General + Neutrophil, Basophil, Eosinophil (Cram)
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Cells in the blood that are involved in defending the body against infective organisms and foreign substances (anatomical and common name)
Leukocytes or white blood cells
What are the two groups of leukocytes?
Granulocytes
Agranulocytes
What are the three types of leukocytes that contain granules in their cytoplasm (ie. granulocytes)?
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Basophils
What are the two types of leukocytes that have few or no granules evident in their cytoplasm (ie. agranulocytes)?
Lymphocytes
Monocytes
What are the six stages of granulocyte development in order?
Myeloblast
Promyelocyte
Myelocyte
Metamyelocyte
Band cell
Segmented granulocyte
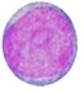
This cell is the same as a progenitor cell, large with a large nucleus, prominent nucleoli and lacy chromatin. Cytoplasm is blue with no visible granules. What stage of granulocyte development is it?
Myeloblast
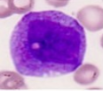
This cell is slightly larger than a myeloblast. It has more cytoplasm and small granules. Cytoplasm is less blue. Chromatin pattern is becoming coarse. Nucleoli present but may be indistinct. What stage of granulocyte development is it?
Promyelocyte
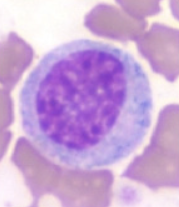
This cell is smaller than a myeloblast. Nucleus is denser and smaller. Nucleoli is absent.What stage of granulocyte development is it?
Myelocyte
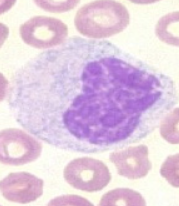
This cell has a nucleus that is starting to become kidney bean shaped. Cytoplasm is less blue, and it may have more granules.What stage of granulocyte development is it?
Metamyelocyte
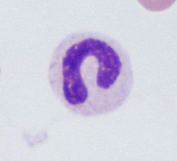
This cell have a curved nucleus. No area of the nucleus is constricted to less than two thirds of the diameter of the rest of the nucleus. What stage of granulocyte development is it?
Band cell
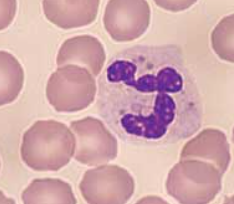
This cell has a lobulated nucleus or has areas of marked constriction. Normally has 2–5 lobes. May have obvious granules.
Segmented granulocyte
What are the two functional systems of leukocytes?
Phagocytic system
Immunocytic system
What are the four leukocytes in the phagocytic system?
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Basophils
Monocytes
What is the leukocyte in the immunocytic system?
Lymphocytes
What are the two types of immunity produced by immunocytic system?
Humoral immunity
Cell mediated immunity
What type of immunity produces antibodies to give immunity?
Humoral immunity
What type of immunity attacks the pathogen with WBC's?
Cell–mediated immunity
What are the three stages of phagocytosis?
Chemotaxis
Adherence
Internalization
What stage of phagocytosis involves phagocytes being attracted to the site by molecules called chemotaxins?
Chemotaxis
What stage of phagocytosis involves phagocytes attaching to the microorganism?
Adherence
What stage of phagocytosis involves the phagocyte invaginating, surrounding, killing, and digesting the microorganism?
Internalization
What is another name for granulocytic cells?
Polymorphonuclear cells (PMN's)
What is the predominant circulating granulocyte, what animal is the exception?
Neutrophils, cattle (lymphocytes are more dominant)
True or false: Neutrophils are the primary defense against bacterial infection
True
What two biologically active molecules do neutrophils secrete?
Enzymes
Chemotactic factors (attract more neutrophils)
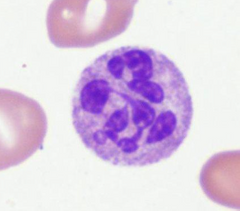
What would this neutrophil be called?
Hypersegmented neutrophil
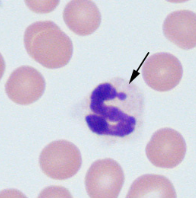
What is this structure called, what does it tell you about the animal?
Barr body, the animal is female
What is the general lifespan of a neutrophil?
Very short, hours to days
Term for increased neutrophil production/release from bone marrow
Neutrophilia
Name for neutrophils lined up along the blood vessle endothelium
Marginating pool
In neutrophilia, neutrophils move from the marginating pool to where?
Circulating pool
What are some conditions that can cause a neutrophilia?
Hemorrhage, hemolysis, toxicity
Term for decreased release of neutrophils from bone marrow
Neutropenia
In neutropenia which pools are neutrophils moving to and from?
From the circulating pool, to the marginating pool
What tendancy of the granules of eosinophils gives this granulocyte its name?
Granules have a strong affinity for eosin
In what two situations are eosinophils more prominent?
Hypersensitivity or allergic reactions
Parasitic infections
What are some conditions that would make eosinophils more prominent?
Feline athsma, allergic bronchitis, flea bite dermatitis, and heartworm
Term for an increase of eosinophils
Eosinophilia
Term for a decrease of eosinophils
Eosinopenia
True or false: Eosinopenia is more concerning finding than eosinophilia
False. Eosinopenia is very normal, 0% isn't a concern.
What kind of drug will cause eosinopenia?
Glucocorticoids
What are the two chemicals released by basophils?
Histamines
Heparin
What symptoms do histamines and heparin produce?
Symptoms of allergies
Term for increased basophils
Basophilia
Term for decreased basophils
Basopenia (just like eosinopenia in that a low number is very normal)
Will long term antibody stimulation (ex. living with a cat while allergic to cats) cause basophilia or basopenia?
Basophilia