Visual Fields
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
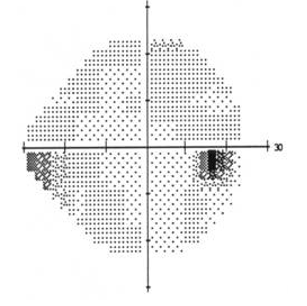
hill of vision
3D model of VF sensitivity
kinetic stimuli
moving target
fixed size & brightness
tests non-seeing to seeing
approach HOV from the sides
static stimuli
fixed sized target but intensity/brightness varies
approach HOV from above
60
what is the extent of the superior VF?
75
what is the extent of the inferior VF?
60
what is the extent of the nasal VF?
100
what is the extent of the temporal VF?
120
what is the extent of the binocular VF?
200-220
what is the extent of the VF of both eyes?
absolute defect
no stimulus perceived anywhere in the affected field
relative defect
VF defect changes in size inversely w/ change in size &/or intensity of stimulus
below
on gaze tracking, blinks are recorded as ticks _____ the line
above
on gaze tracking, gaze shifts of more than 5deg are recorded as ticks _____ the line
20%
fixation losses should be less than ____ for reliability
33%
false positives/negatives are flagged when over _____
25%
false positives/negatives should be less than _____
false positives
pt responding that they saw the stimulus when no light stimuli is presented
false negatives
pt responding that they did not see the stimulus when a light brighter than their threshold is shown
central sparing
center of vision is less affected, can get a ring, often starting at the peak of the rods & spreading
arcuate defects
occur in glaucoma when a bundle of ganglion cell axons is damaged at the optic nerve
central
scotoma involving fixation
cecocentral
scotoma involving fixation to the blind spot
paracentral
scotoma involving the area adjacent to fixation
pericentral
scotoma involving the area surrounding fixation
arcuate scotoma & nasal step (Bjerrum’s area)
coincides w/ anatomy of NFL
extends from the blind spot
does not cross the nasal horizontal midline of the VF
may be isolated w/in Bjerrum’s area
Bjerrums area
A
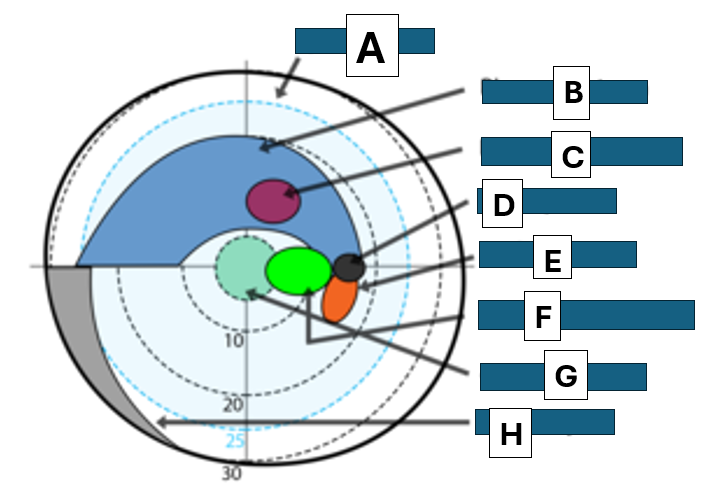
Bjerrum scotoma
B
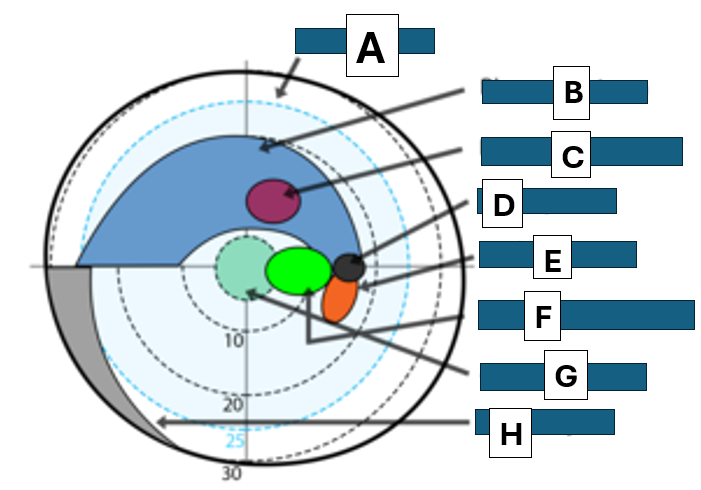
paracentral scotoma
C
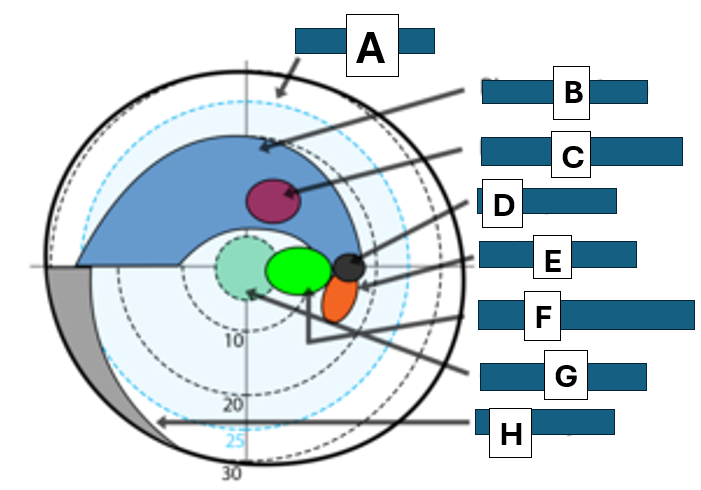
blind spot
D
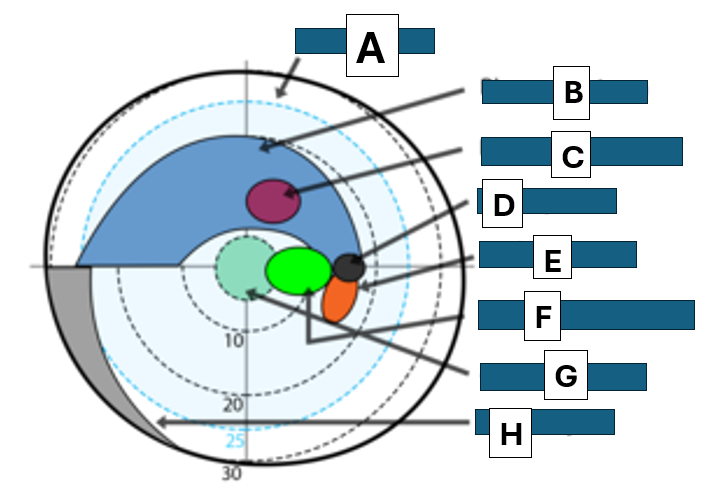
Seidel scotoma
E
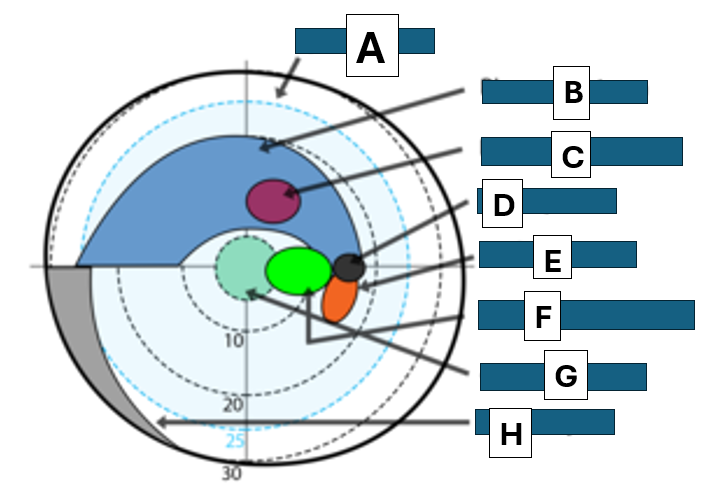
centrocecal scotoma
F
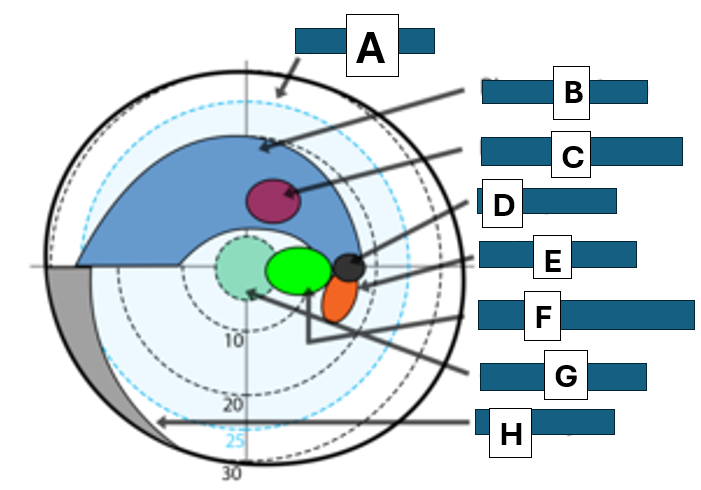
central scotoma
G
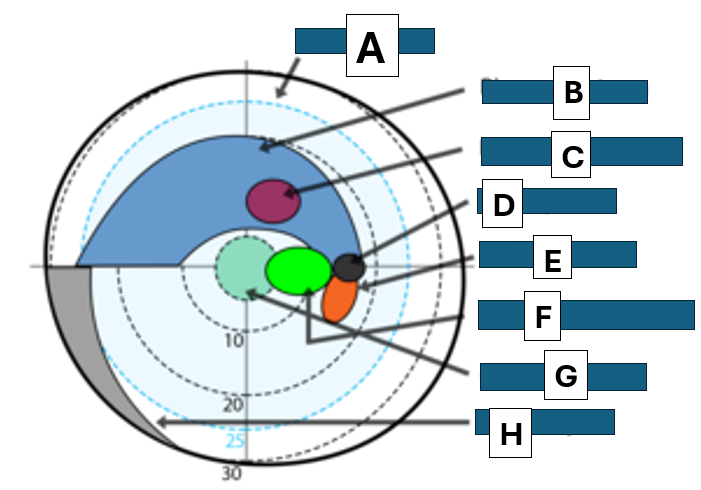
Nasal step
H
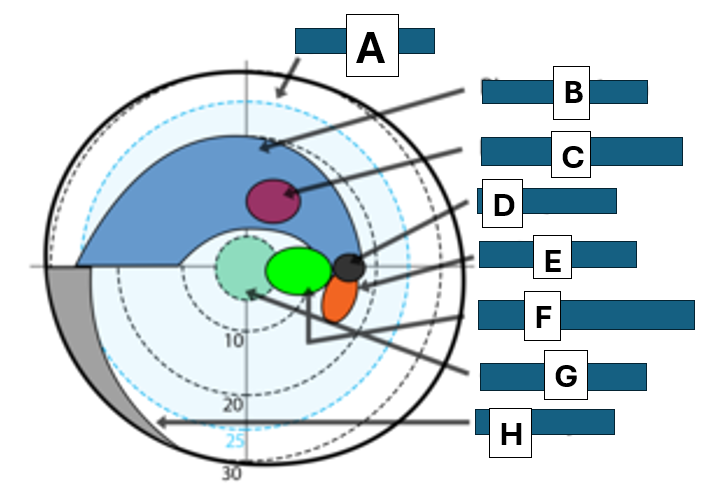
homonymous
defect on the same side of visual space for each eye
right or left
lesion posterior to chiasm
heteronymous
defect on opposite sides of visual space for each eye
bitemporal or binasal
lesion usually at the optic chiasm
junctional scotoma
ipsilateral central scotoma & contralateral superior temporal defect, due to optic chiasm damage
improperly placed trial lens, glaucoma, RP
what are possible reasons for a ring scotoma?
33cm
what is the WD for most perimetry?
glaucoma hemifield test
compares pattern deviation probability scores in 5 zones in the upper field compared to the lower field
localized
respects horizontal meridian
often nasal to blind spot
almost always detectable w/in central 30deg
what are the classic characteristics of a glaucoma VF defect?
optic neuropathy
reduced VA
light brightness
reduced color perception
+APD
total deviation
the average of deviations across all test directions, referred to as the mean deviation; affected by cataracts, RE, & things that cause an overall loss in sensitivity
positive
patients who are able to see dimmer stimuli than others of similar age & race will have ______ values for their MD
negative
pts who require brighter stimuli will have ________ MD values
pattern standard deviation
measures irregularity by summing the absolute value of the difference b/t the threshold value for each point & the average VF sensitivity at each point
0
VF w/ age-normal sensitivity at each point will have a PSD of _____
focal, deep
the largest PSD will be registered for _________ VF defects
30
a central 30-2 VF test measures ____ degrees in any direction
10-2
what VF test would you do to test macular issues?
24-2 or 30-2
what VF test would you do to test glaucoma?
wide field
what test would you do to assess neurological damage of the optic tract?
full threshold strategy
suprathreshold stimulus is presented at each location based on the threshold values from previous points
intensity is decreased at fixed increments until it is no longer seen, then intensity if increased at fixed increments until it is seen again
threshold is taken to be = to the intensity of the last stimulus seen at that location
use smaller steps in intensity & involve more reversals in the direction of presented stimuli
longer test time
every retinal location is tested by all possible luminances
FASTPAC
determines threshold w/ a single reversal using an increment of 3dB
faster
underestimates the severity of VF defects
Swedish interactive threshold algorithm (SITA)
developed for Humphrey perimeter
uses a complex mathematical model to estimate threshold values for each point based on responses to stimuli presented at that location, as well as info gathered from nearby locations
full threshold values are still obtained for the 1st 4 points tested & at least 1 reversal from descending to ascending intensity is obtained for each location
test times in normal individuals are roughly ½ as long as full threshold tests w/ similar or better reproducibility
140
what is the driver’s license requirement of horizontal binocular field?
digital VF
finger counting
tangent screen
what is the preference of VF testing (in order)?
tangent screen
simple, more sensitive than confrontation fields
at 1m, tests VF of radius 30deg
consists of black felt background w/ stitching that indicates 5deg increments, blind spots, & horizontal/vertical/diagonal meridians, central button w/ attached ribbons to set pt distance, wand w/ a white target of various sizes
kinetic test
monocular
double
doubling the test distance while also doubling the target size should _______ the field size
exact same sized field
what might malingerers report when the test distance is doubled on a tangent screen test?
frequency doubling technique
tests to ensure the subject has a statistically normal supra-threshold VF
standard VF screening test in practices
assess M-cell functions
target is a low spatial frequency sinusoidal grating which undergoes high temporal frequency counter-phase flicker
pt perceives a grating w/ 2x as many light/dark bars as actual
unaffected by external room light or pupil size
covers 20deg on all sides of fixation
REPEATABLE & RELIABLE
abnormal GHT
PSD abnormal at P<0.5% level
cluster of 3+ on pattern deviation plot abnormal at P<5% & at least 1 at P<0.01%
what are the requirements for suspect of glaucoma (don’t need all)?
a gaze deviation of magnitude greater than or equal to 5deg
in HFA gaze tracking graph, an upward deflection represents _________
60
a 30-2 humphrey VF measures a total horizontal field of what diameter?
pt’s opposite eye is not covered
a pt performs an OD HFA VF w/ no fixation losses, no FP, no FN. the VF is missing a blind spot, what is the likely cause?
optic nerve & macula
a cecocentral scotoma is an area of reduced retinal sensitivity that involves what structures?
left temporal lobe
you observe a bilateral, congruous, right superior quadrantanopia. describe where the lesion is
posterior
relative to an incongruous VF defect, a congruous VF defect is typically ________ in the visual pathway
pre-chiasmal
a unilateral VF defect is most commonly associated with a lesion in what location of the visual pathway?
right parietal lobe
you observe a bilateral, congruous, left inferior quadrantanopia, where is the lesion?
area adjacent to macula
a para-central scotoma represents an area of reduced retinal sensitivity that involves what area of the retina?
relative
a VF defect in which the retinal sensitivity is less than normal at a given location AND which changes w/ a change in stimulus size or intensity is a _______ defect
all that can be seen, finite portion of visual space that an individual can see
visual field is ________ while visual space is ___________
normal
a mild defect occurs in the outer 12 tested locations on FDT, is this normal or abnormal?
60deg
the tangent screen tests a total visual field diameter of ______ horizontally & vertically
Magnocellular
FDT tests for the death of what type of cell?
HFA 30-2
if a pt performs abnormally on an FDT, what would the next test be?
low, high
Magnocellular cells in the LGN are thought to be responsible for ______ contrast, _____ temporal frequency stimuli detection
greater than or equal to 20%
on an HFA threshold VF printout, fixation losses are flagged as significant & the test should be considered invalid at what level?
PSD
the portion of the HFA threshold VF printout that is most commonly used by the doctor to quickly assess pt diagnosis & management is ______
distance of target from subject, actual target size
what factors have an impact on apparent target size?
pt does not understand test, test anxiety, pt is guessing
what are 3 common sources of FPs?
isopter
all locations in the VF w/ identical retinal sensitivity
greater than or equal to 33%
an HFA threshold VF test is flagged w/ an XX if the number of FPs is _____
-6 to +6
a pt taking an FDT VF can typically do so w/o their glasses if their Rx is ________
arcuate, nasal step, enlarged blindspot
what VF defects are associated w/ glaucoma & nerve fiber diseases?
right congruous hemianopsia
describe this VF defect
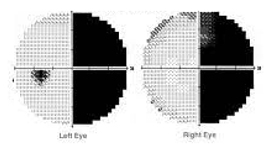
non-congruous hemianopsia
describe this VF defect
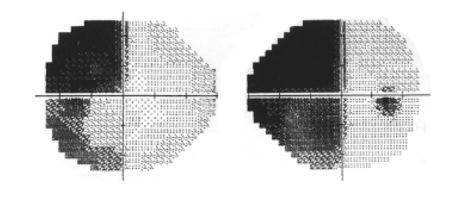
right non-congruous quadranopsia
describe this VF defect
occipital lobe, stroke
describe the location of this lesion & the most probable cause
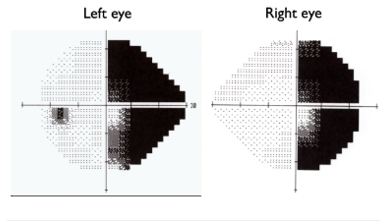
NFL, glaucoma
describe the location of this lesion & the most probable cause
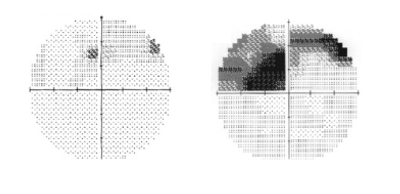
NFL, glaucoma
describe the location of this lesion & the most probable cause
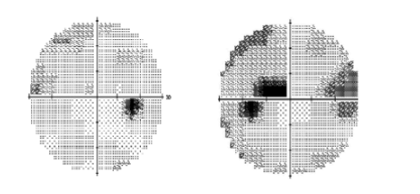
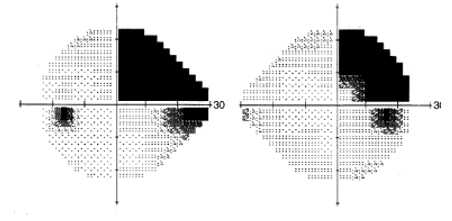
arcuate
what kind of defect is this?

arcuate
what kind of defect is this?
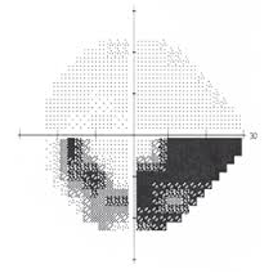
nasal step
what kind of defect is this