Chemistry - chemical change ALL
1/114
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Metal
An element that forms positive ions
pH of metal oxide
Basic
Non-metal
Does not form positive ions
pH of non-metal oxide
Acidic
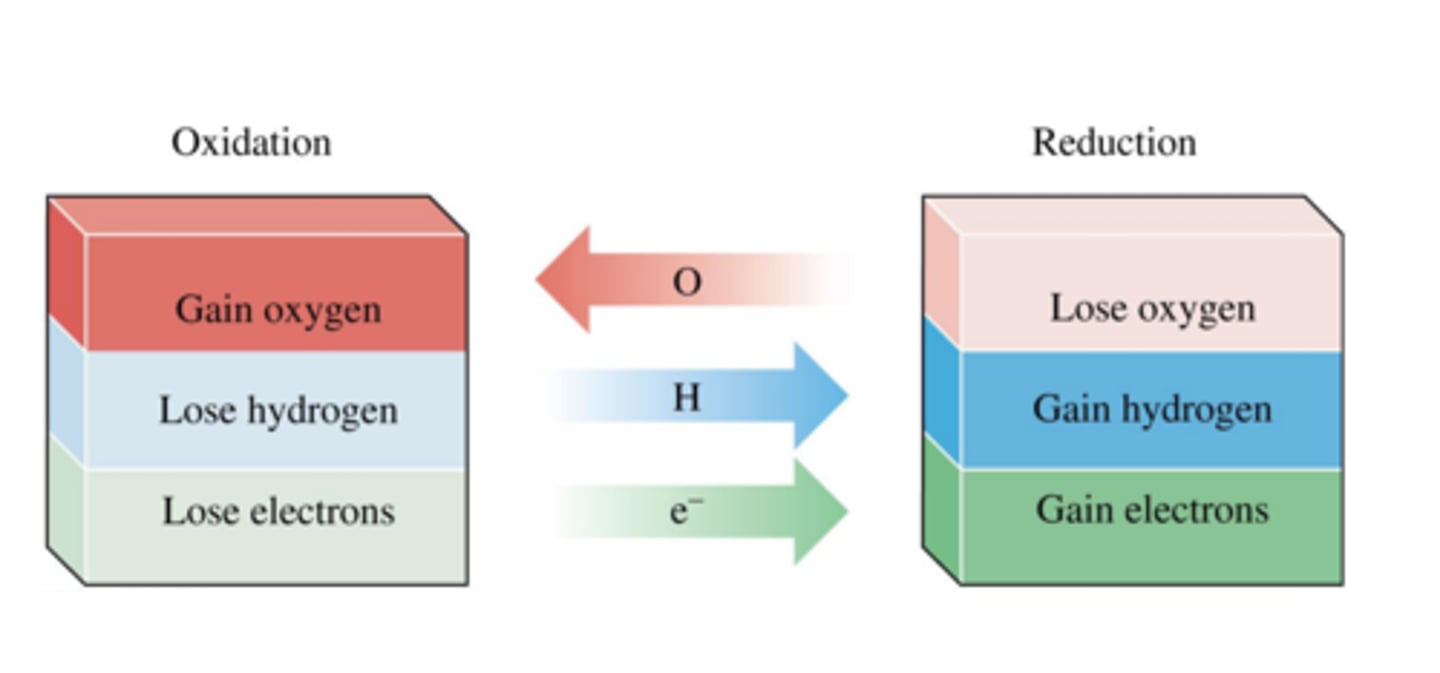
Reduction in terms of oxygen
Loss of oxygen
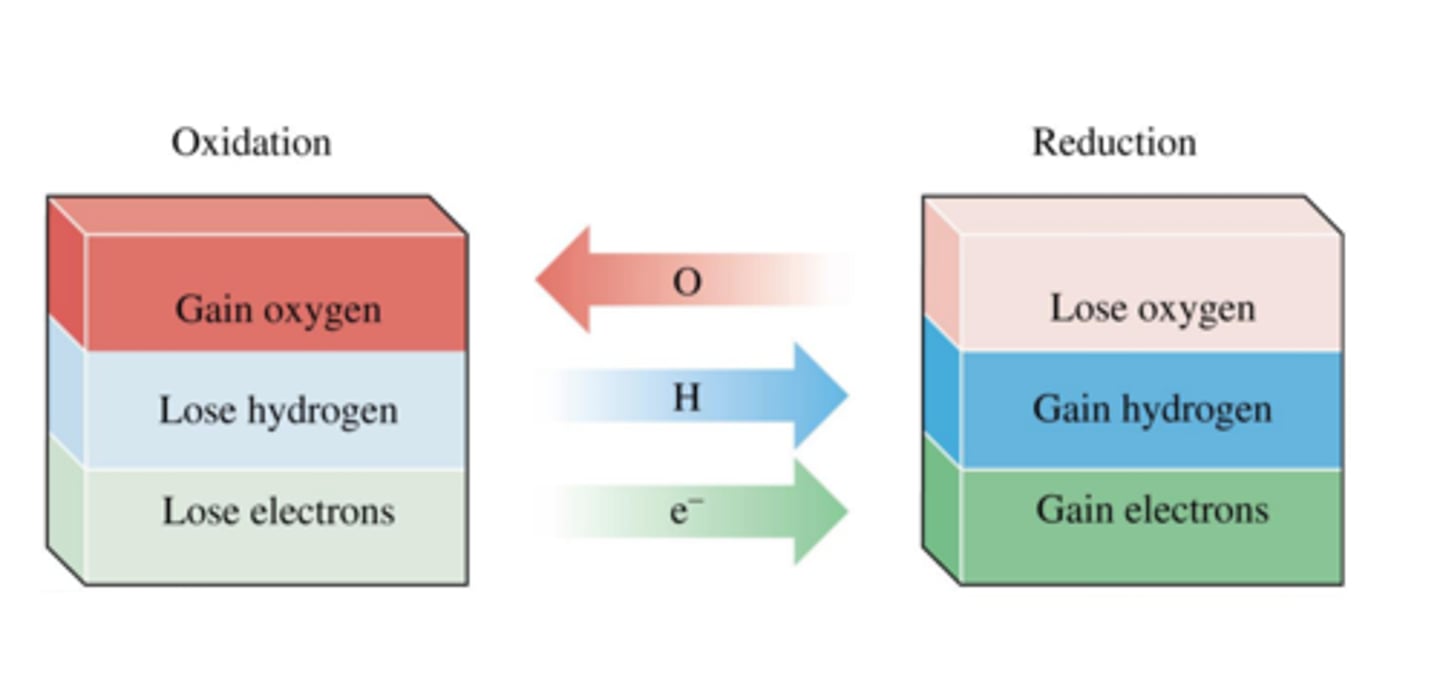
Oxidation in terms of oxygen
Gain of oxygen
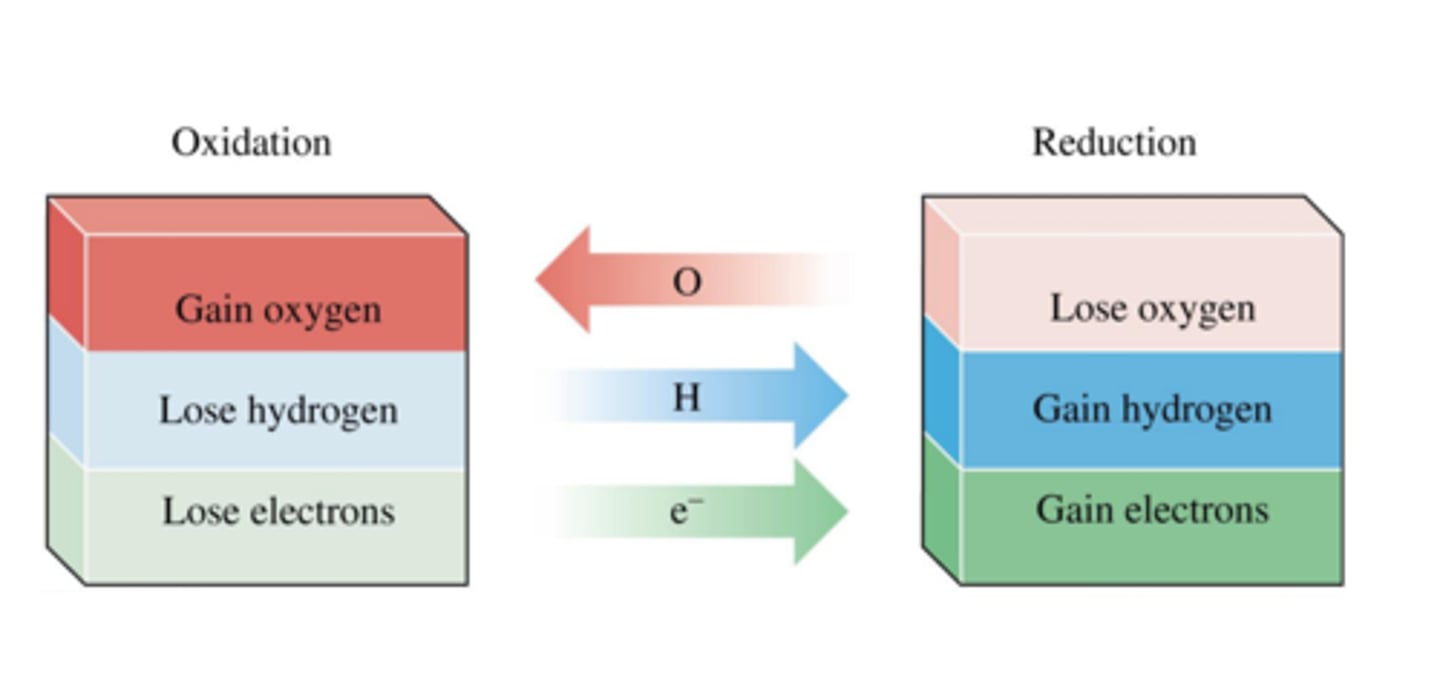
Oxidation in terms of electrons
Loss of electrons
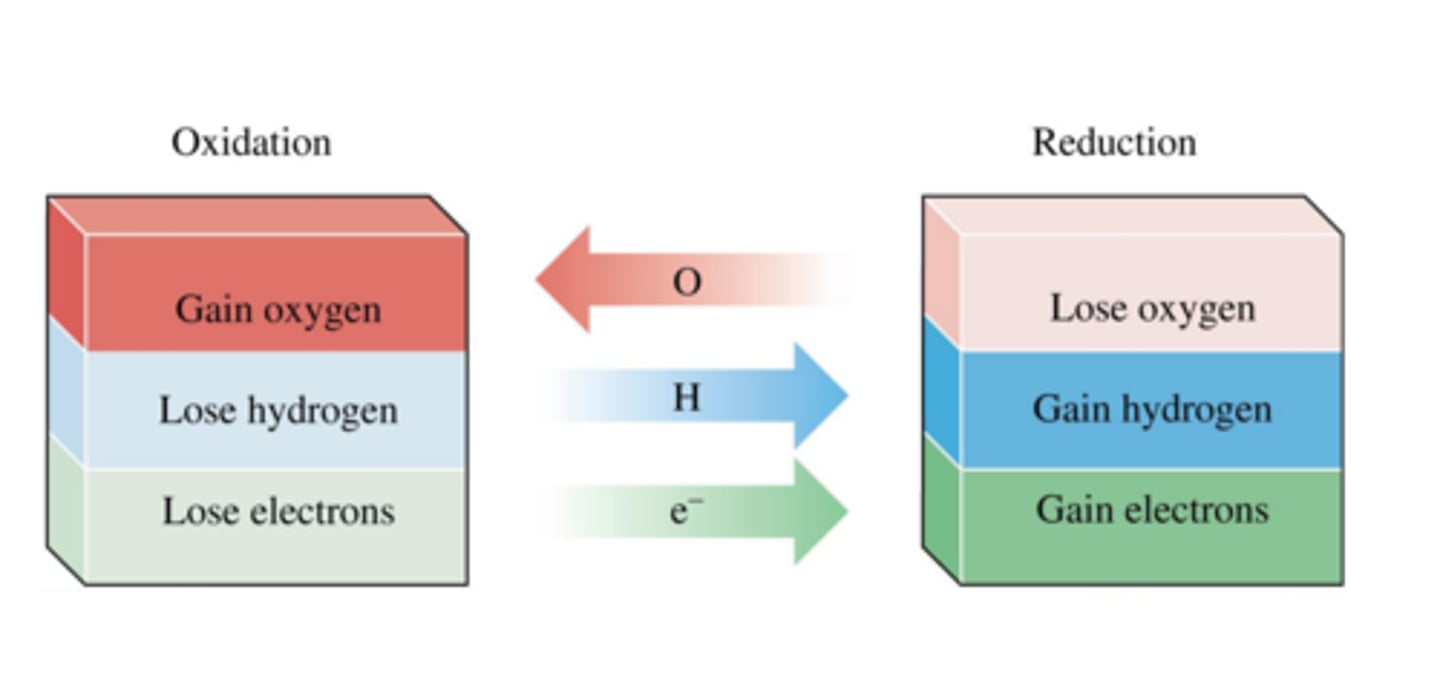
Reduction in terms of electrons
Gain of electrons
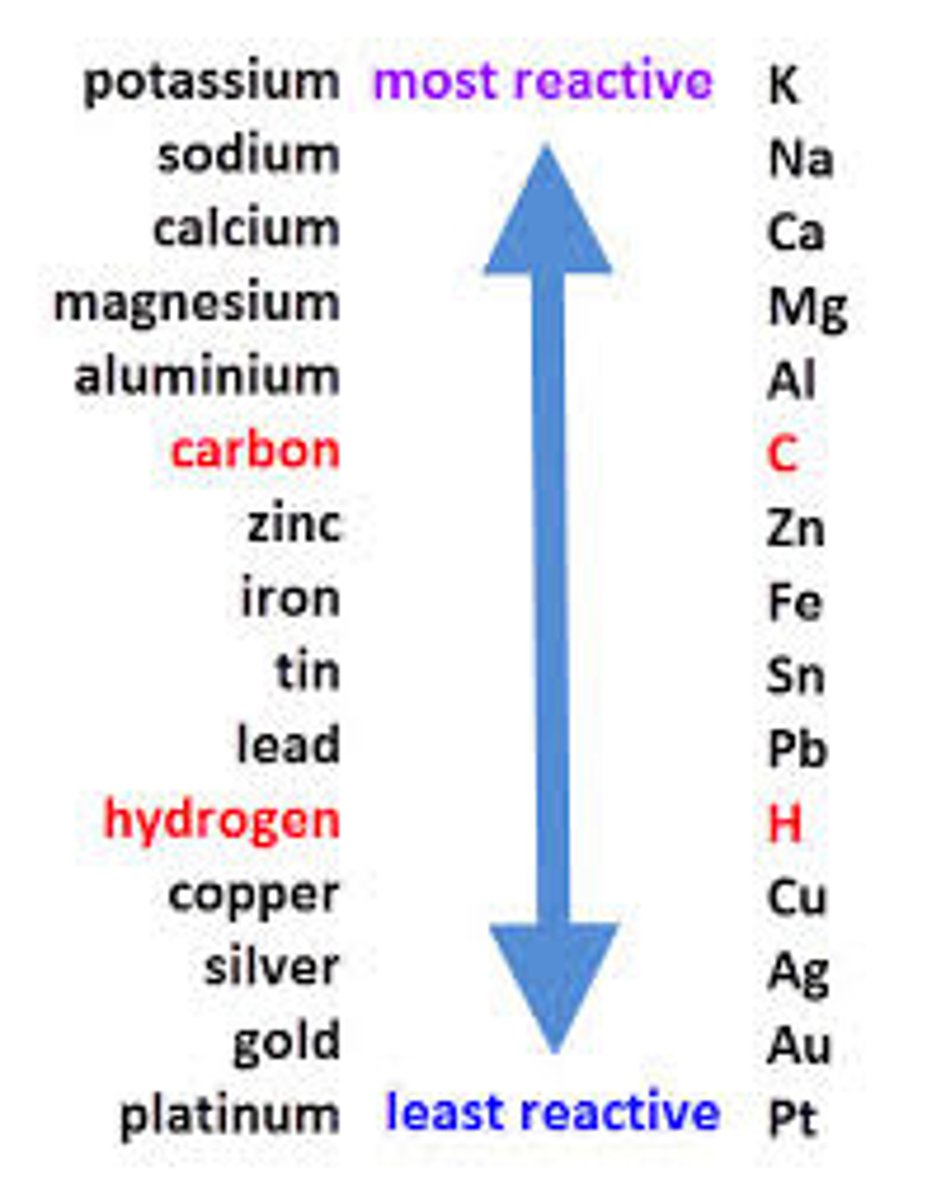
Reactivity
The tendency of a metal to form positive ions
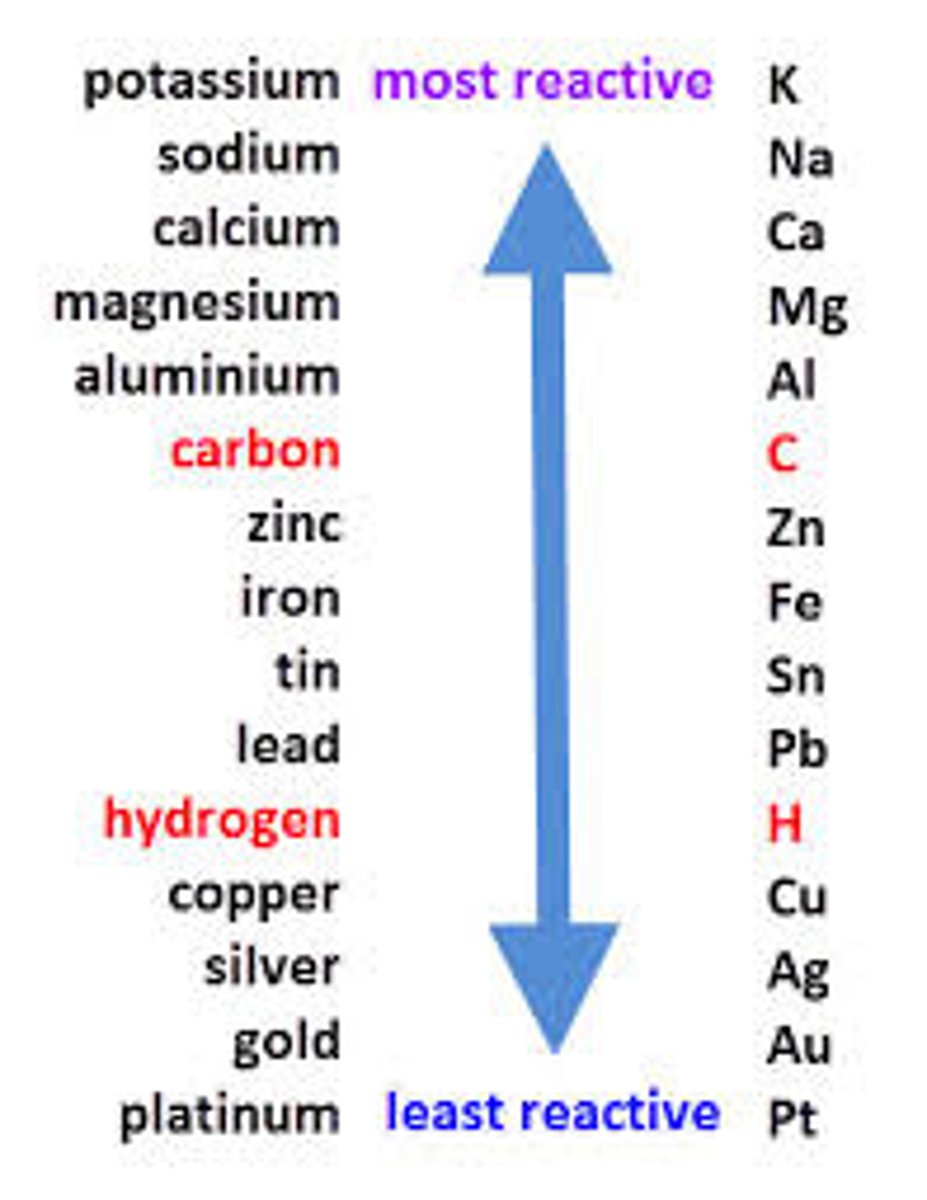
Unreactive metal
Rarely form metal ions

Reactive metals
Readily form metal ions
Reactivity series
A list of metals which shows them in order of their reactivity, with the most reactive at the top.
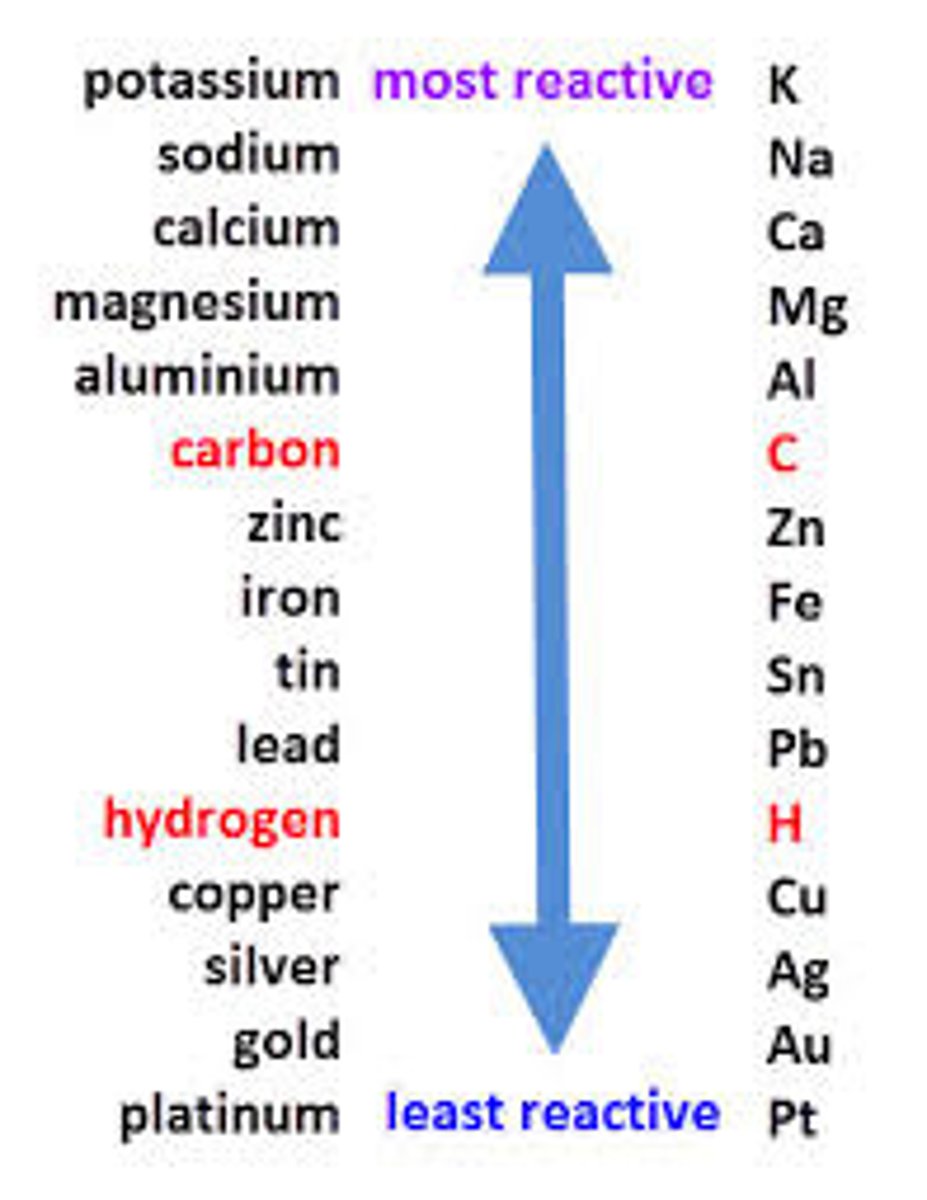
Native metal
Metal found uncombined in the earth - gold, copper, platinum

Ore
a rock that contains enough metal to make it profitable to extract

Extraction of metals
Producing metals from their ore
Extraction of metals less reactive than carbon
Reduction using carbon
Extraction of metals more reactive than carbon
Electrolysis
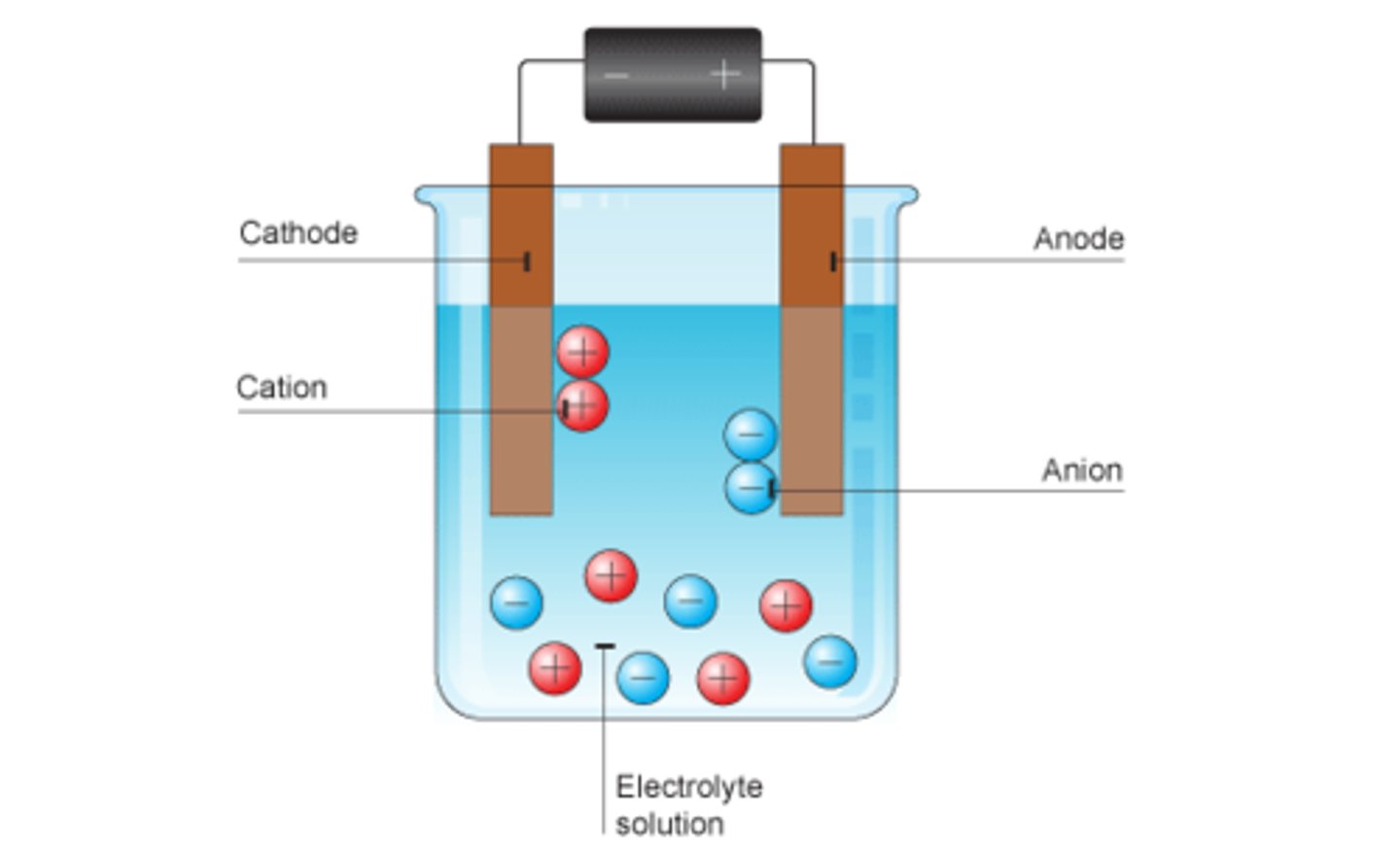
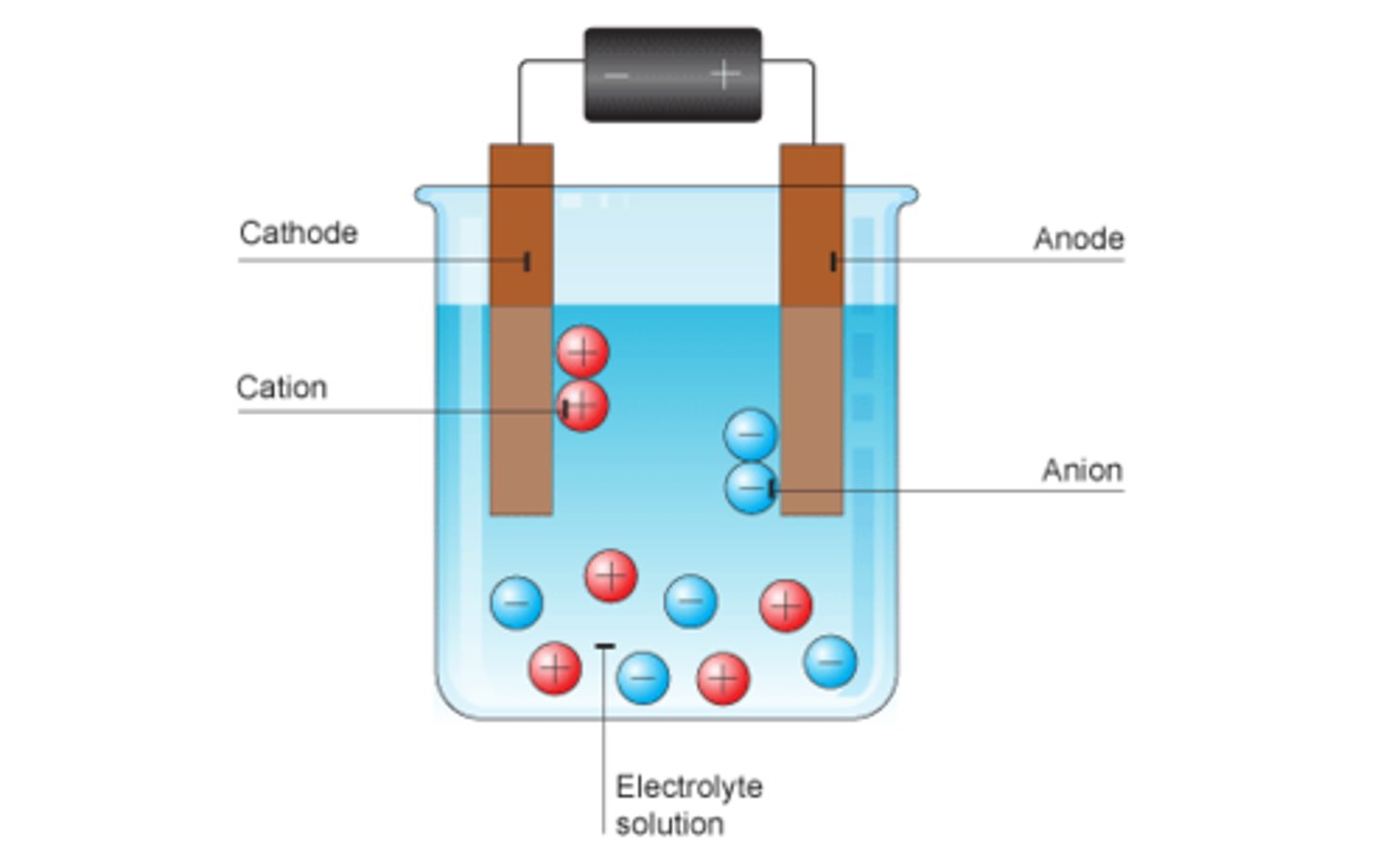
Electrolysis
A process by which an electric current splits up a chemical
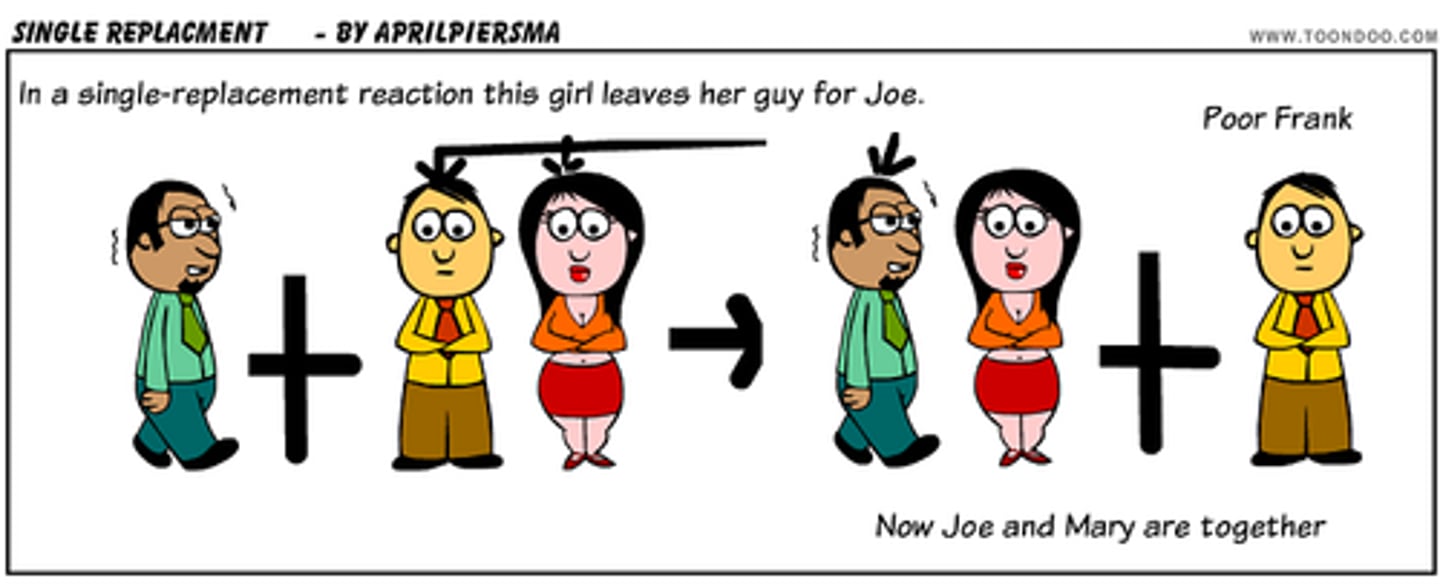
Displacement reaction
A reaction in which a more reactive element replaces a less reactive element in a compound
Metal + Water -->
Metal hydroxide + Hydrogen
Metal + Oxygen -->
Metal oxide

Metal + Acid -->
Salt + Hydrogen
Acid
A substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution.
Base
A substance that reacts with an acid and neutralises it
Alkali
A soluble base, that produces OH- ions in solution
Types of chemicals that are bases
Metal oxides, metal hydroxides, metal carbonates, ammonia
Types of chemicals that are alkalis
Metal hydroxides, ammonia
Strong acids
Acids that fully ionise in water
Weak acids
Acids that only slightly ionise in aqueous solution
Ionise
Split into ions
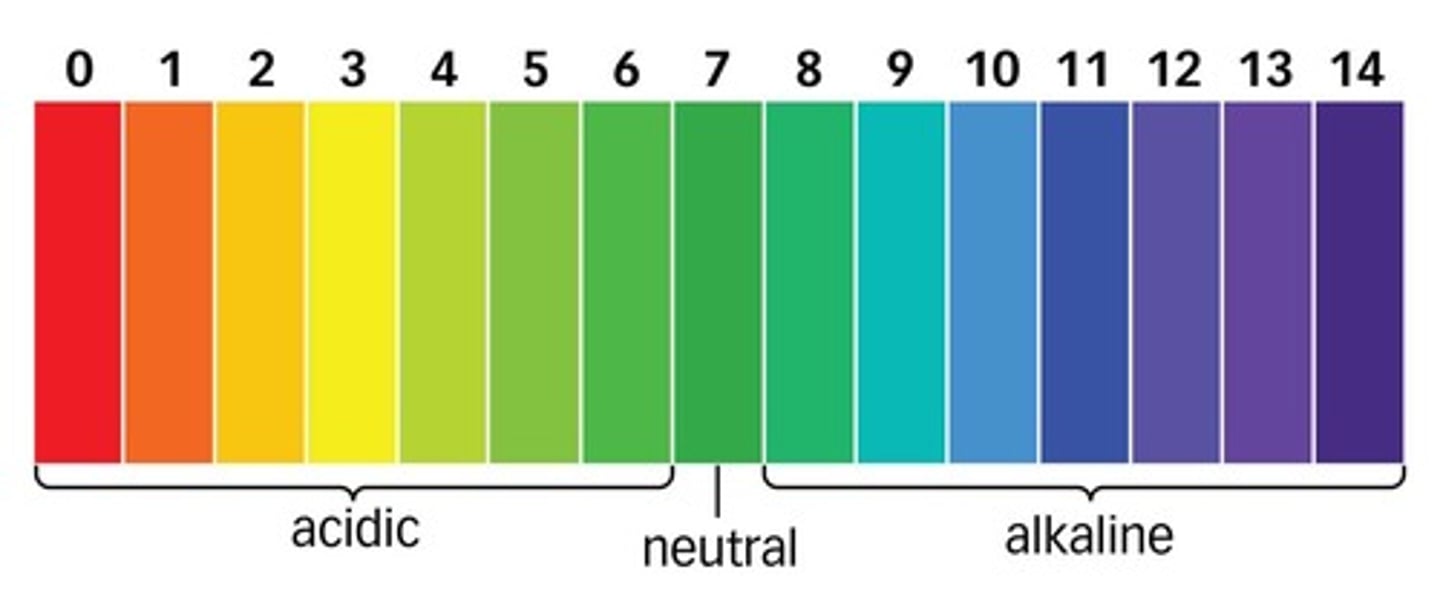
pH
A measure of H+ concentration
Ions produced by acids
H+
Ions produced by alkalis
OH-
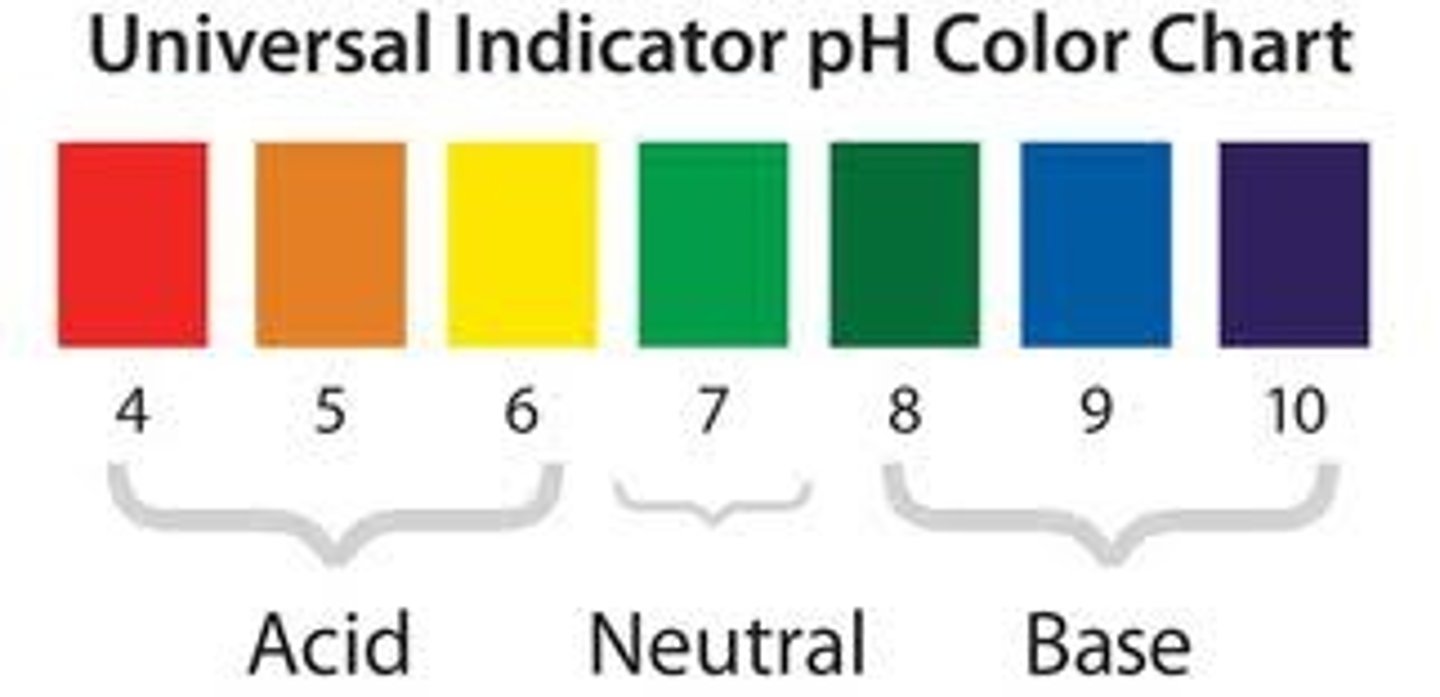
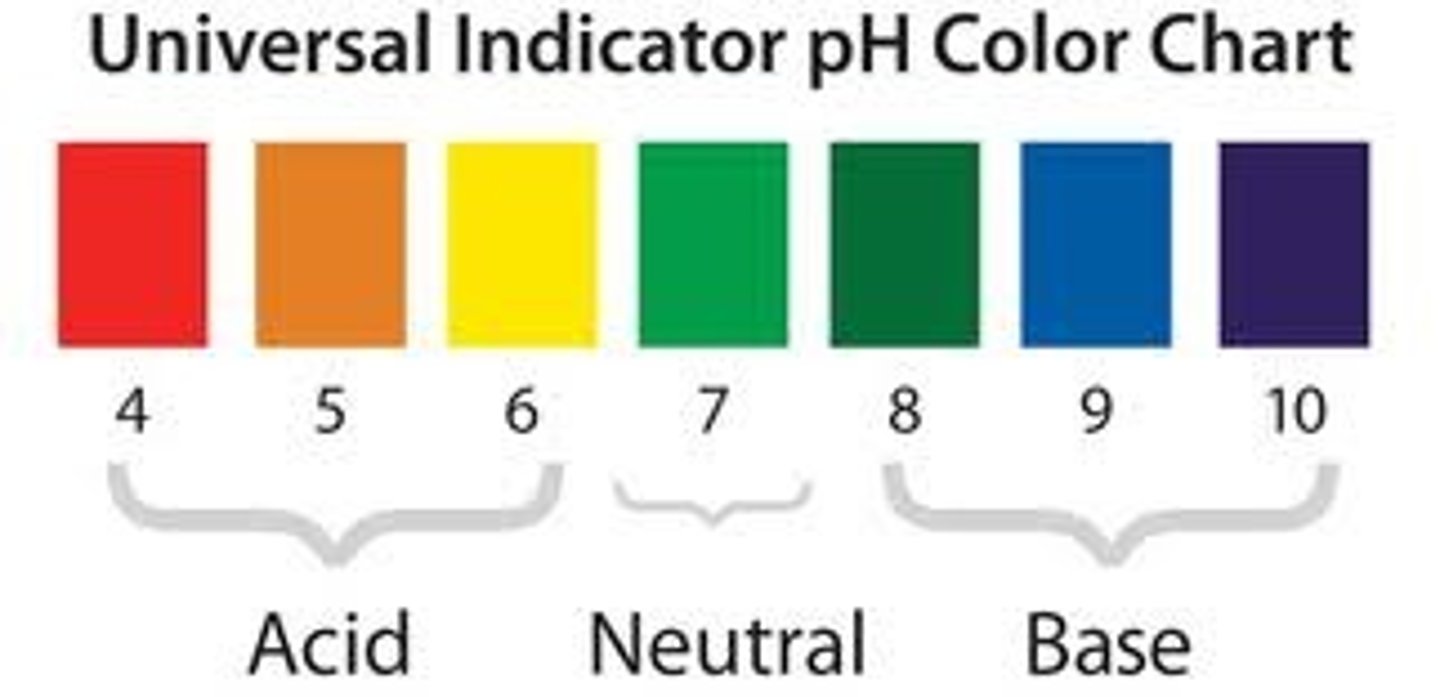
Neutral pH
7

pH of acids
less than 7

pH of alkalis
more than 7

Neutralisation reaction
The reaction of an acid and a base forming a salt and water
Ionic equation for an acid and an alkali
H+(aq) + OH-(aq) --> H2O(l)
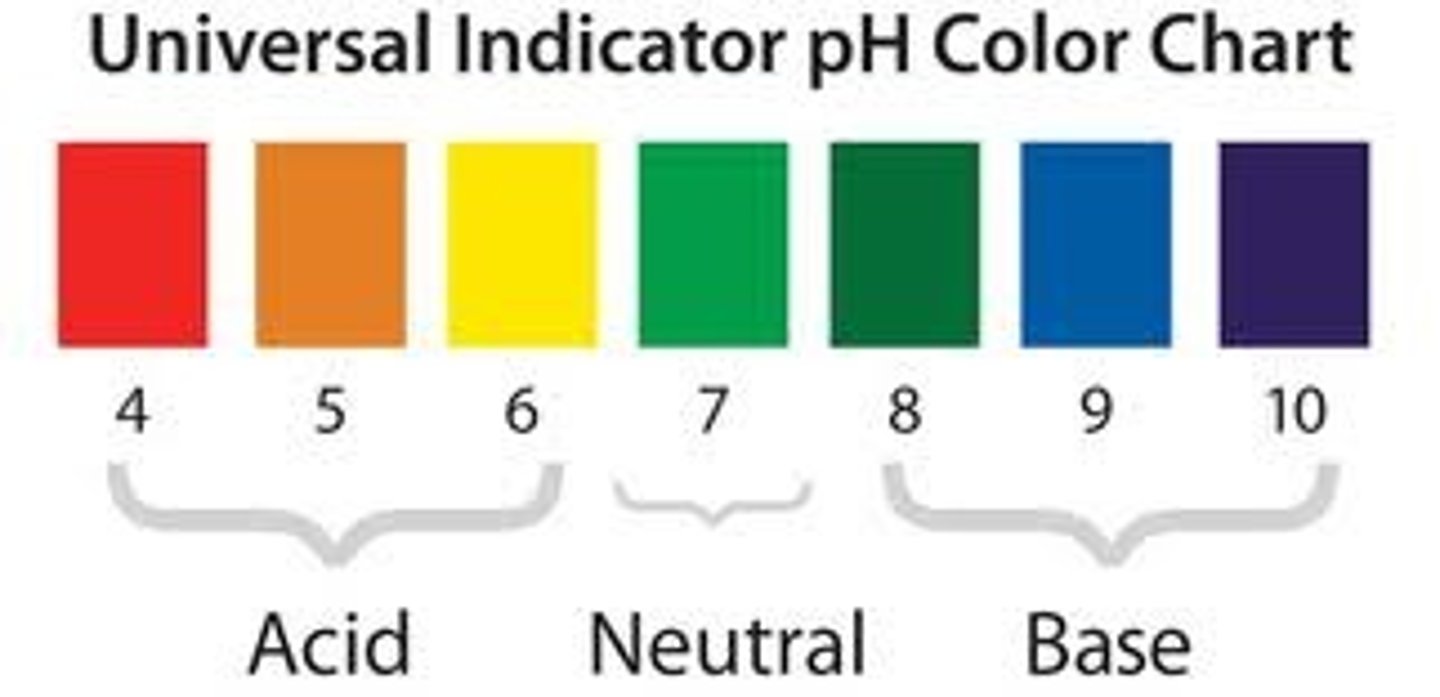
Universal indicator
An indicator with a different colour for each pH value.
If pH decreases by 1
hydrogen ion concentration increases x10
At pH 7
concentration of H+ = concentration of OH-
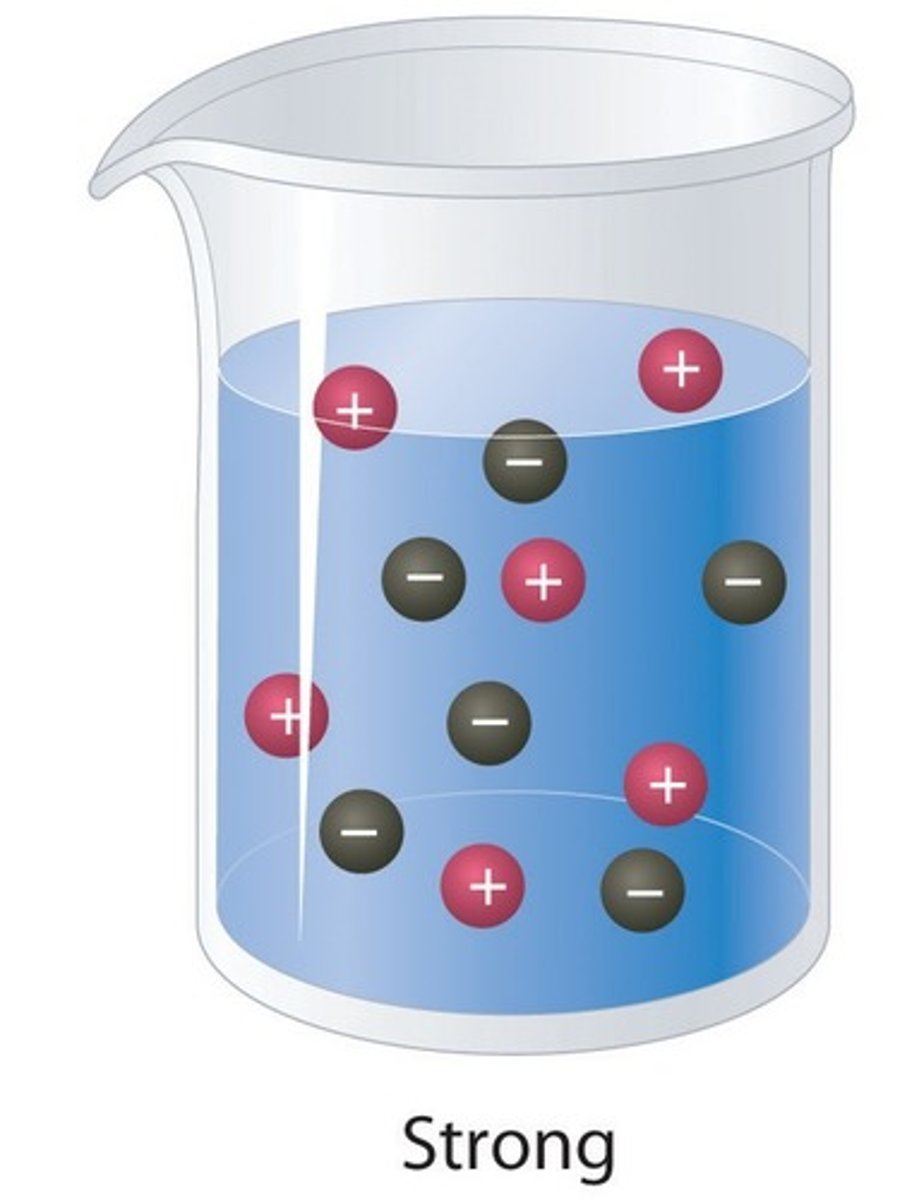
Strong acid
An acid that ionises completely in water
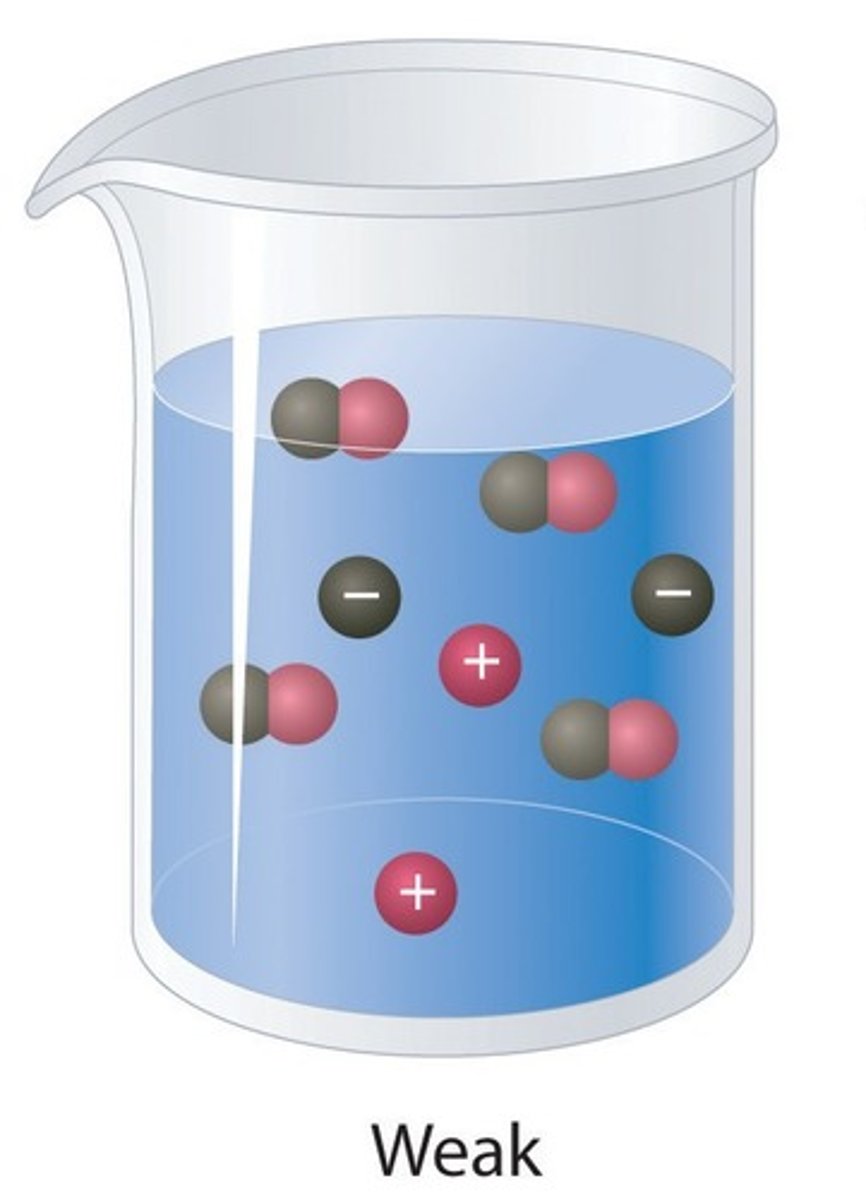
Weak acid
An acid that only partially ionises in water
Metal + Acid -->
Salt + hydrogen
Acid + Base -->
Salt + water
Acid + Carbonate -->
Salt + water + carbon dioxide
Hydrochloric acid
HCl
Sulfuric acid
H2SO4
Nitric acid
HNO3
Type of salt produced by hydrochloric acid
Metal chloride
Type of salt produced by sulfuric acid
Metal sulfate
Type of salt produced by nitric acid
Metal nitrate
Acid
A substance that increases the H+ ion concentration of a solution
Base
A substance that reacts with an acid and neutralises it
Alkali
A soluble base, that produces OH- ions in solution
Types of chemicals that are bases
Metal oxides, metal hydroxides, metal carbonates, ammonia
Types of chemicals that are alkalis
Metal hydroxides, ammonia
Neutralisation reaction
The reaction of an acid and a base forming a salt and water
Ionic equation for neutralisation
H+ + OH- --> H2O
Substance reduced in metal acid reaction
Hydrogen
Substance oxidised in metal acid reaction
Metal
Ions in water
H+ and OH-
H+ is attracted to
Cathode
Discharge of H+
2H+ +2e- --> H2
OH- is attracted to
Anode
Discharge of OH-
4OH- --> O2 + 2H2O + 4e-
Discharged at the cathode in solution
Least reactive element
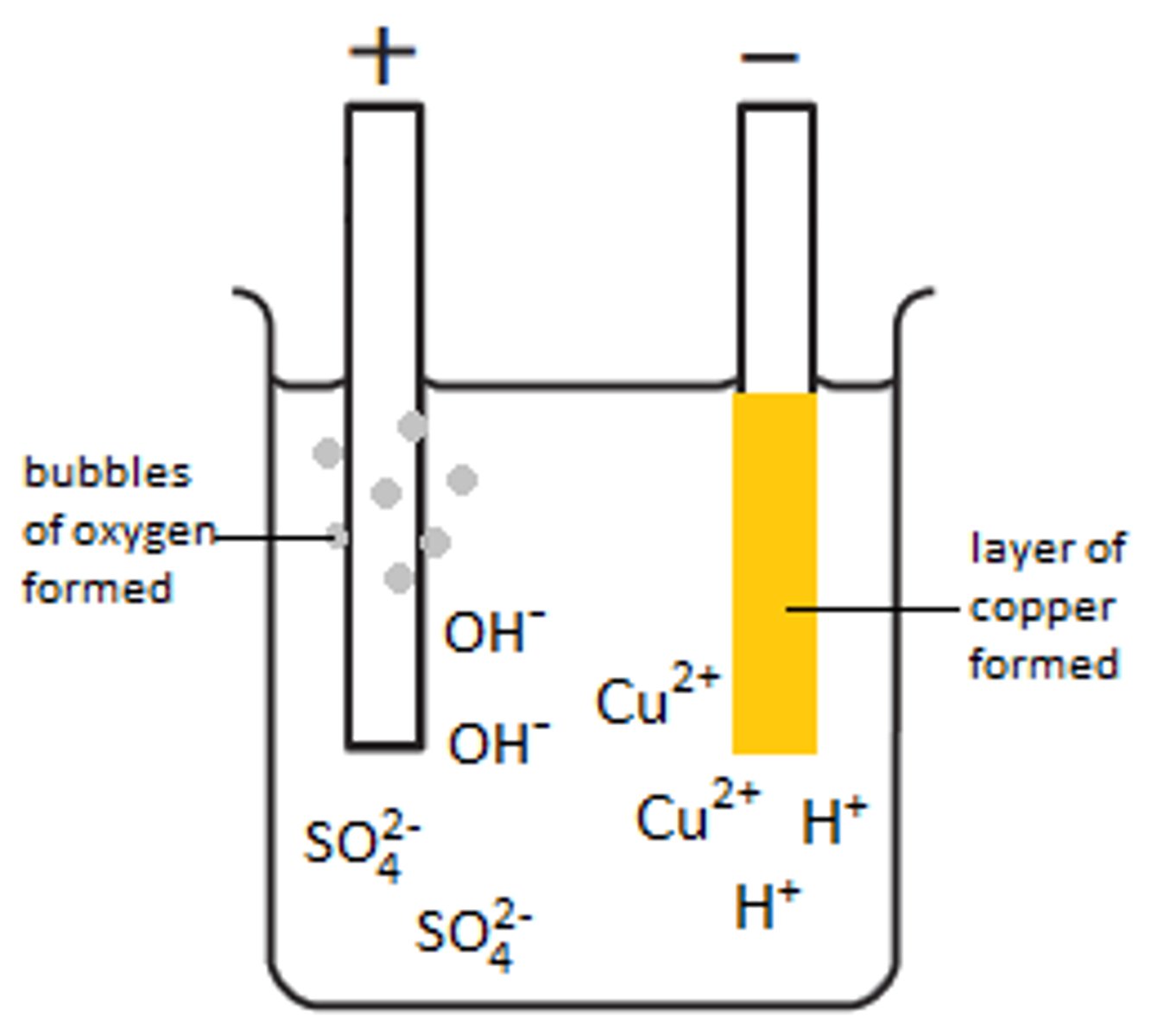
Discharged at the anode in solution
Halide ions, if present, otherwise OH-
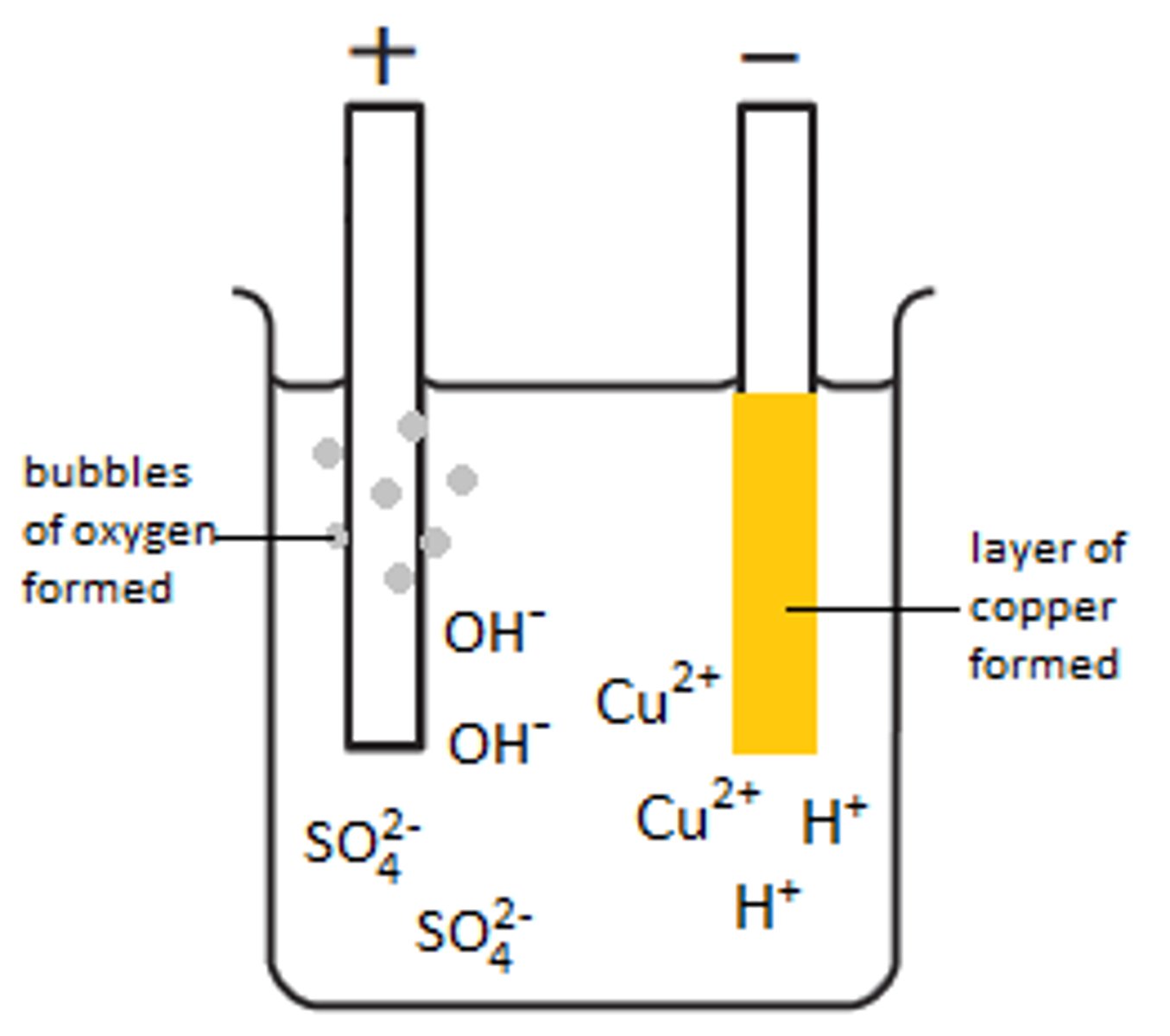
Halide ion
a negative ion formed from a group 7 element
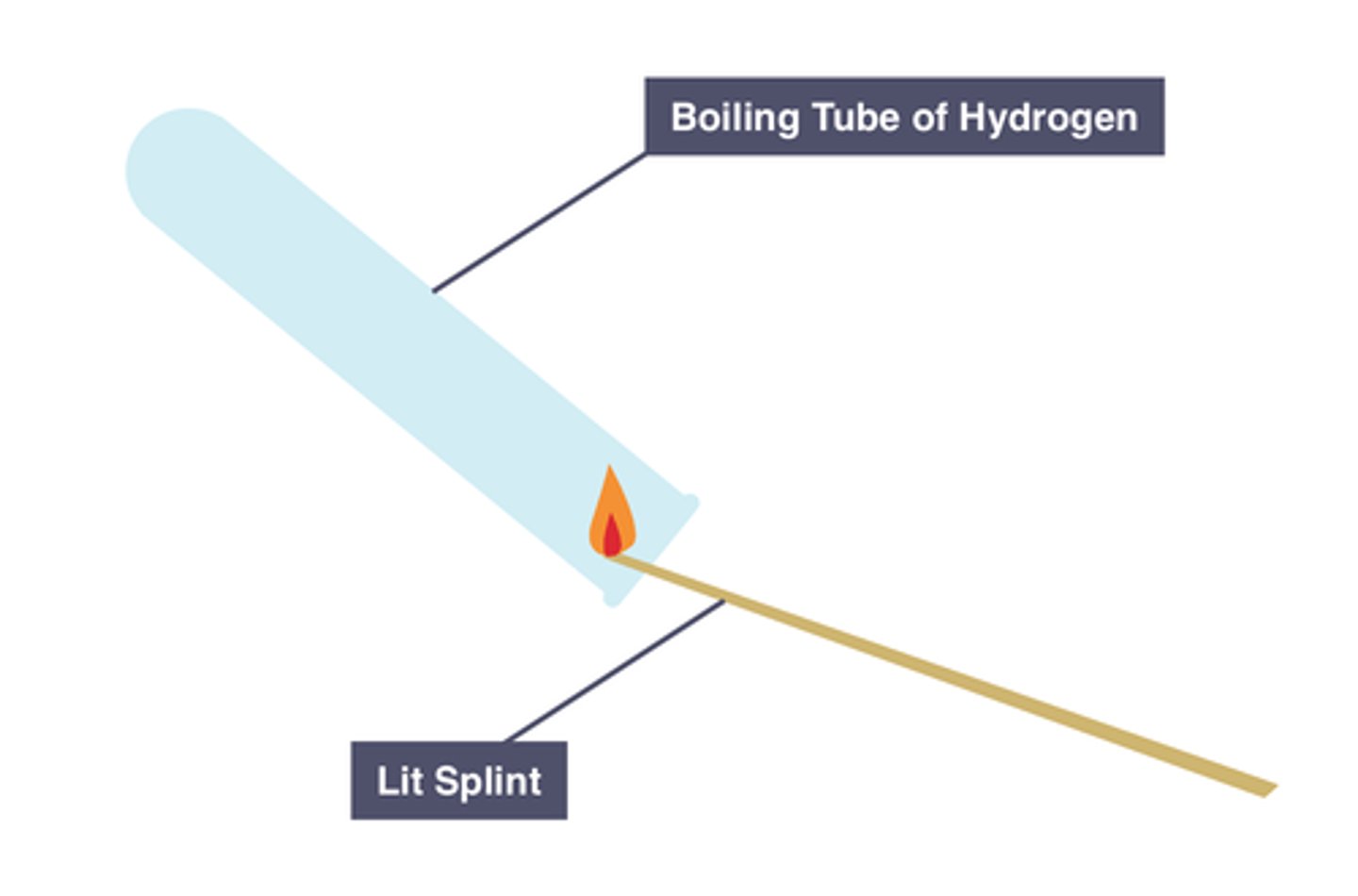
Test for hydrogen
Lit splint produces a squeaky pop
Metals discharged in preference to hydrogen
Copper, Silver, Gold, Platinum
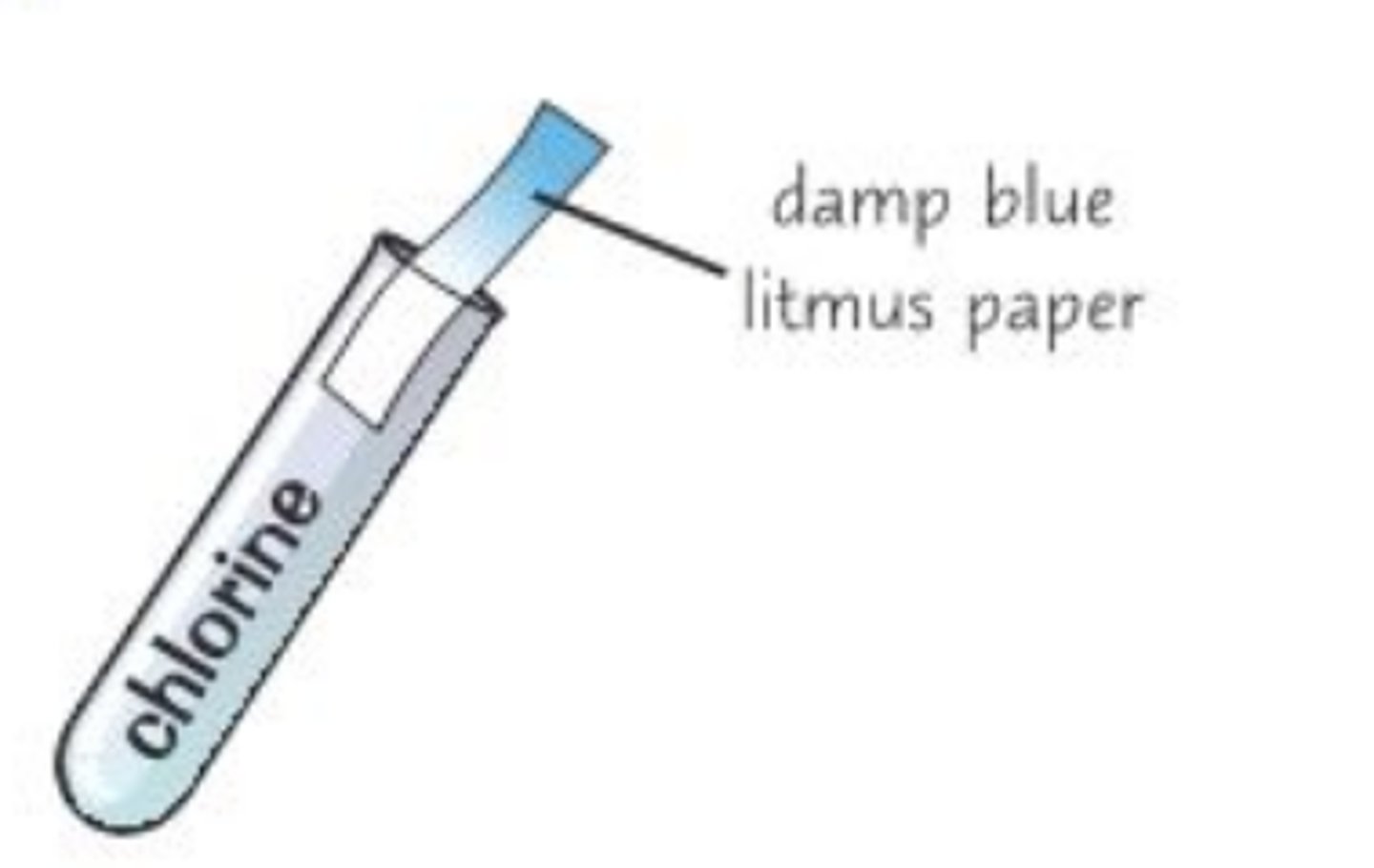
Test for chlorine
Bleaches damp litmus paper
Test for oxygen
Relights a glowing splint

Metals require electrolysis to extract
If they are more reactive than carbon, or react with carbon
Example of a metal more reactive than carbon
Aluminium
Example of a metal that reacts with carbon
Titanium
Reason electrolysis is expensive
Requires lots of energy
2 Reasons electrolysis requires lots of energy
To melt the compound and to produce the electrical current
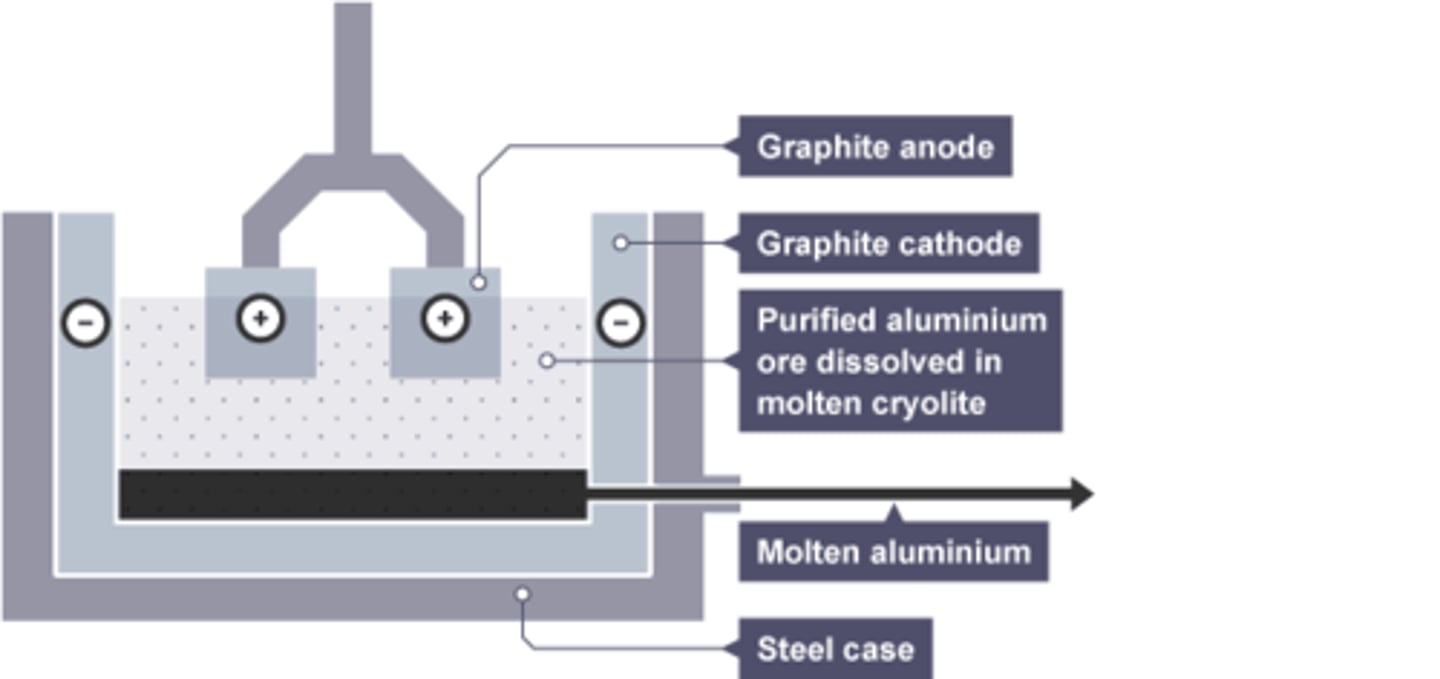
Mixture used in electrolysis of aluminium
Cryolite and aluminium oxide
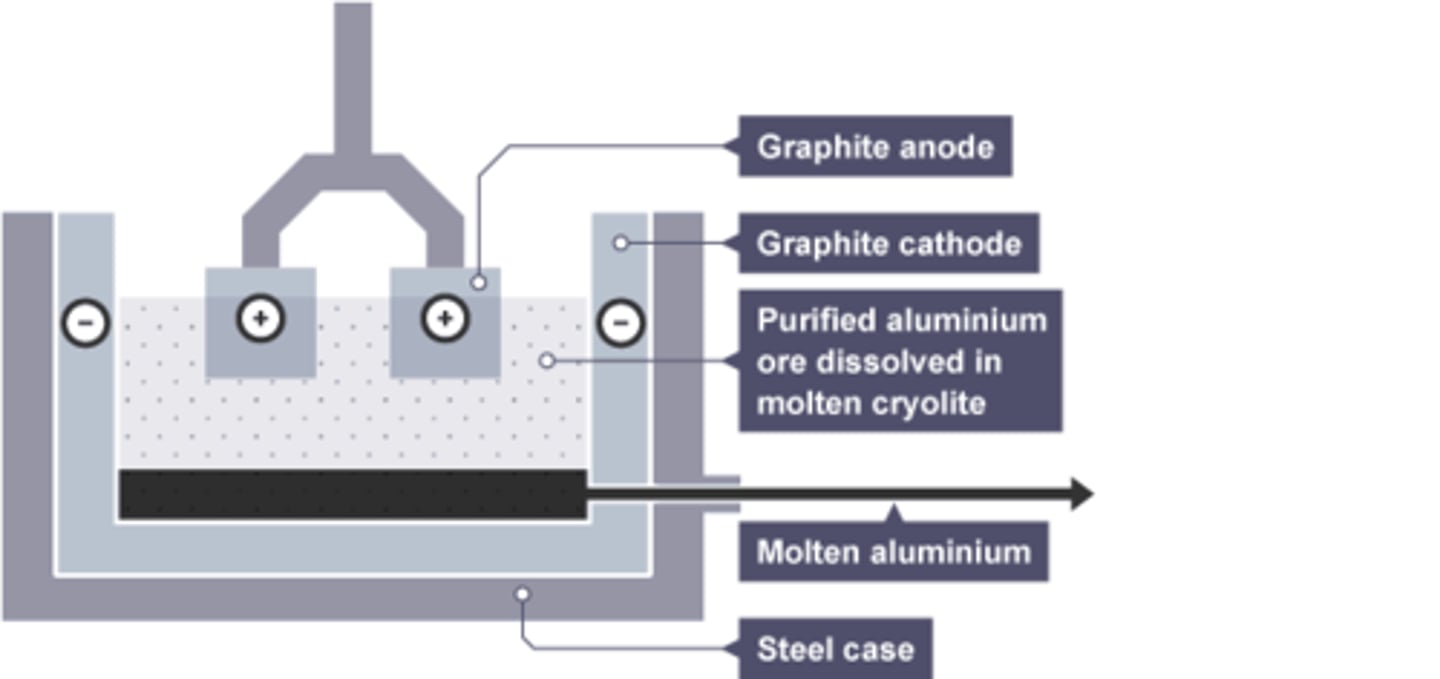
Cryolite
the substance added to aluminium oxide to lower its melting point
Reason cryolite is used
Lowers melting point so reduces energy required
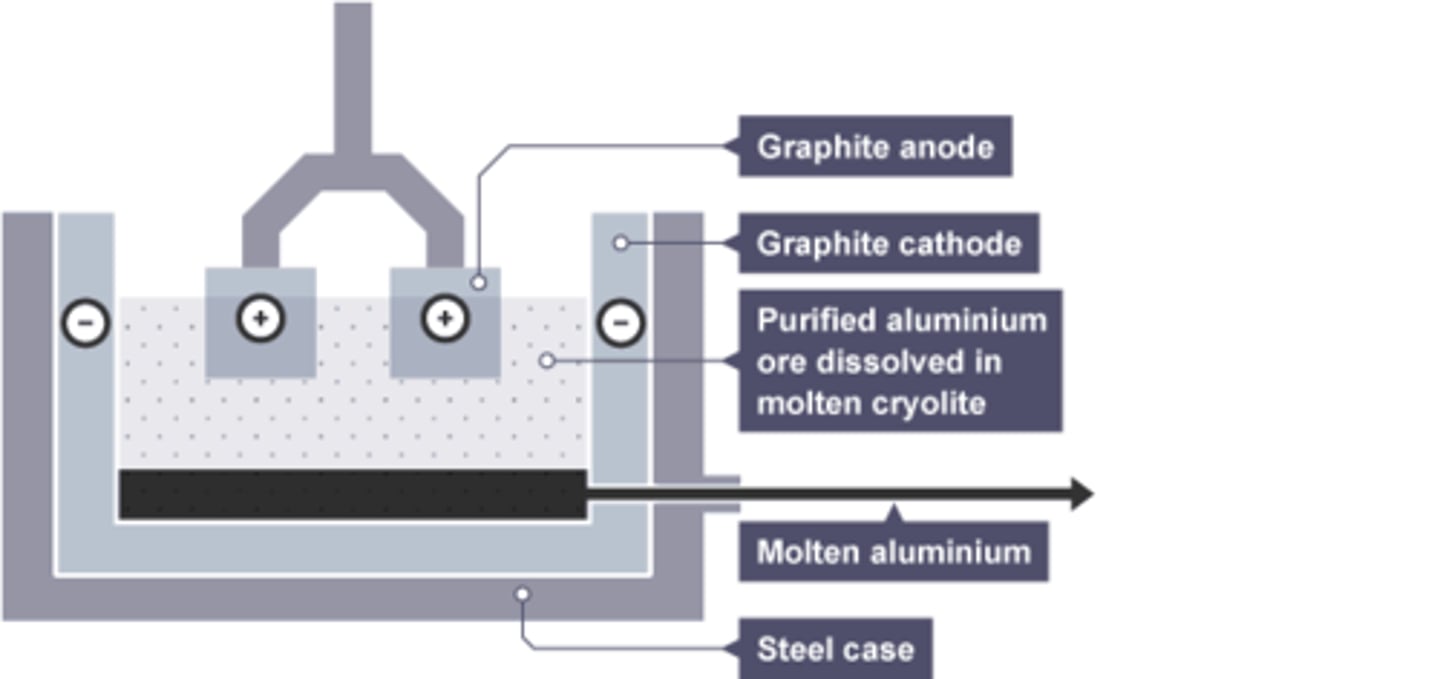
Composition of anode for aluminium extraction
Graphite
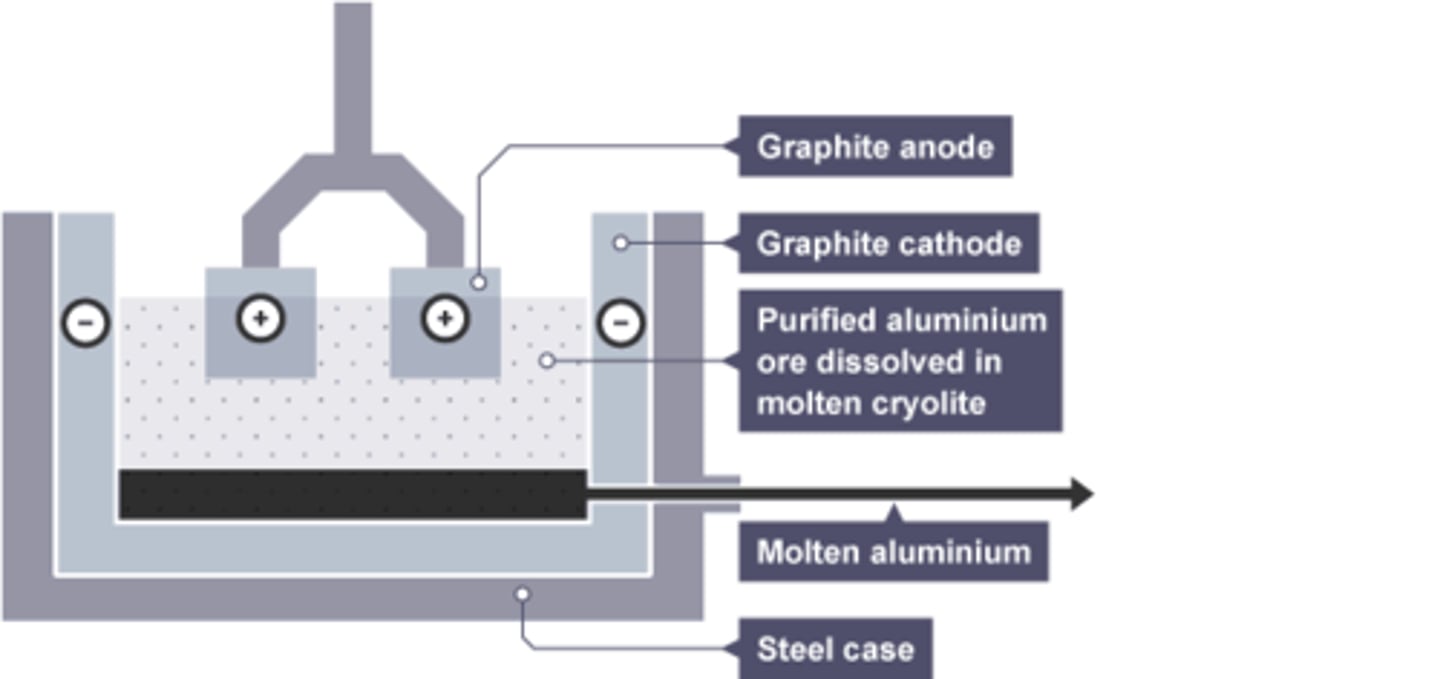
Reason anode requires regular replacement in aluminium extraction
Oxygen is produced at the anode, which reacts with graphite in the anode, wearing it away.
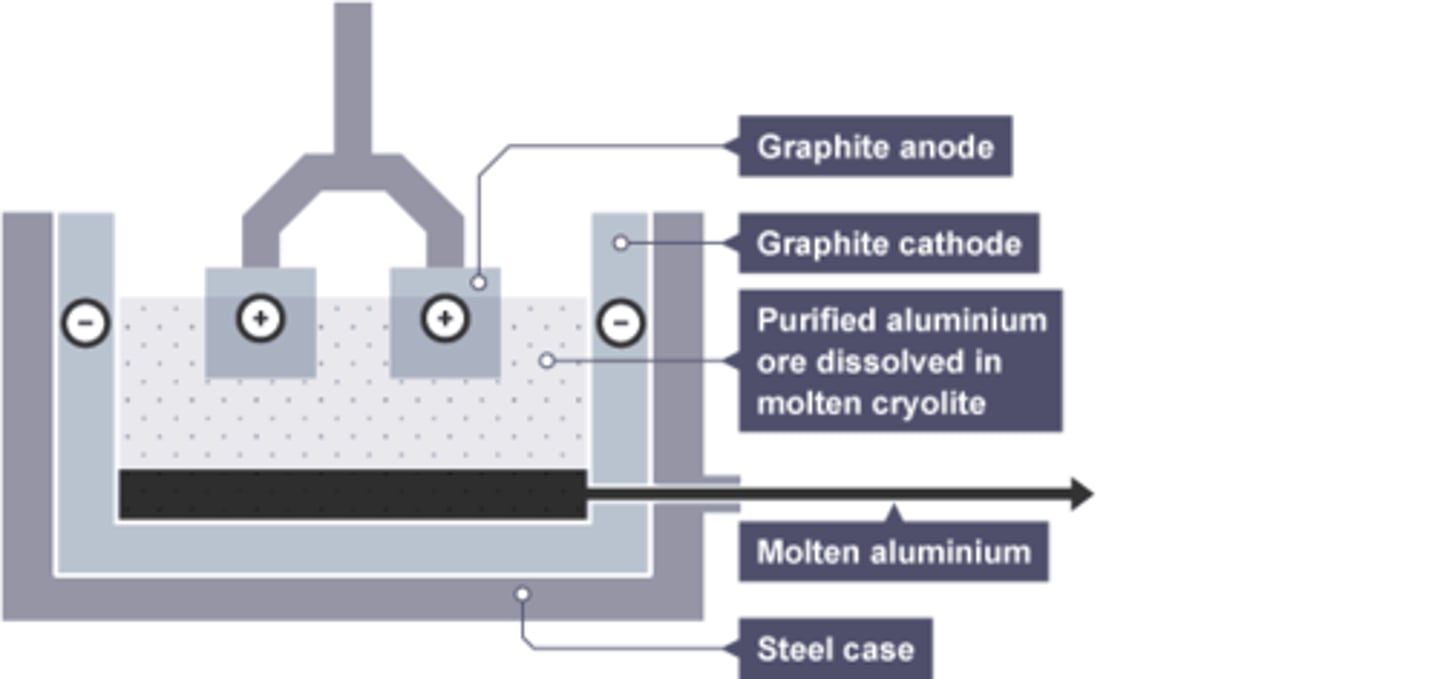
carbon + oxygen -->
carbon dioxide
Substance formed at the anode by aluminium extraction
Oxygen
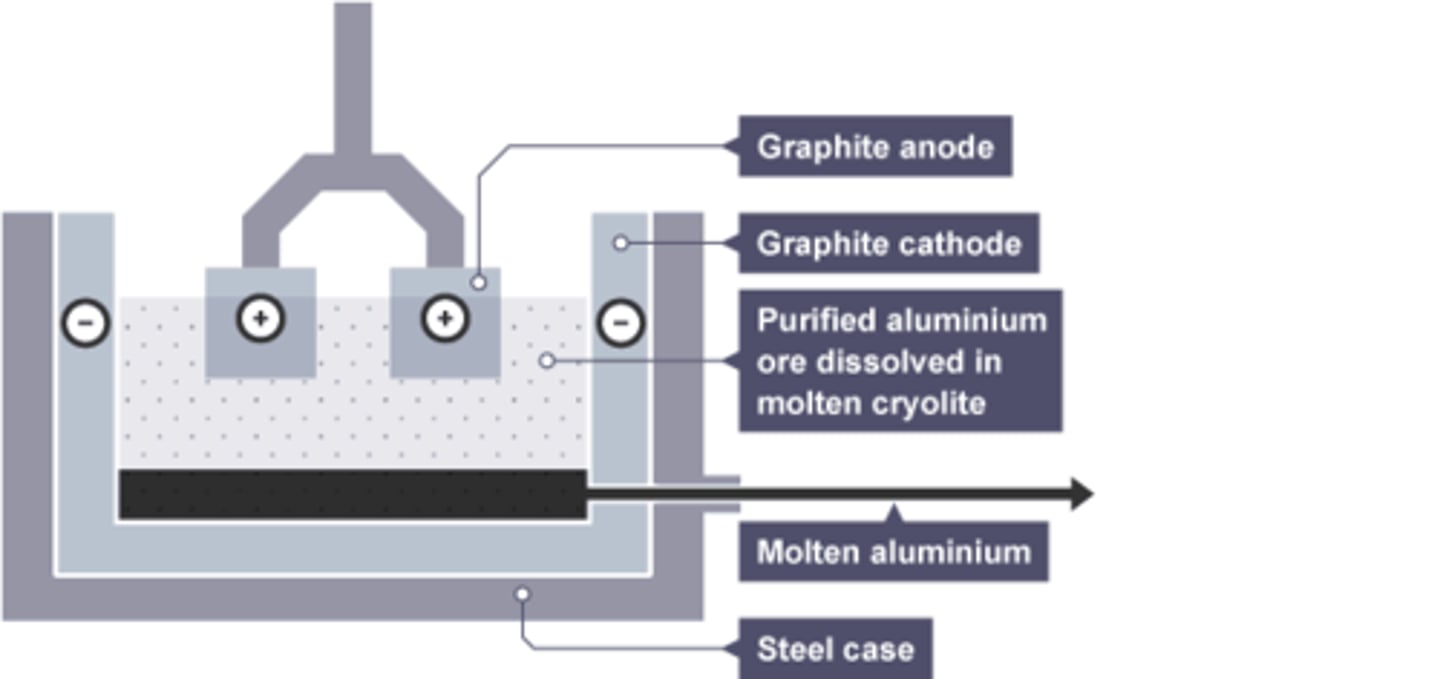
Substance formed at the cathode by aluminium extraction
Molten Aluminium
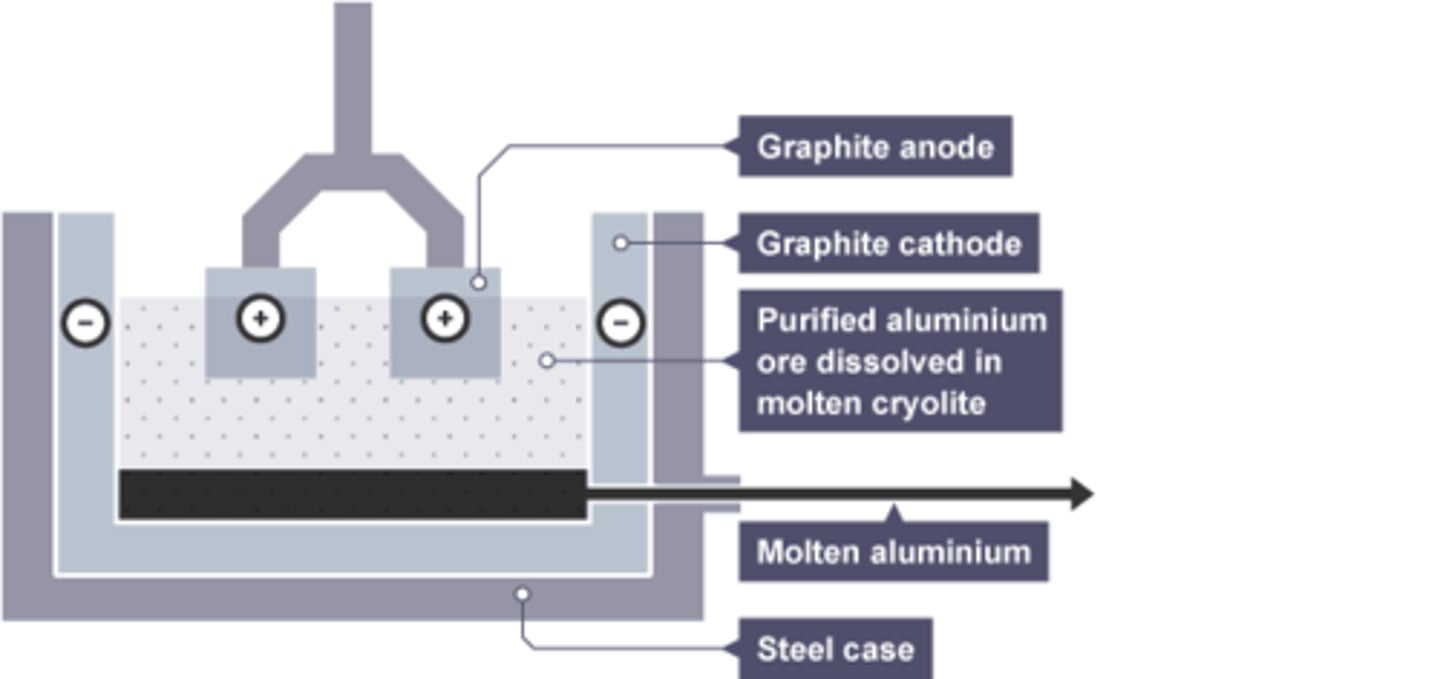
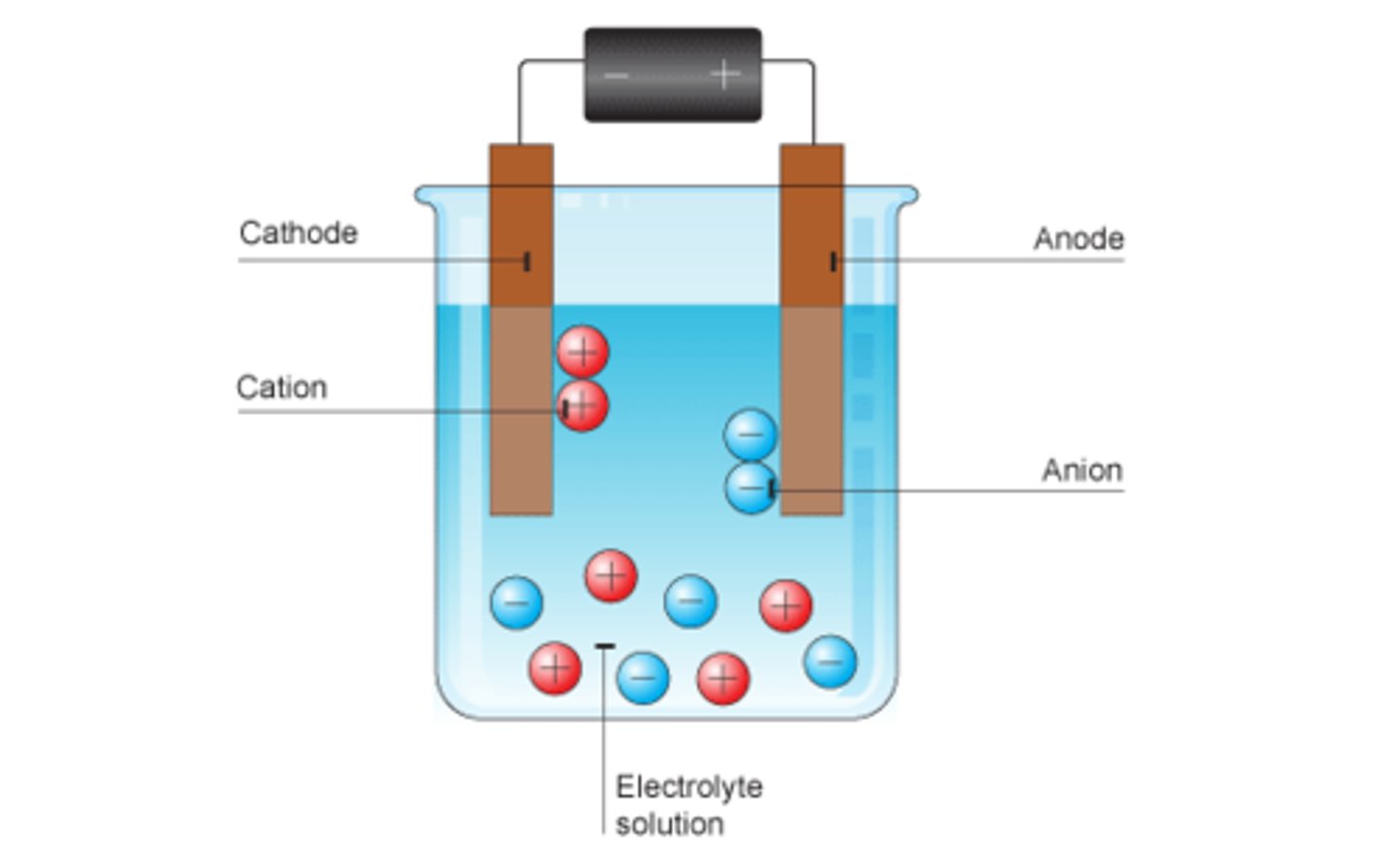
Cathode
Electrode at which reduction occurs
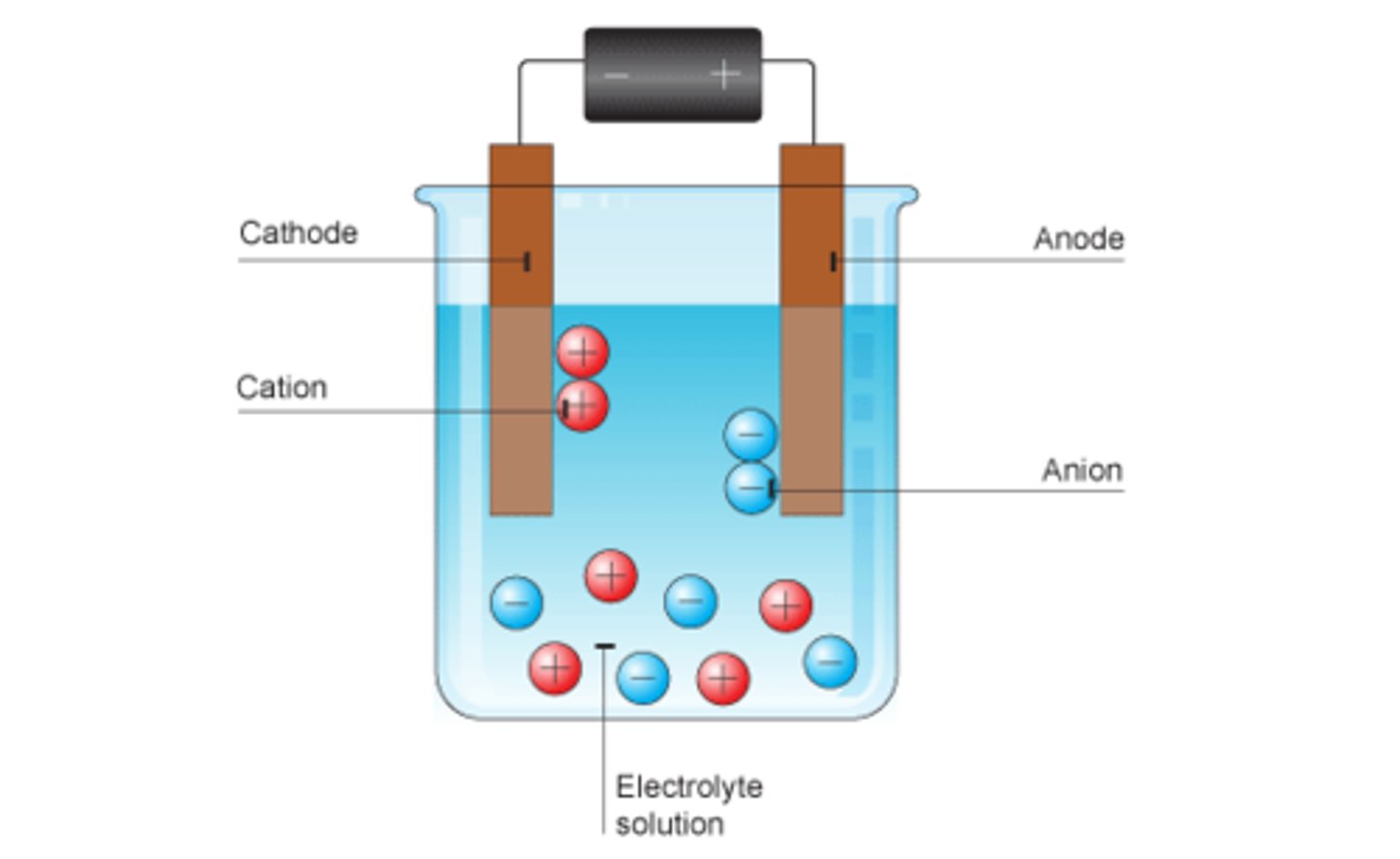
Anode
Electrode at which oxidation occurs
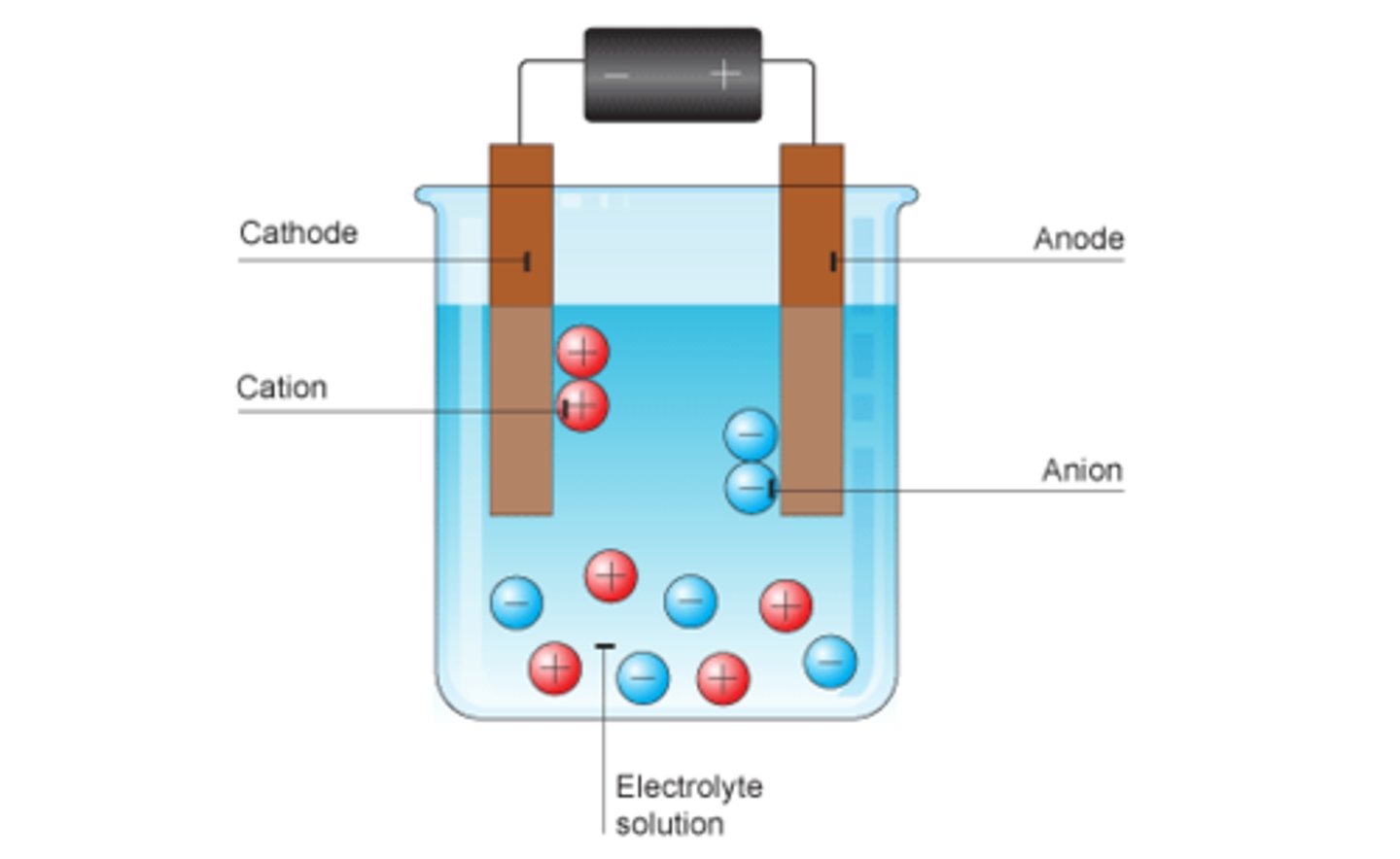
Electrode
A device for conducting electricity into the liquid
Cation
A positively charged ion
Anion
A negatively charged ion
Electrolyte
An ionic compound able to conduct an electric current
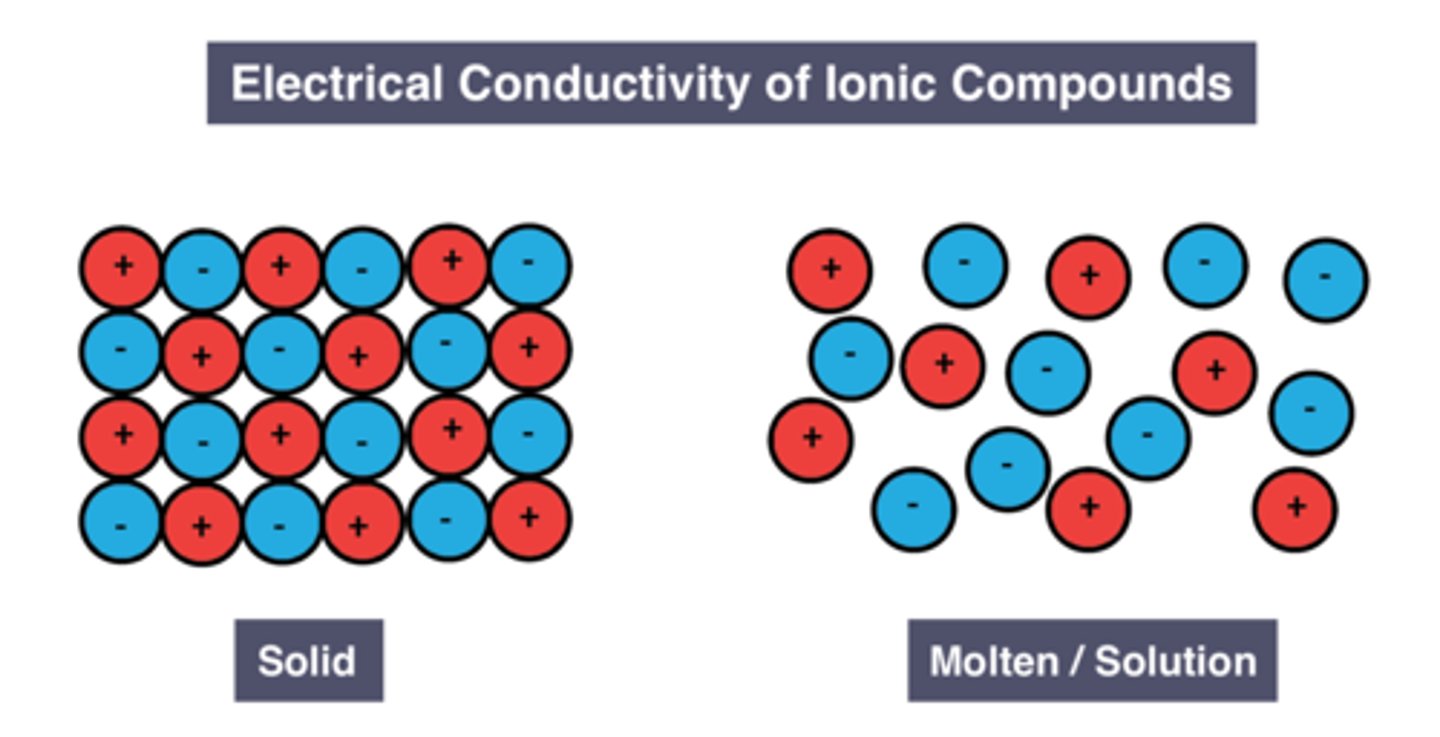
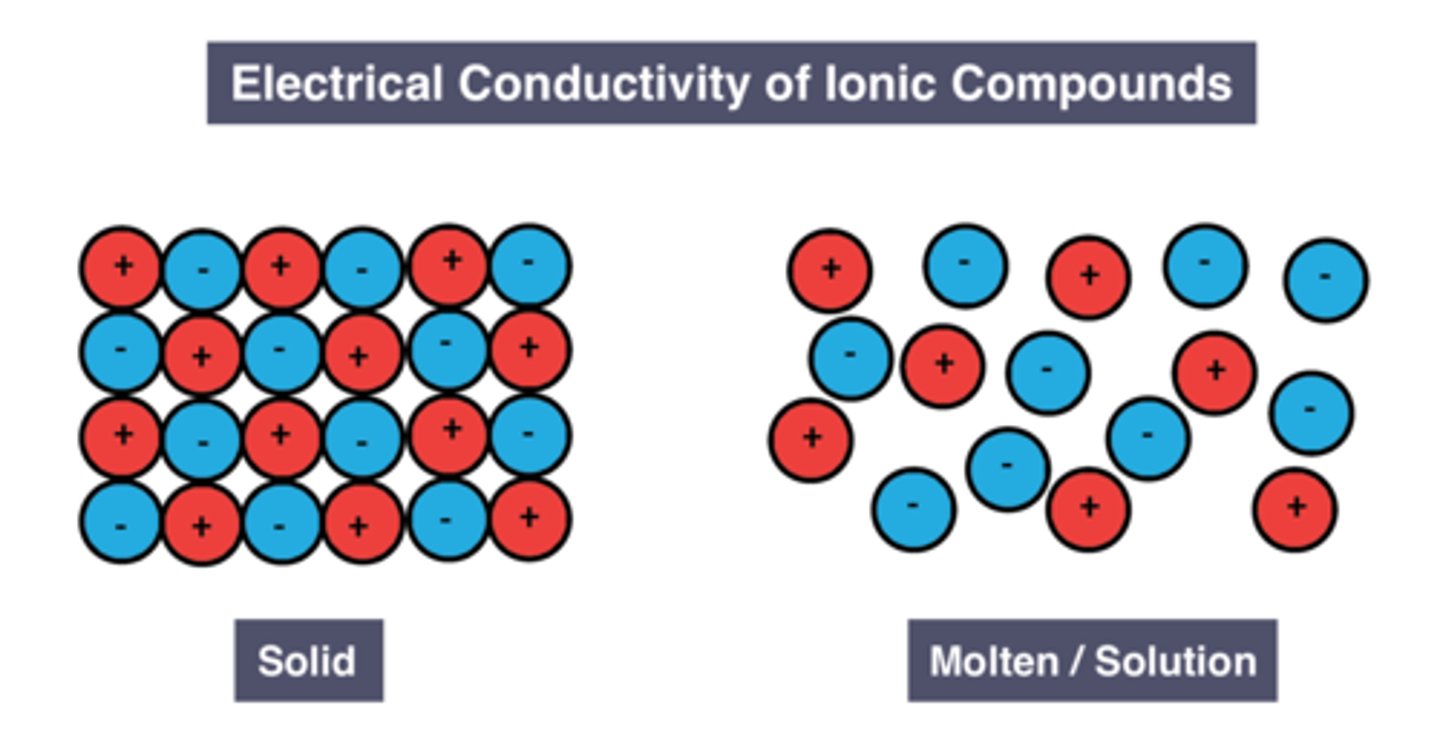
Reason solid ionic substance can't conduct electricity
Ions are in fixed positions
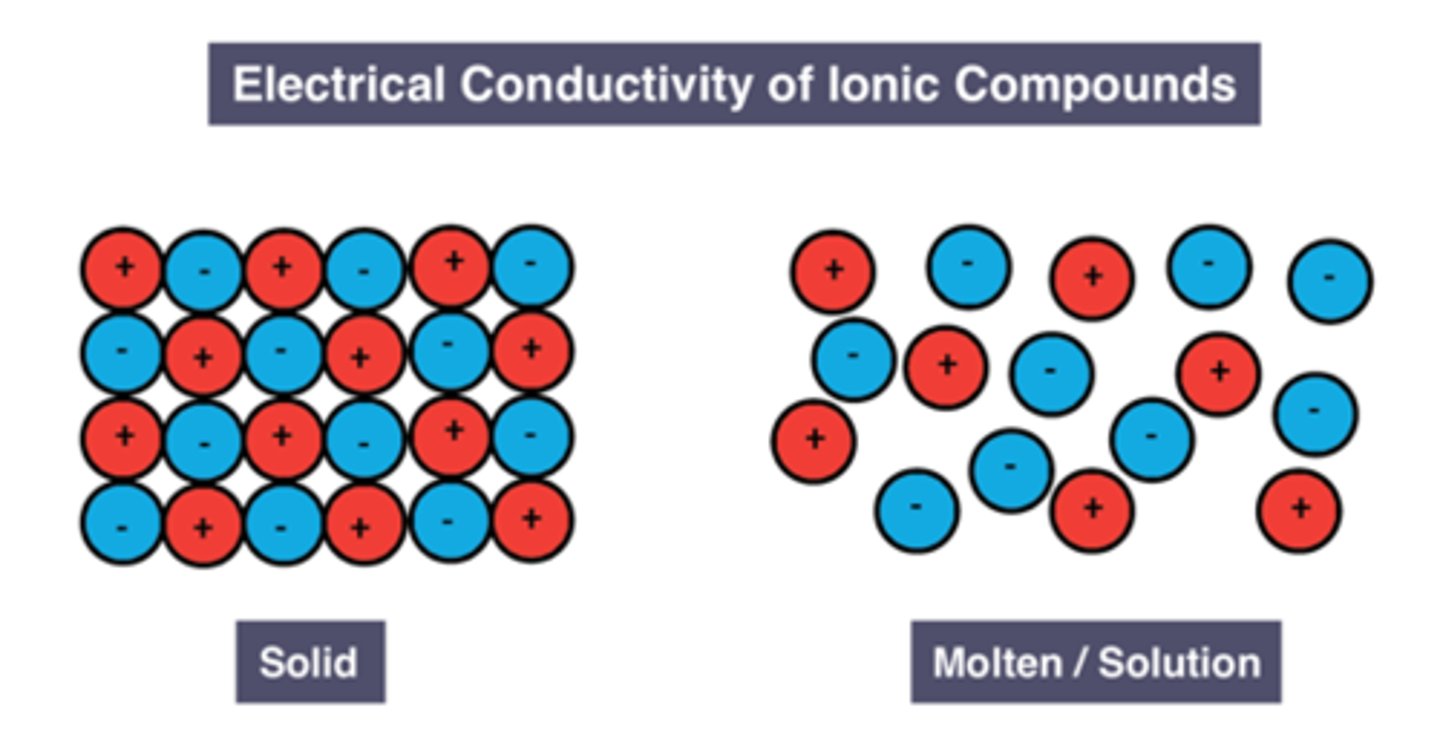
Reason molten/dissolved ionic substances can conduct electricity
Ions are free to move and carry charge
In electrolysis ions go to
Opposite charge electrode
Positive ions go to
Cathode
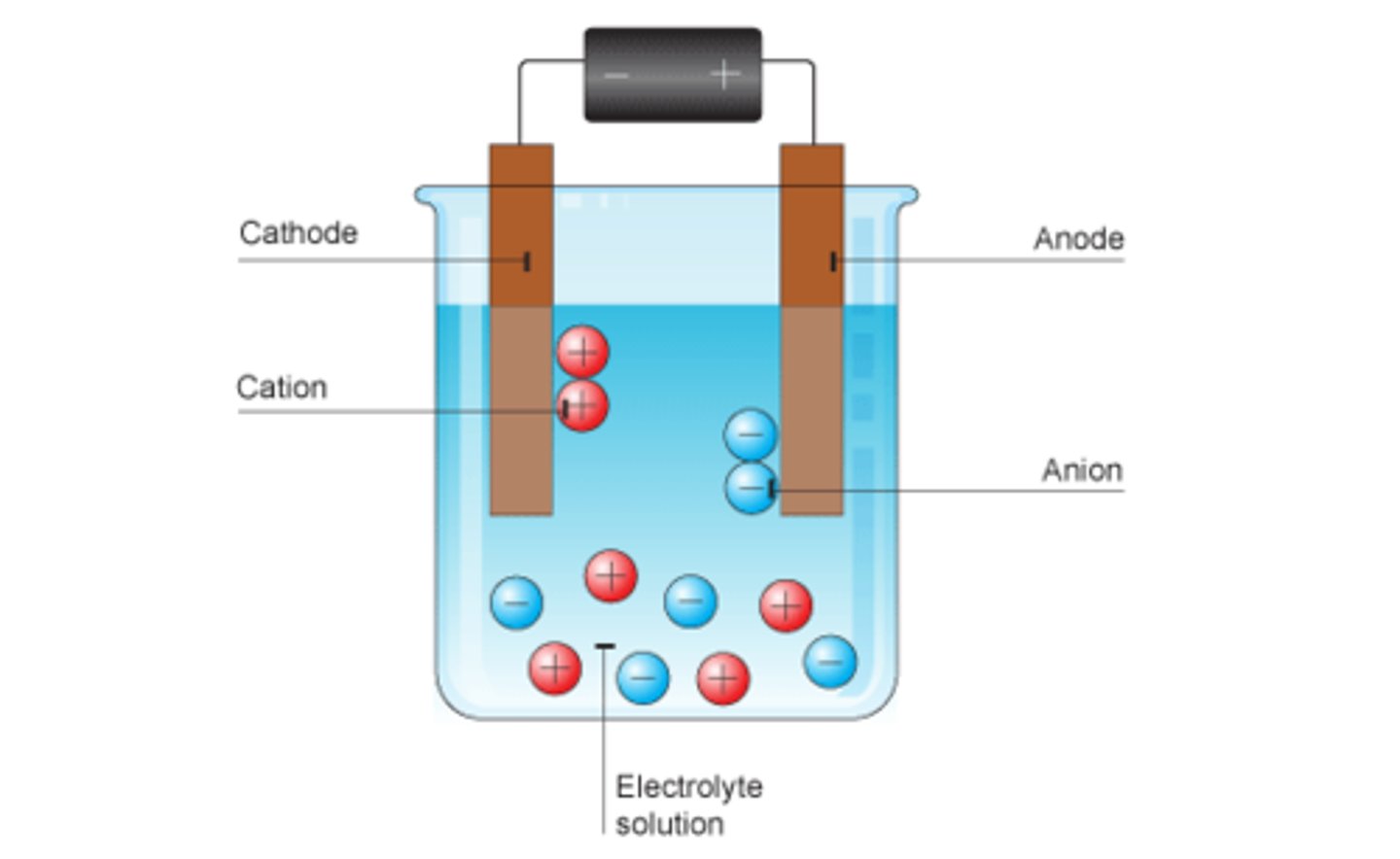
Negative ions go to
Anode
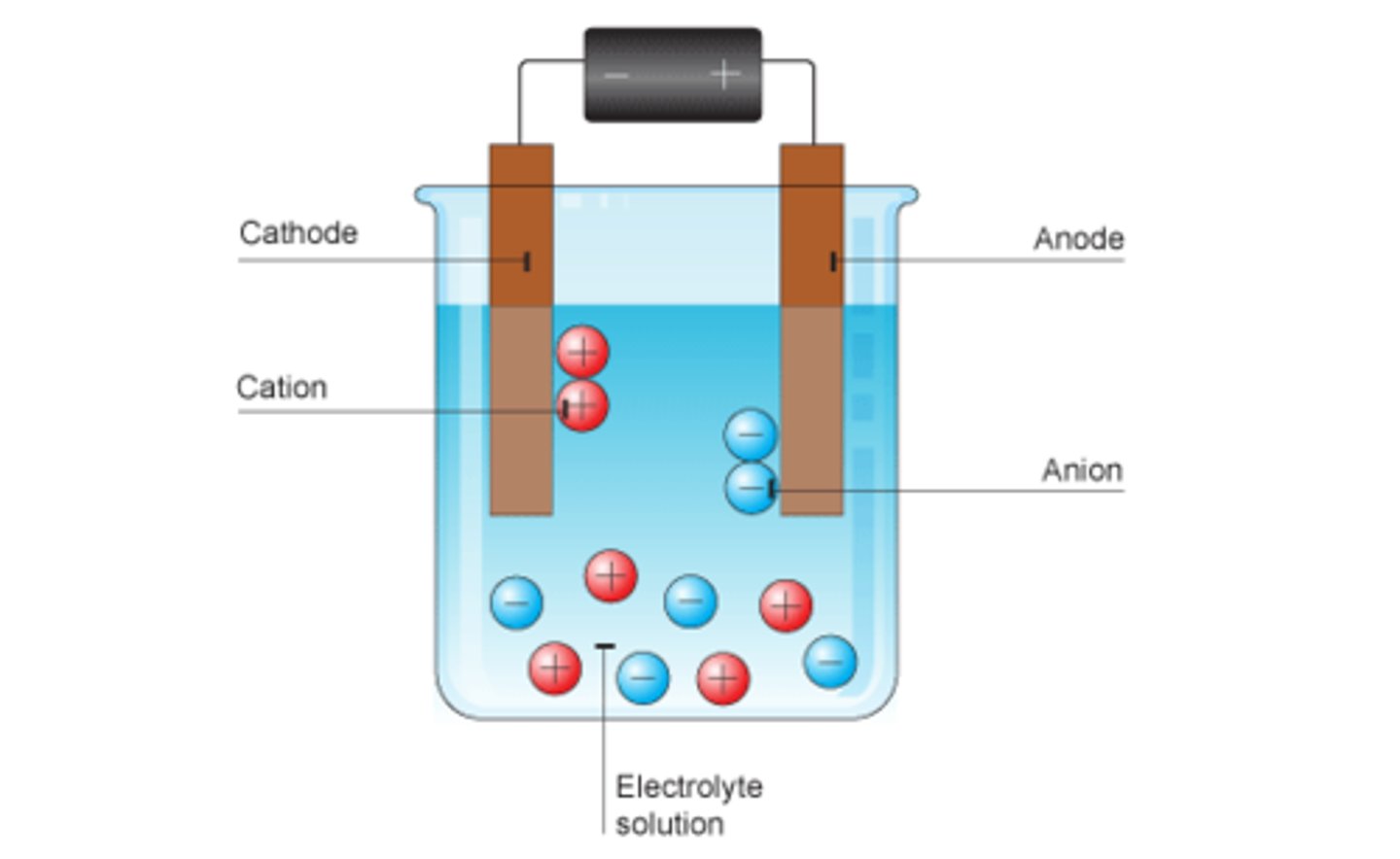
Discharged
Remove an electric charge by adding/removing electrons
Oxidation in terms of electrons
Loss of electrons
Reduction in terms of electrons
Gain of electrons