Biology sem 2 final exam
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/121
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All questions on bio test
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
1
New cards
Meiosis is a process that (increases/reduces) chromosomes to the (haploid/diploid) number, provides genetic (stability/variation), and ensures the correct distribution of (chromosomes/traits/mitochondria/hybrids) into the (zygotes/gametes/somatic cells).
1. reduces
2. haploid
3. variation
4. chromosomes
5. gametes
2
New cards
Mendel was a careful researcher who studied the inheritance of certain traits in garden peas. Which research practices did Mendel use? Choose all that apply.
Responses
a. He allowed eggs to be fertilized only by self-pollination.
\
b.He crossed true-breeding pea plants.
\
c.He analyzed his data mathematically.
\
d.He controlled variables by studying one or two traits at a time.
\
Responses
a. He allowed eggs to be fertilized only by self-pollination.
\
b.He crossed true-breeding pea plants.
\
c.He analyzed his data mathematically.
\
d.He controlled variables by studying one or two traits at a time.
\
\
He crossed true-breeding pea plants.
\
He crossed true-breeding pea plants.
\
3
New cards
Which two genes are most likely to be affected by a crossing-over event?
Responses
a.a pair of genes located on different chromosomes
\
b.a pair of genes separated by a third gene on a chromosome
\
c.a pair of genes located adjacent to each other on a chromosome
\
d.a pair of genes located at opposite ends of a chromosome
\
Responses
a.a pair of genes located on different chromosomes
\
b.a pair of genes separated by a third gene on a chromosome
\
c.a pair of genes located adjacent to each other on a chromosome
\
d.a pair of genes located at opposite ends of a chromosome
\
a pair of genes located at opposite ends of a chromosome
\
\
4
New cards
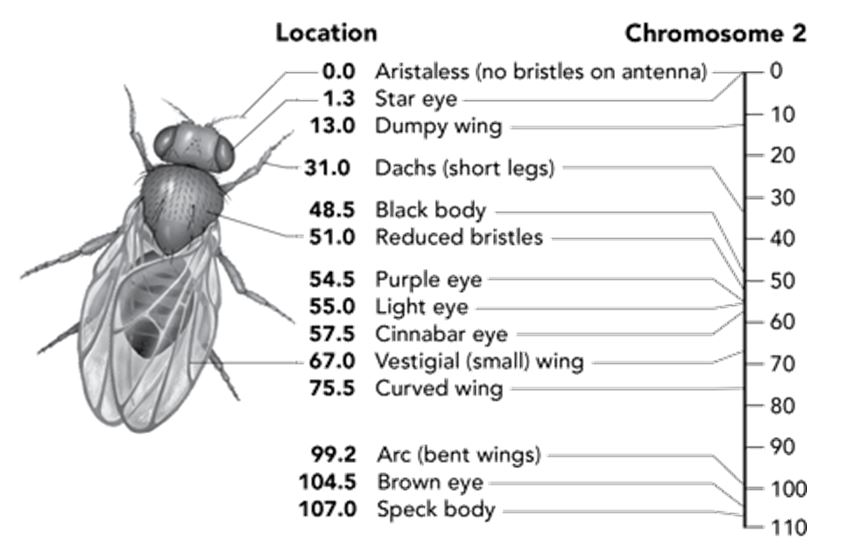
José is really fascinated by what you have shown him so far. He corners you at lunch and asks: “Can crossing-over occur with any combination of genes?” You answer that there are some factors that limit the probability of a particular event. You grab your book again and turn to a gene map showing some of the genes on chromosome 2 of a fruit fly. You explain that the inheritance of some characteristics are linked to other genes, since they are located close to one another on the same chromosome. These genes are less likely to be impacted by crossing over.
\
Using the diagram as a guide, order the following pairs of genes, from least likely to most likely to be impacted by crossing over. Put the least likely to be impacted at the top and the most likely at the bottom.
\
\-Star eye and Dumpy wing
\-Black body and Purple eye
\-Brown eye and Curved wing
\-Black body and Short legs
\
Using the diagram as a guide, order the following pairs of genes, from least likely to most likely to be impacted by crossing over. Put the least likely to be impacted at the top and the most likely at the bottom.
\
\-Star eye and Dumpy wing
\-Black body and Purple eye
\-Brown eye and Curved wing
\-Black body and Short legs
\-Black body and Purple eye
\-Star eye and Dumpy wing
\-Black body and Short legs
\-brown eye and Curved wing
\-Star eye and Dumpy wing
\-Black body and Short legs
\-brown eye and Curved wing
5
New cards
One dog is heterozygous for black fur (Bb), and its mate is homozygous for blonde fur (bb). What is the expected outcome of the cross?
Responses
a.All of the offspring are heterozygous black (Bb)
\
b.Half of the offspring are heterozygous black (Bb); half are blonde (bb)
\
c.Three fourths of the offspring are heterozygous black (Bb); one fourth are blonde (bb)
\
d.One fourth of the offspring are heterozygous black (Bb); one fourth are blonde (bb)
Responses
a.All of the offspring are heterozygous black (Bb)
\
b.Half of the offspring are heterozygous black (Bb); half are blonde (bb)
\
c.Three fourths of the offspring are heterozygous black (Bb); one fourth are blonde (bb)
\
d.One fourth of the offspring are heterozygous black (Bb); one fourth are blonde (bb)
Half of the offspring are heterozygous black (Bb); half are blonde (bb)
\
\
6
New cards
A new homeowner purchased several hydrangea plants that were full of deep blue-violet blooms. When she planted them at her home, however, only the plants near her house bloomed a blue-violet color. Those down the driveway were a vibrant pink. What was the probable cause of the blossom color variation?
Responses
a.The phenotype for hydrangea color is affected by environmental conditions, such as soil.
\
b.There are multiple alleles controlling for flower color, making phenotypes unpredictable.
\
c.The customer must be mistaken, because gene expression can never be altered in a mature organism.
\
d.The driveway plants were homozygous while the ones near the house were heterozygous.
Responses
a.The phenotype for hydrangea color is affected by environmental conditions, such as soil.
\
b.There are multiple alleles controlling for flower color, making phenotypes unpredictable.
\
c.The customer must be mistaken, because gene expression can never be altered in a mature organism.
\
d.The driveway plants were homozygous while the ones near the house were heterozygous.
The phenotype for hydrangea color is affected by environmental conditions, such as soil.
\
\
7
New cards
Match the following vocab words with their textbook definitions.
1. gene
2. allele
3. phenotype
4. genotype
\
WB:
\- physical characteristics of an organism
\-Sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait; factor that is passed from parent to offspring
\-genetic makeup of an organism
\-One of a number of different forms of a gene
\
1. gene
2. allele
3. phenotype
4. genotype
\
WB:
\- physical characteristics of an organism
\-Sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait; factor that is passed from parent to offspring
\-genetic makeup of an organism
\-One of a number of different forms of a gene
\
1\.Sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait; factor that is passed from parent to offspring
2\.One of a number of different forms of a gene
3\.physical characteristics of an organism
4\.genetic makeup of an organism
2\.One of a number of different forms of a gene
3\.physical characteristics of an organism
4\.genetic makeup of an organism
8
New cards
Another customer from a previous season comes into your store confused. A bed of pink four o’clock flowers she planted the previous season self-seeded and produced a mixture of about 1/4 red, 1/4 white, and 1/2 pink flowers this year. The customer wants to know why the pink flowers are now a mix of colors.
Choose the terms that correctly complete the paragraph.
You explain that this is possible because four o’clocks express a(n) (simple dominance/incomplete dominance/codominance) inheritance pattern in which an intermediate phenotype is expressed. This means that (heterozygous/homozygous) plants will be either white or red, but (heterozygous/homozygous) plants will be pink.
Choose the terms that correctly complete the paragraph.
You explain that this is possible because four o’clocks express a(n) (simple dominance/incomplete dominance/codominance) inheritance pattern in which an intermediate phenotype is expressed. This means that (heterozygous/homozygous) plants will be either white or red, but (heterozygous/homozygous) plants will be pink.
1. incomplete dominance
2. homozygous
3. heterozygous
9
New cards
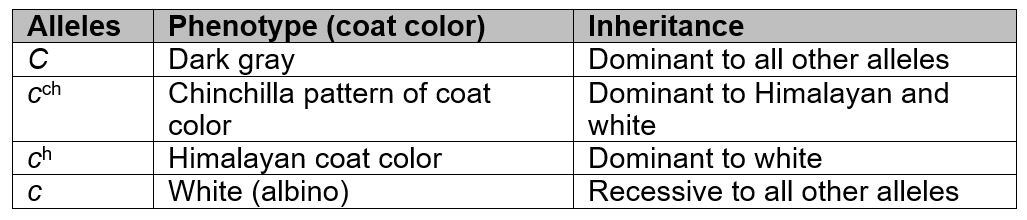
Coat color in rabbits is inherited by multiple alleles for a single gene. The table describes the genes and their inheritance.
\
Would it be possible to obtain a rabbit with Chinchilla coat color if one parent is white and the other parent has a Himalayan coat color?
Responses
a.Yes, if the Himalayan parent rabbit’s genotype is *c*h*c*h.
\
b.Yes, because the *c* allele is recessive to the *c*ch allele.
\
c.No, because the parents have no alleles for Chinchilla.
\
d.No, because the *c*h allele is dominant to the *c*ch allele.
\
\
Would it be possible to obtain a rabbit with Chinchilla coat color if one parent is white and the other parent has a Himalayan coat color?
Responses
a.Yes, if the Himalayan parent rabbit’s genotype is *c*h*c*h.
\
b.Yes, because the *c* allele is recessive to the *c*ch allele.
\
c.No, because the parents have no alleles for Chinchilla.
\
d.No, because the *c*h allele is dominant to the *c*ch allele.
\
No, because the parents have no alleles for Chinchilla.
10
New cards
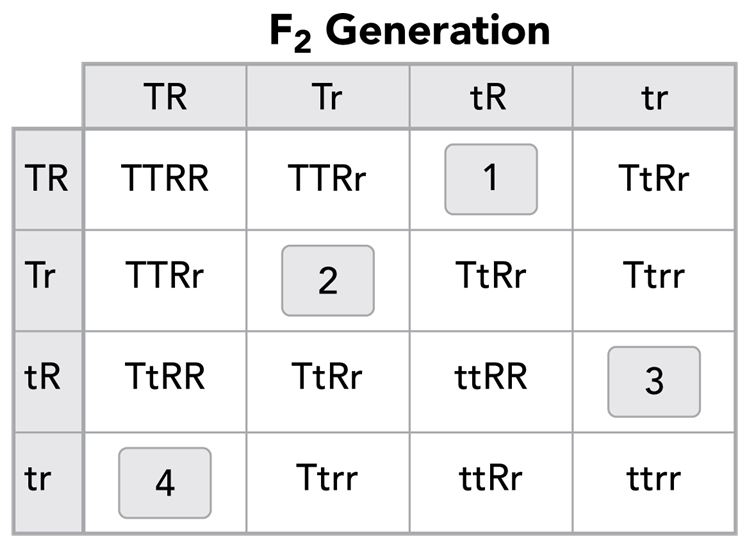
A gardener crosses a true-breeding tall tomato plant bearing red fruit with a true-breeding dwarf tomato plant with yellow fruit. In tomatoes, tall vine (*T*) is dominant to dwarf vine (*t*), and red fruit (*R*) is dominant to yellow fruit *(r).* The results are labeled the F1 generation. Then the gardener allows F1 plants to reproduce by self-pollination, generating the F2 generation.
The Punnett square shows the predicted results of the F2 generation. Some of the entries in the Punnett square are missing.
\
What are the expected phenotype ratios in the F2 generation?
Responses
a.2 tall vine/red fruit; 4 tall vine/yellow fruit; 2 dwarf vine/yellow fruit
\
b.16 tall vine/red fruit; 9 tall vine/yellow fruit; 3 dwarf vine/red fruit; 1 dwarf vine/yellow fruit
\
c.9 tall vine/red fruit; 3 tall vine/yellow fruit; 3 dwarf vine/red fruit;1 dwarf vine/yellow fruit
\
d.4 tall vine/red fruit; 3 tall vine/yellow fruit; 1 dwarf vine/red fruit
\
The Punnett square shows the predicted results of the F2 generation. Some of the entries in the Punnett square are missing.
\
What are the expected phenotype ratios in the F2 generation?
Responses
a.2 tall vine/red fruit; 4 tall vine/yellow fruit; 2 dwarf vine/yellow fruit
\
b.16 tall vine/red fruit; 9 tall vine/yellow fruit; 3 dwarf vine/red fruit; 1 dwarf vine/yellow fruit
\
c.9 tall vine/red fruit; 3 tall vine/yellow fruit; 3 dwarf vine/red fruit;1 dwarf vine/yellow fruit
\
d.4 tall vine/red fruit; 3 tall vine/yellow fruit; 1 dwarf vine/red fruit
\
9 tall vine/red fruit; 3 tall vine/yellow fruit; 3 dwarf vine/red fruit;1 dwarf vine/yellow fruit
11
New cards
A human cell that carries a double set of chromosomes is called a (haploid/diploid) cell. The cell contains 2N = 46, number of chromosomes. One (allele/gene) of each (allele/gene) is located on each (homologous/heterologous/homozygous/heterozygous) chromosome. In sexual reproduction, meiosis produces (haploid/diploid) gametes with one of each kind of chromosome. In humans, these cells contain N = (23/46) number of chromosomes.
1. diploid
2. allele
3. gene
4. homologous
5. haploid
6. 23
12
New cards
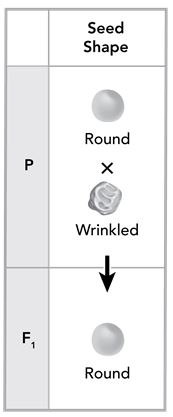
Mendel studied 7 traits in pea plants. One of the monohybrid crosses he made was between plants with round seeds (R) and plants with wrinkled seeds (r). All of the seeds in the F1 generation had a round shape.
\
Next, Mendel allowed the peas in the F1 generation to self-pollinate, forming the F2 generation. What describes Mendel's observations and conclusion about the F2 generation?
Responses
a.One fourth of the F2 plants show the round seed phenotype and are heterozygous for roundness.
\
b.Three fourths of the F2 plants show the round seed phenotype and carry the dominant allele for roundness.
\
c.The F2 plants are all heterozygous.
\
d.The F2 plants all have wrinkled seeds, and some carry the allele for round seeds.
\
Next, Mendel allowed the peas in the F1 generation to self-pollinate, forming the F2 generation. What describes Mendel's observations and conclusion about the F2 generation?
Responses
a.One fourth of the F2 plants show the round seed phenotype and are heterozygous for roundness.
\
b.Three fourths of the F2 plants show the round seed phenotype and carry the dominant allele for roundness.
\
c.The F2 plants are all heterozygous.
\
d.The F2 plants all have wrinkled seeds, and some carry the allele for round seeds.
Three fourths of the F2 plants show the round seed phenotype and carry the dominant allele for roundness.
13
New cards
Match the definition with its vocab word.
1\.principle of dominance
2\.independent assortment
3\.incomplete dominance
4\.codominance
5\.multiple alleles
6\.polygenic trait
\
\
situation in which one allele is not completely dominant over another allele
\
Mendel’s second conclusion, which states that some alleles are dominant and others are recessive
\
one of Mendel’s principles that states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes
\
trait controlled by two or more genes
\
situation in which the phenotypes produced by both alleles are completely expressed
\
a gene with more than two alleles
\
\
1\.principle of dominance
2\.independent assortment
3\.incomplete dominance
4\.codominance
5\.multiple alleles
6\.polygenic trait
\
\
situation in which one allele is not completely dominant over another allele
\
Mendel’s second conclusion, which states that some alleles are dominant and others are recessive
\
one of Mendel’s principles that states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes
\
trait controlled by two or more genes
\
situation in which the phenotypes produced by both alleles are completely expressed
\
a gene with more than two alleles
\
\
1\.Mendel’s second conclusion, which states that some alleles are dominant and others are recessive
\
2\.one of Mendel’s principles that states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes
\
3\.situation in which one allele is not completely dominant over another allele
\
4\.situation in which the phenotypes produced by both alleles are completely expressed
\
5\.a gene with more than two alleles
\
6\.trait controlled by two or more genes
\
2\.one of Mendel’s principles that states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes
\
3\.situation in which one allele is not completely dominant over another allele
\
4\.situation in which the phenotypes produced by both alleles are completely expressed
\
5\.a gene with more than two alleles
\
6\.trait controlled by two or more genes
14
New cards
What happens to the two cells formed at the end of meiosis I? Choose two correct answers.
Responses
a.Each chromosome is replicated and pairs with its homologous chromosome.
\
b.Four haploid daughter cells are formed during meiosis II.
\
c.Four diploid gametes are produced during meiosis II.
\
d.Chromosomes do not replicate and the paired chromatids separate.
\
Responses
a.Each chromosome is replicated and pairs with its homologous chromosome.
\
b.Four haploid daughter cells are formed during meiosis II.
\
c.Four diploid gametes are produced during meiosis II.
\
d.Chromosomes do not replicate and the paired chromatids separate.
\
\-Four haploid daughter cells are formed during meiosis II.
\-Chromosomes do not replicate and the paired chromatids separate.
\-Chromosomes do not replicate and the paired chromatids separate.
15
New cards
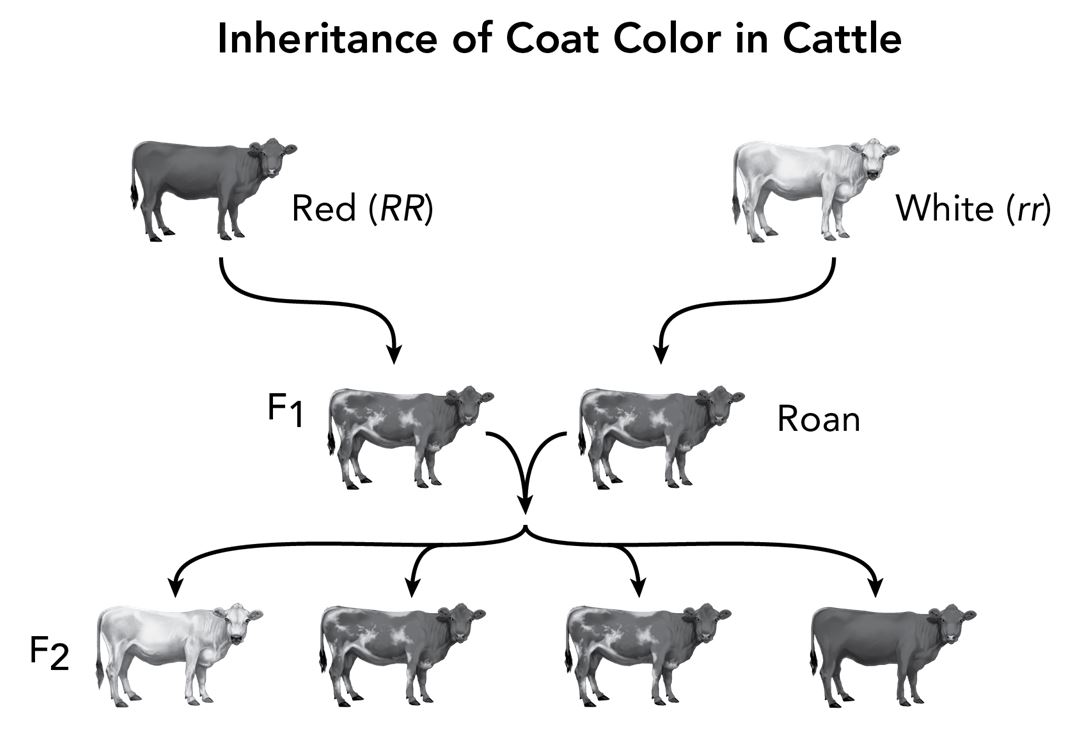
In cattle, if a red cow is crossed with a white bull, a mixture of red and white color, called roan, is produced in the F1 generation. Crosses between animals in the F1 generation produce white, roan, and red cattle in the F2 generation.
\
What is the pattern of inheritance shown in these types of cattle?
Responses
\
a.simple dominance
\
b.codominance
\
c.incomplete dominance
\
d.polygenics
\
\
What is the pattern of inheritance shown in these types of cattle?
Responses
\
a.simple dominance
\
b.codominance
\
c.incomplete dominance
\
d.polygenics
\
codominance
16
New cards
One dog is heterozygous for black fur (Bb), and its mate is homozygous for blonde fur (bb). The first litter of the two dogs produces 3 puppies that each had black fur. If the dogs have a second litter, what is the probability of one of the puppies having black fur?
Responses
\
a.0%
\
b.1/4 or 25%
\
c.1/2 or 50%
\
d.3/4 or 75%
\
e.100%
\
Responses
\
a.0%
\
b.1/4 or 25%
\
c.1/2 or 50%
\
d.3/4 or 75%
\
e.100%
\
1/2 or 50%
17
New cards
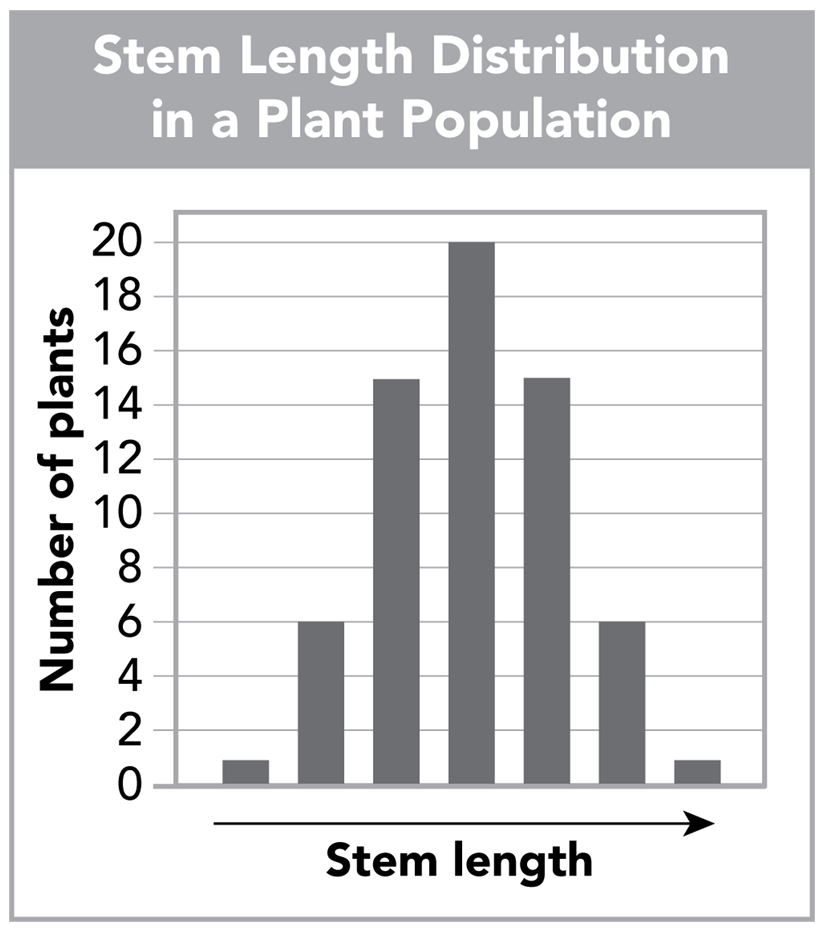
A plant’s stem length distribution was graphed from the F1 generation of a cross. Seven categories of stem length phenotypes were observed.
\
What pattern of inheritance is suggested by the graph?
Responses
\
a.codominance
\
b.polygenic inheritance
\
c.multiple alleles
\
d.incomplete dominance
\
What pattern of inheritance is suggested by the graph?
Responses
\
a.codominance
\
b.polygenic inheritance
\
c.multiple alleles
\
d.incomplete dominance
polygenic inheritance
18
New cards
How does the double-helical structure of DNA explain how the molecules can be copied or replicated?
Responses
a.The nitrogenous bases line up on each strand and are attached to each other.
\
b.Because of base pairing, each strand has all the information to serve as a template for the synthesis of the other strand.
c.The nitrogenous bases on one strand are copied to the other strand.
\
d.Each strand receives the information from the DNA polymerase attached to the replication fork.
Responses
a.The nitrogenous bases line up on each strand and are attached to each other.
\
b.Because of base pairing, each strand has all the information to serve as a template for the synthesis of the other strand.
c.The nitrogenous bases on one strand are copied to the other strand.
\
d.Each strand receives the information from the DNA polymerase attached to the replication fork.
Because of base pairing, each strand has all the information to serve as a template for the synthesis of the other strand.
\
\
19
New cards
In the Hershey-Chase experiment, the components of bacteriophages were labeled with radioactive isotopes of sulfur and phosphorus. What was the Hershey-Chase experiment designed to determine?
Responses
a.whether or not bacteriophages can infect bacteria
\
b.whether cells use DNA or proteins to store genetic information
\
c.whether or not viruses satisfy the criteria for life
\
d.whether DNA or RNA is the genetic material of the virus
Responses
a.whether or not bacteriophages can infect bacteria
\
b.whether cells use DNA or proteins to store genetic information
\
c.whether or not viruses satisfy the criteria for life
\
d.whether DNA or RNA is the genetic material of the virus
whether cells use DNA or proteins to store genetic information
20
New cards
If 35% of an organism’s DNA is adenine, what is the percentage of guanine?
Responses
a.15%
\
b.35%
\
c.70%
\
d.50%
\
Responses
a.15%
\
b.35%
\
c.70%
\
d.50%
\
15%
21
New cards

The sequence of nitrogenous bases on a portion of a strand of DNA is shown in the diagram. From left to right, what is the corresponding sequence of the complementary strand?
\
Responses
* C C A C T G A
\
* G G U G T A T
\
* T T A G A T C
\
* G G T G A C T
\
Responses
* C C A C T G A
\
* G G U G T A T
\
* T T A G A T C
\
* G G T G A C T
C C A C T G A
22
New cards
Match the enzyme with its role in DNA replication.
\
1\.DNA Polymerase
\
2\.Helicase
\
3\.Ligase
\
4\.Primase
\
WB:
joins nucleotides to synthesize a new complementary strand of DNA
\
adds a primer to start DNA replication
\
covalently bonds the backbone of the new strand of DNA
\
breaks hydrogen bonds, unzipping DNA
\
\
\
1\.DNA Polymerase
\
2\.Helicase
\
3\.Ligase
\
4\.Primase
\
WB:
joins nucleotides to synthesize a new complementary strand of DNA
\
adds a primer to start DNA replication
\
covalently bonds the backbone of the new strand of DNA
\
breaks hydrogen bonds, unzipping DNA
\
\
1. joins nucleotides to synthesize a new complementary strand of DNA
2. breaks hydrogen bonds, unzipping DNA
3. covalently bonds the backbone of the new strand of DNA
4. adds a primer to start DNA replication \n
23
New cards
A scientist uses radioactive isotopes to label a double-stranded molecule of DNA. Then the DNA undergoes replication with non-radioactive nucleotides present. Where are the two original radioactive strands of DNA?
Responses
* Both strands are intact, and each are part of a different molecule of DNA.
\
* One strand is intact, and the other strand is broken apart and distributed among the new DNA molecules.
\
* Both strands are intact, and both are part of the same molecule of DNA.
\
* Both strands are intact broken apart, and their pieces are distributed among the new DNA molecules.
\
Responses
* Both strands are intact, and each are part of a different molecule of DNA.
\
* One strand is intact, and the other strand is broken apart and distributed among the new DNA molecules.
\
* Both strands are intact, and both are part of the same molecule of DNA.
\
* Both strands are intact broken apart, and their pieces are distributed among the new DNA molecules.
\
Both strands are intact, and each are part of a different molecule of DNA.
24
New cards
As cells pass through the cell cycle, their volume of DNA alternately halves and doubles. Which statement about DNA correctly explains this pattern?
Responses
* DNA replication occurs during all phases of the cell cycle.
\
* DNA replication occurs only during the G1 phase of the cell cycle.
\
* DNA replication occurs only during the S phase of the cell cycle.
\
* DNA replication occurs randomly, and is unrelated to the cell cycle.
\
Responses
* DNA replication occurs during all phases of the cell cycle.
\
* DNA replication occurs only during the G1 phase of the cell cycle.
\
* DNA replication occurs only during the S phase of the cell cycle.
\
* DNA replication occurs randomly, and is unrelated to the cell cycle.
\
DNA replication occurs only during the S phase of the cell cycle.
25
New cards
What does DNA stand for?
Responses
* Does Not Apply
\
* Determines Nucleus Activity
\
* Deoxyriboncleic Acid
\
* Dextrose Nucleotide Atom
\
Responses
* Does Not Apply
\
* Determines Nucleus Activity
\
* Deoxyriboncleic Acid
\
* Dextrose Nucleotide Atom
\
Deoxyriboncleic Acid
26
New cards
The enzyme DNA (nuclease/telomerase/polymerase) joins (amino acids/nucleotides/sugars) to synthesize a new (complementary/opposite/paired) DNA strand.
1. polymerase
2. nucleotides
3. complementary
27
New cards
Who discovered the structure of DNA and built a model of it?
Responses
* Franklin
\
* Hershey and Chase
\
* Avery
\
* Watson and Crick
Responses
* Franklin
\
* Hershey and Chase
\
* Avery
\
* Watson and Crick
Watson and Crick
28
New cards
Which of the following statements correctly describes how the leading and the lagging strands of DNA formed during DNA replication differ?
Responses
* The leading strand is synthesized in the same direction as the movement of the replication fork, and the lagging strand is synthesized in the opposite direction.
\
* The leading strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing strand, and the lagging strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 5' end.
\
* The lagging strand is synthesized continuously, whereas the leading strand is synthesized in short fragments that are ultimately stitched together.
\
* The leading strand is synthesized at twice the rate of the lagging strand.
\
Responses
* The leading strand is synthesized in the same direction as the movement of the replication fork, and the lagging strand is synthesized in the opposite direction.
\
* The leading strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing strand, and the lagging strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 5' end.
\
* The lagging strand is synthesized continuously, whereas the leading strand is synthesized in short fragments that are ultimately stitched together.
\
* The leading strand is synthesized at twice the rate of the lagging strand.
\
The leading strand is synthesized in the same direction as the movement of the replication fork, and the lagging strand is synthesized in the opposite direction.
\
\
29
New cards
Which of the following statements correctly describes one characteristic of DNA replication in eukaryotes?
Responses
* Helicase joins the Okazaki fragments together in the lagging strand.
\
* In the leading strand, DNA is replicated in short pieces called Okazaki fragments, which are then joined together at the end of the process.
\
* DNA is replicated in the 3' to 5' direction in the leading strand.
\
* In the lagging strand, DNA is replicated in short pieces called Okazaki fragments, which are then joined together at the end of the process.
\
Responses
* Helicase joins the Okazaki fragments together in the lagging strand.
\
* In the leading strand, DNA is replicated in short pieces called Okazaki fragments, which are then joined together at the end of the process.
\
* DNA is replicated in the 3' to 5' direction in the leading strand.
\
* In the lagging strand, DNA is replicated in short pieces called Okazaki fragments, which are then joined together at the end of the process.
\
In the lagging strand, DNA is replicated in short pieces called Okazaki fragments, which are then joined together at the end of the process.
30
New cards
After replication, ______.
Responses
* one new DNA double helix consists of two old strands and the other new DNA double helix consists of two new strands
\
* each new DNA double helix contains 25% of the old DNA double helix
\
* each new DNA double helix consists of one old strand and one new strand
\
* each new DNA double helix consists of two old strands
\
Responses
* one new DNA double helix consists of two old strands and the other new DNA double helix consists of two new strands
\
* each new DNA double helix contains 25% of the old DNA double helix
\
* each new DNA double helix consists of one old strand and one new strand
\
* each new DNA double helix consists of two old strands
\
each new DNA double helix consists of one old strand and one new strand
31
New cards
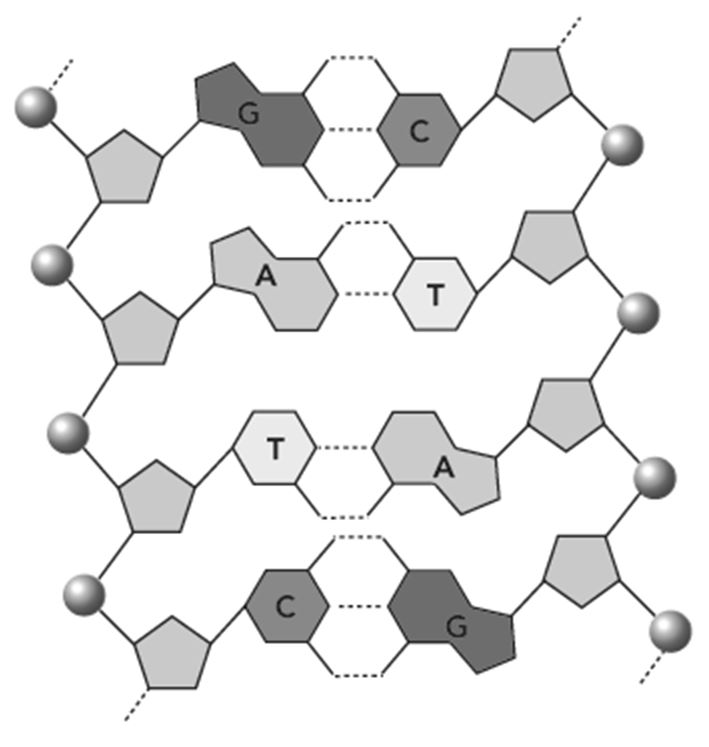
This figure shows a section of a double-stranded DNA molecule.
\
What aspects of the structure of DNA are explained by this model? Select all that apply.
Responses
* Adenine is paired with thymine and guanine is paired with cytosine.
\
* The two strands of DNA each have phosphate-sugar backbones.
\
* Paired nucleotides are held together by hydrogen bonds.
\
* Paired nucleotides are held together by covalent bonds.
\
\
What aspects of the structure of DNA are explained by this model? Select all that apply.
Responses
* Adenine is paired with thymine and guanine is paired with cytosine.
\
* The two strands of DNA each have phosphate-sugar backbones.
\
* Paired nucleotides are held together by hydrogen bonds.
\
* Paired nucleotides are held together by covalent bonds.
\
* Adenine is paired with thymine and guanine is paired with cytosine.
\
* The two strands of DNA each have phosphate-sugar backbones.
\
* Paired nucleotides are held together by hydrogen bonds.
\
\
* The two strands of DNA each have phosphate-sugar backbones.
\
* Paired nucleotides are held together by hydrogen bonds.
\
32
New cards
Frederic Griffith used the word transformation to describe the changes in bacteria that he observed. Which is the most useful definition of transformation?
Responses
* a permanent change in the function or activity of a cell
\
* a permanent change in the genetic composition of an organism
\
* a temporary change in the genetic composition of an organism
\
* a permanent change in gene expression
\
Responses
* a permanent change in the function or activity of a cell
\
* a permanent change in the genetic composition of an organism
\
* a temporary change in the genetic composition of an organism
\
* a permanent change in gene expression
\
a permanent change in the genetic composition of an organism
33
New cards
The backbone of DNA consists of ______.
Responses
* a repeating sugar-nucleotide-sugar-nucleotide pattern
\
* a repeating sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate pattern
\
* nitrogenous bases
\
* paired nucleotides
\
Responses
* a repeating sugar-nucleotide-sugar-nucleotide pattern
\
* a repeating sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate pattern
\
* nitrogenous bases
\
* paired nucleotides
\
a repeating sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate pattern
34
New cards
In DNA, thymine always pairs with (cytosine/guanine/adenine) and cytosine always pairs with (adenine/guanine/thymine) by forming (hydrogen bonds/covalent bonds/ionic bonds) across complementary strands.
1. adenine
2. guanine
3. hydrogen bonds
35
New cards
A molecular biologist is developing a computer model of the transcription of a gene into RNA. Which event should be included in the model before transcription occurs?
Responses
* RNA polymerase inserting itself into the gene
\
* the joining together of exons to form the gene
\
* RNA polymerase binding to a region near the gene, called the promoter
\
* the removal of introns from the gene
Responses
* RNA polymerase inserting itself into the gene
\
* the joining together of exons to form the gene
\
* RNA polymerase binding to a region near the gene, called the promoter
\
* the removal of introns from the gene
RNA polymerase binding to a region near the gene, called the promoter
\
\
36
New cards
There are three main types of RNA. Which type or types of RNA contain a copy of the instructions that a gene carries?
Responses
* mRNA and tRNA
\
* mRNA only
\
* mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA
\
* rRNA only
\
Responses
* mRNA and tRNA
\
* mRNA only
\
* mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA
\
* rRNA only
\
mRNA only
37
New cards
Which analogy best describes the role of homeotic genes, which are found in many organisms?
Responses
* They act like a switch for initiating a pattern of development and cell differentiation.
\
* They act like mechanics that fix mistakes in DNA replication or transcription.
\
* They act like brakes for stopping differentiation and preserving a certain body plan.
\
* They act like a role of dice that allows for unique variations in an organism.
\
Responses
* They act like a switch for initiating a pattern of development and cell differentiation.
\
* They act like mechanics that fix mistakes in DNA replication or transcription.
\
* They act like brakes for stopping differentiation and preserving a certain body plan.
\
* They act like a role of dice that allows for unique variations in an organism.
\
They act like a switch for initiating a pattern of development and cell differentiation.
38
New cards
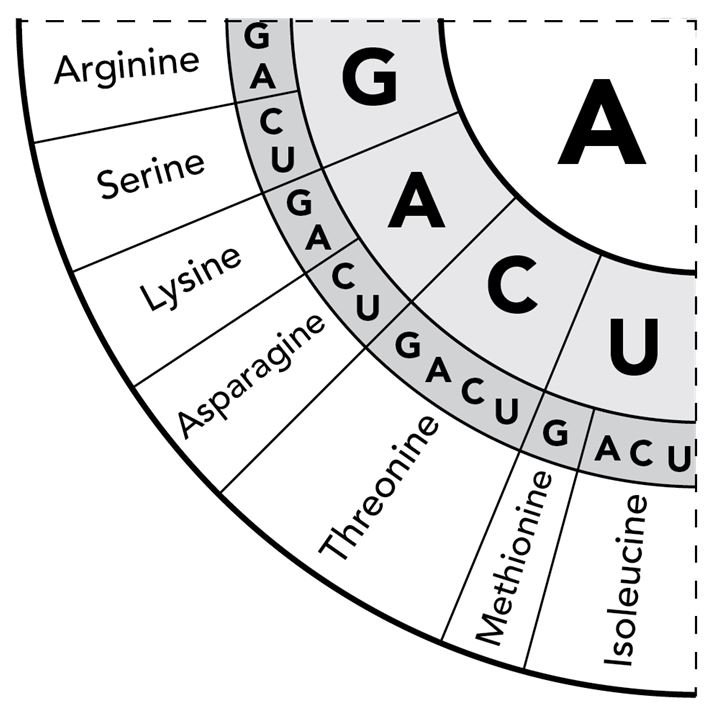
The diagram shows a portion of the genetic code. The diagram is read from the center of the circle outwards. So, the codon AGU is translated as serine, which is an amino acid.
\
A sequence of mRNA contains the following bases, which are translated as three codons.
ACUACGACA
Which amino acids are produced by this sequence? Select all of the amino acids that apply.
Responses
* threonine and arginine only
\
* threonine only
\
* threonine, arginine, and isoleucine
\
* arginine, serine, and isoleucine
\
A sequence of mRNA contains the following bases, which are translated as three codons.
ACUACGACA
Which amino acids are produced by this sequence? Select all of the amino acids that apply.
Responses
* threonine and arginine only
\
* threonine only
\
* threonine, arginine, and isoleucine
\
* arginine, serine, and isoleucine
threonine only
39
New cards
What is the most significant cause of cell differentiation in a multicellular organism?
Responses
* differences in gene regulation and gene expression among the cells
\
* differences in the genetic code used by different cells
\
* differences in the number of chromosomes per cell
\
* differences in the DNA that is copied and distributed among the cells
\
Responses
* differences in gene regulation and gene expression among the cells
\
* differences in the genetic code used by different cells
\
* differences in the number of chromosomes per cell
\
* differences in the DNA that is copied and distributed among the cells
\
differences in gene regulation and gene expression among the cells
40
New cards
A point mutation changes a codon in an mRNA molecule. Will the mutation affect the polypeptide that forms? Why?
Responses
* No. The structure of DNA, and not RNA, determines the polypeptide.
\
* Maybe. Some codons are translated into two or more amino acids.
\
* Yes. Each amino acid is specified by only one codon.
\
* Maybe. Some sets of codons are translated into the same amino acid.
Responses
* No. The structure of DNA, and not RNA, determines the polypeptide.
\
* Maybe. Some codons are translated into two or more amino acids.
\
* Yes. Each amino acid is specified by only one codon.
\
* Maybe. Some sets of codons are translated into the same amino acid.
Maybe. Some sets of codons are translated into the same amino acid.
41
New cards
In eukaryotic cells, how do transcription factors act to control gene expression?
Responses
* They bind to regulatory regions of DNA near the genes.
\
* They remove introns from pre-mRNA.
\
* They insert themselves into DNA near the beginning of a gene.
\
* They code for the synthesis of RNA polymerase.
\
Responses
* They bind to regulatory regions of DNA near the genes.
\
* They remove introns from pre-mRNA.
\
* They insert themselves into DNA near the beginning of a gene.
\
* They code for the synthesis of RNA polymerase.
\
They bind to regulatory regions of DNA near the genes.
42
New cards
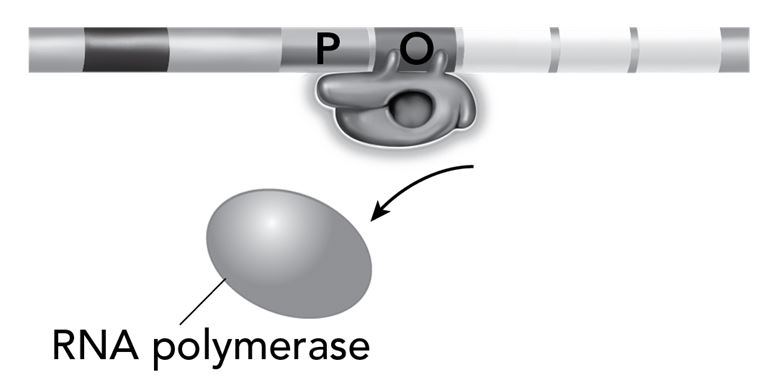
The diagram illustrates part of the function of the lac operon. It shows the operator region (O) and a protein that is bound to it. The diagram also shows the enzyme RNA polymerase.
\
What is the function of the protein that is bound to the operator region?
Responses
* It is an enzyme that will allow transcription to occur.
\
* It is lactase, the enzyme that dissolves lactose, and the product of the operon.
\
* It is an enzyme that will break apart the operon into three separate pieces.
\
* It is a repressor protein that stops transcription from occurring.
\
What is the function of the protein that is bound to the operator region?
Responses
* It is an enzyme that will allow transcription to occur.
\
* It is lactase, the enzyme that dissolves lactose, and the product of the operon.
\
* It is an enzyme that will break apart the operon into three separate pieces.
\
* It is a repressor protein that stops transcription from occurring.
It is a repressor protein that stops transcription from occurring.
43
New cards
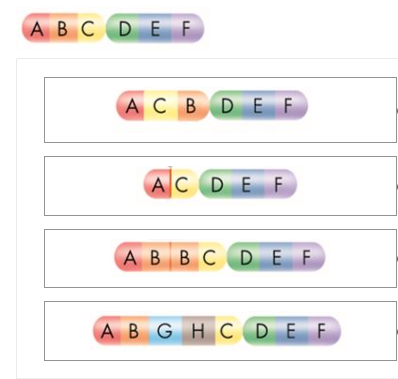
WB:
* duplication
* deletion
* inversion
* translocation
* duplication
* deletion
* inversion
* translocation
1. inversion
2. deletion
3. duplication
4. translocation
44
New cards
1\.missense
\
2\.nonsense
\
3\.silent
\
4\.frameshift
\
WB:
early stop codon causing a shorter polypeptide strand
\
1 amino acid is replaced with a different amino acid
\
all amino acids from that point on are changed
\
none
\
2\.nonsense
\
3\.silent
\
4\.frameshift
\
WB:
early stop codon causing a shorter polypeptide strand
\
1 amino acid is replaced with a different amino acid
\
all amino acids from that point on are changed
\
none
1. 1 amino acid is replaced with a different amino acid
\
2. early stop codon causing a shorter polypeptide strand
\
3. none
\
4. all amino acids from that point on are changed
45
New cards
A science researcher has developed a computer model of the process of DNA replication in a eukaryotic cell. The model includes the following sequence of bases in one strand of the DNA molecule.
AACCTGGCCATGGACCTTTATATAAACTAGGAT
The researcher wants to revise the model to show the transcription of DNA to form mRNA.
Which base sequence in the DNA molecule identifies the region where a transcription factor will bind, allowing RNA polymerase to attach to the molecule?
Responses
* AGGAT
\
* TATATA
\
* AACCTG
\
* TGGA
\
AACCTGGCCATGGACCTTTATATAAACTAGGAT
The researcher wants to revise the model to show the transcription of DNA to form mRNA.
Which base sequence in the DNA molecule identifies the region where a transcription factor will bind, allowing RNA polymerase to attach to the molecule?
Responses
* AGGAT
\
* TATATA
\
* AACCTG
\
* TGGA
\
TATATA
46
New cards
DNA and RNA are very similar yet different molecules. DNA has a (1) sugar while RNA has a (2) sugar. DNA is (3) stranded while RNA is (4) stranded. DNA and RNA both have the nucleotides (5), (6), (7), but DNA has (8) while RNA has (9).
\
WB:
* ribose
* thymine
* cytosine
* uracil
* guanine
* single
* deoxyribose
* adenine
* double
\
WB:
* ribose
* thymine
* cytosine
* uracil
* guanine
* single
* deoxyribose
* adenine
* double
1. deoxyribose
2. ribose
3. double
4. single
5. adenine
6. guanine
7. cytosine
8. thymine
9. uracil
47
New cards
Which statement best describes how tRNA molecules assemble amino acids into a polypeptide?
Responses
* Three tRNA molecules assemble the polypeptide, and the others assist them.
\
* The different tRNA molecules act in a specific order, one after the other like an assembly line.
\
* Each tRNA molecules assembles a different part of the polypeptide, and all at the same time.
\
* One tRNA molecule assembles the polypeptide, and the others assist it.
Responses
* Three tRNA molecules assemble the polypeptide, and the others assist them.
\
* The different tRNA molecules act in a specific order, one after the other like an assembly line.
\
* Each tRNA molecules assembles a different part of the polypeptide, and all at the same time.
\
* One tRNA molecule assembles the polypeptide, and the others assist it.
The different tRNA molecules act in a specific order, one after the other like an assembly line.
48
New cards
DNA: AAC CTG GCC ATG GAC CTT TAT ATA AAC TAG GAT
A student claims that the mRNA will include the following base sequence.
UUG GUC CGG UAC CUG GAA AUA UAU UUG AUC CUA
A researcher argues the student’s claim is faulty. The mRNA likely will not include the sequence that the student proposes.
Which features of transcription support the researcher’s argument?
Responses
* Base sequence in a DNA molecule may be transcribed into introns of pre-mRNA, or may not be transcribed at all.
\
* Many base sequences are cut out of the DNA molecule before transcription occurs
\
* After translation, introns and exons are added to pre-mRNA to form completed mRNA.
\
* Transcription produces a molecule of mRNA with the same bases as DNA, and in the same order.
\
A student claims that the mRNA will include the following base sequence.
UUG GUC CGG UAC CUG GAA AUA UAU UUG AUC CUA
A researcher argues the student’s claim is faulty. The mRNA likely will not include the sequence that the student proposes.
Which features of transcription support the researcher’s argument?
Responses
* Base sequence in a DNA molecule may be transcribed into introns of pre-mRNA, or may not be transcribed at all.
\
* Many base sequences are cut out of the DNA molecule before transcription occurs
\
* After translation, introns and exons are added to pre-mRNA to form completed mRNA.
\
* Transcription produces a molecule of mRNA with the same bases as DNA, and in the same order.
\
Base sequence in a DNA molecule may be transcribed into introns of pre-mRNA, or may not be transcribed at all.
49
New cards
What is the role of the anticodon in the process of translation?
Responses
* The anticodon binds to a codon on rRNA.
\
* The anticodon binds to the promoter, a region of DNA.
\
* The anticodon binds to a specific amino acid.
\
* The anticodon binds to a codon on mRNA.
Responses
* The anticodon binds to a codon on rRNA.
\
* The anticodon binds to the promoter, a region of DNA.
\
* The anticodon binds to a specific amino acid.
\
* The anticodon binds to a codon on mRNA.
The anticodon binds to a codon on mRNA.
50
New cards
A normal polypeptide includes the following sequence of amino acids. (Note: Each amino acid is named by a three-letter abbreviation.) \n Iso-**Leu**-Pro-**Val**-His-**Ser**-Thr-**Met**
After a mutation, the amino acid sequence becomes the following: \n Iso-**Leu**-Pro-**Val**-Tyr-**Arg**-Iso-**Gly**
Which of the following changes to a nitrogenous base in mRNA is most likely to have occurred?
Responses
* The codon ACU was removed and not replaced.
\
* A cytosine (C) was replaced with a uracil (U).
\
* A uracil (U) was replaced with a thymine (T).
\
* An adenine (A) was removed and not replaced.
\
After a mutation, the amino acid sequence becomes the following: \n Iso-**Leu**-Pro-**Val**-Tyr-**Arg**-Iso-**Gly**
Which of the following changes to a nitrogenous base in mRNA is most likely to have occurred?
Responses
* The codon ACU was removed and not replaced.
\
* A cytosine (C) was replaced with a uracil (U).
\
* A uracil (U) was replaced with a thymine (T).
\
* An adenine (A) was removed and not replaced.
\
An adenine (A) was removed and not replaced.
51
New cards
Robert is studying a long list of letters. The letters represent the order of nitrogenous bases in a molecule of mRNA. The first several bases in the list are shown below.
AUGCCACAGGUUCAUCCGAA…
To identify the amino acid sequence encoded by the mRNA, which would be the most useful first step for Robert to follow?
Responses
* Calculate the frequencies of each letter.
\
* Separate the list into three-letter “words” called codons.
\
* Count the number of letters in the list.
\
* Separate the list into two-, three- and four-letter “words.”
\
AUGCCACAGGUUCAUCCGAA…
To identify the amino acid sequence encoded by the mRNA, which would be the most useful first step for Robert to follow?
Responses
* Calculate the frequencies of each letter.
\
* Separate the list into three-letter “words” called codons.
\
* Count the number of letters in the list.
\
* Separate the list into two-, three- and four-letter “words.”
\
Separate the list into three-letter “words” called codons.
52
New cards
Raul is using a computer model to investigate meiosis. He directs the model to show a nondisjunction of chromosome 21 during meiosis I. How many copies of chromosome 21 should the model display in each gamete that is produced?
Responses
* either 2 copies or no copies
\
* 1 copy
\
* either 3 copies or 1 copy
\
* 2 copies
\
Responses
* either 2 copies or no copies
\
* 1 copy
\
* either 3 copies or 1 copy
\
* 2 copies
\
either 2 copies or no copies
53
New cards
Frieda is studying an example of a human karyotype. She makes the following claim about the karyotype.
“I can determine which sex chromosome was donated by the male parent, and which sex chromosome was donated by the female parent.”
Frieda’s claim is accurate under which of these conditions?
Responses
* The karyotype was taken from a female.
\
* The karyotype was taken from a male.
\
* The karyotype includes three copies of an autosome.
\
* The karyotype was taken from a newborn baby.
\
“I can determine which sex chromosome was donated by the male parent, and which sex chromosome was donated by the female parent.”
Frieda’s claim is accurate under which of these conditions?
Responses
* The karyotype was taken from a female.
\
* The karyotype was taken from a male.
\
* The karyotype includes three copies of an autosome.
\
* The karyotype was taken from a newborn baby.
\
The karyotype was taken from a male.
54
New cards
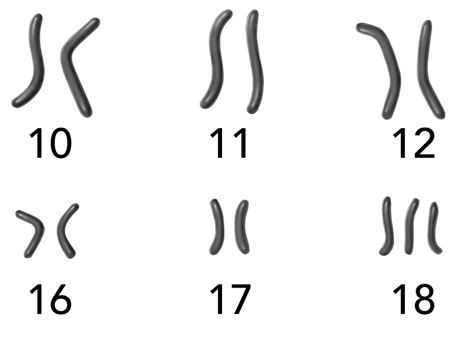
The karyotype supports the following explanation of events. During the process of gamete formation in the (male/female/male or female) parent of the patient, one pair of chromosomes failed to (elongate/replicate/uncoil/separate) during a stage of (mitosis/meiosis/DNA replication).
1. male or female
2. separate
3. meiosis
55
New cards
A genetic disorder is caused by an allele of a sex-linked gene, located on the Y chromosome. How is the disorder inherited?
Responses
* only from the father, to either a son or daughter
\
* from either parent to a son only
\
* only from the mother to a son
\
* only from the father to a son
\
Responses
* only from the father, to either a son or daughter
\
* from either parent to a son only
\
* only from the mother to a son
\
* only from the father to a son
\
only from the father to a son
56
New cards
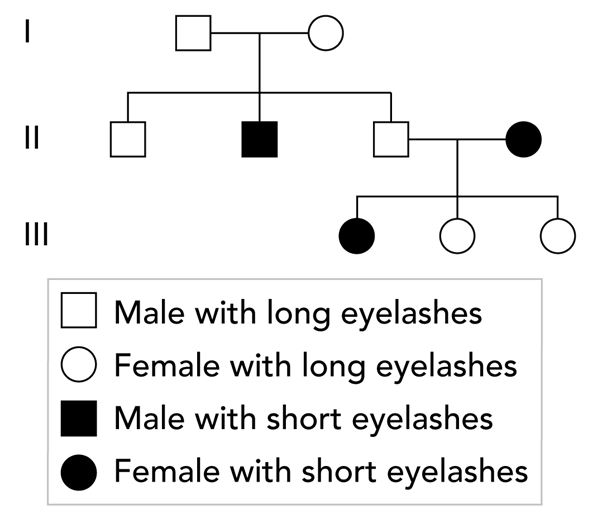
A team of scientists is studying the inheritance of eyelash length in humans. Eyelash length is either long or short, and is controlled by a single autosomal gene.
The eyelash lengths of the members of one family are shown in the pedigree below. The pedigree labels the generations I, II, and III. The male and female in Generation I are the parents of the three males shown in Generation II, and are the grandparents of the three females shown in Generation III.
\
Based on the pedigree, are short eyelashes determined by a recessive allele or a dominant allele? What reason explains this answer?
Responses
* A recessive allele, because short eyelashes are less common in the family.
\
* A dominant allele, because short eyelashes are absent in generation I.
\
* A recessive allele, because two parents with long eyelashes can have children with short eyelashes.
\
* A dominant allele, because short eyelashes are less common in the family
The eyelash lengths of the members of one family are shown in the pedigree below. The pedigree labels the generations I, II, and III. The male and female in Generation I are the parents of the three males shown in Generation II, and are the grandparents of the three females shown in Generation III.
\
Based on the pedigree, are short eyelashes determined by a recessive allele or a dominant allele? What reason explains this answer?
Responses
* A recessive allele, because short eyelashes are less common in the family.
\
* A dominant allele, because short eyelashes are absent in generation I.
\
* A recessive allele, because two parents with long eyelashes can have children with short eyelashes.
\
* A dominant allele, because short eyelashes are less common in the family
A recessive allele, because two parents with long eyelashes can have children with short eyelashes.
57
New cards
Since Gabriel’s father is not colorblind, Gabriel must have inherited the allele from his mother, Catalina. She is called a carrier, because she has only one copy of the allele and thus does not express the trait. Given this combination of parents, which of these statements is INCORRECT about the odds of passing the trait onto any future children?
Responses
* There is a 25% chance of having a child who is colorblind.
\
* There is a 0% chance that a daughter will have the condition.
\
* There is a 50% chance that a daughter will be a carrier.
\
* There is a 50% chance that a son will be colorblind.
Responses
* There is a 25% chance of having a child who is colorblind.
\
* There is a 0% chance that a daughter will have the condition.
\
* There is a 50% chance that a daughter will be a carrier.
\
* There is a 50% chance that a son will be colorblind.
There is a 25% chance of having a child who is colorblind.
58
New cards
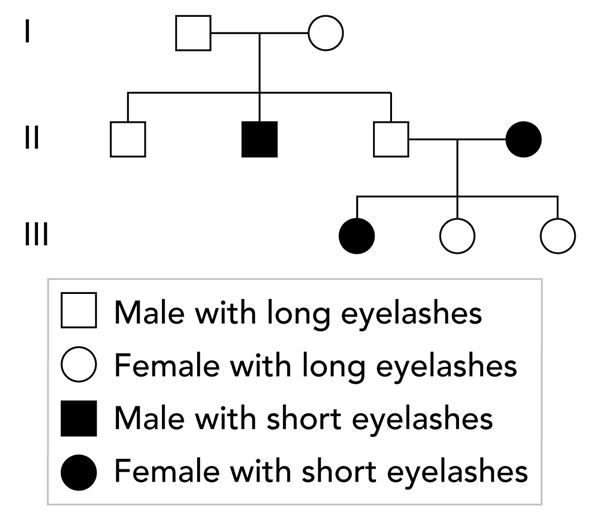
A team of scientists is studying the inheritance of eyelash length in humans. Eyelash length is either long or short, and is controlled by a single autosomal gene.
The eyelash lengths of the members of one family are shown in the pedigree below. The pedigree labels the generations I, II, and III. The male and female in Generation I are the parents of the three males shown in Generation II, and are the grandparents of the three females shown in Generation III.
\
Three family members each have short eyelashes. These family members include one male and two females.
Which statement accurately compares the genotypes for eyelash length among the three family members?
Responses
* The two females have the same genotype for eyelash length, while the male has a different genotype.
\
* Either two or three family members may have the same genotype for eyelash length, or each genotype may be unique.
\
* All three of the family members have the same genotype for eyelash length.
\
* The three family members each have a unique genotype for eyelash length.
The eyelash lengths of the members of one family are shown in the pedigree below. The pedigree labels the generations I, II, and III. The male and female in Generation I are the parents of the three males shown in Generation II, and are the grandparents of the three females shown in Generation III.
\
Three family members each have short eyelashes. These family members include one male and two females.
Which statement accurately compares the genotypes for eyelash length among the three family members?
Responses
* The two females have the same genotype for eyelash length, while the male has a different genotype.
\
* Either two or three family members may have the same genotype for eyelash length, or each genotype may be unique.
\
* All three of the family members have the same genotype for eyelash length.
\
* The three family members each have a unique genotype for eyelash length.
All three of the family members have the same genotype for eyelash length.
59
New cards
Mr. and Mrs. Howard are deciding whether to have children. A physician advises them both to be tested for the allele that causes Tay-Sachs Disease, which is a fatal genetic disorder. The couple asks the following question to the physician:
“Neither of us have Tay-Sachs Disease, so how could our children inherit it?”
Which is the most accurate and useful response to the Howards’ question?
Responses
* Tay-Sachs is caused by a Y-linked allele, so you both could be carriers.
\
* Tay-Sachs is caused by a recessive allele, so you both could be carriers.
\
* Tay-Sachs is caused by an X-linked allele, so you both could be carriers.
\
* Tay-Sachs is caused by a dominant allele, so either of you could be a carrier.
\
“Neither of us have Tay-Sachs Disease, so how could our children inherit it?”
Which is the most accurate and useful response to the Howards’ question?
Responses
* Tay-Sachs is caused by a Y-linked allele, so you both could be carriers.
\
* Tay-Sachs is caused by a recessive allele, so you both could be carriers.
\
* Tay-Sachs is caused by an X-linked allele, so you both could be carriers.
\
* Tay-Sachs is caused by a dominant allele, so either of you could be a carrier.
\
Tay-Sachs is caused by a recessive allele, so you both could be carriers.
60
New cards
A karyotype is assembled from the cell of a human donor who has a genetic disorder. Which disorder can be determined by studying the karyotype?
Responses
* an X-linked genetic disorder, such as color blindness
\
* a genetic disorder caused by a point mutation, such as sickle cell disease
\
* a chromosomal disorder, such as Down syndrome
\
* a genetic disorder caused by a dominant allele, such as Huntington’s disease
\
Responses
* an X-linked genetic disorder, such as color blindness
\
* a genetic disorder caused by a point mutation, such as sickle cell disease
\
* a chromosomal disorder, such as Down syndrome
\
* a genetic disorder caused by a dominant allele, such as Huntington’s disease
\
a chromosomal disorder, such as Down syndrome
61
New cards
Sickle cell disease and cystic fibrosis are both serious genetic disorders. Which statement provides the strongest explanation for why the alleles remain relatively common in the human population?
Responses
* The disease-causing alleles continue to arise from mutations to normal genes.
\
* Inheriting two copies of a disease-causing allele can be advantageous.
\
* The symptoms of the diseases are becoming less serious over time.
\
* Inheriting only one copy of a disease-causing allele can be advantageous.
\
Responses
* The disease-causing alleles continue to arise from mutations to normal genes.
\
* Inheriting two copies of a disease-causing allele can be advantageous.
\
* The symptoms of the diseases are becoming less serious over time.
\
* Inheriting only one copy of a disease-causing allele can be advantageous.
\
Inheriting only one copy of a disease-causing allele can be advantageous.
62
New cards
Horace is using a computer model to study the relationship between the genes and phenotype of an individual. In one experiment, Horace alters the nucleotide sequence in one of the model genes. In response, the computer shows that the eye color of the individual changes from brown to blue.
How did the change in the gene cause the change in phenotype?
Responses
* by altering the number of chromosomes in the cell
\
* by affecting the arrangement of glucose molecules in a carbohydrate
\
* by affecting the amino acid sequence of a protein
\
* by directing the cell to produce a carbohydrate instead of a protein
\
How did the change in the gene cause the change in phenotype?
Responses
* by altering the number of chromosomes in the cell
\
* by affecting the arrangement of glucose molecules in a carbohydrate
\
* by affecting the amino acid sequence of a protein
\
* by directing the cell to produce a carbohydrate instead of a protein
\
by affecting the amino acid sequence of a protein
63
New cards
Lucille has her personal genome analyzed. The report states that her genome includes one copy of the defective allele that causes cystic fibrosis, an autosomal recessive disease. Lucille is surprised by the report, because she is unaware of the disease in her family history, and she shows no symptoms of it.
Lucille asks a genetic counselor if her future children are at risk for suffering the serious symptoms of cystic fibrosis. Which of the following replies is the most accurate response to Lucille’s question?
Responses
* A future child might suffer from cystic fibrosis if the father’s genetic report is the same as Lucille’s report.
\
* A future child has no risk of suffering from cystic fibrosis.
\
* A future child has a 50 percent chance of suffering from cystic fibrosis.
\
* A future child has a 25 percent chance of suffering from cystic fibrosis.
Lucille asks a genetic counselor if her future children are at risk for suffering the serious symptoms of cystic fibrosis. Which of the following replies is the most accurate response to Lucille’s question?
Responses
* A future child might suffer from cystic fibrosis if the father’s genetic report is the same as Lucille’s report.
\
* A future child has no risk of suffering from cystic fibrosis.
\
* A future child has a 50 percent chance of suffering from cystic fibrosis.
\
* A future child has a 25 percent chance of suffering from cystic fibrosis.
A future child might suffer from cystic fibrosis if the father’s genetic report is the same as Lucille’s report.
64
New cards
A scientist has identified a protein that she claims is the product of a sex-linked gene. To gather evidence to support this claim, which action would be MOST useful for the scientist to take?
Responses
* Locate the gene on an autosome.
\
* Look for a gene that is expressed only in females.
\
* Look for a gene that is expressed only in adults.
\
* Locate the gene on the X or Y chromosome.
\
Responses
* Locate the gene on an autosome.
\
* Look for a gene that is expressed only in females.
\
* Look for a gene that is expressed only in adults.
\
* Locate the gene on the X or Y chromosome.
\
Locate the gene on the X or Y chromosome.
65
New cards
The sequencing of the human genome was an important step in understanding human genetic disorders like colorblindness. Through sequencing, scientists have been able to pinpoint the specific genes involved and which chromosomes they are located on. Order the steps of human genome sequencing, with the first step on top and the last step on the bottom. \n
* Cut DNA using restriction enzymes to create smaller fragments.
* Extract DNA from cells.
* Separate DNA fragments by size so fragments can be isolated.
* Analyze the fragment sequences for overlaps to create a complete genome.
* Sequence each fragment.
* Cut DNA using restriction enzymes to create smaller fragments.
* Extract DNA from cells.
* Separate DNA fragments by size so fragments can be isolated.
* Analyze the fragment sequences for overlaps to create a complete genome.
* Sequence each fragment.
\
1. Extract DNA from cells.
2. Cut DNA using restriction enzymes to create smaller fragments.
3. Separate DNA fragments by size so fragments can be isolated.
4. Sequence each fragment.
5. Analyze the fragment sequences for overlaps to create a complete genome.
66
New cards
Gel electrophoresis is successful because of which property of the DNA fragments?
Responses
* The DNA fragments may be positively-charged, negatively-charged, or neutral.
\
* The DNA fragments travel at different speeds through the gel.
\
* The DNA fragments travel at the same speed through the gel.
\
* The DNA fragments chemically react with the gel in different ways.
Responses
* The DNA fragments may be positively-charged, negatively-charged, or neutral.
\
* The DNA fragments travel at different speeds through the gel.
\
* The DNA fragments travel at the same speed through the gel.
\
* The DNA fragments chemically react with the gel in different ways.
The DNA fragments travel at different speeds through the gel.
67
New cards
Steven develops a pedigree for earlobe attachment in a large family. Earlobes can be either free or attached. What information about earlobe attachment can Steven MOST LIKELY determine by analyzing the pedigree?
Responses
* the dominant and recessive forms of the trait
\
* the location of the gene for the trait on a chromosome
\
* the percentage of each form of the trait in the human population
\
* the type of mutation that caused the two forms of the trait
\
Responses
* the dominant and recessive forms of the trait
\
* the location of the gene for the trait on a chromosome
\
* the percentage of each form of the trait in the human population
\
* the type of mutation that caused the two forms of the trait
\
the dominant and recessive forms of the trait
68
New cards
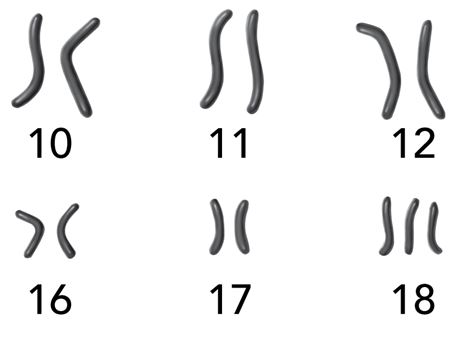
The diagram below shows a section of a karyotype. The karyotype was created from a cell sample that was obtained from a patient at a hospital.
\
Which conclusion about the patient do the karyotype data most strongly support?
Responses
* The patient has no abnormalities or disorders that are due to the chromosomes shown in the karyotype.
\
* The patient may or may not have a chromosomal disorder, depending on the full karyotype.
\
* The patient has an abnormal number of autosomes that likely is causing severe symptoms.
\
* The patient has an abnormal number of sex chromosomes that likely is causing severe symptoms.
\
Which conclusion about the patient do the karyotype data most strongly support?
Responses
* The patient has no abnormalities or disorders that are due to the chromosomes shown in the karyotype.
\
* The patient may or may not have a chromosomal disorder, depending on the full karyotype.
\
* The patient has an abnormal number of autosomes that likely is causing severe symptoms.
\
* The patient has an abnormal number of sex chromosomes that likely is causing severe symptoms.
The patient has an abnormal number of autosomes that likely is causing severe symptoms.
69
New cards
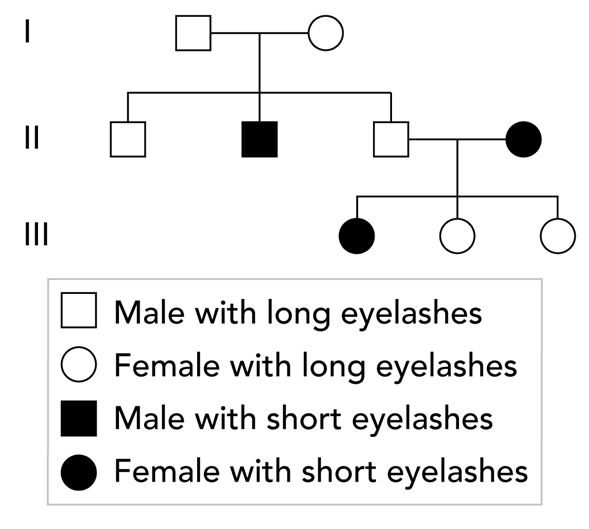
A team of scientists is studying the inheritance of eyelash length in humans. Eyelash length is either long or short, and is controlled by a single autosomal gene.
The eyelash lengths of the members of one family are shown in the pedigree below. The pedigree labels the generations I, II, and III. The male and female in Generation I are the parents of the three males shown in Generation II, and are the grandparents of the three females shown in Generation III.
\
Some of the family members must be heterozygous for the trait of eyelash length, meaning their genotypes include one allele for long eyelashes and one allele for short eyelashes. In which generation are these family members?
Responses
* I. and II. only
\
* III. only
\
* II. and III. only
\
* I., II., and III.
The eyelash lengths of the members of one family are shown in the pedigree below. The pedigree labels the generations I, II, and III. The male and female in Generation I are the parents of the three males shown in Generation II, and are the grandparents of the three females shown in Generation III.
\
Some of the family members must be heterozygous for the trait of eyelash length, meaning their genotypes include one allele for long eyelashes and one allele for short eyelashes. In which generation are these family members?
Responses
* I. and II. only
\
* III. only
\
* II. and III. only
\
* I., II., and III.
I., II., and III.
70
New cards
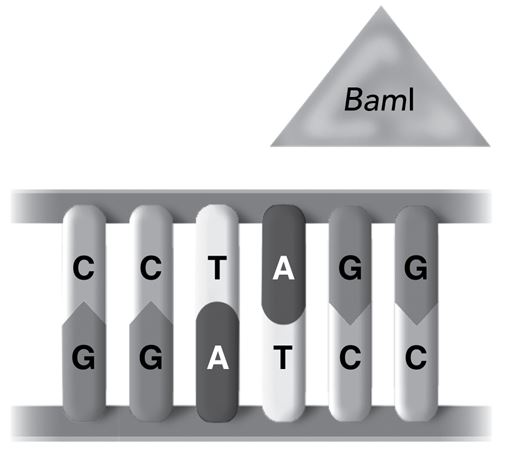
The diagram shows a restriction enzyme, called BamI, that is attached to a section of a DNA molecule.
\
How will the restriction enzyme act?
Responses
* It will cut the DNA at a specific location, and into three or more pieces.
\
* It will cause a frameshift mutation, such as by removing guanine (G).
\
* It will cut the DNA at a specific location, and into two pieces.
\
* It will cause a point mutation, such as by substituting guanine (G) for cytosine (C).
\
\
How will the restriction enzyme act?
Responses
* It will cut the DNA at a specific location, and into three or more pieces.
\
* It will cause a frameshift mutation, such as by removing guanine (G).
\
* It will cut the DNA at a specific location, and into two pieces.
\
* It will cause a point mutation, such as by substituting guanine (G) for cytosine (C).
\
It will cut the DNA at a specific location, and into two pieces.
71
New cards
A scientist has divided a DNA molecule into several fragments. Next, the scientist would use gel electrophoresis to accomplish which task?
Responses
* separating the fragments into two groups, based on electric charge
\
* cutting the fragments into smaller pieces at specific locations
\
* identifying the fragments that end in specific nucleotide sequences
\
* separating the fragments by size
\
Responses
* separating the fragments into two groups, based on electric charge
\
* cutting the fragments into smaller pieces at specific locations
\
* identifying the fragments that end in specific nucleotide sequences
\
* separating the fragments by size
\
separating the fragments by size
72
New cards
The allele for colorblindness is located on the X chromosome, so it is (1). Normally, colorblindness is a (2) trait and requires two copies of the allele. Since (3) have two X chromosomes, they do not exhibit any symptoms if they have only one colorblindness allele. However, since (4) have only one X chromosome, they need to inherit the allele only once to express the trait.
\
WB:
* autosomal
* recessive
* females
* dominant
* males
* sex-linked
\
WB:
* autosomal
* recessive
* females
* dominant
* males
* sex-linked
1. sex-linked
2. recessive
3. females
4. males
73
New cards
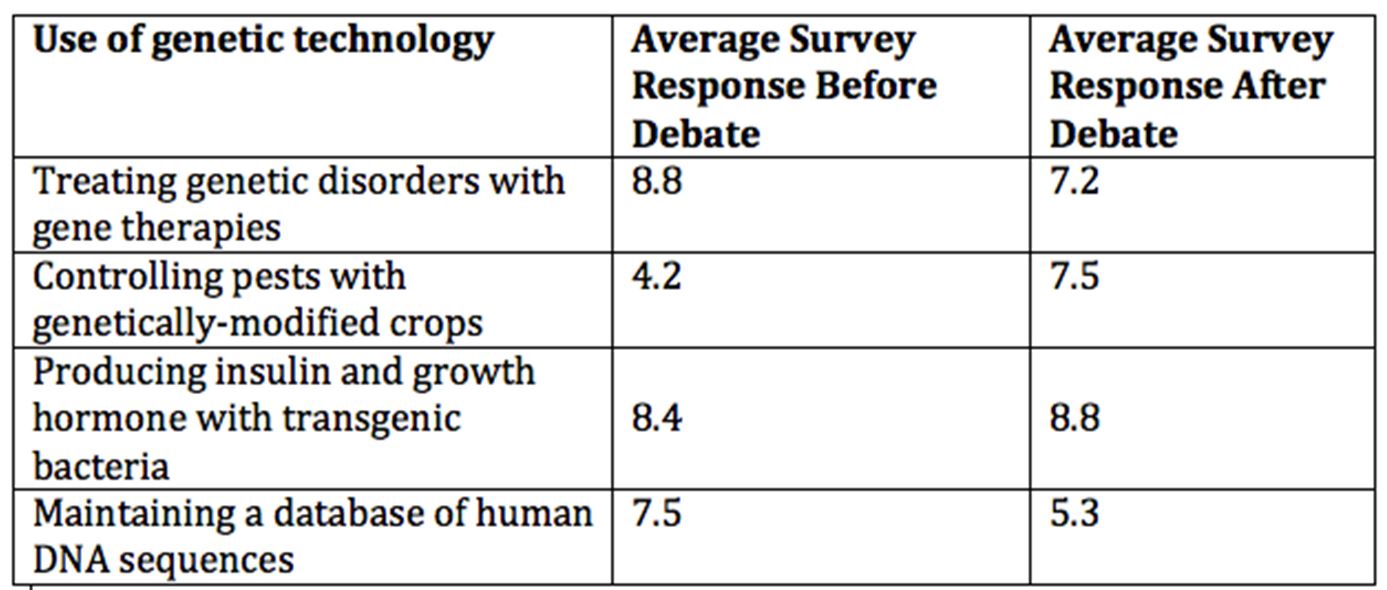
A group of biology students at Fern Hill High School staged a debate about the pros and cons of genetic technologies. Other students observed the debate and took notes.
Both before and after the debate, the students completed a survey about their support for various uses of genetic technology. For each use, the students rated their support on a scale of 0 to 10. A score of 0 means that the student strongly opposes the use of the technology, while a score of 10 means that the student strongly supports the use.
The table shows the average survey responses of the students.
\
Based on inferences from data in the table, which of the following arguments from the debate MOST LIKELY had the strongest effect on the survey responses?
Responses
* Laws can protect the privacy of information obtained from human DNA analysis.
\
* By releasing their own pesticides, GM plants decrease the need for widespread pesticide use.
\
* Some environmentalists are concerned that GM plants could spread harmful genes to wild plants.
\
* Gene therapy, if successful, could offer a cure for a genetic disorder.
\
Both before and after the debate, the students completed a survey about their support for various uses of genetic technology. For each use, the students rated their support on a scale of 0 to 10. A score of 0 means that the student strongly opposes the use of the technology, while a score of 10 means that the student strongly supports the use.
The table shows the average survey responses of the students.
\
Based on inferences from data in the table, which of the following arguments from the debate MOST LIKELY had the strongest effect on the survey responses?
Responses
* Laws can protect the privacy of information obtained from human DNA analysis.
\
* By releasing their own pesticides, GM plants decrease the need for widespread pesticide use.
\
* Some environmentalists are concerned that GM plants could spread harmful genes to wild plants.
\
* Gene therapy, if successful, could offer a cure for a genetic disorder.
\
By releasing their own pesticides, GM plants decrease the need for widespread pesticide use.
\
\
74
New cards
A team of scientists is studying the genome of the pine tree. They have identified a gene that produces a protein that is specific to pine trees that can be useful to humans. Which of the following would need to be done to create recombinant DNA?
Responses
* identifying the sequence of nucleotides in the gene
\
* making multiple copies of the section of DNA that contains the gene
\
* engineering bacteria to use the gene to produce the pine tree protein
\
* identifying the transcription factors that control the expression of the gene
Responses
* identifying the sequence of nucleotides in the gene
\
* making multiple copies of the section of DNA that contains the gene
\
* engineering bacteria to use the gene to produce the pine tree protein
\
* identifying the transcription factors that control the expression of the gene
engineering bacteria to use the gene to produce the pine tree protein
75
New cards
Listed below are several claims that were made during the debate. Which claim can be evaluated by applying the methods of science or engineering (has or can have scientific evidence to support it)?
Responses
* Genetically-modified (GM) foods pose no threats to health safety because they are chemically equivalent with non-GM foods.
\
* A scientist who develops a new technique for generating recombinant DNA should have the right to patent his or her invention.
\
* Young patients should be excluded from experiments in gene therapy because the risks are too high.
\
* If transferring genes from one species to another serves a useful purpose, then doing so is morally acceptable.
\
Responses
* Genetically-modified (GM) foods pose no threats to health safety because they are chemically equivalent with non-GM foods.
\
* A scientist who develops a new technique for generating recombinant DNA should have the right to patent his or her invention.
\
* Young patients should be excluded from experiments in gene therapy because the risks are too high.
\
* If transferring genes from one species to another serves a useful purpose, then doing so is morally acceptable.
\
Genetically-modified (GM) foods pose no threats to health safety because they are chemically equivalent with non-GM foods.
76
New cards
A scientist wants to splice together two sections of DNA. One section is from bacterial DNA, and the other section is from the DNA of a plant. The scientist begins by using restriction enzymes to cut both the bacterial and plant DNA molecules. Which statement BEST explains the restriction enzymes that the scientist should use?
Responses
* By using the same restriction enzyme on both DNA molecules, the “sticky ends” will combine.
\
* By using different restriction enzymes on each DNA molecule, the “sticky ends” will remain uncombined.
\
* By using different restriction enzymes on each DNA molecule, the “sticky ends” will combine.
\
* Any combination of restriction enzymes will allow the “sticky ends” to combine.
Responses
* By using the same restriction enzyme on both DNA molecules, the “sticky ends” will combine.
\
* By using different restriction enzymes on each DNA molecule, the “sticky ends” will remain uncombined.
\
* By using different restriction enzymes on each DNA molecule, the “sticky ends” will combine.
\
* Any combination of restriction enzymes will allow the “sticky ends” to combine.
By using the same restriction enzyme on both DNA molecules, the “sticky ends” will combine.
77
New cards
Gaia is a prized dairy cow that produces a very large volume of milk. An animal breeder is debating whether to produce clones of Gaia. If the cloning process is successful, which outcome is MOST likely?
Responses
* All of the clones have the same gene-controlled traits as Gaia.
\
* The clones are genetically identical with one another, but not with Gaia.
\
* The genes of the clones allow them to produce more milk than Gaia could produce.
\
* The clones are genetically similar with one another and with Gaia, but are not identical.
Responses
* All of the clones have the same gene-controlled traits as Gaia.
\
* The clones are genetically identical with one another, but not with Gaia.
\
* The genes of the clones allow them to produce more milk than Gaia could produce.
\
* The clones are genetically similar with one another and with Gaia, but are not identical.
All of the clones have the same gene-controlled traits as Gaia.
78
New cards
A scientist claims that genetically modified (GM) crops can help improve the environment and benefit ecosystems. Which statement provides the STRONGEST evidence in support of this claim?
Responses
* Animal pollinators may spread the genes from GM crops to wild plants.
\
* GM crops that resist herbicides allow farmers to use stronger herbicides to kill weeds.
\
* Some seeds from GM crops may germinate in wilderness areas.
\
* GM crops that make their own pesticide allow farmers to avoid spreading pesticides over fields.
\
Responses
* Animal pollinators may spread the genes from GM crops to wild plants.
\
* GM crops that resist herbicides allow farmers to use stronger herbicides to kill weeds.
\
* Some seeds from GM crops may germinate in wilderness areas.
\
* GM crops that make their own pesticide allow farmers to avoid spreading pesticides over fields.
\
GM crops that make their own pesticide allow farmers to avoid spreading pesticides over fields.
79
New cards
Two individuals each donated a DNA sample for DNA fingerprinting. The diagram shows the same section of the same chromosome from each sample.
In the process of DNA fingerprinting, restriction enzymes were used to cut the DNA into fragments. Each fragment contains either a gene or a section of noncoding repeated sequences between two genes. Then gel electrophoresis was used to separate the fragments.
\
Suppose the techniques of DNA fingerprinting were applied only to the sections of the chromosomes shown in the diagram. Would the techniques be useful for distinguishing the two samples? Why or why not?
Responses
* Yes, because the techniques identify the locations of genes on chromosomes.
\
* Yes, because the techniques separate DNA fragments by size.
\
* No, because the three genes have identical nucleotide sequences.
\
* No, because each chromosome contains the same three genes.
\
In the process of DNA fingerprinting, restriction enzymes were used to cut the DNA into fragments. Each fragment contains either a gene or a section of noncoding repeated sequences between two genes. Then gel electrophoresis was used to separate the fragments.
\
Suppose the techniques of DNA fingerprinting were applied only to the sections of the chromosomes shown in the diagram. Would the techniques be useful for distinguishing the two samples? Why or why not?
Responses
* Yes, because the techniques identify the locations of genes on chromosomes.
\
* Yes, because the techniques separate DNA fragments by size.
\
* No, because the three genes have identical nucleotide sequences.
\
* No, because each chromosome contains the same three genes.
\
Yes, because the techniques separate DNA fragments by size.
80
New cards
The diagram shows the process of making recombinant DNA and using it to transform a bacterial cell. The recombinant DNA is made by inserting a human gene into a bacterial plasmid. Note that the plasmid contains several genes for antibiotic resistance, including ampr, tetr, and ori.
\
Which is the most likely purpose of the transgenic bacteria that are engineered by this process?
Responses
* using bacteria to produce large quantities of a human protein, such as growth hormone
\
* removing traits of antibiotic resistance from bacteria population
\
* developing bacteria for use in gene therapy
\
* developing new drugs to fight antibiotic-resistant bacteria
\
Which is the most likely purpose of the transgenic bacteria that are engineered by this process?
Responses
* using bacteria to produce large quantities of a human protein, such as growth hormone
\
* removing traits of antibiotic resistance from bacteria population
\
* developing bacteria for use in gene therapy
\
* developing new drugs to fight antibiotic-resistant bacteria
using bacteria to produce large quantities of a human protein, such as growth hormone
81
New cards
Most plastics tend to persist in the environment because natural processes do not degrade them effectively. A scientist thinks that a new strain of bacteria can be developed to break apart plastics. To develop this strain of bacteria, the scientist proposes to subject a colony of bacteria to powerful mutagens.
Which statement BEST explains why the scientist’s proposal could be successful?
Responses
* Mutagens act to preserve beneficial traits and reduce harmful traits within a population.
\
* Mutagens that are properly chosen can produce any specific trait.
\
* A specific trait becomes more likely as genes from other species are added to a population using biotechnology.
\
* A specific trait becomes more likely as the mutagen helps develop an increase in genetic diversity.
Which statement BEST explains why the scientist’s proposal could be successful?
Responses
* Mutagens act to preserve beneficial traits and reduce harmful traits within a population.
\
* Mutagens that are properly chosen can produce any specific trait.
\
* A specific trait becomes more likely as genes from other species are added to a population using biotechnology.
\
* A specific trait becomes more likely as the mutagen helps develop an increase in genetic diversity.
A specific trait becomes more likely as the mutagen helps develop an increase in genetic diversity.
82
New cards
1. Biotechnology
\
2. Recombinant DNA
\
3. Plasmid
\
4. Transgenic
\
5. Clone
\
6. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
\
WB:
\
* small, circular piece of DNA located in the cytoplasm of many bacteria
\
* DNA produced by combining DNA from two or more different sources
\
* the process of manipulating organisms, cells, or molecules, to produce specific products
\
* term used to refer to an organism that contains genes from other organisms
\
* member of a population of genetically identical cells produced from a single cell
\
* The technique used by biologists to make many copies of a particular gene \n
\
\
* the process of manipulating organisms, cells, or molecules, to produce specific products
\
* DNA produced by combining DNA from two or more different sources
\
* small, circular piece of DNA located in the cytoplasm of many bacteria
\
* term used to refer to an organism that contains genes from other organisms
\
* member of a population of genetically identical cells produced from a single cell
\
* The technique used by biologists to make many copies of a particular gene
\
* DNA produced by combining DNA from two or more different sources
\
* small, circular piece of DNA located in the cytoplasm of many bacteria
\
* term used to refer to an organism that contains genes from other organisms
\
* member of a population of genetically identical cells produced from a single cell
\
* The technique used by biologists to make many copies of a particular gene
83
New cards
Researchers are investigating the use of gene therapy as a treatment option for human genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis. When gene therapy is successful, how does it treat the disorder?
Responses
* by deactivating, or “turning off,” one or more genes
\
* by replacing a faulty gene with a normal gene in the human genome
\
* by activating, or “turning on,” one or more genes
\
* by incorporating a human gene into the genomes of bacteria or other organisms
\
Responses
* by deactivating, or “turning off,” one or more genes
\
* by replacing a faulty gene with a normal gene in the human genome
\
* by activating, or “turning on,” one or more genes
\
* by incorporating a human gene into the genomes of bacteria or other organisms
\
by replacing a faulty gene with a normal gene in the human genome
84
New cards
Kathy donates a sample of her DNA for scientific analysis. Can the analysis reveal private information about her? Why or why not?
Responses
* Yes. It can reveal ethnic heritage, the presence of certain diseases, and evidence for criminal cases.
\
* No. It can only reveal her gender, as well as chromosomal disorders such as Down syndrome.
\
* Yes. It can determine her approximate age, height, and weight.
\
* No. It can only reveal a sequence of nucleotides and the presence of certain genes.
\
Responses
* Yes. It can reveal ethnic heritage, the presence of certain diseases, and evidence for criminal cases.
\
* No. It can only reveal her gender, as well as chromosomal disorders such as Down syndrome.
\
* Yes. It can determine her approximate age, height, and weight.
\
* No. It can only reveal a sequence of nucleotides and the presence of certain genes.
\
Yes. It can reveal ethnic heritage, the presence of certain diseases, and evidence for criminal cases.
85
New cards
A forensics expert has obtained a sample of human blood from a crime scene. How can DNA fingerprinting be useful for identifying the person who left the blood at the crime scene?
Responses
* by identifying certain genetically controlled traits of suspects, such as eye shape and blood type
\
* by comparing DNA from the blood cells with DNA from suspects
\
* by comparing karyotypes made from blood cells at the crime scene and blood cells from suspects
\
* by identifying the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA of blood cells
Responses
* by identifying certain genetically controlled traits of suspects, such as eye shape and blood type
\
* by comparing DNA from the blood cells with DNA from suspects
\
* by comparing karyotypes made from blood cells at the crime scene and blood cells from suspects
\
* by identifying the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA of blood cells
by comparing DNA from the blood cells with DNA from suspects
86
New cards
In a class discussion about genetically modified (GM) foods, Jan claims that these foods are safe to eat. She cites scientific studies that compare GM and non-GM foods. The studies provide evidence that the GM foods have no effect on human health.
Which of the following statements provides the strongest argument AGAINST Jan’s claim?
Responses
* GM plants incorporate genes from bacteria or other organisms.
\
* GM foods are relatively new, so their long-term effects cannot be evaluated yet.
\
* Scientists have yet to sequence the complete genome of most GM plants.
\
* Many consumers avoid GM foods and other products of genetic technology.
\
Which of the following statements provides the strongest argument AGAINST Jan’s claim?
Responses
* GM plants incorporate genes from bacteria or other organisms.
\
* GM foods are relatively new, so their long-term effects cannot be evaluated yet.
\
* Scientists have yet to sequence the complete genome of most GM plants.
\
* Many consumers avoid GM foods and other products of genetic technology.
\
GM foods are relatively new, so their long-term effects cannot be evaluated yet.
87
New cards
Darwin collected and studied a variety of fossils. The fossils provided clues to ancient organisms. As Darwin concluded, how did ancient organisms compare to modern species?
Responses
* The ancient organisms were similar to modern species, but differed in several ways.
\
* The ancient organisms were larger or smaller than modern species, but otherwise identical.
\
* The ancient organisms were very different from modern species, and lacked any significant similarities.
\
* The ancient organisms were identical to modern species.
Responses
* The ancient organisms were similar to modern species, but differed in several ways.
\
* The ancient organisms were larger or smaller than modern species, but otherwise identical.
\
* The ancient organisms were very different from modern species, and lacked any significant similarities.
\
* The ancient organisms were identical to modern species.
The ancient organisms were similar to modern species, but differed in several ways.
88
New cards
The adaptations of a pelican include its long, pouch-like beak. Why is the beak of the pelican an example of an adaptation?
Responses
* The shape and structure of the beak are inherited and help the pelican survive in its environment.
\
* The shape and structure of the beak have remained the same over many generations.
\
* All birds have beaks, but the beaks vary among different species.
\
* The beak is a unique feature that is found only in pelicans.
Responses
* The shape and structure of the beak are inherited and help the pelican survive in its environment.
\
* The shape and structure of the beak have remained the same over many generations.
\
* All birds have beaks, but the beaks vary among different species.
\
* The beak is a unique feature that is found only in pelicans.
The shape and structure of the beak are inherited and help the pelican survive in its environment.
89
New cards
Darwin developed and proposed the Theory of Evolution during the 1800s. Since that time, due in part to advances in technology, scientists have expanded their knowledge and ideas about biological systems. Which statement describes an example of evidence acquired in the past 100 years and its relationship to the Theory of Evolution?
Responses
* New evidence from fossils provides evidence that one species does not descend from another.
\
* New evidence from molecular biology provides evidence that life evolved from many ancestors, not a single ancestor.
\
* New evidence from biogeography provides evidence that one species does not descend from another.
\
* New evidence from molecular biology provides overwhelming support that all life evolved from a single ancestor.
Responses
* New evidence from fossils provides evidence that one species does not descend from another.
\
* New evidence from molecular biology provides evidence that life evolved from many ancestors, not a single ancestor.
\
* New evidence from biogeography provides evidence that one species does not descend from another.
\
* New evidence from molecular biology provides overwhelming support that all life evolved from a single ancestor.
New evidence from molecular biology provides overwhelming support that all life evolved from a single ancestor.
90
New cards
Raphael runs a computer simulation of a population of beetles in a garden ecosystem. The simulation begins with 300 beetles, divided equally among red, tan, and brown variants, and with equal numbers of males and females. The simulation assumes that female beetles each lay 50 eggs in each reproduction cycle, and that individual beetles live for at most 2 reproductive cycles.
The table shows the numbers of each beetle variant over 7 reproduction cycles. Only adult beetles are counted.
\
Which conclusion about the simulated beetle population does the data support?
Responses
* Throughout the simulation, brown is the most advantageous color for the beetles.
\
* Throughout the simulation, red is the least advantageous color for the beetles.
\
* In additional reproductive cycles, the maroon variants would become more common.
\
* The fitness of the beetle variants changed during the simulation.
The table shows the numbers of each beetle variant over 7 reproduction cycles. Only adult beetles are counted.
\
Which conclusion about the simulated beetle population does the data support?
Responses
* Throughout the simulation, brown is the most advantageous color for the beetles.
\
* Throughout the simulation, red is the least advantageous color for the beetles.
\
* In additional reproductive cycles, the maroon variants would become more common.
\
* The fitness of the beetle variants changed during the simulation.
The fitness of the beetle variants changed during the simulation.
91
New cards
Charles Darwin applied a wide variety of observations to help him develop his ideas about evolution. Which general statement describes several of the observations that Darwin made and considered, and later incorporated into his Theory of Evolution?
Responses
* Fossils show that ancient species were identical or nearly identical to modern species.
\
* All species use DNA to carry and translate genetic information.
\
* Species may vary from place to place, but most species are distributed widely on all continents.
\
* Species on islands tend to resemble mainland species, yet differ from them in many ways.
Responses
* Fossils show that ancient species were identical or nearly identical to modern species.
\
* All species use DNA to carry and translate genetic information.
\
* Species may vary from place to place, but most species are distributed widely on all continents.
\
* Species on islands tend to resemble mainland species, yet differ from them in many ways.
Species on islands tend to resemble mainland species, yet differ from them in many ways.
92
New cards
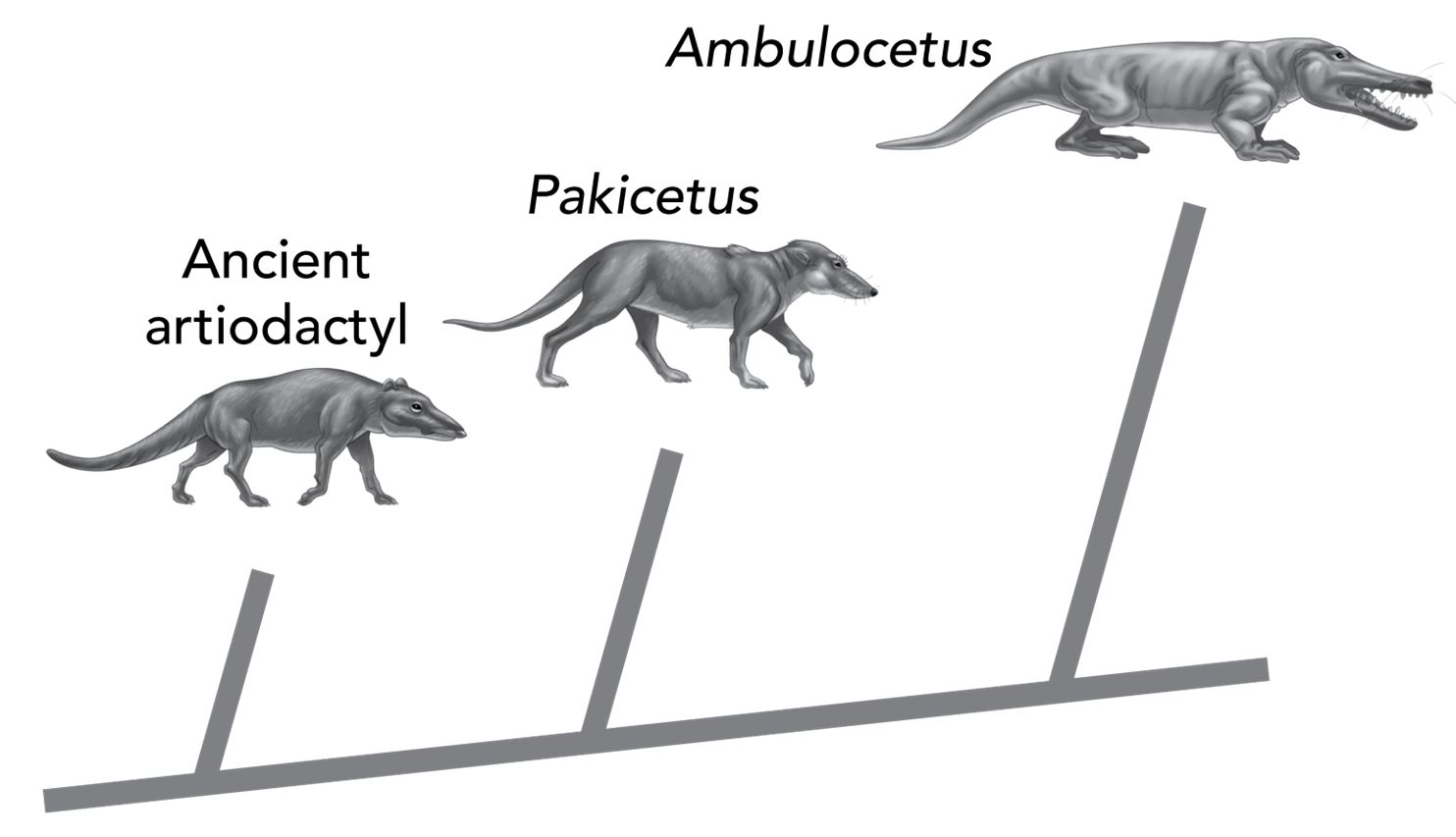
The diagram describes a proposed evolutionary relationship among three ancient species, all of which were relatives of modern whales.
\
What evidence would MOST STRONGLY support the evolutionary relationship described in the diagram?
Responses
* a comparison of the fossil skeletons of the species
\
* a comparison of the ages of the fossils of each species
\
* the number of fossil discoveries of each species
\
* data from experiments on whale behavior
\
What evidence would MOST STRONGLY support the evolutionary relationship described in the diagram?
Responses
* a comparison of the fossil skeletons of the species
\
* a comparison of the ages of the fossils of each species
\
* the number of fossil discoveries of each species
\
* data from experiments on whale behavior
a comparison of the fossil skeletons of the species
93
New cards
A population of male and female goats is stranded on a large island. The goats differ from one another in several ways, including fur color, ear shape, and preferred food.
A scientist predicts that the average ear shape of the goats will change gradually over time. According to Darwin’s ideas about evolution and natural selection, the accuracy of the prediction depends on which of these conditions?
Responses
* The island lacks natural predators of goats.
\
* Certain ear shapes help the goats survive and reproduce on the island.
\
* The island provides enough food to support an increase in the goat population.
\
* Certain ear shapes allow the goats to hear a wider variety of sounds.
\
A scientist predicts that the average ear shape of the goats will change gradually over time. According to Darwin’s ideas about evolution and natural selection, the accuracy of the prediction depends on which of these conditions?
Responses
* The island lacks natural predators of goats.
\
* Certain ear shapes help the goats survive and reproduce on the island.
\
* The island provides enough food to support an increase in the goat population.
\
* Certain ear shapes allow the goats to hear a wider variety of sounds.
\
Certain ear shapes help the goats survive and reproduce on the island.
94
New cards
Edwin is studying a population of rabbits in the neighborhood that surrounds his home. He observes a variety of fur colors among the rabbits, including gray, white, and brown. The rabbit fur also has a variety of markings, including spots and bands.
Edwin argues that natural selection will occur on the rabbit population. It will result in a change in the distribution of fur colors and markings.
Which observation would provide the STRONGEST evidence in support of Edwin’s argument?
Responses
* Most of the rabbits are wildlife, while some are pets.
\
* Neighborhood plants can support a large increase in the rabbit population.
\
* A new predator tends to hunt more white rabbits than gray or brown rabbits.
\
* Fur color and markings do not affect the running speed of a rabbit.
Edwin argues that natural selection will occur on the rabbit population. It will result in a change in the distribution of fur colors and markings.
Which observation would provide the STRONGEST evidence in support of Edwin’s argument?
Responses
* Most of the rabbits are wildlife, while some are pets.
\
* Neighborhood plants can support a large increase in the rabbit population.
\
* A new predator tends to hunt more white rabbits than gray or brown rabbits.
\
* Fur color and markings do not affect the running speed of a rabbit.
A new predator tends to hunt more white rabbits than gray or brown rabbits.
95
New cards
Scientists before Darwin had proposed that living things could change over time. Why was Darwin’s theory of evolution more powerful and useful than the proposals of the other scientists?
Responses
* Darwin used logical reasoning to argue that living things could change.
\
* Darwin explained the mechanism by which evolution occurred.
\
* Darwin cited examples from nature that were based on observations.
\
* Darwin hypothesized that evidence from DNA and genes would explain how evolution occurs.
\
Responses
* Darwin used logical reasoning to argue that living things could change.
\
* Darwin explained the mechanism by which evolution occurred.
\
* Darwin cited examples from nature that were based on observations.
\
* Darwin hypothesized that evidence from DNA and genes would explain how evolution occurs.
\
Darwin explained the mechanism by which evolution occurred.
96
New cards
John states the following claim.
“Biogeography provides evidence for the theory of evolution.
To support this claim, which evidence would be MOST useful for John to cite?
Responses
* Polar bears and grizzly bears are similar in many ways, but are adapted to live in different regions.
\
* Farm crops developed in Asia are now raised successfully in regions all over the world.
\
* Fossils of plants and animals have been found on Antarctica, which now is covered in ice.
\
* A sequence of fossils shows that horses became smaller over time.
\
“Biogeography provides evidence for the theory of evolution.
To support this claim, which evidence would be MOST useful for John to cite?
Responses
* Polar bears and grizzly bears are similar in many ways, but are adapted to live in different regions.
\
* Farm crops developed in Asia are now raised successfully in regions all over the world.
\
* Fossils of plants and animals have been found on Antarctica, which now is covered in ice.
\
* A sequence of fossils shows that horses became smaller over time.
\
Polar bears and grizzly bears are similar in many ways, but are adapted to live in different regions.
97
New cards
Charles Darwin focused on three patterns of diversity during his time observing nature on his voyage. In the time since his voyage, other species of penguins have been documented, and their evolutionary relationships with other birds have been discovered.
Read each sentence about patterns of diversity, then drag and drop the pattern of diversity it represents.
\
1. Penguins evolved from birds with wings used for flight.
2. Several different penguin species inhabit Antarctica.
3. At least 17 different penguin species inhabit the world.
\
WB:
* Species vary over time
* Species vary globally
* Species vary locally
Read each sentence about patterns of diversity, then drag and drop the pattern of diversity it represents.
\
1. Penguins evolved from birds with wings used for flight.
2. Several different penguin species inhabit Antarctica.
3. At least 17 different penguin species inhabit the world.
\
WB:
* Species vary over time
* Species vary globally
* Species vary locally
1. Species vary over time
2. Species vary locally
3. Species vary globally
98
New cards
Since Darwin published On the Origins of Species, scientists have pursued different areas of research to test his theory of natural selection. Researchers have found that different penguin species have similar DNA sequences, also called (biogeography/vestigial structures/homologous structures/genetic codes), which supports Darwin's ideas about a common ancestor. Other scientists have compared the structures of the wings of penguins to the structures of the wings of other species of birds, such as seagulls. The wings of penguins and the wings of seagulls are (biogeography/vestigial structures/homologous structures/genetic codes), because they are similar in structure and derived from a common ancestor but have evolved to fulfill different purposes. The penguin's wings are also an example of (biogeography/vestigial structures/homologous structures/genetic codes), because penguins can no longer use them to fly. Scientists studying (biogeography/vestigial structures/homologous structures/genetic codes) have hypothesized that the Galápagos penguin evolved from Humboldt penguins that were carried from Chile and Peru by ocean currents.
1. genetic codes
2. homologous structures
3. vestigial structures
4. biogeography
99
New cards
The wings of ostriches are examples of vestigial structures. The wings provide evidence for which of these evolutionary relationships?
Responses
* An ancestor of ostriches had useful wings.
\
* An ancestor of ostriches had vestigial structures.
\
* A new bird species without wings will evolve from ostriches.
\
* A new bird species that has useful wings will evolve from ostriches.
\
Responses
* An ancestor of ostriches had useful wings.
\
* An ancestor of ostriches had vestigial structures.
\
* A new bird species without wings will evolve from ostriches.
\
* A new bird species that has useful wings will evolve from ostriches.
\
An ancestor of ostriches had useful wings.
100
New cards
DeMarco is comparing the bodies of a typical bird and winged insect, as shown in the diagram.
\
DeMarco is constructing an argument that the wings of the bird and insect are analogous structures. Which statement provides the STRONGEST evidence for this argument?
Responses
* The two types of wings are covered in different materials.
\
* The two types of wings grow and develop from similar or identical embryonic tissues.
\
* The two types of wings have different shapes and sizes.
\
* The two types of wings grow and develop from different embryonic tissues.
\
\
DeMarco is constructing an argument that the wings of the bird and insect are analogous structures. Which statement provides the STRONGEST evidence for this argument?
Responses
* The two types of wings are covered in different materials.
\
* The two types of wings grow and develop from similar or identical embryonic tissues.
\
* The two types of wings have different shapes and sizes.
\
* The two types of wings grow and develop from different embryonic tissues.
\
The two types of wings grow and develop from different embryonic tissues.