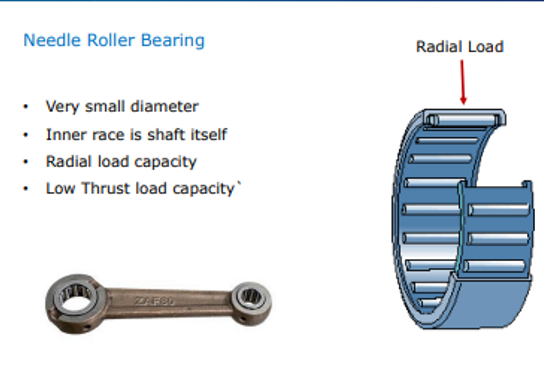
Needle roller bearings radial and thrust load capacity
Can take radial loads
Low thrust load capacity
Taper roller bearing radial and thrust load capacity
Good Radical load capacity
Can withstand thrust loads in one direction
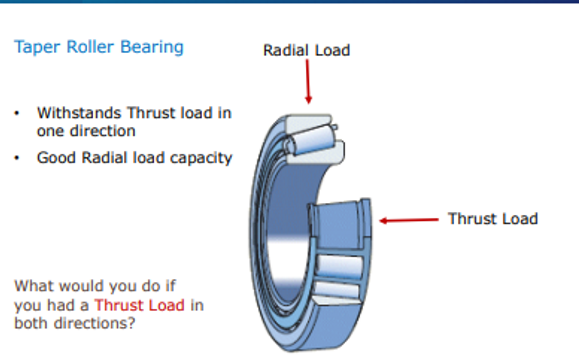
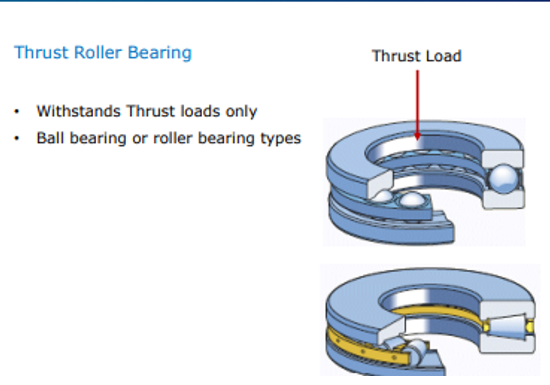
What type of rolling element bearing can only withstand thrust loads?
Thrust roller bearing
Bearing life- what do these mean:
Basic static load rating
Basic dynamic load rating
Rated life
Basic static load rating - Maximum radial load of non rotating bearing
Basic dynamic load rating (C) - constant radial load (P) which it can withstand for 1 million revolutions
Rated life - number of revolutions bearing expected to last
L10 = number of revolutions

Plain vs rolling element bearing