Overview of Brain Structures and Neuron Function
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
Cerebrum
The largest part of the brain, responsible for thinking, problem-solving, memory, and voluntary movements.
Cerebellum
The brain structure that controls balance, coordination, and fine motor movements.
Ventricles
Fluid-filled spaces in the brain that produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to protect and nourish the brain.
Gray Matter
Contains neuron cell bodies; processes information and controls decision-making.
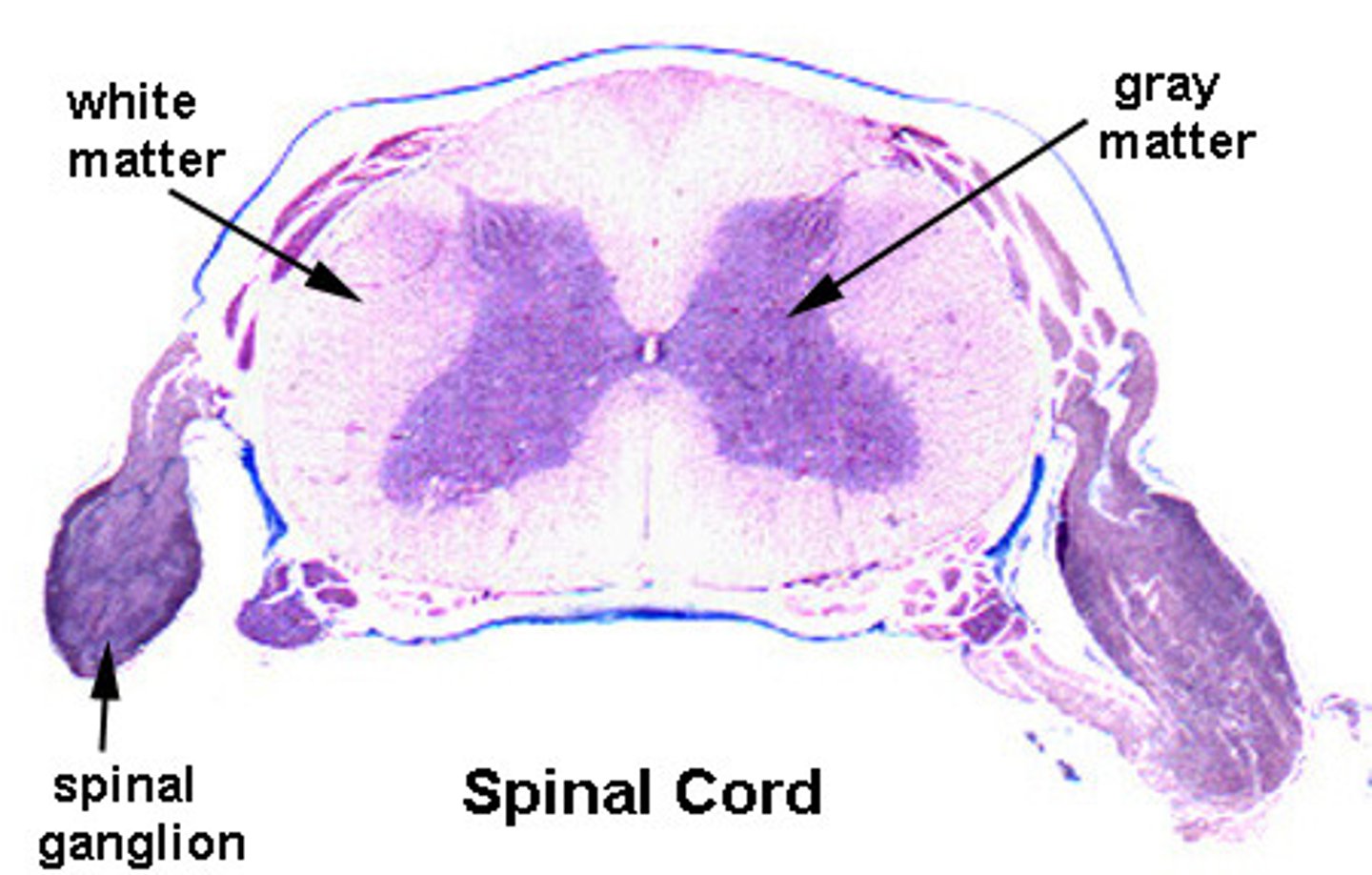
White Matter
Contains myelinated axons; transmits signals quickly between different brain regions.
Nerve Fibers
Axons that transmit electrical signals across the nervous system.
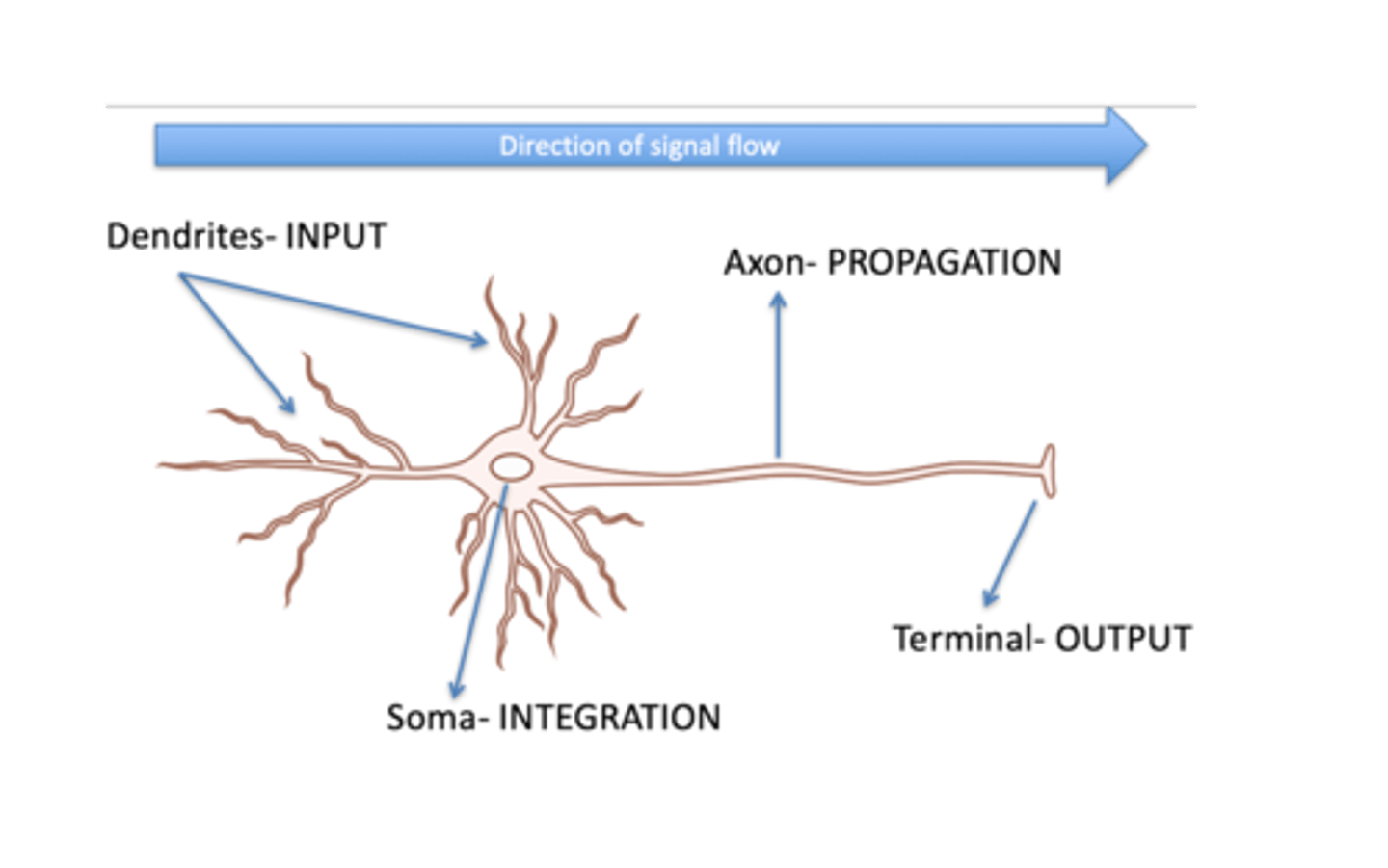
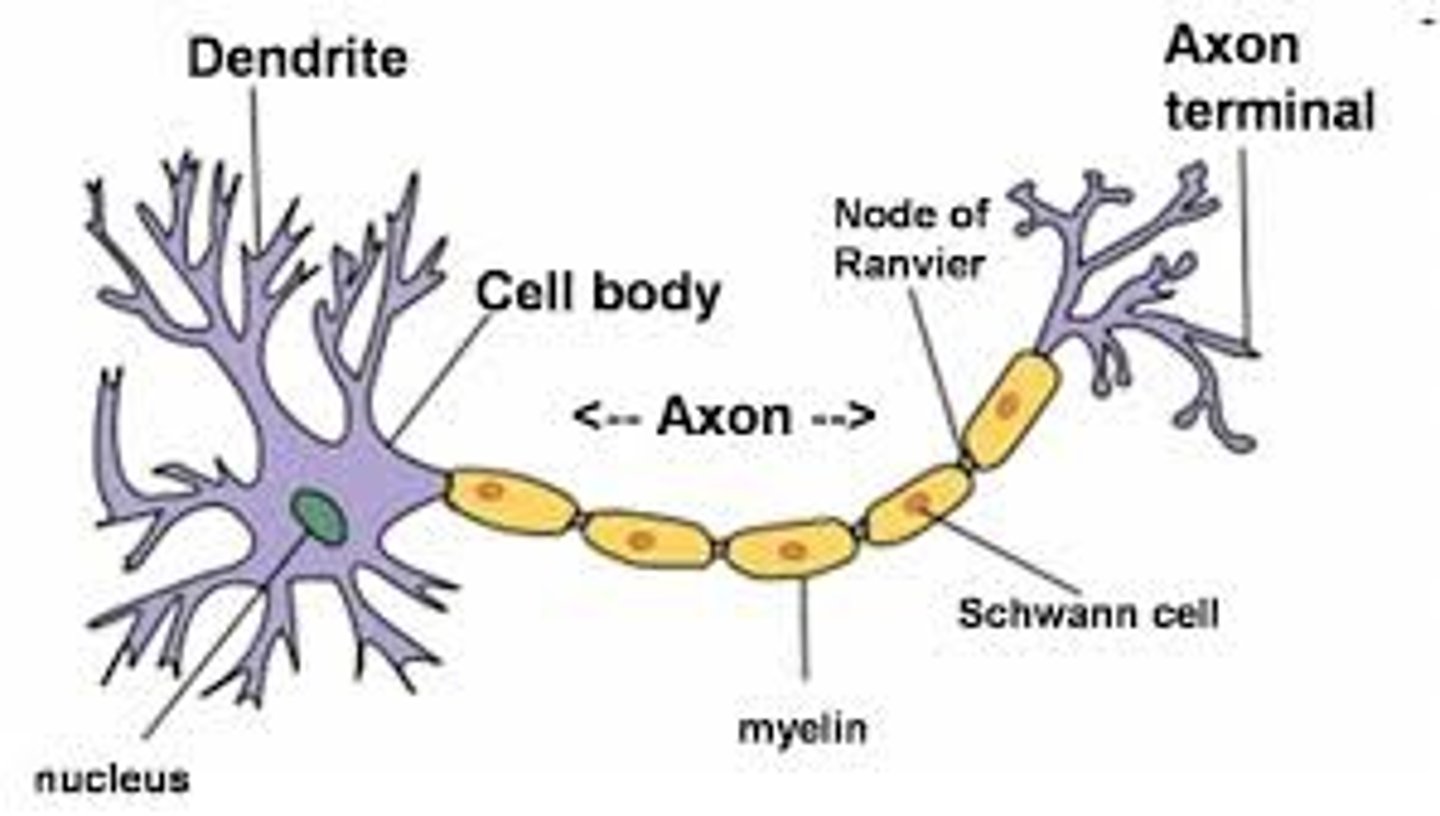
Neuron
The basic cell of the nervous system that sends and receives electrical and chemical messages.
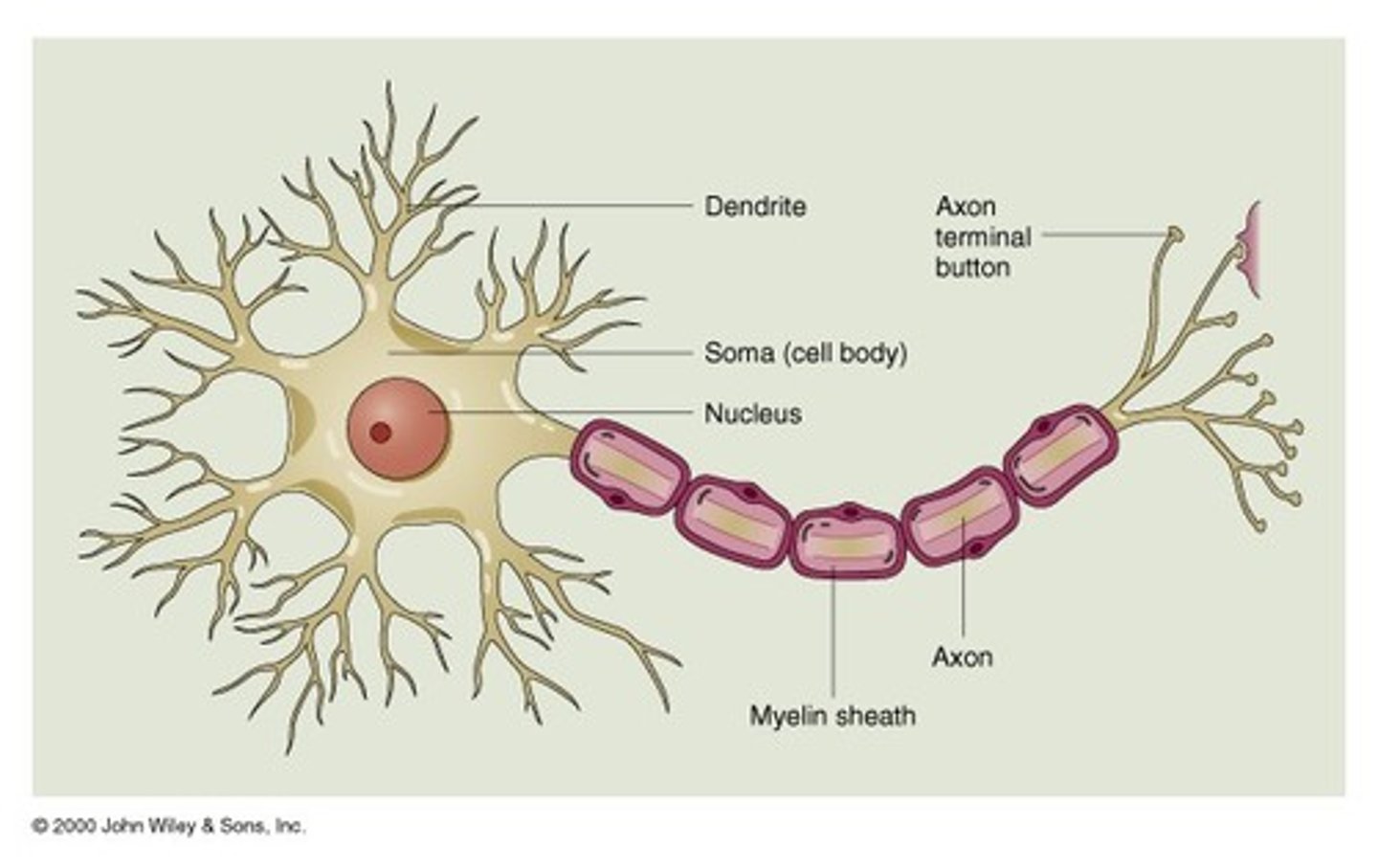
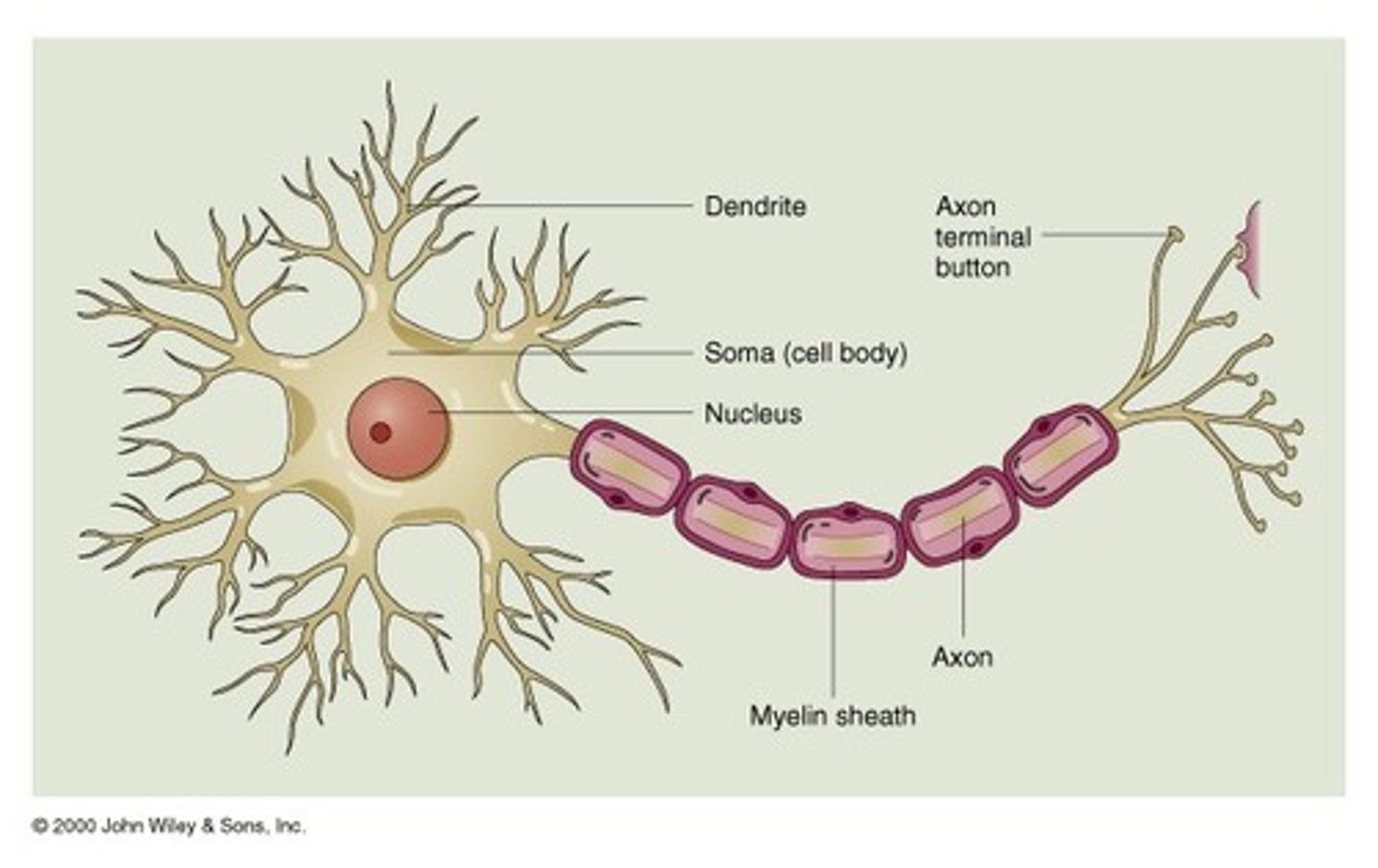
Axon
A long fiber that transmits signals away from the neuron's cell body.
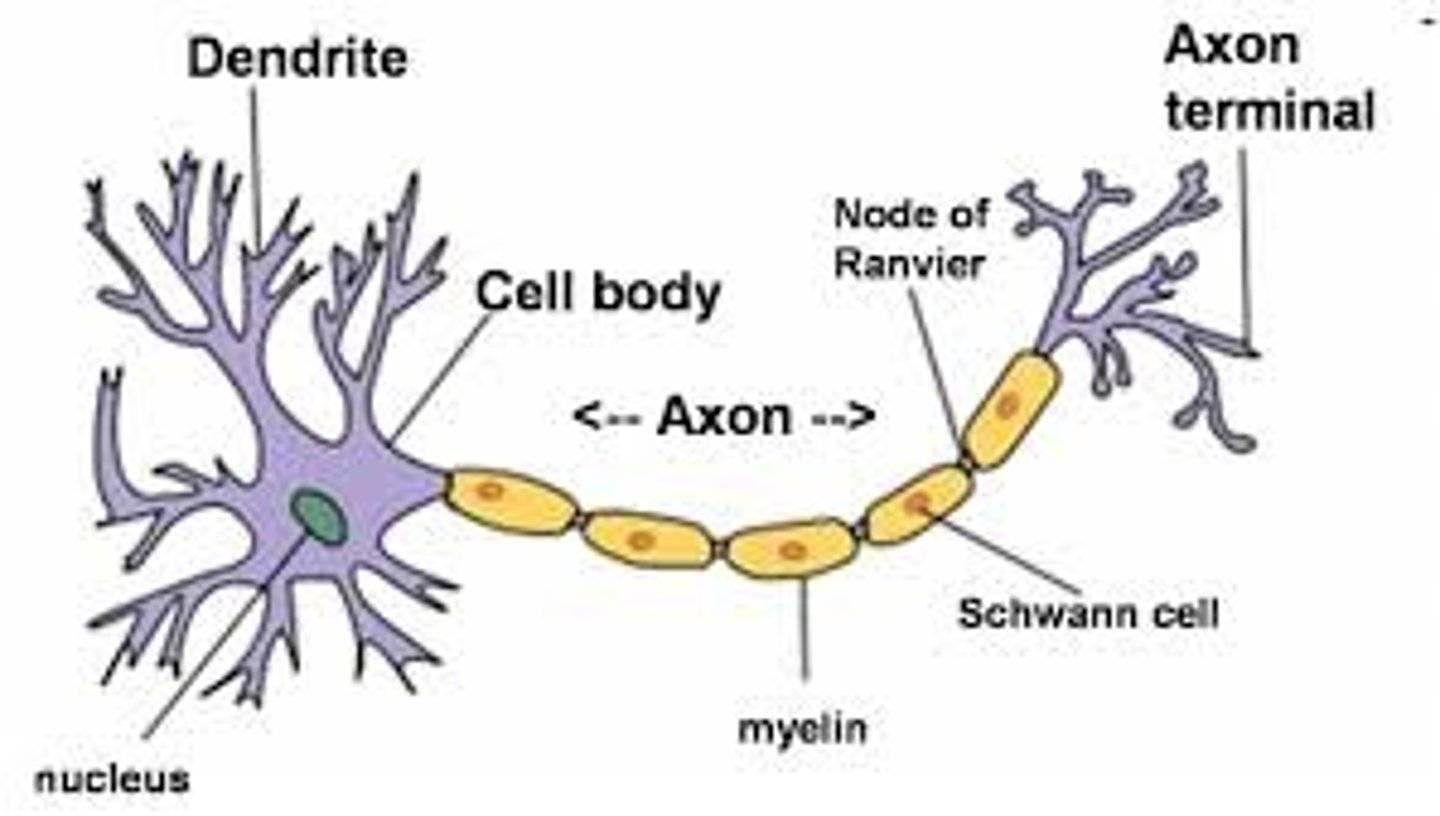
Dendrites
Short branches that receive signals from other neurons.
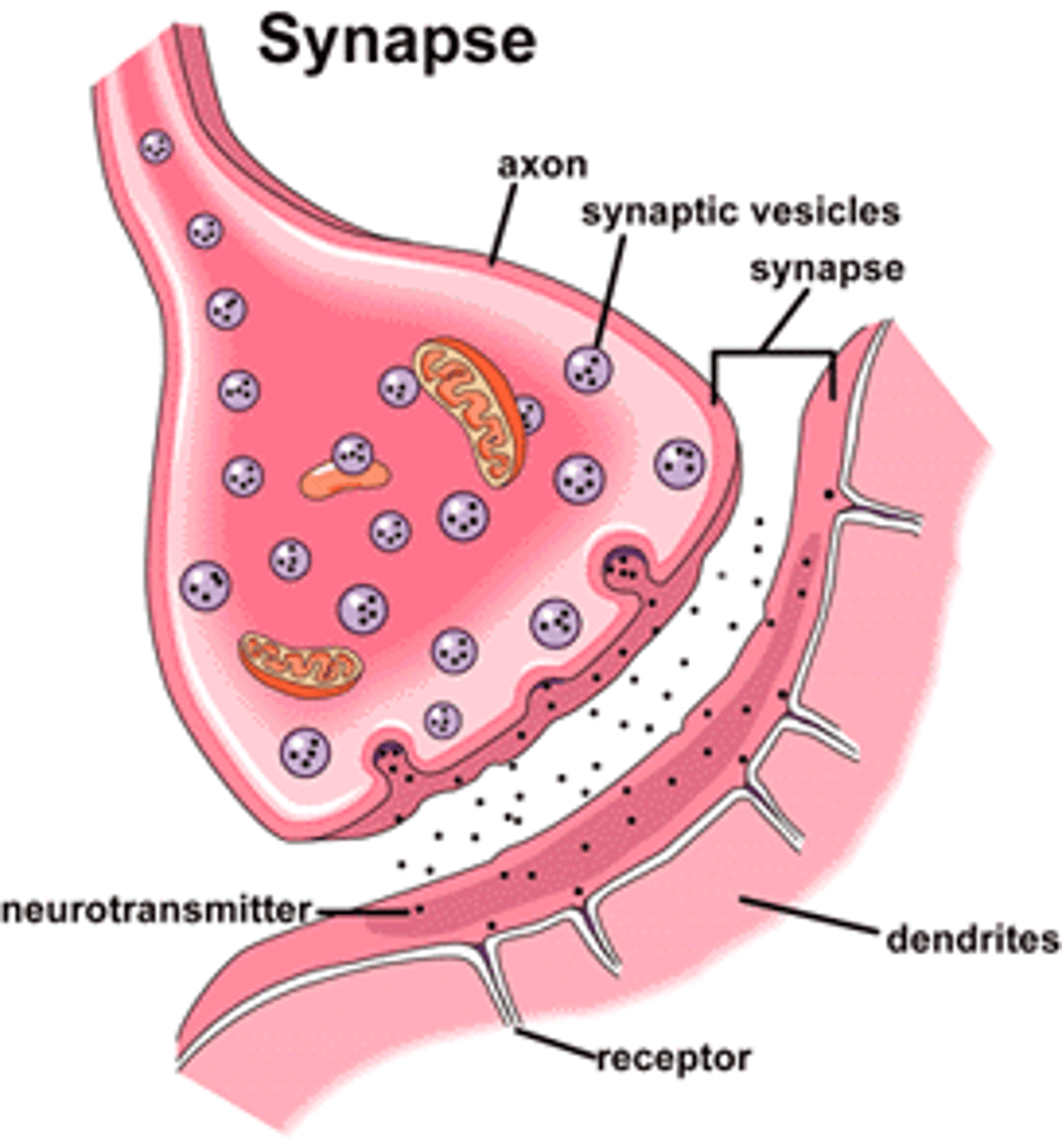
Synapse
The tiny gap between neurons where neurotransmitters are released to pass signals.
Soma (Cell Body/Perikaryon)
The main part of a neuron that contains the nucleus and controls cell functions.
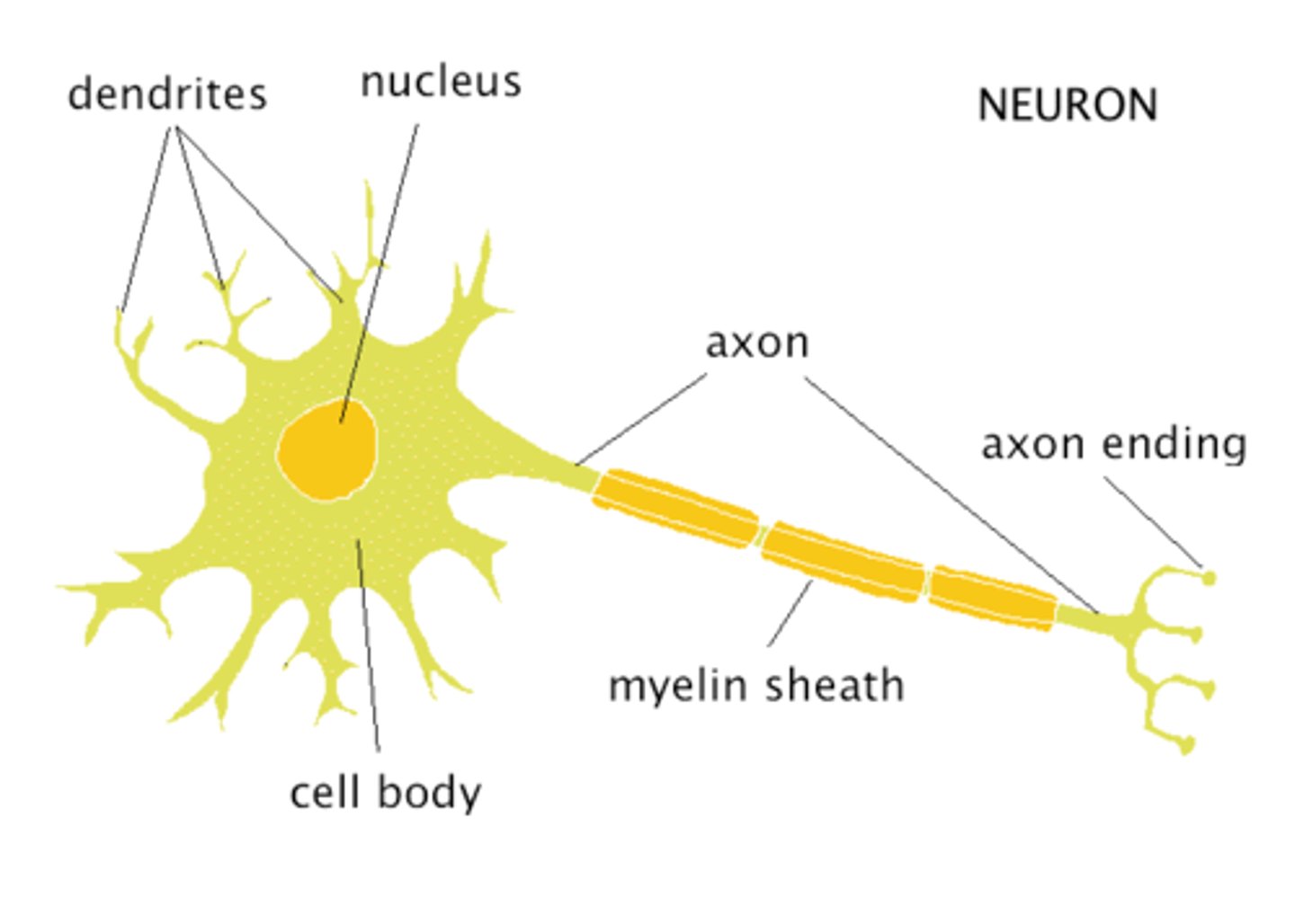
Nucleus
Stores genetic material and controls neuron activity.
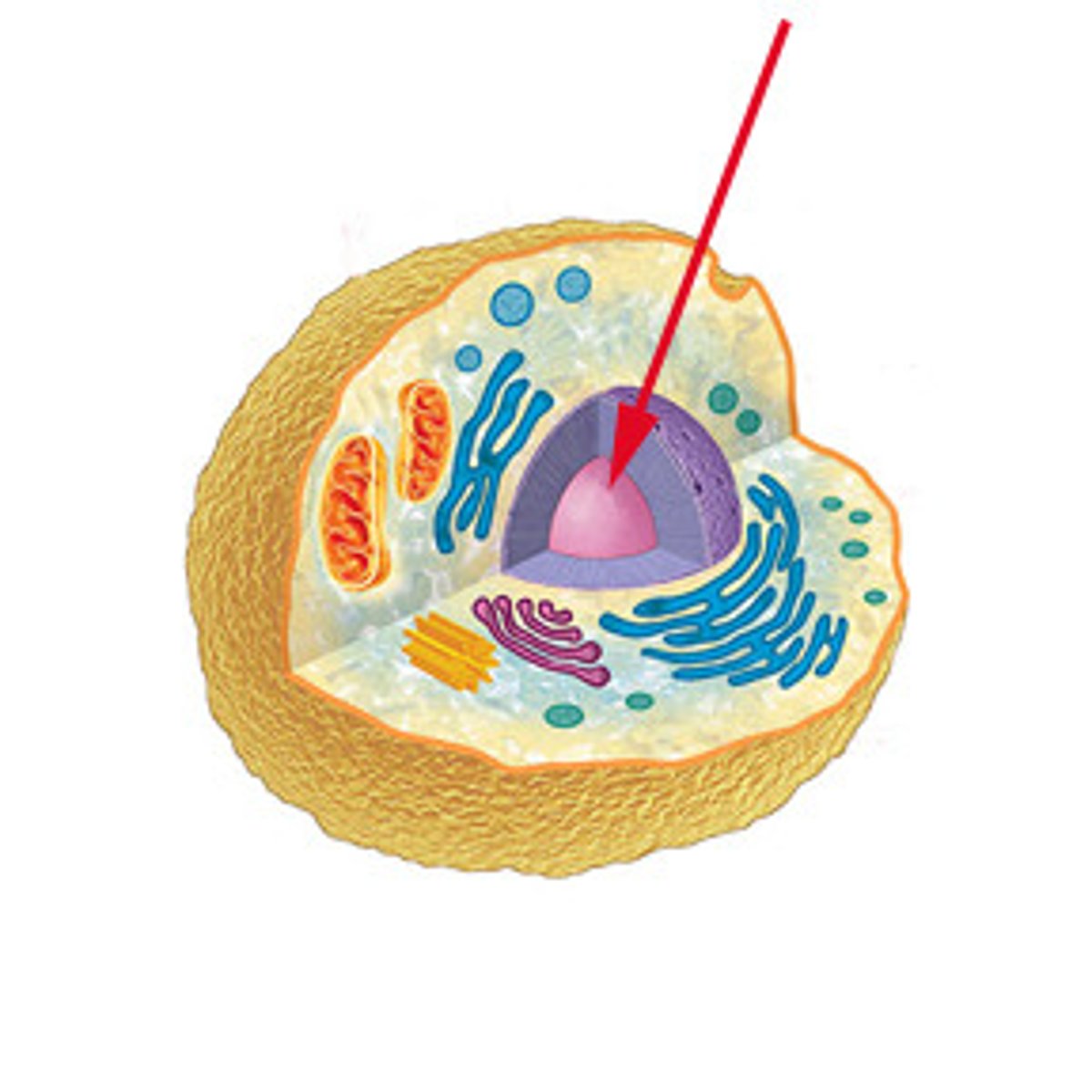
Ribosomes & Rough ER
Produce proteins necessary for neuron function.
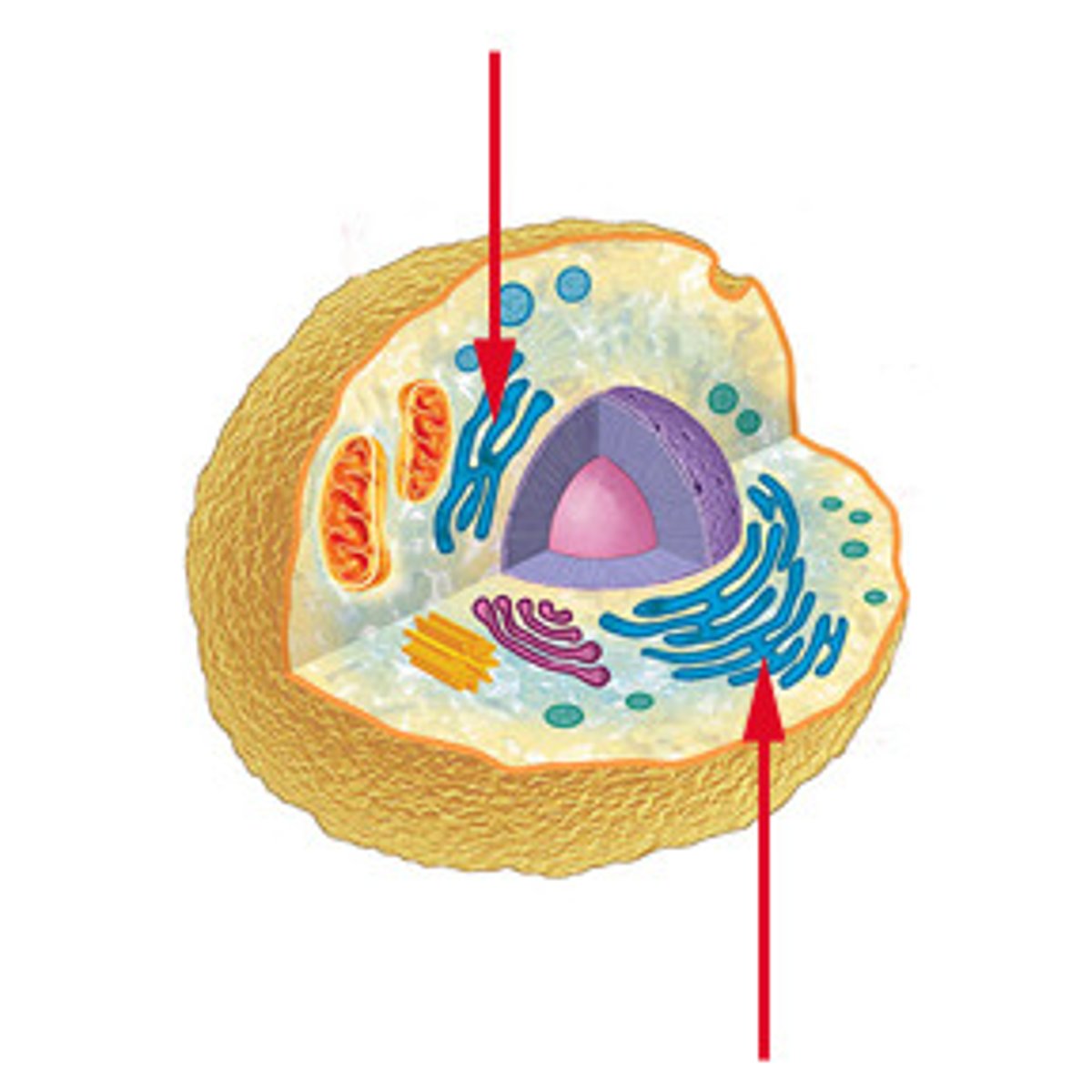
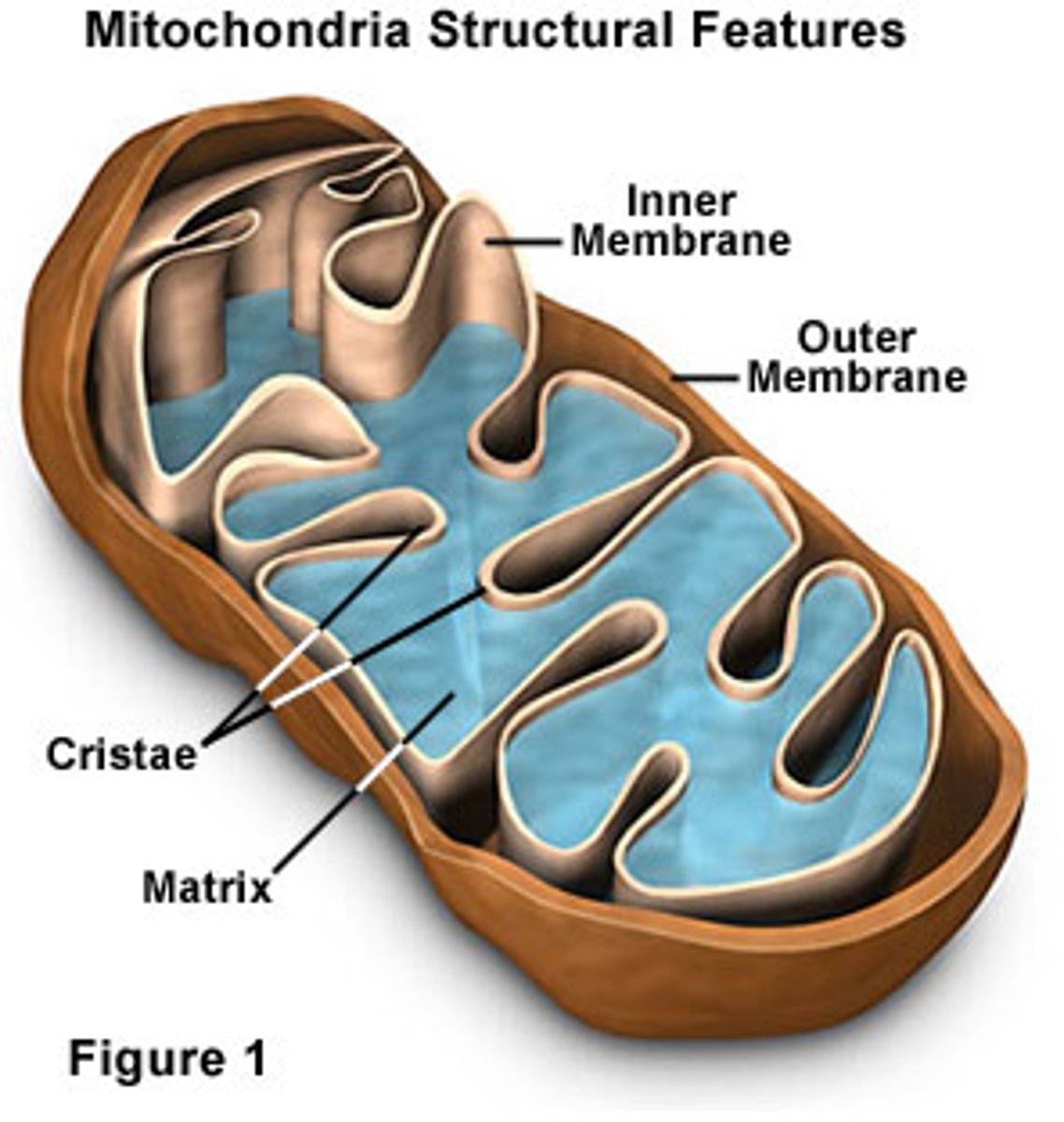
Mitochondria
Provides energy for the neuron.
Connectional Specificity
Neurons form precise connections with specific other neurons rather than random ones.
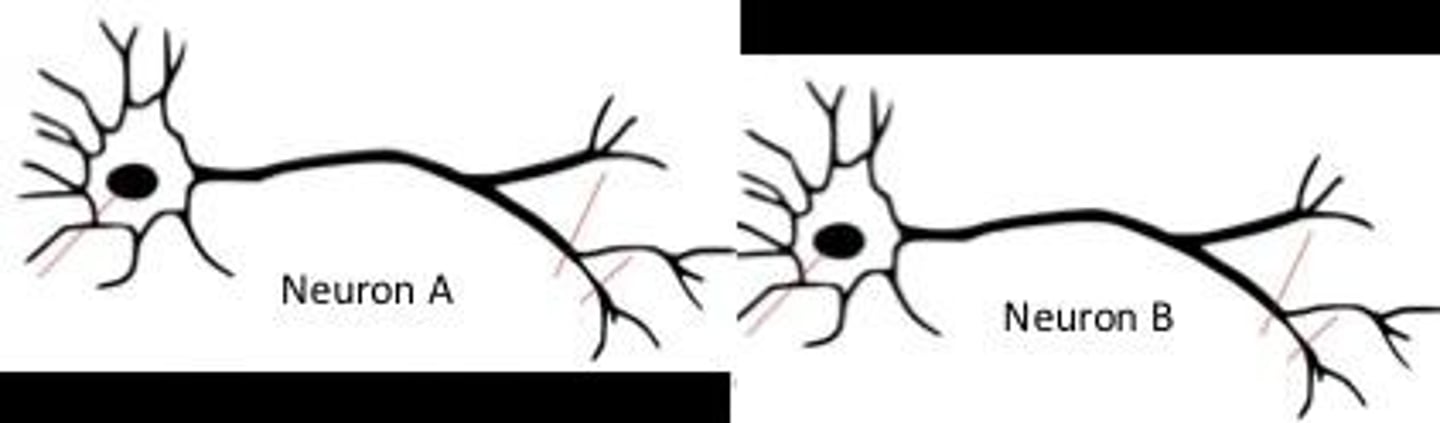
Dynamic Polarization
Electrical signals flow in one direction within a neuron, from dendrites to the axon.
Axonal Transport
The process of moving materials inside a neuron.
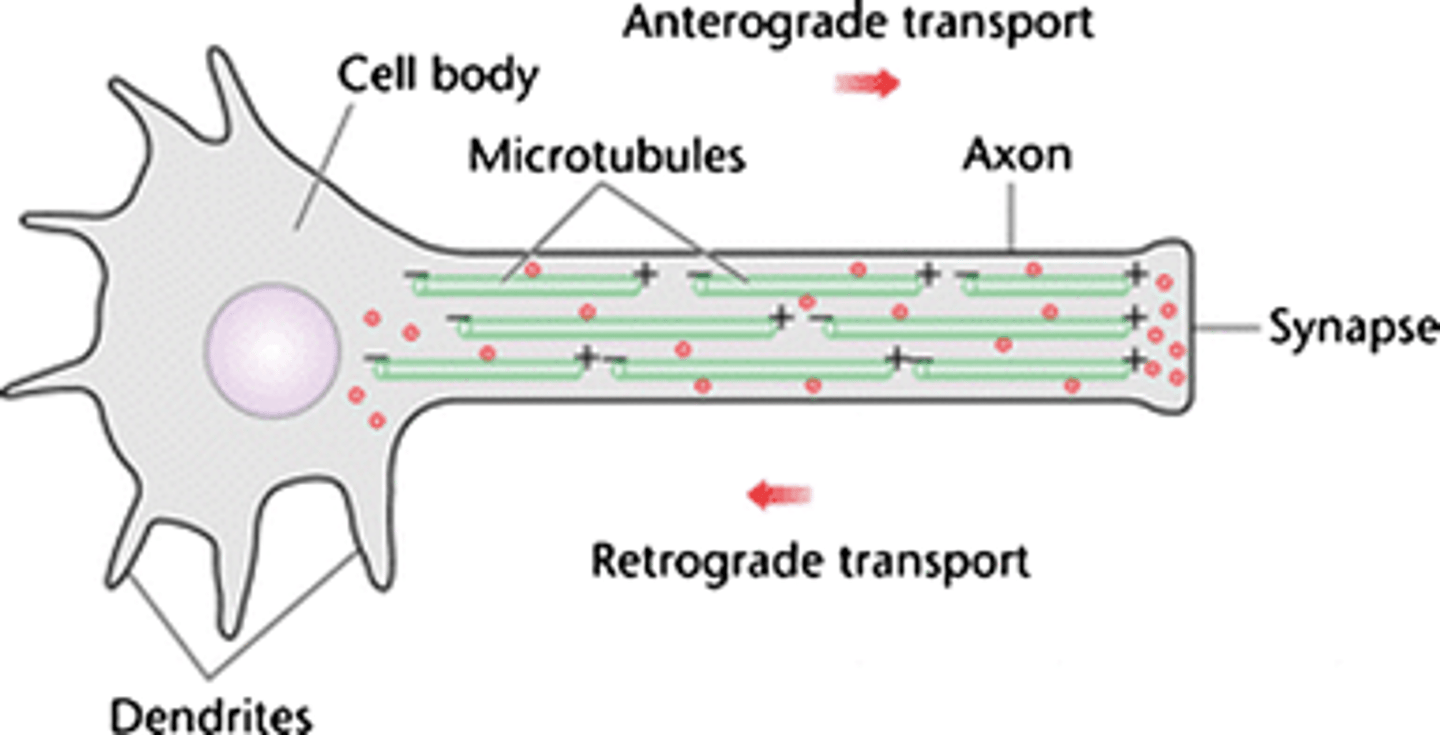
Anterograde Transport
Moves materials from the cell body to the axon terminal (forward, using kinesin).
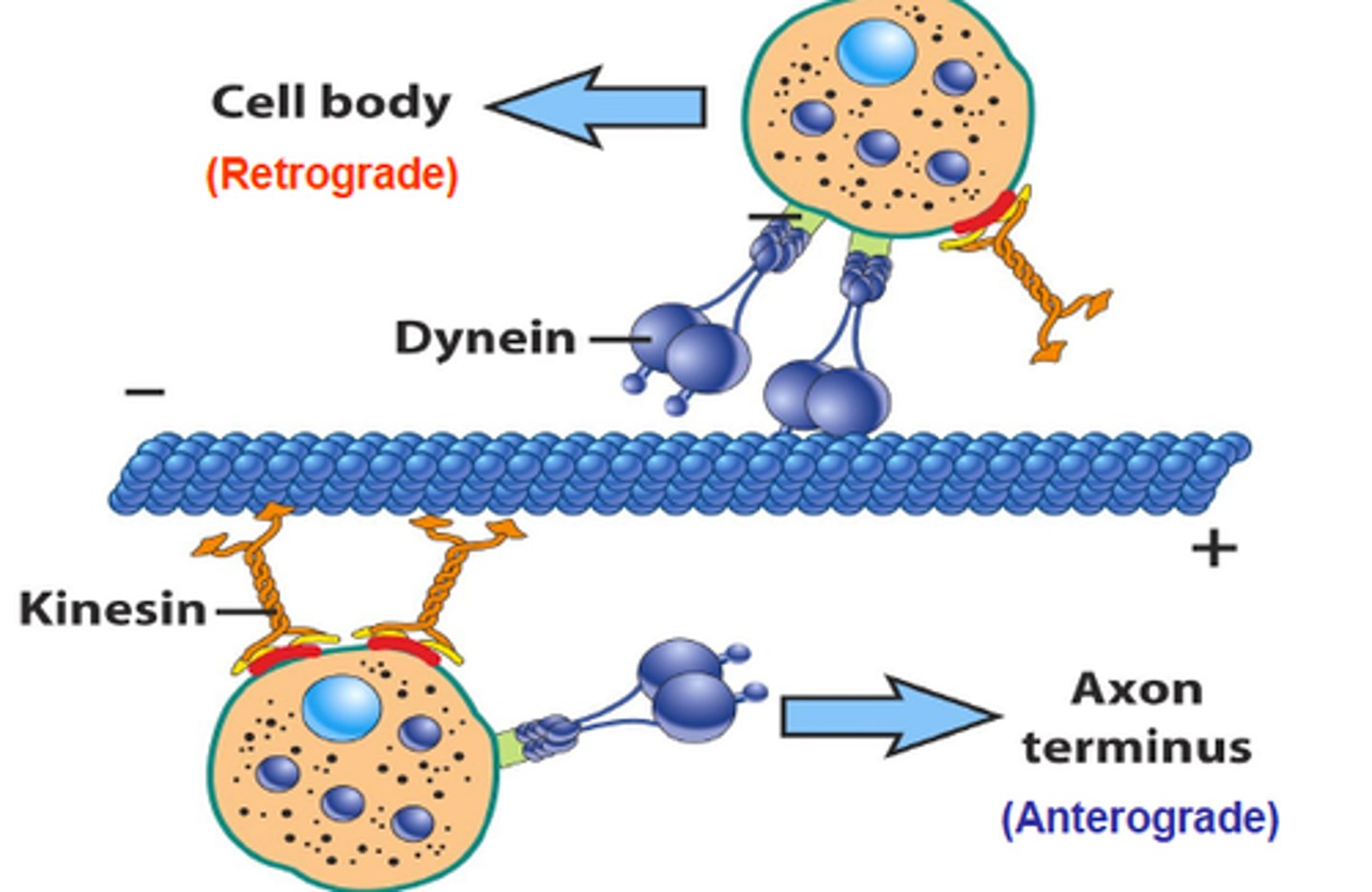
Retrograde Transport
Moves materials from the axon terminal back to the soma (backward, using dynein).
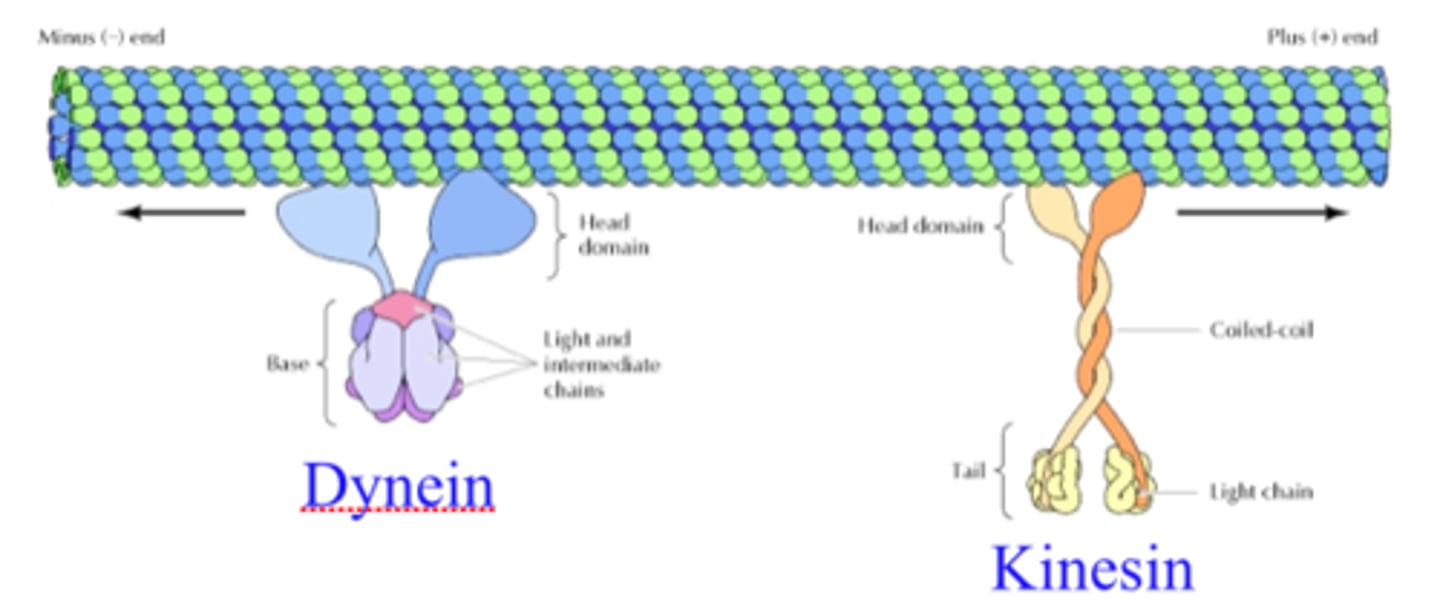
Kinesin
A motor protein that carries materials along microtubules in the anterograde direction.
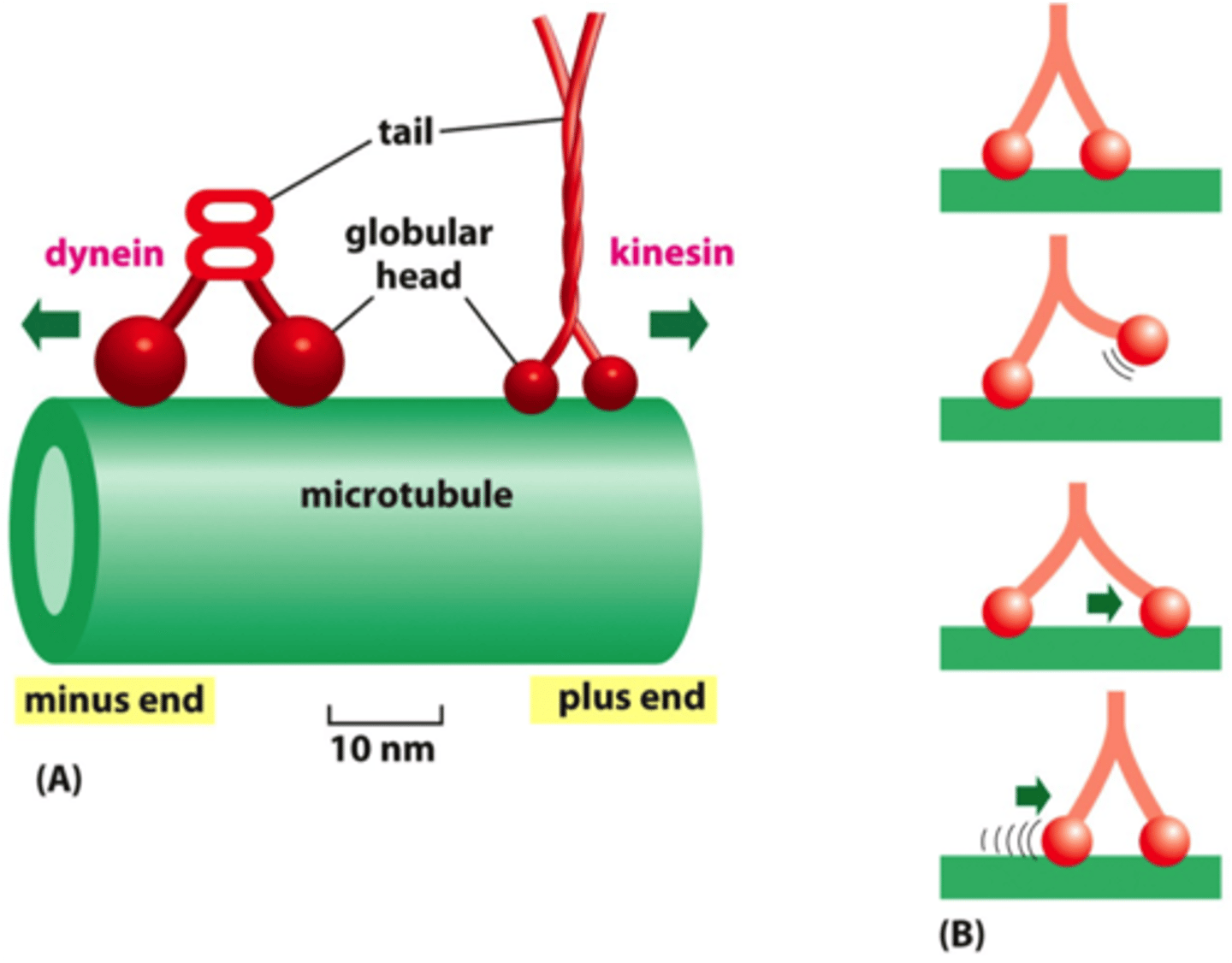
Dynein
A motor protein that carries materials in the retrograde direction.
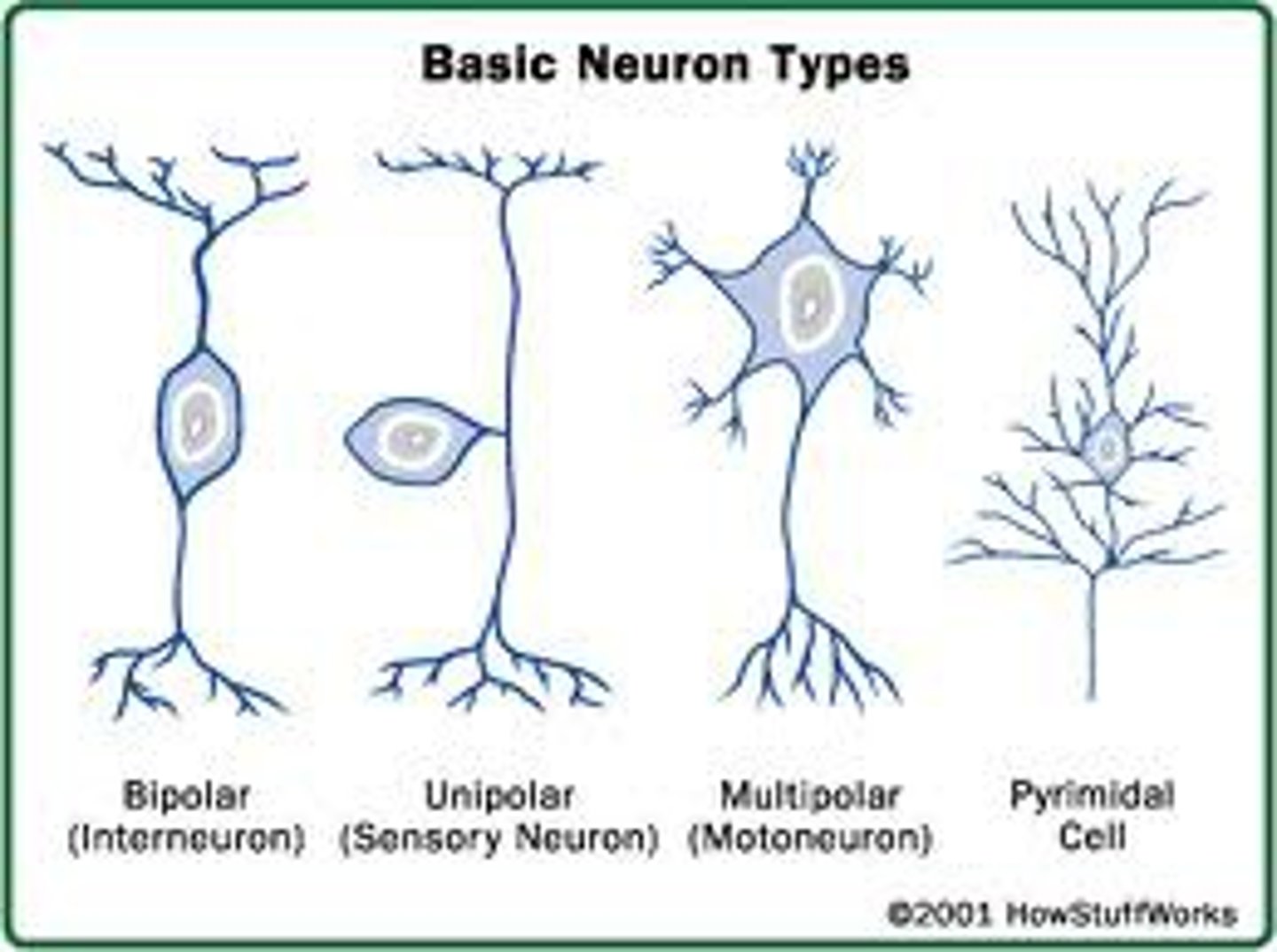
Unipolar Neuron
One extension from the soma.
Pseudounipolar Neuron
One extension that splits into two.
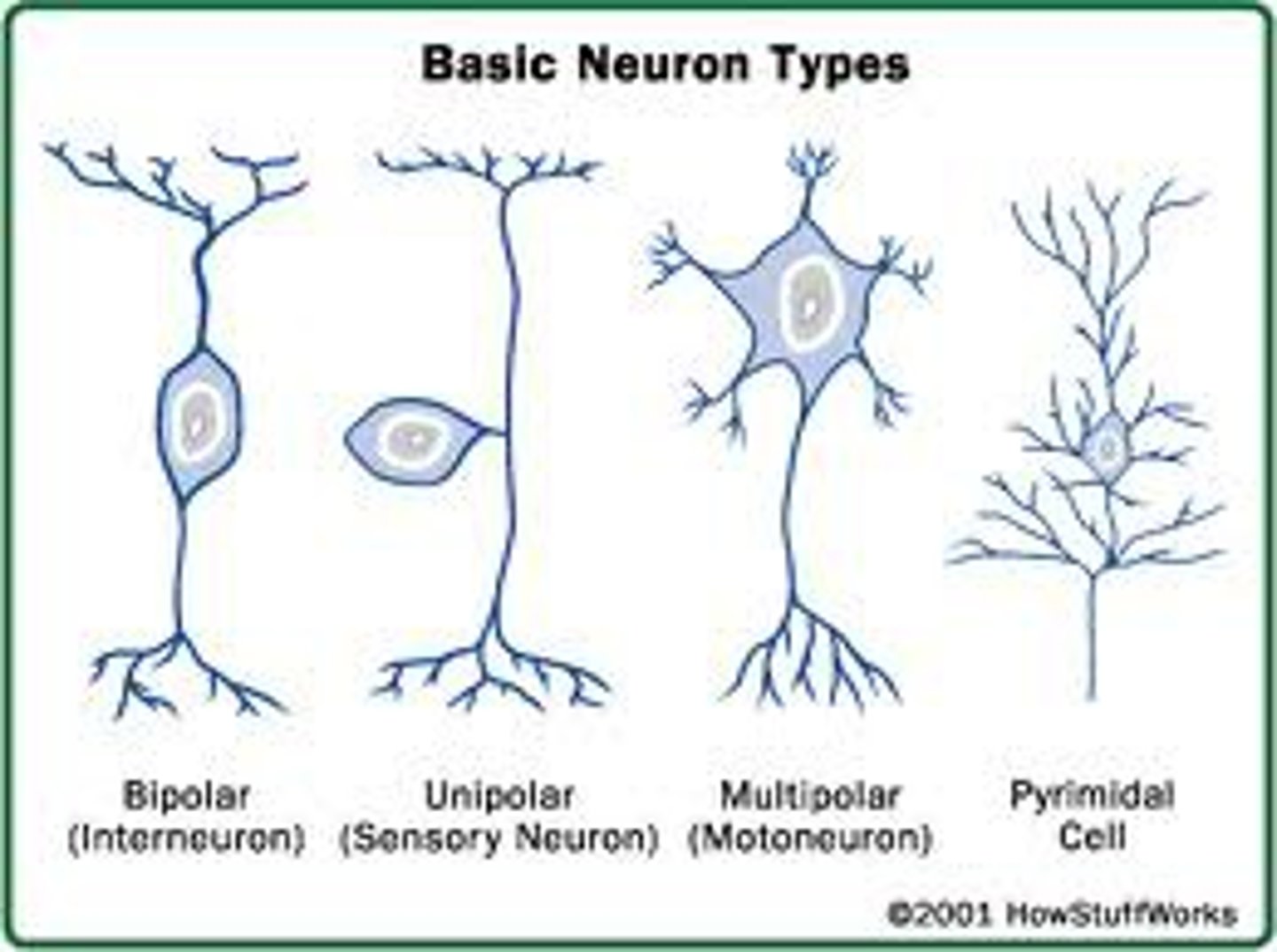
Bipolar Neuron
Two processes (one dendrite, one axon).
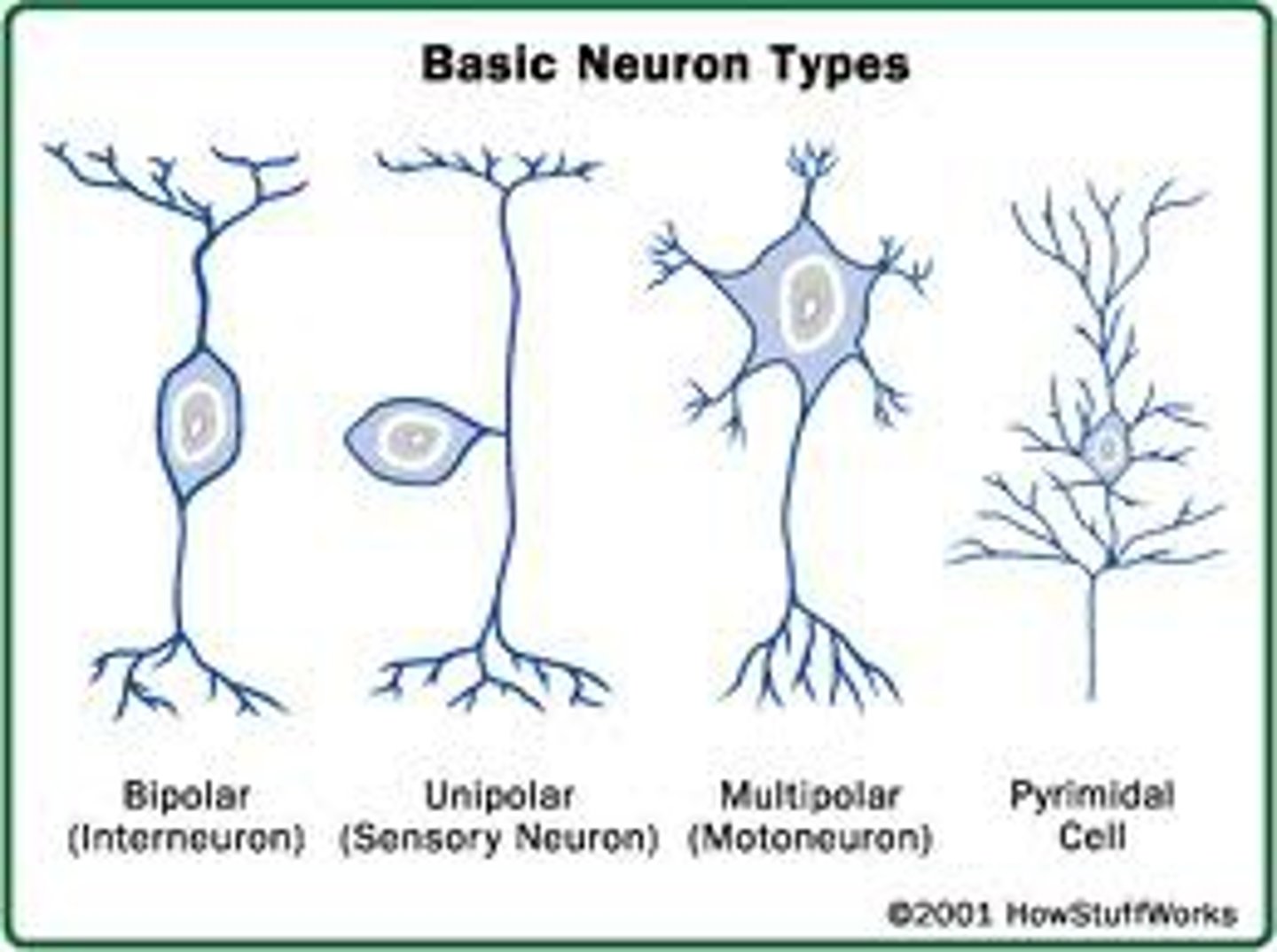
Multipolar Neuron
Multiple dendrites, one axon (most common).
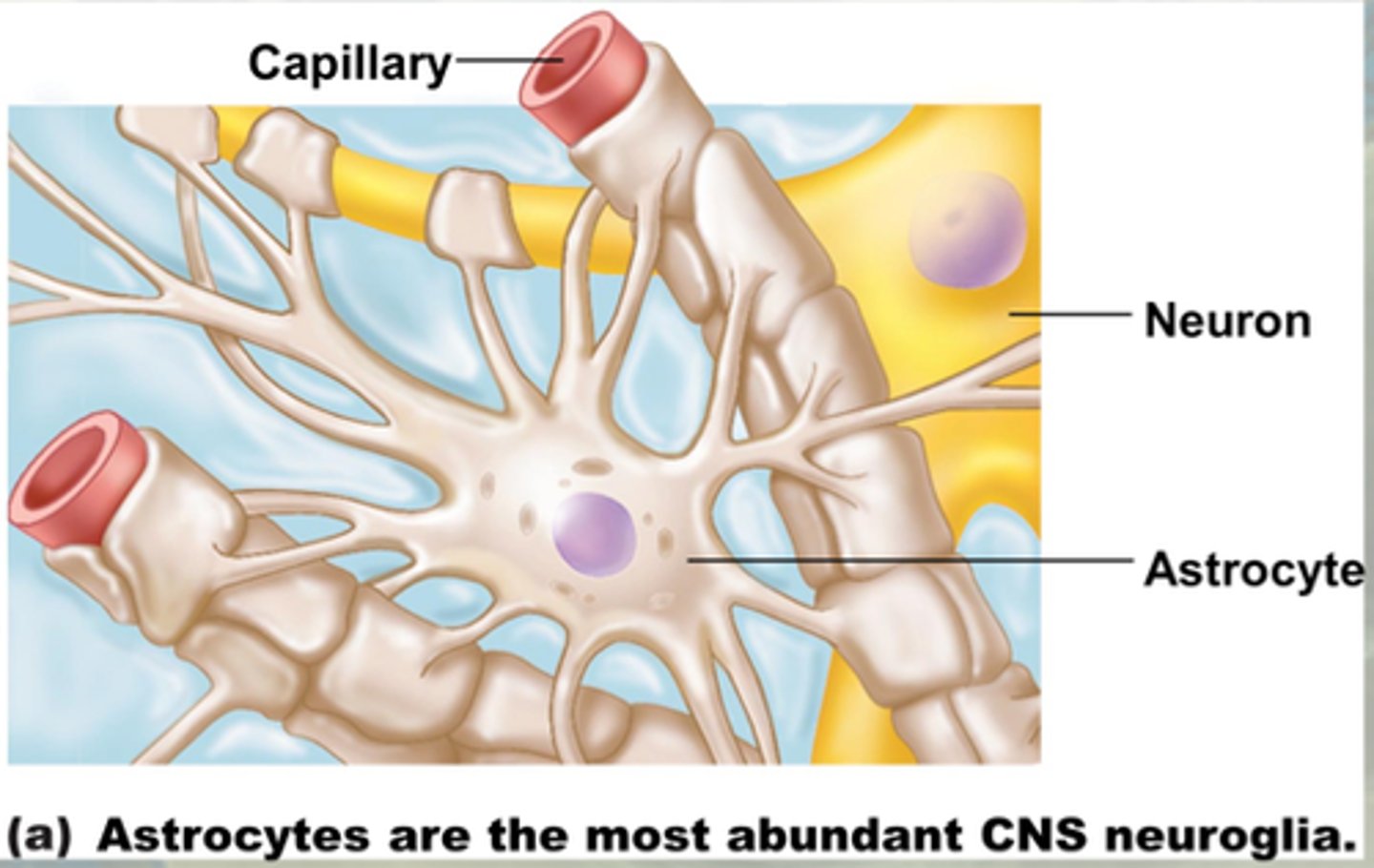
Astrocytes
Star-shaped cells that provide nutrients, clean waste, and maintain the blood-brain barrier.
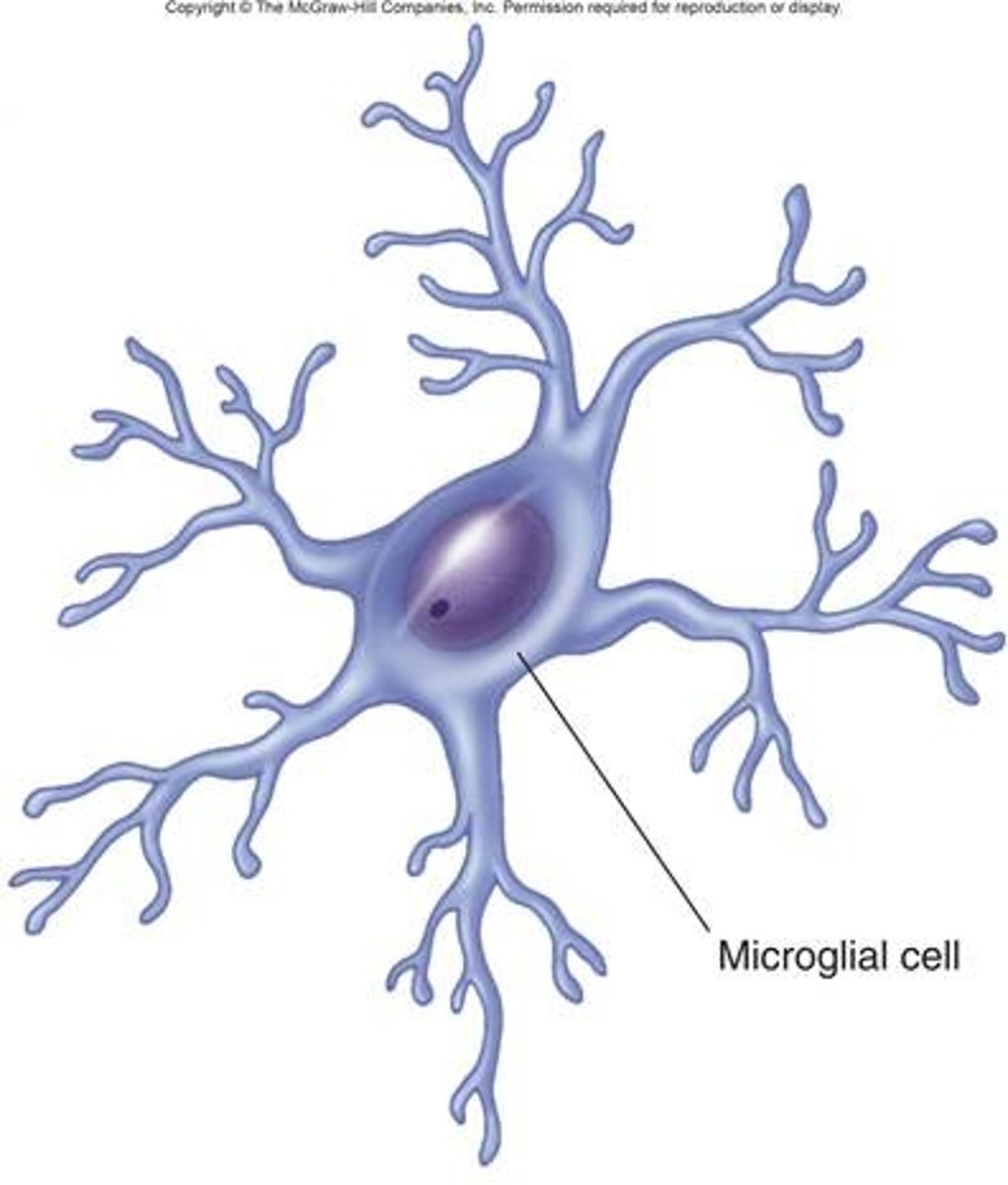
Microglia
Act as the brain's immune cells, removing dead cells and fighting infections.
Myelin
A fatty coating around axons that speeds up electrical signals.
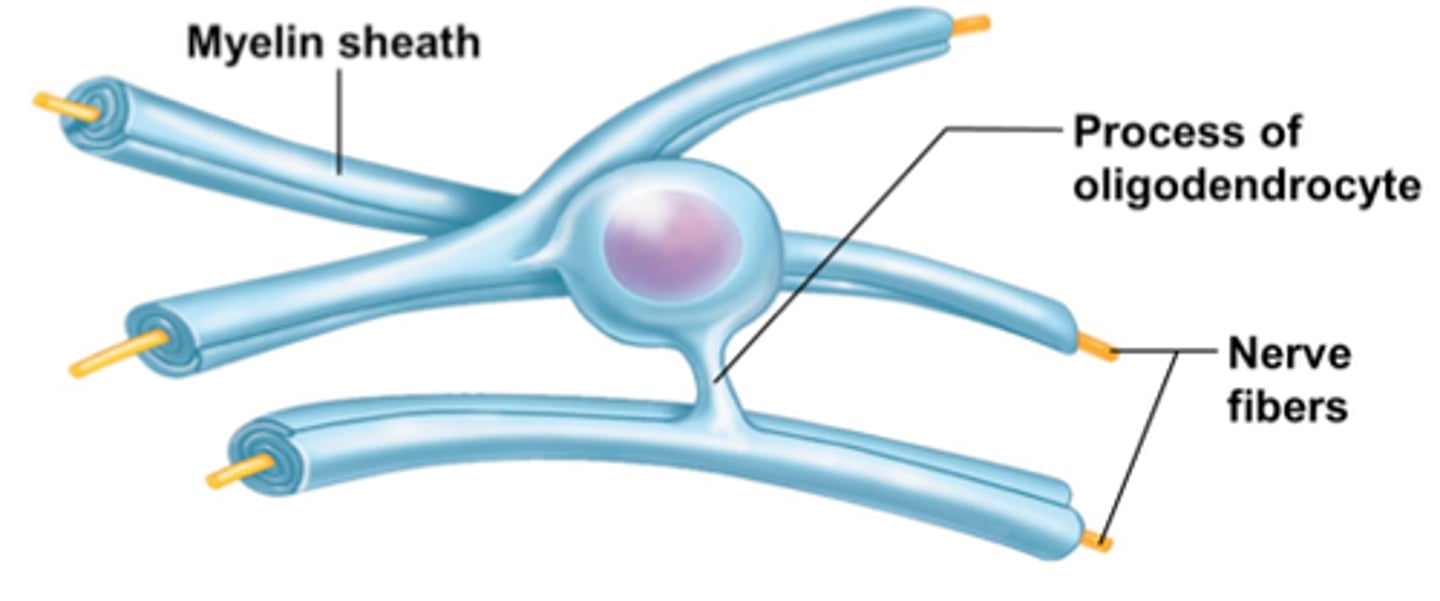
Oligodendrocytes
Myelinate axons in the central nervous system (CNS) (brain and spinal cord).
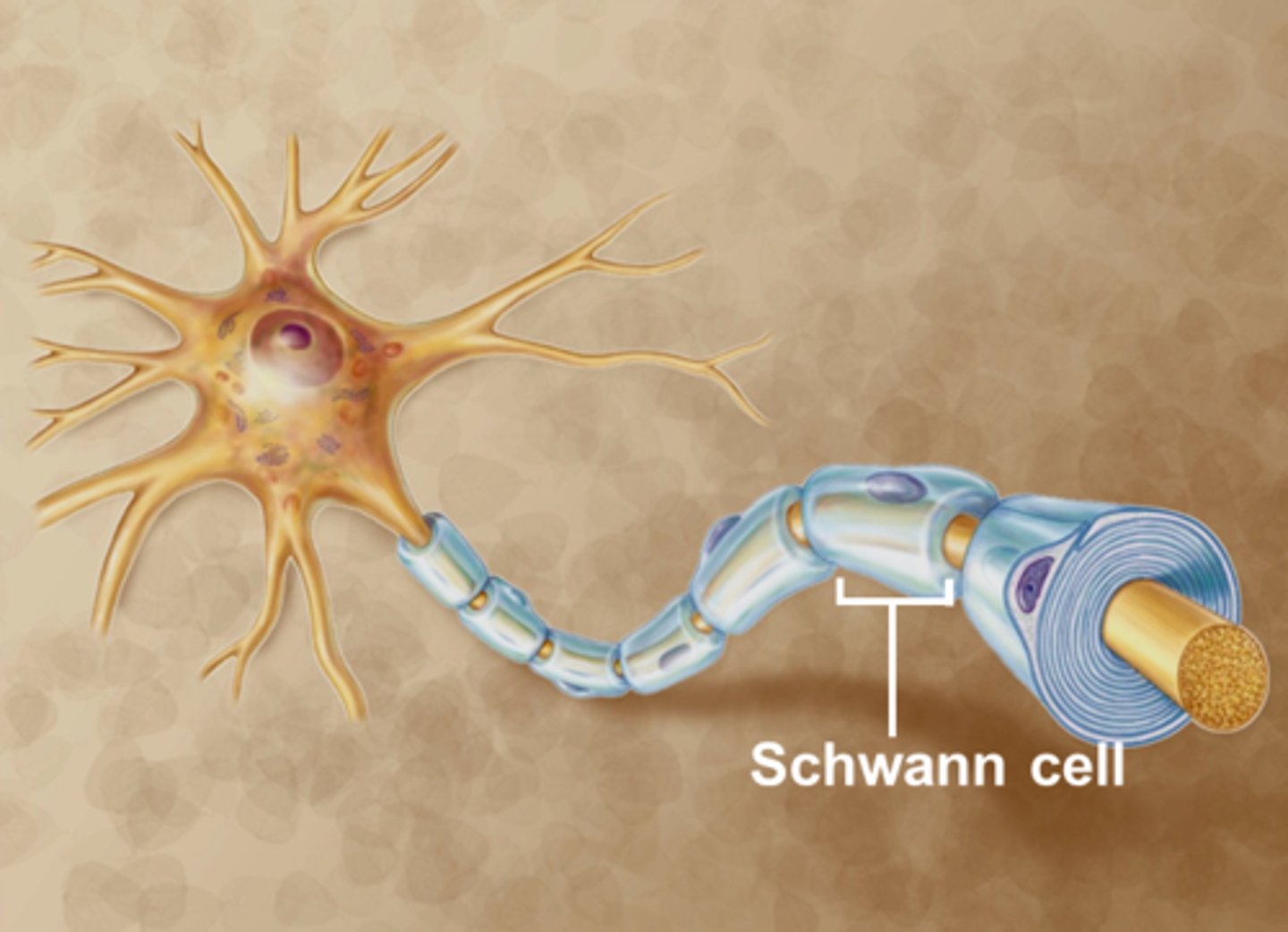
Schwann Cells
Myelinate axons in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) (nerves outside the brain and spinal cord).
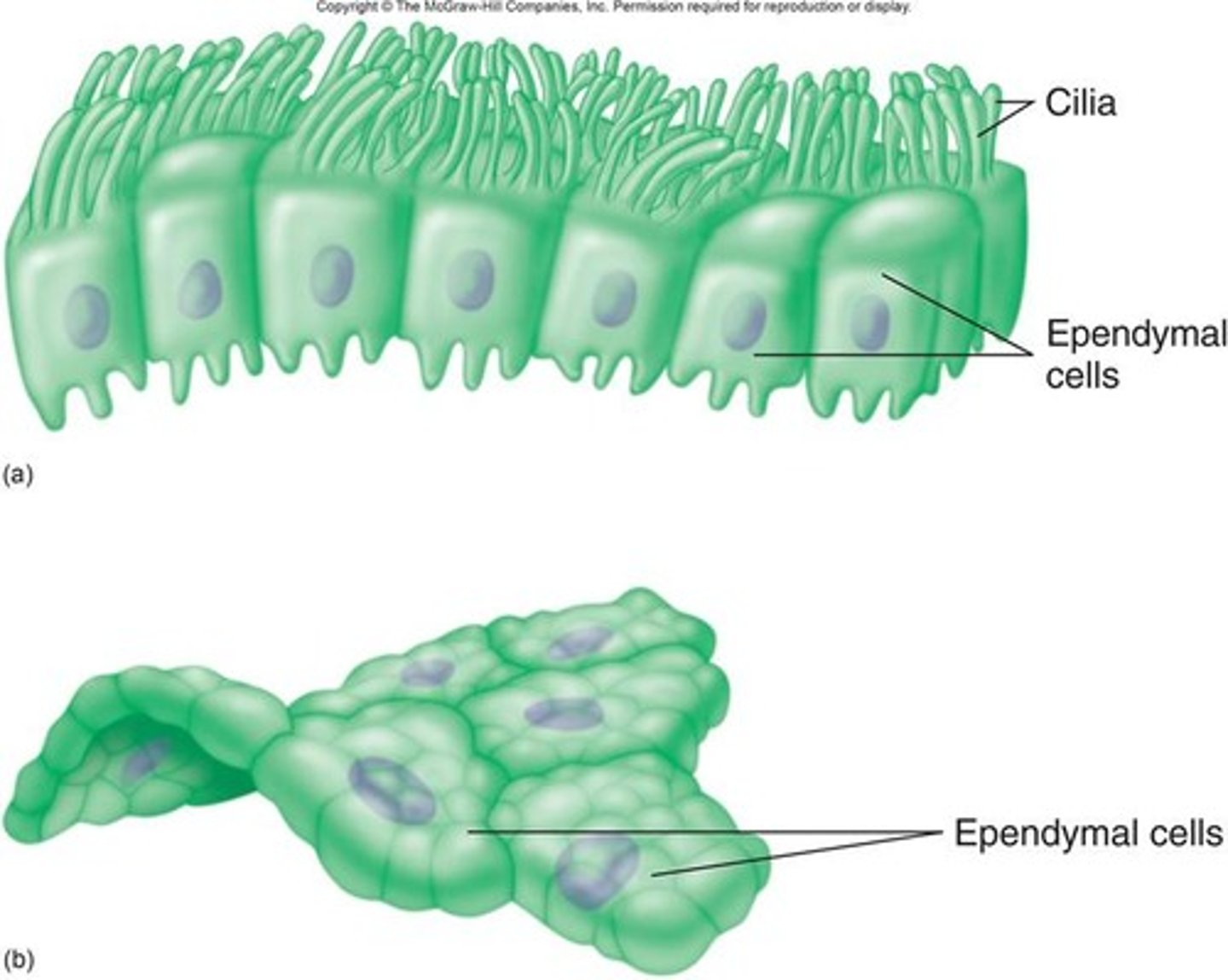
Ependymal Cells
Produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and help circulate it in the brain's ventricles.
Neural Signal
The way neurons send messages using electrical and chemical signals.
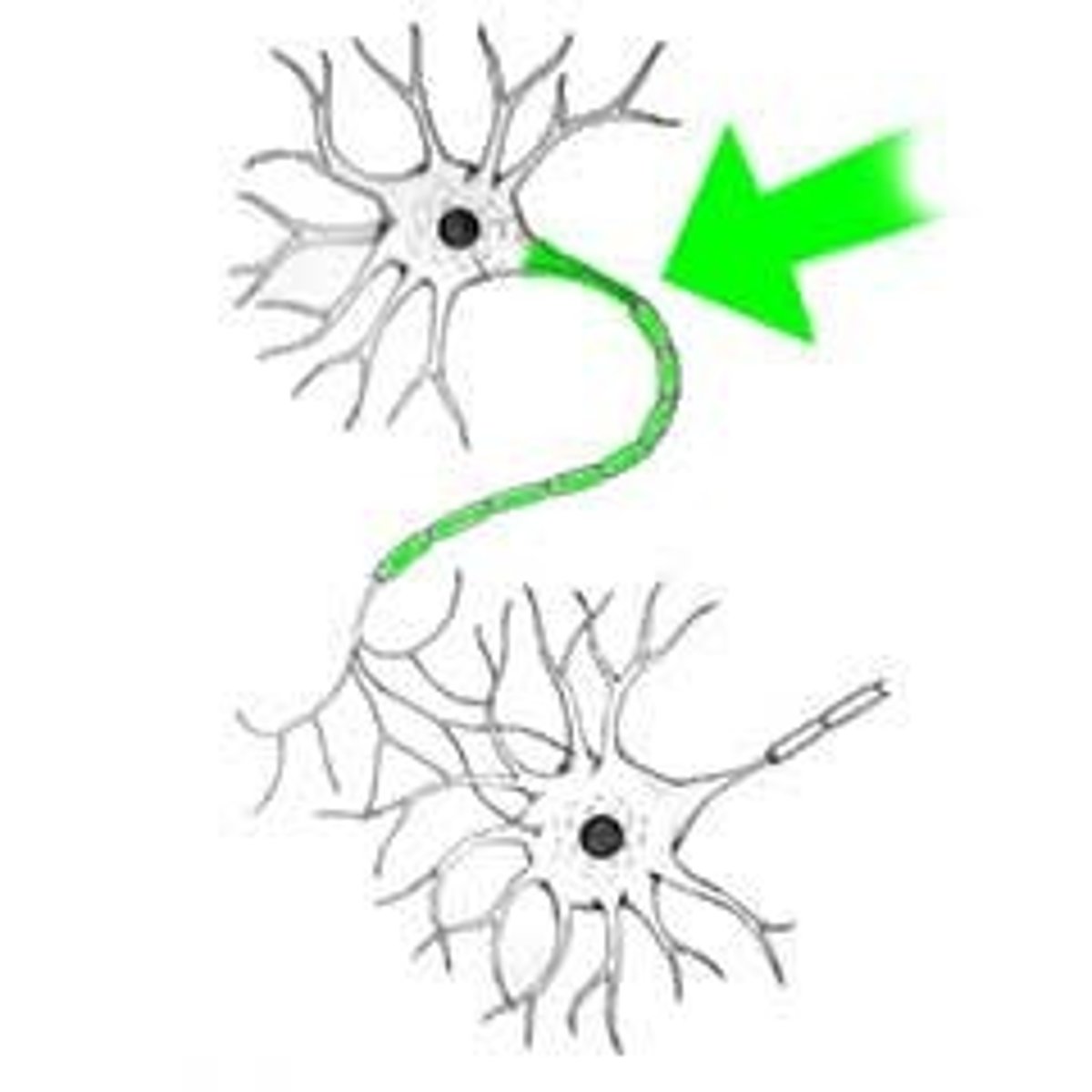
Rate Code
The brain understands information based on how fast neurons fire signals.
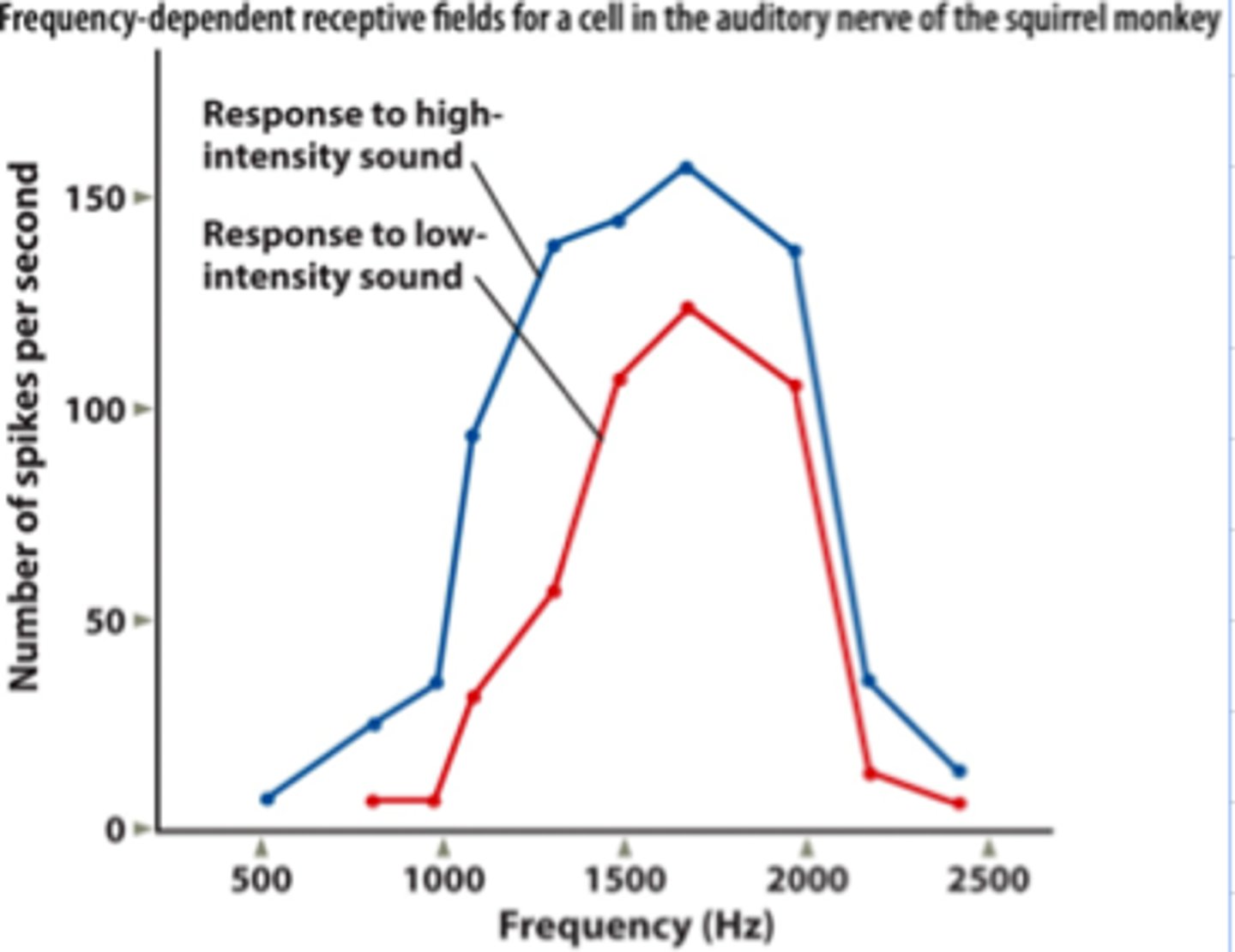
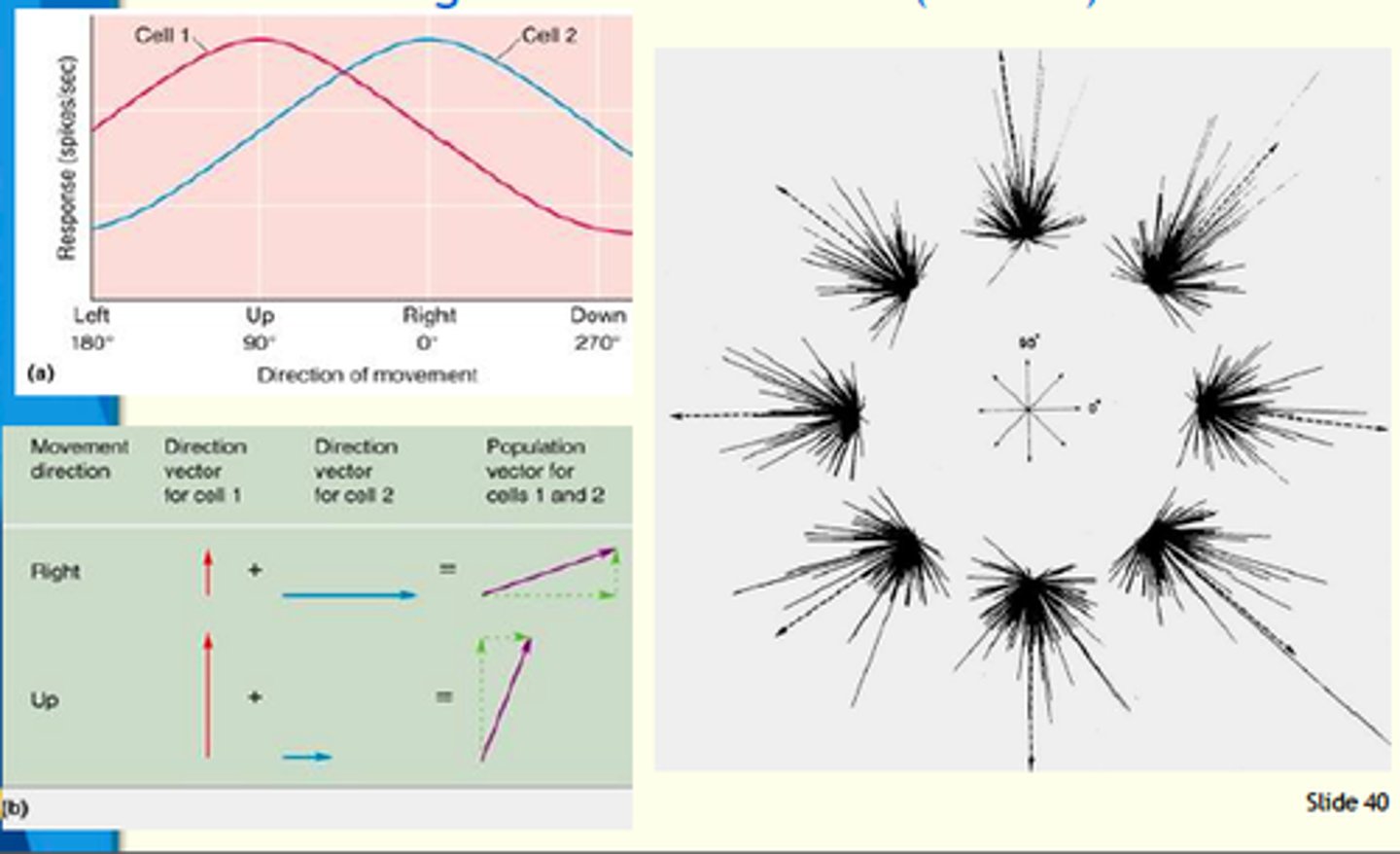
Population Code
Information is carried by groups of neurons working together.
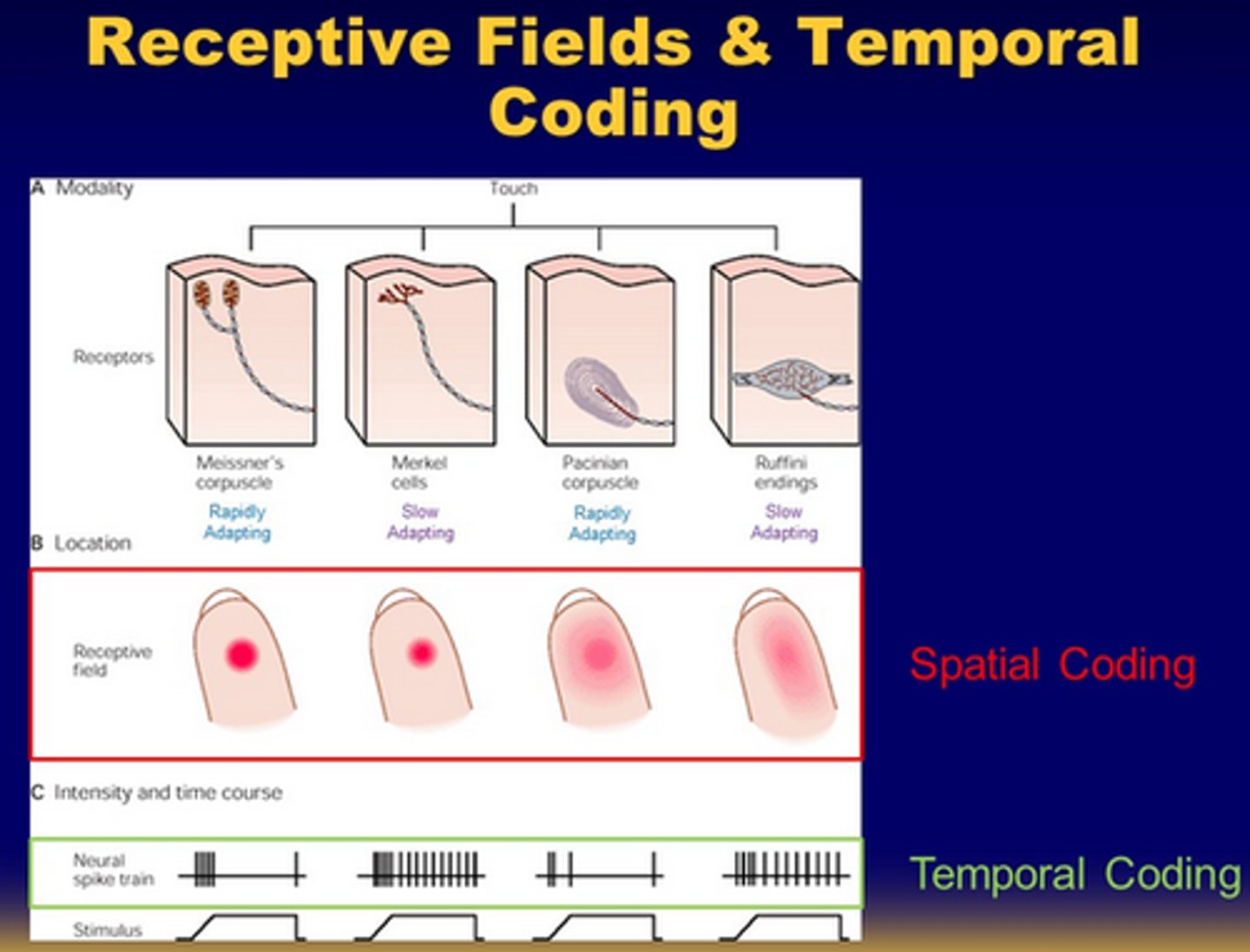
Temporal Code
The timing of neuron signals carries information.
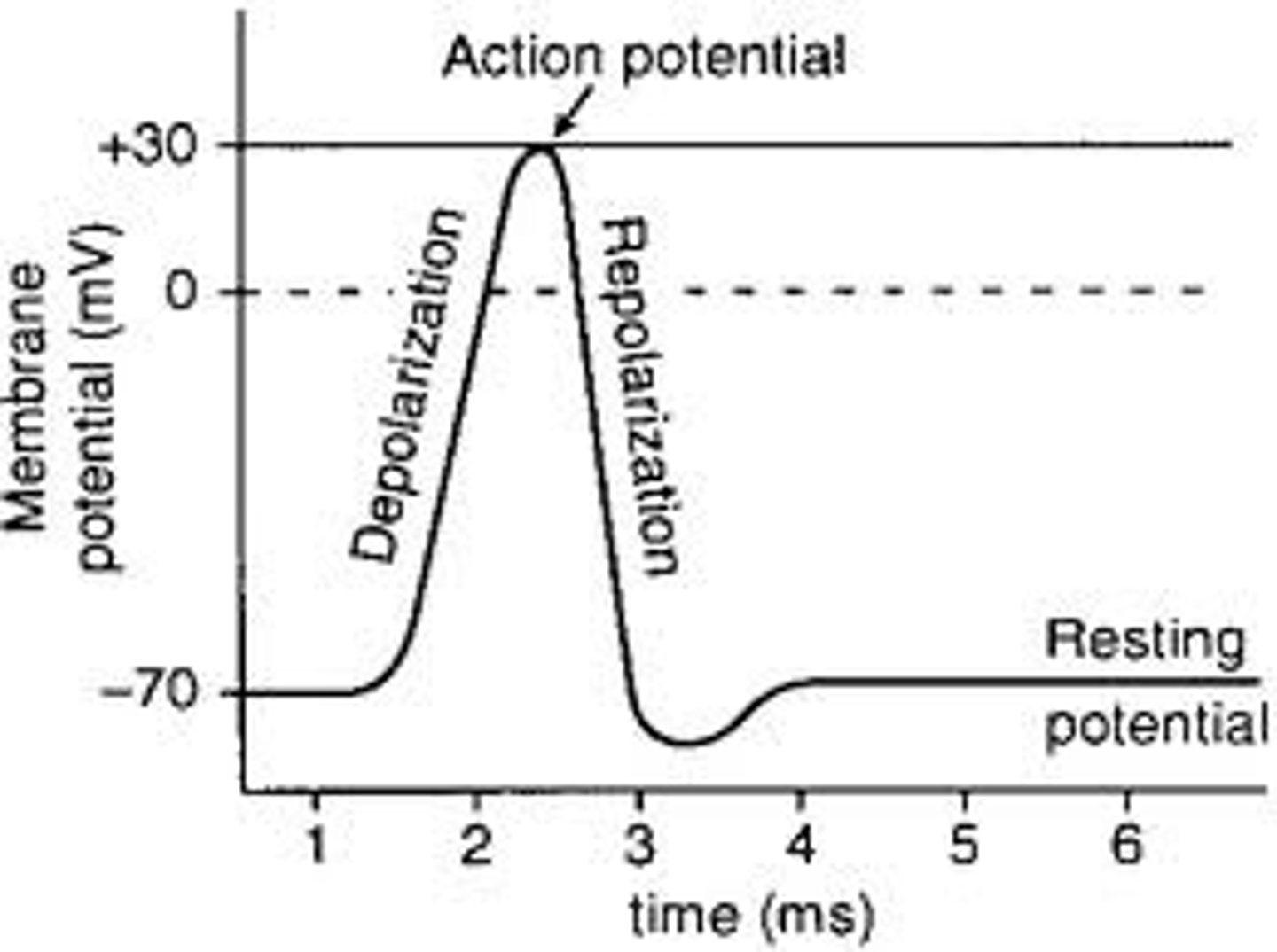
Resting Membrane Potential
The natural electrical charge inside a neuron when it's not sending signals. Usually around -70mV.
Ion
A tiny charged particle.
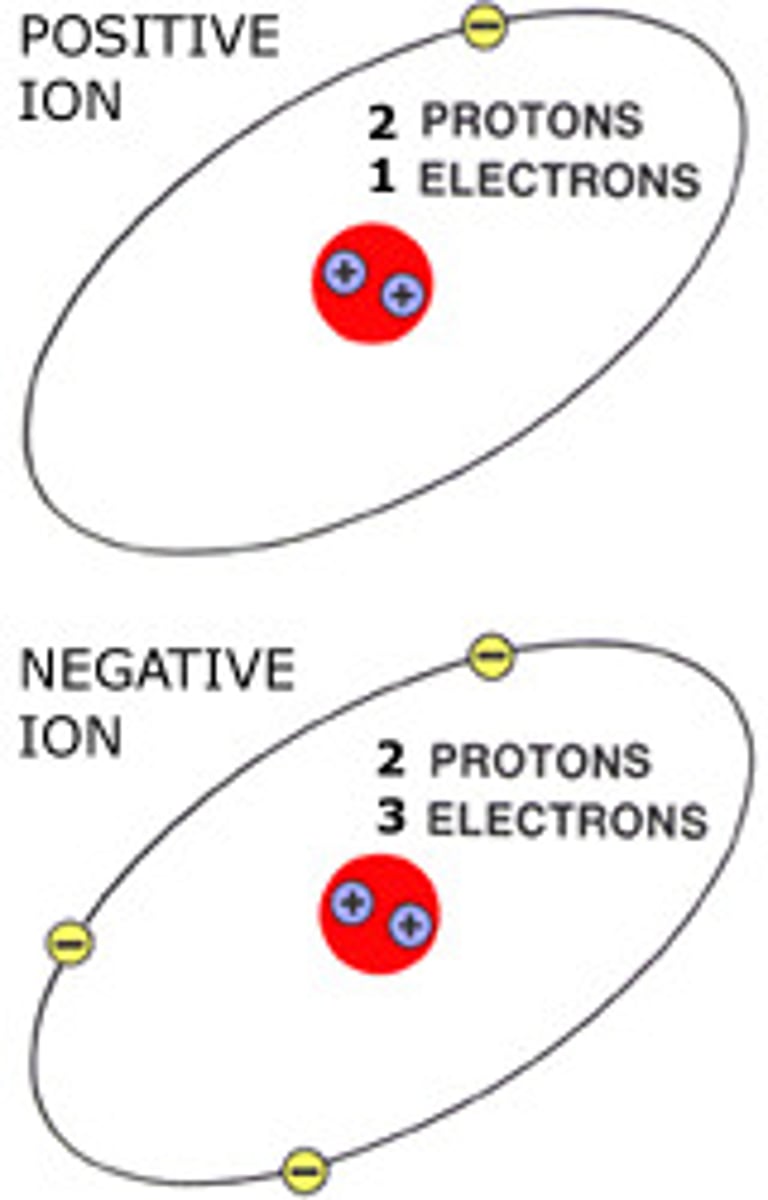
Cation
A positively charged ion (e.g., Na⁺, K⁺).

Anion
A negatively charged ion (e.g., Cl⁻).
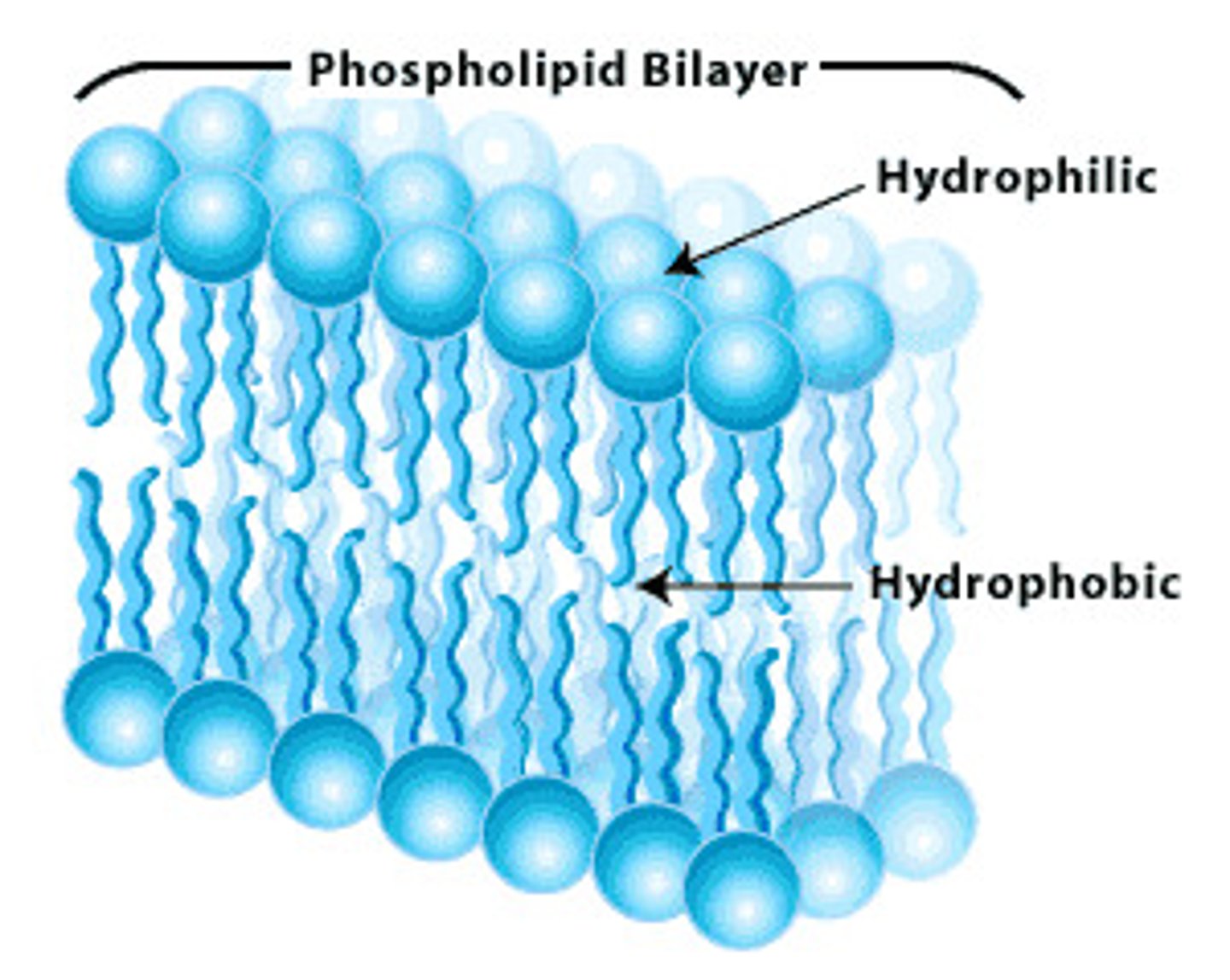
Lipid Bilayer
The double-layered, fatty covering of a cell that keeps the inside separate from the outside.
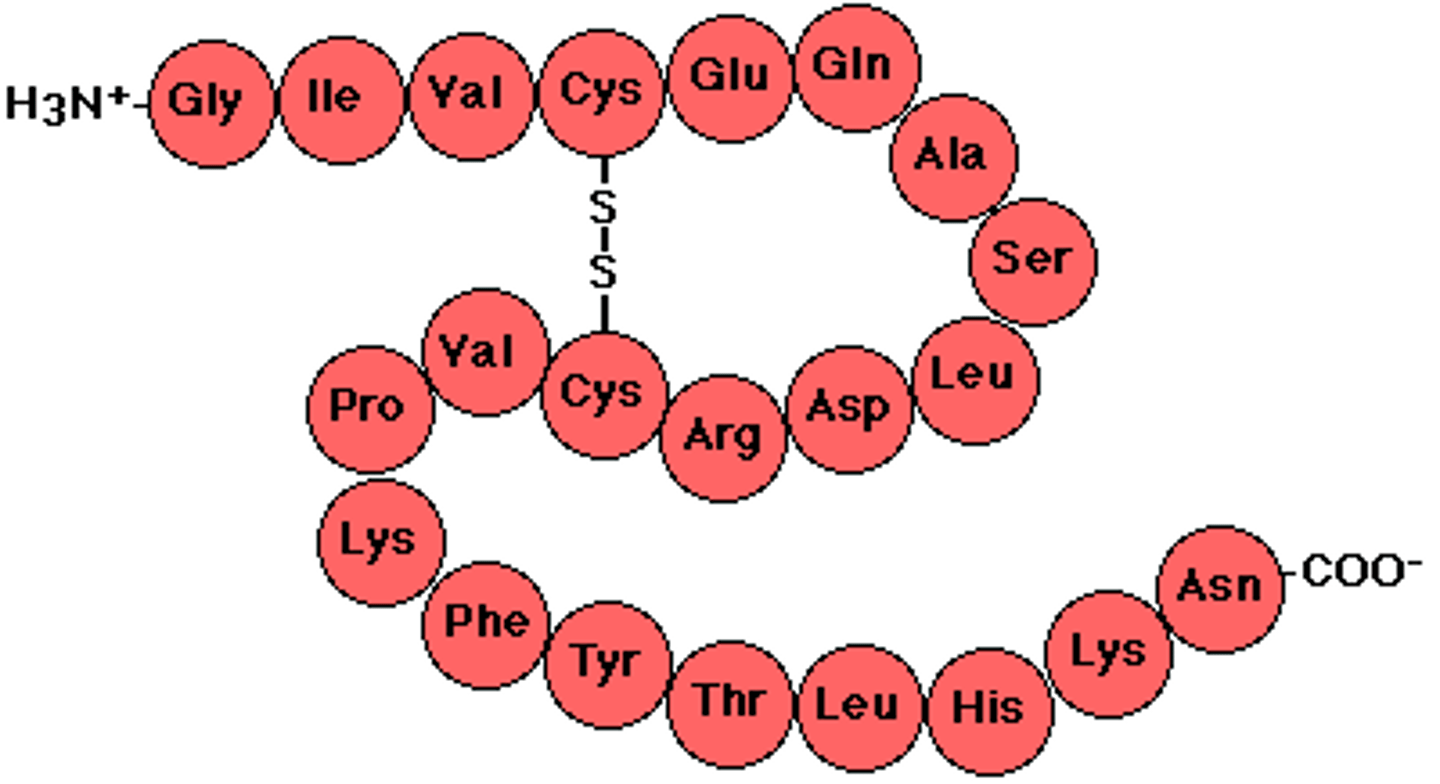
Polypeptide
A chain of amino acids that make up proteins, which help cells function.
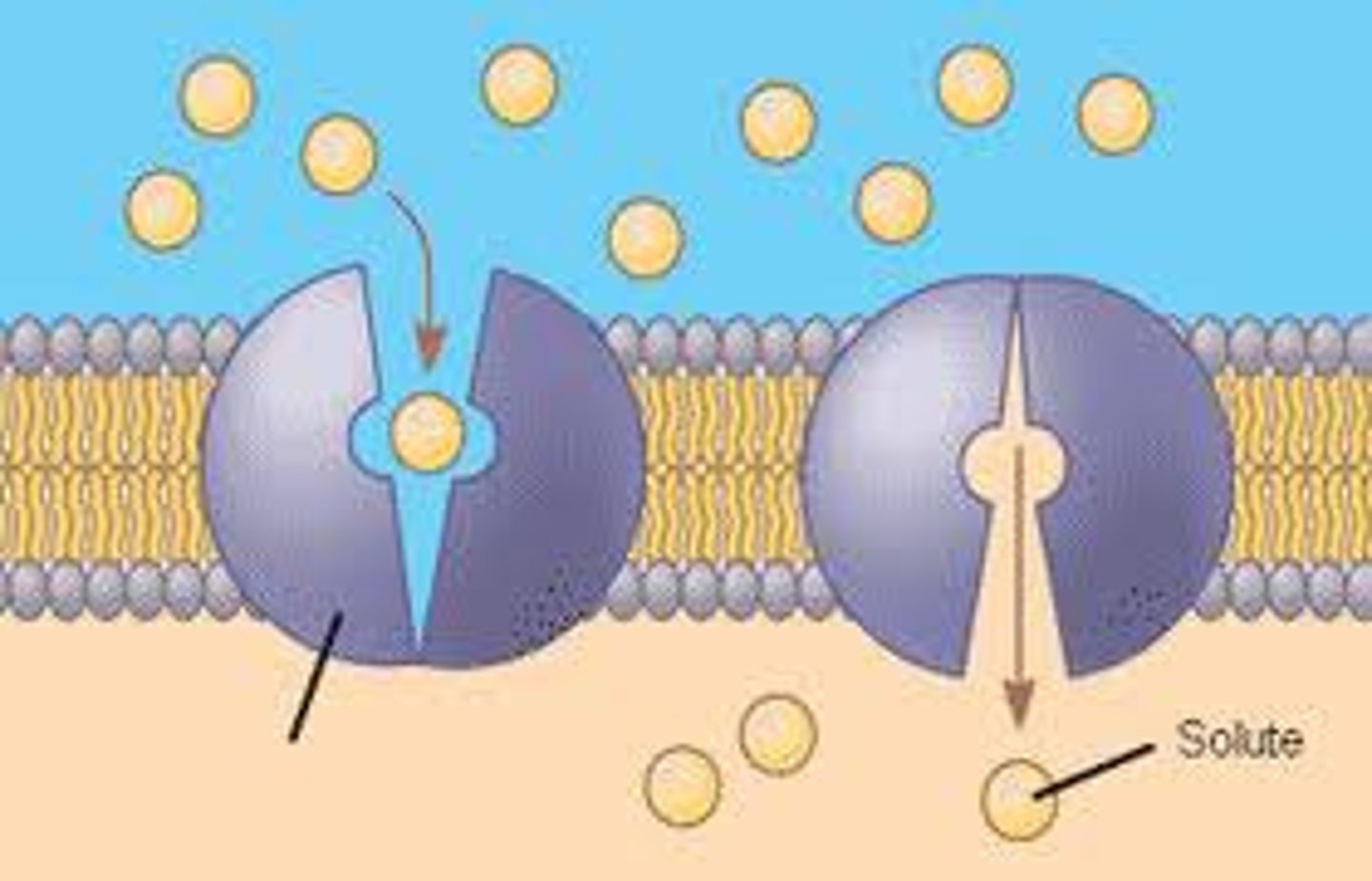
Ion Channel
A tiny tunnel in the cell membrane that allows specific ions to move in or out.
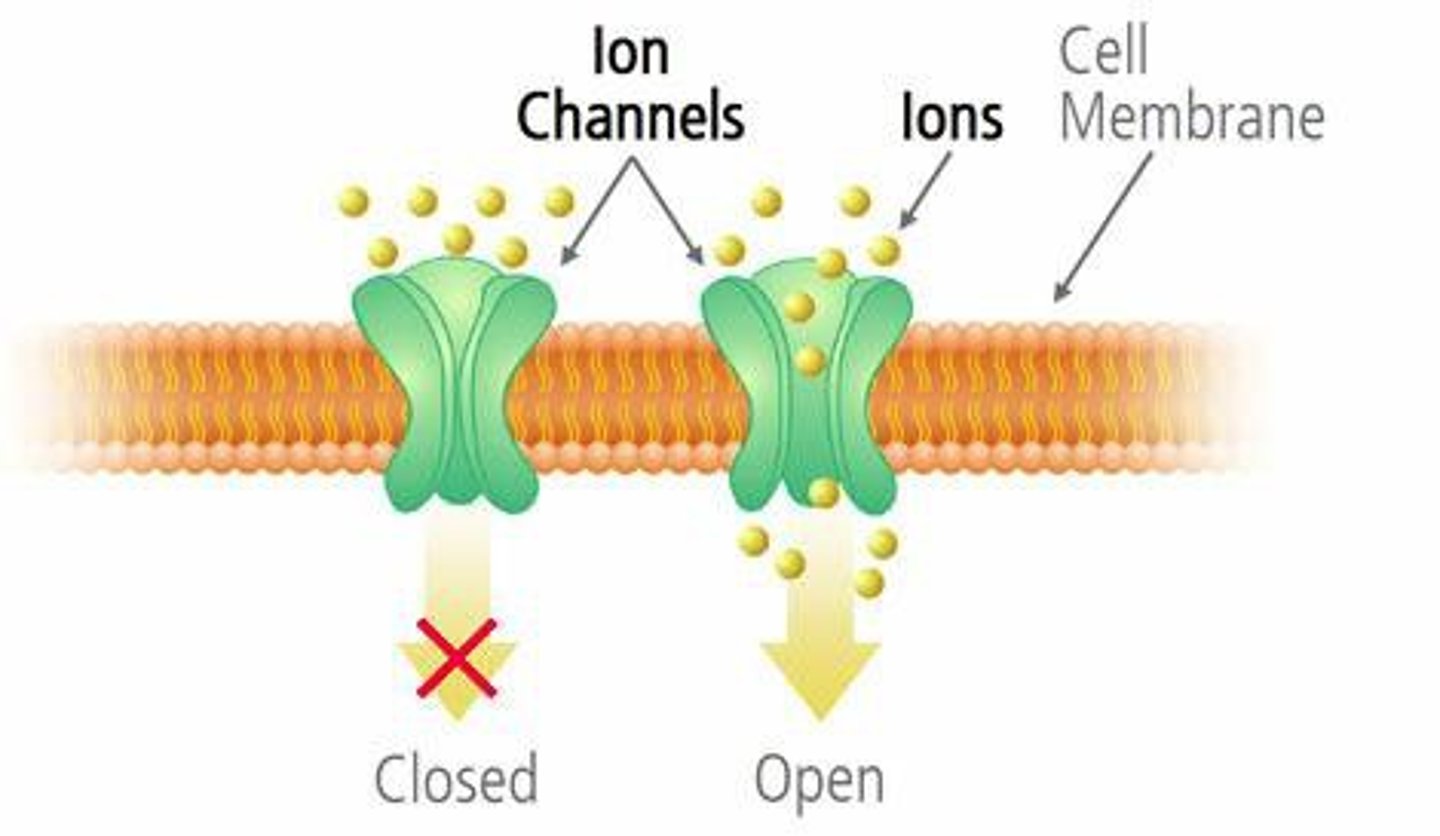
Selective Permeability of a Membrane
The membrane only lets certain things pass through, like specific ions.
Ion Pump
A special protein that pushes ions across the membrane, often using energy (ATP).
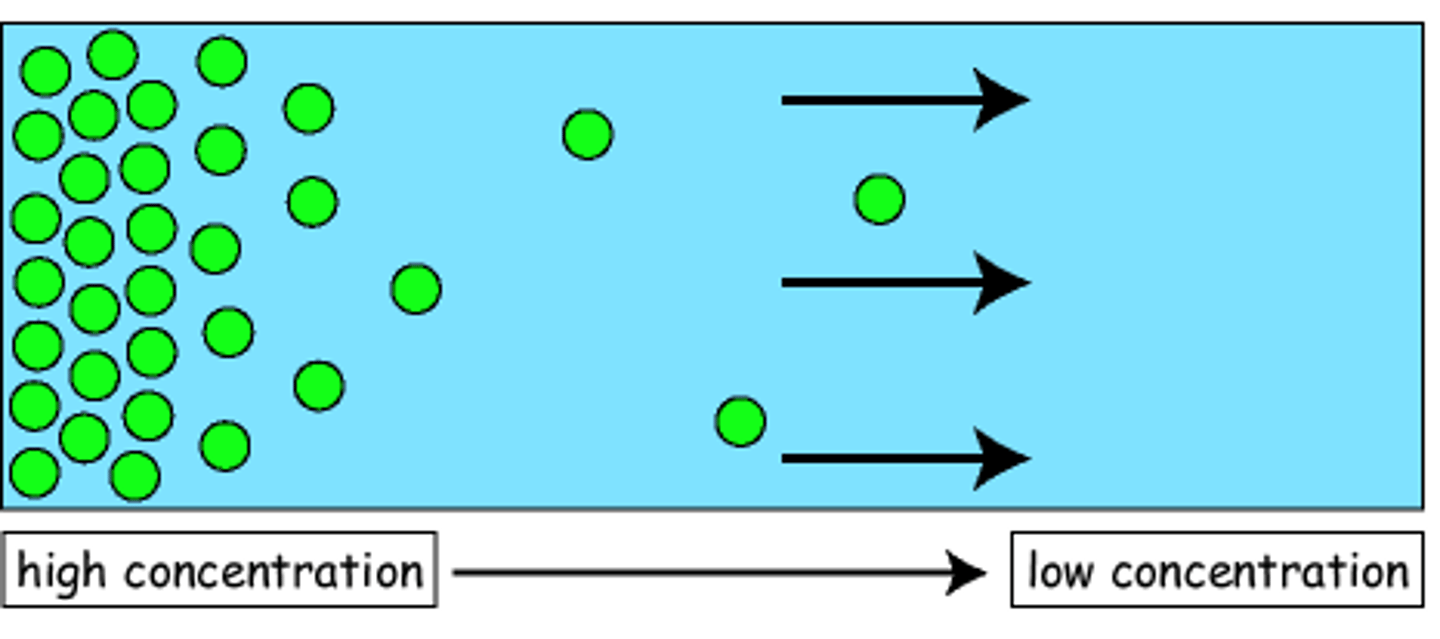
Diffusion
When molecules naturally spread out from an area of high concentration to low concentration.
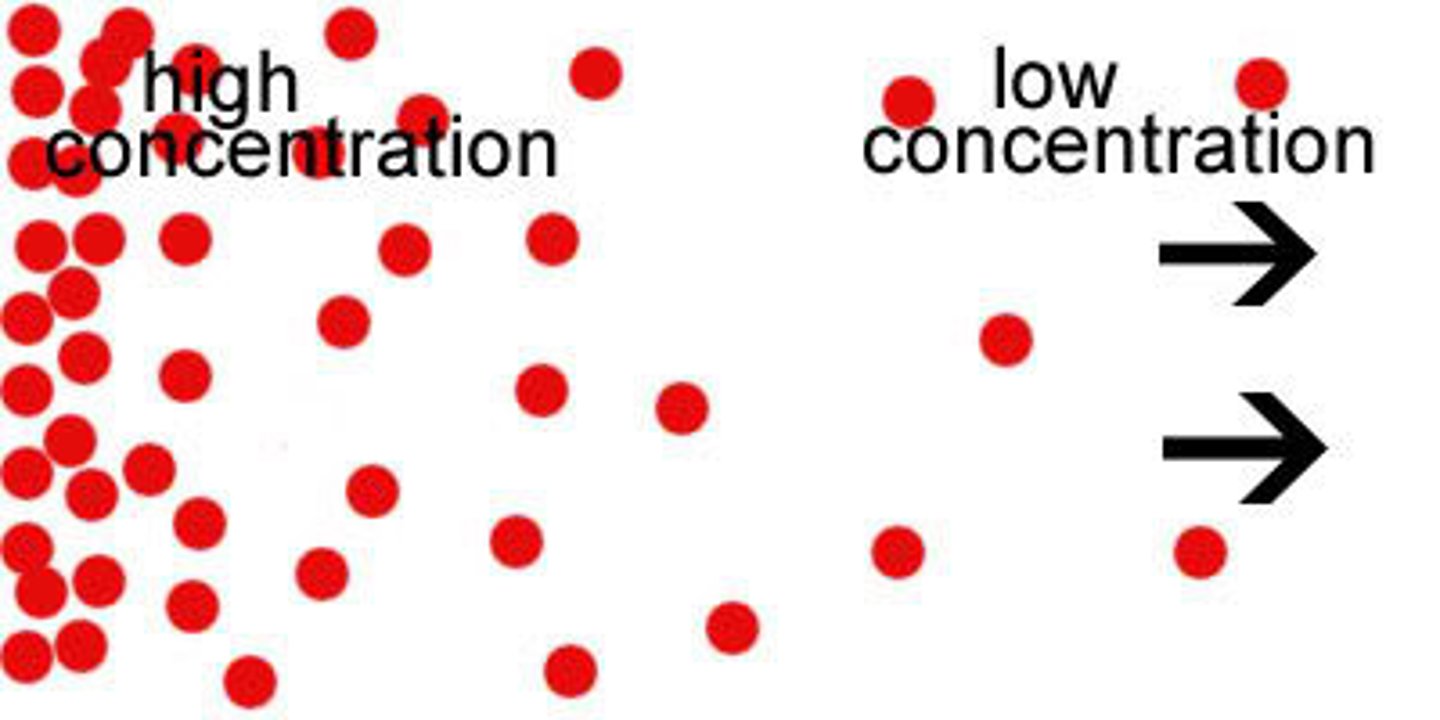
Concentration Gradient
The difference in the amount of a substance between two areas, which causes diffusion.
Electrical Current
The flow of electrical charge, like a river of electrons or ions moving through a conductor.
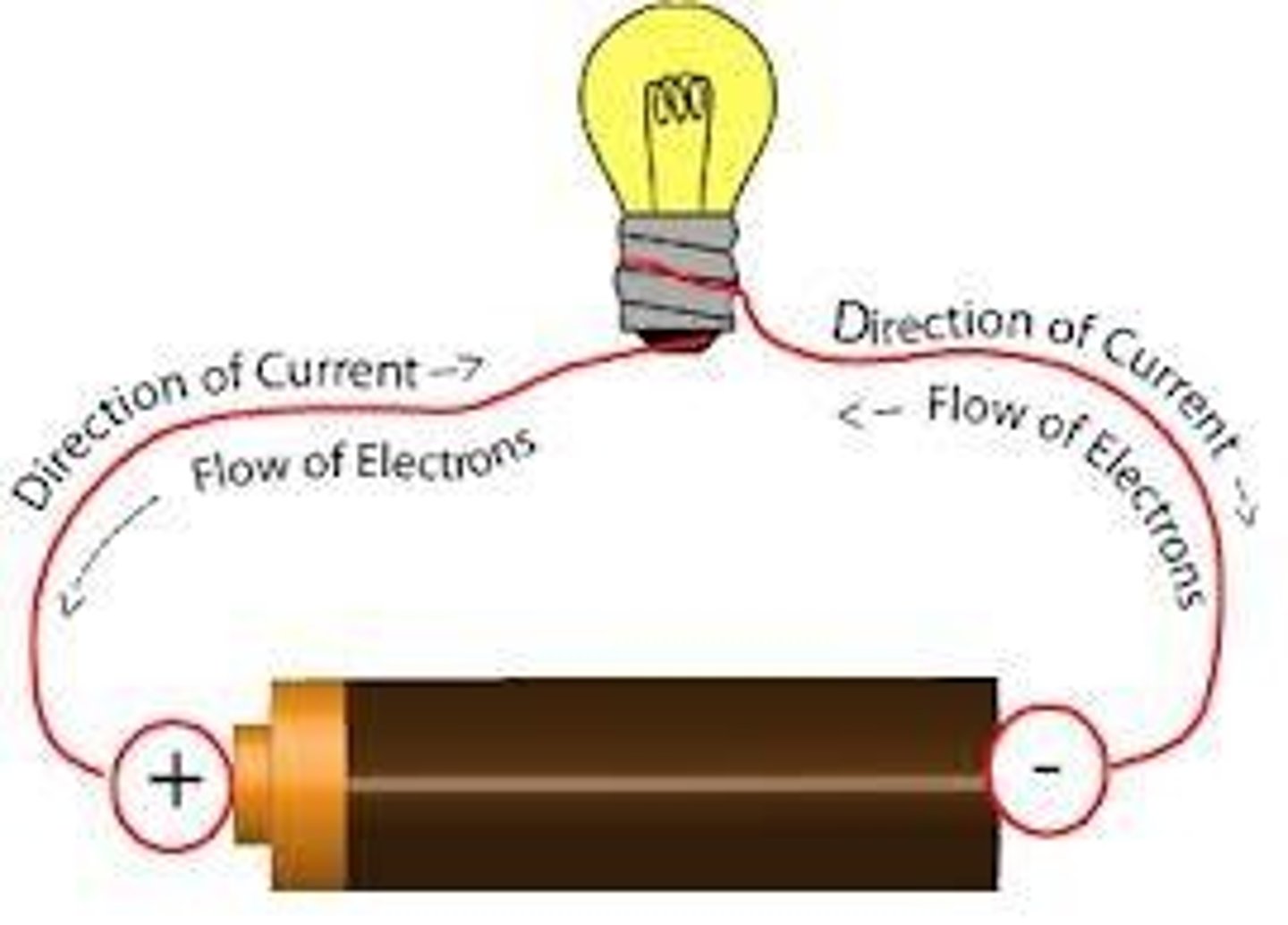
Electrical Potential (Voltage)
The force that pushes electrical charge, like the pressure in a water pipe.
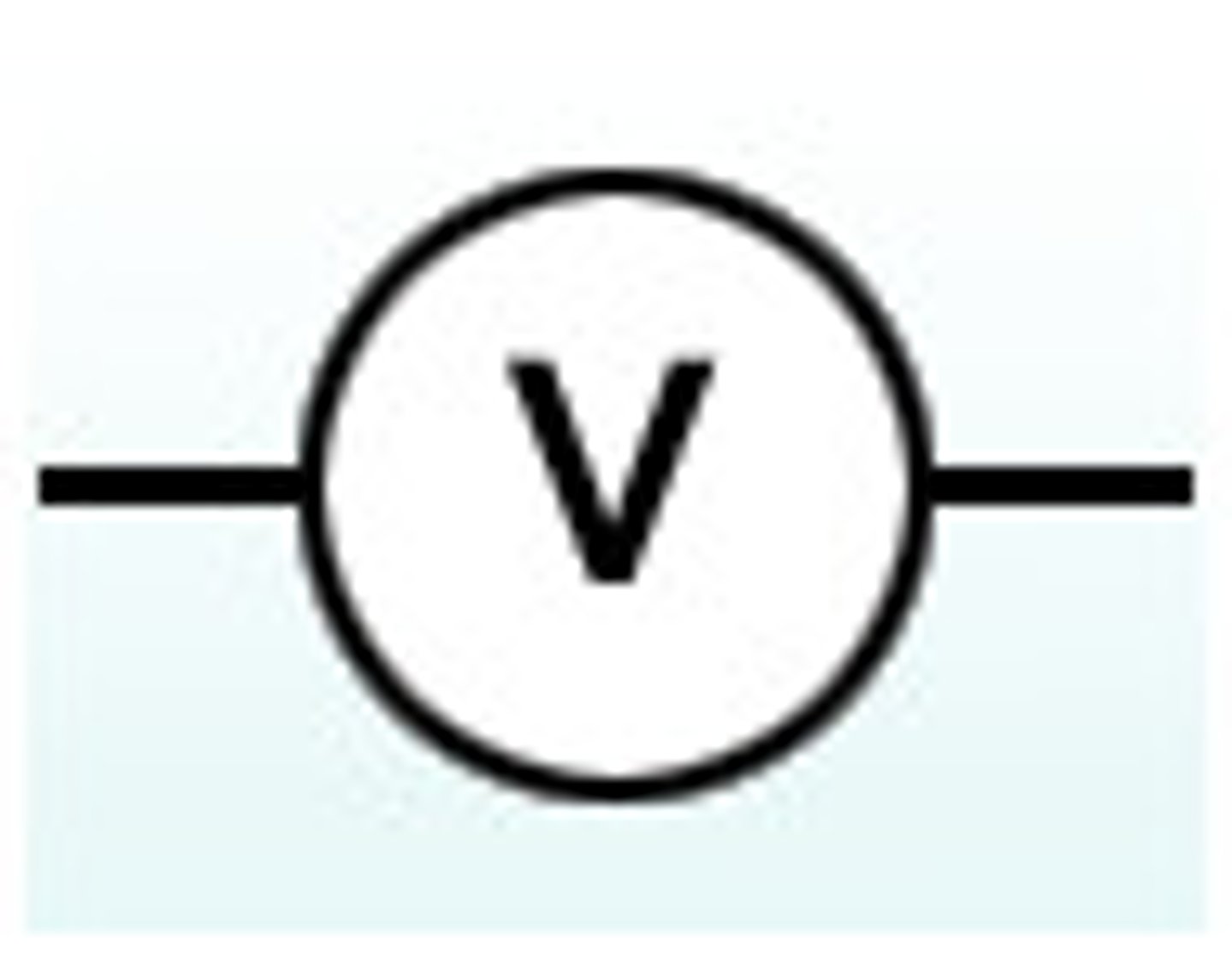
Voltage
Another word for electrical potential, measured in volts (V) or millivolts (mV).

Electrical Conductance
How easily electricity (or ions) can flow through something. High conductance = easy flow.
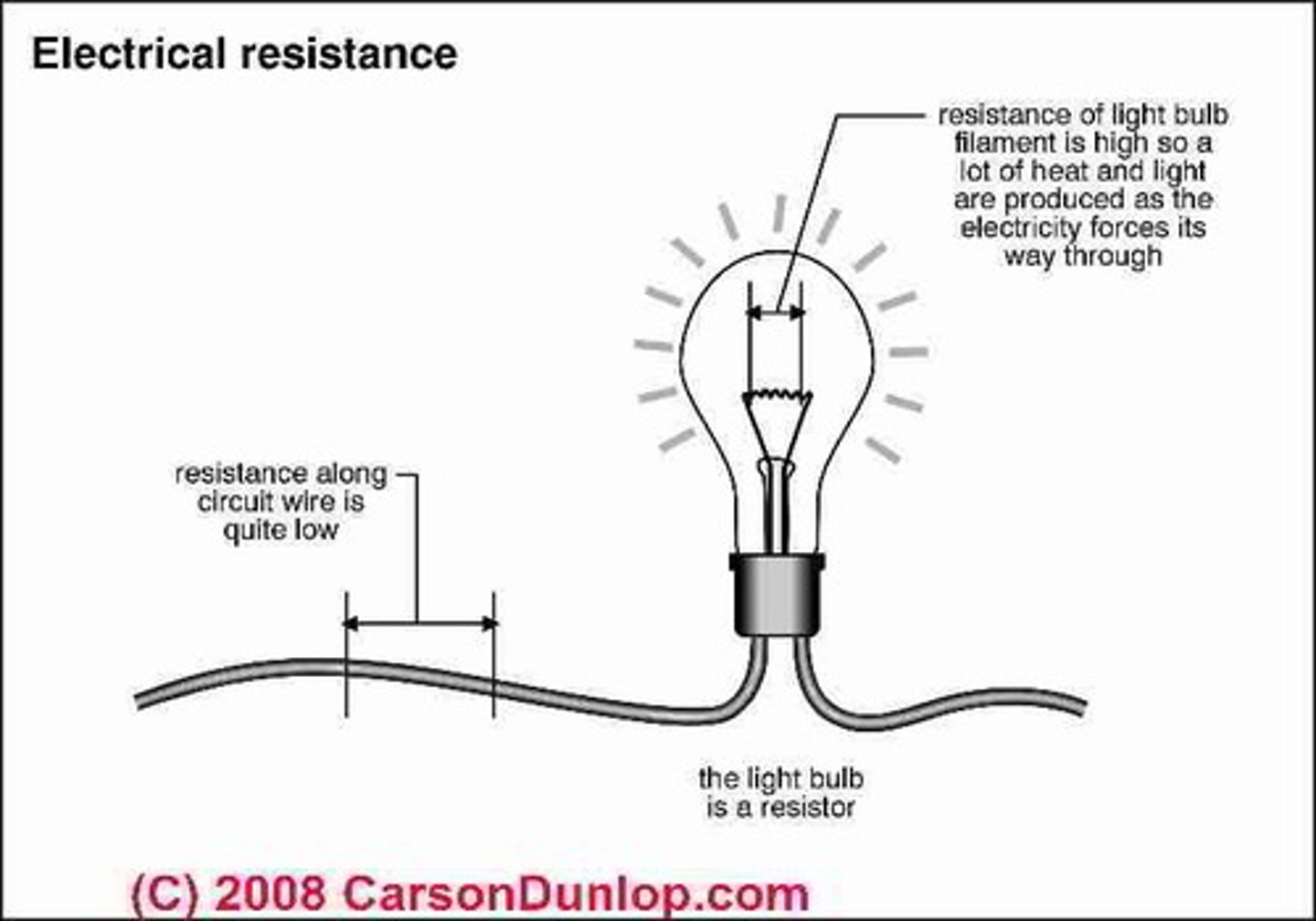
Electrical Resistance
How much something blocks the flow of electricity. High resistance = hard for electricity to pass.
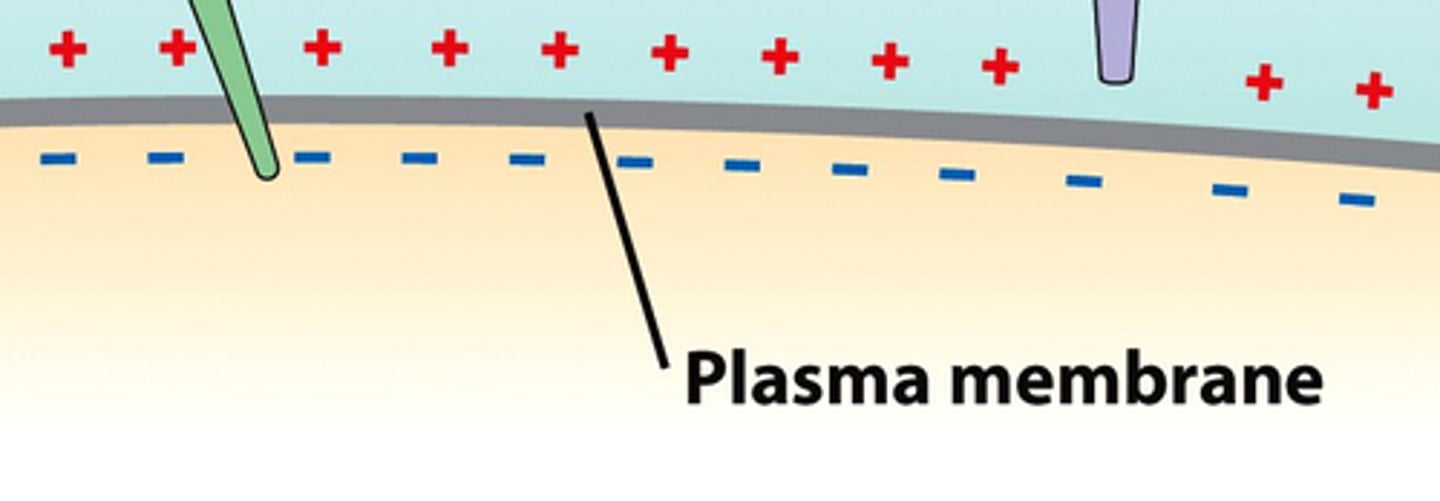
Membrane Potential
The difference in electrical charge inside vs. outside a neuron. This is how neurons send signals.
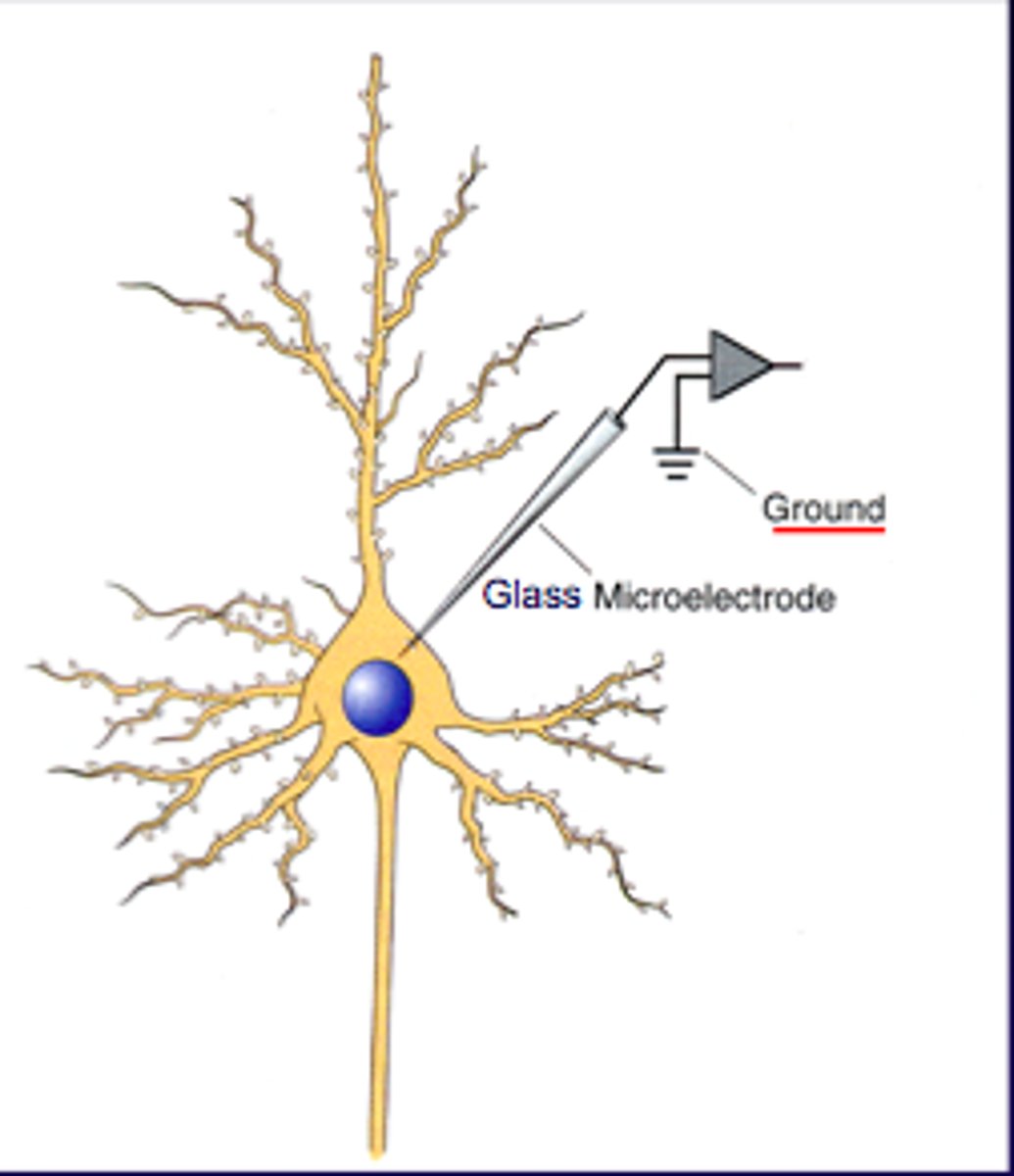
Microelectrode
A tiny needle-like tool that can measure the electrical charge inside a neuron.
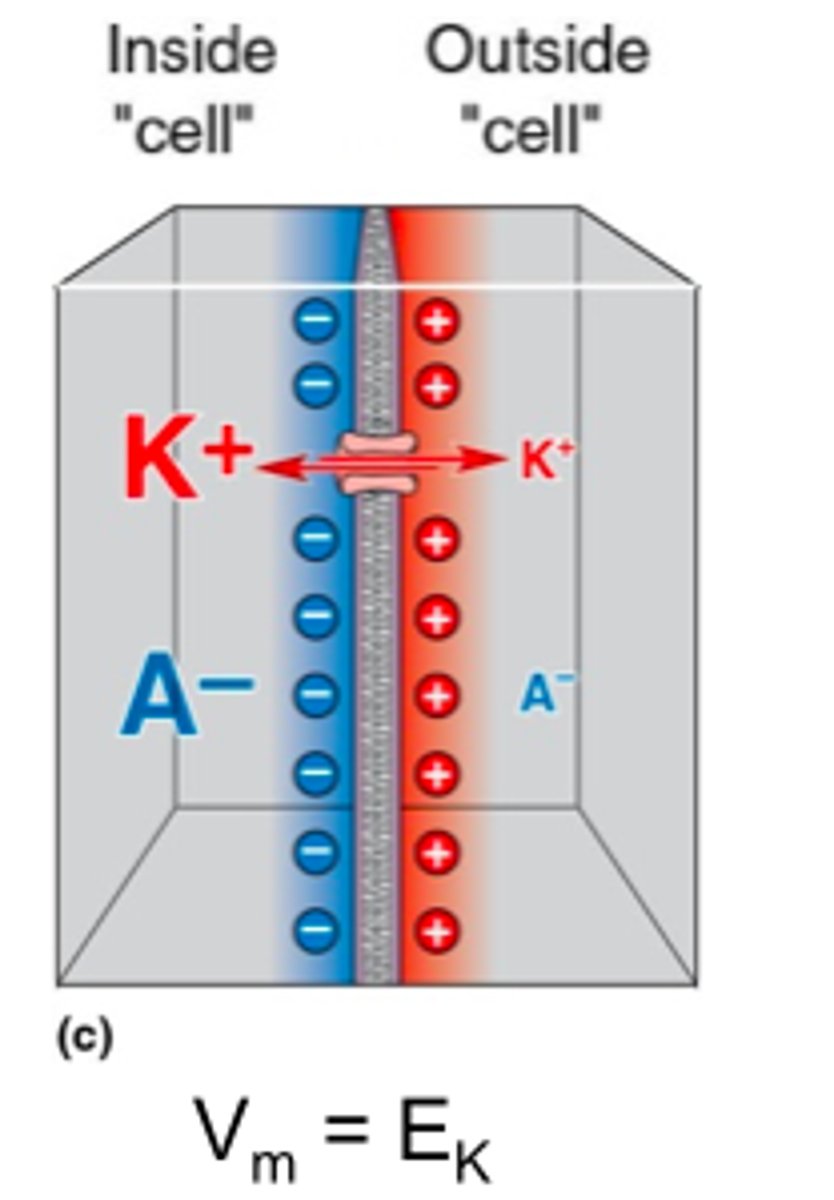
Ionic Equilibrium Potential
The point where an ion is balanced between inside and outside the cell, so it stops moving.
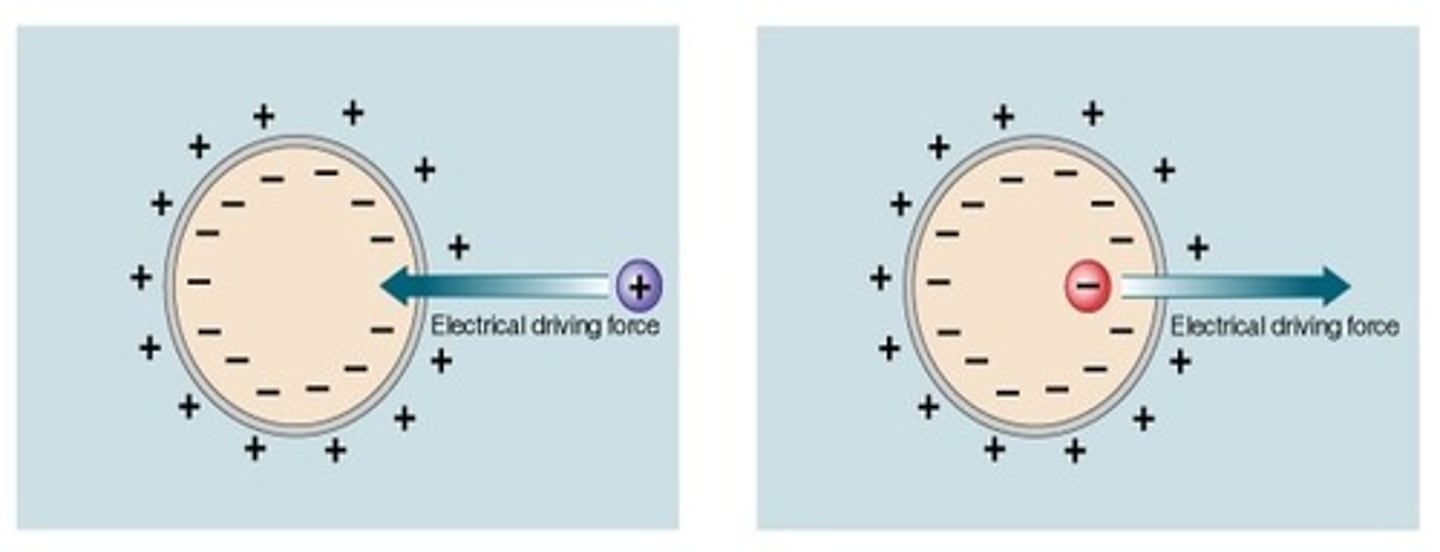
Ionic Driving Force
The push or pull on an ion based on its equilibrium potential and membrane potential.
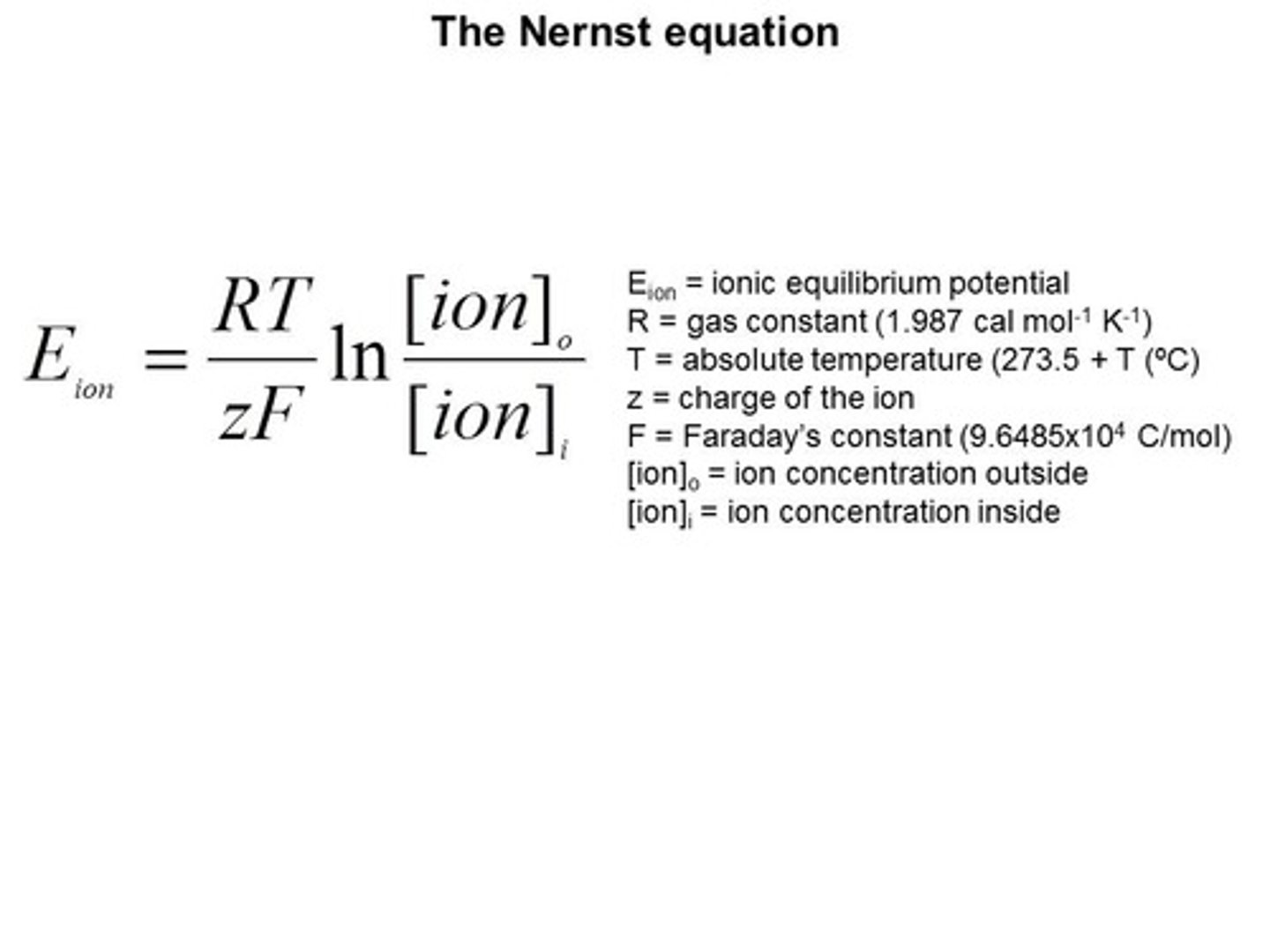
Nernst Equation
A formula that calculates an ion's equilibrium potential based on its concentration inside vs. outside the cell.
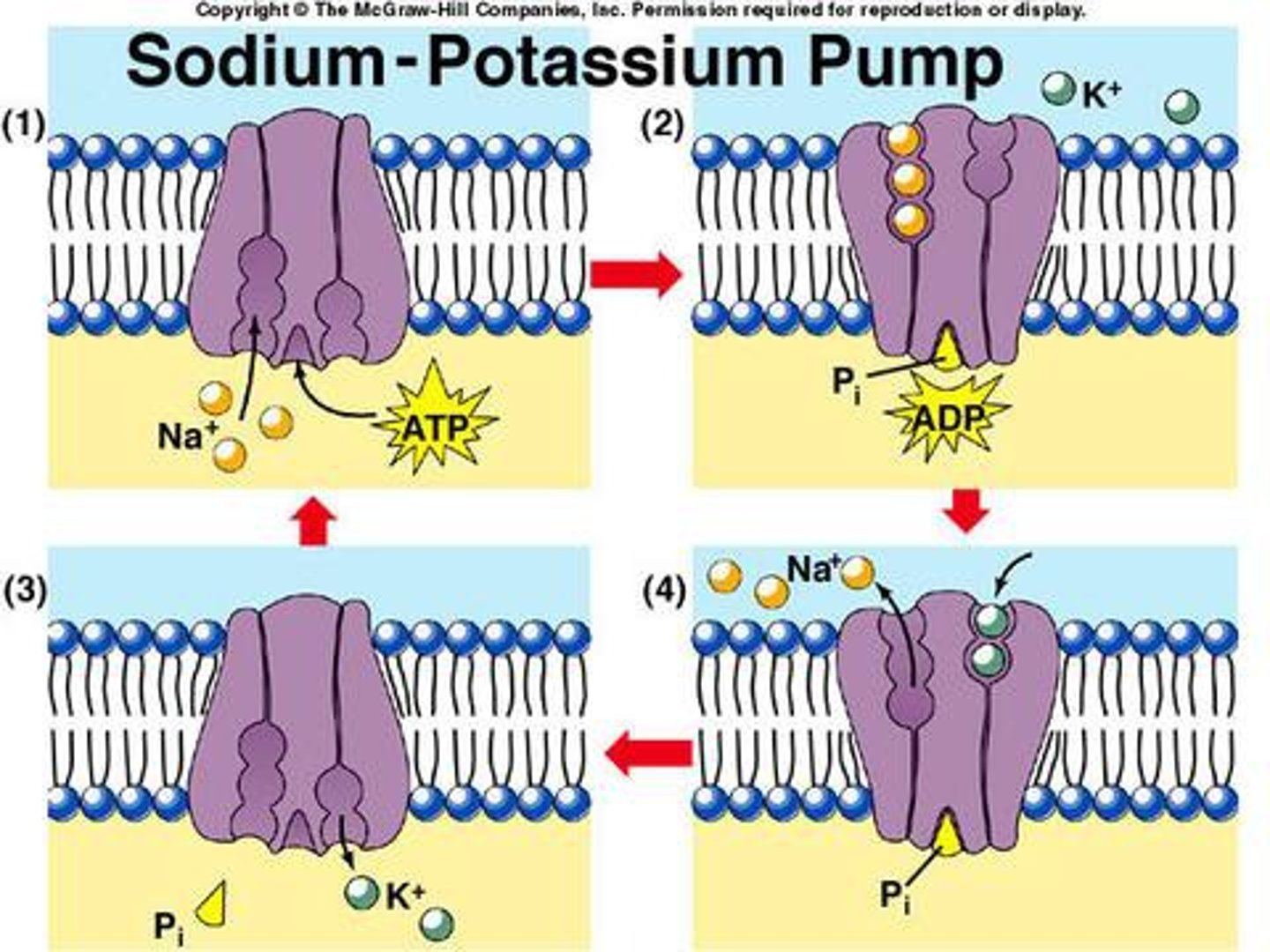
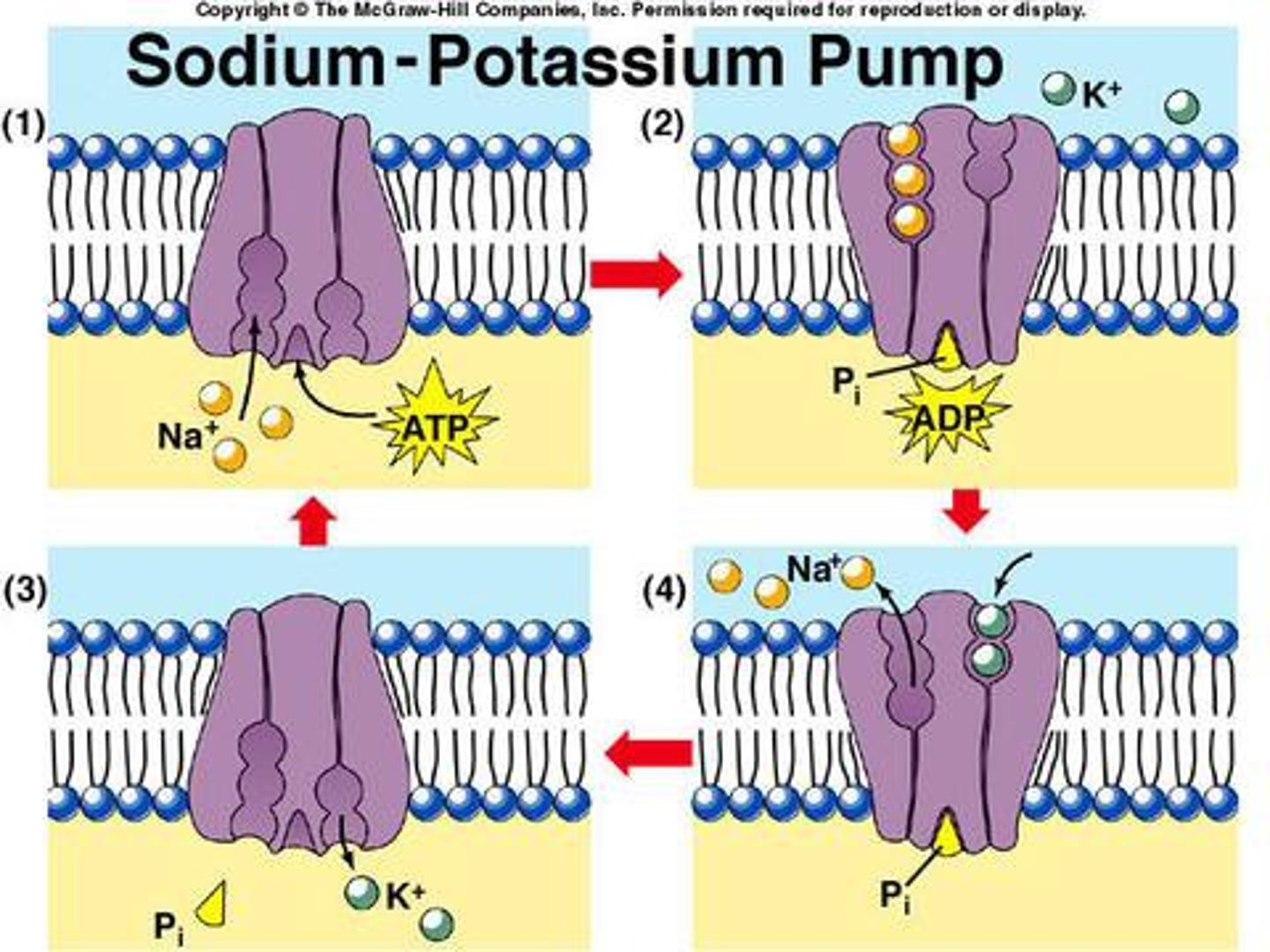
Sodium-Potassium Pump
A special pump that moves sodium (Na⁺) out and potassium (K⁺) in, helping the neuron stay at rest.
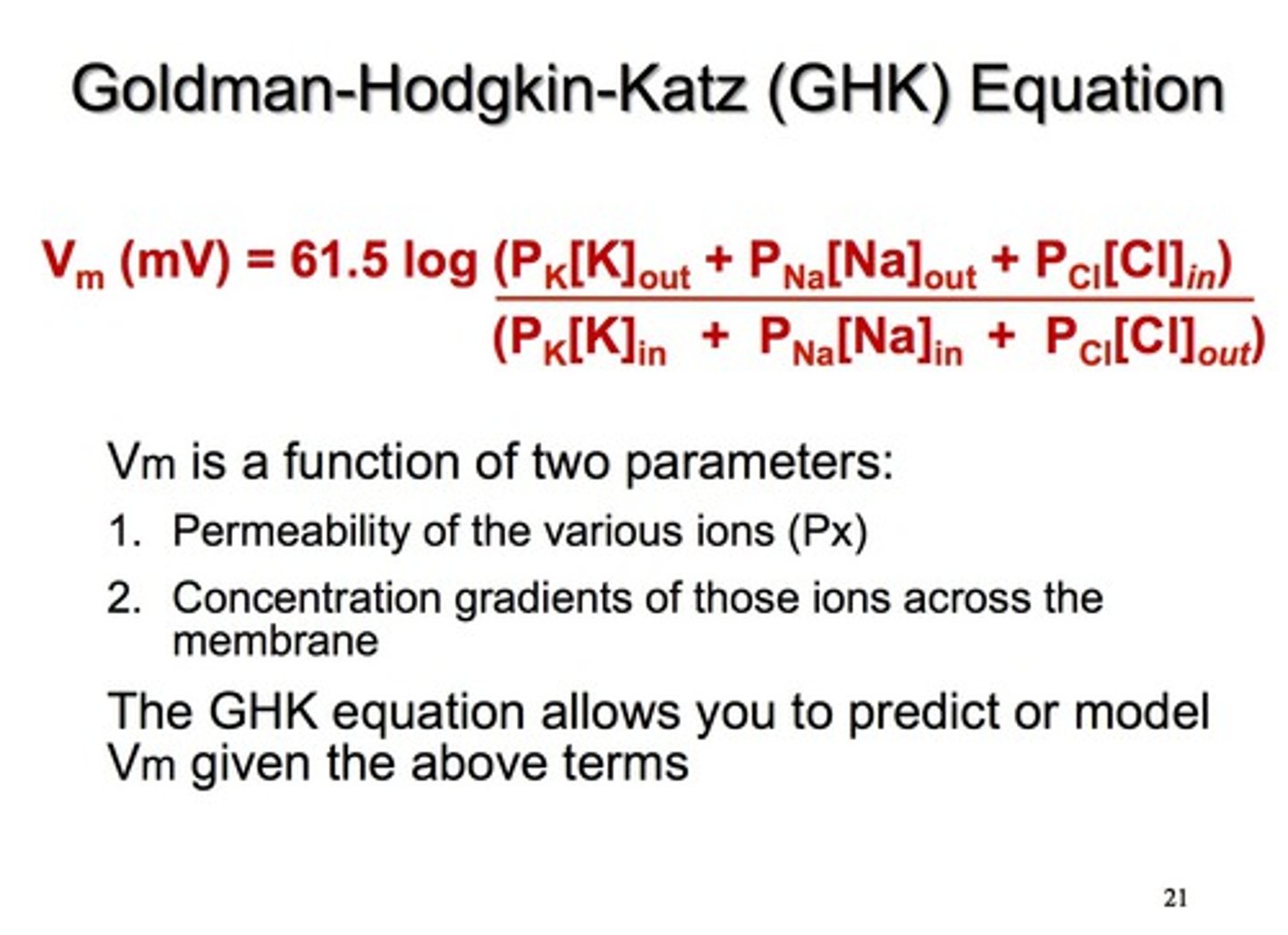
Goldman Equation
A formula that calculates the membrane potential by considering multiple ions (not just one like Nernst does).
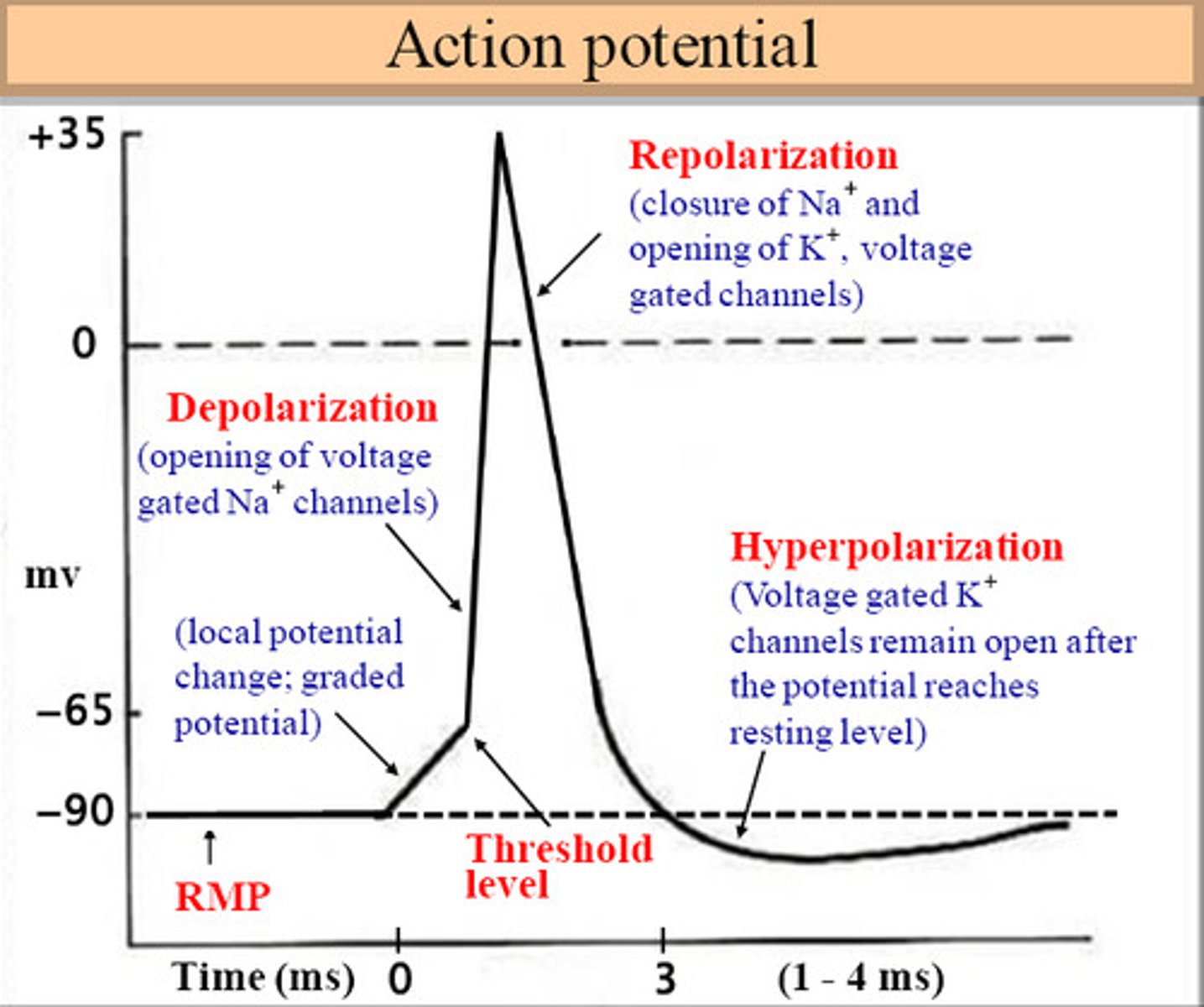
Depolarization
When the inside of a neuron becomes more positive, making it more likely to fire a signal.
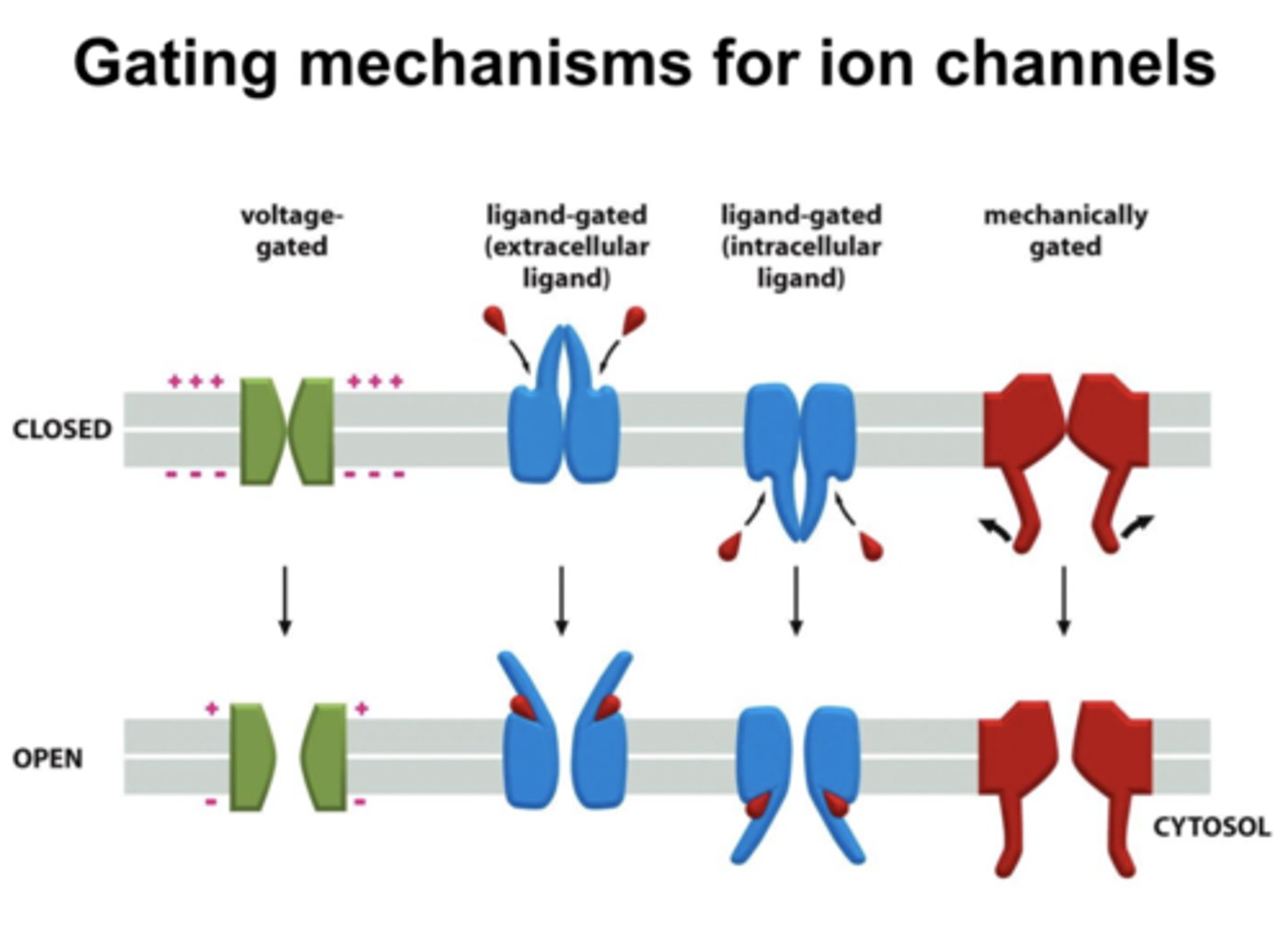
Gating (of Ion Channels)
When ion channels open or close, controlling which ions can enter or leave the neuron.
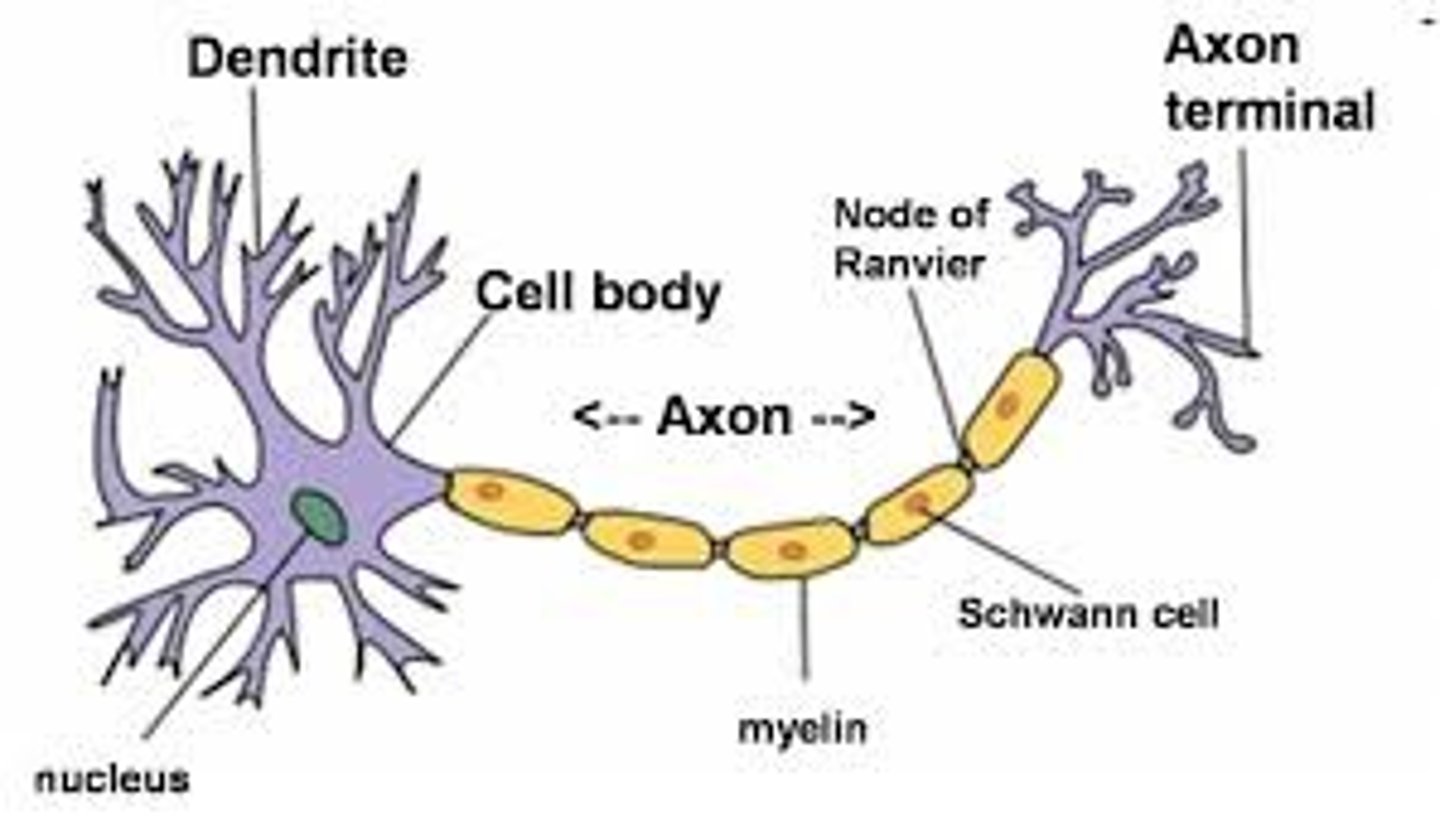
Axon
The long, thin part of a neuron that sends electrical signals away from the cell body to communicate with other neurons.
Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels
Special gates in the axon that open when the neuron needs to send a signal, letting sodium (Na⁺) rush in.
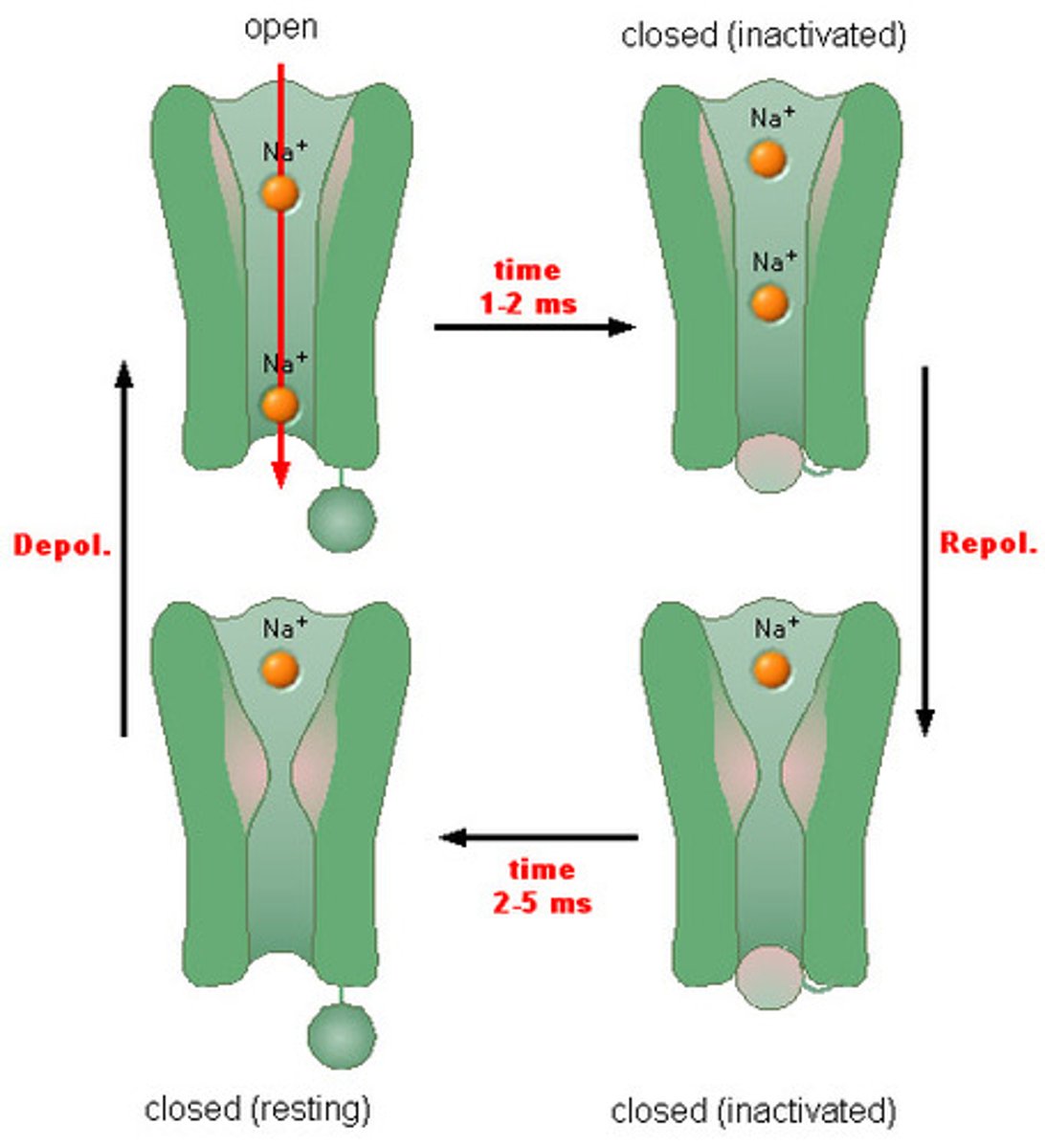
Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels
Gates that open after sodium, letting potassium (K⁺) flow out to reset the neuron.
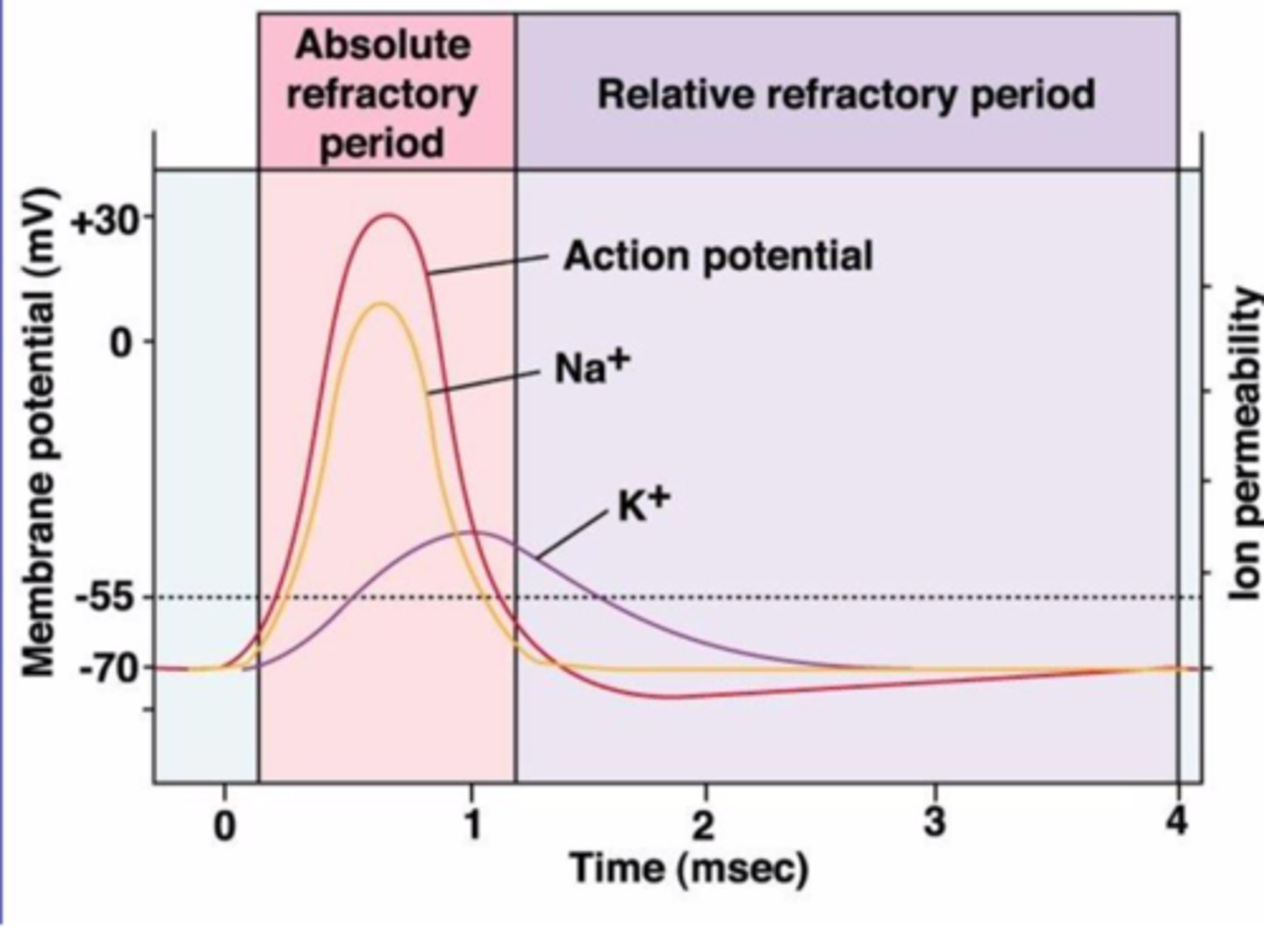
Threshold
The point where a neuron must reach to send a signal (~ -55mV). If it doesn't reach this, no signal happens.

Rising Phase
Sodium (Na⁺) rushes into the axon, making it more positive inside.
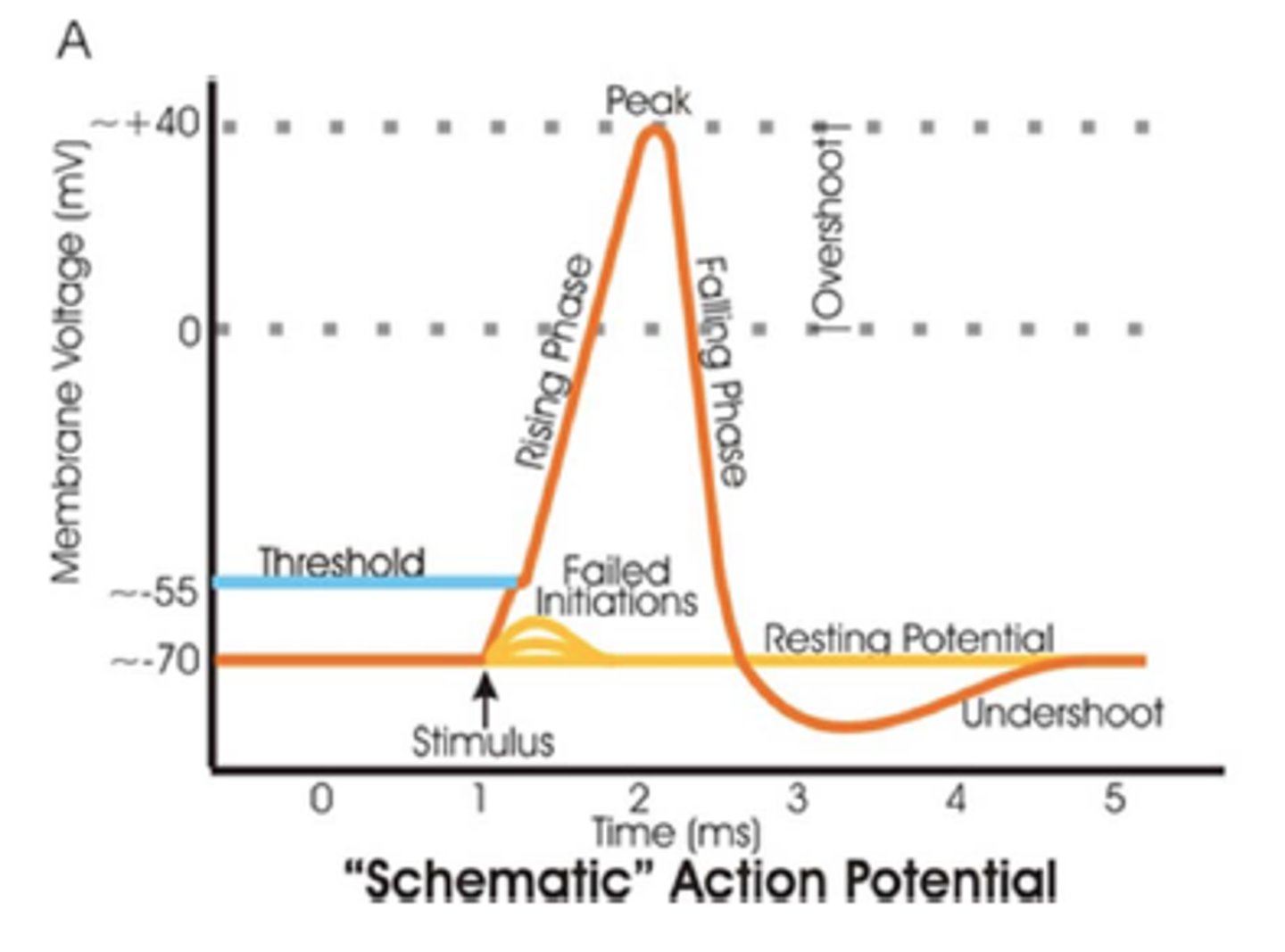
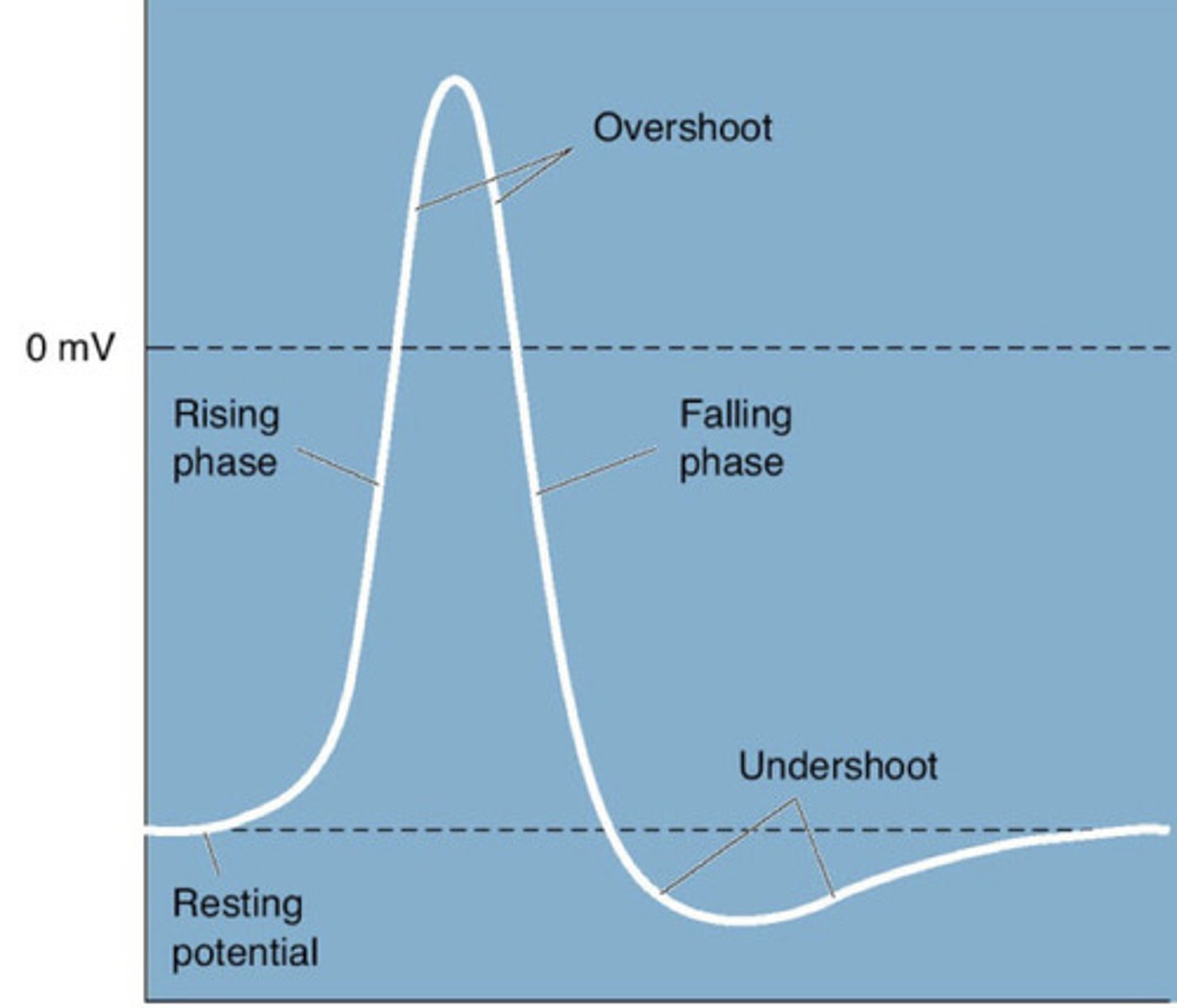
Overshoot
The inside of the neuron becomes more positive than the outside.
Falling Phase
Potassium (K⁺) flows out of the neuron, making the inside negative again.
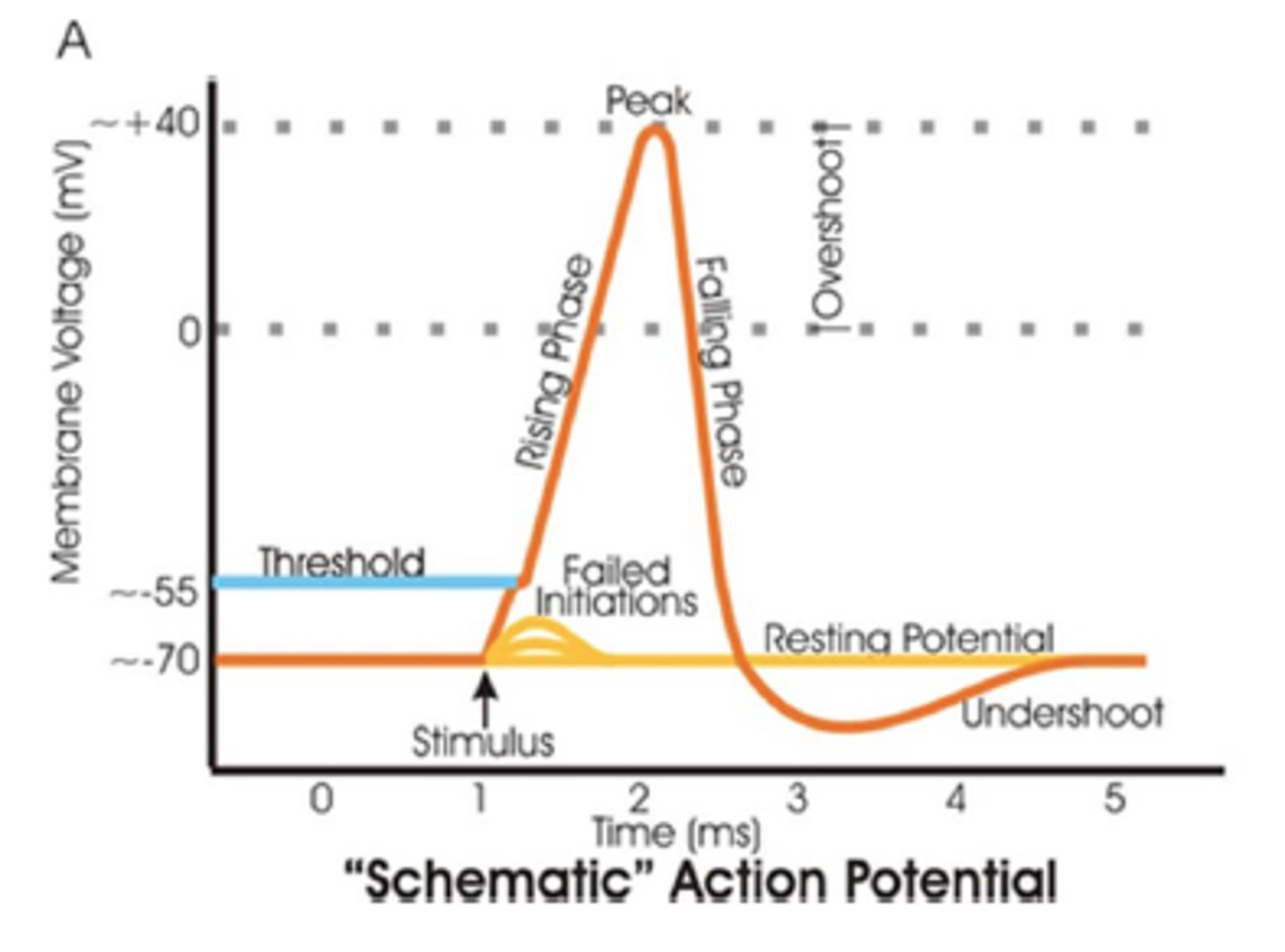
Undershoot (Hyperpolarization/After-Hyperpolarization)
The neuron becomes even more negative than its resting state before returning to normal.
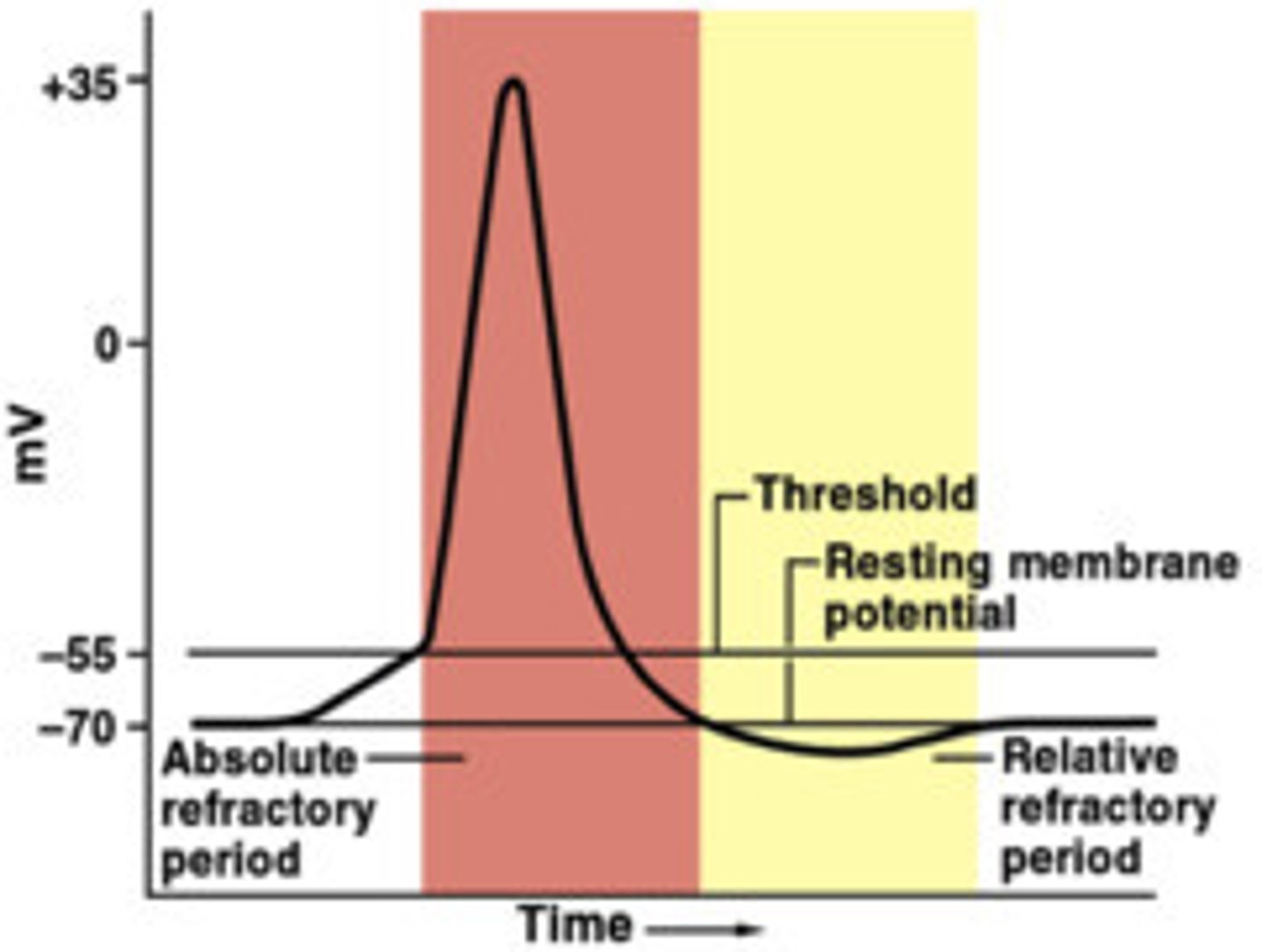
Absolute Refractory Period
The neuron cannot fire another signal because sodium channels are completely inactive.
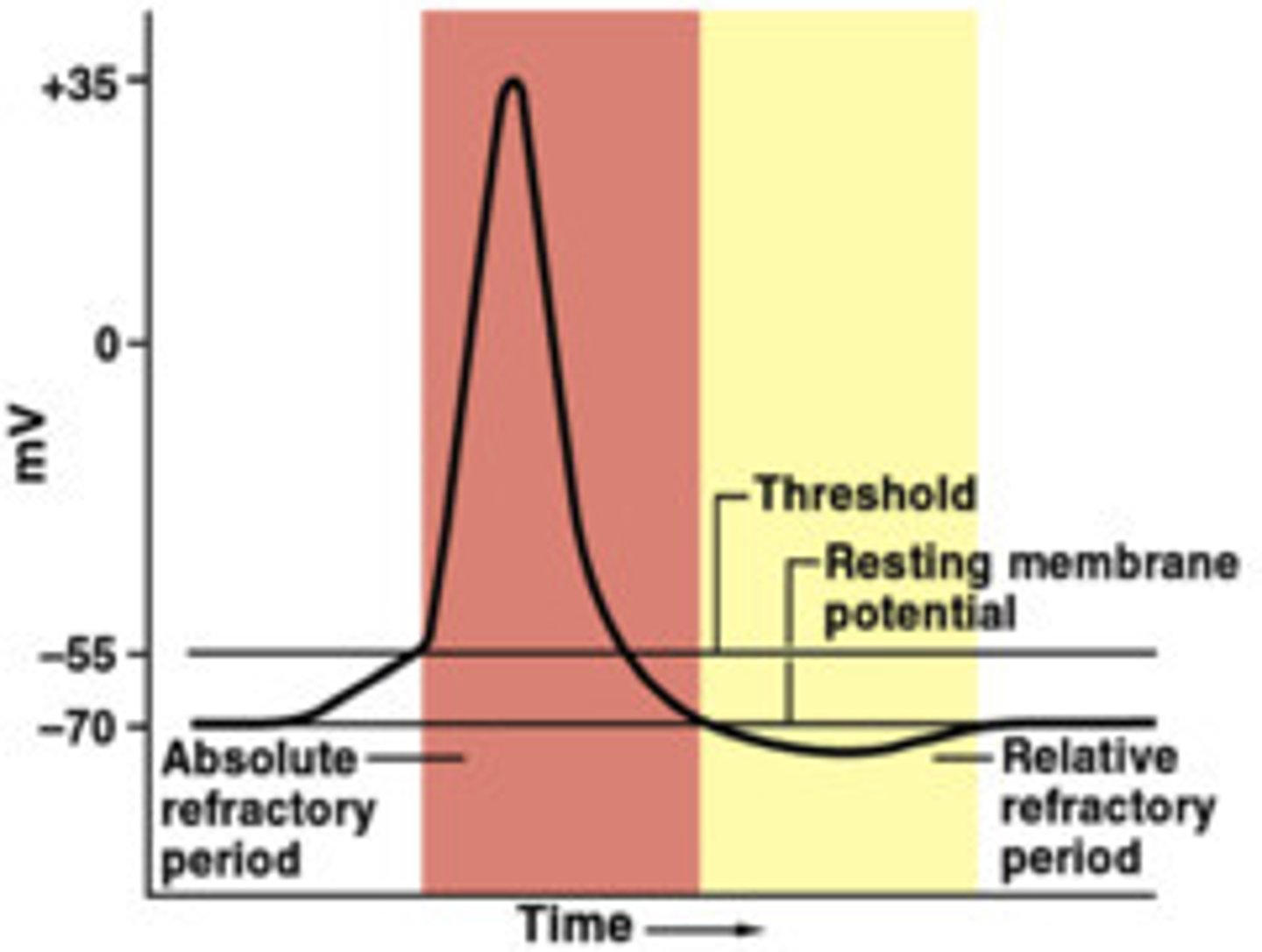
Relative Refractory Period
The neuron can fire another signal, but only if it gets a very strong stimulus because it's still recovering.
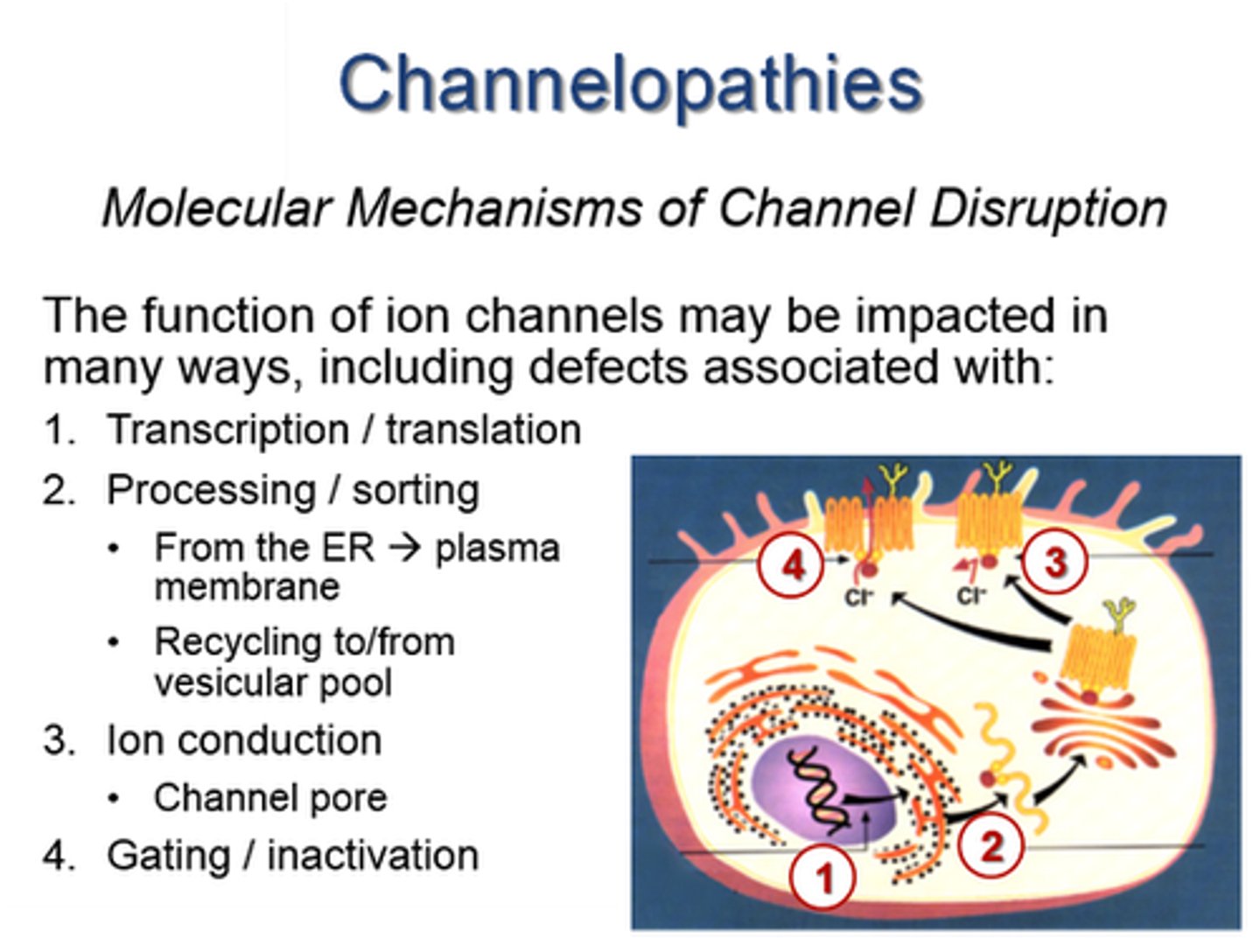
Channelopathy
A disease caused by defective ion channels, which can affect neuron signaling (e.g., epilepsy).
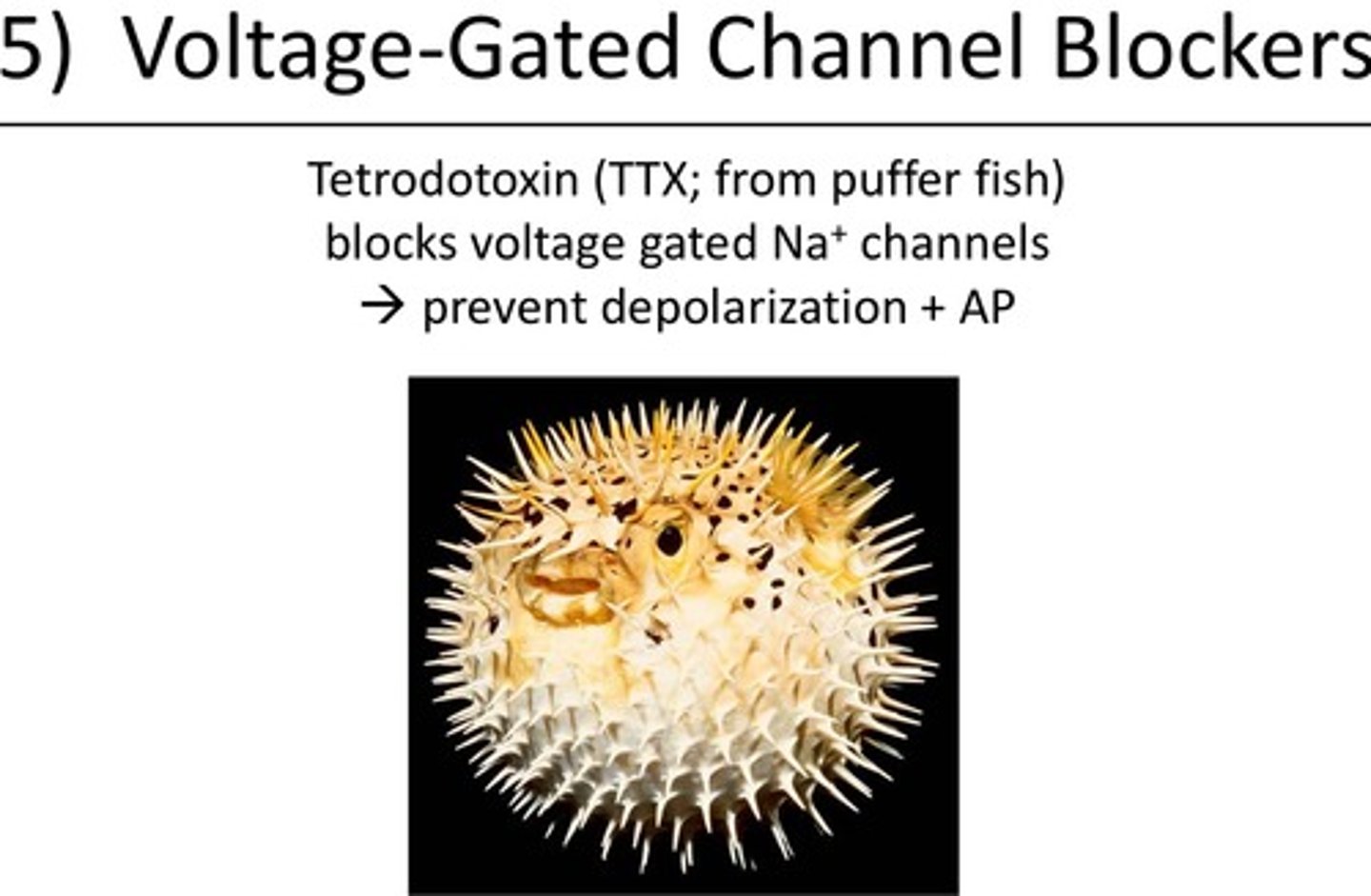
Tetrodotoxin (TTX)
A deadly toxin found in pufferfish that blocks sodium channels, preventing neurons from sending signals.
Myelination
A fatty covering (myelin) around the axon that makes signals travel much faster.
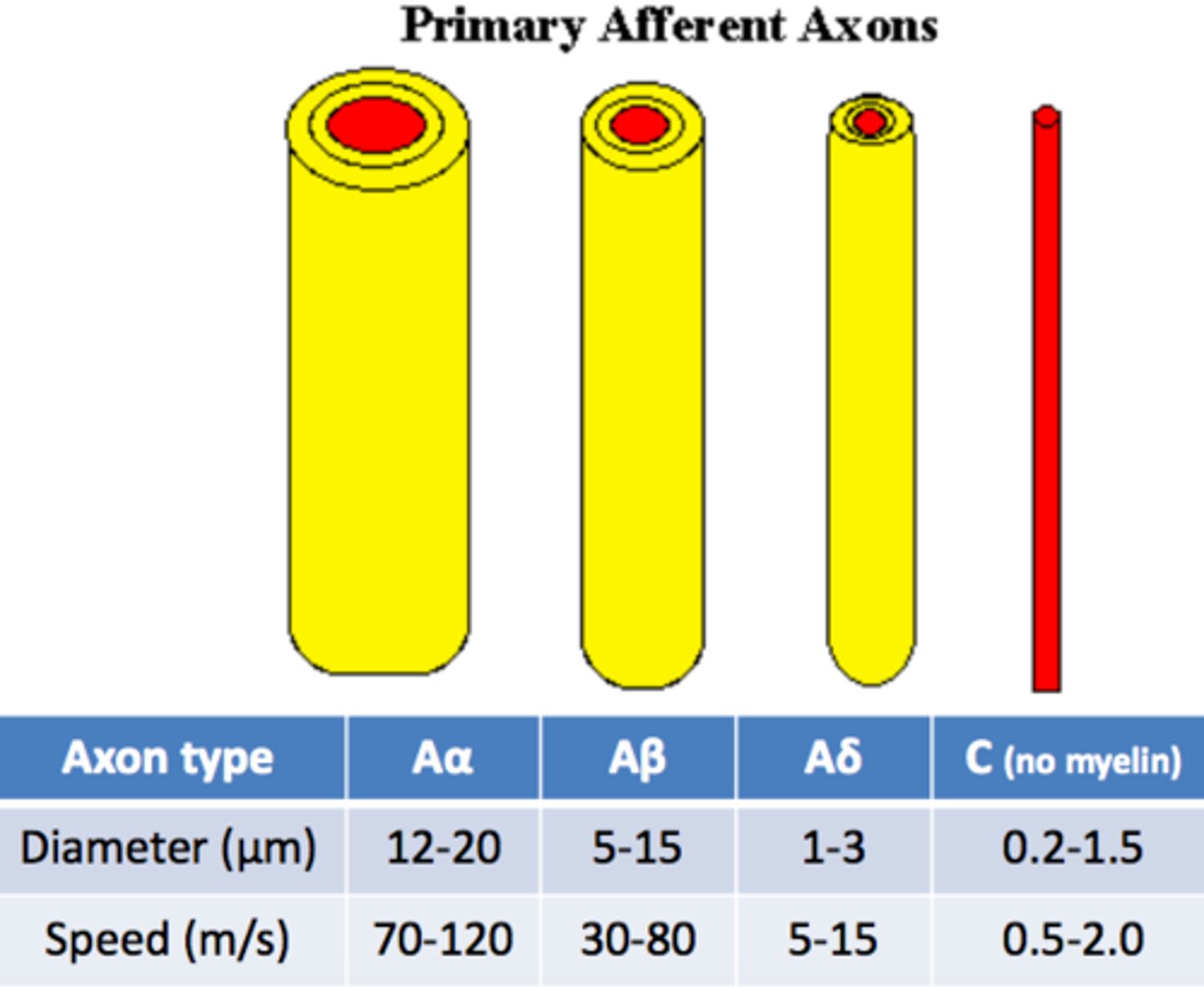
Axon Width
Thicker axons send signals faster because there is less resistance to ion flow.
Myelinated Axon
An axon covered with myelin, making signals travel quickly.
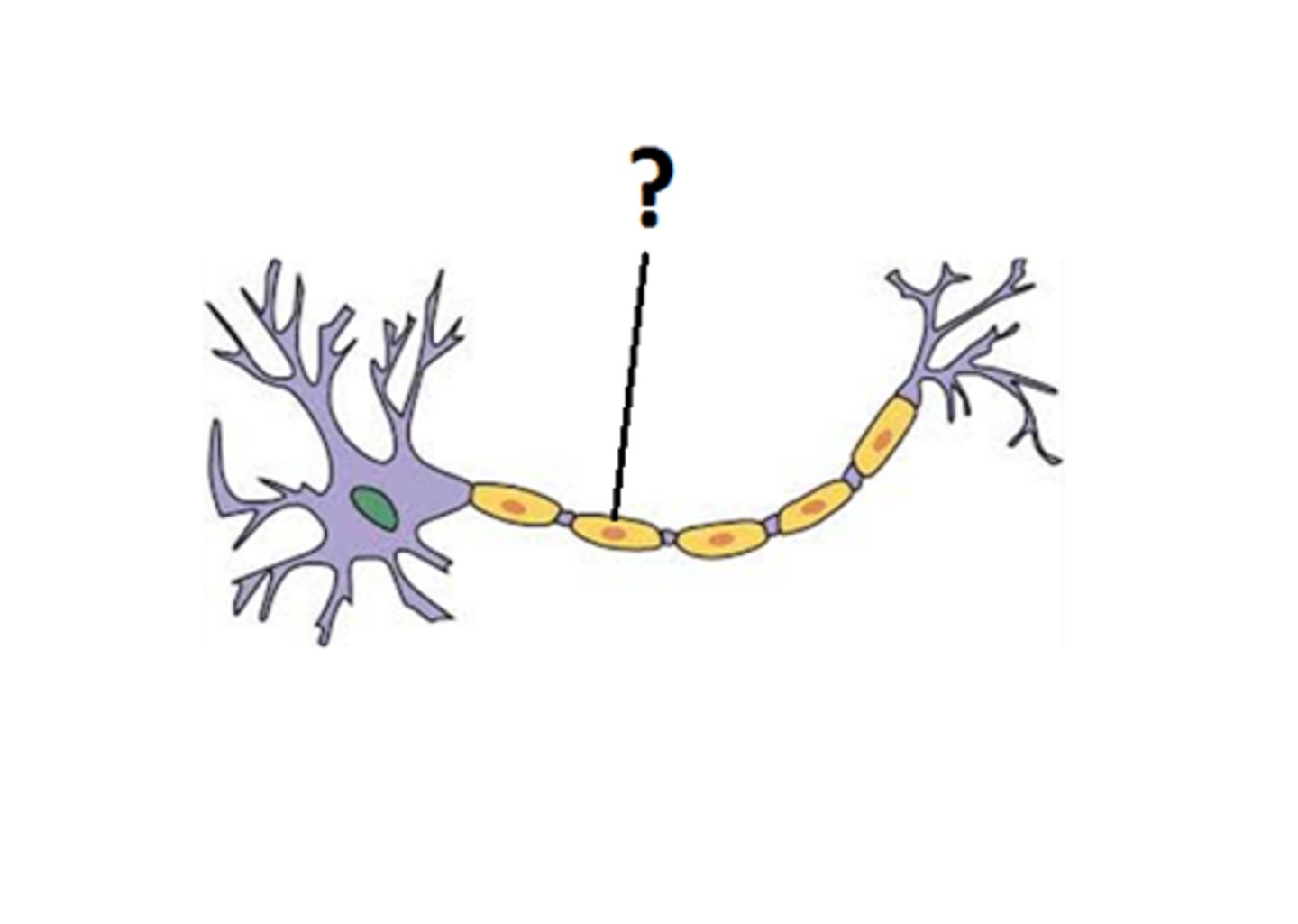
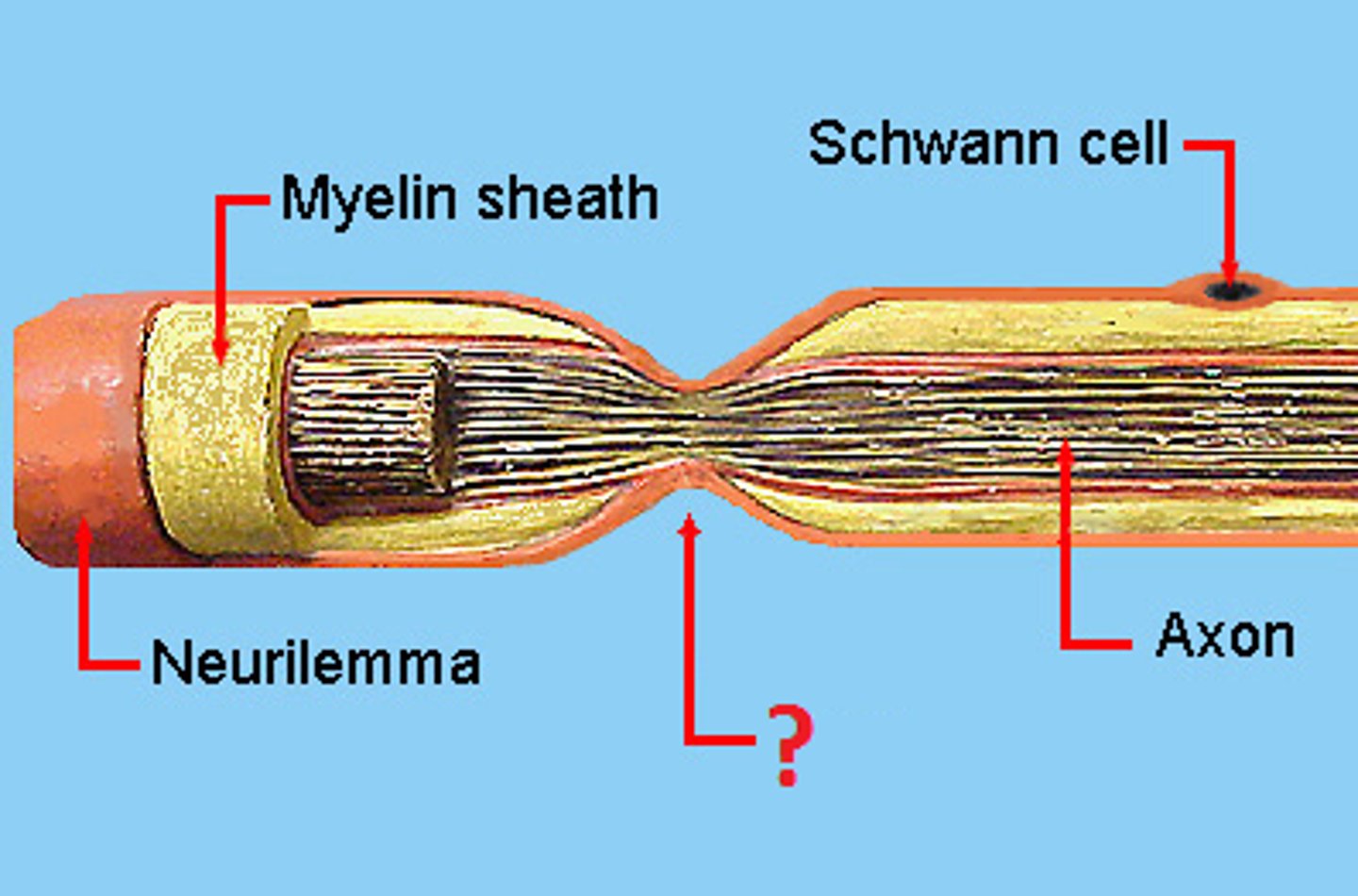
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps between myelin where ion channels are located, helping speed up signals.
Saltatory Conduction
How signals jump from one Node of Ranvier to another instead of moving slowly down the axon.
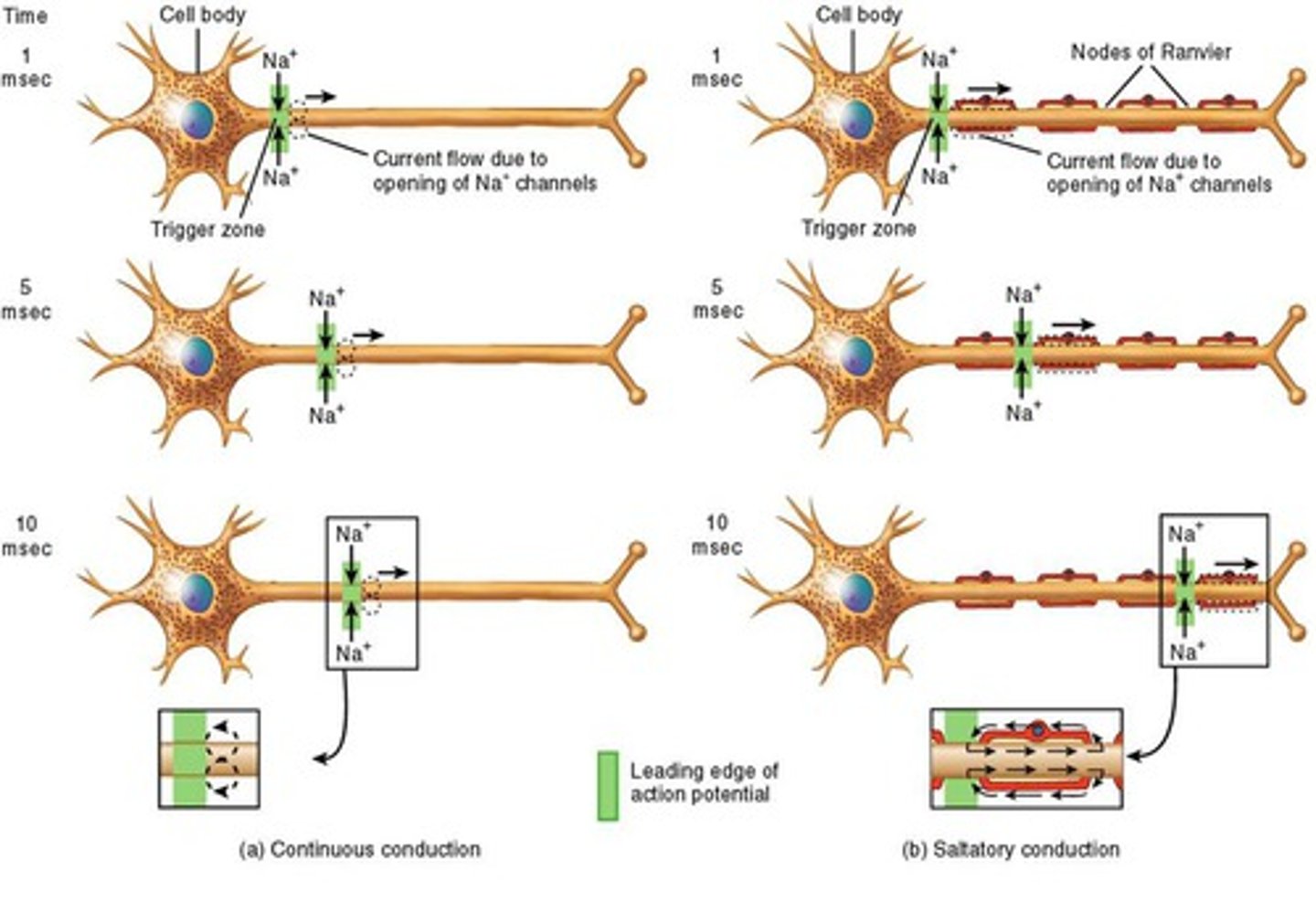
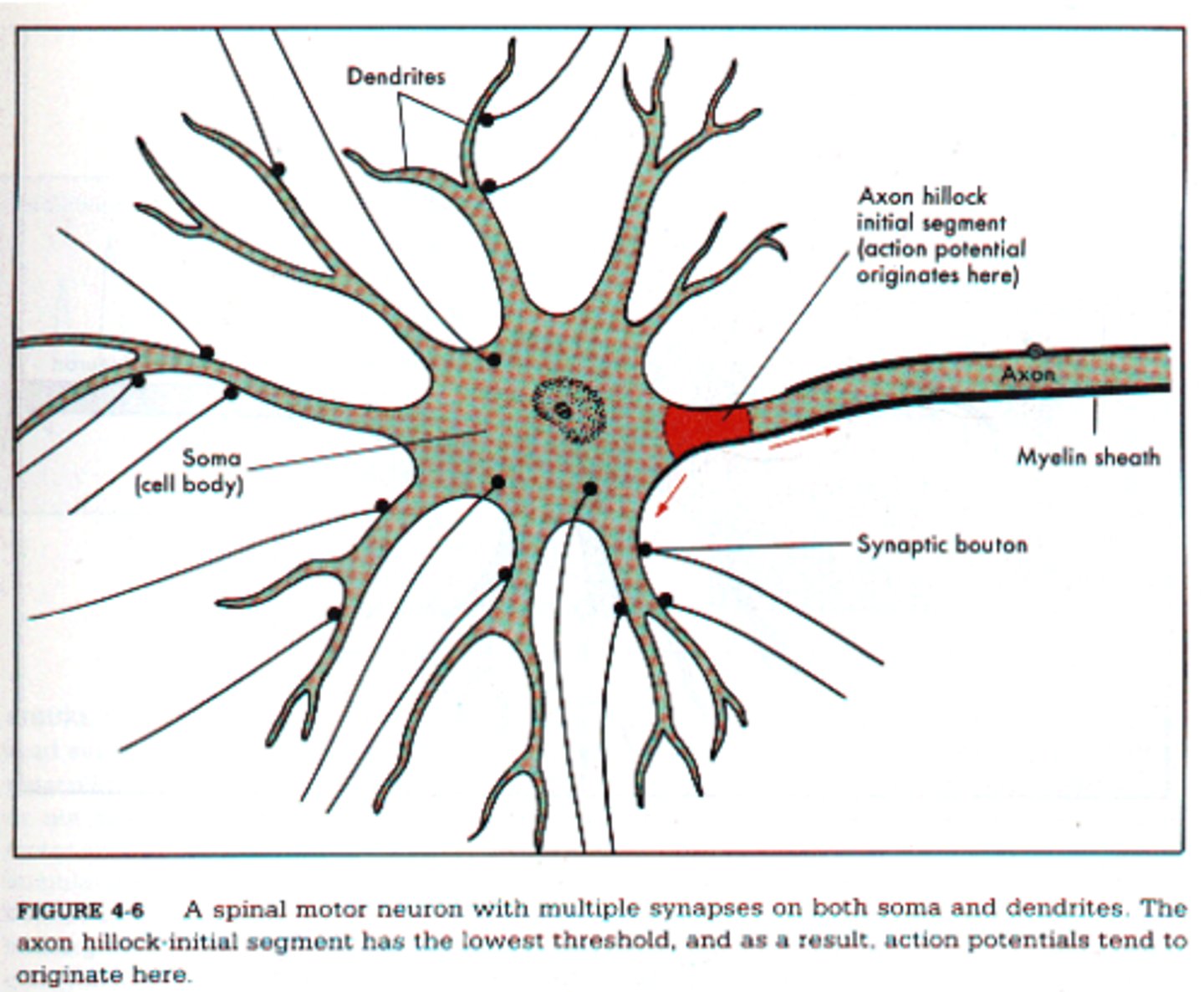
Spike-Initiation Zone
The part of a neuron (usually the axon hillock) where action potentials (signals) begin.
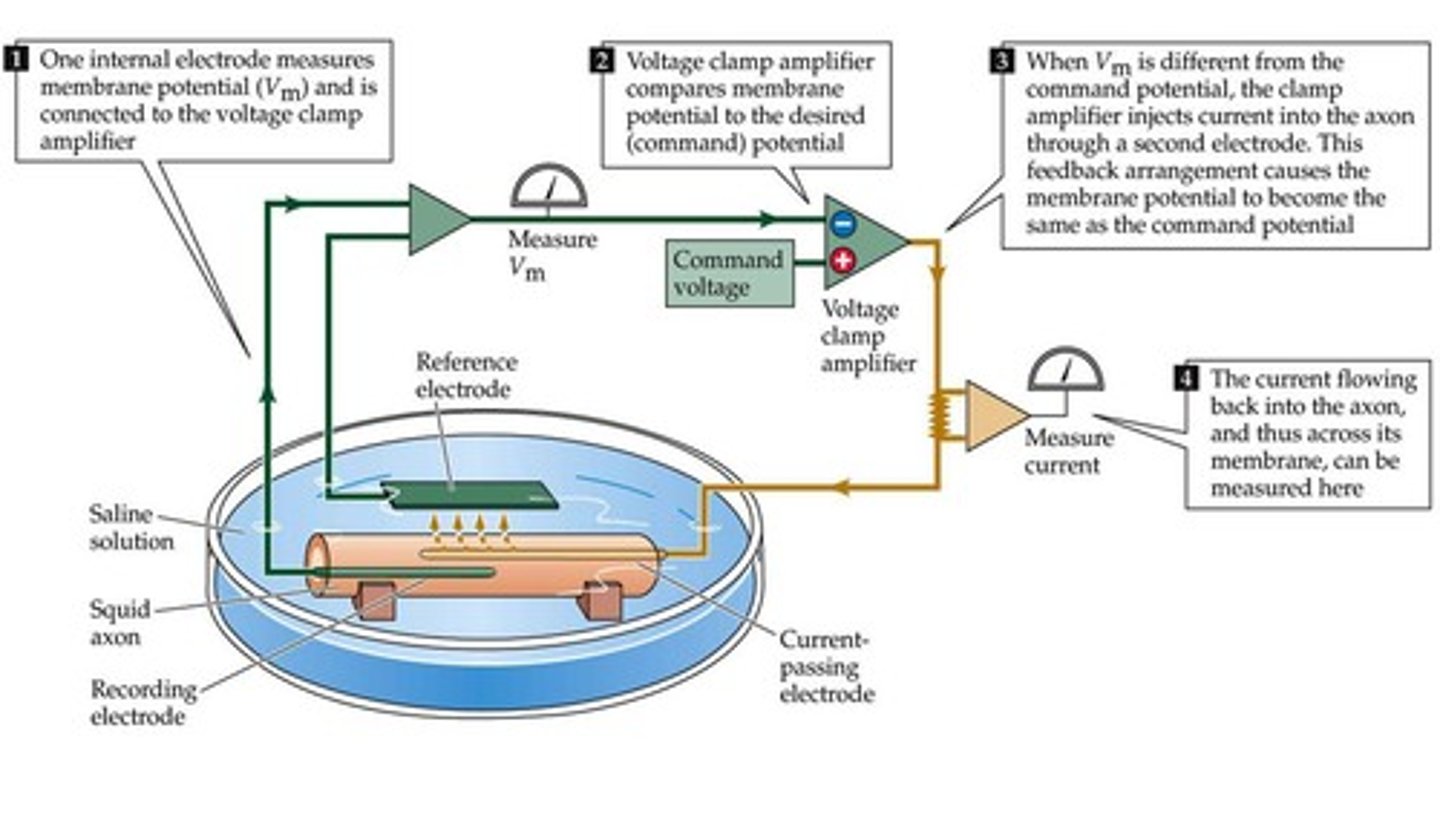
Oscilloscope/Voltammeter
A tool that measures electrical signals inside neurons.
Voltage Clamp
A technique that holds the voltage of a neuron steady to study ion channel activity.
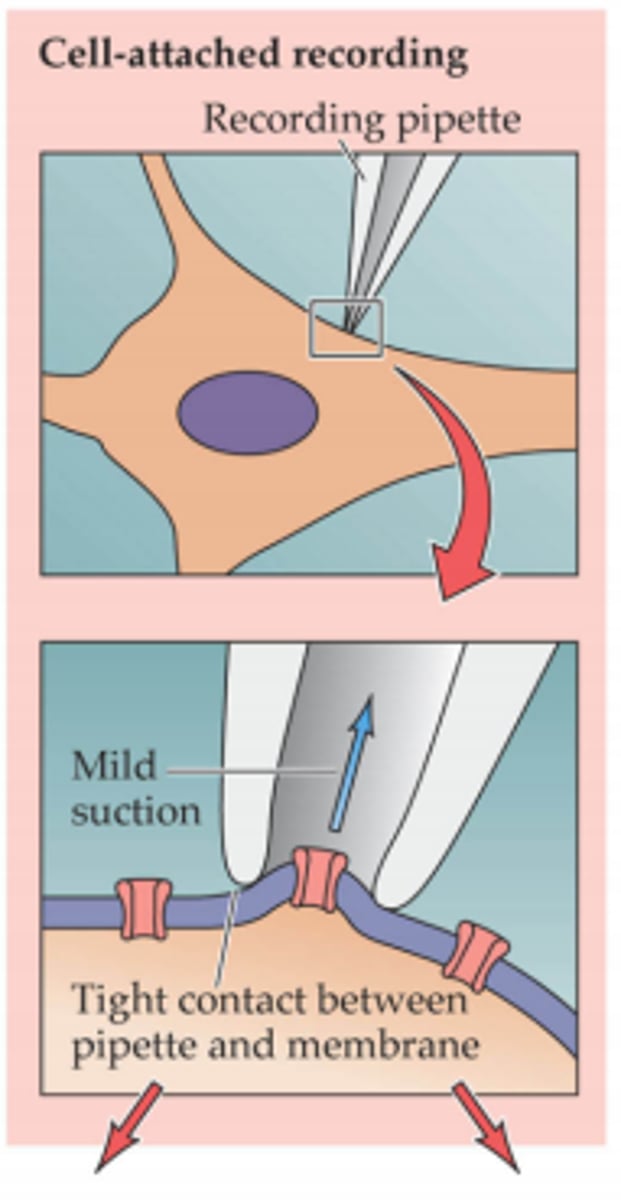
Patch Clamp
A method used to study the activity of one single ion channel in a neuron.
Synaptic Transmission
The process where one neuron sends a signal to another neuron or muscle using chemicals or electricity.
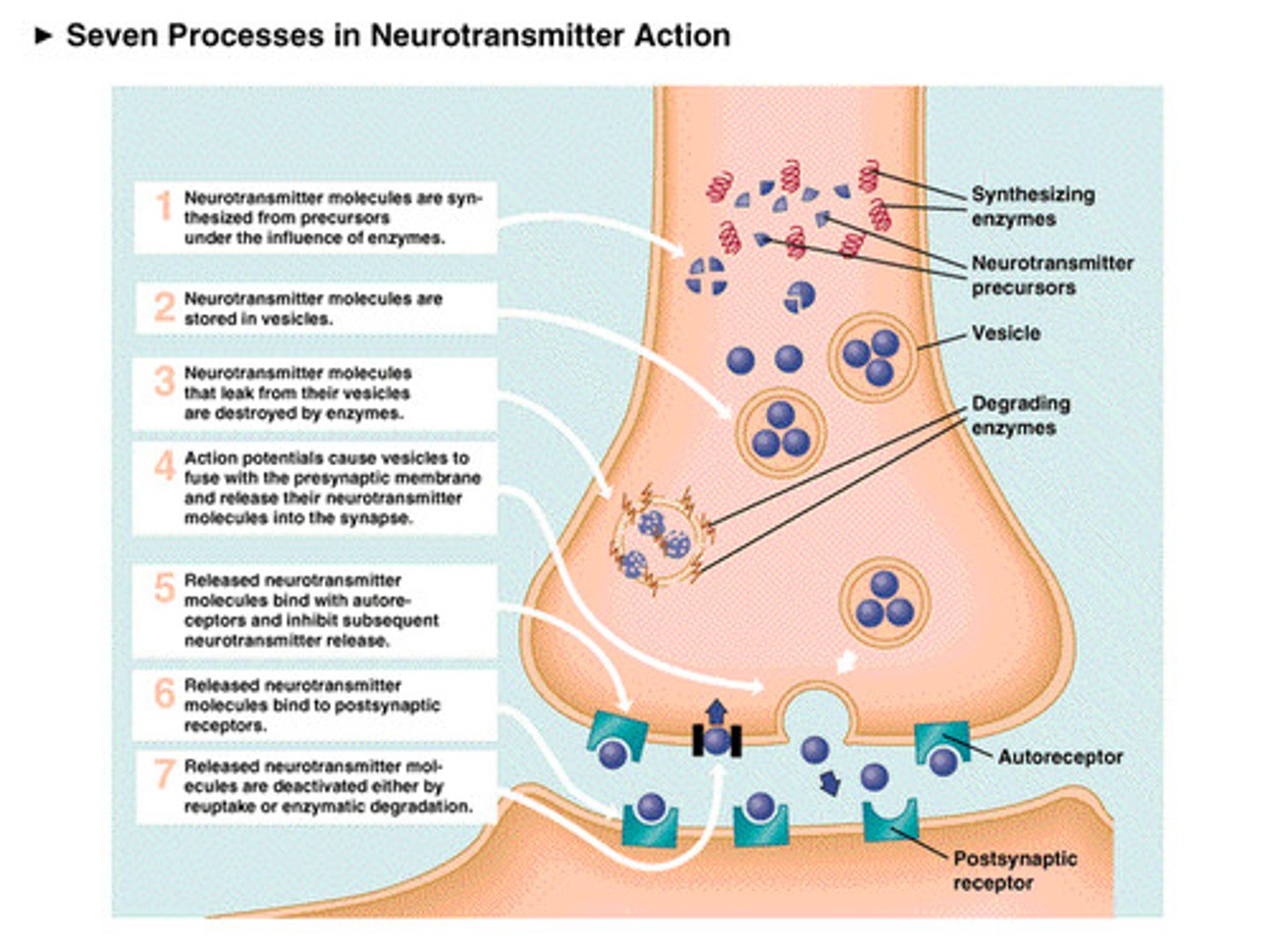
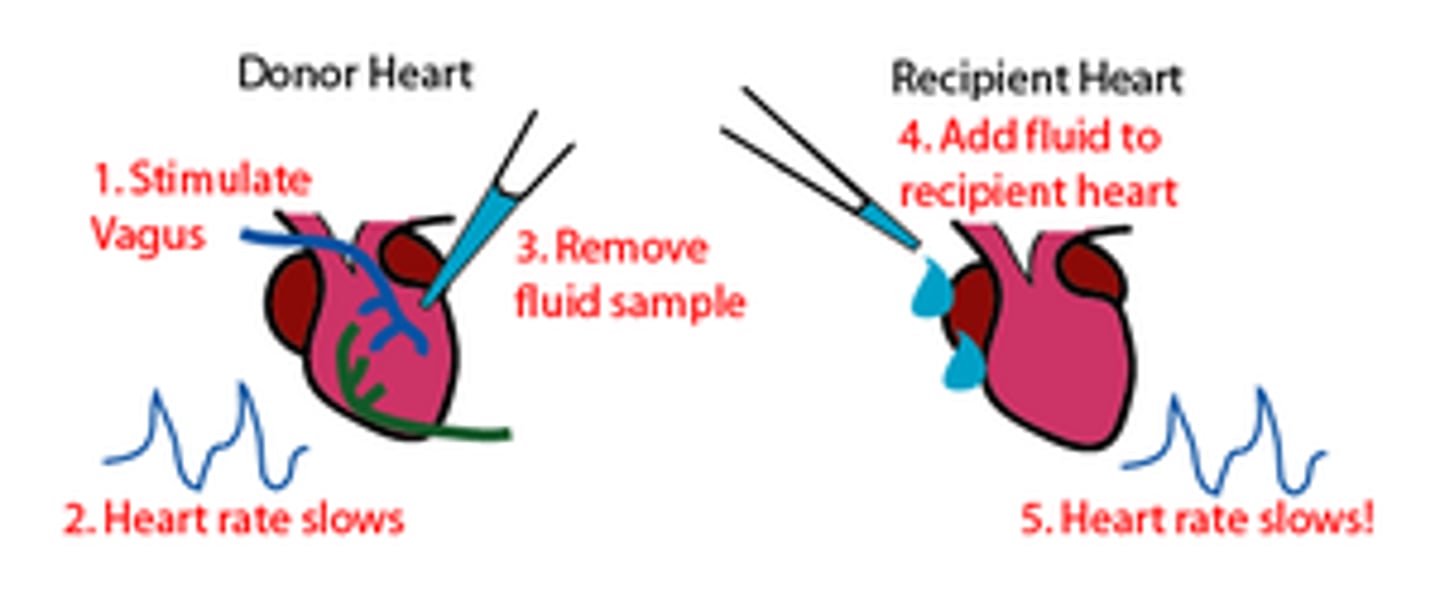
Loewi Experiment
Otto Loewi discovered that nerves release chemicals to control the heart.
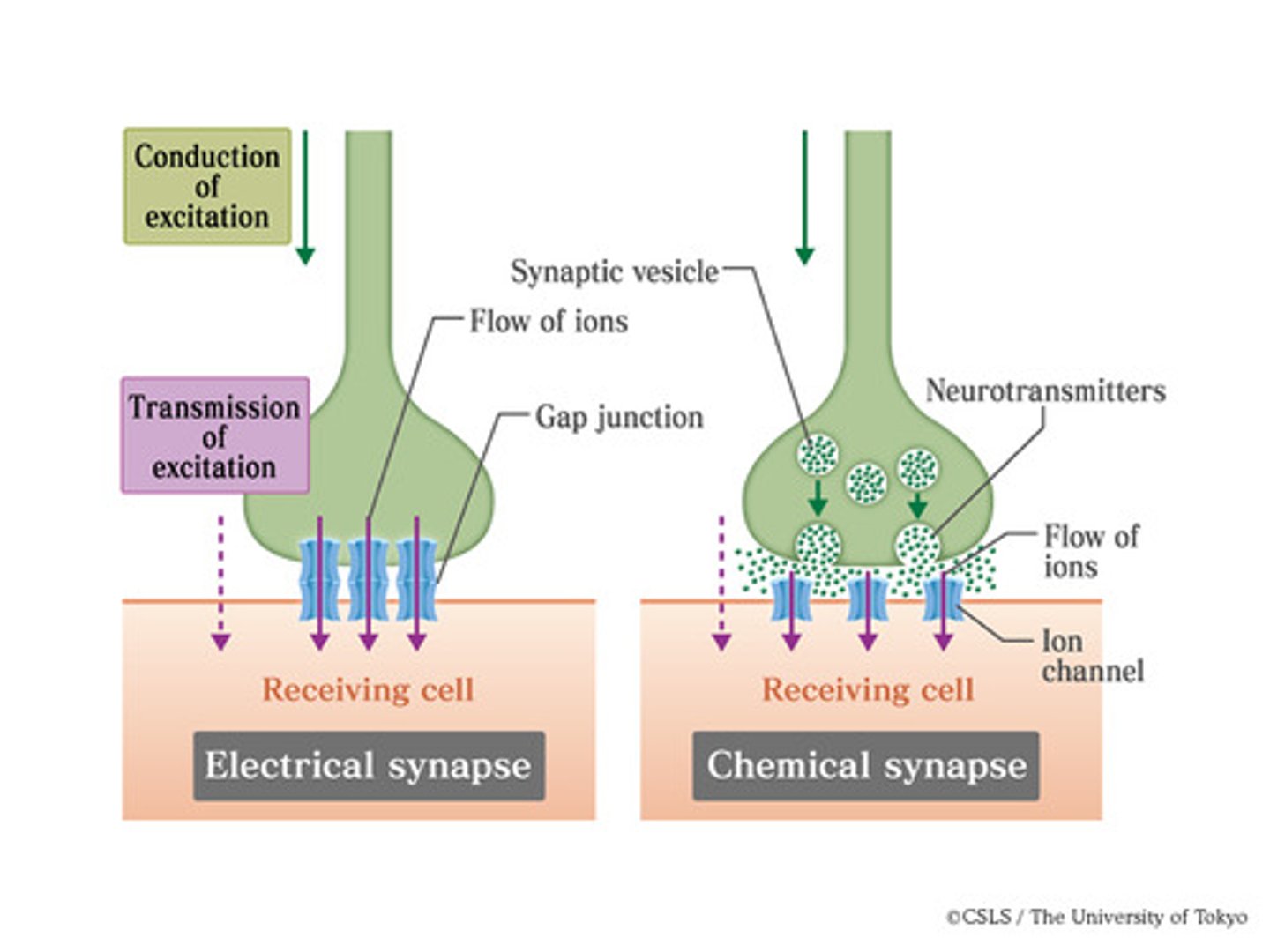
Electrical Synapse
A direct, fast connection between neurons where signals pass through gap junctions (tiny tunnels between cells).
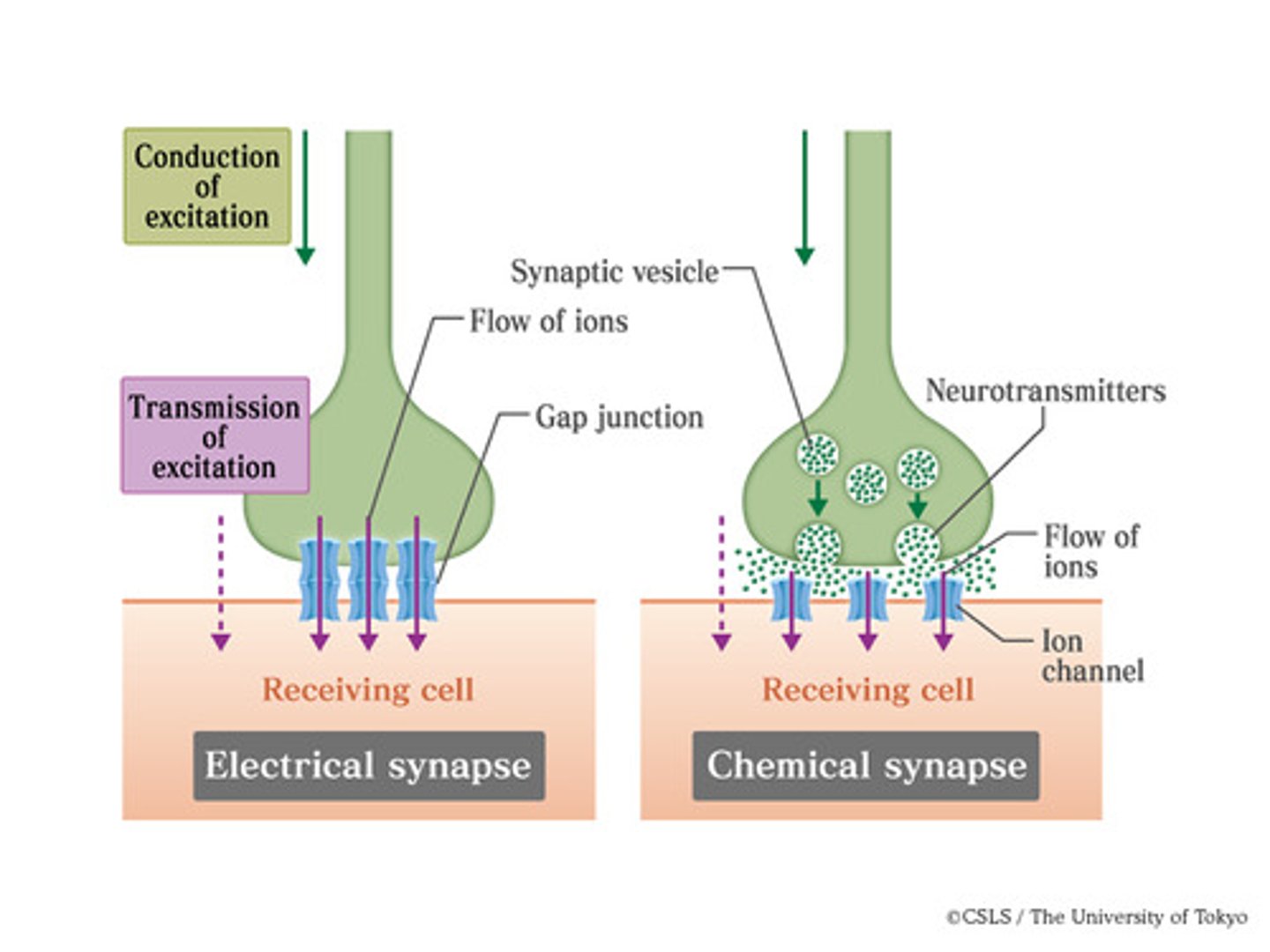
Chemical Synapse
A slower but more flexible way of communication where a neuron releases neurotransmitters to send messages.
Postsynaptic Potential
The change in electrical charge inside the receiving neuron after getting a signal.
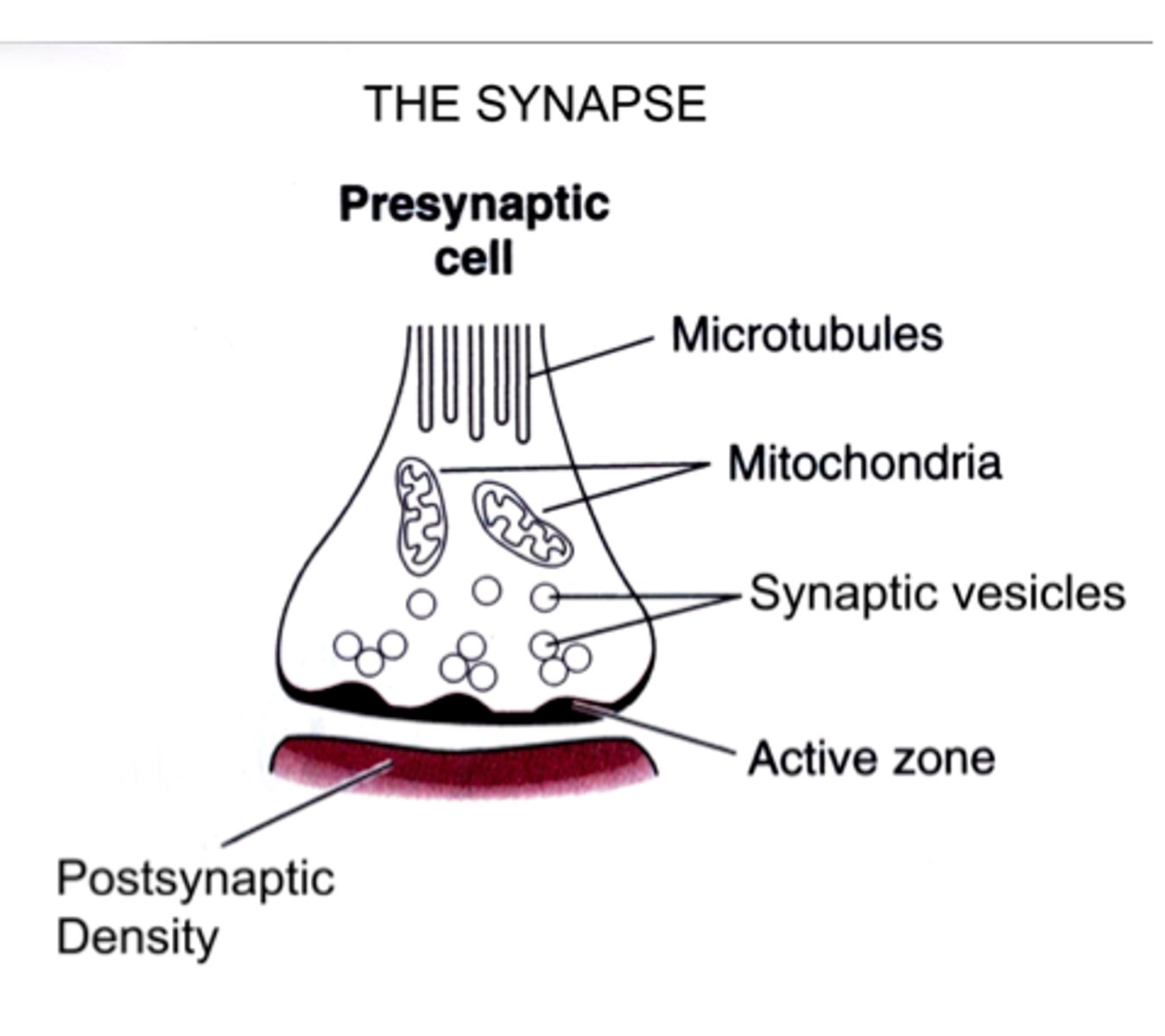
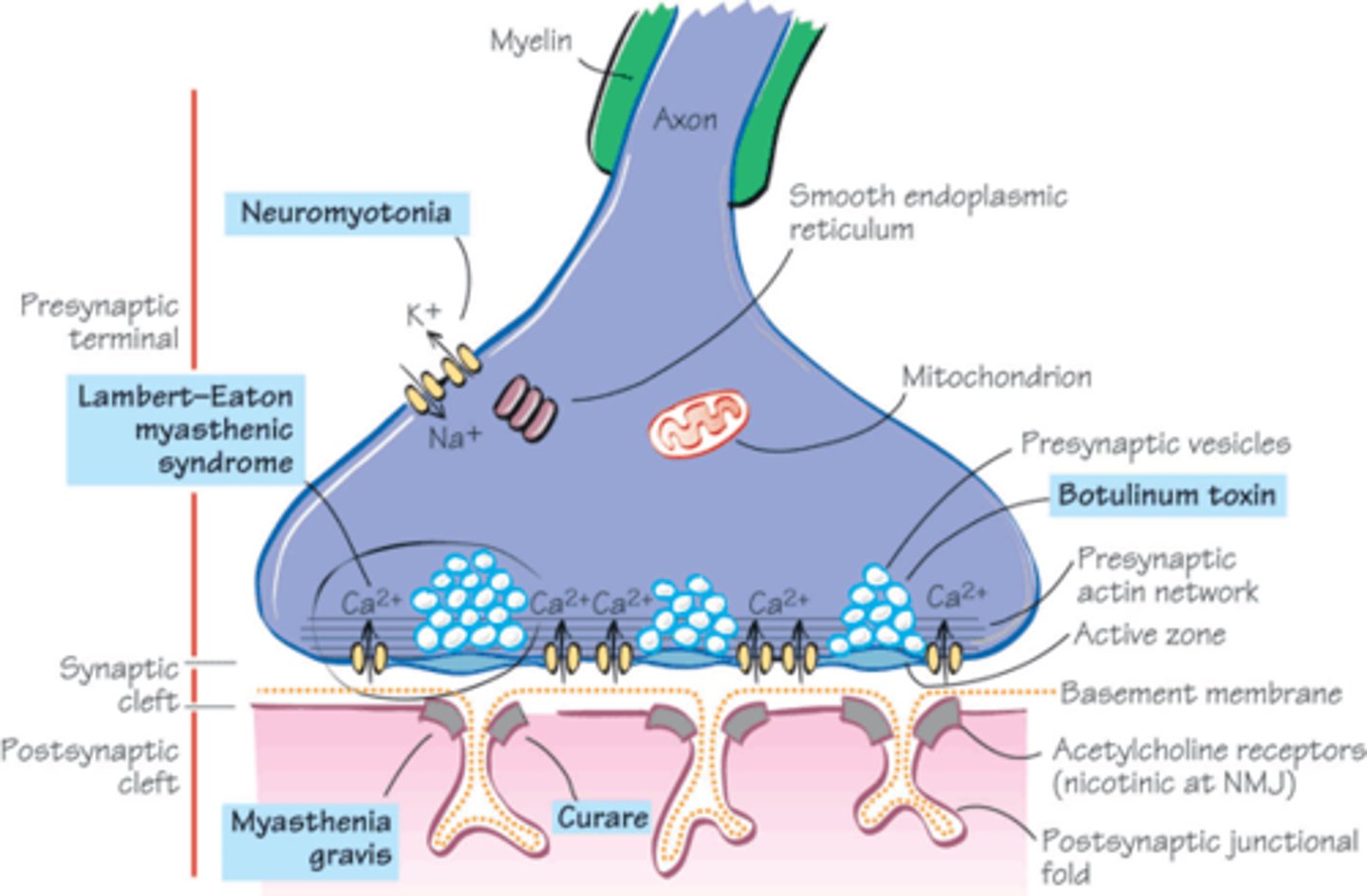
Active Zone
The area in a neuron's axon terminal where neurotransmitters are released.
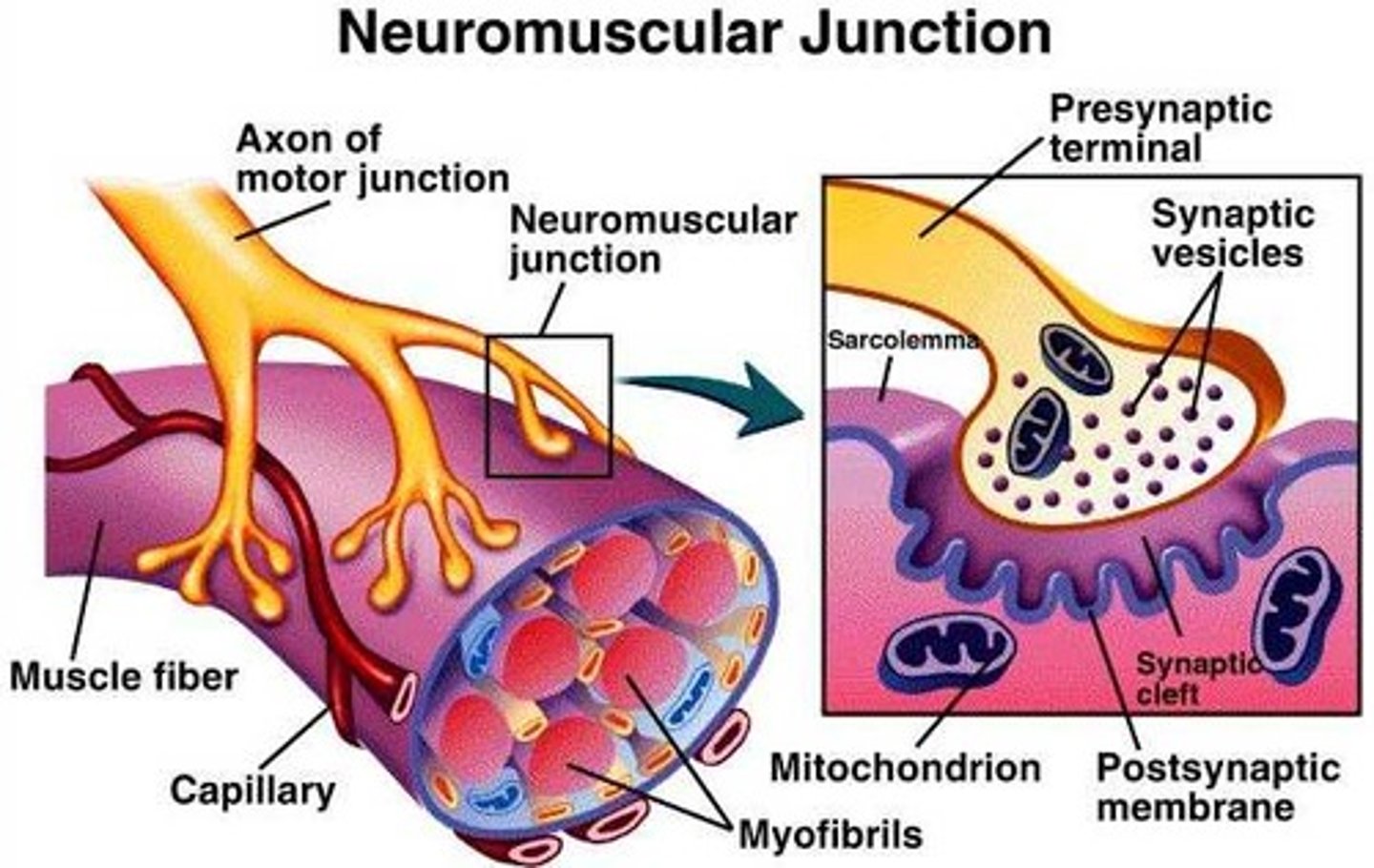
Neuromuscular Junction
The synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle, where signals tell muscles to contract.
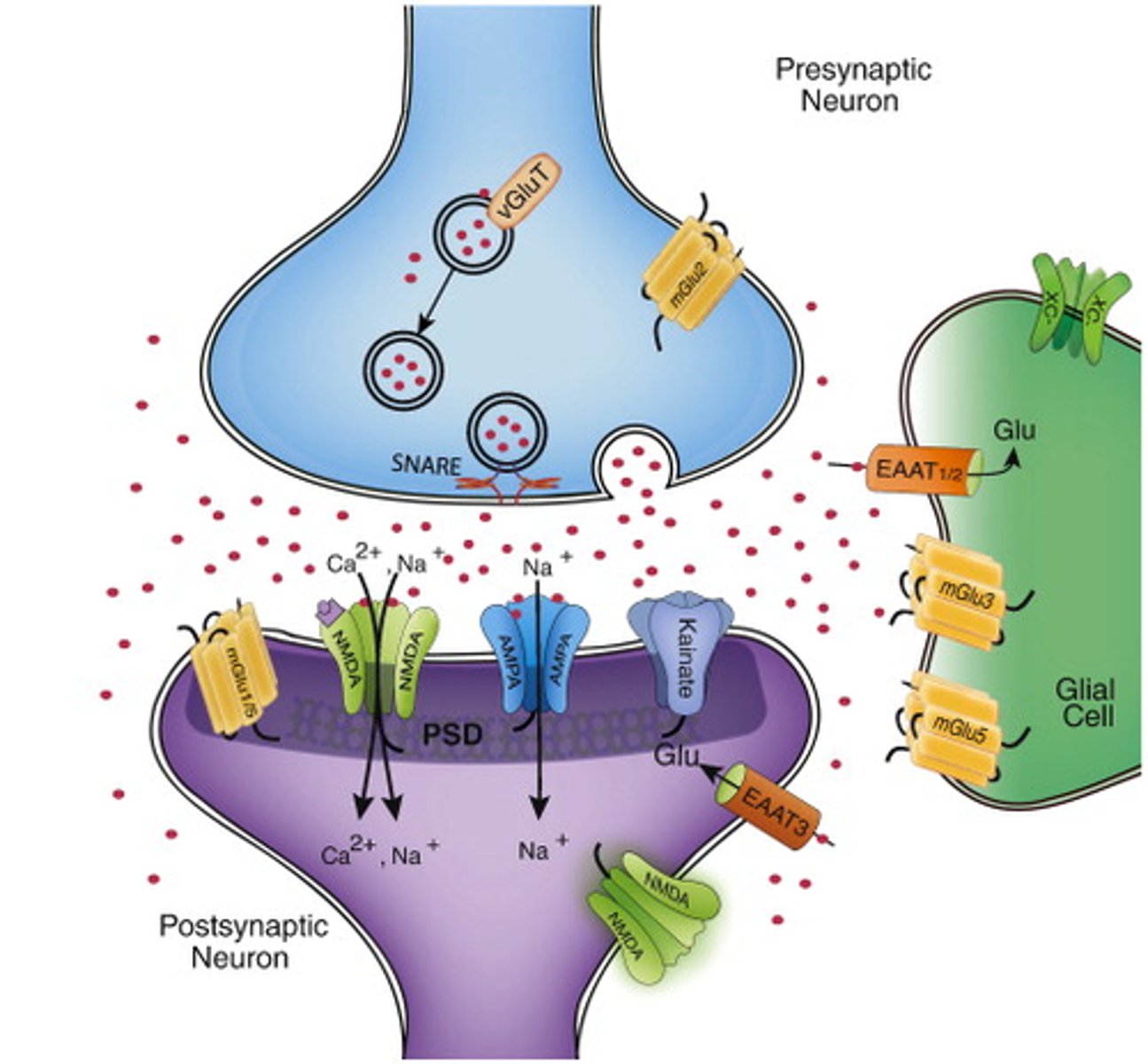
Glutamate
The main excitatory neurotransmitter, helping neurons send signals.
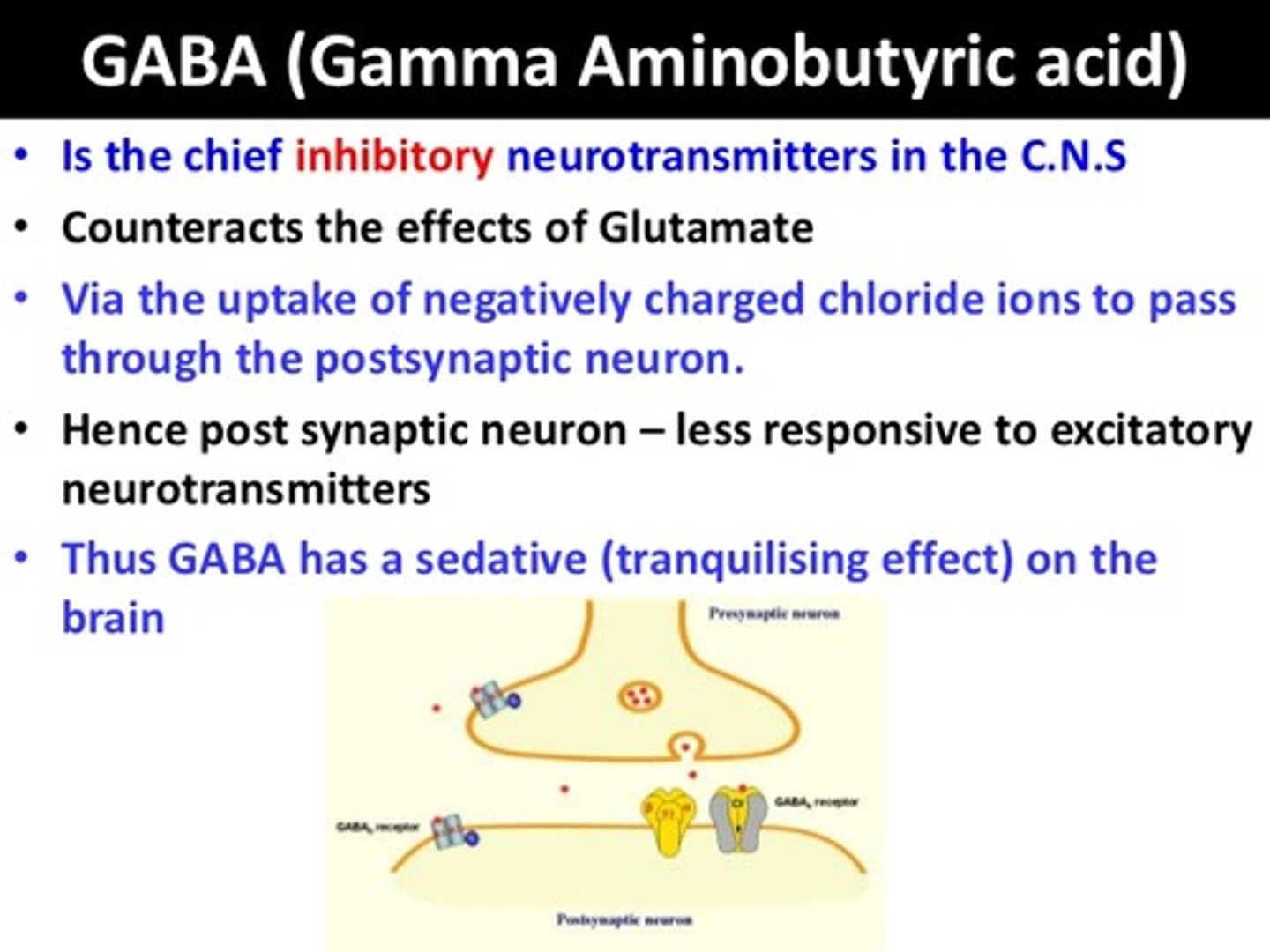
GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid) & Glycine
The main inhibitory neurotransmitters, helping neurons slow down or stop firing.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
A neurotransmitter that helps with muscle movement, learning, and memory.
Transporters
Proteins that move neurotransmitters back into the neuron after they are used.
Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel
A special gate that opens when a neuron is ready to release neurotransmitters, allowing calcium (Ca²⁺) inside.
Exocytosis
The process of releasing neurotransmitters from the neuron.
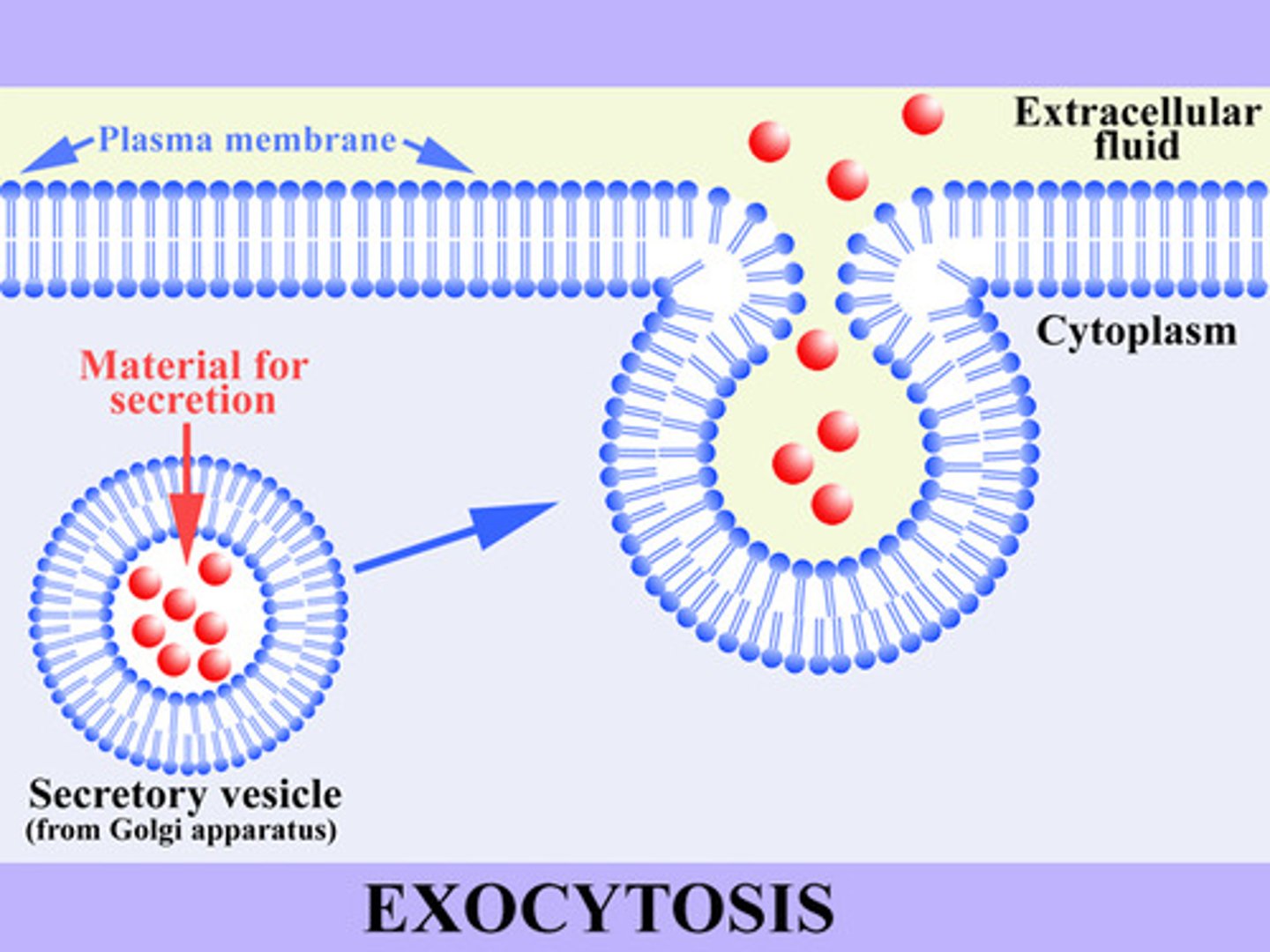
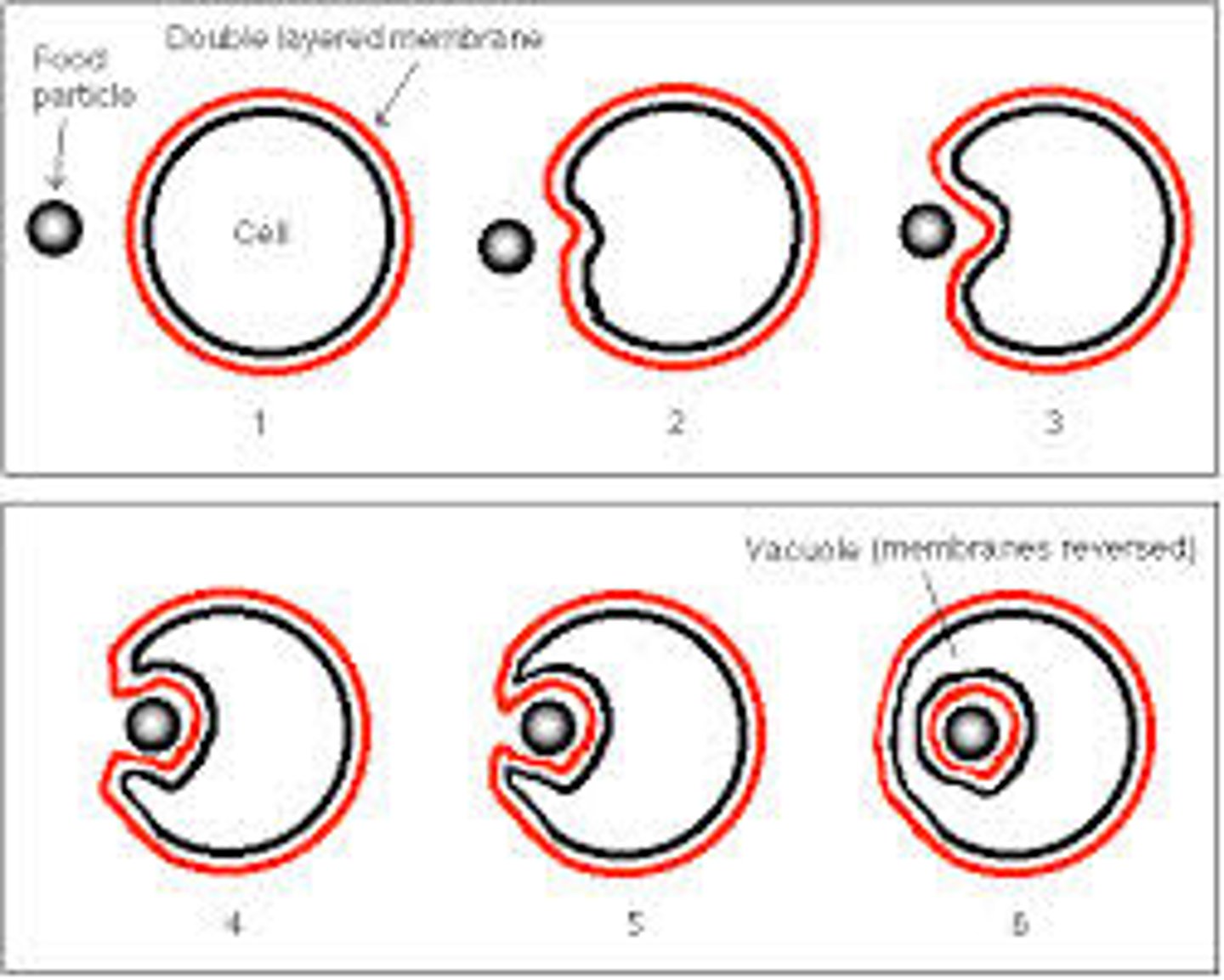
Endocytosis
The process of recycling neurotransmitter vesicles after release.
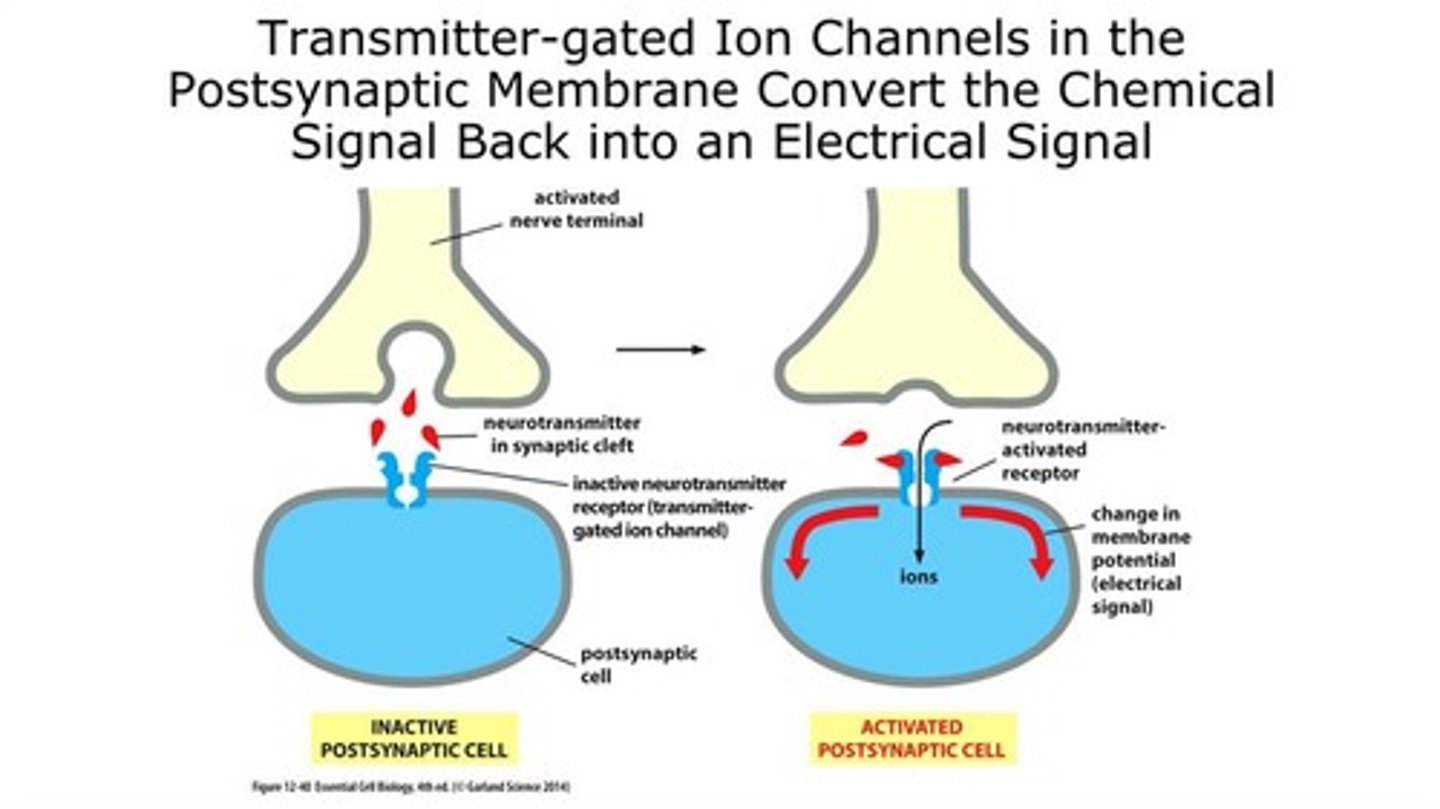
Transmitter-Gated Ion Channels
Special channels that open when a neurotransmitter binds, letting ions in or out.
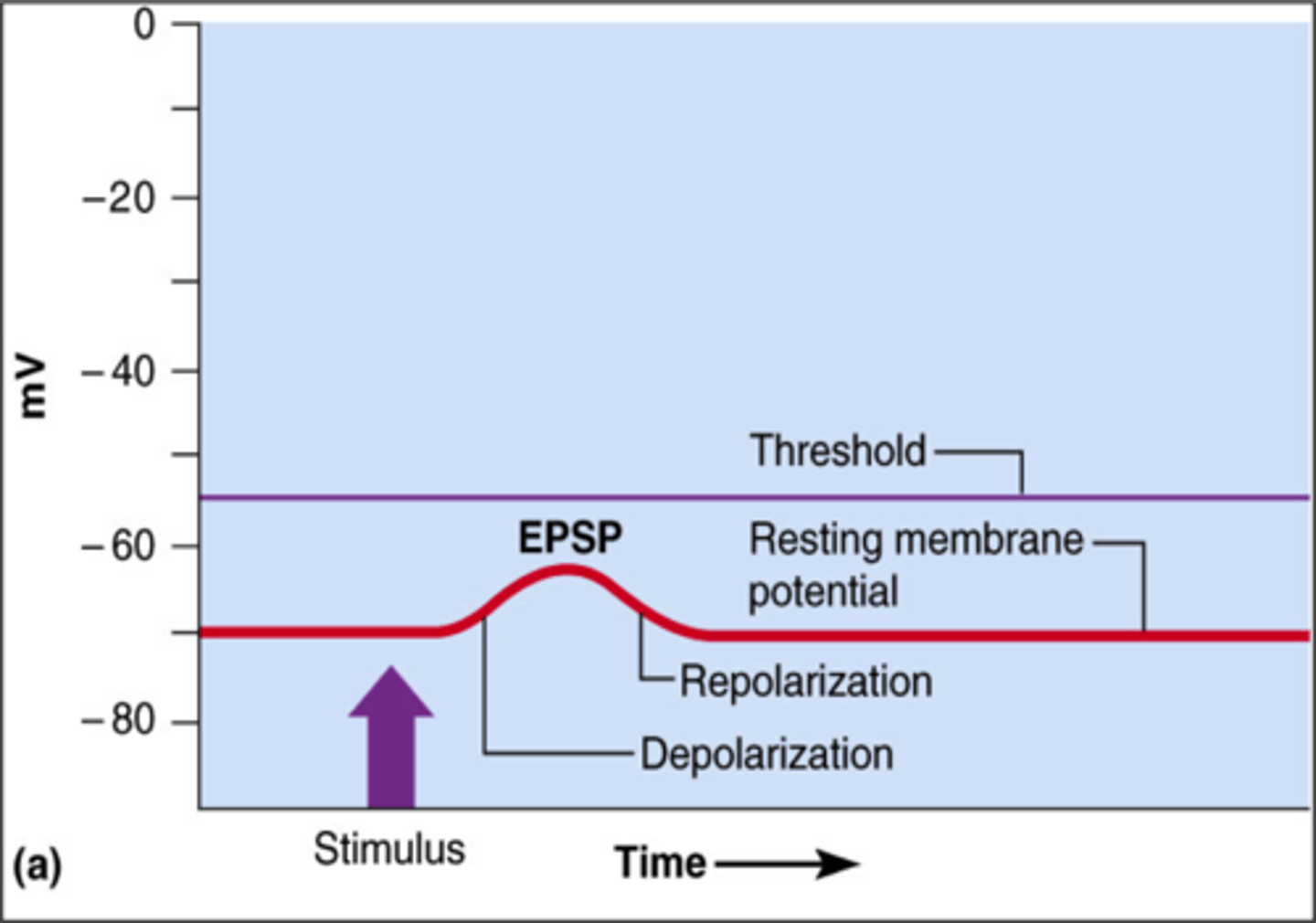
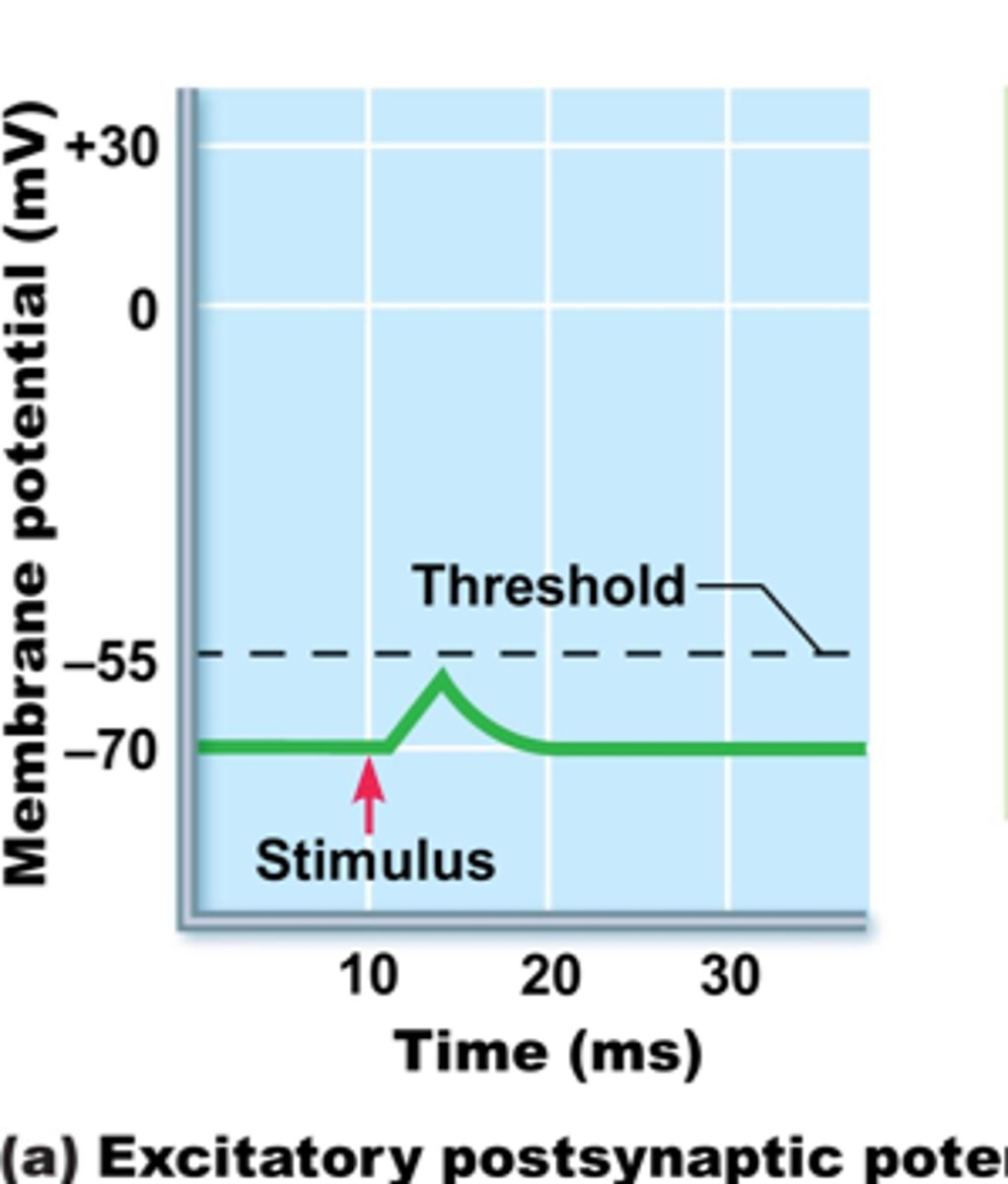
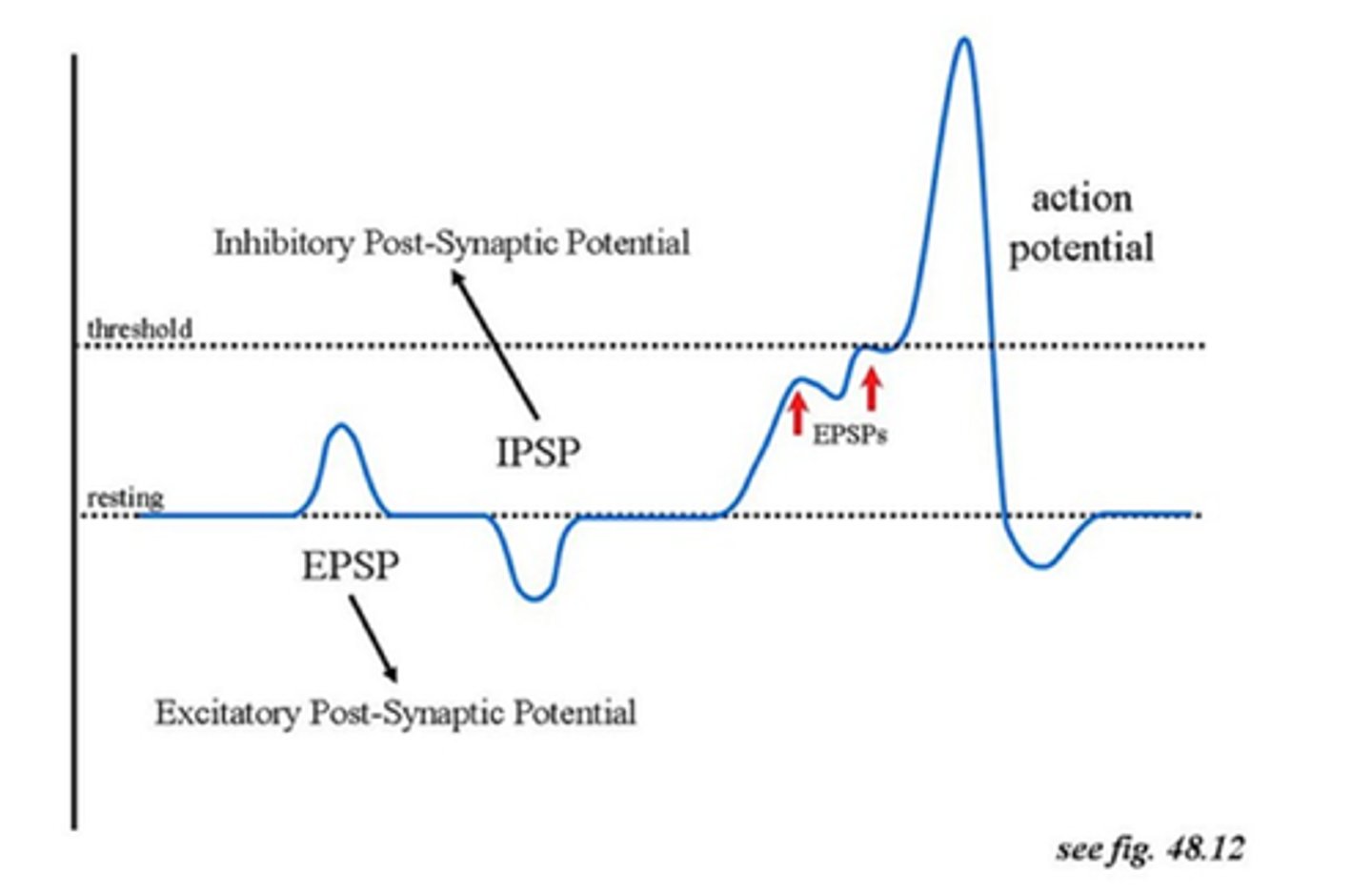
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP)
A signal that makes the next neuron more likely to fire (caused by positive ions entering).
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential (IPSP)
A signal that makes the next neuron less likely to fire (caused by negative ions entering).
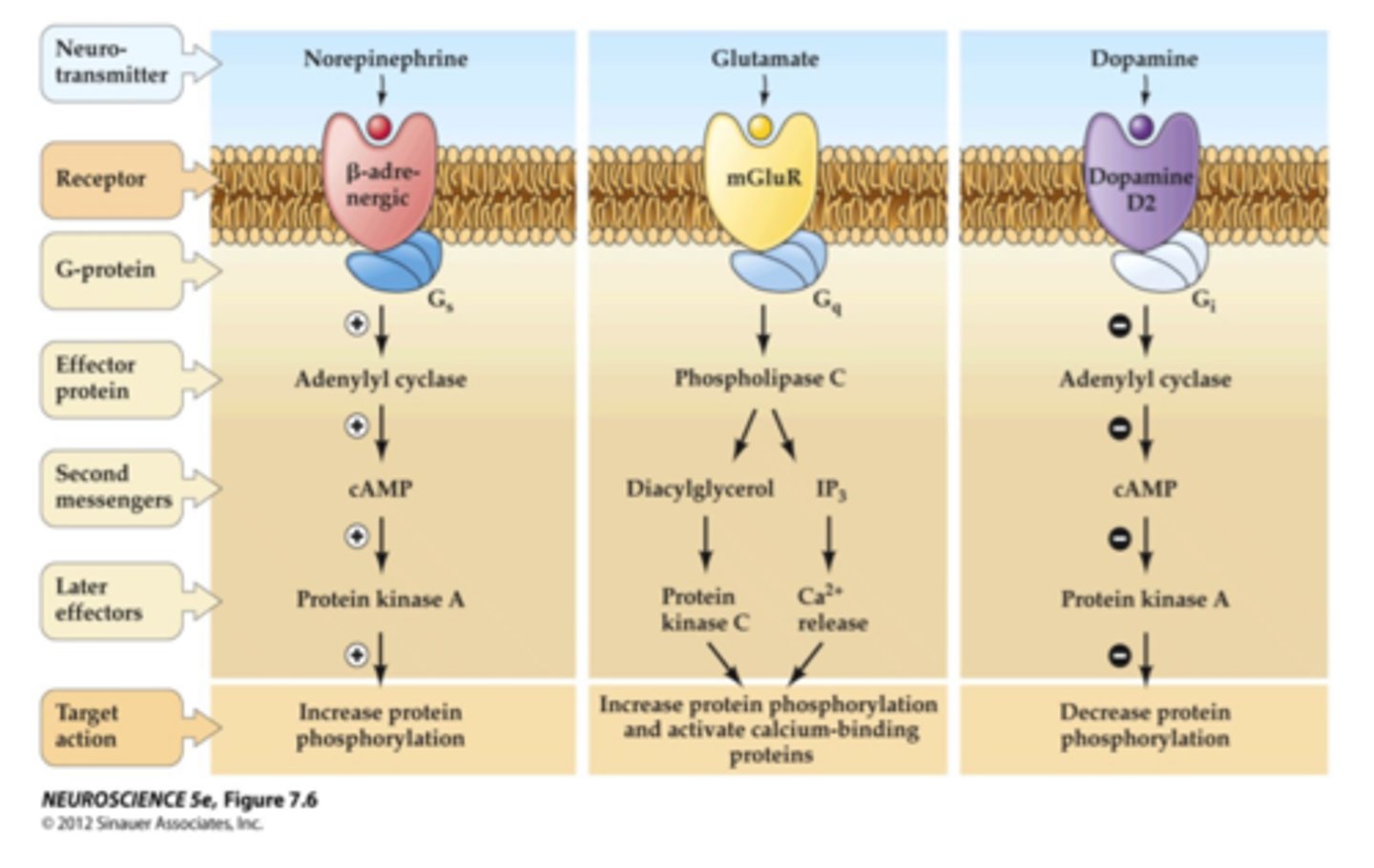
G-Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs)
A type of receptor that starts a slow but long-lasting signal inside the neuron.
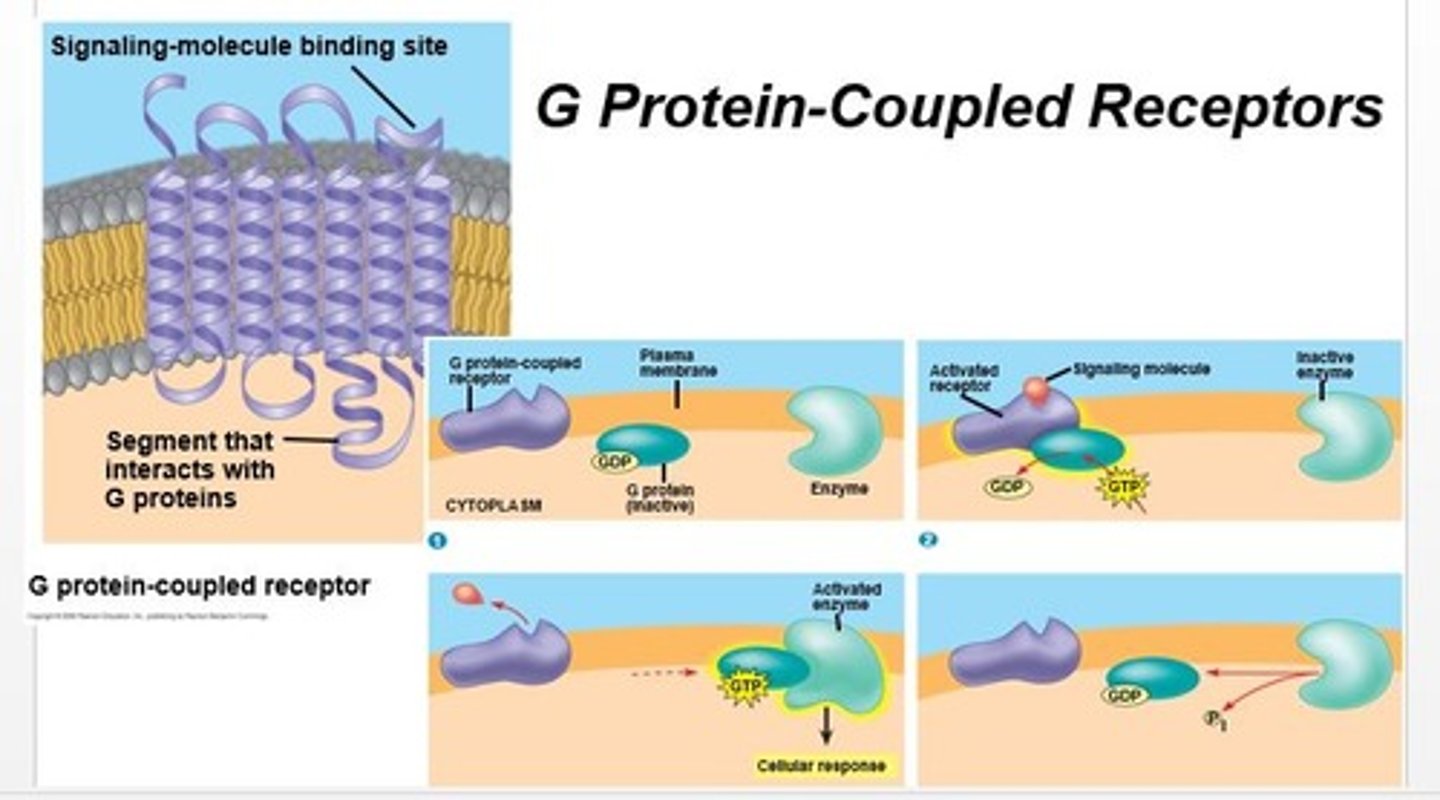
Second Messengers & Metabotropic Receptors
These help relay signals inside the cell when GPCRs are activated.