Campbell Biology: Chapter 6
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
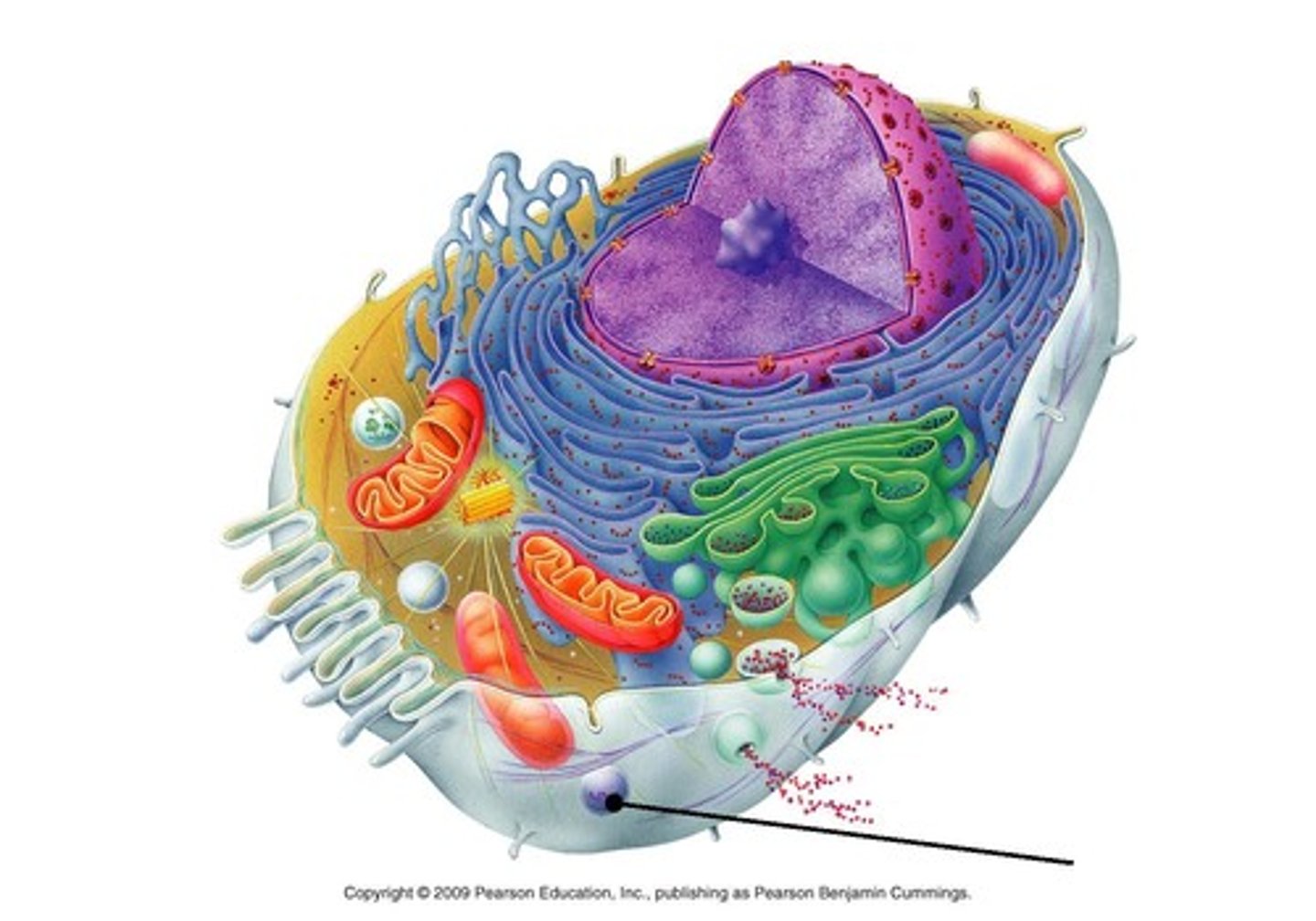
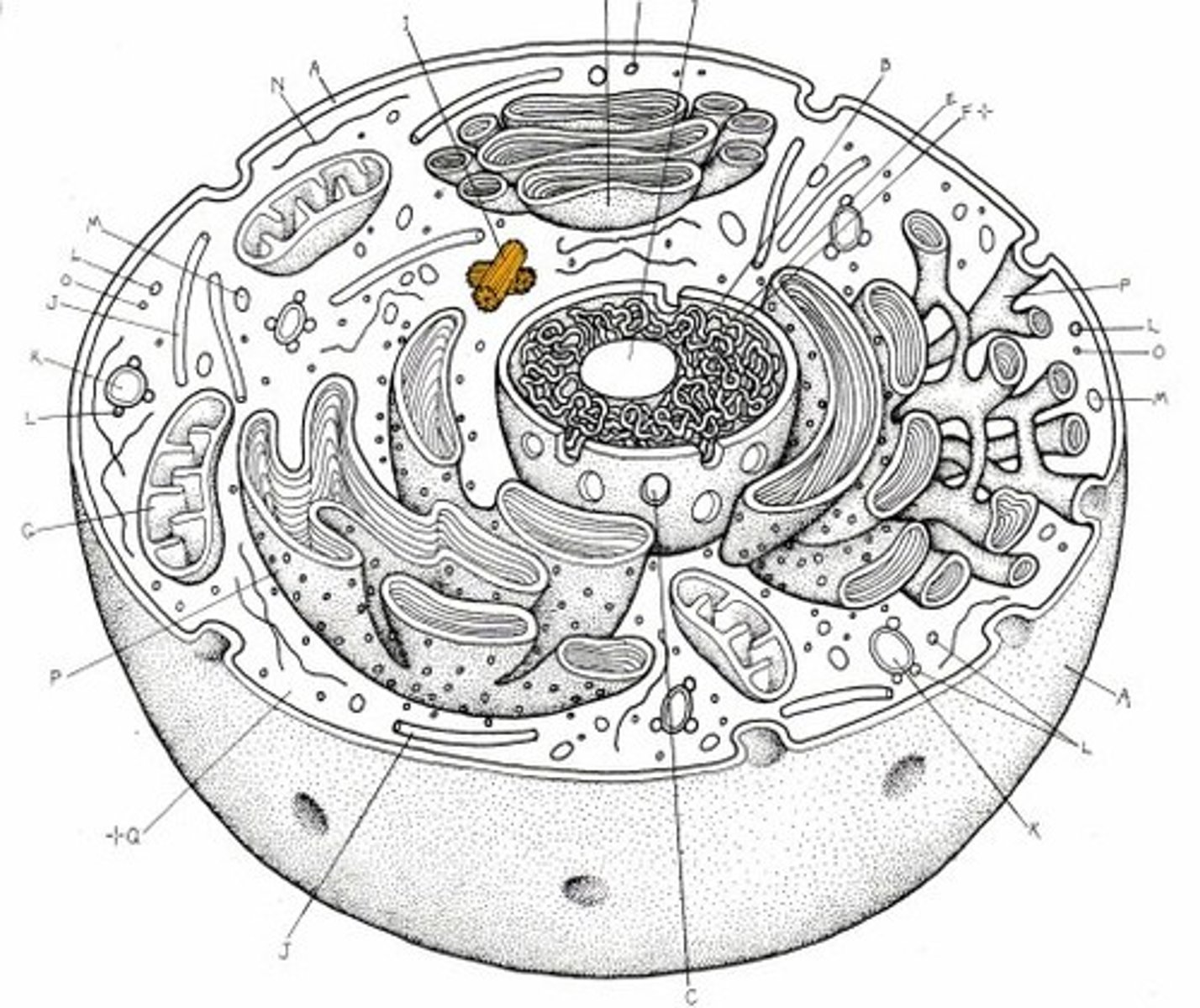
Organelle
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell
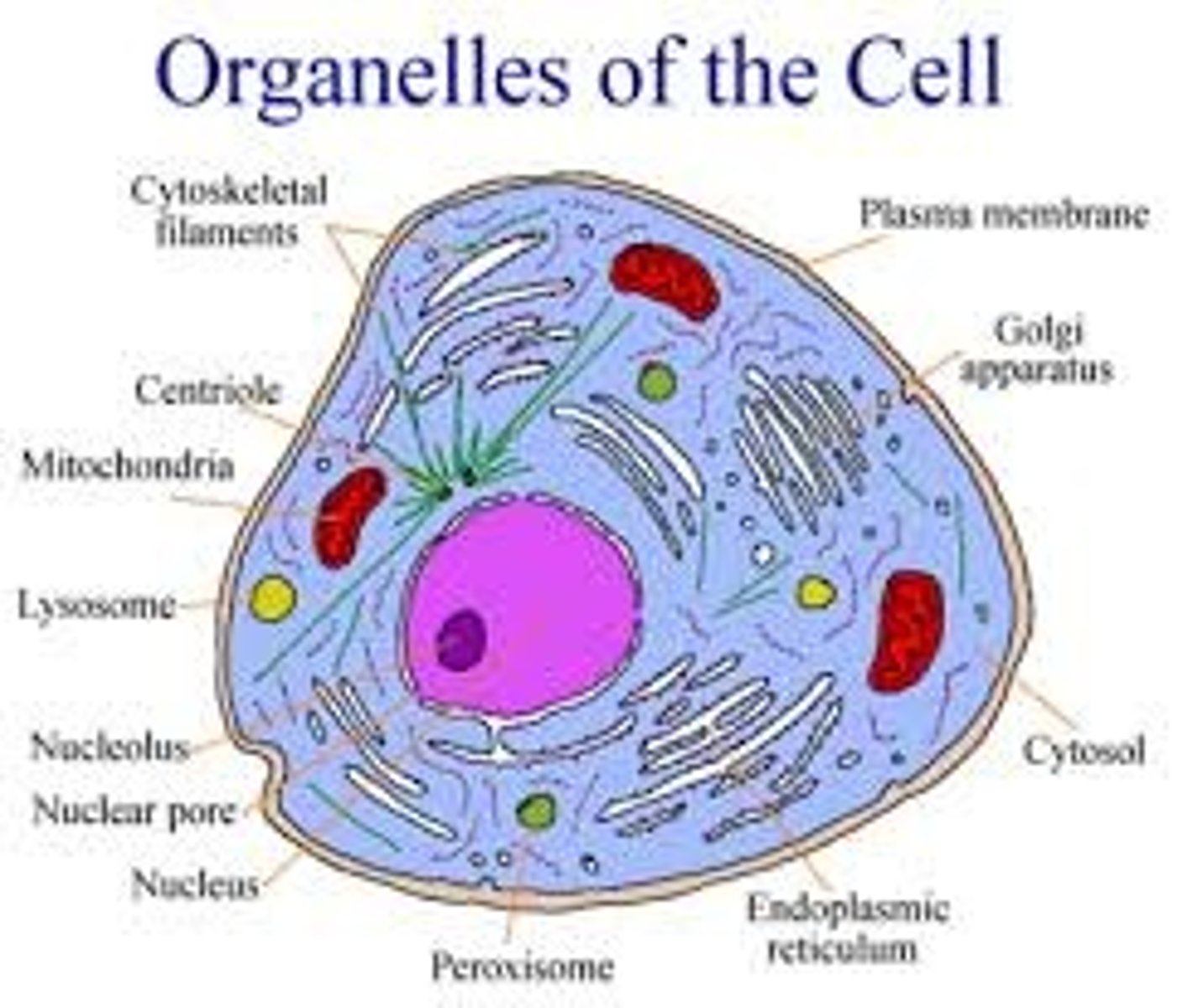
Cytosol
A semifluid, jellylike substance inside all cells.
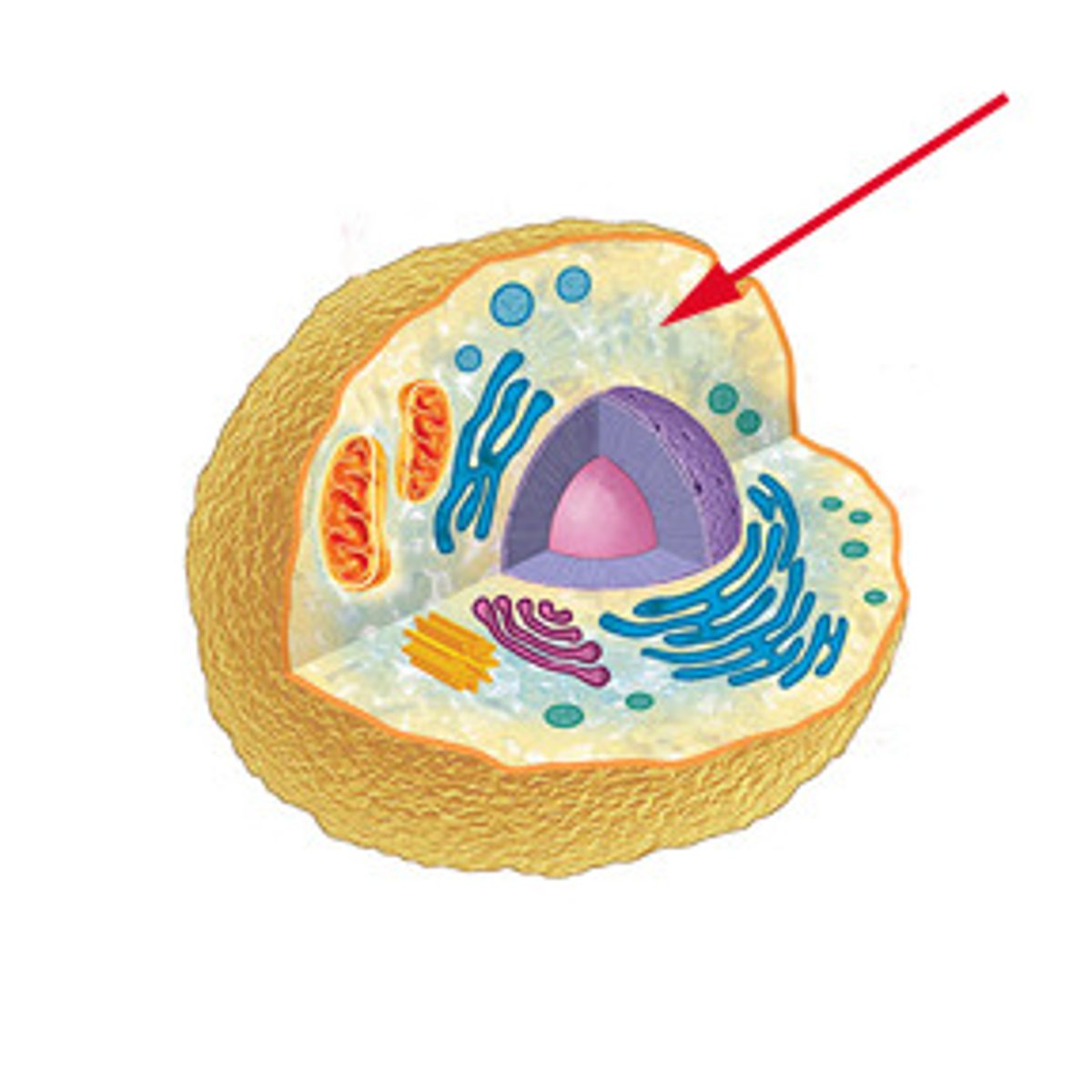
Eukaryotic cell
A type of cell with a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles. Examples of organisms with these cells are protists, plants, fungi, and animals.
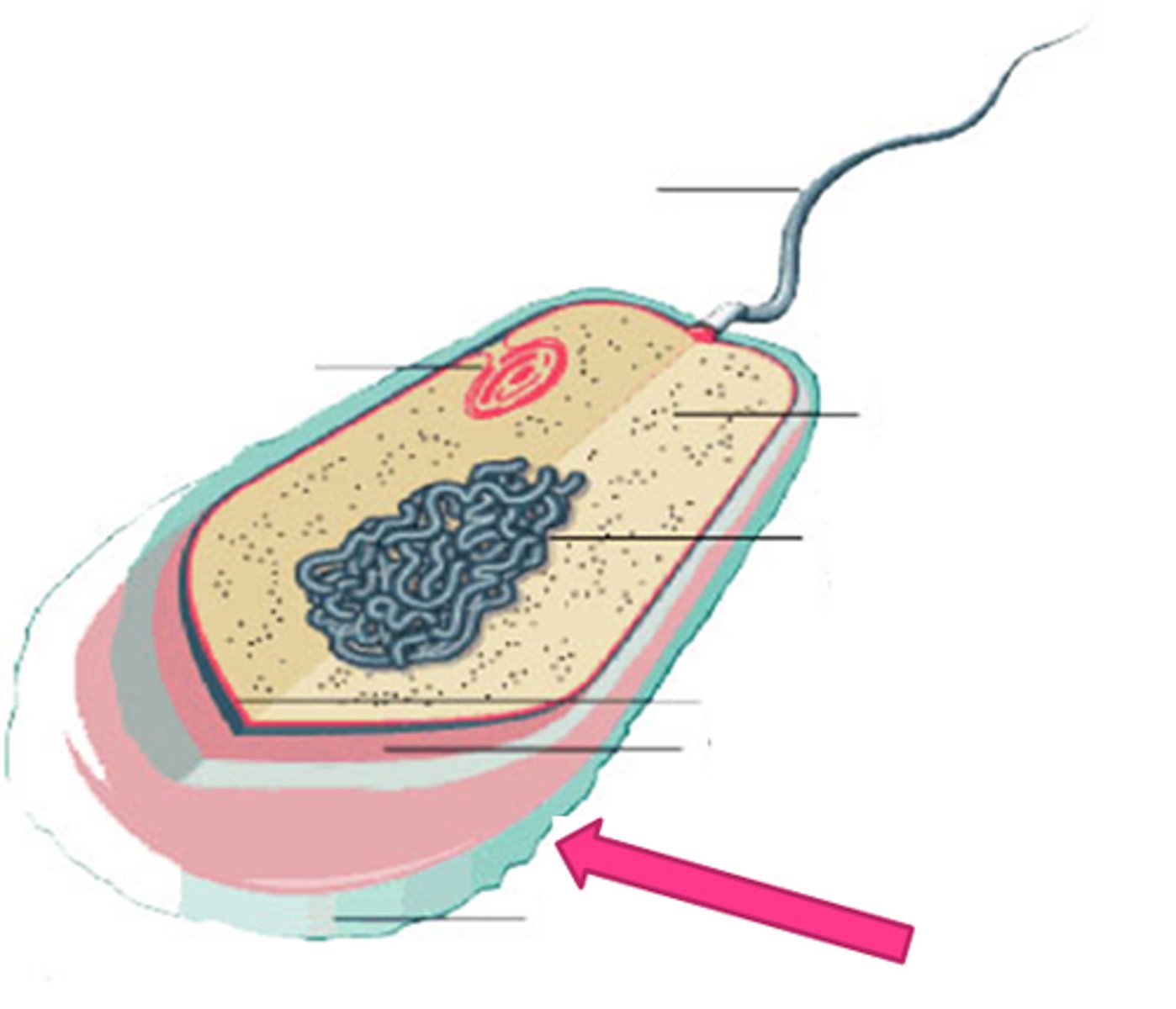
Prokaryotic Cell
A type of cell lacking a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles; found only in the domains Bacteria and Archaea.
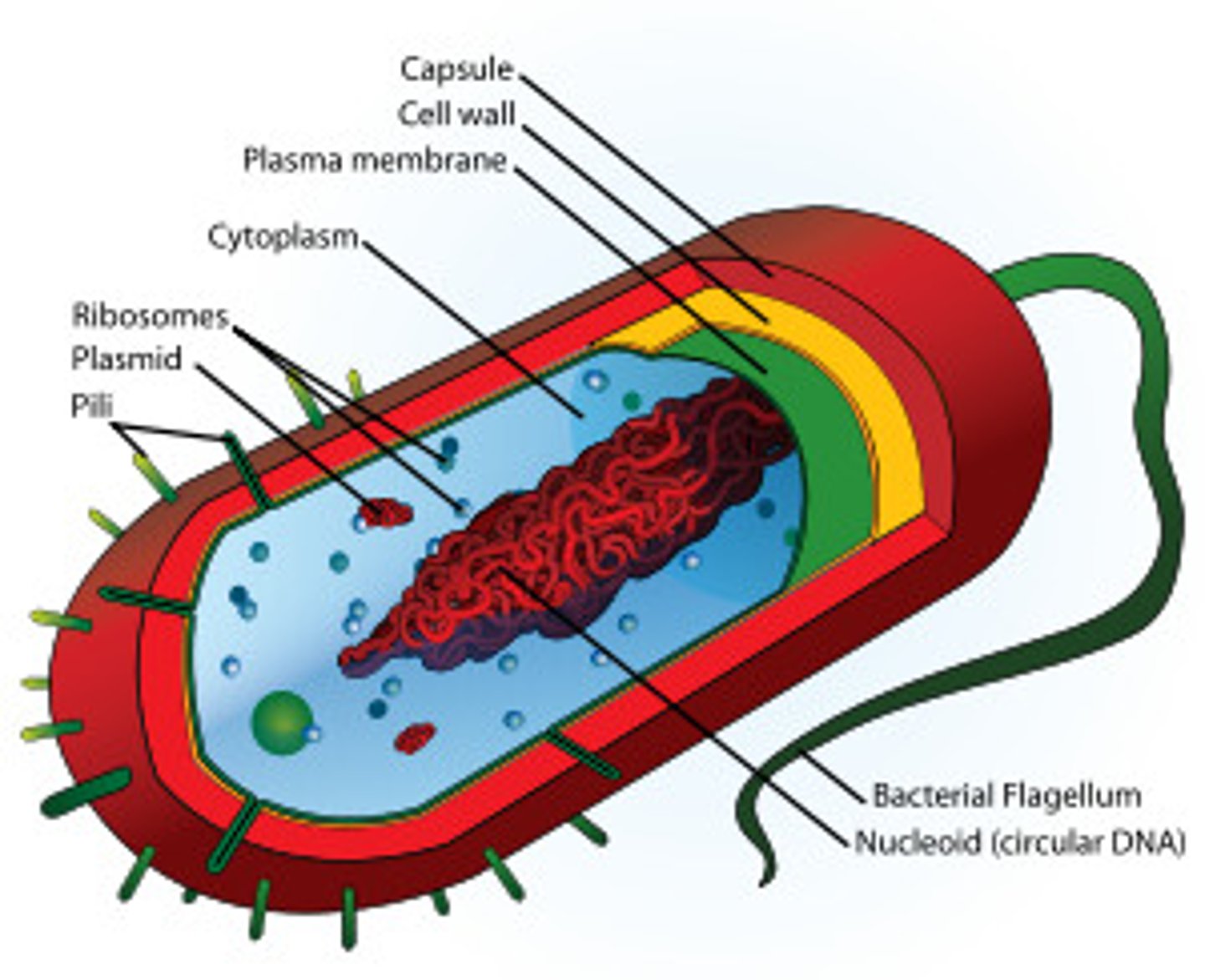
Nucleoid
A dense region of DNA in a prokaryotic cell.
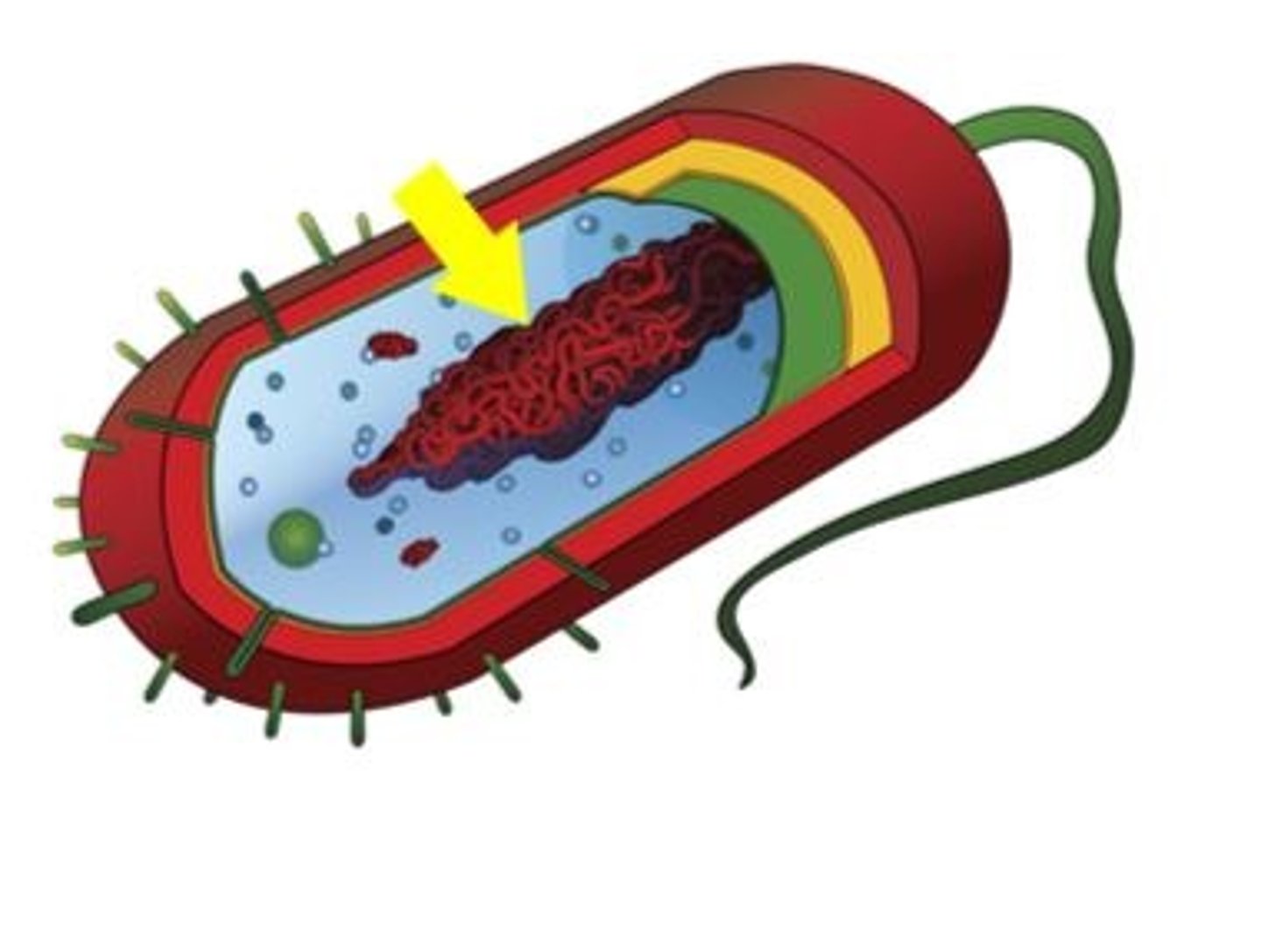
Capsule
A sticky layer that surrounds the cell walls of some bacteria, protecting the cell surface and sometimes helping to glue the cell to surfaces.
Cytoplasm
The interior of a cell.
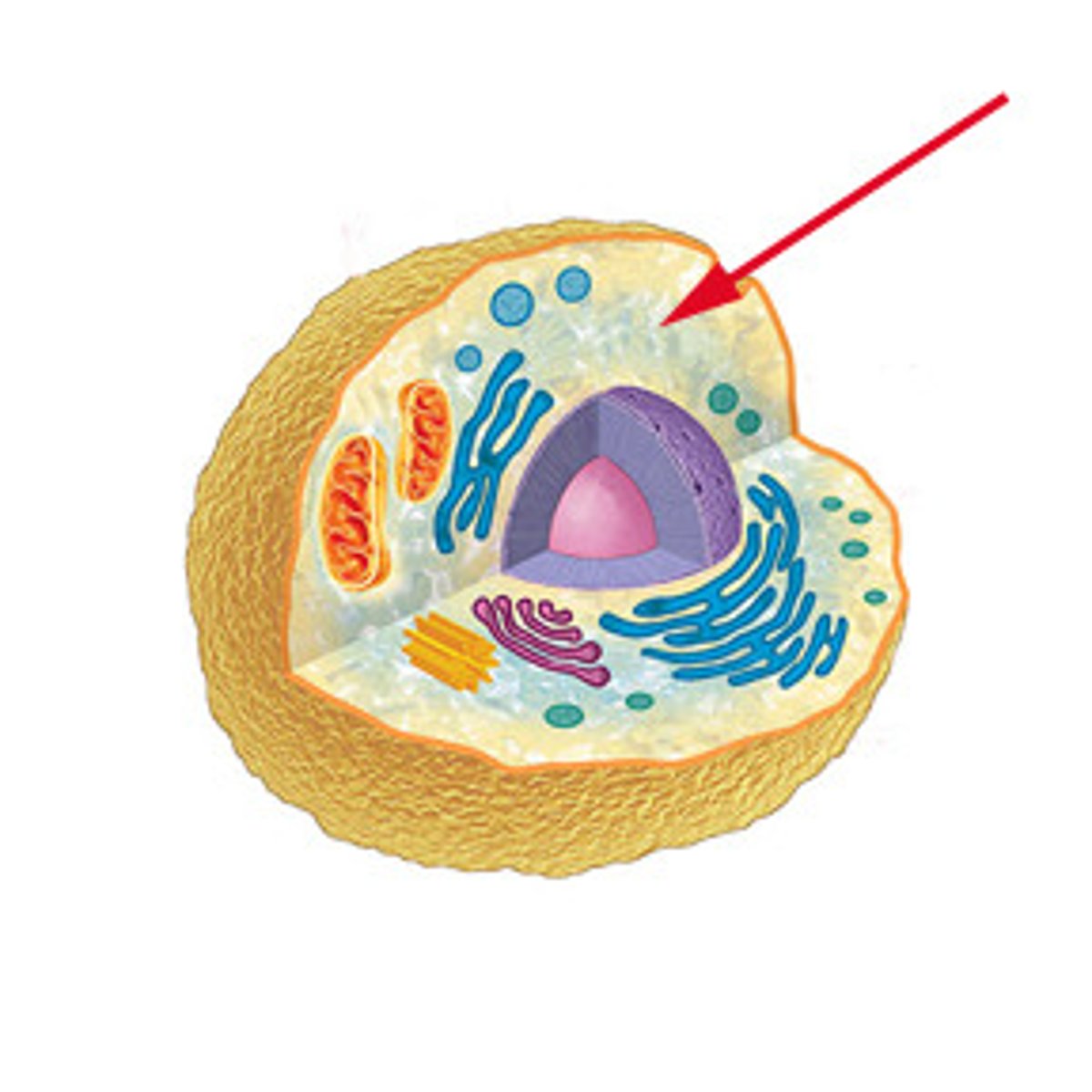
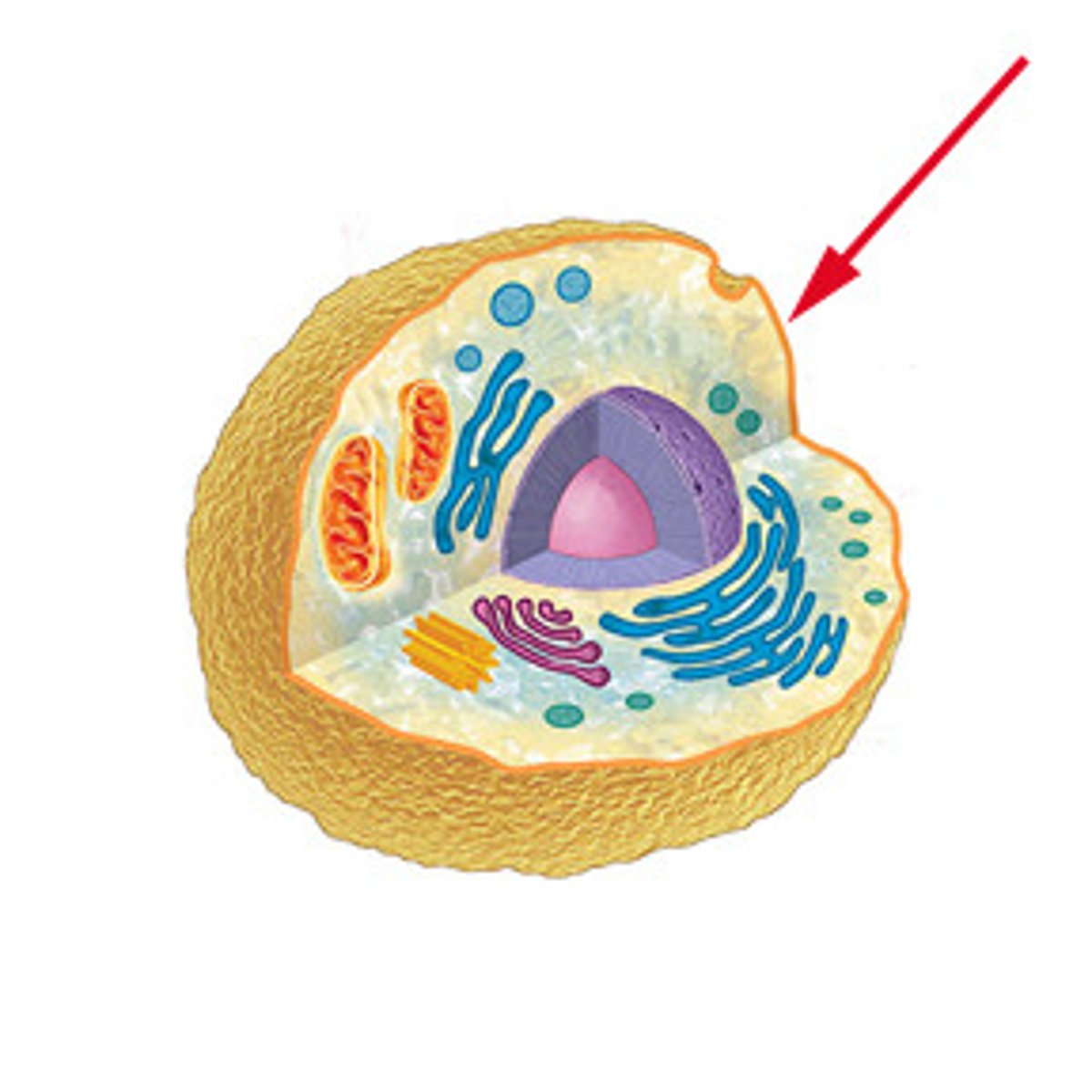
Plasma membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
Nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
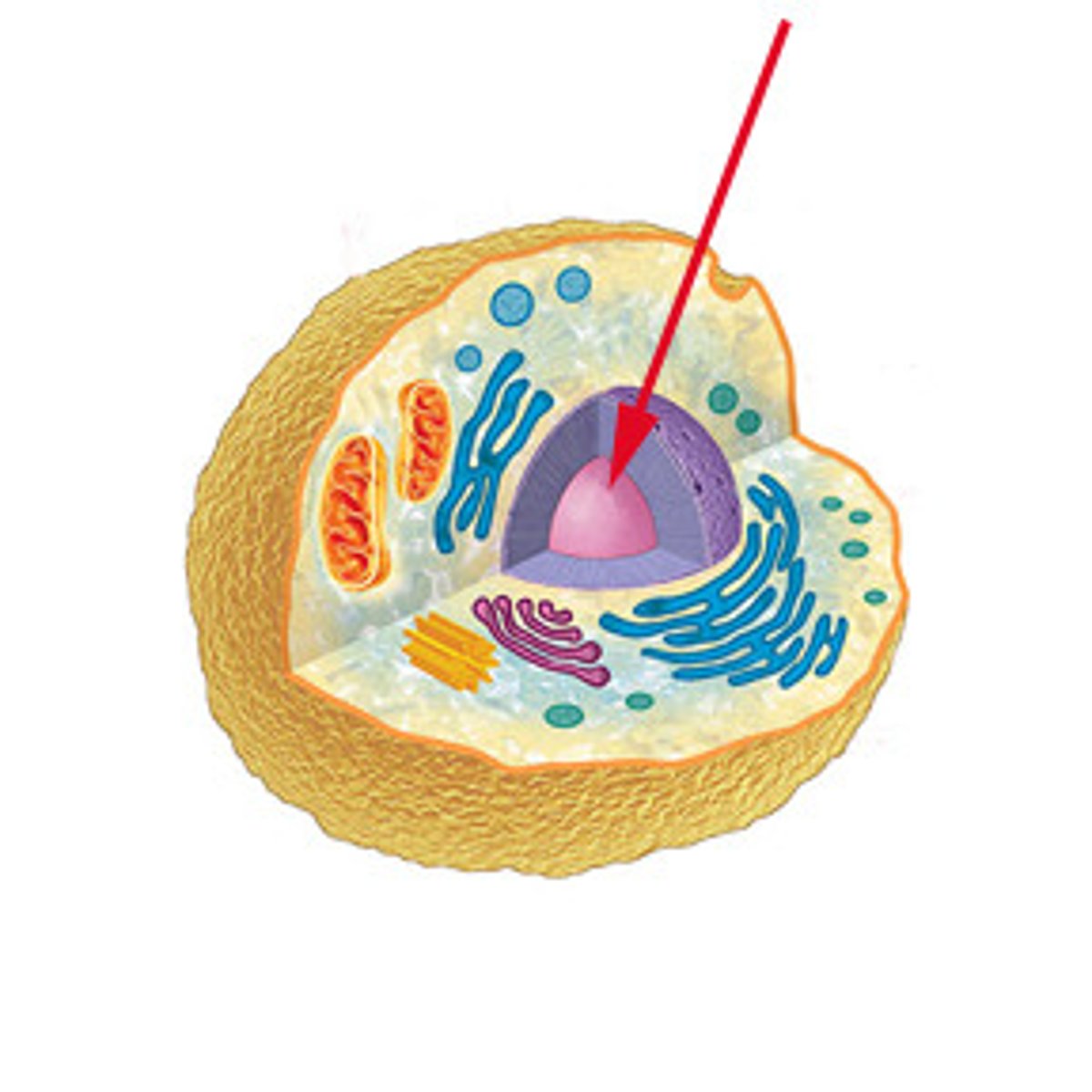
Nuclear envelope
A double membrane that surrounds the nucleus in the cell
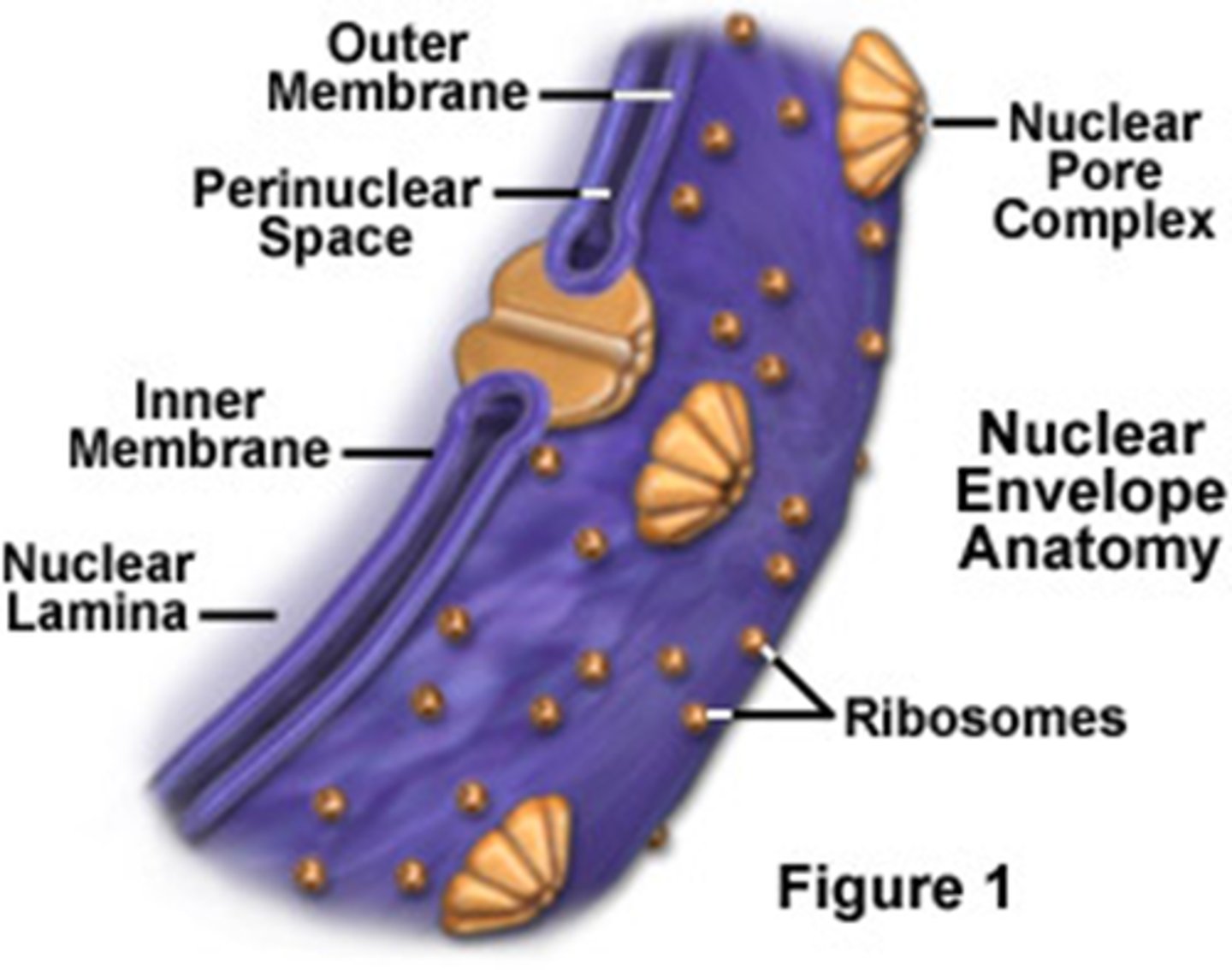
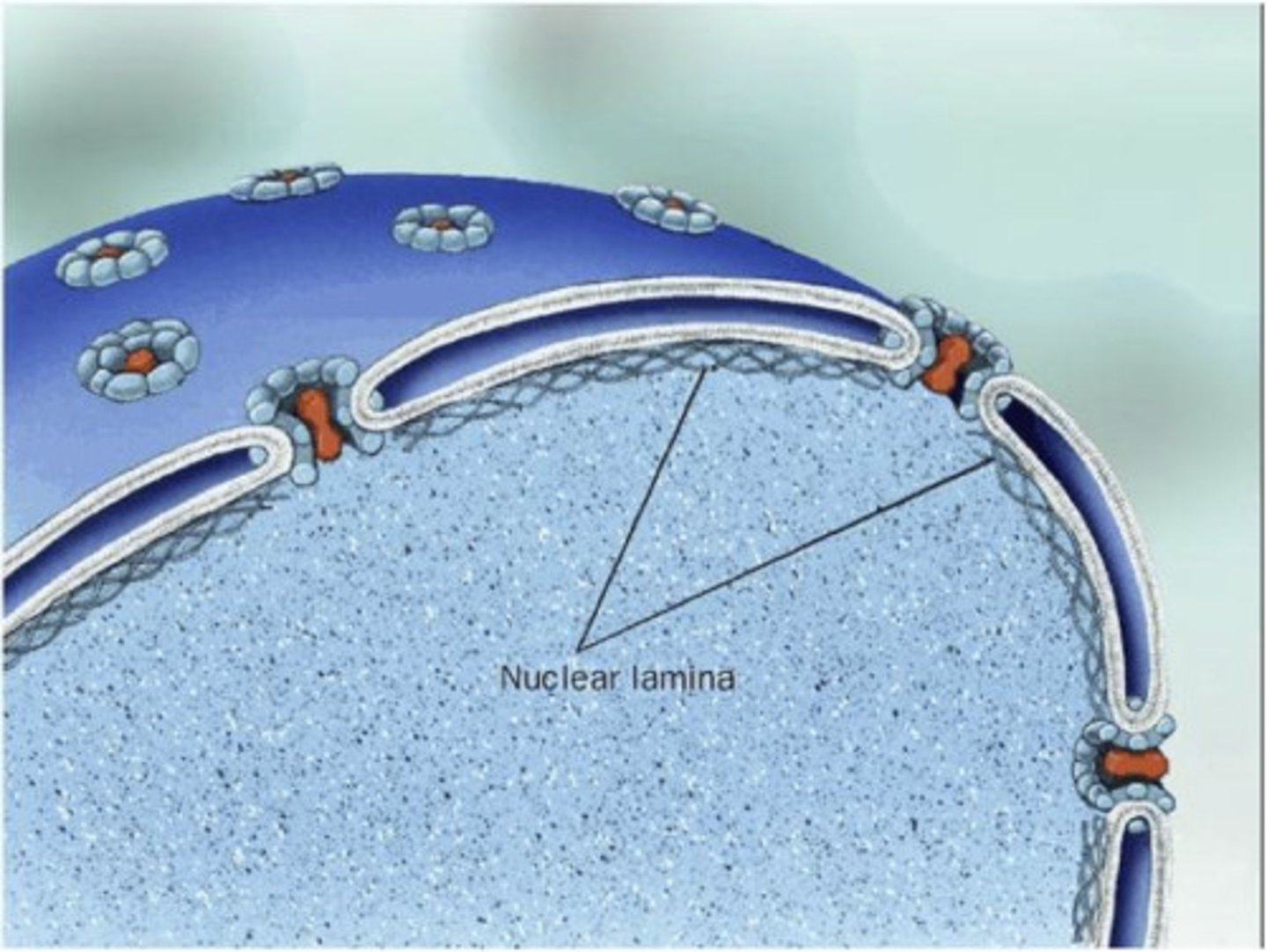
Nuclear lamina
A netlike array of protein filaments lining the inner surface of the nuclear envelope; it helps maintain the shape of the nucleus.
Chromosomes
Structures that carry the genetic information.
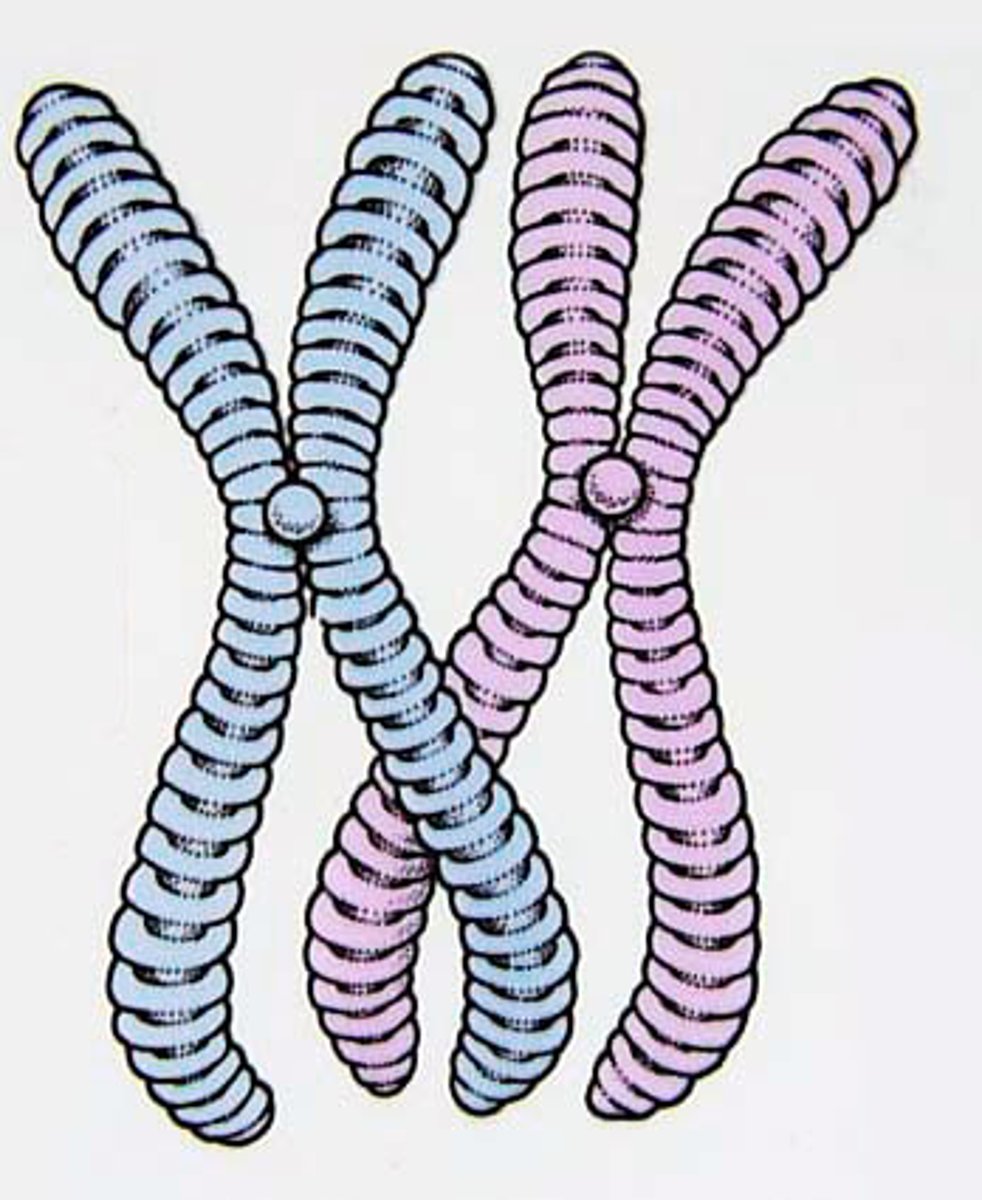
Chromatin
The complex of DNA and proteins making up chromosomes.
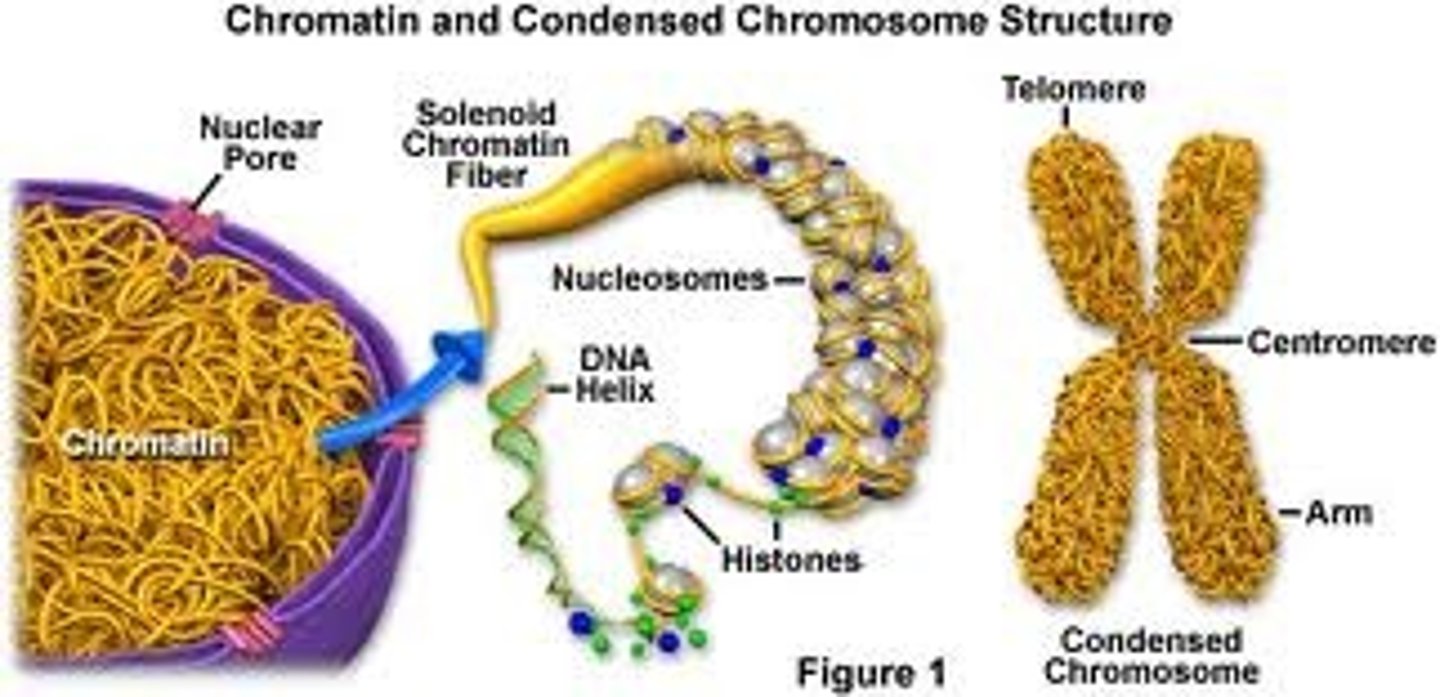
Nucleolus
A specialized structure in the nucleus, formed from various chromosomes and active in the synthesis of ribosomes
Ribosomal RNA
A nucleic acid found in all living cells. Plays a role in transferring information from dNA to the protein-forming system of the cell.
Ribosomes
Complexes made of ribosomal RNA and protein that carry out protein synthesis.
Free ribosomes
Ribosomes suspended in the cytosol.
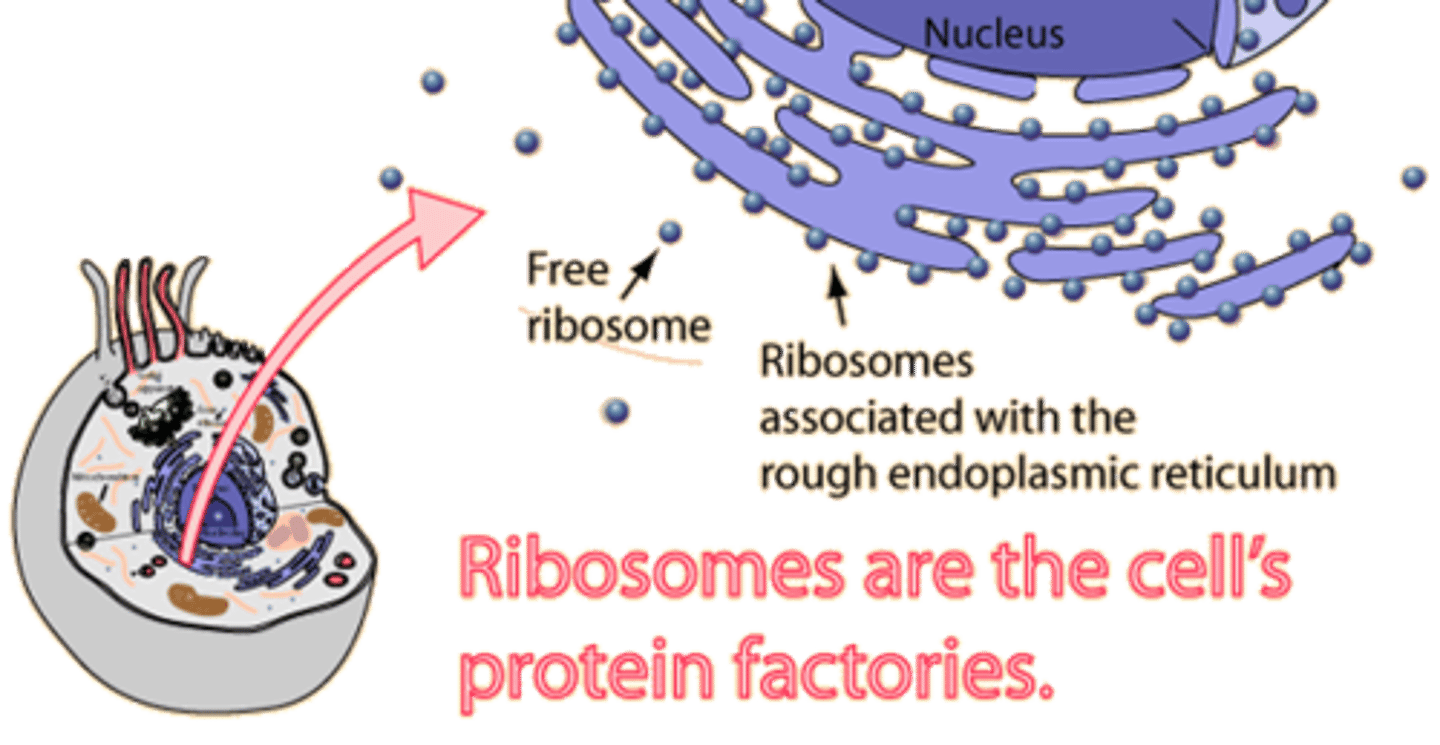
Bound ribosomes
Ribosomes attached to the outside of the endoplasmic reticulum or nuclear envelope.
Endomembrane system
The collection of membranes inside and around a eukaryotic cell, related either through direct physical contact or by the transfer of membranous vesicles.

Vesicle
A membrane bound sac that contains materials involved in transport of the cell.
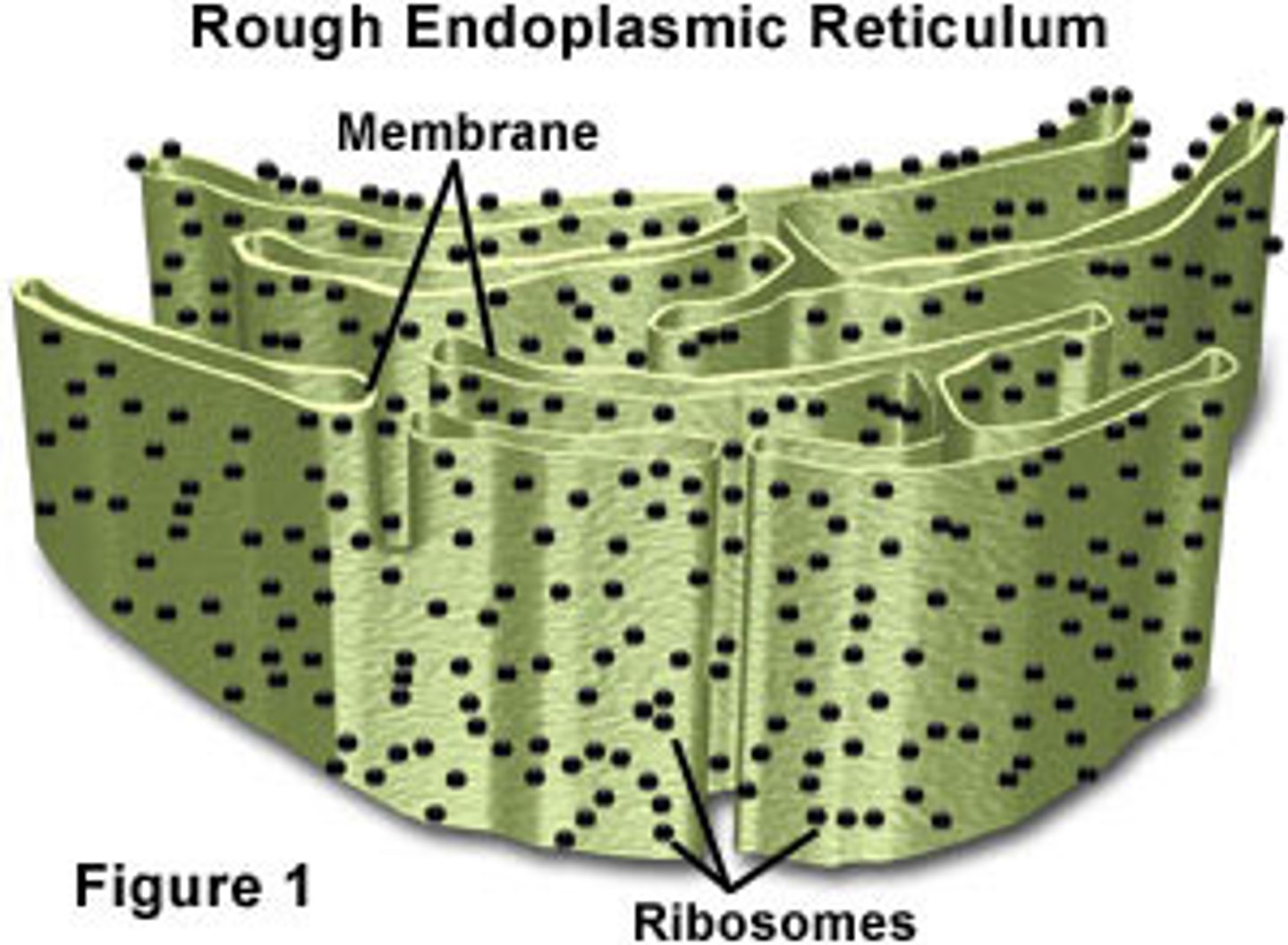
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
An endomembrane system covered with ribosomes where many proteins for transport are assembled.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
An endomembrane system where lipids are synthesized, calcium levels are regulated, and toxic substances are broken down.
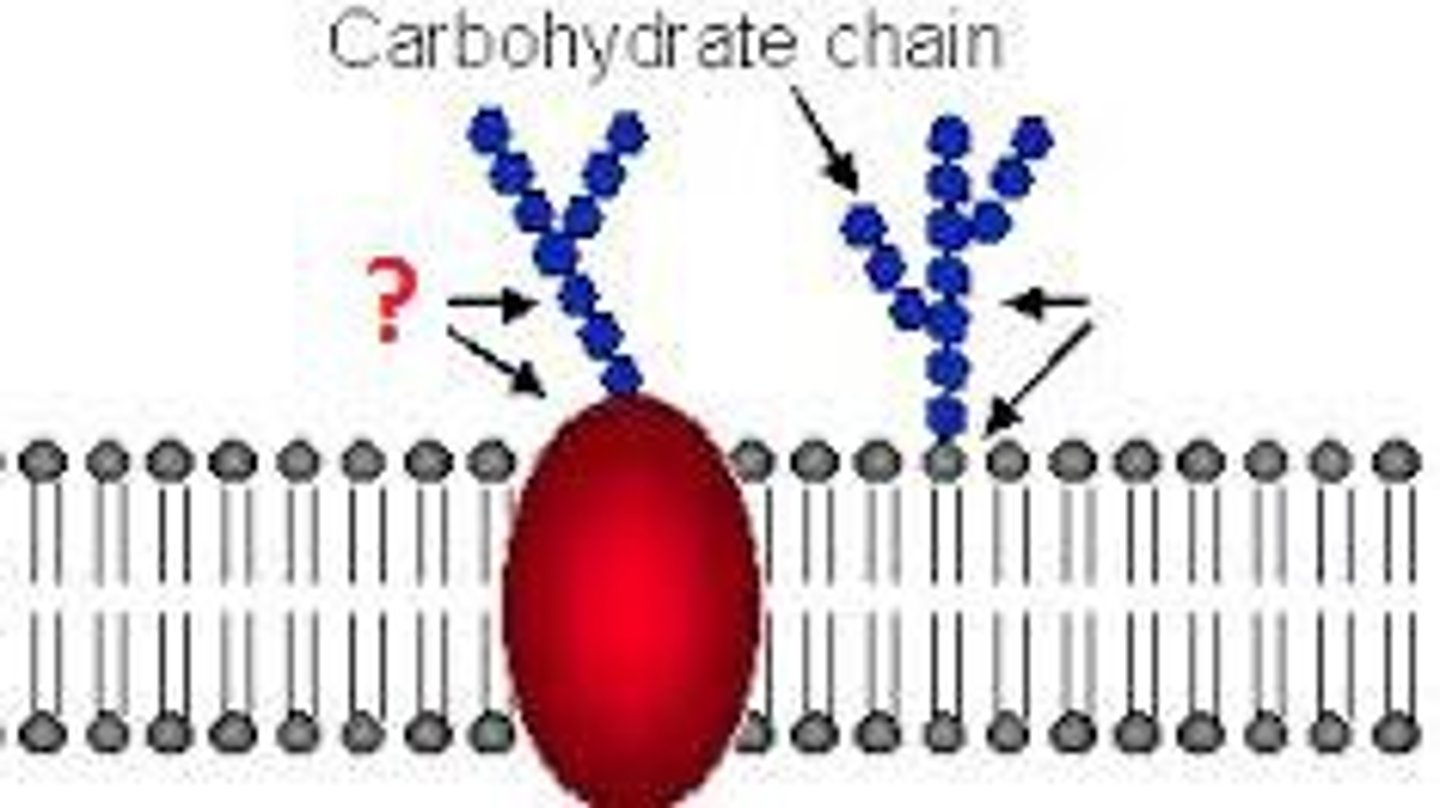
Glycoproteins
A protein with one or more covalently attached carbohydrates.
Transport vesicle
Tiny sac-like structures that are in transit from one part of the cell to another.
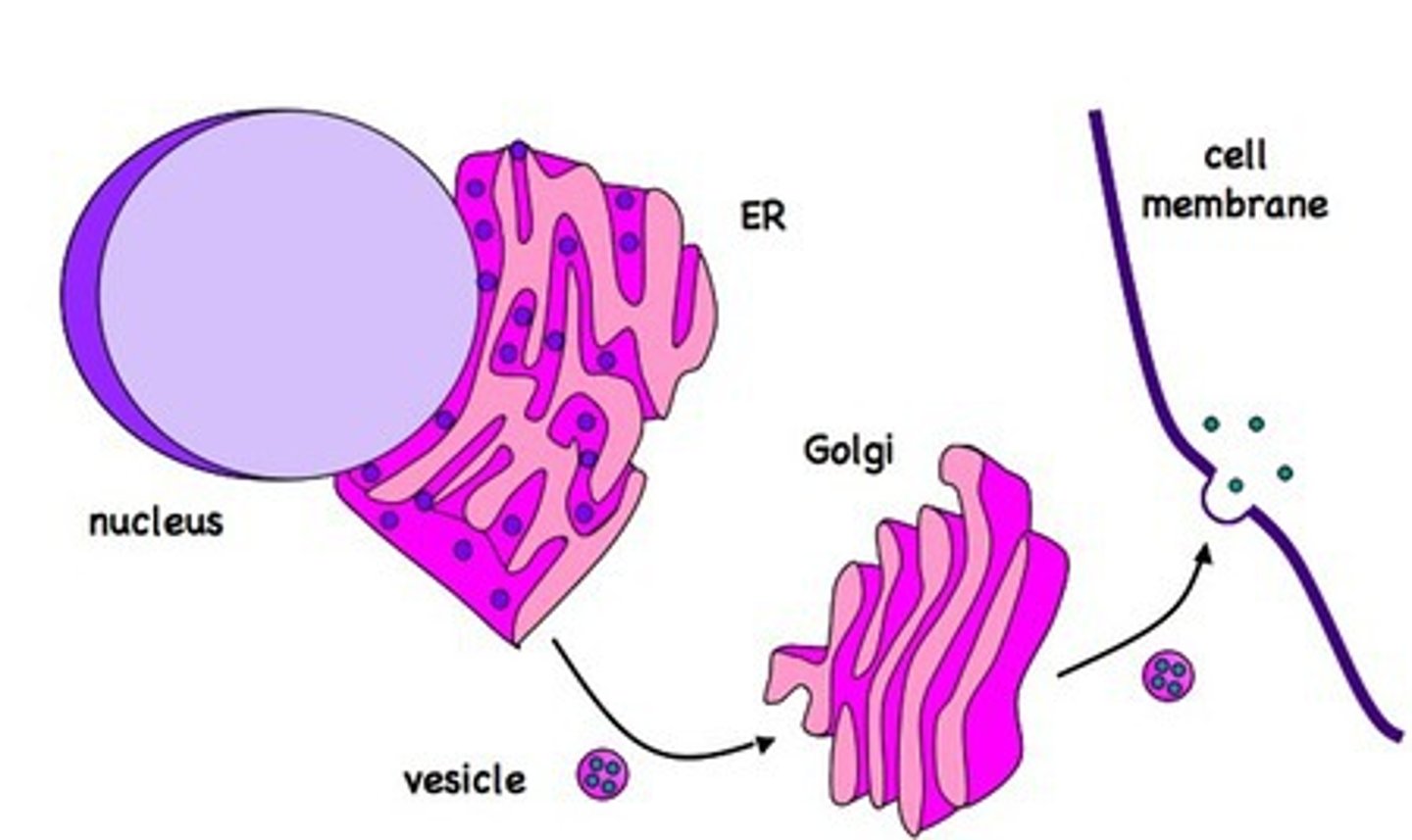
Golgi apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell
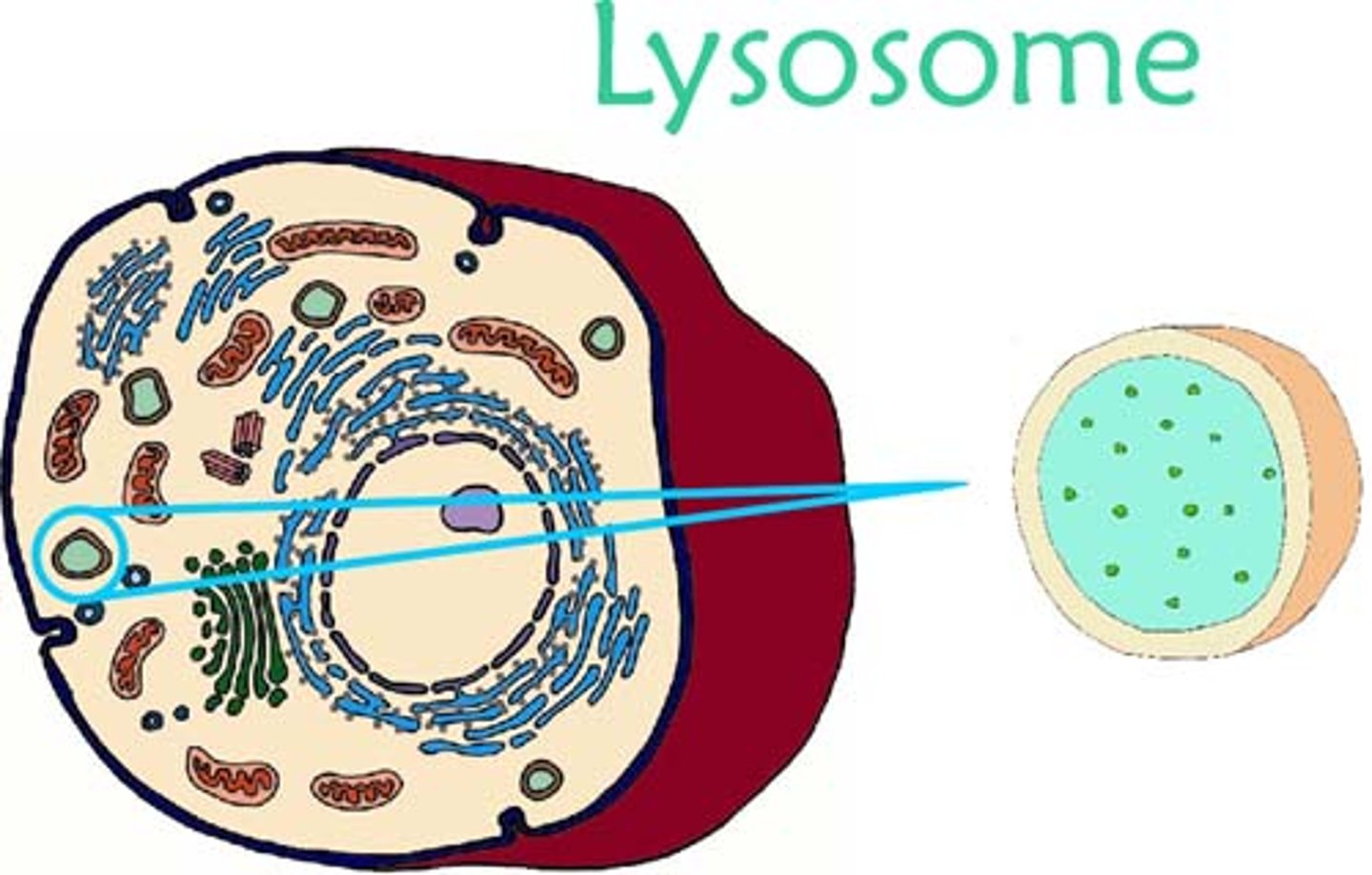
Lysosome
A membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that many eukaryotic cells use to digest macromolecules.
Phagocytosis
A process which engulfs smaller organisms or food particles.
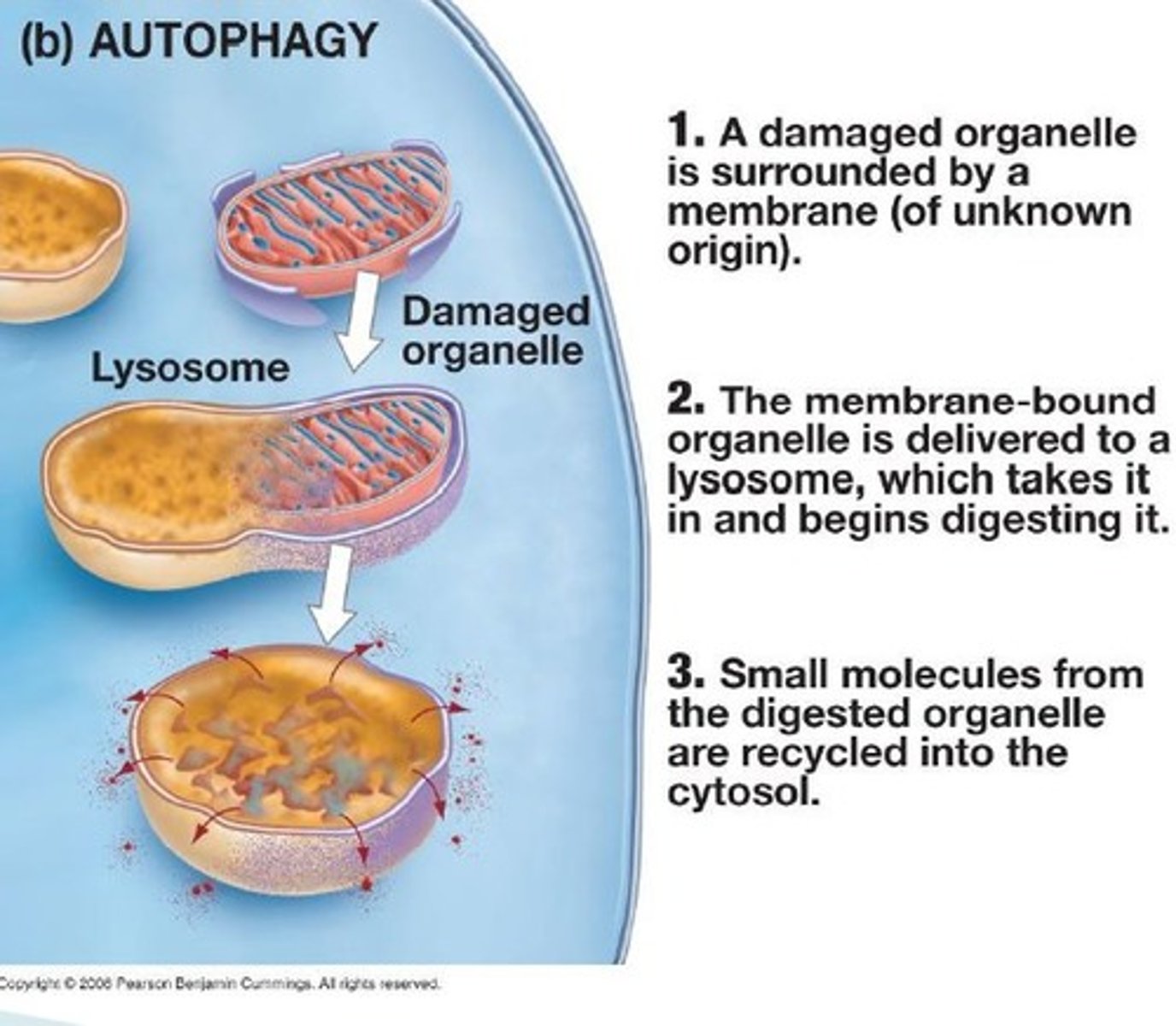
Autophagy
A process in which cells recycle their own organic material through the use of hydrolytic enzymes.
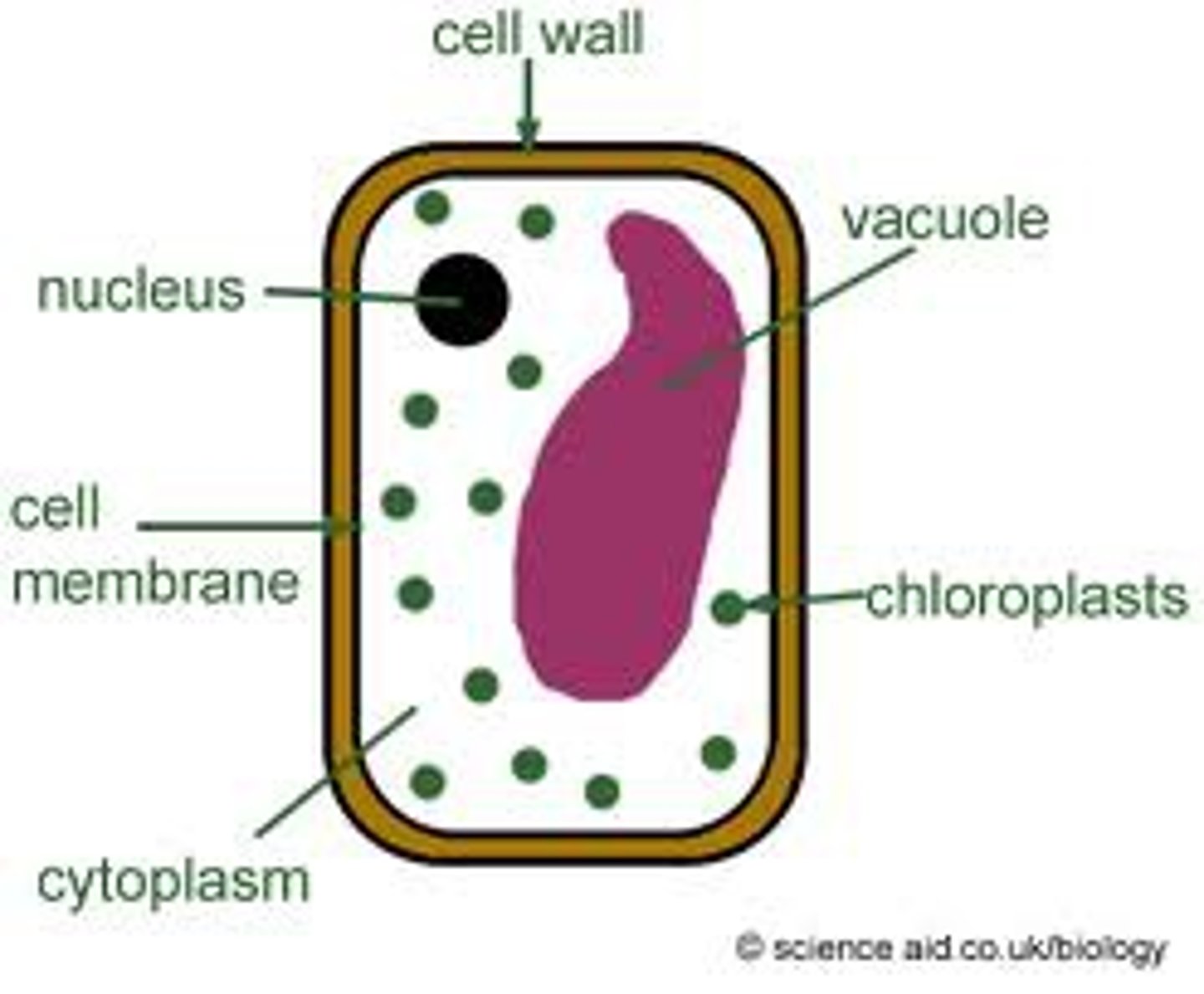
Vacuole
Large vesicles derived from the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus.
Food vacuoles
A membrane sac formed by phacogytosis; pinches off of the plasma membrane and encloses a food particle
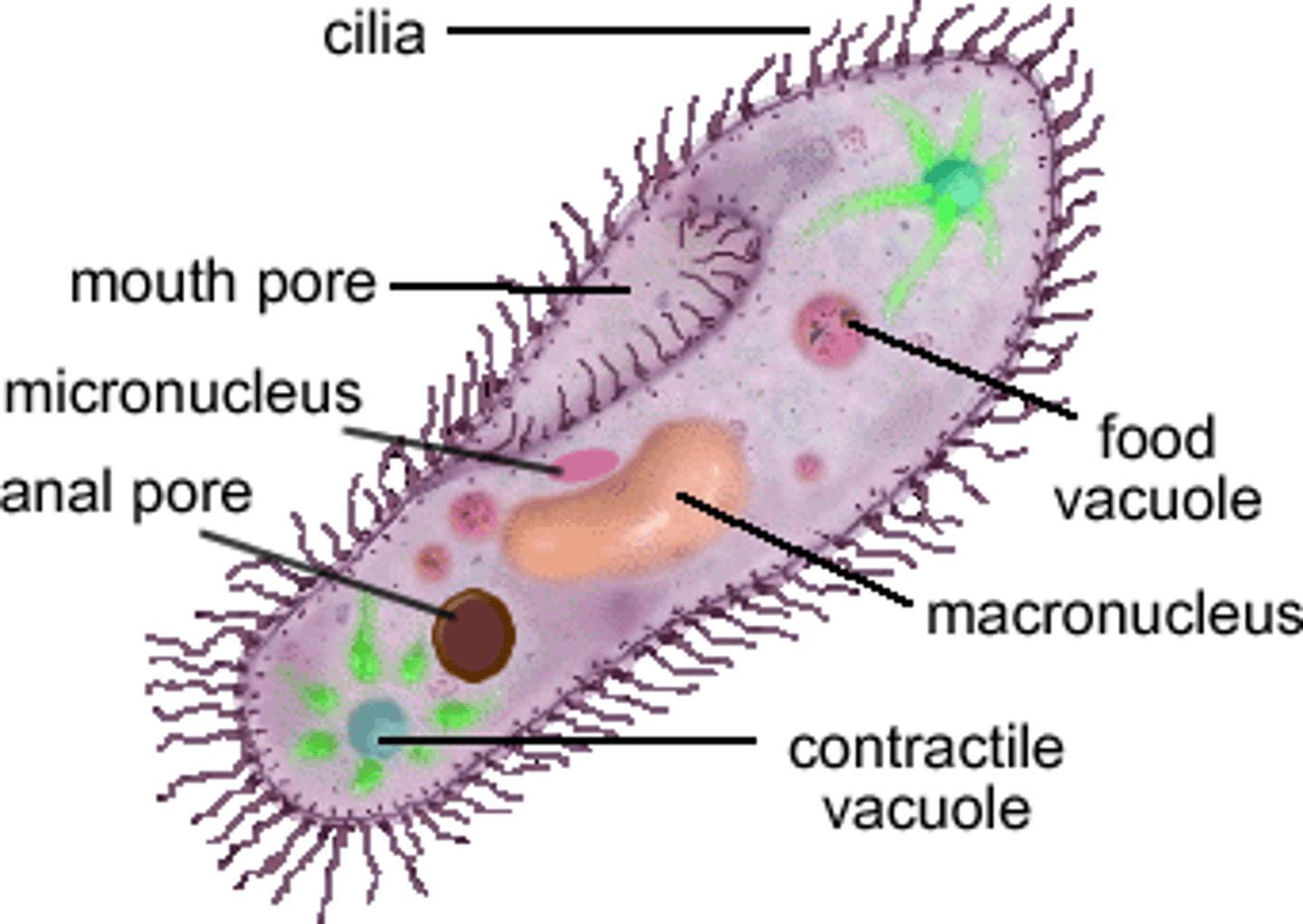
Contractile vacuoles
A membranous sac that helps move excess water out of the cell.
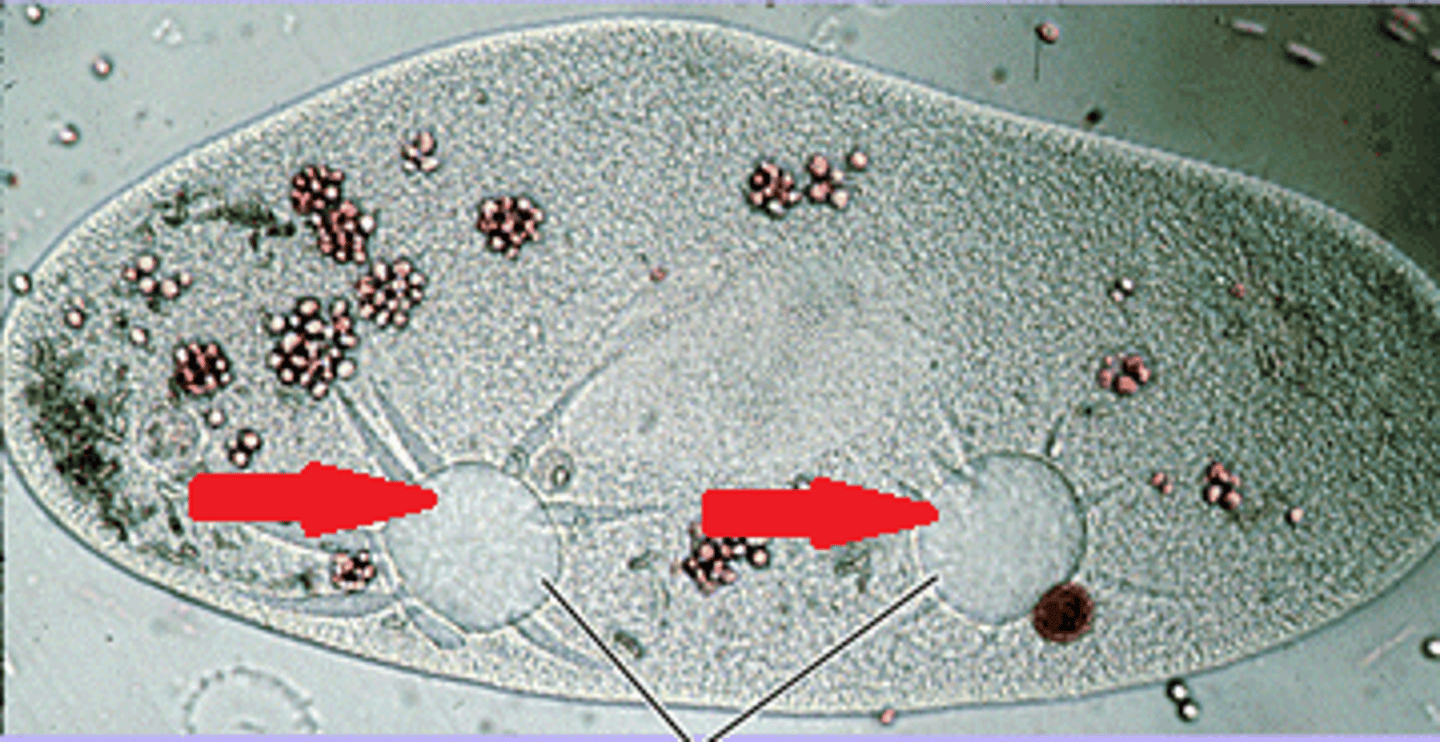
Central vacuole
A large vacuole that rests at the center of most plant cells and is filled with a solution that contains a high concentration of solutes.
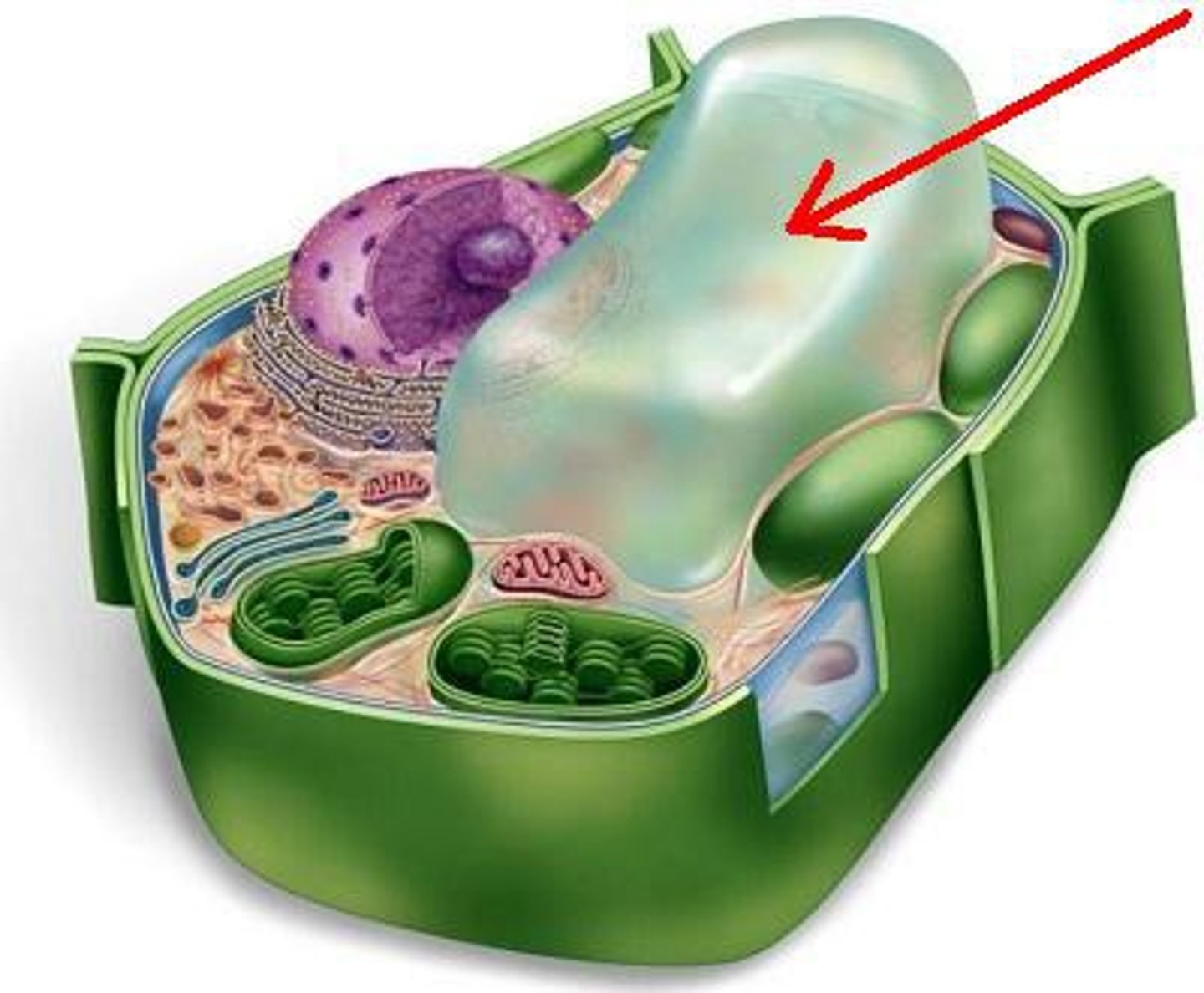
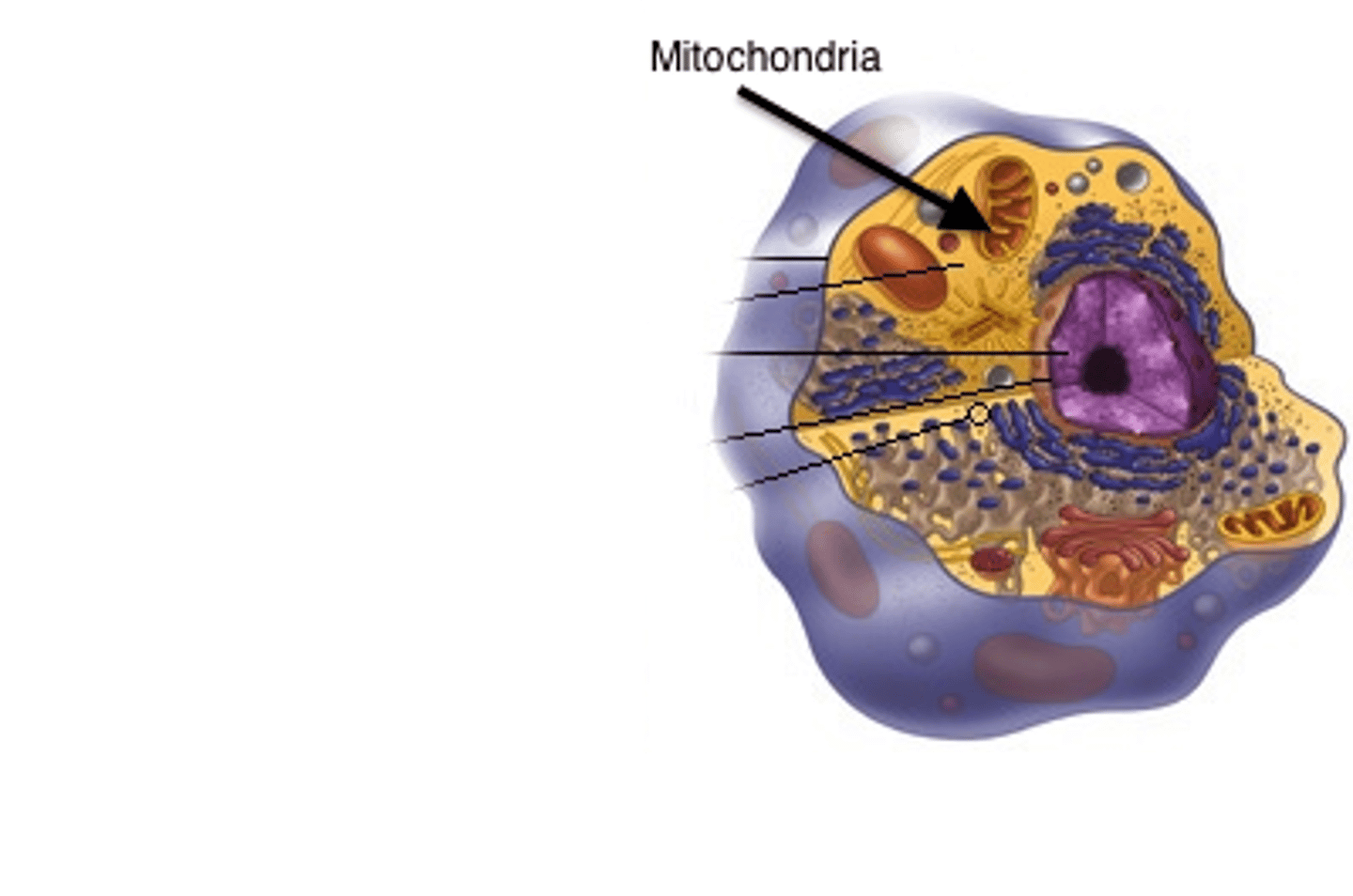
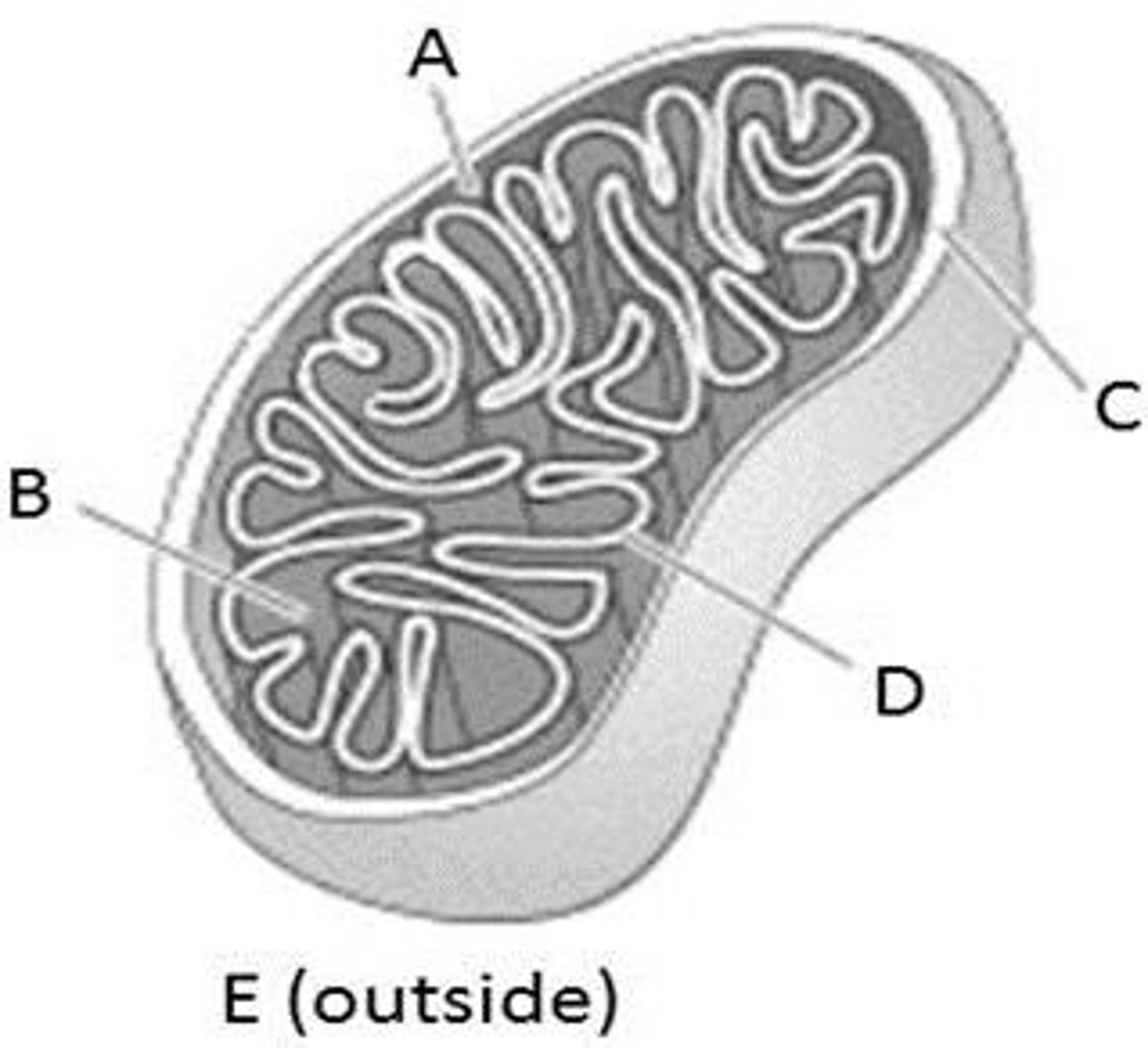
Mitochondria
The sites of cellular respiration.
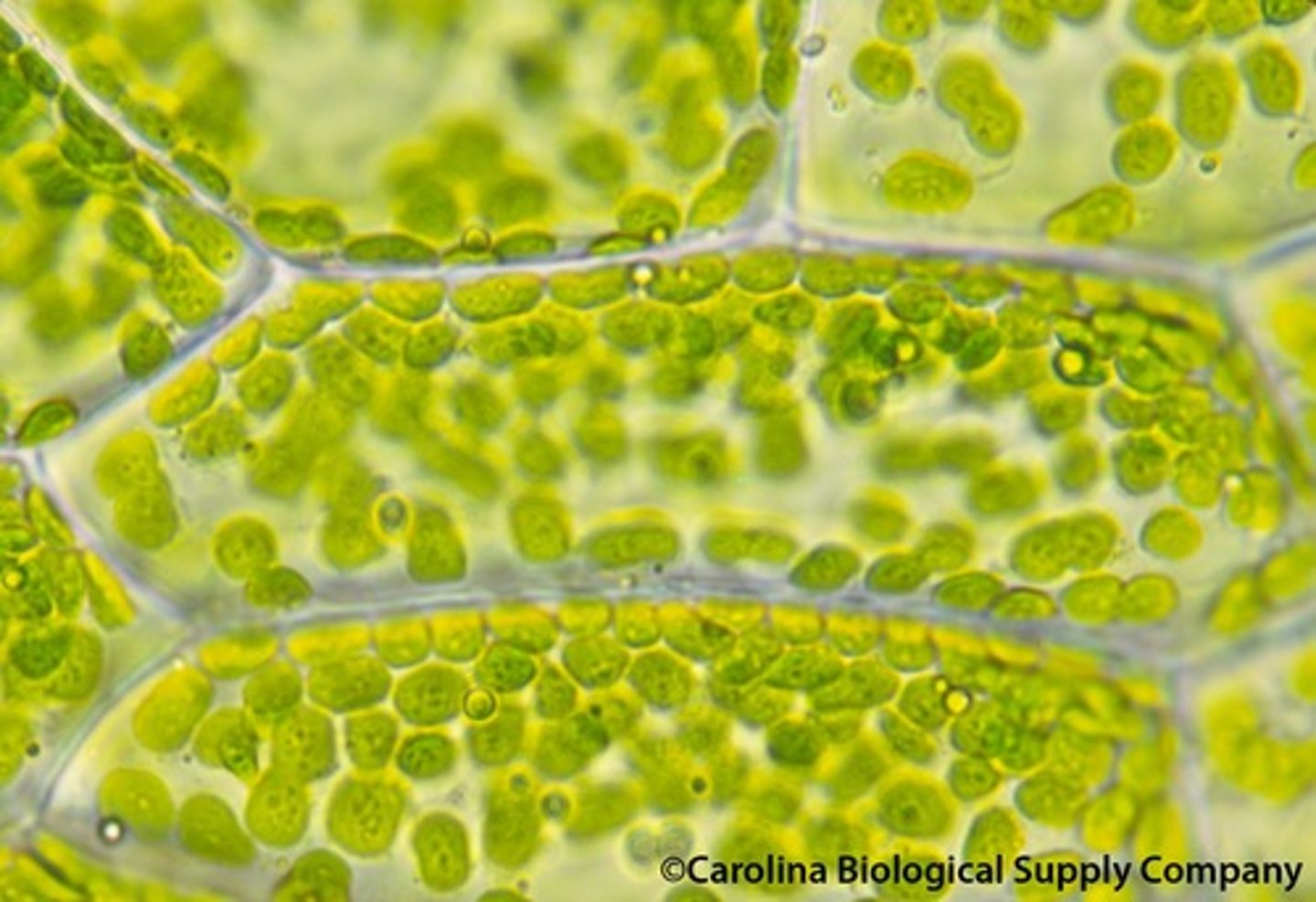
Chloroplasts
The sites of photosynthesis.
Endosymbiont theory
The theory that mitochondria and plastids, including chloroplasts, originated as prokaryotic cells engulfed by an ancestral eukaryotic cell. The engulfed cell and its host cell then evolved into a single organism.
Cristae
Infoldings of the inner membrane of a mitochondrion that houses the electon transport chain and the enzyme catalyzing the synthesis of ATP.

Mitochondrial matrix
The compartment of the mitochondrion enclosed by the inner membrane and containing enzymes and substrates for the Krebs cycle.
Thylakoid
A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy into chemical energy.
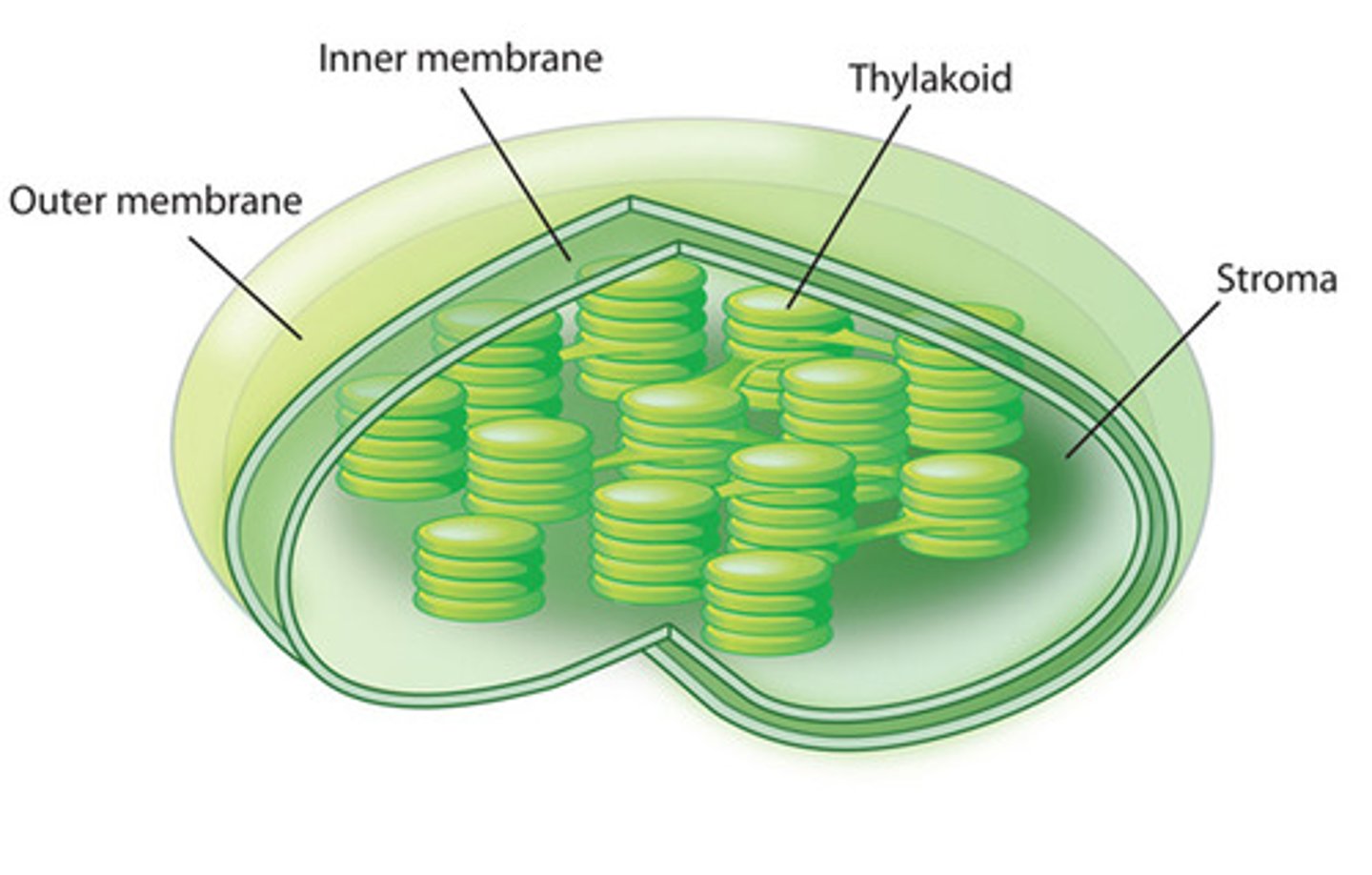
Granum
A stack of thylakoids in a chloroplast
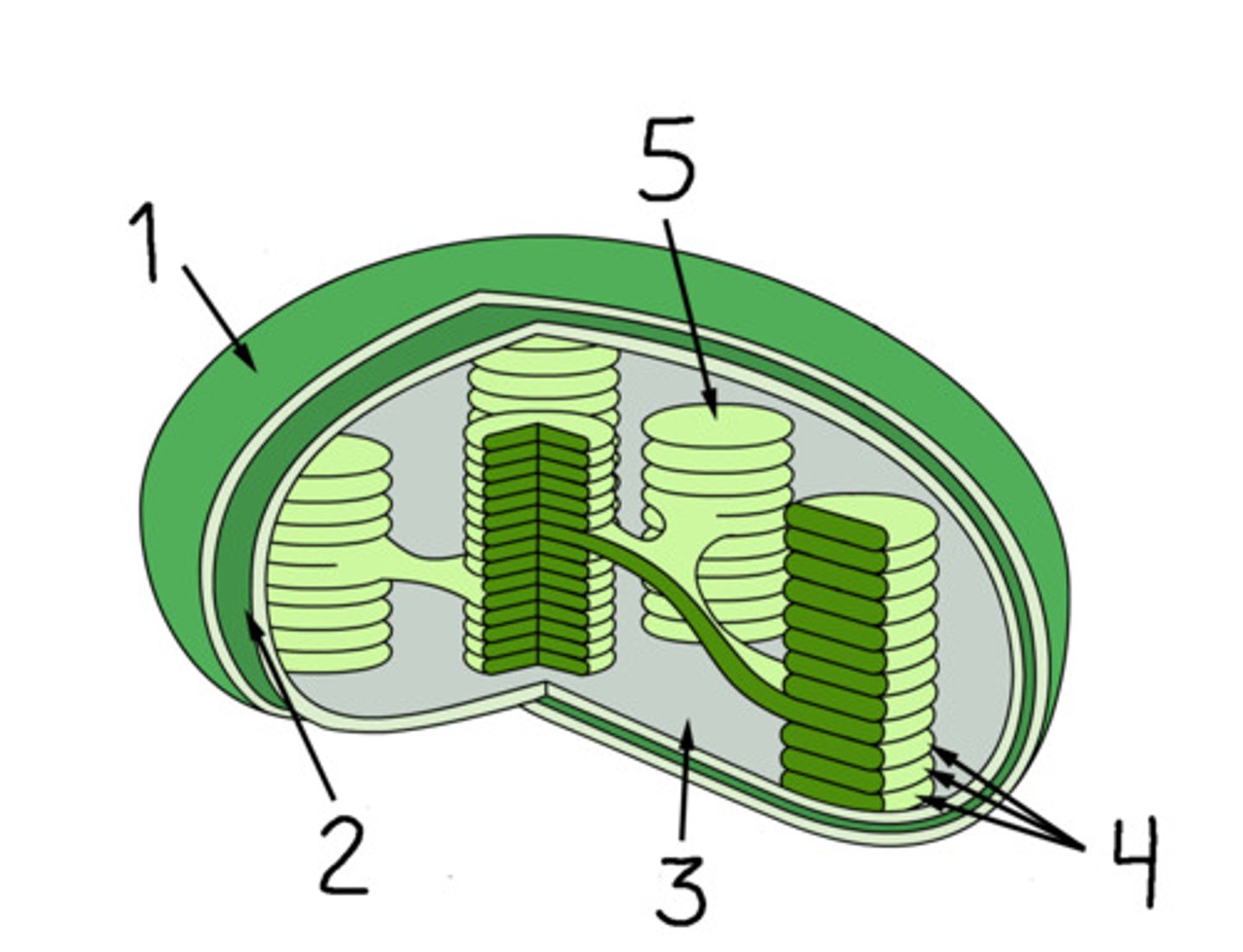
Stroma
In plants, the solution that surrounds the thylakoids in a chloroplast.
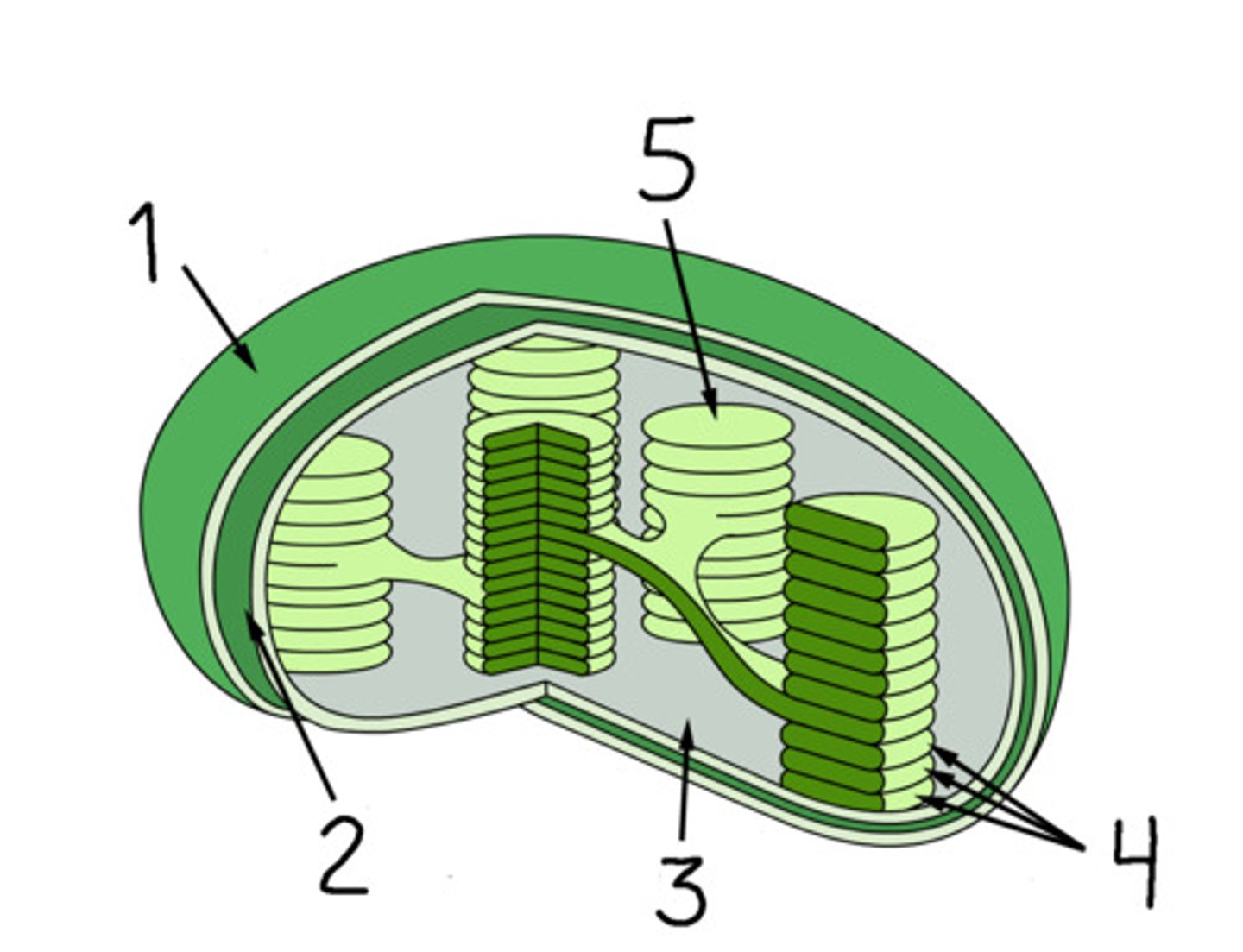
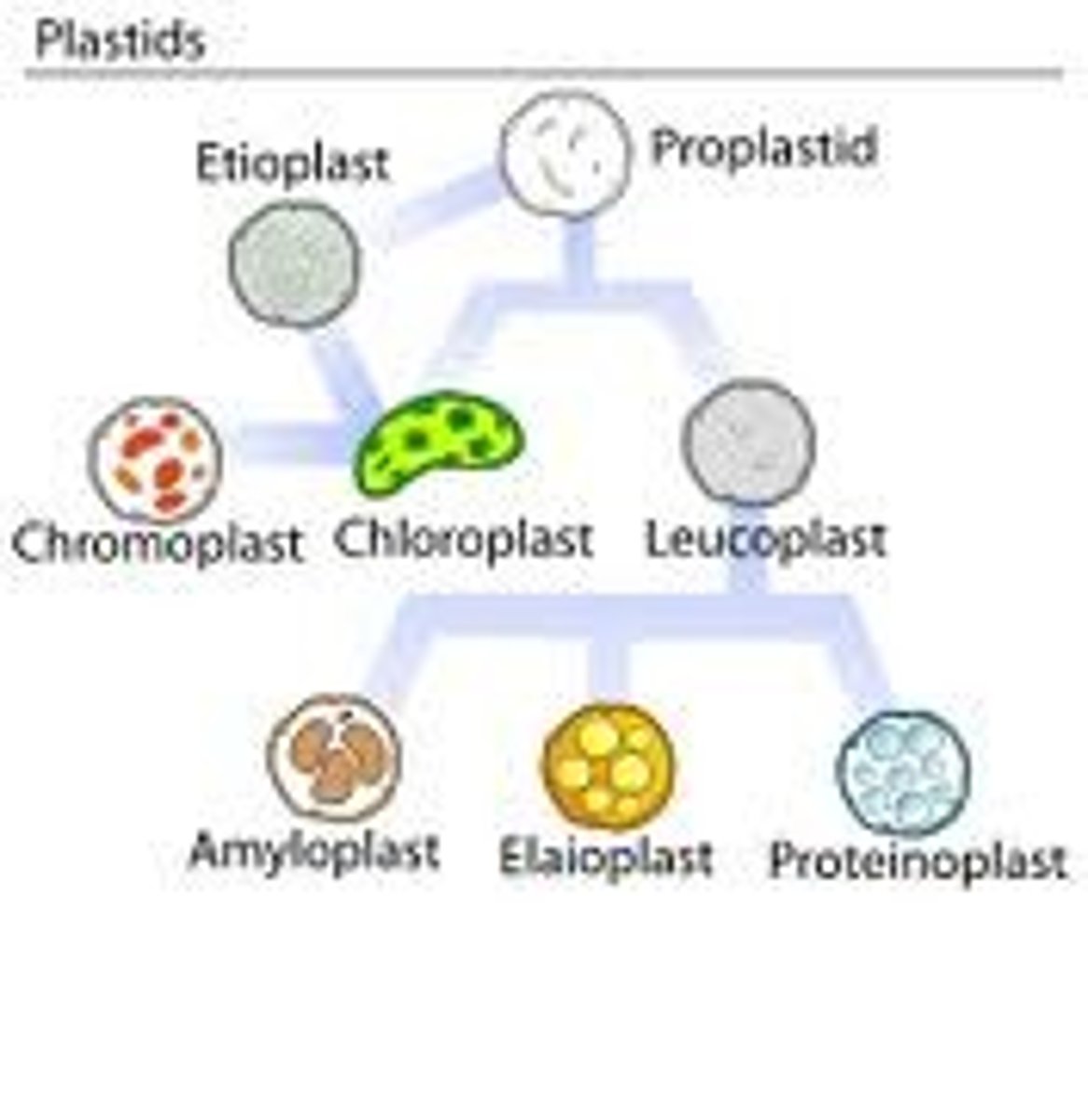
Plastid
A group of membrane‐bound organelles commonly found in photosynthetic organisms and mainly responsible for the synthesis and storage of food.
Peroxisome
A specialized metabolic compartment, bounded by a single membrane , containing enzymes that remove hydrogen atoms from various substrates and transfer them to oxygen, producing hydrogen peroxide.
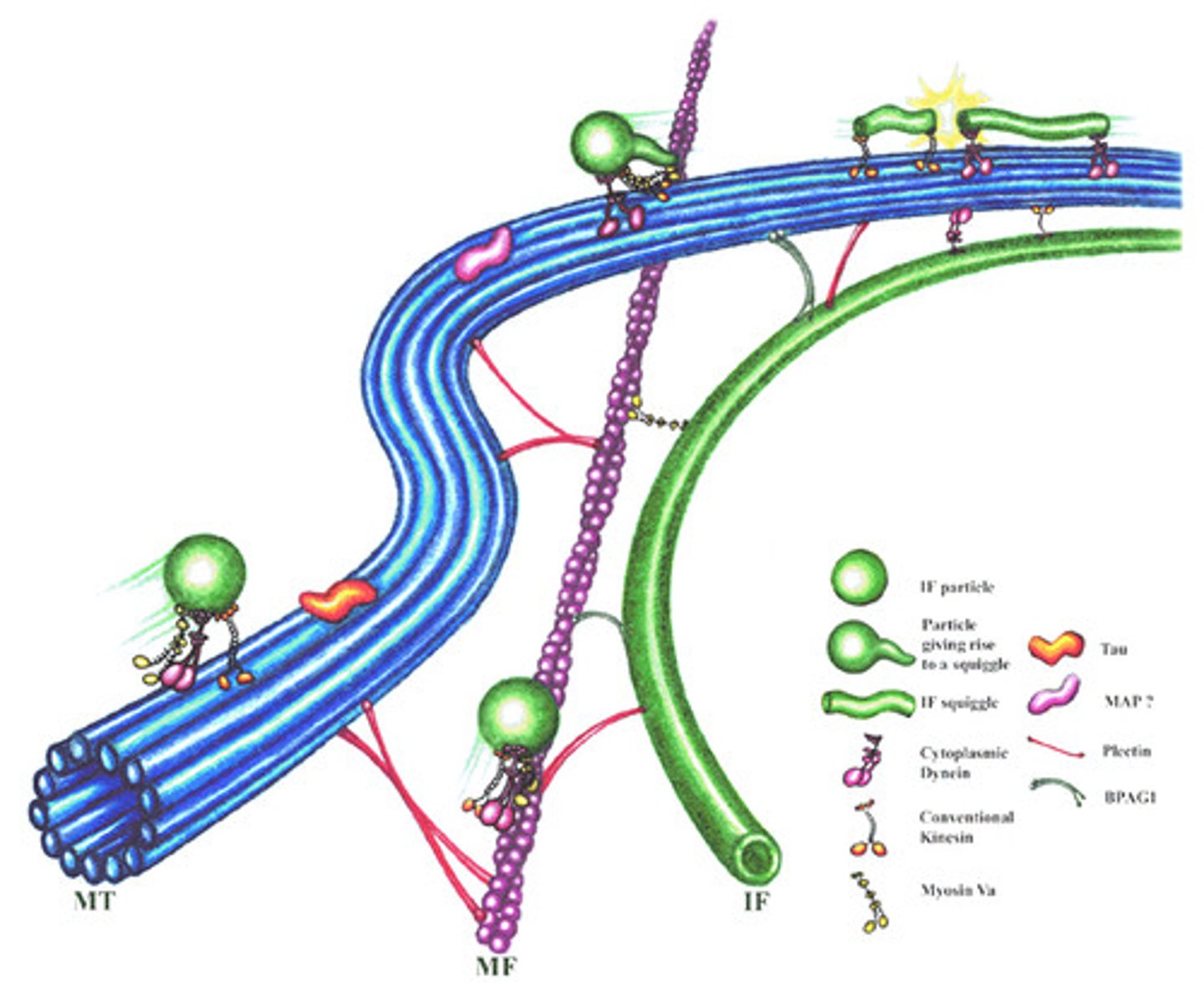
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm.
Microtubule
A hollow rod composed of tubulin proteins that makes up part of the cytoskeleton in all eukaryotic cells and is found in cilia and flagella.
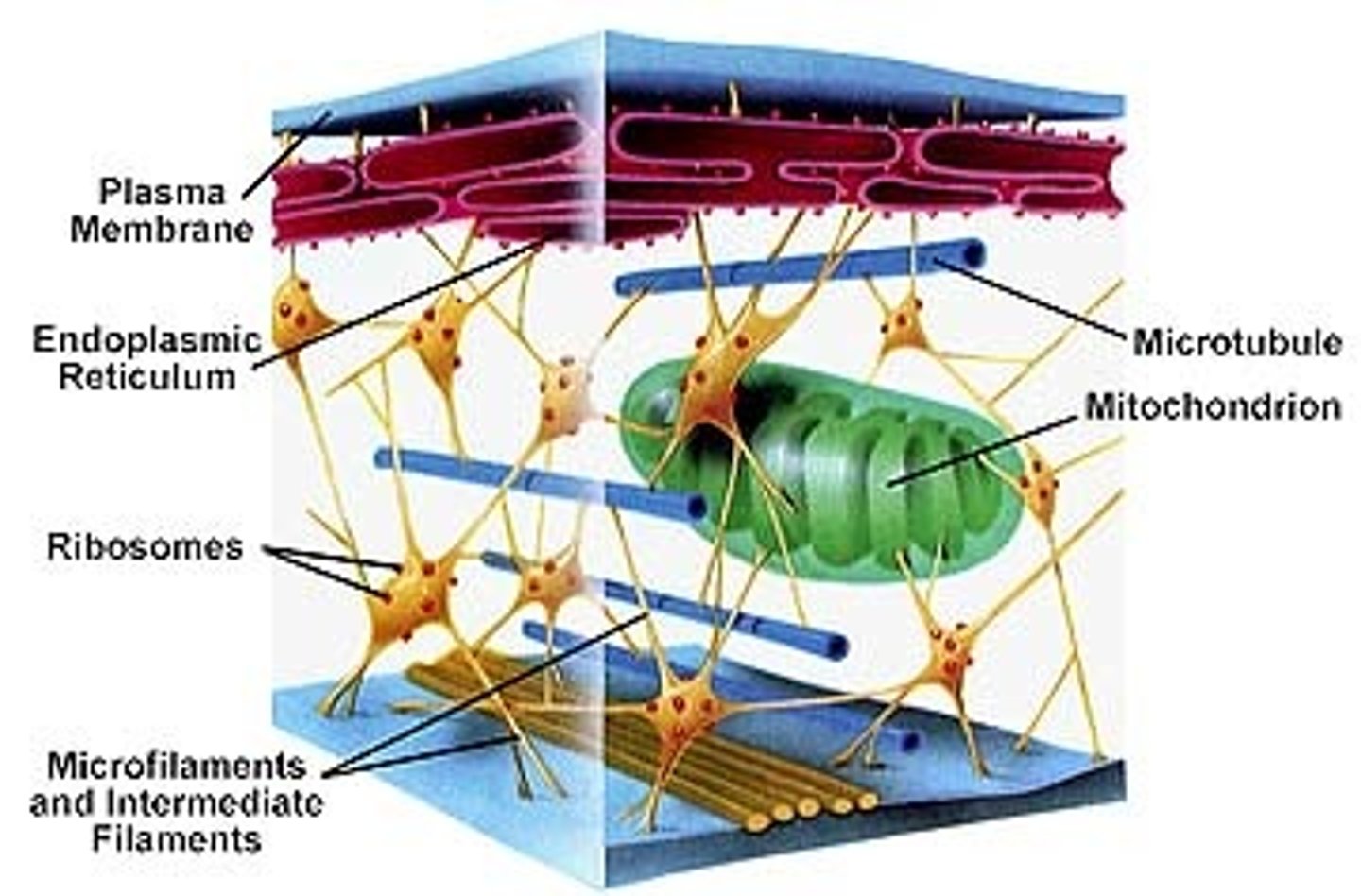
Microfilament
Long, thin fibers that function in the movement and support of the cell
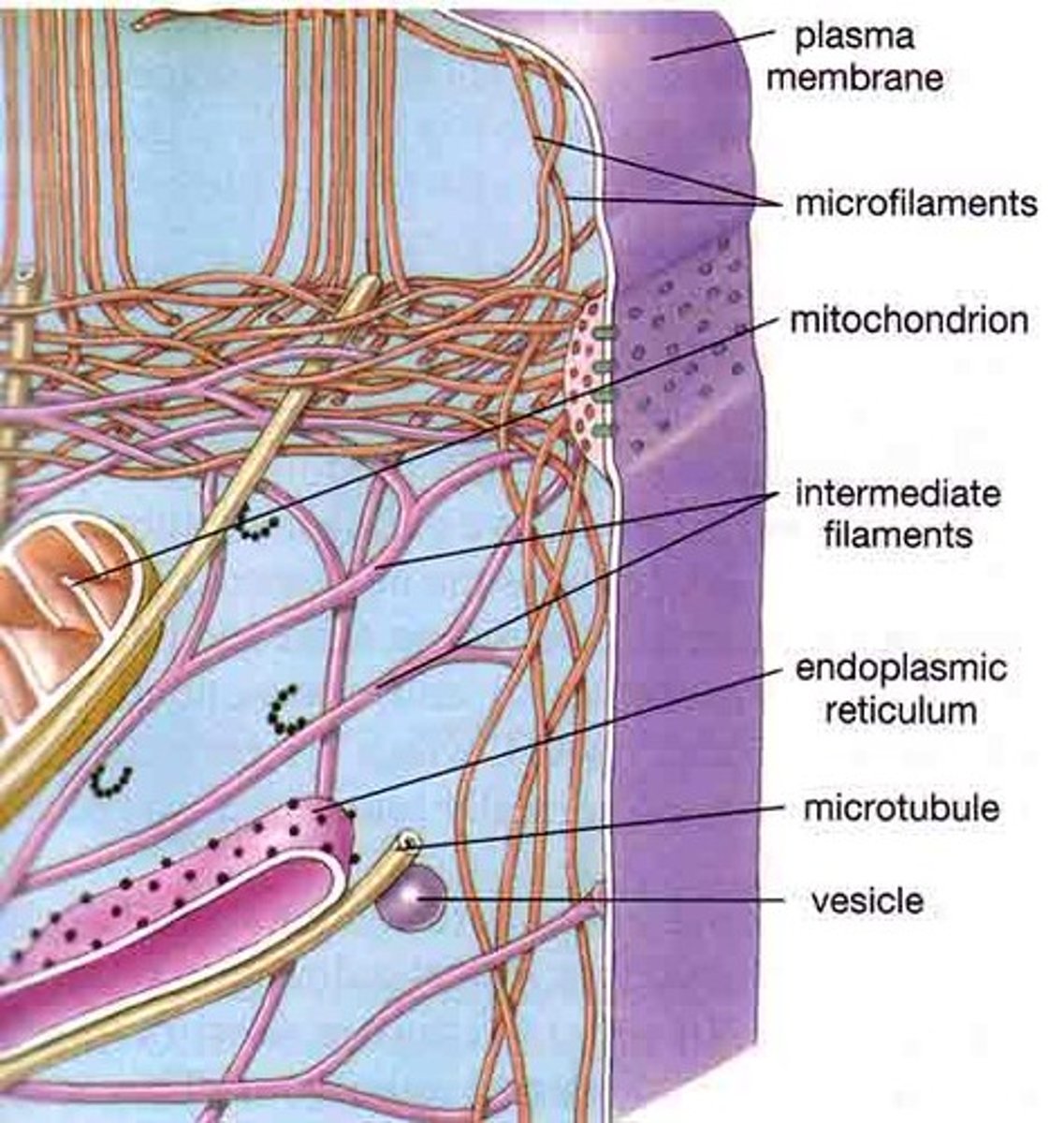
Intermediate filaments
Threadlike proteins in the cell's cytoskeleton that are roughly twice as thick as microfilaments
Centrosome
A region in animal cells often located near the nucleus where microtubules grow from.
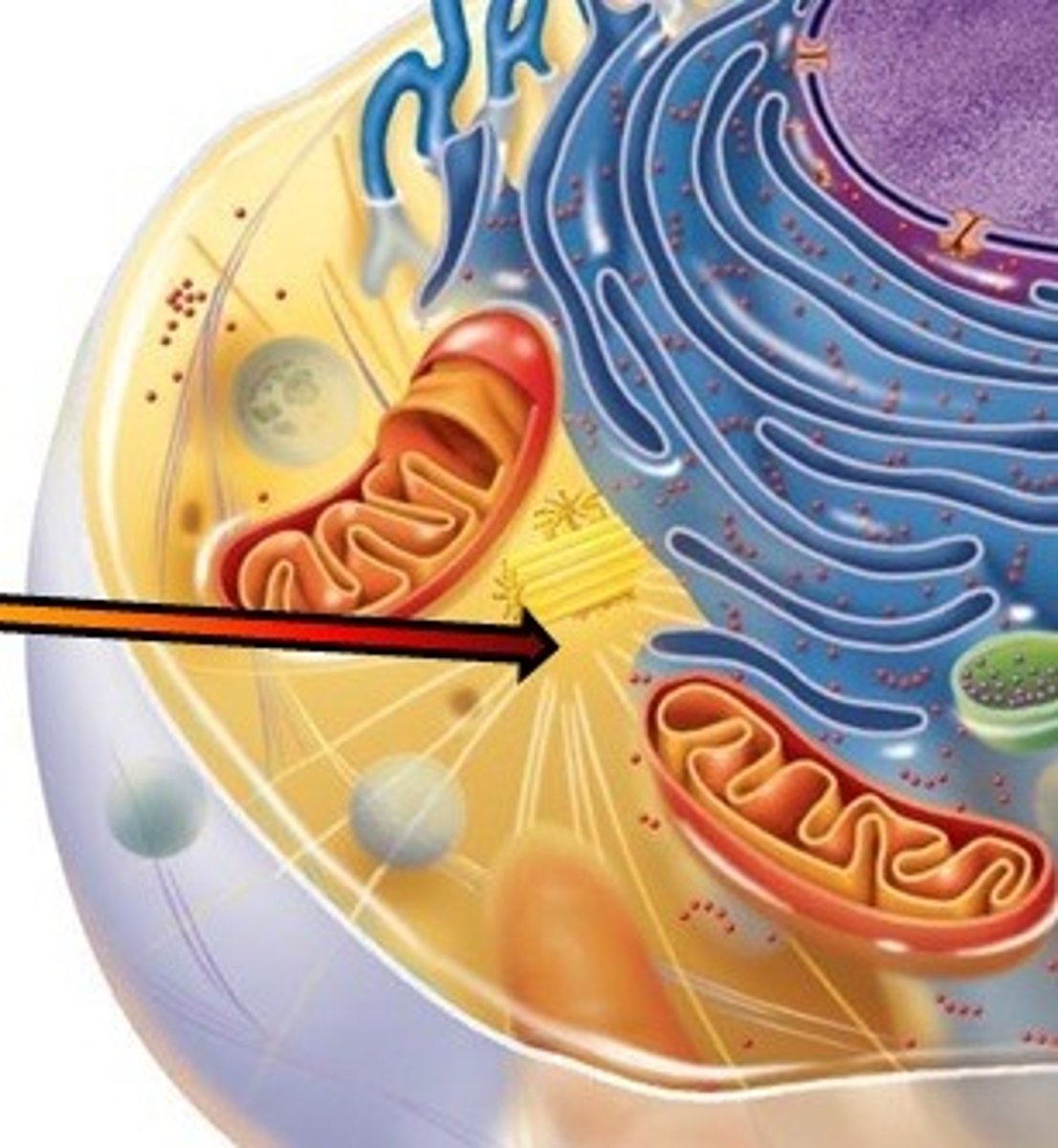
Centrioles
Cell organelle that aids in cell division in animal cells only
Flagella
A long, whip-like filament that helps in cell motility.
Cilia
Hairlike projections that extend from the plasma membrane and are used for locomotion
Cell Wall
An extracellular structure of plant cells that protects the plant cell, maintains its shape, and prevents excessive uptake of water.
Primary cell wall
In plants, a relatively thin and flexible layer first secreted by a young cell.
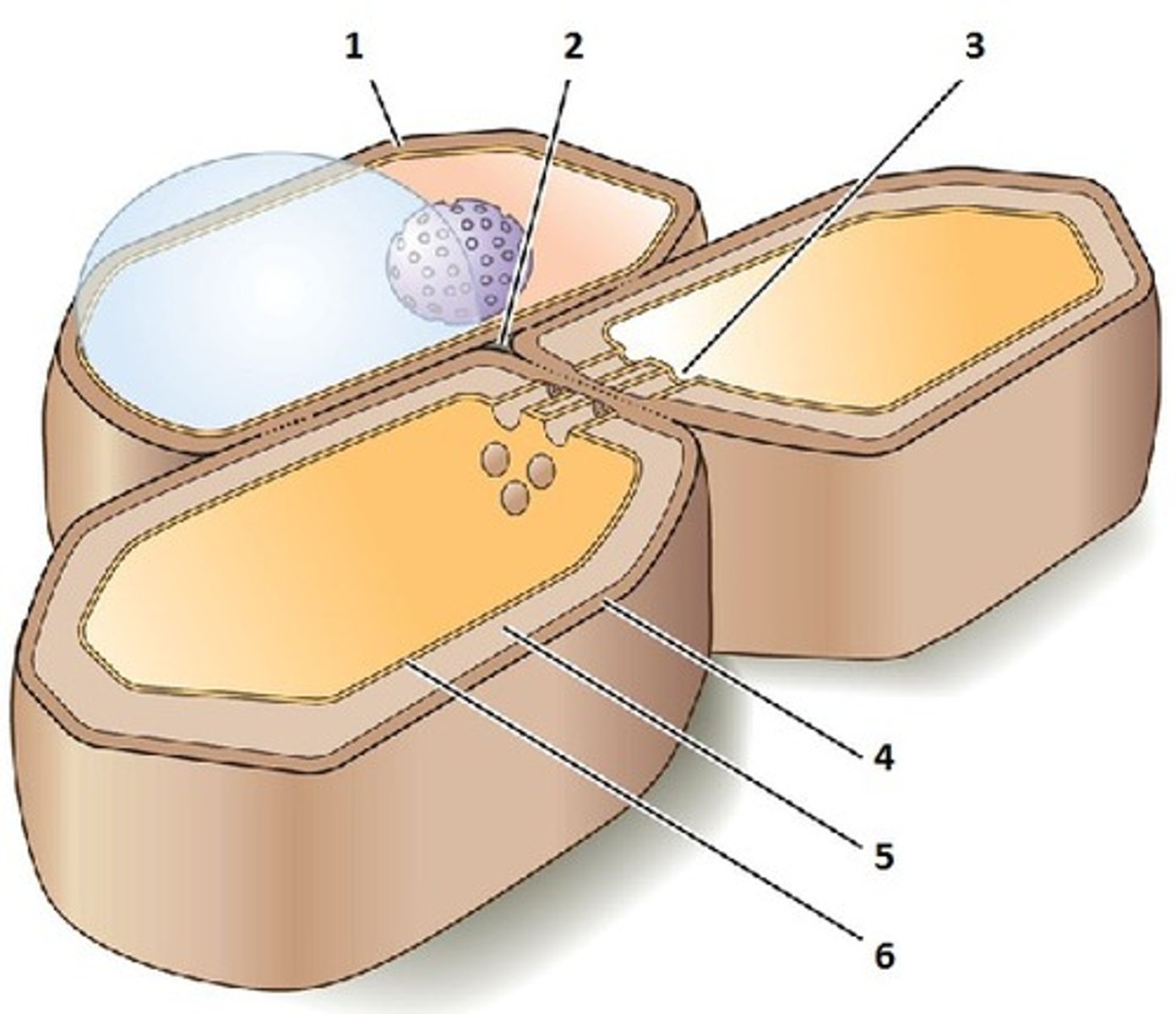
Middle lamella
A thin layer rick in sticky polysaccharides called pectins that glues adjacent cells together.
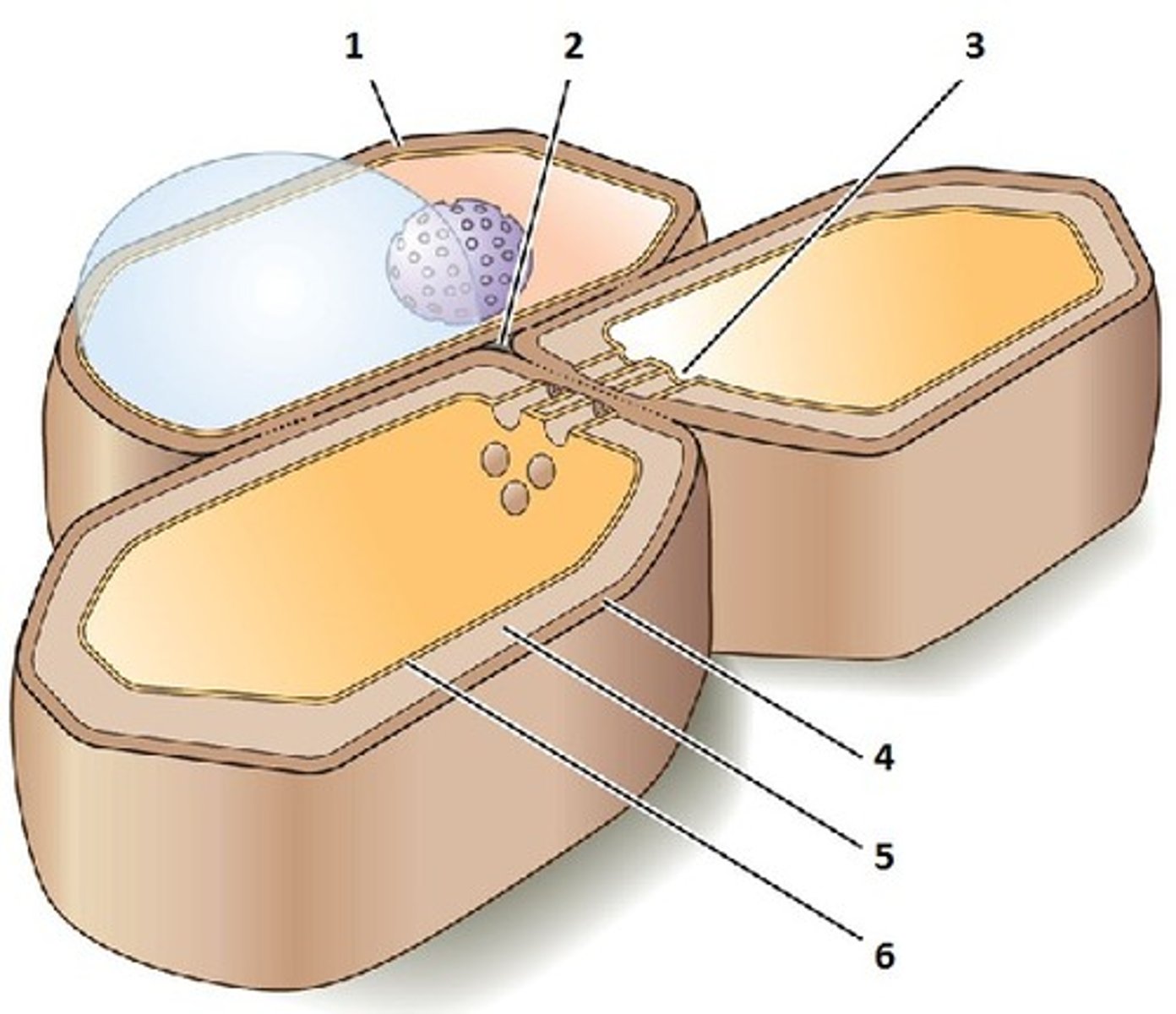
Secondary cell wall
In plants, a strong and durable matrix often deposited in several laminated layers for cell protection and support.
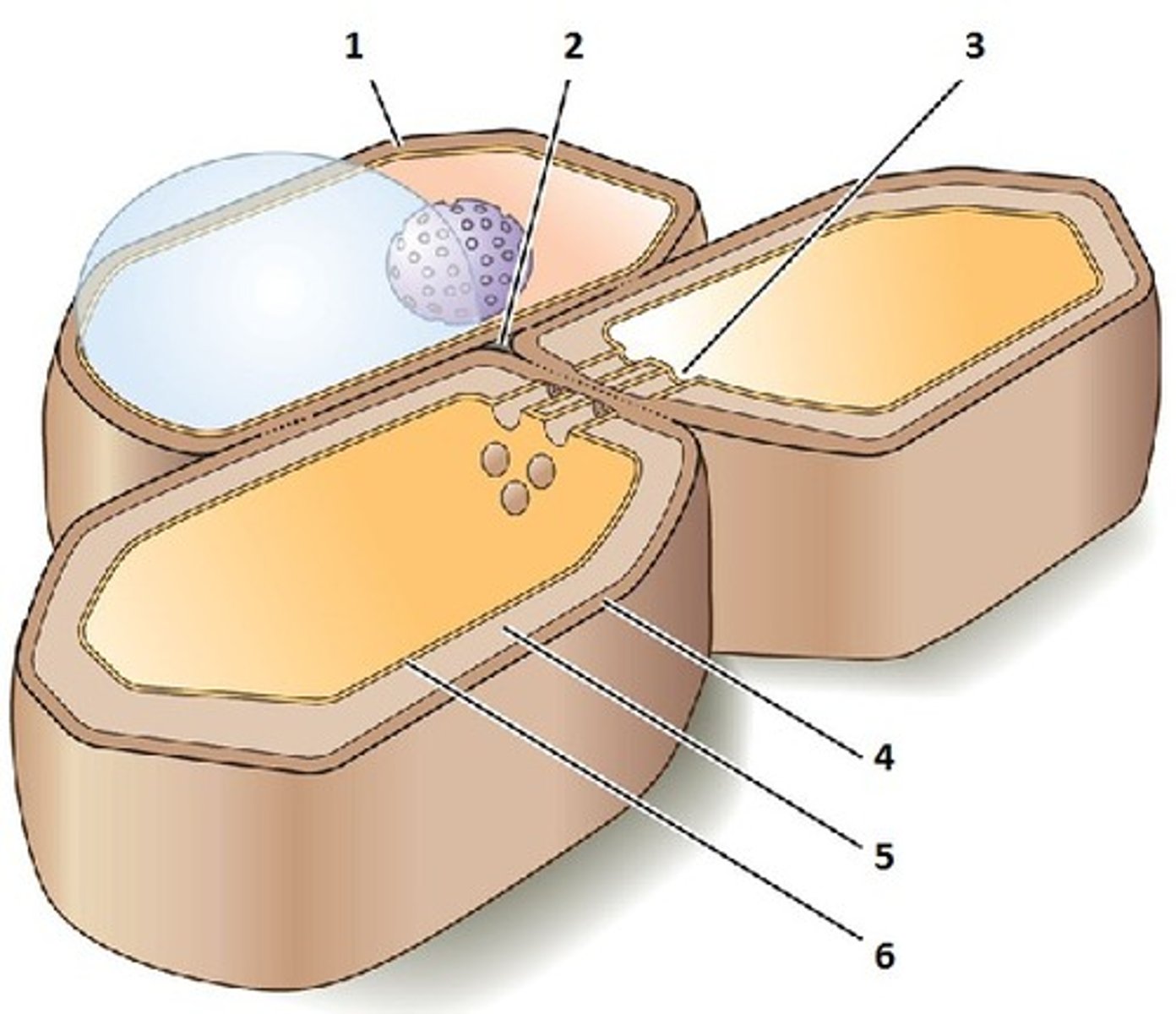
Extracellular Matrix
The substance in which animal tissue cells are embedded, consisting of protein and polysaccharides.
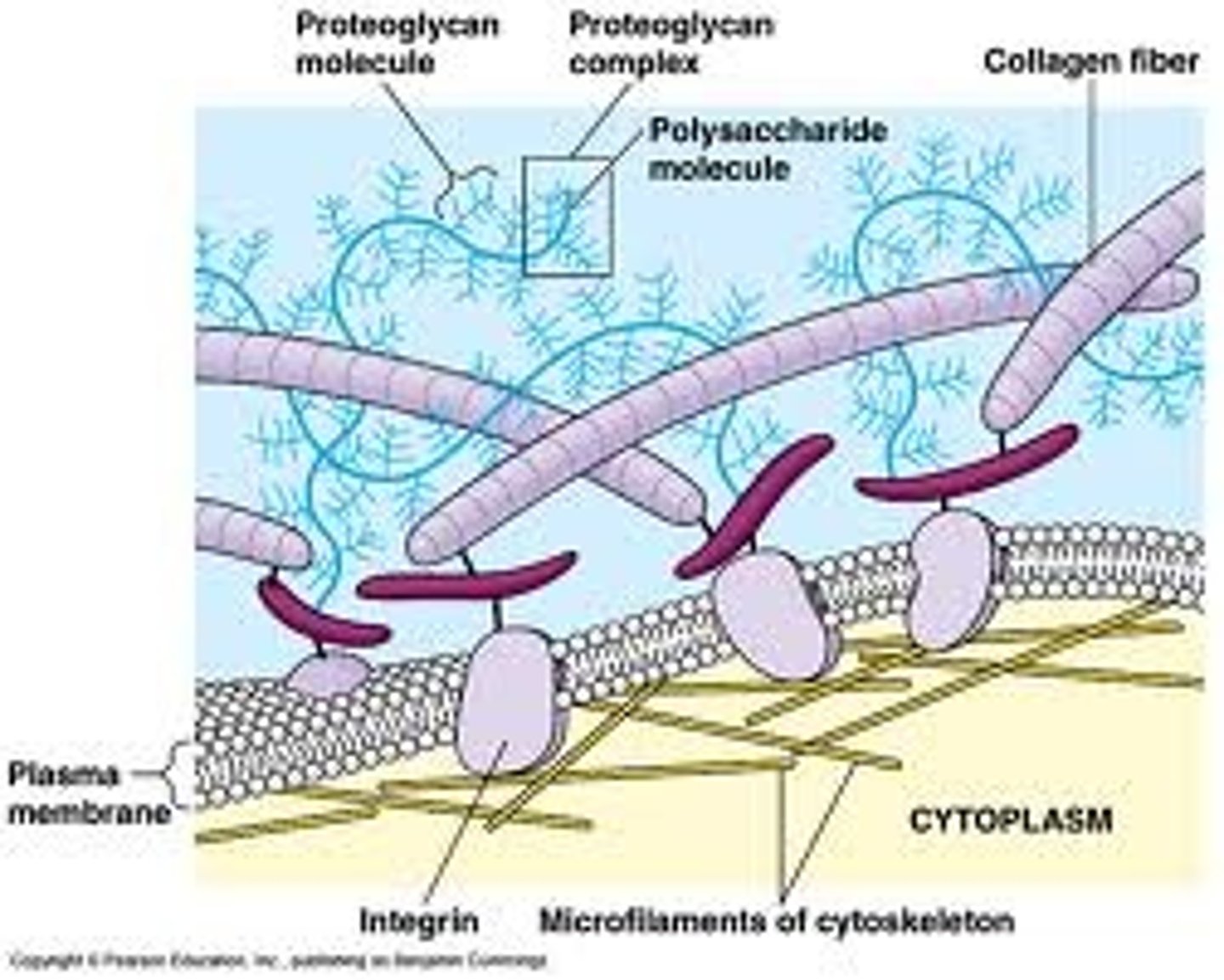
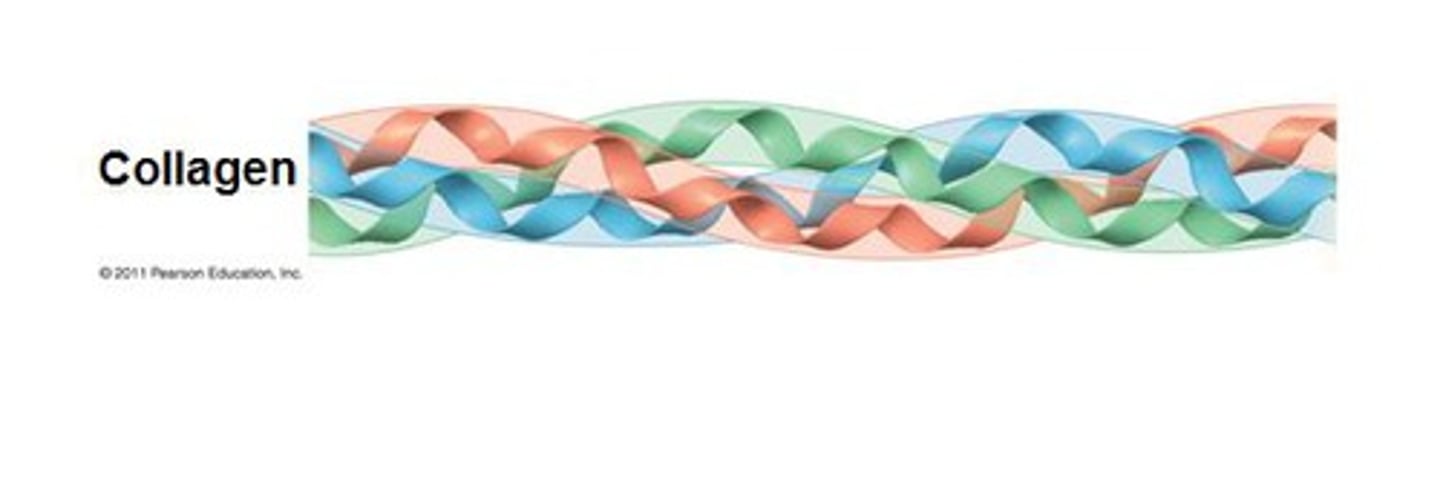
Collagen
A glycoprotein in the extracellular matrix of animal cells that forms strong fibers, found extensively in connective tissue and bone; the most abundant protein in the animal kingdom.
Plasmodesmata
An open channel in the cell wall of plants through which strands of cytosol connect from adjacent cells
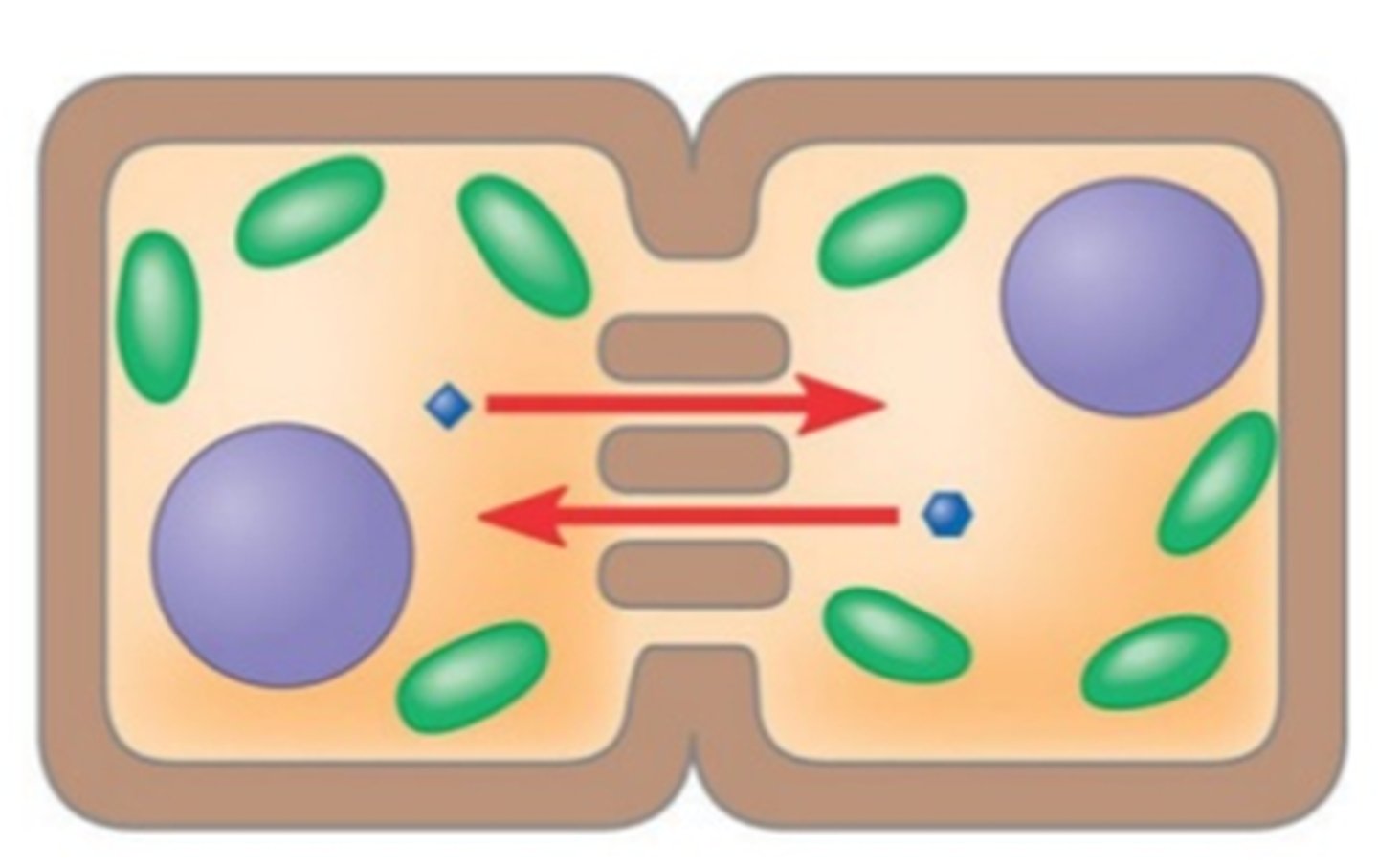
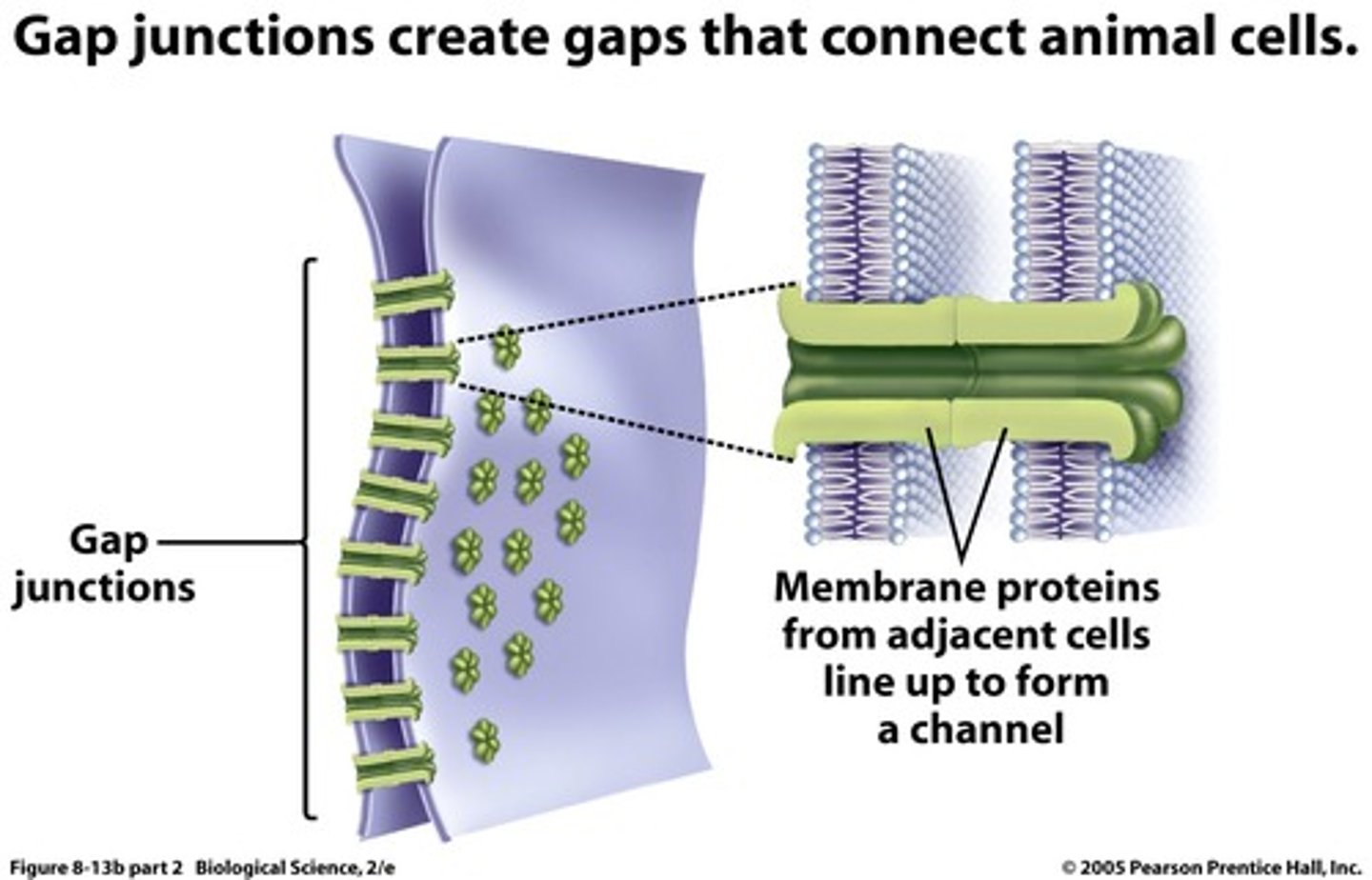
Gap junctions
Structures between animal cells that provide cytoplasmic channels from one cell to an adjacent cell and are necessary for communication between cells in many types of tissues.