Muscle and Nervous Tissue: Properties, Anatomy, and Physiology
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What are the four main properties of muscle tissue?
Electrical excitability, contractility, extensibility, and elasticity.
What surrounds and protects the entire muscle?
Epimysium, a connective tissue layer.
What is the function of fascia in muscle anatomy?
Fascia separates neighboring muscles and is continuous with the epimysium.
What are tendons?
White fibrous chords of dense regular connective tissue that attach muscle to bone.
What is the difference between origin and insertion in muscle attachments?
Origin is the more stationary bone attachment, while insertion is the more mobile end, usually distal.
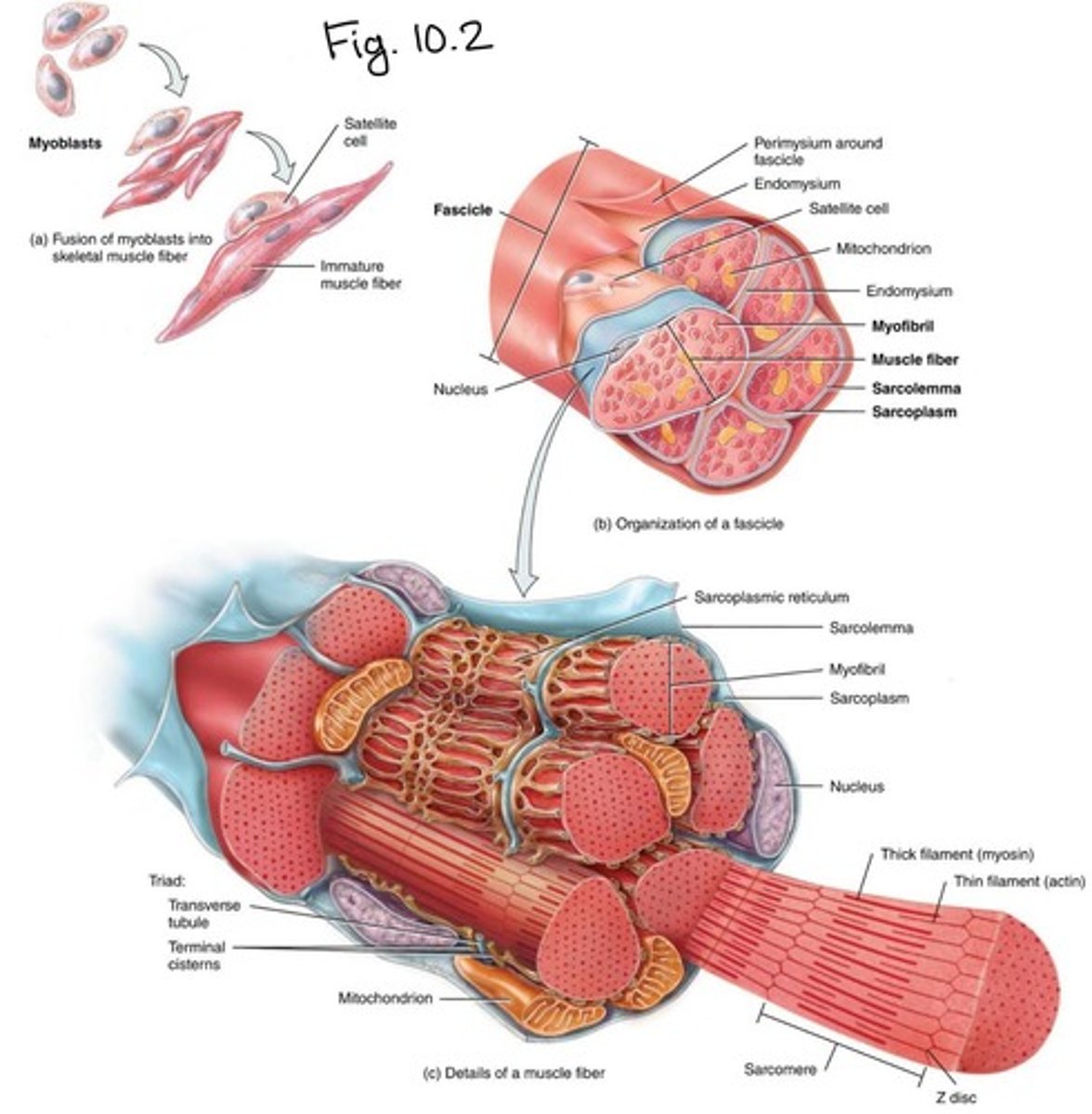
What are myoblasts?
Immature cells that give rise to mature muscle fibers.
What is hypertrophy in muscle tissue?
The enlargement of existing muscle fibers in response to growth hormone.
What is the role of the sarcolemma?
It is the plasma membrane of muscle fibers.
What is the function of T tubules?
They carry electrical charges from the surface to the interior of muscle fibers.
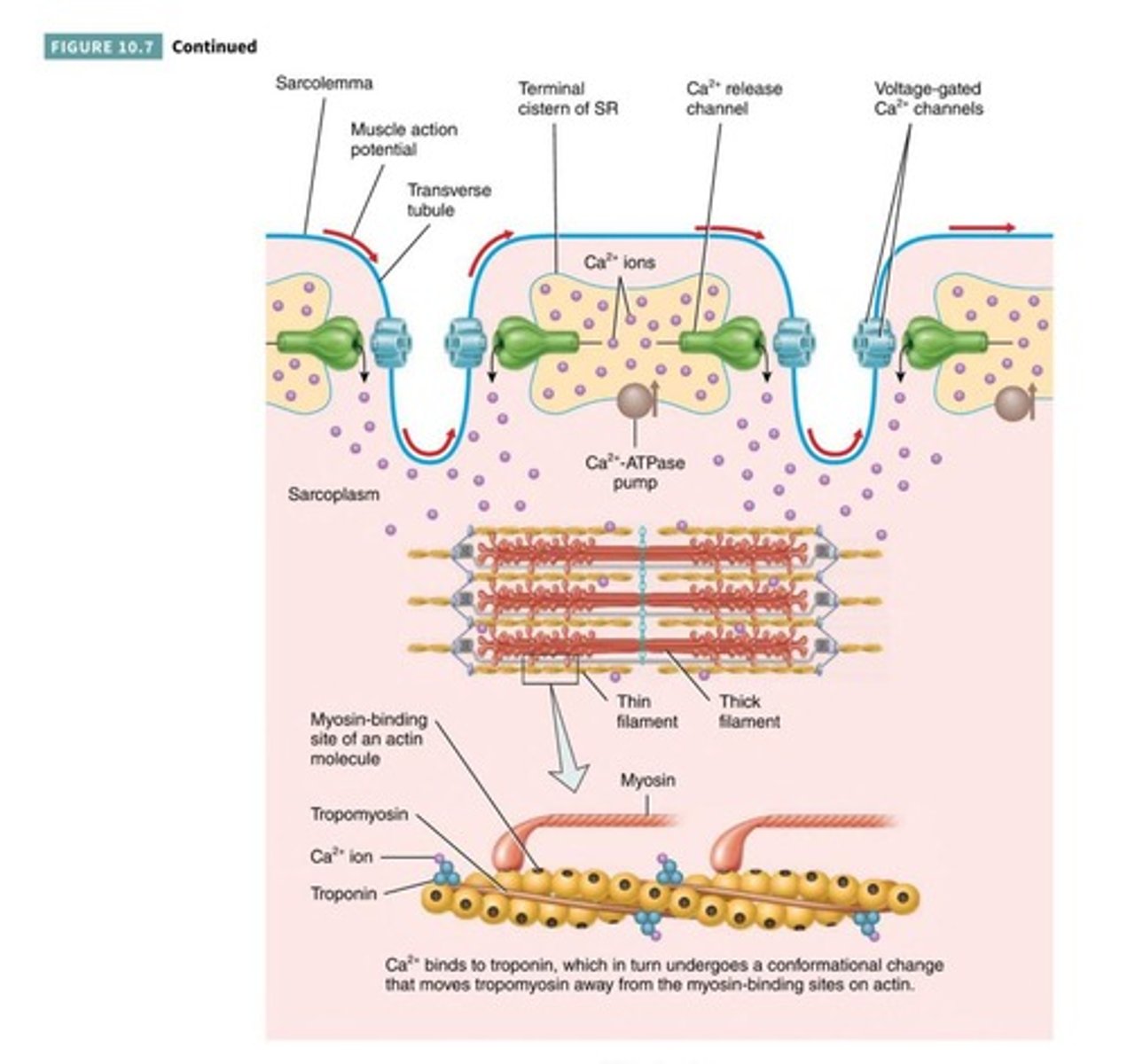
What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)?
A structure that encircles myofibrils and stores calcium ions.
What is a triad in muscle fibers?
A structure consisting of one T tubule and two terminal cisternae.
What are the three ways ATP is generated in muscle metabolism?
Phosphorylation of ADP by creatine phosphate, aerobic metabolism, and anaerobic metabolism.
What is muscle fatigue?
The inability of muscle to maintain a particular strength of contraction over time.
What is oxygen debt?
The difference between resting rate of oxygen consumption and the rate following exercise.
What is isotonic contraction?
A contraction where muscle tension remains constant while the muscle length changes.
What is isometric contraction?
A contraction where muscle develops tension but does not change length.
What is a twitch contraction?
The mechanical response of a muscle fiber or motor unit to a single action potential.
What influences the development of muscle tension?
The frequency of stimulation and the relationship between contraction and relaxation.
What is a motor unit?
The motor neuron and the muscle fibers it innervates, serving as a functional unit of muscle activity.
What are the three types of skeletal muscle fibers?
Slow oxidative, fast oxidative-glycolytic, and fast glycolytic.
What are the effects of aerobic exercise on skeletal muscle?
Increases capillary density, myoglobin, and mitochondria, but only slightly increases fiber diameter.
What characterizes visceral smooth muscle?
It is a single unit smooth muscle that can contract without external stimuli and is connected by gap junctions.
What is the role of calmodulin in smooth muscle contraction?
Calmodulin activates myosin light chain kinase, facilitating contraction.
What is myasthenia gravis?
An autoimmune disorder that leads to muscle weakness due to blocked sodium channels at the neuromuscular junction.
What are the three main functions of the nervous system?
1. Sensory input 2. Integrative process 3. Motor output
What are the two types of nervous tissue?
1. Neurons 2. Neuroglia
What is the role of astrocytes in the nervous system?
Astrocytes support neurons, wrap around blood capillaries, and help regulate the chemical environment.
What is the function of oligodendrocytes?
Oligodendrocytes form myelin sheaths around several axons.
What is the role of microglia?
Microglia remove debris through phagocytosis.
What do ependymal cells do?
Ependymal cells line brain ventricles and produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
What is myelin composed of?
80% lipid and 20% protein.
What is a ganglion?
A cluster of neuron cell bodies in the PNS.
What is a tract in the nervous system?
A bundle of axons in the CNS.
What is gray matter composed of?
Unmyelinated axons, neuroglia, dendrites, and neural cell bodies.
What is the resting membrane potential (RMP)?
The electrical charge across the plasma membrane, typically around -70 mV.
What causes depolarization in a neuron?
An influx of sodium ions (Na+) into the cell.
What is the difference between graded potentials and action potentials?
Graded potentials are local changes in membrane potential, while action potentials are large, rapid changes that propagate along the axon.
What is the threshold level for generating an action potential?
-55 mV.
What is saltatory conduction?
The process where action potentials jump from node to node along myelinated axons.
What are the three types of nerve fibers?
1. Type A: largest diameter, myelinated, fastest 2. Type B: medium diameter, myelinated, medium speed 3. Type C: smallest diameter, unmyelinated, slowest.
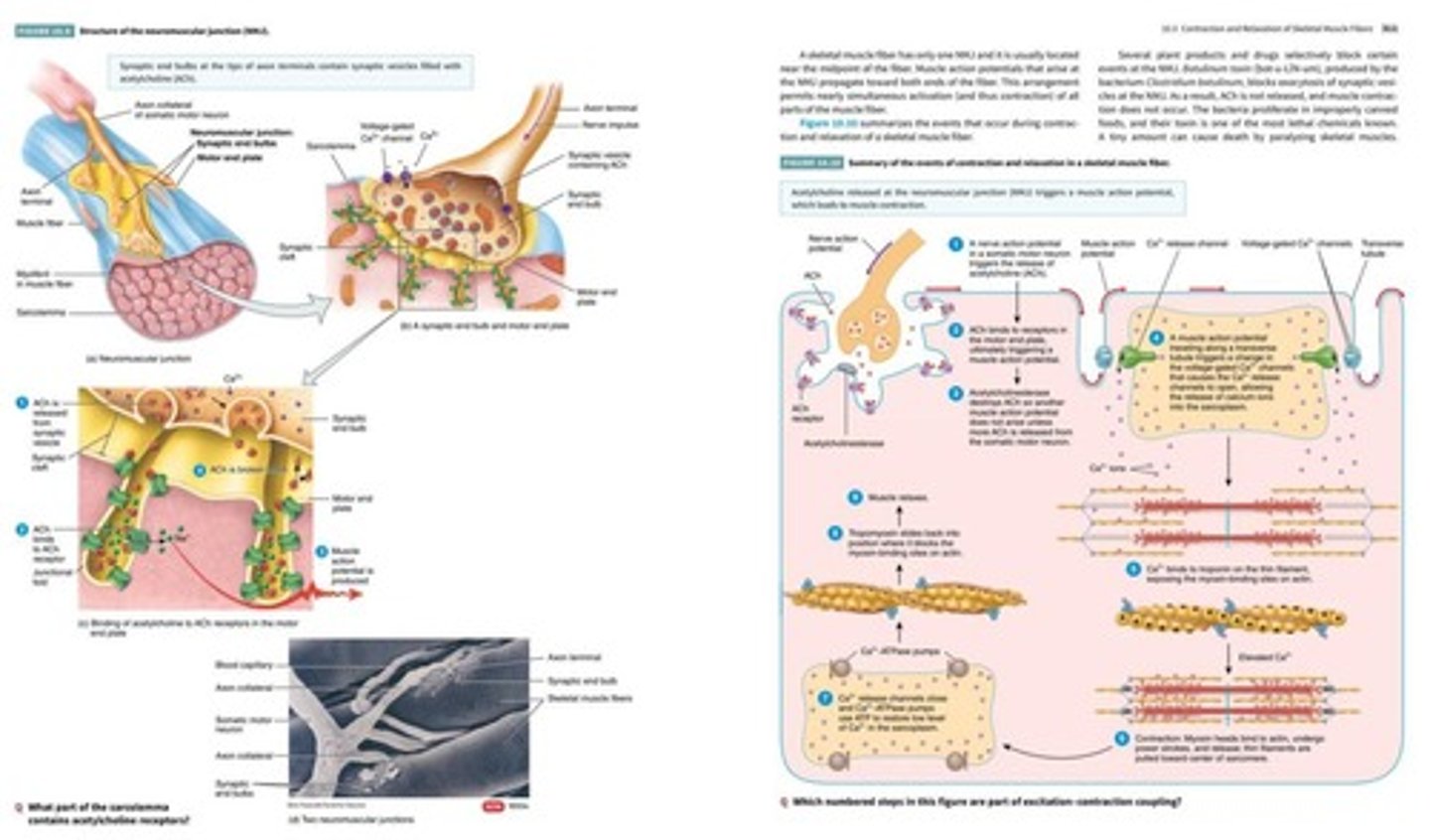
What is synaptic transmission?
The process where electrical activity from one neuron influences another neuron at a synapse.
What are the steps involved in chemical synaptic transmission?
1. Action potential arrives at axon terminal 2. Voltage-gated calcium channels open 3. Calcium enters the axon terminal 4. Exocytosis of neurotransmitter occurs 5. Neurotransmitter binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron.
What is the difference between excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP and IPSP)?
EPSP depolarizes the postsynaptic neuron, increasing the likelihood of firing an action potential, while IPSP hyperpolarizes it, decreasing that likelihood.
What is summation in the context of postsynaptic potentials?
The process of adding together EPSPs and IPSPs to determine whether the postsynaptic neuron will fire an action potential.
What are neurotransmitters?
Chemical signaling substances that activate specific receptors on target neurons.
Name two classes of neurotransmitters.
1. Acetylcholine 2. Amino acids (e.g., glutamate, GABA).
What is the role of anticholinesterases?
They slow down the breakdown of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction.
What is the function of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)?
SSRIs increase serotonin levels in the brain by inhibiting its reuptake.