uplearn fission and fusion
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Identify Einstein’s famous equation.
E=mc2
Identify all the interpretations of E=mc2
mass is a form of energy
energy has mass
definition of the rest mass
the rest mass is the mass of an object or particle when it is stationary
definition of the mass defect
The mass defect is the difference between the mass of a nucleus and the sum of the masses of its nucleons if they were completely separated
definition of the binding energy of the nucleus
The minimum energy required to separate the nucleus into its constituent protons and neutrons
Identify the correct statement about binding energy
The higher the binding energy, the more tightly bound the nucleus is, so it will take more energy to split the nucleus up
Identify the correct statement about binding energy
When protons and neutrons become more tightly bound, the binding energy increases, and energy is released
The mass defect
The mass defect is defined as the difference between the mass of a nucleus and the sum of the mass of its nucleons if they were completely separated
Identify the correct binding energy per nucleon versus nucleon number graph from the options below.
Correct answersYour answers
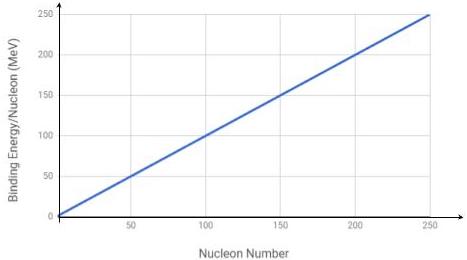
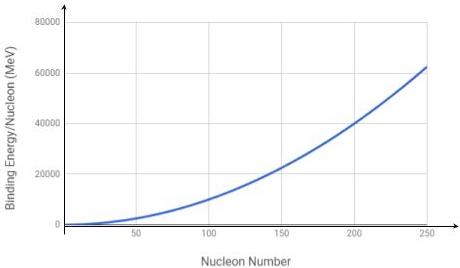
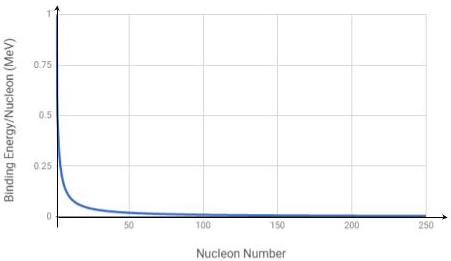
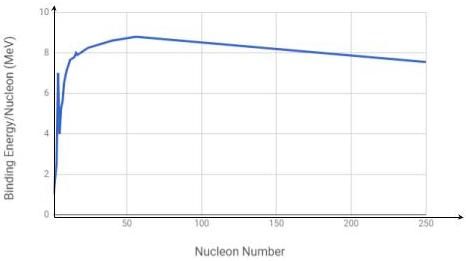
D
The graph of binding energy per nucleon versus nucleon number is shown below.
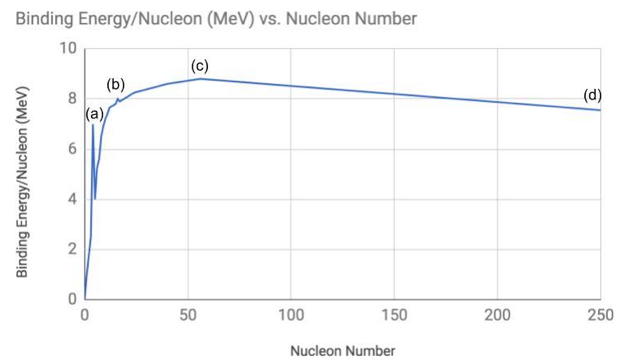
Identify the labelled point on the graph above that corresponds to the element iron
C
Nuclear fission occurs when…
Nuclear fission occurs when a large nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei
The sum of the binding energies of the smaller nuclei is greater than the binding energy of the larger nucleus
true
Fusion
Fusion is when two smaller nuclei join together to form one larger nucleus
Identify the statement that correctly gives the ratio of uranium isotopes on Earth
The ratio of uranium isotopes on Earth is 0.70% uranium-235: 99.3% uranium-238
Slow neutrons
also called thermal neutrons
chain reactions
initial neutrons in a fission reaction cause exponential increase in neutrons, which causes an exponential growth in the rate of fission reactions
Identify the option that correctly identifies the number of neutrons N produced after n generations of a nuclear fission reaction. You can assume that every produced neutron creates a further fission reaction
N=3n
Identify whether the statements below about the nuclear decay of uranium-235 are true
The total binding energy after the fission reaction is greater than the total binding energy before the fission reaction
Energy is released during a fission reaction. Which of the following is the energy released as?
Gamma rays
Neutrinos
Kinetic energy of neutrons
Kinetic energy of daughter nuclei
Slow neutrons
those with a mean kinetic energy equal to the thermal energy of particles in reactor core
Fuel rods:
Made of enriched uranium
Moderator:
A substance in a fission reactor that slows down fast neutrons so that they can be absorbed by Uranium-235 to continue the nuclear reaction. Often made from graphite or water
Control rods:
Absorb neutrons and can control the rate of the reactions or stop them altogether. They are made of boron-coated steel
Coolant:
A substance that is heated by energy from fission reactions and removes the thermal energy from the reactor core
How many fast neutrons are usually produced in each fission?
3
How many slow neutrons should the control rods allow to continue?
1
Which of the following is a waste product of the fission process?
Plutonium-239
Which of the following are advantages of generating electricity from nuclear fission?
A small amount of fuel is needed to produce a lot of electricity
Clean (no CO2 produced)
Why is it important to consider safe, long-term storage of nuclear waste?
Waste is highly radioactive and has a very long half-life
Nuclear fusion is a reaction that takes place in the core of stars like the Sun.
Identify all the conditions required for fusion to take place.
High pressure is required
The temperature needs to be greater than 100 million Kelvin
The proton-proton chain is a series of fusion reactions. In the first step two protons fuse to make a deuterium nucleus.
Identify the equation for this reaction
11p+11p—>21H+0+1e+electron neutrino
During the second step of the proton-proton chain, a helium nucleus is formed.
Identify the equation of the second step of the proton-proton chain.
1/1P+2/1H—>3/2He
During the third step of the proton-proton chain, a helium-4 nucleus is formed.
Identify the equation of the third step of the proton-proton chain
3/2He+3/2He—>4/2He+2 1/1p
Rest mass
mass of an object or particle when it is stationary
Mass defect
the difference between the mass of a nucleus and the sum of the masses of its nucleons if they were completely separated
Binding energy
the minimum energy required to separate a nucleus into its constituent protons or neutrons
Fission
when a large nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei after absorbing a neutron
Fusion
fusion is when two smaller nuclei join together to form one larger nucleus
Thermal neutrons
a neutron in a fission reaction that has a mean kinetic energy approximately equal to the thermal energy of the particles in the reactor core. Also called a slow neutron
Reactor core
a concrete-steel encasement around a the core of a nuclear reactor